Preparing and Wear-Resisting Property of Al2O3/Cu Composite Material Enhanced Using Novel In Situ Generated Al2O3 Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis Procedure
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
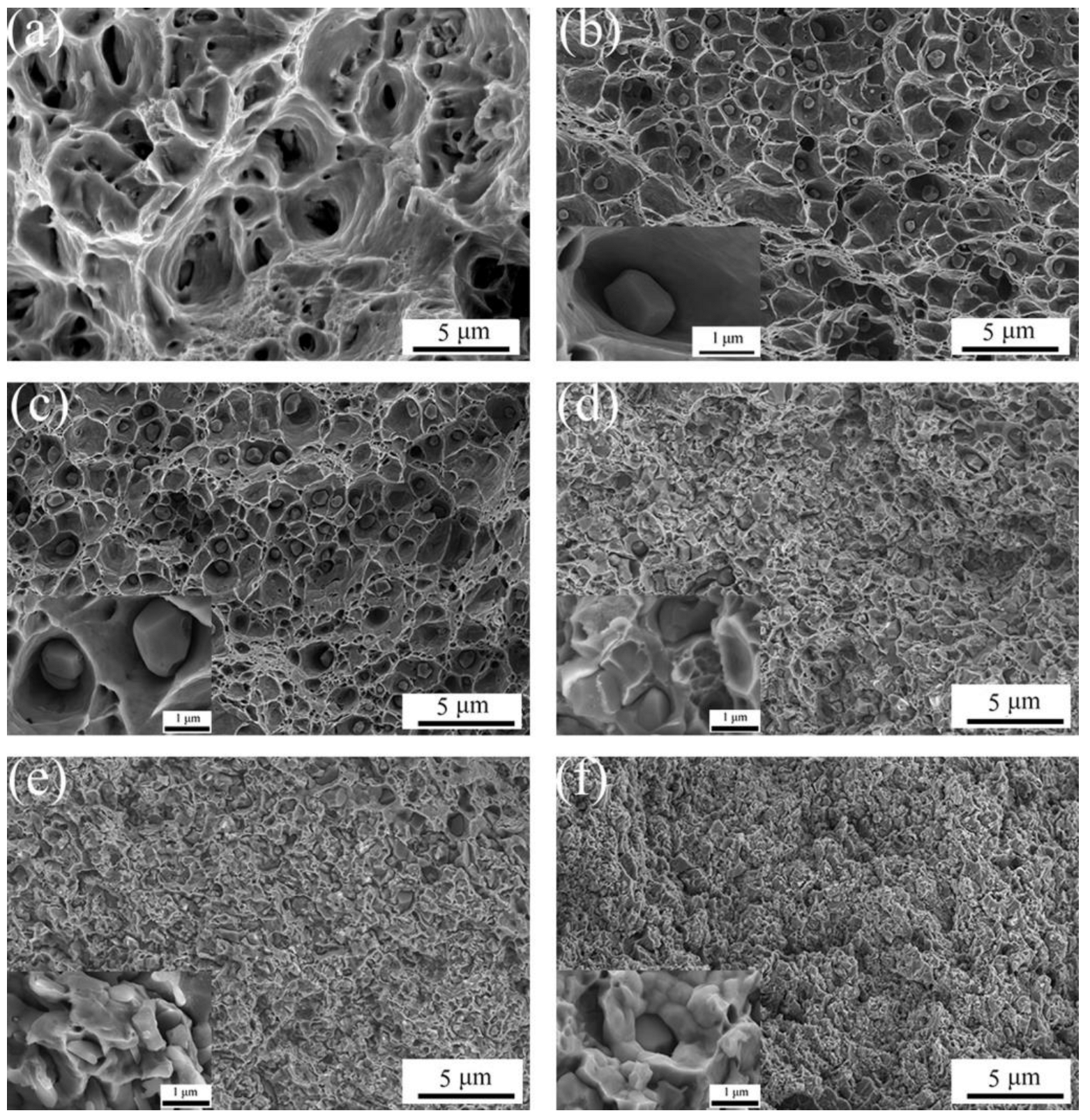
3.1. Preparation of Al2O3/Cu Composite Powder
3.2. Effect of SPS Temperature on the Density and Hardness of ACCM
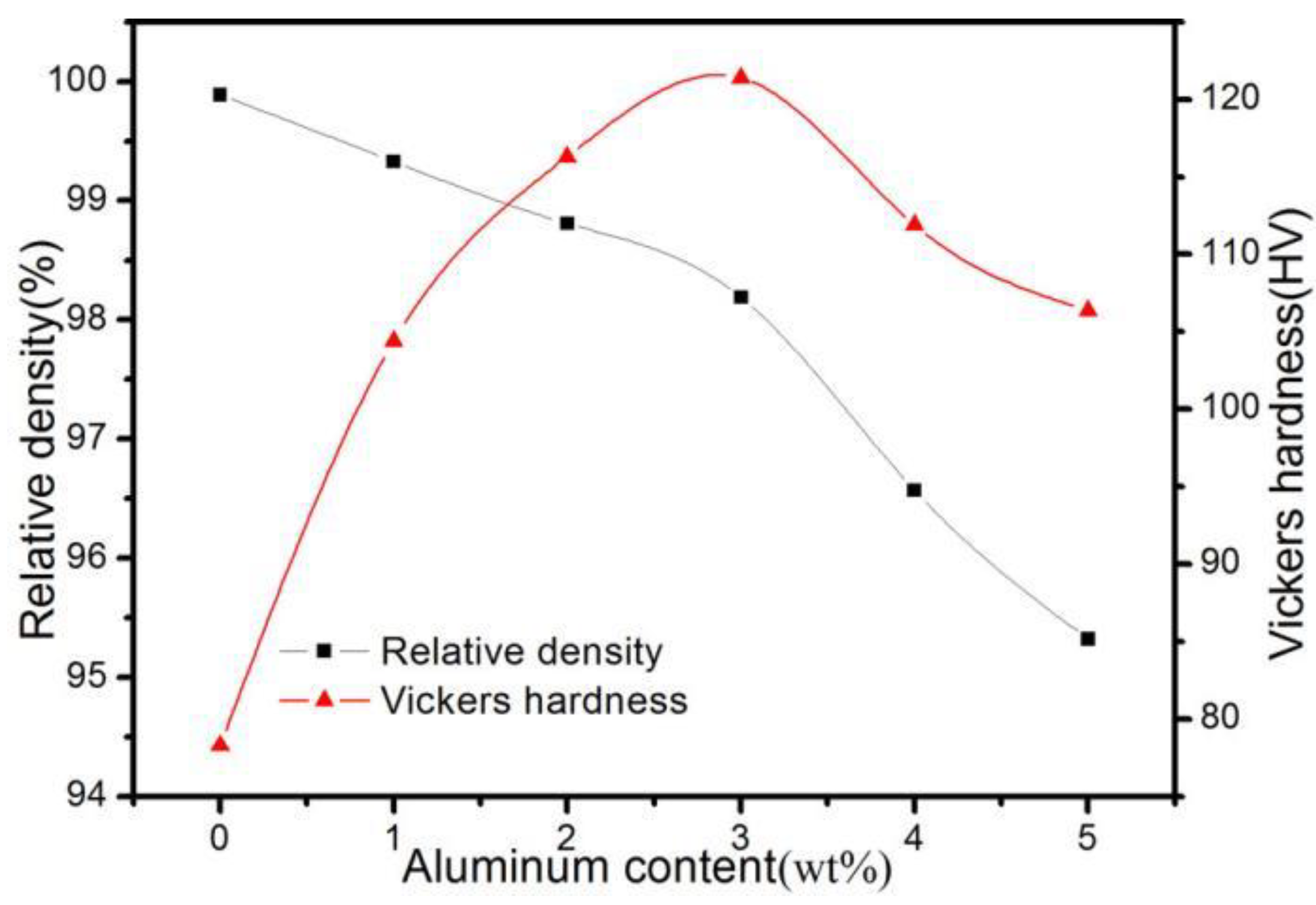
3.3. Effect of Al2O3 Content on the Relative Density and Hardness of ACCM
3.4. Effect of Al2O3 Content on the Electrical Conductivity of ACCM
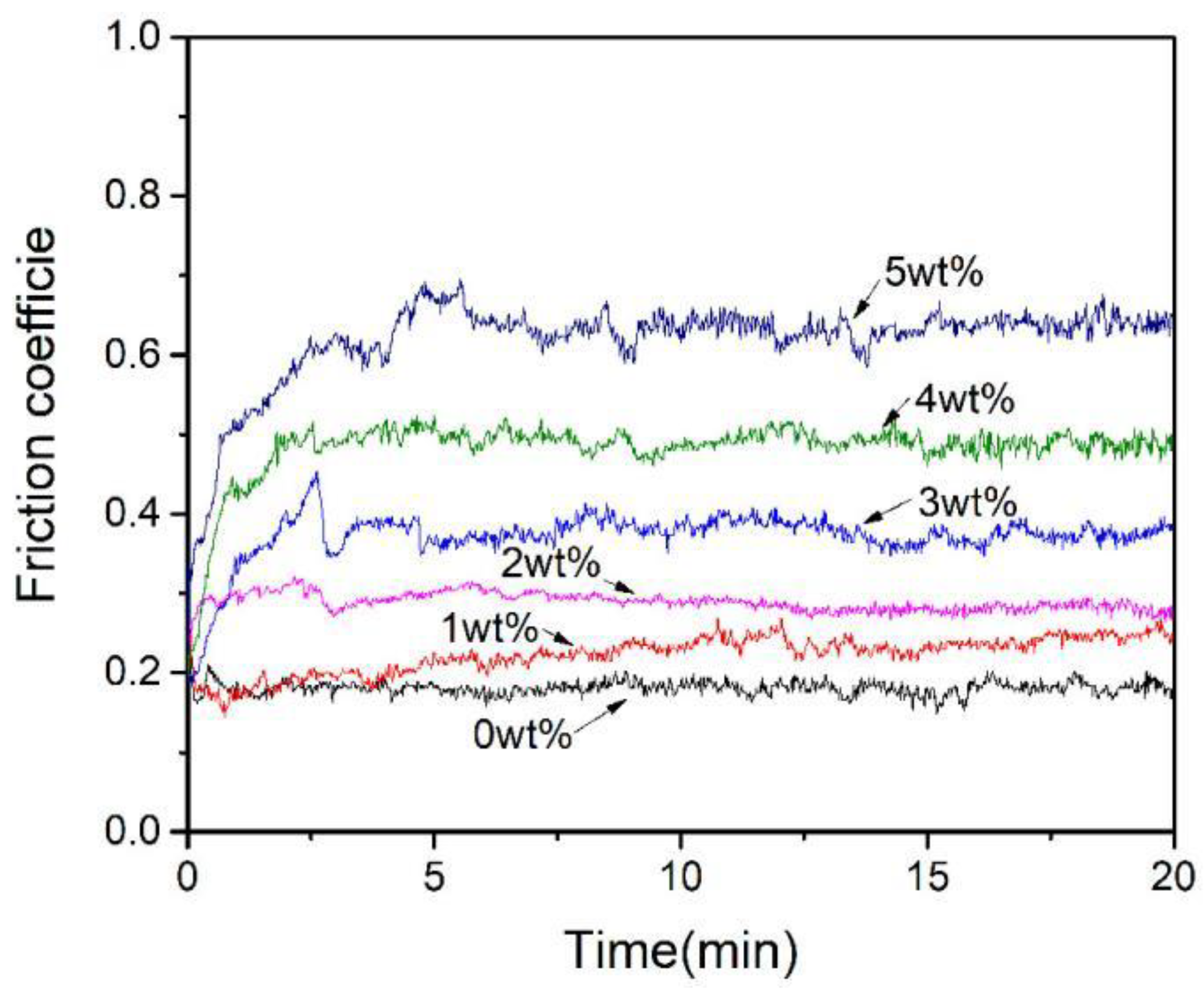
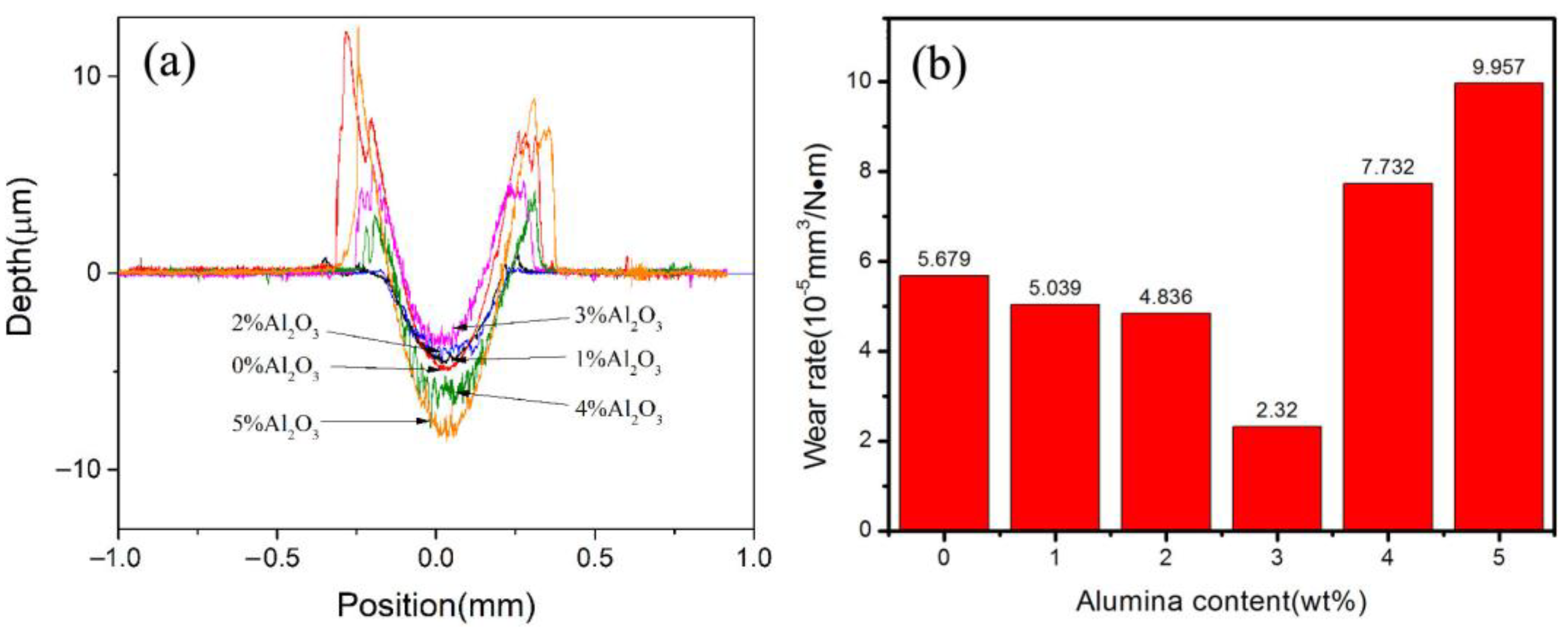
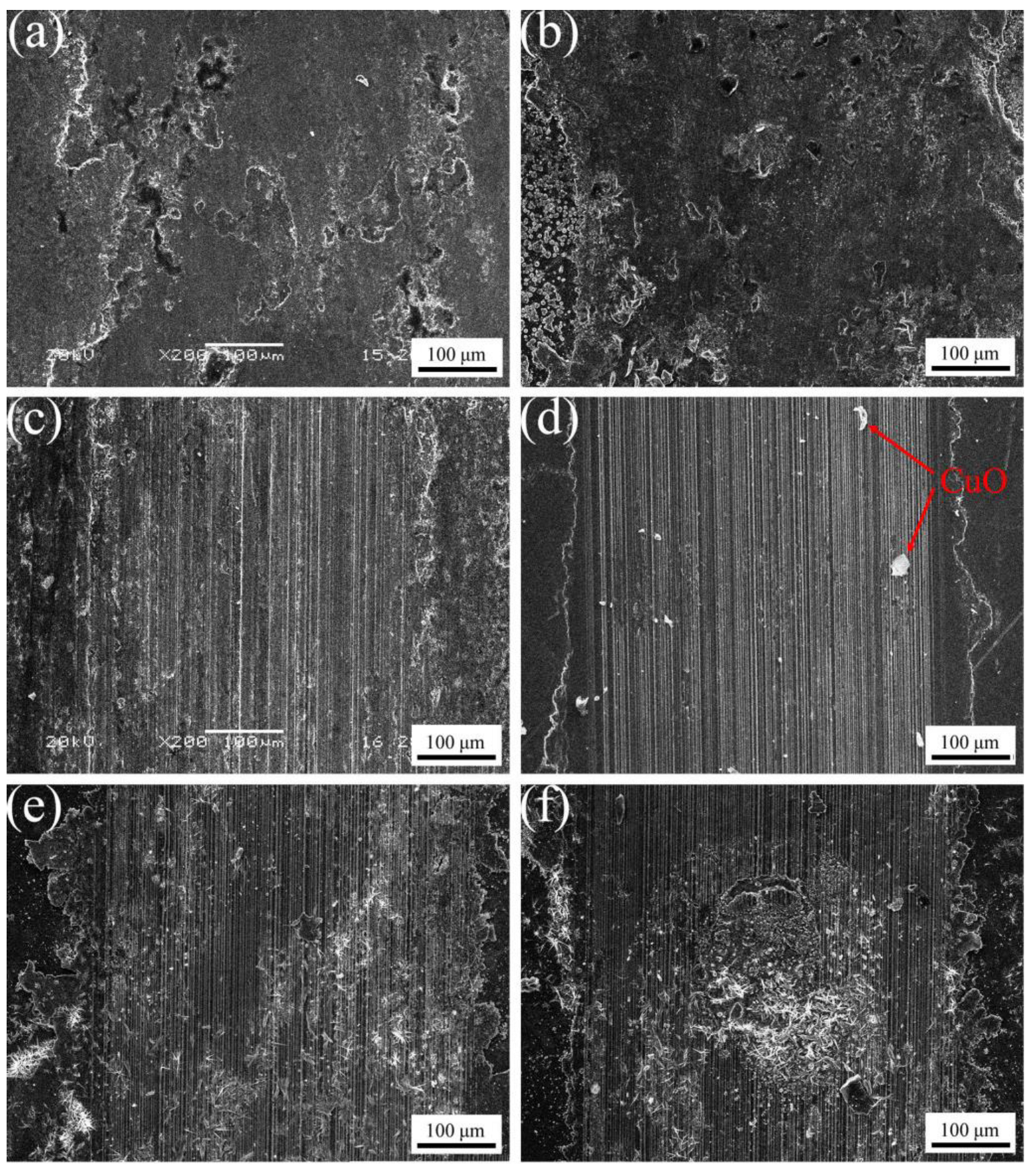
3.5. Effect of Al2O3 Content on the Friction and Wear Performance of ACCM
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The samples with the addition of various Al2O3 contents exhibit better dispersity than the samples without the addition of Al2O3. The ACCP with 3 wt.% Al2O3 content exhibits the smallest particle size and the best particle dispersity.
- (2)
- The relative density and hardness of the ACCM first increase and then decrease with the increase of the SPS temperature. When the SPS temperature is 775 °C, the relative density and hardness of the ACCM reach the maximum value (98.19% and 121.4 HV).
- (3)
- The hardness of the ACCM first increases and then decreases with the increase of Al2O3 contents, and reach the highest value (121.4 HV) with 3 wt.% Al2O3 content. Furthermore, the relative density and electrical conductivity of the ACCM decrease with the increase of Al2O3 contents. However, the friction coefficient of the ACCM increases with the increase of Al2O3 content. Moreover, the wear-resisting property improves first and then deteriorates with increase in Al2O3 contents. The ACCM with 3 wt.