A Study of Grain Selection in Two-Dimensional (2D) Grain Selectors during the Investment Casting of Single-Crystal Superalloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
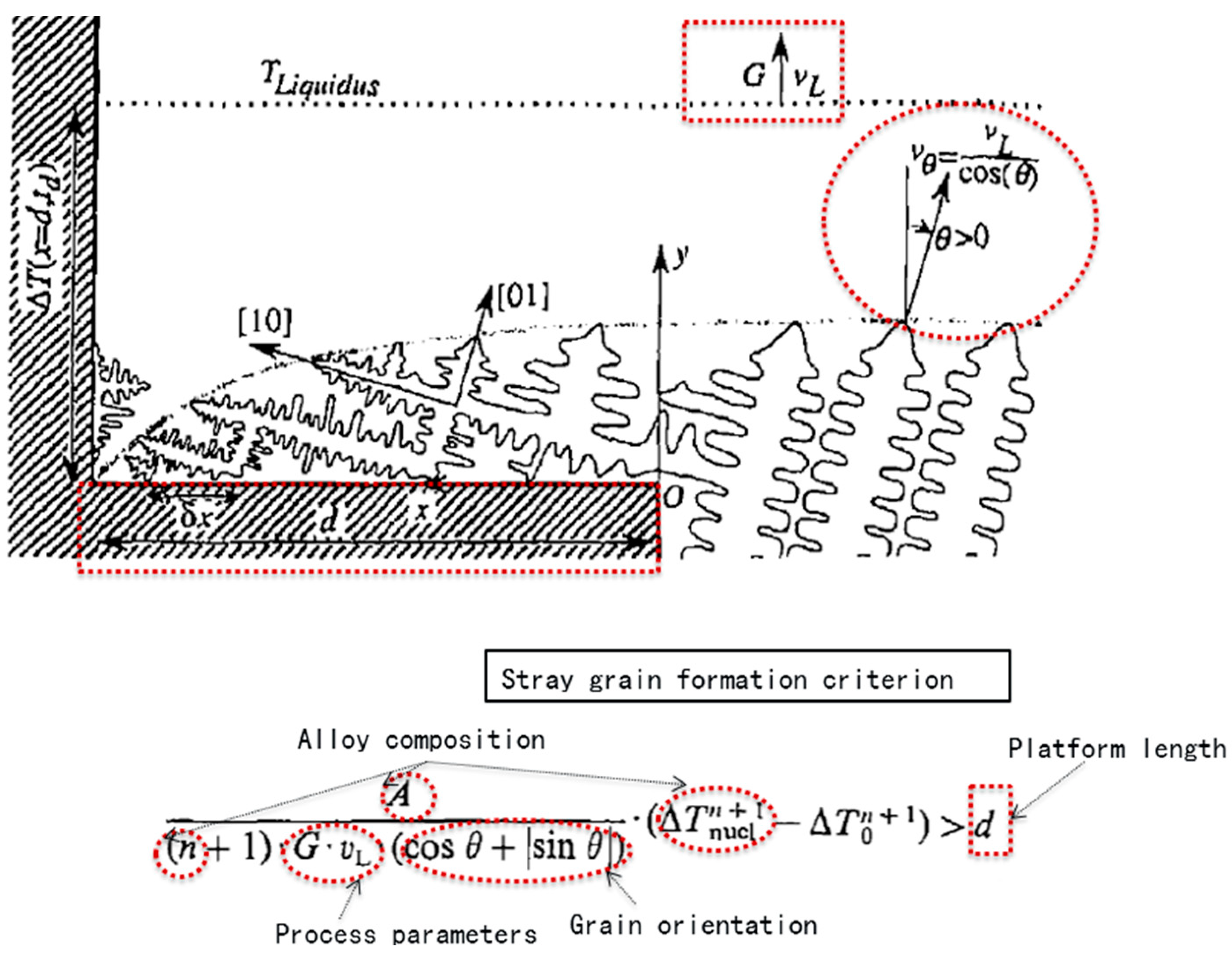
2.1. Test and Calculation Method
Experimental Method
2.2. Numeral Simulation
- Finite element technology, which is capable of fully simulating thermal flow stress without the need for coupling with a third-party software.
- Accurate geometry description, which is excellent for complex shapes.
- Integrated CAD (Computer-Aided Design)/CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering), which can read data from a mainstream software directly and has a powerful geometry repair capability [38].
