Use of Insect-Derived Chitosan for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Wastewater: Process Optimization Using a Central Composite Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction and Characterization of Chitosan
2.3. Experimental Design
3. Results and Discussion
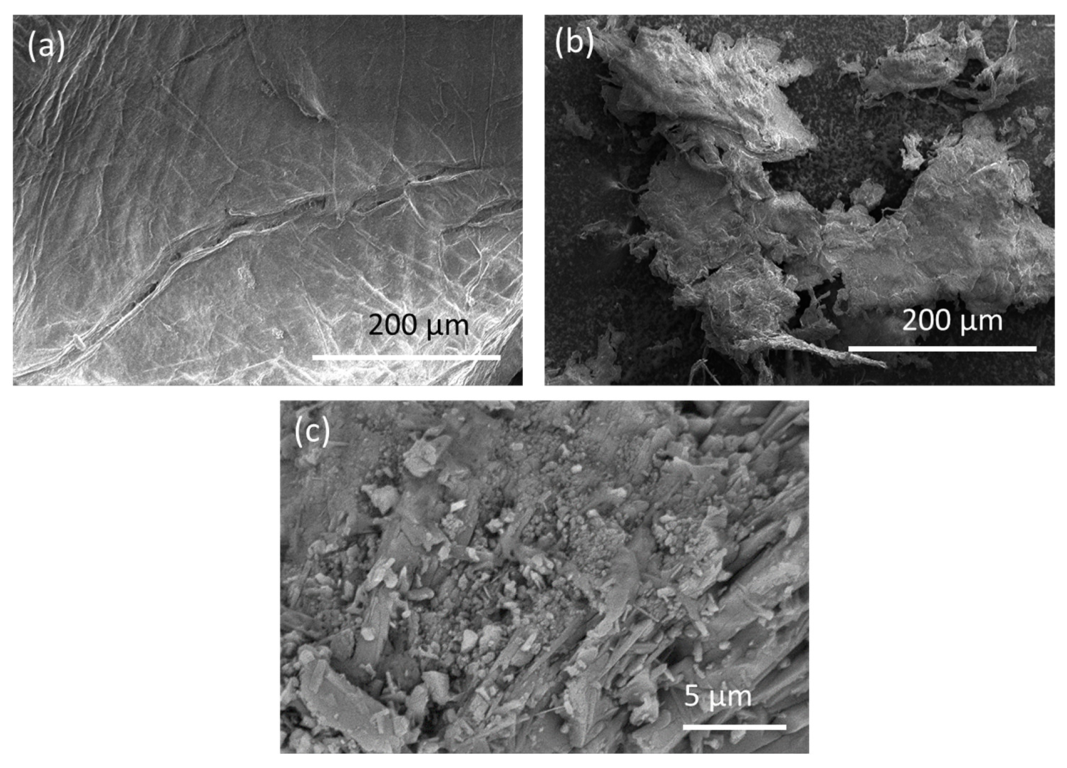
3.1. Characteristics of Chitosan
3.2. Analytical Statistics and Model Fitting
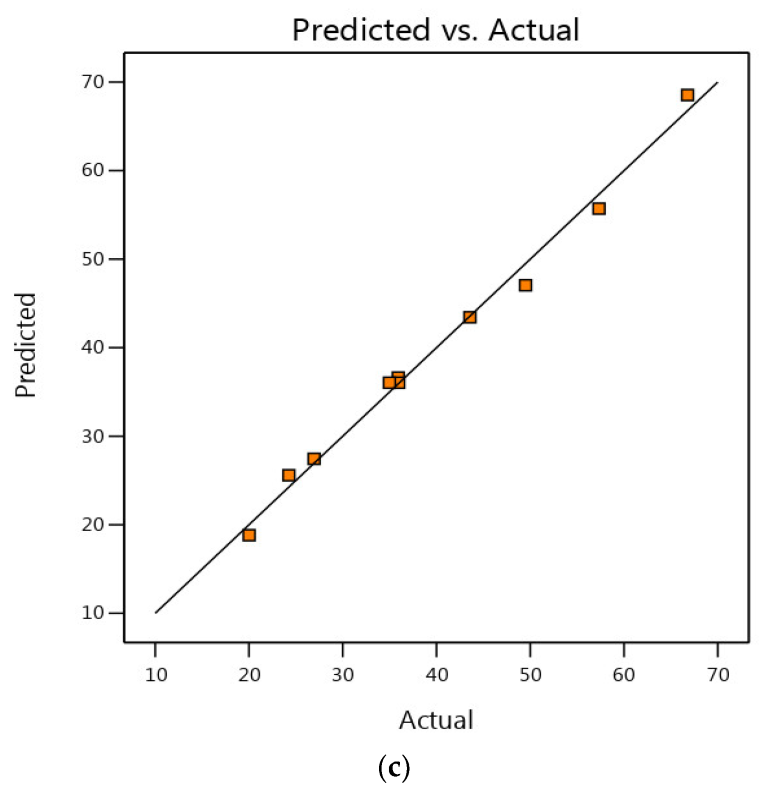
3.3. Internal vs. Normal
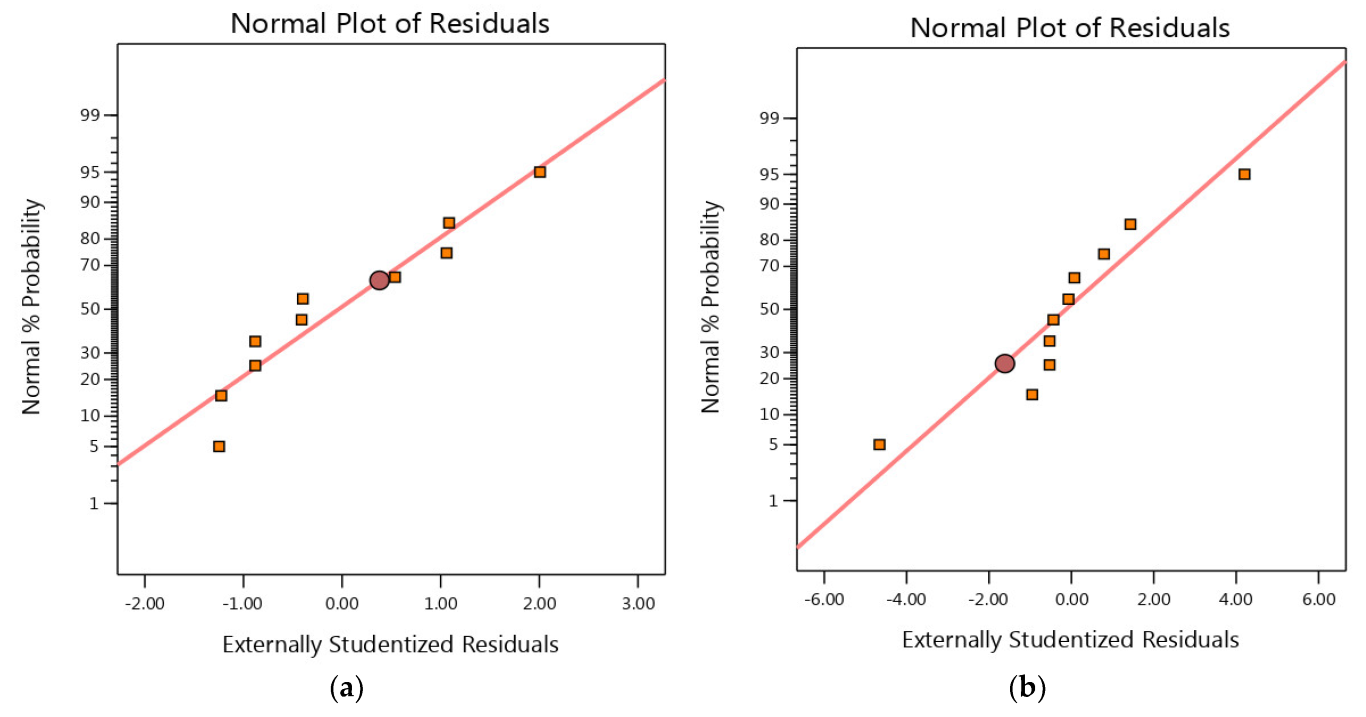
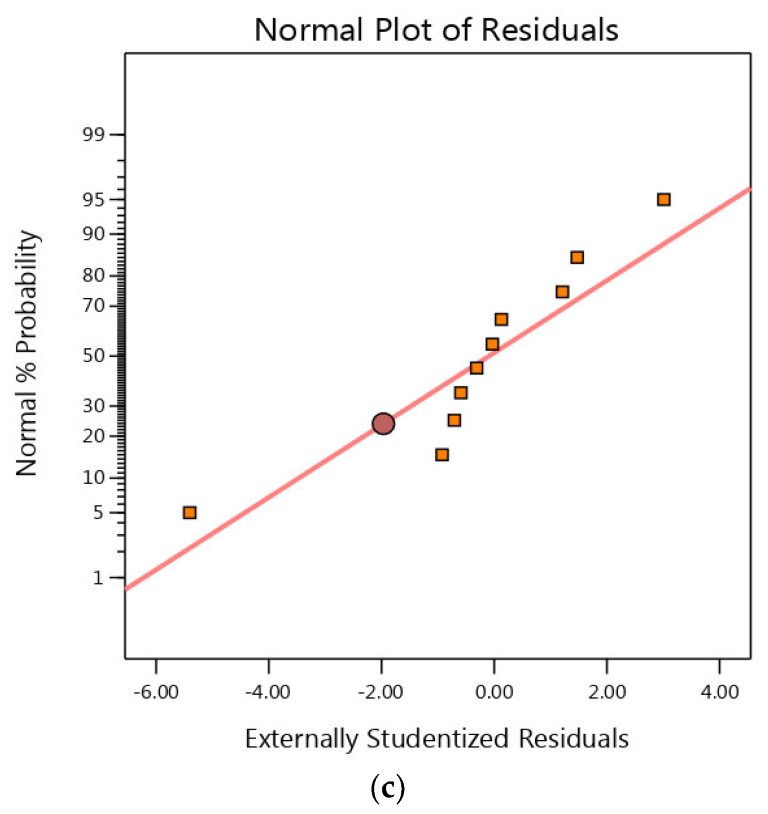
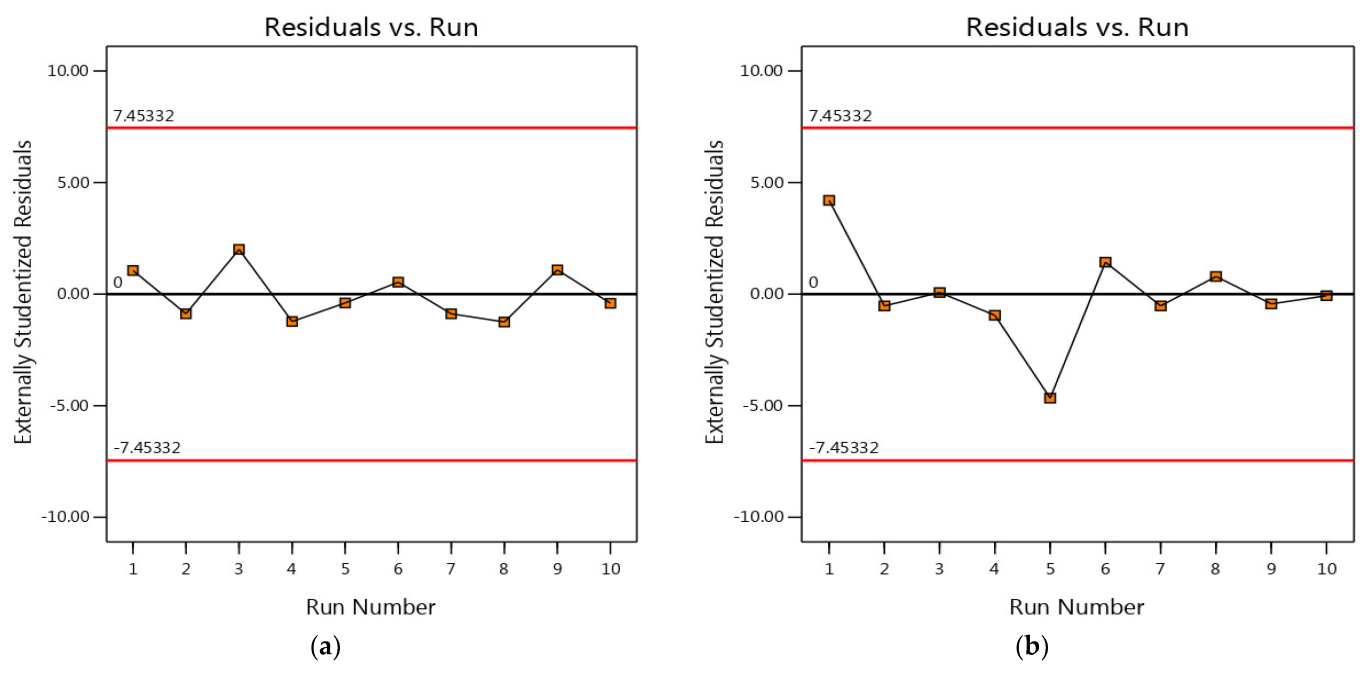
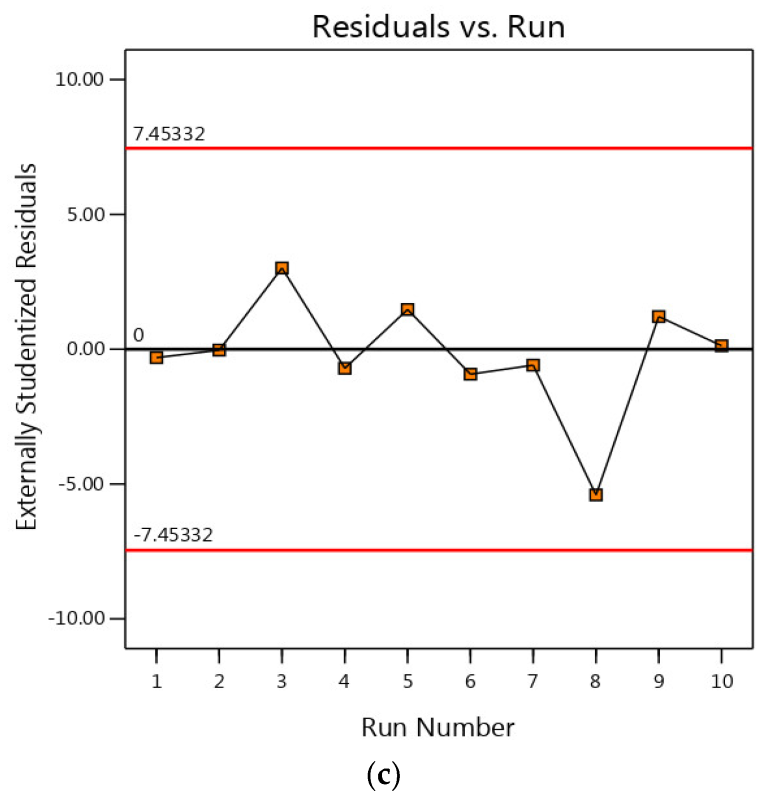
3.4. Residual Analysis
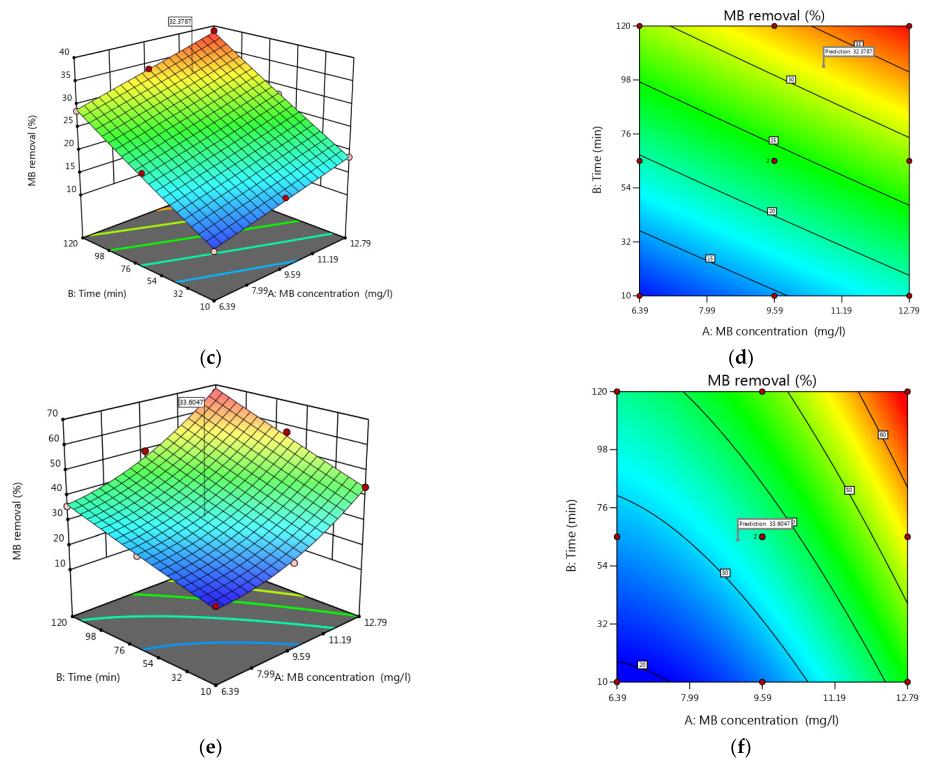
3.5. Process Factors’ Impact on MB Removal
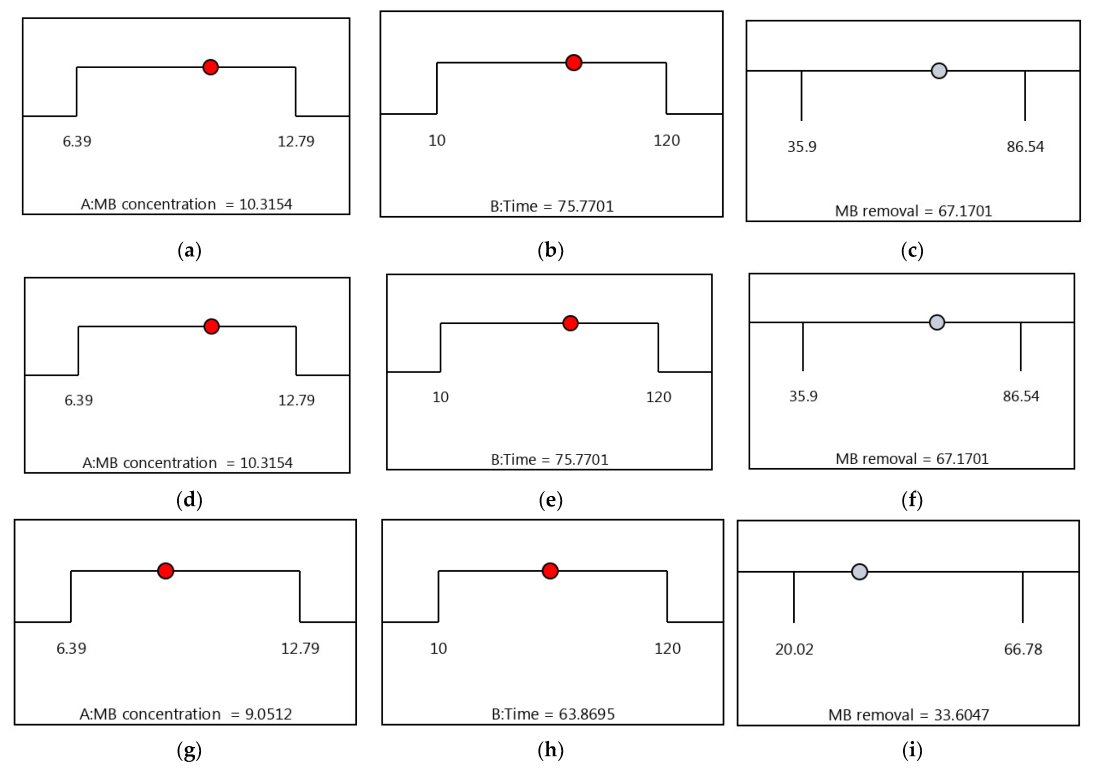
3.6. Optimization by the Desirability Functions
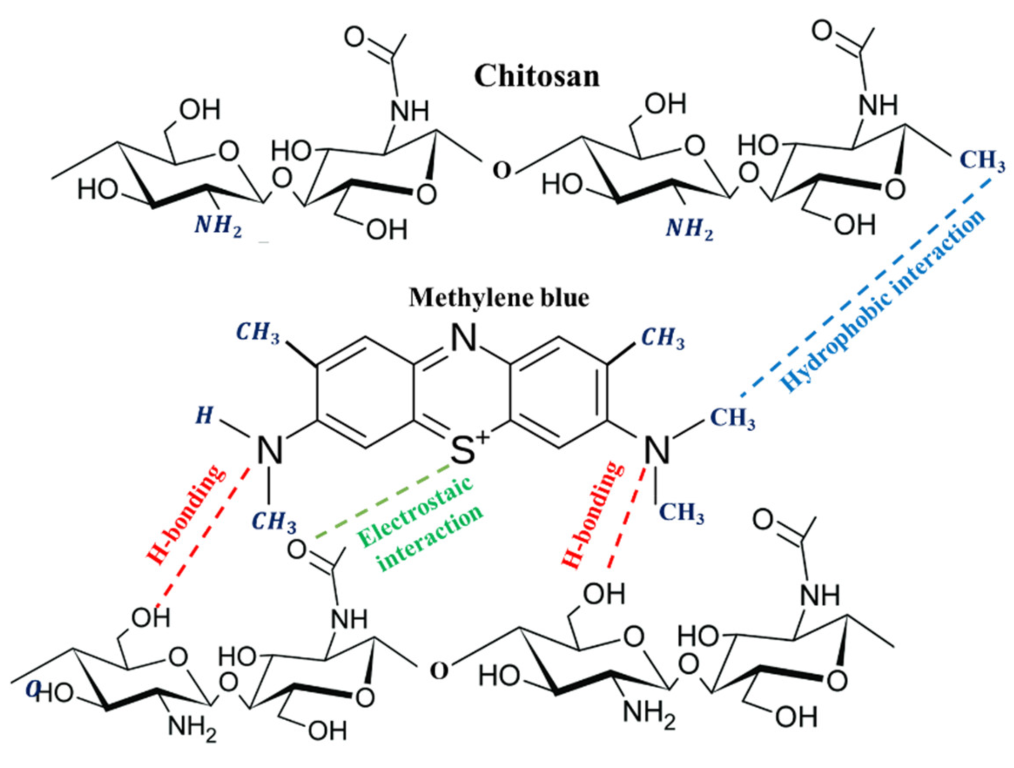
4. Mechanism of Interaction and MB Dye Removal
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nnaji, C.O.; Jeevanandam, J.; Chan, Y.S.; Danquah, M.K.; Pan, S.; Barhoum, A. Engineered nanomaterials for wastewater treatment: Current and future trends. Fundam. Nanopart. 2018, 129–168. [Google Scholar]
- Adejumoke, A.I.; Babatunde, O.A.; Abimbola, P.O.; Tabitha, A.A.A.; Adewumi, O.D.; Toyin, A.O. Water pollution: Effects, prevention, and climatic impact. Water Chall. Urban. World 2018, 33, 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Hamimed, S.; Jebli, N.; Othmani, A.; Hamimed, R.; Barhoum, A.; Chatti, A. Nanocelluloses for Removal of Heavy Metals From Wastewater. In Handbook of Nanocelluloses: Classification, Properties. Fabrication, and Emerging Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jahan, N.; Tahmid, M.; Shoronika, A.Z.; Fariha, A.; Roy, H.; Pervez, M.N.; Cai, Y.; Naddeo, V.; Islam, M.S. A Comprehensive Review on the Sustainable Treatment of Textile Wastewater: Zero Liquid Discharge and Resource Recovery Perspectives. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, K.G.; Arumugam, V.; Barhoum, A. Nanocellulose-Based Materials for Wastewater Treatment. In Handbook of Nanocelluloses: Classification, Properties, Fabrication, and Emerging Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Chantarasiri, A. Klebsiella and Enterobacter isolated from mangrove wetland soils in Thailand and their application in biological decolorization of textile reactive dyes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Kooh, M.R.R.; Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N. Effective and simple NaOH-modification method to remove methyl violet dye via Ipomoea aquatica roots. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2021, 2021, 5932222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaimi, N.; Kooh, M.R.R.; Lim, C.M.; Chou Chao, C.T.; Chou Chau, Y.F.; Mahadi, A.H.; Chiang, H.P.; Haji Hassan, N.H.; Thotagamuge, R. The use of gigantochloa bamboo-derived biochar for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 8245797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iber, B.T.; Kasan, N.A.; Torsabo, D.; Omuwa, J.W. A review of various sources of chitin and chitosan in nature. J. Renew. Mater. 2022, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, I.B.; Emran, T.B.; Hemmami, H.; Zeghoud, S.; Laouini, S.E. Nanomaterials based on chitosan for skin regeneration: An update. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 594–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatullayeva, S.; Tagiyev, D.; Zeynalov, N.; Mammadova, S.; Aliyeva, E. Recent advances of chitosan-based polymers in biomedical applications and environmental protection. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, R.C.F.; Ng, T.B.; Wong, J.H.; Chan, W.Y. Chitosan: An update on potential biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5156–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshad, R.A.I.; Jishan, T.A.; Chowdhury, N.N. Chitosan and its broad applications: A brief review. J. Clin. Exp. Investig. 2021, 12, em00779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Li, B.; Celi, N.; Cai, J.; Zhang, D. Efficient removal of Pb(II) from aqueous systems using spirulina-based biohybrid magnetic helical microrobots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 53131–53142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Che, X.; Pei, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Li, C. Biofibrous nanomaterials for extracting strategic metal ions from water. Exploration 2022, 2, 20220050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somsesta, N.; Sricharoenchaikul, V.; Aht-Ong, D. Adsorption removal of methylene blue onto activated carbon/cellulose biocomposite films: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 240, 122221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.E. Nanoadsorbents for water and wastewater remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, I.B.; Hemmami, H.; Laouini, S.E.; Abdelaziz, A.G.; Barhoum, A. Influence of chitosan source and degree of deacetylation on antibacterial activity and adsorption of AZO dye from water. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Mitropoulos, A.C. Chitosan adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 1800–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamad, A.A.; Zeghoud, S.; Amor, I.B.; Hemmami, H. Chitosan-based hydrogels for wound healing: Correspondence. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 1821–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødde, R.H.; Einbu, A.; Vårum, K.M. A seasonal study of the chemical composition and chitin quality of shrimp shells obtained from northern shrimp (Pandalus borealis). Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Yu, D.; Xu, Y.; Wang, B.; Xia, W. Development and properties of bacterial cellulose, curcumin, and chitosan composite biodegradable films for active packaging materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, N.H.; El-Samie, E.A.; Salah, T.; Saad, G.R.; Elwahy, A.H. Isolation and characterization of chitosan from different local insects in Egypt. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Martinez, S.S.; Shahtaheri, S.J.; Yaghmaeian, K.; Badiei, A.; Nazmara, S.; Naddafi, K. Response surface methodology modeling to improve degradation of Chlorpyrifos in agriculture runoff using TiO2 solar photocatalytic in a raceway pond reactor. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugashini, S.; Begum, K.M.S. Optimization using central composite design (CCD) for the biosorption of Cr(VI) ions by cross linked chitosan carbonized rice husk (CCACR). Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2013, 15, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leardi, R. Experimental design in chemistry: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 652, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Mao, M.; Guo, H.; Dai, Y. Extraction optimization of the polysaccharide from Adenophorae Radix by central composite design. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 67, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, P.; Purkait, M.K. Green synthesized iron nanoparticles supported on pH responsive polymeric membrane for nitrobenzene reduction and fluoride rejection study: Optimization approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, I.B.; Hemmami, H.; Laouini, S.E.; Mahboub, M.S.; Barhoum, A. Sol-Gel Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Different Chitosan Sources: Effects on Antibacterial Activity and Photocatalytic Degradation of AZO Dye. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Baran, T.; Erdoğan, S.; Menteş, A.; Özüsağlam, M.A.; Çakmak, Y.S. Physicochemical comparison of chitin and chitosan obtained from larvae and adult Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata). Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 45, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metin, C.; Alparslan, Y.; Baygar, T.; Baygar, T. Physicochemical, microstructural and thermal characterization of chitosan from blue crab shell waste and its bioactivity characteristics. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2552–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-X.; Lin, D.-Q.; Yao, S.-J. Design of chitosan and its water soluble derivatives-based drug carriers with polyelectrolyte complexes. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 6236–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, I.B.; Hemmami, H.; Laouini, S.E.; Temam, H.B.; Zaoui, H.; Barhoum, A. Biosynthesis MgO and ZnO nanoparticles using chitosan extracted from Pimelia Payraudi Latreille for antibacterial applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassanayake, R.S.; Acharya, S.; Abidi, N. Biopolymer-based materials from polysaccharides: Properties, processing, characterization and sorption applications. In Advanced Sorption Process Applications; Edebali, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva Alves, D.C.; Healy, B.; Pinto, L.A.D.A.; Cadaval, T.R.S.A., Jr.; Breslin, C.B. Recent developments in chitosan-based adsorbents for the removal of pollutants from aqueous environments. Molecules 2021, 26, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharby, N.F.; Almutairi, R.S.; Mohamed, N.A. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue dye by novel crosslinked O-CM-Chitosan hydrogel in aqueous solution: Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics. Polymers 2021, 13, 3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.S.; Azmi, N.A.S.; Chin, S.X.; Zakaria, S.; Chia, C.H. Chitosan-Bead-Encapsulated Polystyrene Sulfonate for Adsorption of Methylene Blue and Regeneration Studies: Batch and Continuous Approaches. Polymers 2023, 15, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheikh, S.M.; Barhoum, A.; El-Sherbiny, S.; Morsy, F.; El-Midany, A.A.-H.; Rahier, H. Preparation of superhydrophobic nanocalcite crystals using Box–Behnken design. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A.; Dargahi, A.; Almasi, A. Biological removal of diazinon in a moving bed biofilm reactor–process optimization with central composite design. Toxin Rev. 2021, 40, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiru, T. P-value, a