% Al2O3 content exhibits the highest wear resistance with the minimum wear rate (2.32 × 10−5 mm3(N·m)).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Pang, X.J.; Xu, Y.J.; Lu, H.H.; Jiang, P.; Yang, J.; Liao, Z.Q. Microstructure, mechanical and tribological properties of in situ MoB reinforced Cu-Al matrix composites. Tribol. Int. 2023, 177, 107941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.B.; Huang, D.J.; Liu, H.; Ma, W.L.; Liu, F.X.; Zhang, H. Largely enhanced thermal conductivity of graphene/copper composites with highly aligned graphene network. Carbon 2018, 127, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.Y.; Zhang, X.; Shi, C.S.; Liu, E.Z.; He, C.N.; He, F.; Zhao, N.Q. In situ synthesis of high content graphene nanoplatelets reinforced Cu matrix composites with enhanced thermal conductivity and tensile strength. Powder Technol. 2020, 362, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bao, R.; Yi, J.H.; Fang, D. Fabrication of CNT/Cu composites with enhanced strength and ductility by SP combined with optimized SPS method. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 747, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.Y.; Jiang, X.S.; Shao, Z.Y.; Sun, H.L.; Fang, Y.J.; Shu, R. Fabrication and mechanical properties of nano-carbon reinforced laminated Cu matrix composites. Powder Technol. 2022, 395, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Mei, Q.S.; Li, J.Y.; Li, C.L.; Wan, L.; Mei, X.M.; Chen, Z.H.; Xu, T.; Wang, Y.C.; Tan, Y.Y. Achieving synergistic strengthening and enhanced comprehensive properties of Cu matrix composites at high strength level by incorporating nanocarbons and Al2O3 dual reinforcements. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 839, 142859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.Y.; Zhang, X.; Shi, C.S.; Zhao, D.D.; Liu, E.Z.; He, C.N.; Zhao, N.Q. Comprehensive performance regulation of Cu matrix composites with graphene nanoplatelets in situ encapsulated Al2O3 nanoparticles as reinforcement. Carbon 2022, 188, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elwahed, M.S.; Meselhy, A.F. Experimental investigation on the mechanical, structural and thermal properties of Cu–ZrO2 nanocomposites hybridized by graphene nanoplatelets. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 9198–9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahheidary, F.; Tolaminejad, B.; Momeni, A. Surface composite on cu substrate with SiO2 reinforcement fabricated by severe plastic deformation: Microstructure, mechanical and tribological properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 793, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetterli, M.; Tavangar, R.; Weberb, L.; Kelly, A. Influence of the elastic properties of the phases on the coefficient of thermal expansion of a metal matrix composite. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmouz, M.; Asadi, P.; Givi, M.K.B.; Taherishargh, M. Investigation of mechanical properties of Cu/SiC composite fabricated by FSP: Effect of SiC particles size and volume Fraction. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2011, 528, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Cao, F.; Feng, P.; Zuo, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, W.; Liang, S. Experimental verification and numerical analysis on plastic deformation and mechanical properties of the in-situ TiB2 homogeneous composites and TiB2/Cu network composites prepared by powder metallurgy. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 920, 165897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, A.; Megahed, A.A. Prediction of abrasive wear rate of in situ Cu-Al2O3 nanocomposite using artificial neural networks. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 62, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Safaei, H. Characterization of Ni-Cu matrix, Al2O3 reinforced nano-composite coatings prepared by electrodeposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 456, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ďurišinová, K.; Ďurišin, J.; Ďurišin, M. Microstructure and properties of nanocrystalline copper strengthened by a low amount of Al2O3 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, D.; Kong, C.; Munroe, P.; Torrens, R. Thermal stability of the nanostructure of mechanically milled Cu–5 vol% Al2O3 nanocomposite powder particles. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 29, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Anas, M. An investigative review of squeeze casting: Processing effects & impact on properties. Mater. Today 2020, 26, 1914–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Abyzov, A.M.; Shakhov, F.M.; Averkin, A.I.; Nikolaev, V.I. Mechanical properties of adiamond-copper composite with high thermal conductivity. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Li, X.X.; Chen, H.; Li, T.B.; Su, W.; Guo, S.D. Investigation on microstructure and properties of Cu-Al2O3 composites fabricated by a novel in–situ reactive synthesis. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.Z.; Zhan, Z.J.; Cao, H.Y.; Guo, C.H. Microstructure and properties of the laser cladded in-situ ZrB2-ZrC/Cu composite coatings on copper substrate. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 396, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beygi, H.; Sajjadi, S.A.; Zebarjad, S.M. An optimization analysis on electroless deposition of Al2O3/Cu core-shell nanostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 261, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.L.; Huang, W.; Wang, B. A novel method for the preparation of Cu/Al2O3 Nanocomposite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 7, 2935–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethő, D.; Kurusta, T.; Kristály, F.; Mikó, T.; Gácsi, Z. The effect of ball to powder ratio on the processing of a novel Mo-Cu-Al2O3 composite. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 101, 105657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkovic, V.; Bozic, D.; Jovanovic, M.T. Effects of copper and Al2O3 particles on characteristics of Cu-Al2O3 composites. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1962–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Liang, H.S.; Zhao, X.R.; Wu, H.J. Glycine-assisted solution combustion synthesis of NiCo2O4 electromagnetic wave absorber with wide absorption bandwidth. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 22313–22320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.C.; Yu, J.C.; Zhang, Y.J.; Gong, H.Y.; Xie, B.Y.; Lin, X.; Sheng, M.M.; Mao, J.J.; Jing, J. Microwave-induced solution combustion synthesis and luminescent properties of nano-sized powders with different Nd concentrations. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 17891–17895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntola, P.; Friedrich, H.B.; Mahomed, A.S.; Olivier, E.J.; Govender, A.; Singh, S. Exploring the role of fuel on the microstructure of VOx/MgO powders prepared using solution combustion synthesis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 278, 125602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, A.M.; Wang, Z.Q.; Rafi, U.D.; Dong, Y.H.; Guo, C.G.; Liu, W.H.; Xu, H.M.; Wang, L. Citric acid-assisted combustion-nitridation-denitridation synthesis of well-distributed W-Cu nanocomposite powders. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 70, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, A.M.; Guo, Z.Q.; Rafi, U.D.; Dong, Y.H.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.H.; Xu, H.M.; Guo, C.G. Effect of fuel type on the aminolysis synthesis of CrN powders from combustion synthesis precursors. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Huang, X.; Guo, J. Improvement of interfacial wettability of Al2O3 based. Mater. Rev. 2001, 15, 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Liu, Z.; Yu, L.M.; Ma, Z.Q.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Wang, Z.M. Effect of WC nanoparticles on the thermal stability and mechanical performance of dispersion-reinforced Cu composites. Scr. Mater. 2023, 222, 115030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.G.; Chen, W.G.; Dong, L.L.; Li, H.Y.; Fu, Y.Q. Enhancing copper infiltration into alumina using sparking plasma sintering to achieve high performance Al2O3/Cu composites. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoun, A.M.; Meselhy, A.F.; Abdallah, A.W. Microstructural, mechanical and wear behavior of electroless assisted silver coated Al2O3-Cu nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 266, 124562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.H.; Song, K.X.; Liang, S.H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.M. Effect of Al2O3 particle size on electrical wear performance of Al2O3/Cu composites. Tribol. Trans. 2016, 3, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, A.; Shaat, M. The dependence of accumulative roll bonded copper mechanical properties on grain sub-division, stacking faults, and lattice strains. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 756, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Sadoun, A.M.; Elmahdy, M.; Abouelmagd, G.; Mazen, A.A. Development and performance analysis of novel in situ Cu–Ni/Al2O3 nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 22672–22680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xiao, S.; Lu, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, B.; Xu, W.; Jia, C.; Qu, X. Fabrication, mechanical properties and electrical conductivity of Al2O3 reinforced Cu/CNTs composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 782, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.F. A review of recent research on mechanics of multifunctional composite materials and structures. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 2793–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-wazery, M.; El-Desouky, A.R.; Hameda, O.A.; Fathy, A.; Mansour, N.A. Electrical and mechanical performance of zirconia-nickel functionally graded materials. Int. J. Eng. 2013, 26, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoun, A.M.; Fathy, A. Experimental study on tribological properties of Cu-Al2O3 nanocomposite hybridized by graphene nanoplatelets. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 24784–24792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, B.; Adem, K. The effect of Al2O3 on the friction performance of automotive brake friction materials. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Memar, S.; Azadi, M.; Abdoos, H. An evaluation on microstructure, wear, and compression behavior of Al2O3/brass matrix nanocomposites fabricated by stir casting method. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarajan, Z. Tribological properties of brass-graphite composite. Metall. Res. Technol. 2014, 111, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Bouchart, V.; Chevrier, P.; Ding, H. Densification behavior and wear performance of brass-based composite reinforced with SiO2 nanoparticles: Switchable water pump clutch application. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