| Material | Temperature (°C) |
| Casting | 1475 |
| Chill plate | 750 |
| Mold | 1550 |
| Coolant | T = 400 °C for cropped Bridgman model |
| Baffle | 750 |
| Heater | 1550 |
| Chamber | 150 |
3. Results and Discussion
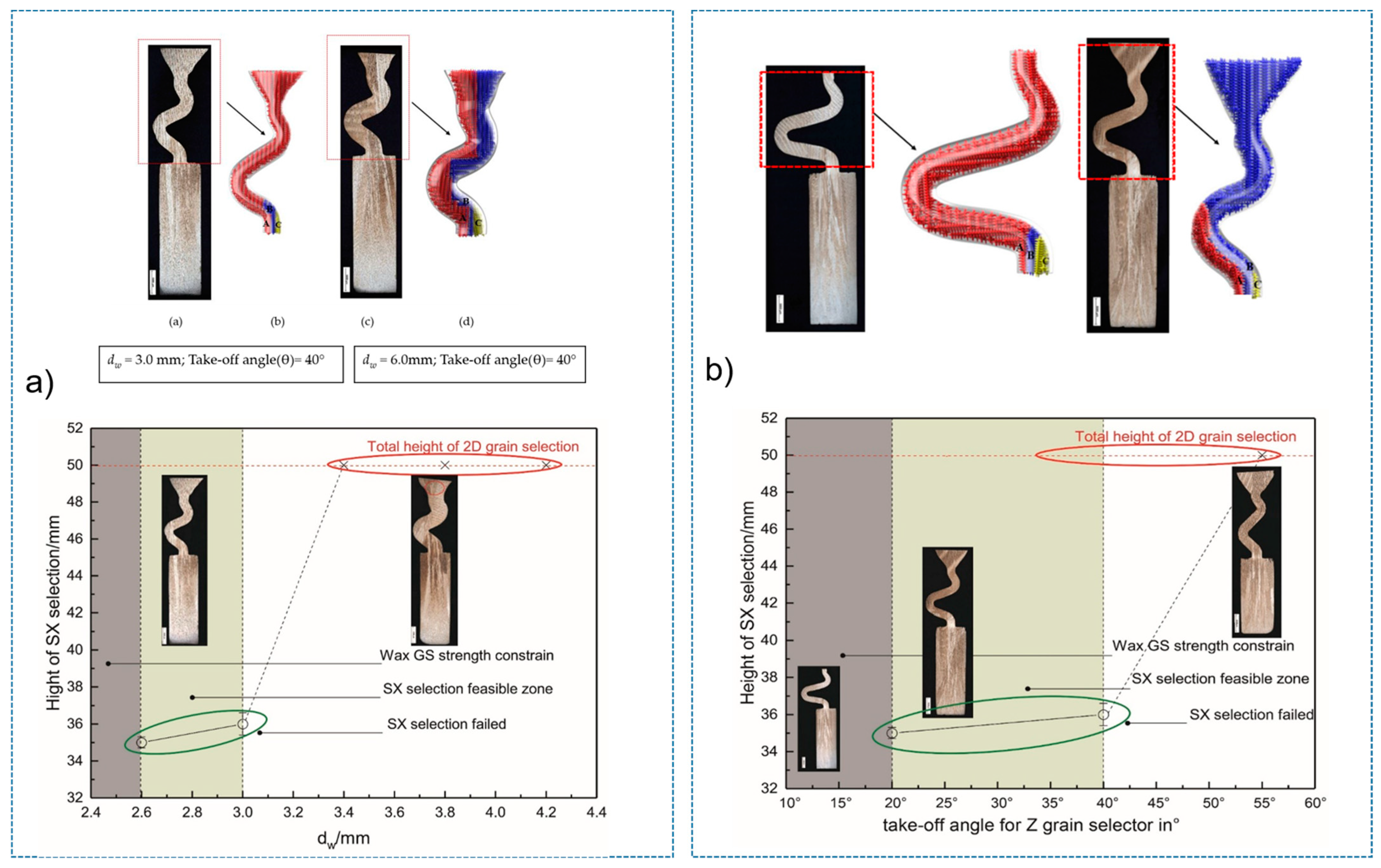
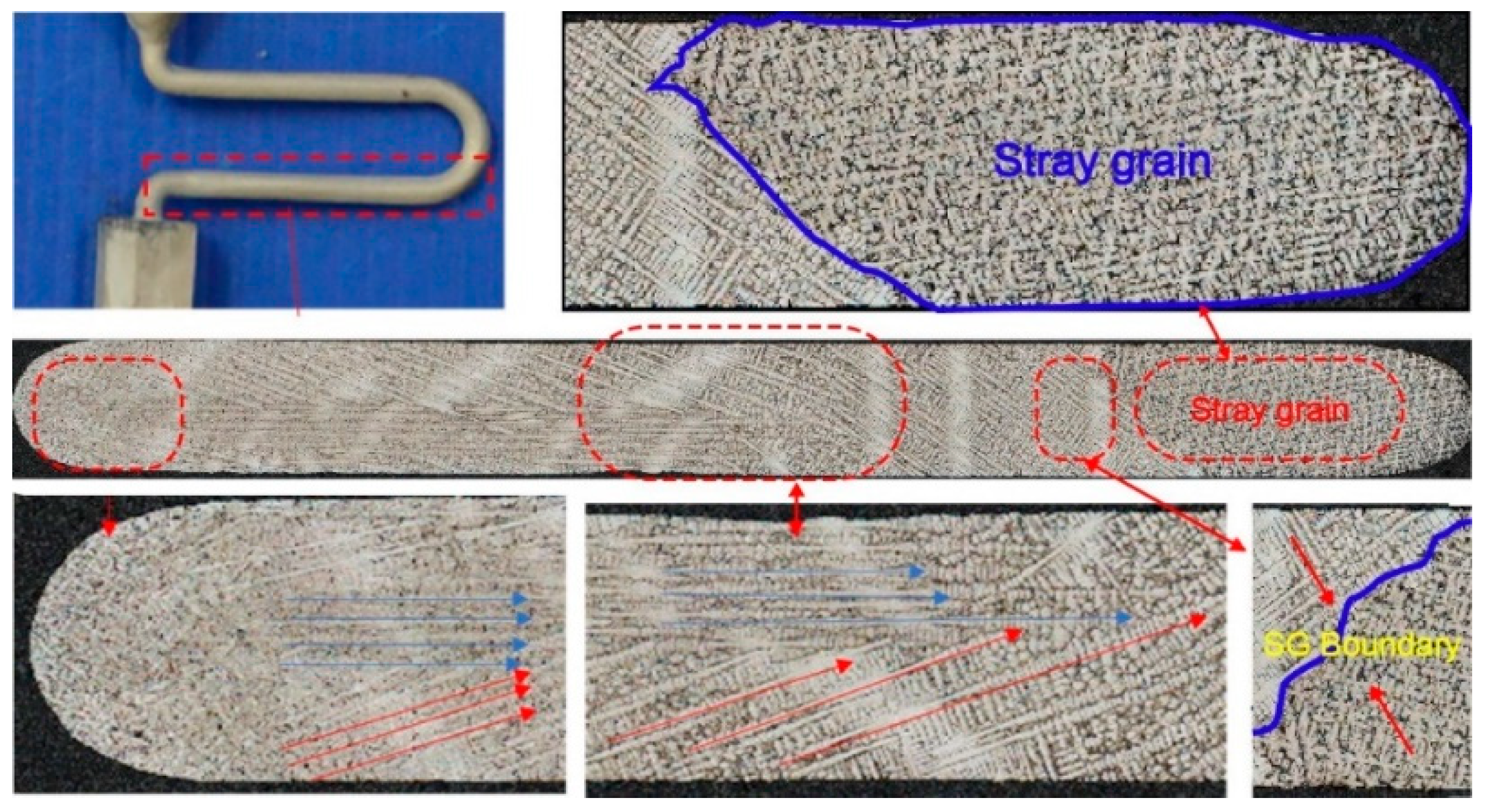
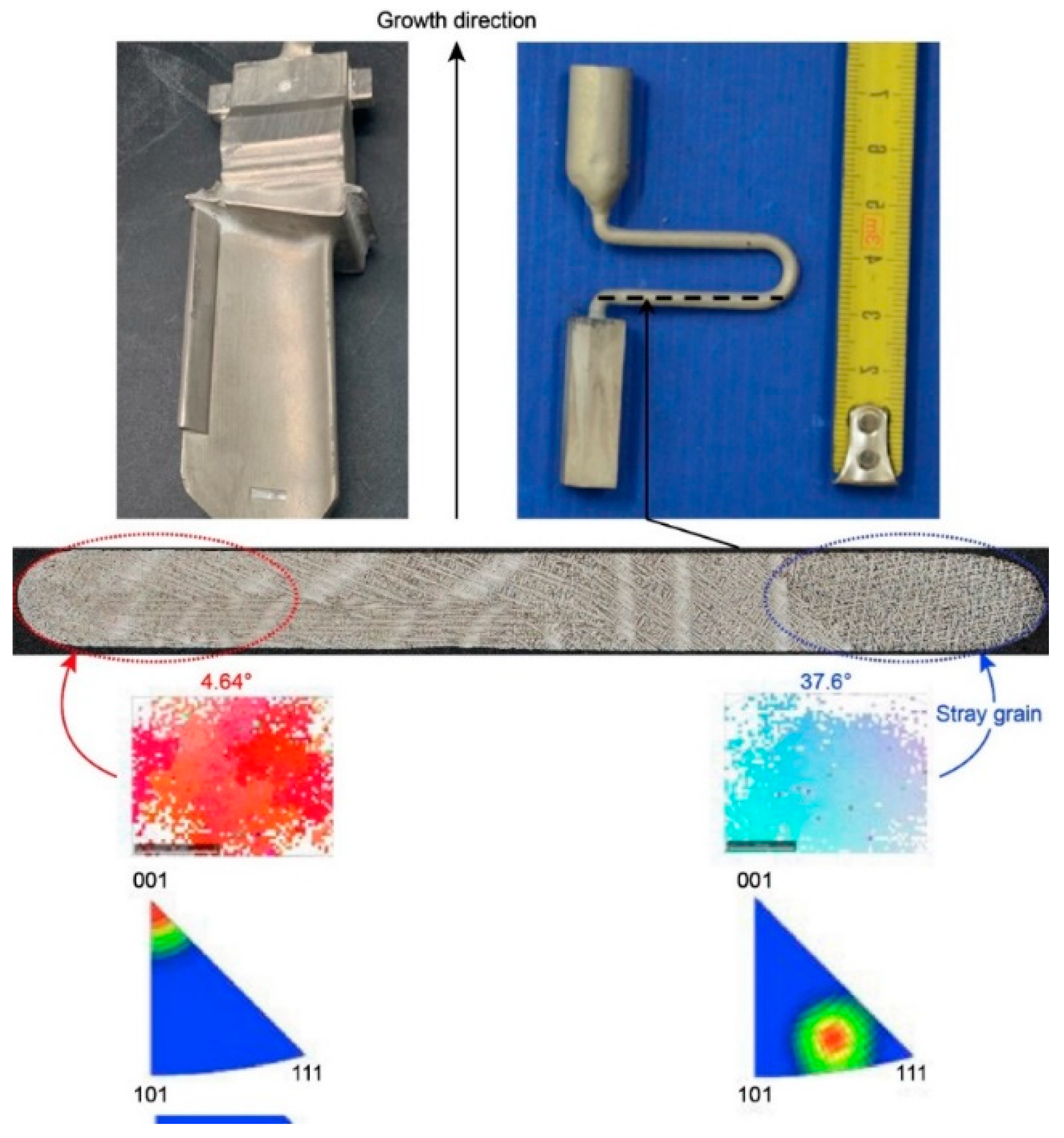
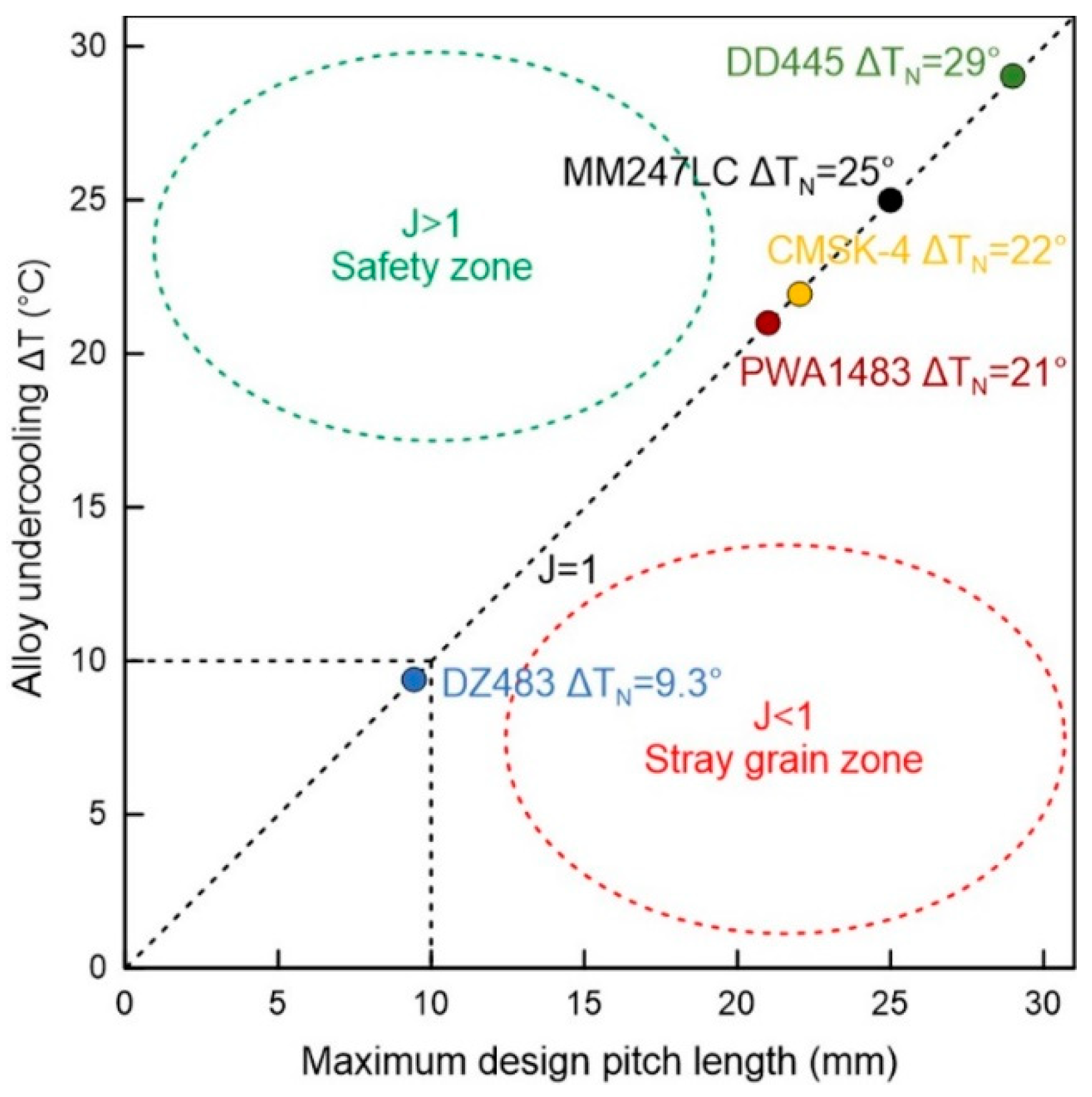
3.1. Selection Behavior and Efficiency of 2D Grain Selectors
3.2. Influence of Undercooling on Grain Selection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Q.; Li, H. High Temperature Alloy; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rolls-Royce. The Jet Engine, 4th ed.; The Technical Publications Department, Rolls-Royce plc: Derby, UK, 1992; pp. 1–200. [Google Scholar]
- Aveson, J.; Tennant, P.; Foss, B.; Shollock, B.; Stone, H.; D’Souza, N. On the origin of sliver defects in single crystal investment castings. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 5162–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidn, D. Single Crystal Superalloys. In Superalloys, Supercomposites, and Superalloys; Tien, J., Caulfield, T., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA; Boston, MA, USA, 1989; pp. 149–182. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Ness, D.; Lee, P.; D’Souza, N. Simulation of stray grain formation during single crystal seed melt-back and initial withdrawal in the Ni-base superalloy CMSX4. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 413, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, N.; Djakovic, A.; Shollock, B.; Mclean, M.; D’Souza, N.; Jennings, P. Defect grain in the melt-back region of CMSX-4 single crystal seeds. Superalloy 2004, 2004, 719–726. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.; D’Souza, N.; Dong, H. Grain Selection in Spiral Selectors During Investment Casting of Single-Crystal Turbine Blades: Part I. Experimental Investigation. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 3430–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Dong, H.; D’Souza, N.; Gebelin, J.; Reed, R. Grain Selection in Spiral Selectors During Investment Casting of Single-Crystal Components: Part II. Numerical Modeling. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 3439–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higginbotham, G.J.S. From research to cost-effective directional solidification and single-crystal production-an integrated approach. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1986, 2, 442–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Hou, G.; Tian, W. Grain sorting behavior of single crystal superalloys. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2001, 11, 176–178. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.; Marquis, P. Role of silica binder in investment casting. Br. Ceram. Trans. 1995, 94, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Versnyder, F.; Shank, M. The development of columnar grain and single crystal high temperature materials through directional solidification. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1970, 6, 213–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulette, M.; Spiling, P.; Arthey, R. Superalloy. In Cost Effective Single Crystals; Gell, M., Kortovich, C., Bricknell, R., Eds.; The Minerals, Metals & Mateials Society: New York, NY, USA; Warrendale, PA, USA, 1984; pp. 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H. A Study of Solidification Structure Evolution during Investment Casting of Ni-Based Superalloy for Aero-Engine Turbine Blades. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.J.; Dong, H.B.; Atkinson, H.V.; Lee, P.D. Simulation of the Columnar to Equiaxed Transition in Alloy Solidification- the Effect of Nucleation Undercooling, Density of Nuclei in Bulk Liquid and Alloy Solidification Range on the Transition. Solid State Phenom. 