true test of statistical significance? A cautionary note. Ann. Ib. Postgrad. Med. 2008, 6, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, C.; Batlle, X.; Labarta, A. The effect of oleic acid on the synthesis of Fe 3− x O 4 nanoparticles over a wide size range. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 27373–27379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Rajput, P.; Sharma, P.; Verma, A.K.; Agarwal, S.; Garg, M.C. Application of RSM for Bioremoval of Methylene Blue Dye from Industrial Wastewater onto Sustainable Walnut Shell (Juglans regia) Biomass. Water 2022, 14, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekarska, K.; Sikora, M.; Owczarek, M.; Jóźwik-Pruska, J.; Wiśniewska-Wrona, M. Chitin and Chitosan as Polymers of the Future—Obtaining, Modification, Life Cycle Assessment and Main Directions of Application. Polymers 2023, 15, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Codes | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | ||
| MB concentration (mg/L) | A | 6.39 | 9.59 | 12.79 |
| Time (min) | B | 10.00 | 65.00 | 120.00 |
| Characteristics of Chitosan | Sources of Chitosan Extracts | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CS-BL | CS-PF | CS-MD | |
| Yield (Y) | 41.5 ± 0.5% | 50.3 ± 0.3% | 57.9 ± 0.2% |
| Moisture content (MC) | 17.2 ± 0.2% | 14.3 ± 0.3% | 7.8 ± 0.1% |
| Ash content (AC) | 1.6 ± 0.1% | 2.1 ± 0.1% | 8.2 ± 0.2% |
| Water-binding capacity (WBC) | 515.5 ± 6.5% | 287.1 ± 5.8% | 301.1 ± 4.3% |
| Fat-binding capacity (FBC) | 433.4 ± 11.3% | 296.8 ± 14% | 455.2 ± 13.2% |
| Degree of deacetylation (DD) | 87.1 ± 0.2% | 88.3 ± 0.1% | 84.1 ± 0.3% |
| Crystallinity index | 84 ± 0.1% | 73 ± 0.4% | 81 ± 0.2% |