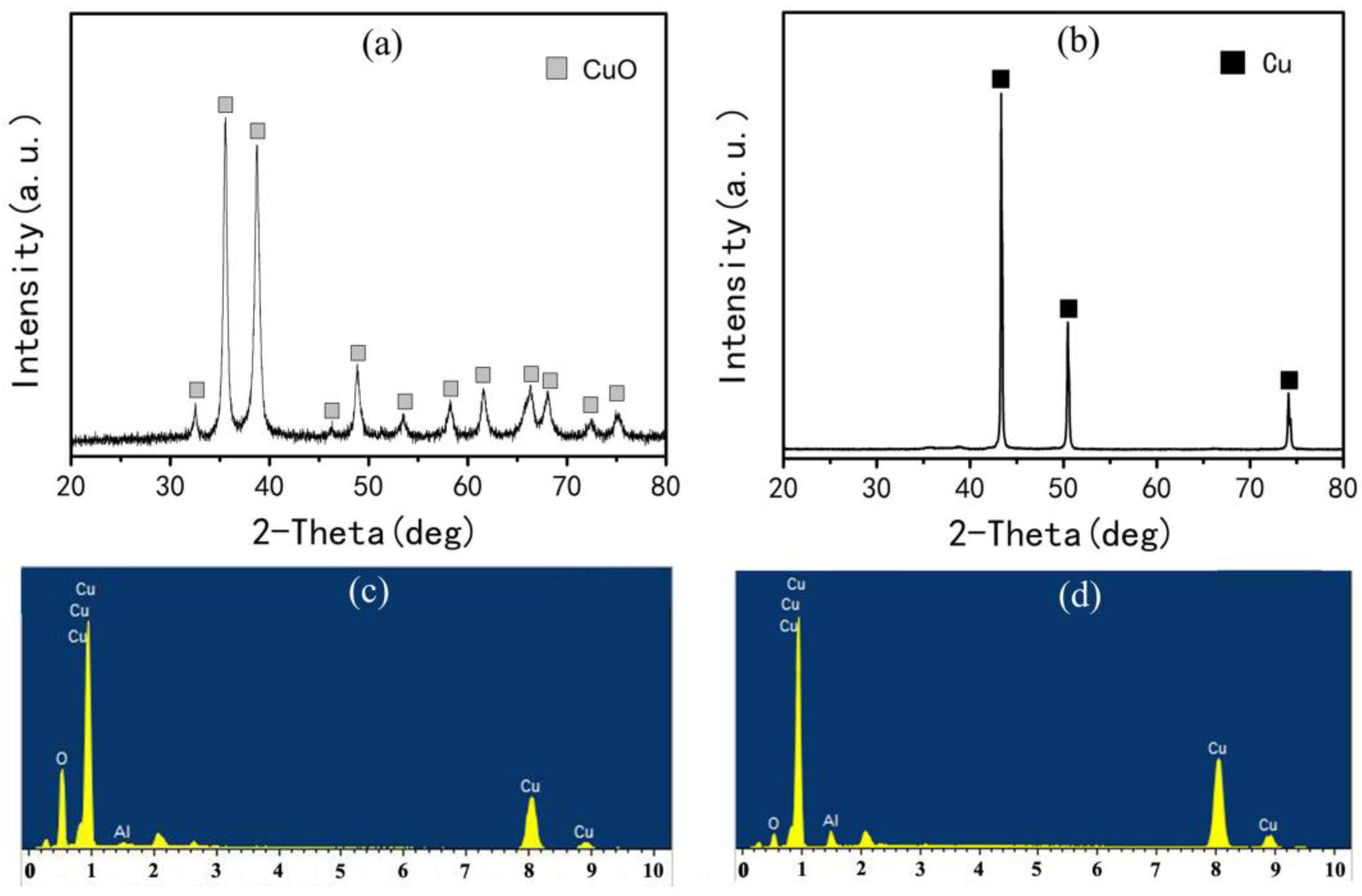
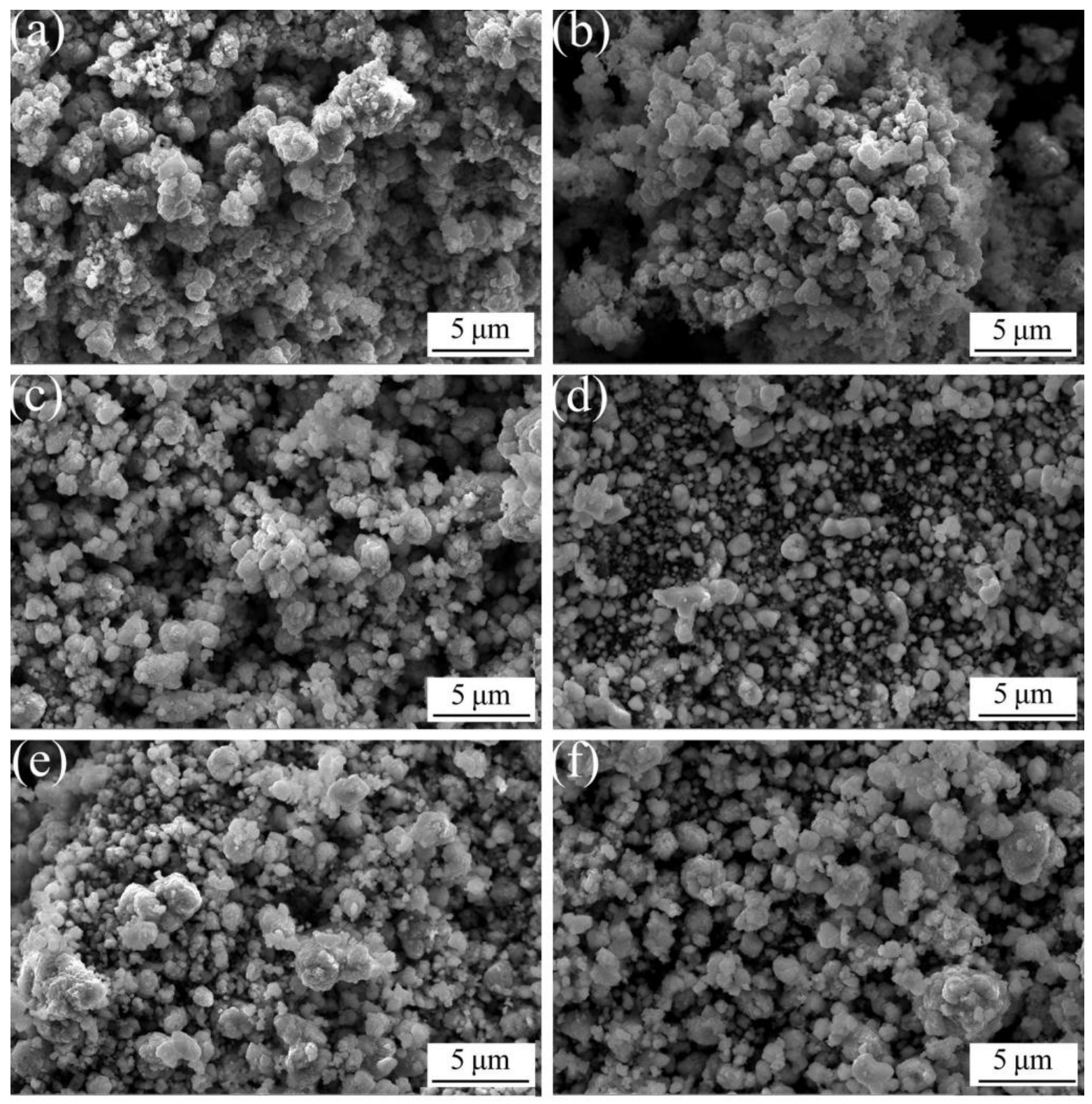
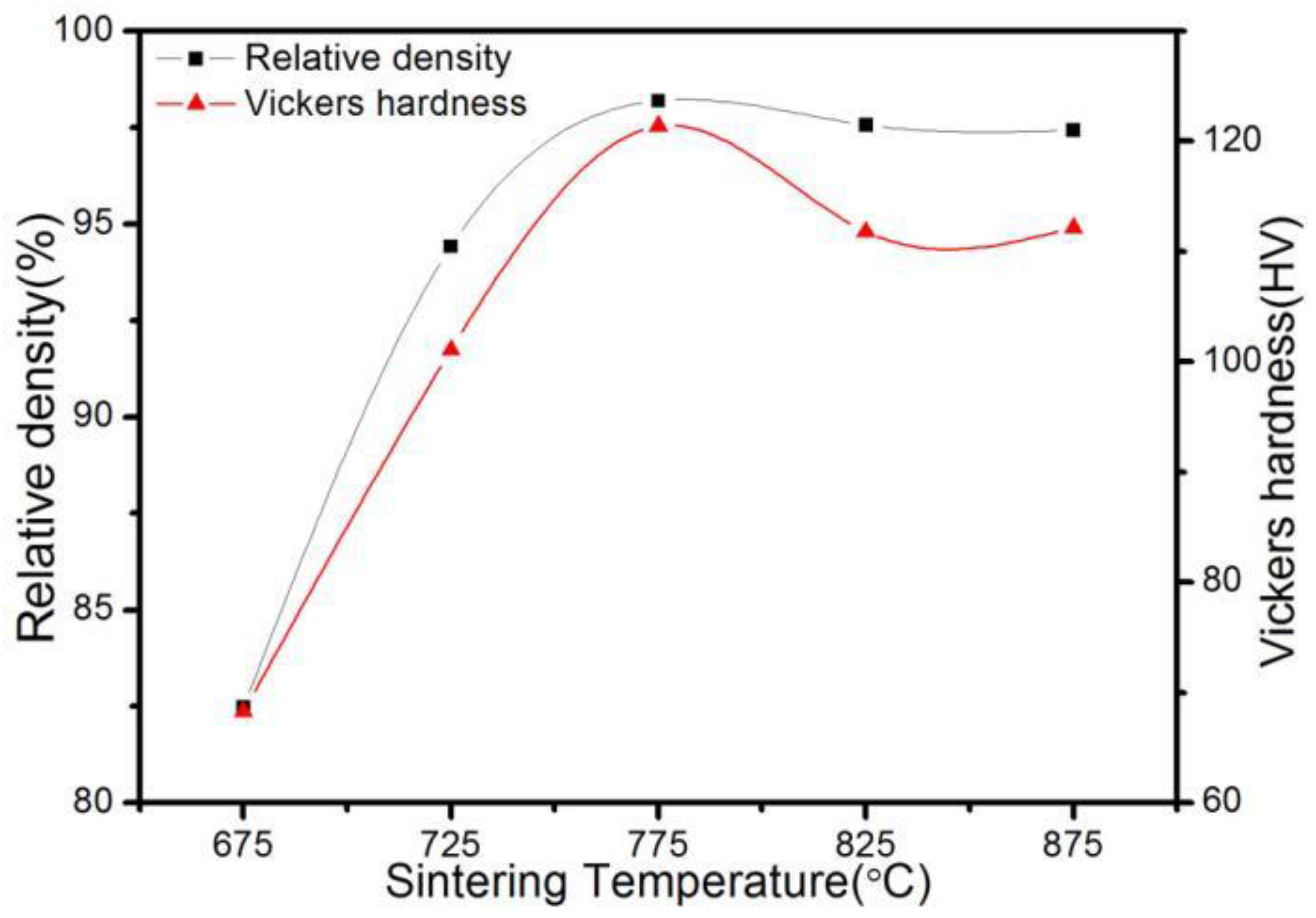
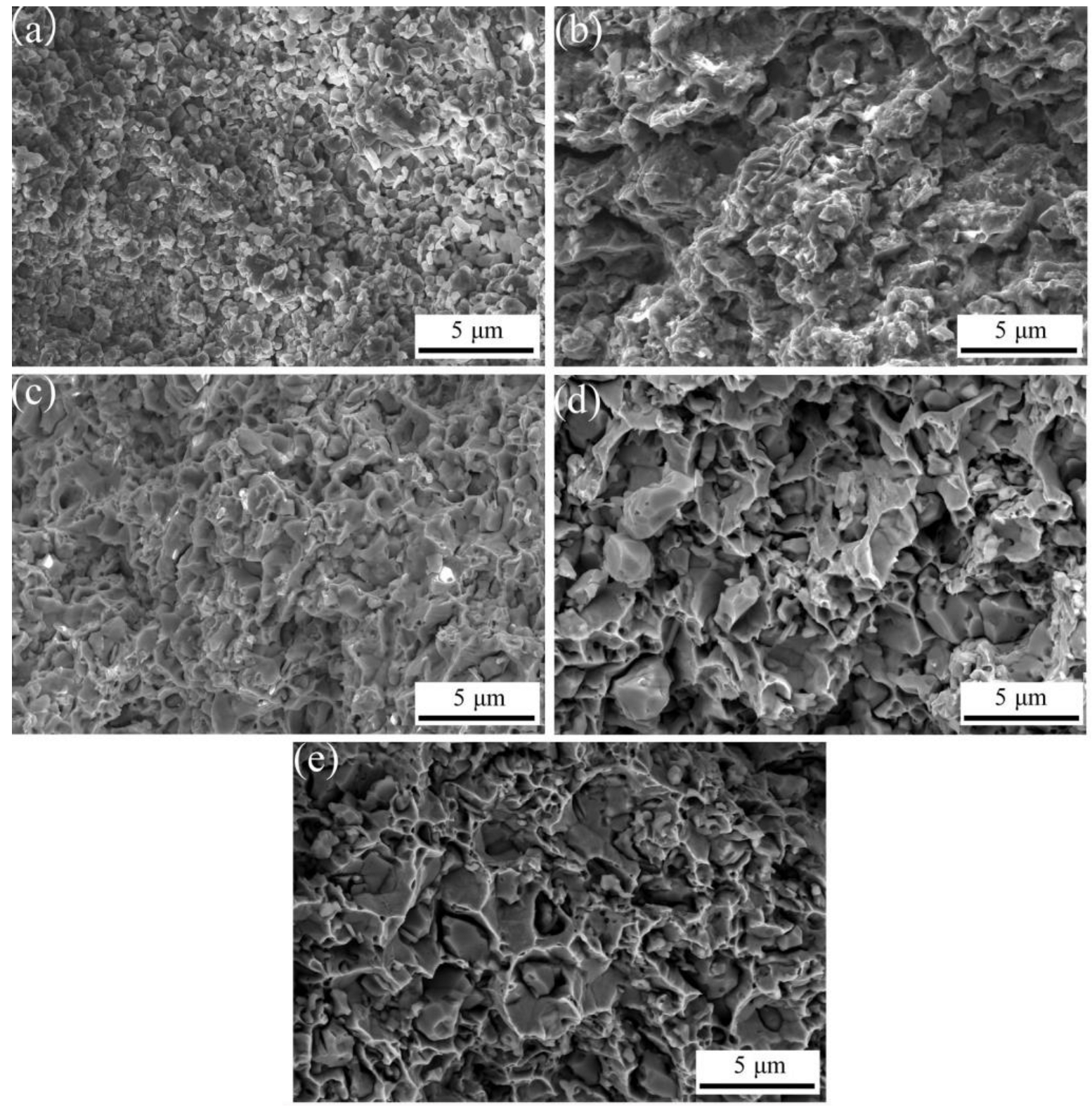

| Al2O3 content (wt.%) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| SSA (m2/g) | 3.6 | 4.3 | 4.8 | 6.2 | 5.7 | 4.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Ud-din, R.; Yang, T.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Chu, A.; Zhao, Y. Preparing and Wear-Resisting Property of Al2O3/Cu Composite Material Enhanced Using Novel In Situ Generated Al2O3 Nanoparticles. Materials 2023, 16, 4819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134819
Chen Y, Ud-din R, Yang T, Li T, Li C, Chu A, Zhao Y. Preparing and Wear-Resisting Property of Al2O3/Cu Composite Material Enhanced Using Novel In Situ Generated Al2O3 Nanoparticles. Materials. 2023; 16(13):4819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134819
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Youming, Rafi Ud-din, Teng Yang, Tao Li, Chuanghao Li, Aimin Chu, and Yuping Zhao. 2023. "Preparing and Wear-Resisting Property of Al2O3/Cu Composite Material Enhanced Using Novel In Situ Generated Al2O3 Nanoparticles" Materials 16, no. 13: 4819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134819
APA StyleChen, Y., Ud-din, R., Yang, T., Li, T., Li, C., Chu, A., & Zhao, Y. (2023). Preparing and Wear-Resisting Property of Al2O3/Cu Composite Material Enhanced Using Novel In Situ Generated Al2O3 Nanoparticles. Materials, 16(13), 4819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134819