2008, 139, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.; Gebelin, J.; D’Souza, N.; Brown, P.; Dong, H. Effect of spiral shape on grain selection during casting of single crystal turbine blades. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2009, 22, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Xie, G.; Shen, J. Selection Behavior of a Grain Selector During Directional Solidification Process. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2011, 23, 361–364. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Lee, P. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 18, 055008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, J.; Jin, T.; Sun, X.; Sun, C.; Hu, Z. Evolution of Grain Selection in Spiral Selector during Directional Solidification of Nickel-base Superalloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Kim, I.; Jo, C.; Ogi, K. Grain structure prediction of Ni-base superalloy castings using the cellular automaton-finite element method. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 449, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgman, P. Crystals and Their Manufacture. U.S. Patent 1793672, 24 February 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Q. Multi-scale simulation of directional dendrites growth in super-alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 238, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, D.; Chalmers, B. The origin of the preferred orientation in the columnar zone of ingots. Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Eng. 1959, 215, 447. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Volek, A.; Green, N. Mechanism of competitive grain growth in directional solidification of a nickel-base superalloy. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 2631–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, M.; Yu, D.; Zhou, X.; Gu, Y.; Fu, H. Dependence of competitive grain growth on secondary dendrite orientation during directional solidification of a Ni-based superalloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, F.; Ma, D. Bührig-Polaczek. Development of a high-efficiency z-form selector for single crystal blades and corresponding grain selection mechanism. Materials 2019, 12, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, S.; Wittenzellner, T.; Frieß, J.; Ma, D.; Bührig-Polaczek, A. Using a Three-Dimensional Reduction Method in the High-Efficiency Grain Selector and Corresponding Grain Selection Mechanism. Materials 2019, 12, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, F.; Ma, D.; Bührig-Polaczek, A. Grain selection in a high-efficiency 2D grain selector during casting of single-crystal superalloys. Materials 2019, 12, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalin, R.; Pankratov, V. Single-Crystal Casting of Nickel-Base Superalloys by Directional Rapid Solidifications. Metall. Sci. Technol. 1992, 10, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, J. Cellular and Primary Dendrite Arm Spacings, Solidification and Casting of Metals; Hunt, J.D., Ed.; The Metals Society: London, UK, 1979; pp. 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kurz, W.; Fisher, D. Dendrite Growth at the Limit of Stability: Tip Radius and Spacing. Acta Metall. 1981, 29, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somboonsuk, K.; Mason, J.; Trivedi, R. Interdendritic Spacing: Part I. Experimental Studies. Metall. Trans. A 1984, 15, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Overfelt, R. Influence of Directional Solidification Variables on the Cellular and Primary Dendrite Arm Spacings of PWA1484. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 3521–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Sahm, P. Primary Spacing in Directional Solidification. Metall. Trans. A 1998, 29, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, R.; Somboonsuk, K. Constrained Dendritic Growth and Spacing. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1984, 65, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-C.; Glicksman, M. Fundamentals of Dendritic Solidification-I: Steady-State Tip Growth. Acta Metall. 1981, 29, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quested, P.; Mclean, M. Effect of Variations in Temperature Gradient and Solidification Rate on Microstructure and Creep Behaviour of IN 738LC, Solidification Technology in the Foundry and Cast House; The Metals Society: London, UK, 1983; pp. 586–591. [Google Scholar]
- ProCAST User Manual; Version 2004.1; ESI Group: Paris, France, 2004.
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Ma, D. 2-D Selector Simulation Studies on Grain Selection for Single Crystal Superalloy of CM247LC. Materials 2019, 12, 3829. [Google Scholar]
- Rappaz, M.; Gandin, C.A. Probabilistic Modeling of Microstructure Formation in Solidification Processes. Acta Metall. Mater. 1993, 41, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
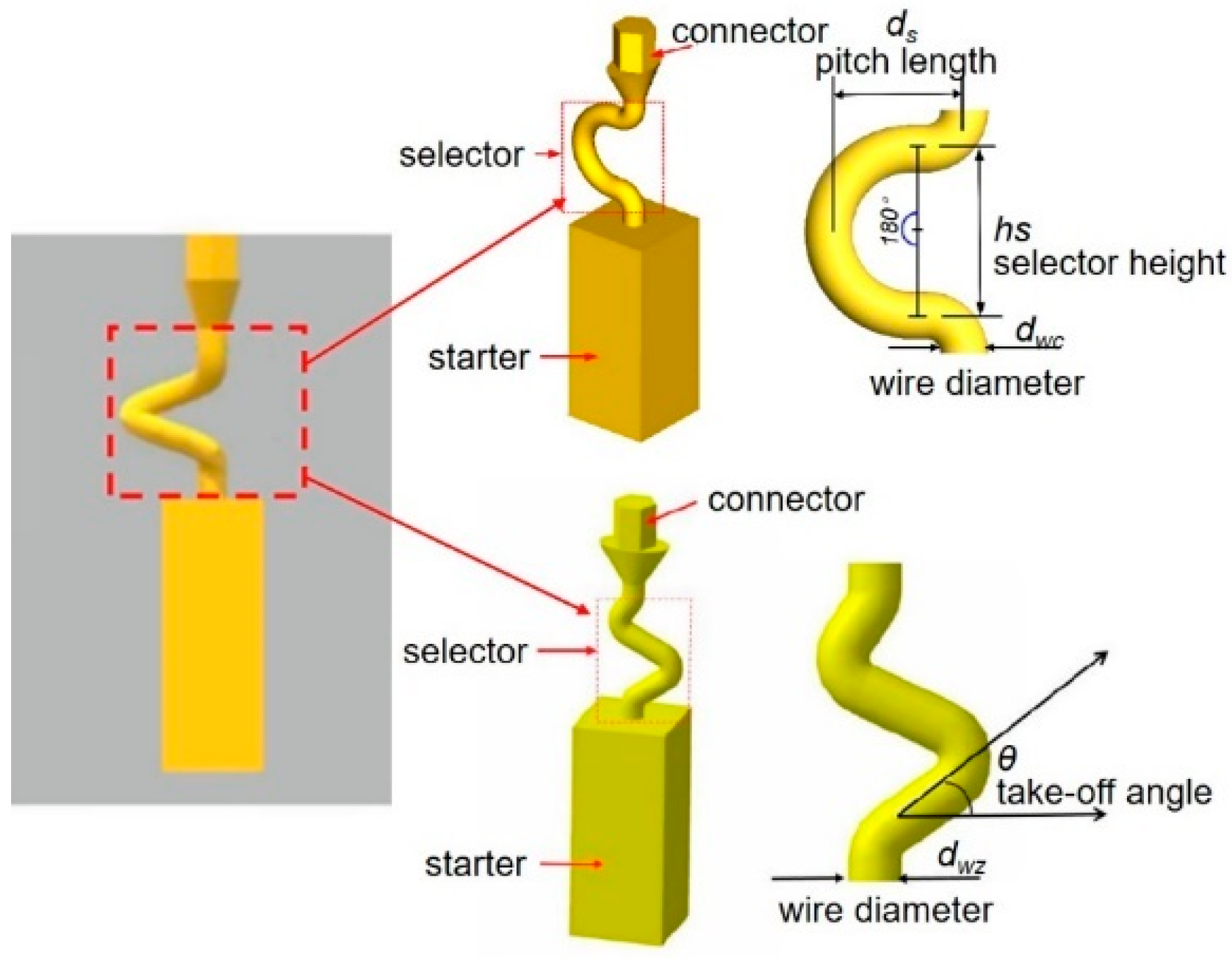
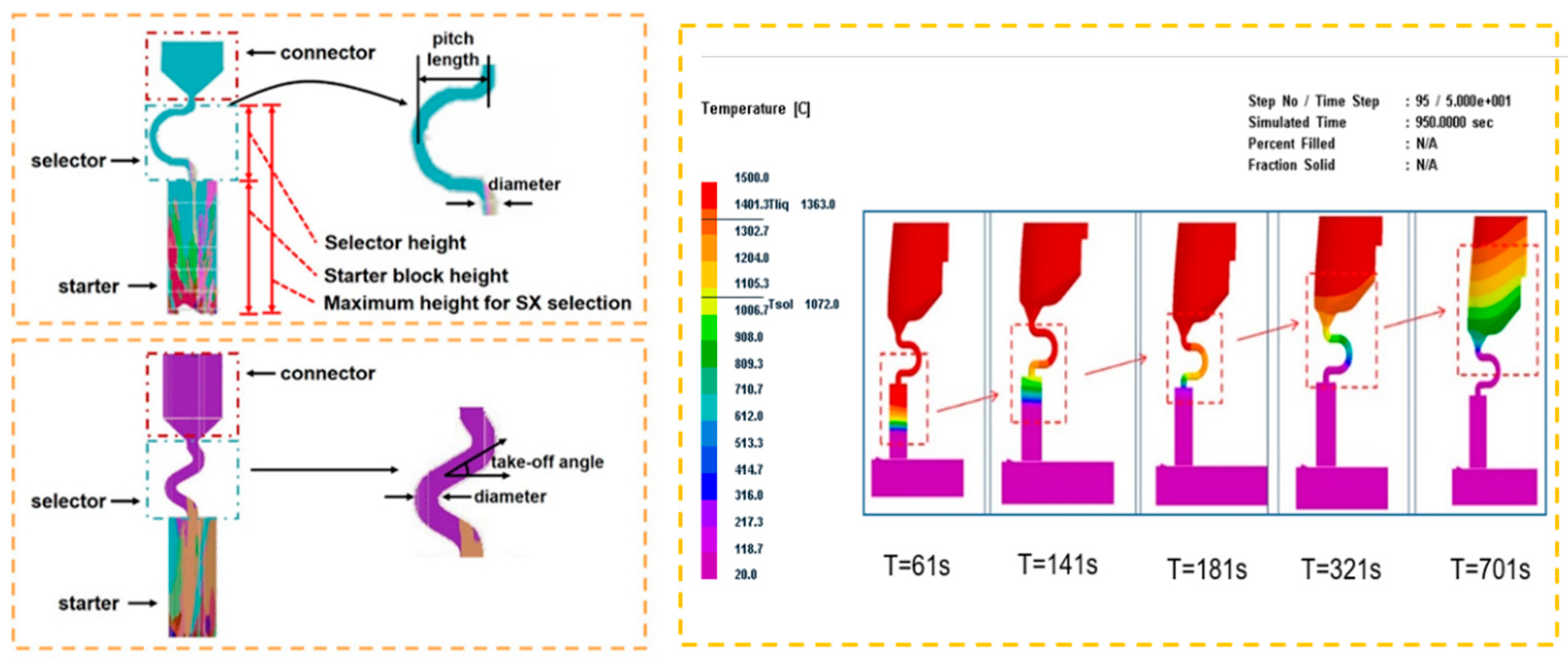
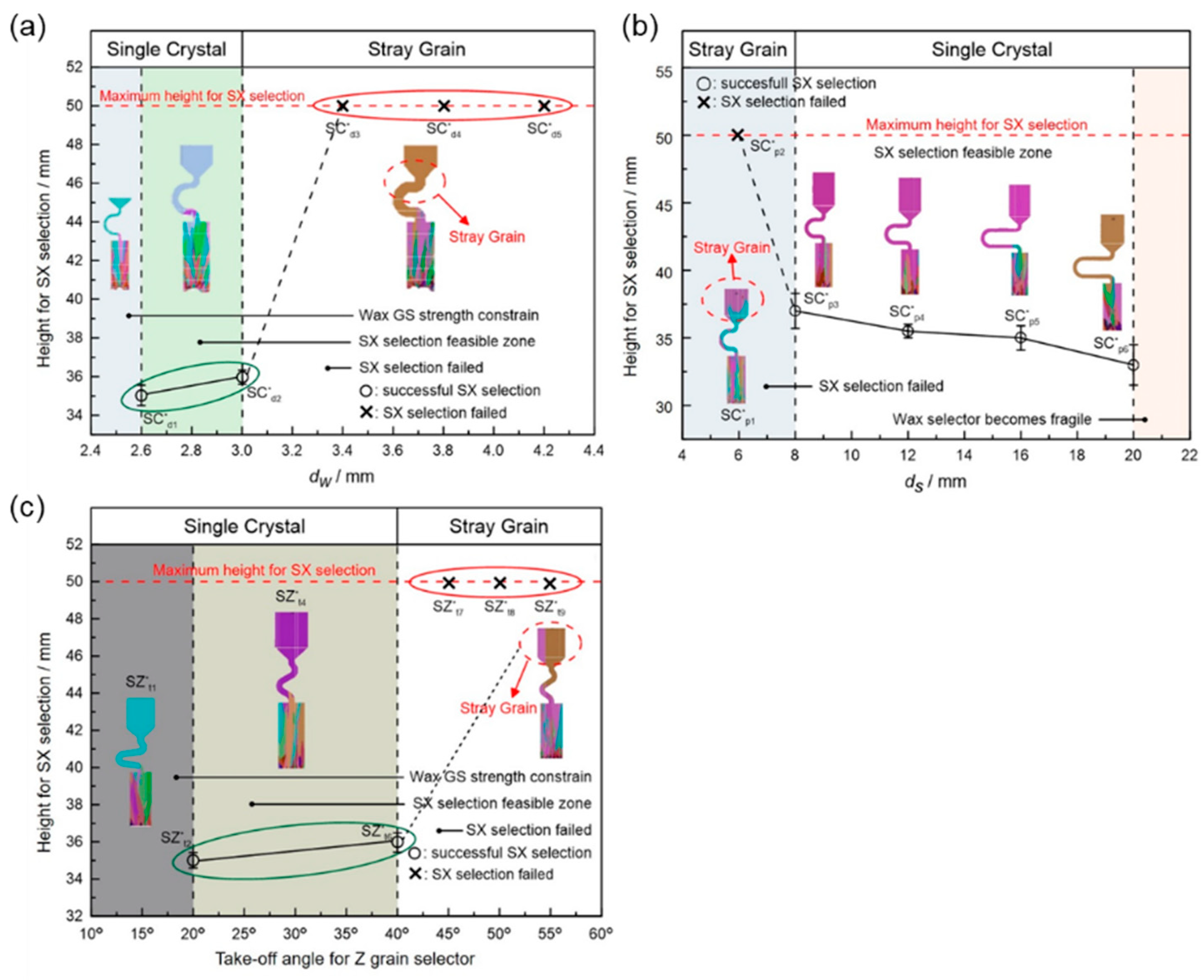

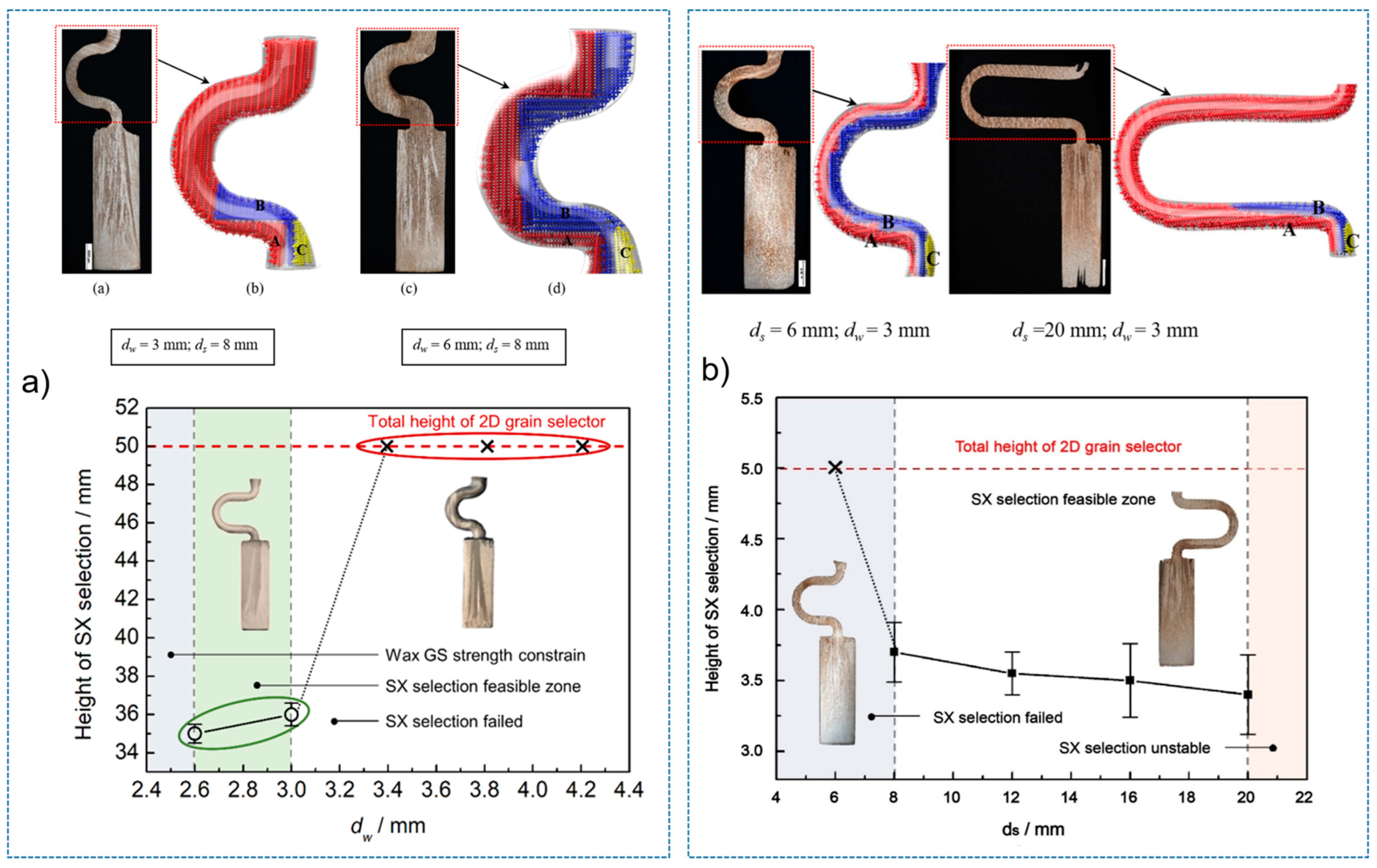



| Alloy | Elements (wt.%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Ti | Cr | Mo | Co | W | Ta | Hf | C | Ni | |
| Wt.% | 5.49 | 0.74 | 8.03 | 0.5 | 9.41 | 9.87 | 2.9 | 1.36 | 0.094 | Bal. |
| C-Form Grain Selector with Variant Diameters | Single-Crystal | Stray Grain | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
| Stray grain | No | Yes | ||||||
| Probe | SCd1 | SCd2 | SCd3 | SCd4 | SCd5 | SCd6 | SCd7 | SCd8 |
| Diameter (mm) | 2.6 | 3.0 | 3.4 | 3.8 | 4.2 | 5.4 | 6.0 | 6.6 |
| Pitch Length (mm) | 8 | |||||||
| Selector Height (mm) | 10 | |||||||
| Starter Block Size (mm) | 10 (L) × 10 (W) × 30 (H) | |||||||
| C-Form Grain Selector with Variant Pitch Lengths | Stray Grain | Single Crystal | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
| Stray grain | Yes | No | ||||||
| Probe | SCp1 | SCp2 | SCp3 | SCp4 | SCp5 | SCp6 | SCp7 | SCp8 |
| Pitch Length (mm) | 4 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 22 | 26 |
| Diameter (mm) | 3 | |||||||
| Selector Height (mm) | 10 | |||||||
| Starter Block Size (mm) | 10 (L) × 10 (W) × 30 (H) | |||||||
| Z-Form Grain Selector with Variant Take-Off Angles | Single Crystal | Stray Grain | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
| Stray grain | No | Yes | |||||||
| Sample | SZt1 | SZt2 | SZt3 | SZt4 | SZt5 | SZt6 | SZt7 | SZt8 | SZt9 |
| Take-off angle | 15° | 20° | 25° | 30° | 35° | 40° | 45° | 50° | 55° |
| Diameter (mm) | 3 | ||||||||
| Selector Height (mm) | 10 | ||||||||
| Starter Block Size (mm) | 10 (L) × 10 (W) × 30 (H) | ||||||||
| Z-Form Grain Selector with Variant Diameters | Single Crystal | Stray Grain | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
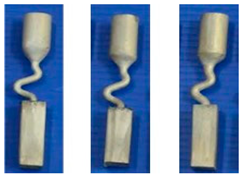 |  | |||||
| Stray grain | No | Yes | ||||
| Probe | SZd1 | SZd2 | SZd3 | SZd4 | SZd5 | SZd6 |
| Diameter (mm) | 1.8 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 4.2 | 5.0 | 6.0 |
| Take-off angle | 30° | |||||
| Selector Height (mm) | 10 | |||||
| Starter Block Size(mm) | 10 (L) × 10 (W) × 30 (H) | |||||
| C-form Grain Selector with a Varied Wire Diameter | Single Crystal | Stray Grain | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
| Stray Grain | No | Yes | ||||||
| Probe | SC *d1 | SC *d2 | SC *d3 | SC *d4 | SC *d5 | SC *d6 | SC *d7 | SC *d8 |
| Diameter (mm) | 2.6 | 3.0 | 3.4 | 3.8 | 4.2 | 5.4 | 6.0 | 6.6 |
| Pitch Length (mm) | 8 | |||||||
| Selector Height (mm) | 10 | |||||||
| Starter Block Size (mm) | 10 (L) × 10 (W) × 30 (H) | |||||||
| C-Form Grain Selector with a Varied Pitch Length | Stray Grain | Single Crystal | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  | 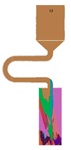 |  | 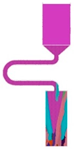 | |
| Stray Grain | Yes | No | ||||||
| Probe | SC *p1 | SC *p2 | SC *p3 | SC *p4 | SC *p5 | SC *p6 | SC *p7 | SC *p8 |
| Pitch length (mm) | 4 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 22 | 26 |
| Diameter (mm) | 3 | |||||||
| Selector Height (mm) | 10 | |||||||
| Starter Block Size (mm) | 10 (L) × 10 (W) × 30 (H) | |||||||
| Z-Form Grain Selector with a Varied Take-Off Angle | Single Crystal | Stray Grain | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |  |  | 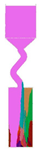 |  | |
| Stray Grain | No | Yes | |||||||
| Probe | SZ *t1 | SZ *t2 | SZ *t3 | SZ *t4 | SZ *t5 | SZ *t6 | SZ *t7 | SZ *t8 | SZ *t9 |
| Take-off angle | 15° | 20° | 25° | 30° | 35° | 40° | 45° | 50° | 55° |
| Diameter (mm) | 3 | ||||||||
| Selector Height (mm) | 10 | ||||||||
| Starter Block Size (mm) | 10 (L) × 10 (W) × 30 (H) | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Wang, F.; Ma, D. A Study of Grain Selection in Two-Dimensional (2D) Grain Selectors during the Investment Casting of Single-Crystal Superalloy. Materials 2023, 16, 4112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16114112
Zhu X, Wang F, Ma D. A Study of Grain Selection in Two-Dimensional (2D) Grain Selectors during the Investment Casting of Single-Crystal Superalloy. Materials. 2023; 16(11):4112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16114112
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xintao, Fu Wang, and Dexin Ma. 2023. "A Study of Grain Selection in Two-Dimensional (2D) Grain Selectors during the Investment Casting of Single-Crystal Superalloy" Materials 16, no. 11: 4112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16114112
APA StyleZhu, X., Wang, F., & Ma, D. (2023). A Study of Grain Selection in Two-Dimensional (2D) Grain Selectors during the Investment Casting of Single-Crystal Superalloy. Materials, 16(11), 4112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16114112