| Experiment Order | Experimental Factors | Response (MB Removal) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MB Concentration (mg/L) | Time (min) | Actual | Predicted | |||||
| CS-BL | CS-PF | CS-MD | CS-BL | CS-PF | CS-MD | |||
| 1 | 6.39 | 10 | 35.9 | 10.3 | 20.0 | 36.3 | 10.9 | 18.8 |
| 2 | 12.79 | 10 | 50.9 | 18.5 | 43.6 | 51.3 | 18.6 | 43.4 |
| 3 | 6.39 | 120 | 74.6 | 28.7 | 35.9 | 75.6 | 29.0 | 36.6 |
| 4 | 12.79 | 120 | 86.5 | 38.8 | 66.8 | 87.6 | 38.6 | 68.5 |
| 5 | 6.39 | 65 | 55.5 | 20.5 | 27.0 | 54.1 | 19.6 | 27.5 |
| 6 | 12.79 | 65 | 69.0 | 28.0 | 57.3 | 67.6 | 28.3 | 55.7 |
| 7 | 9.59 | 10 | 45.7 | 15.2 | 24.3 | 44.9 | 14.6 | 25.6 |
| 8 | 9.59 | 65 | 60.6 | 23.5 | 36.0 | 62.0 | 23.8 | 36.0 |
| 9 | 9.59 | 120 | 84.7 | 33.7 | 49.5 | 82.7 | 33.6 | 47.1 |
| 10 | 9.59 | 65 | 60.6 | 23.5 | 36.0 | 62.0 | 23.8 | 36.0 |
| Source (CS-PF) | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
| Model | 2424.35 | 5 | 484.87 | 128.39 | 0.0002 a |
| A | 273.65 | 1 | 273.65 | 72.46 | 0.0010 |
| B | 2139.10 | 1 | 2139.10 | 566.41 | <0.0001 |
| AB | 2.27 | 1 | 2.27 | 0.5998 | 0.4819 |
| A2 | 2.87 | 1 | 2.87 | 0.7603 | 0.4325 |
| B2 | 7.78 | 1 | 7.78 | 2.06 | 0.2246 |
| Residual | 15.11 | 4 | 3.78 | -- | -- |
| Lack of fit | 15.11 | 3 | 5.04 | -- | -- |
| Pure error | 0.0000 | 1 | -- | -- | -- |
| Total | 2439.45 | 9 | -- | -- | -- |
| Model: quadratic; R2: 0.9916; R2 adjusted: 0.9810; R2 predicted: 0.9135; adequate precision: 31.2851; S.D: 2.05; CV: 5.19. | |||||
| Source (CS-BL) | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
| Model | 658.33 | 5 | 131.67 | 283.23 | <0.0001 a |
| A | 112.75 | 1 | 112.75 | 242.55 | <0.0001 |
| B | 544.35 | 1 | 544.35 | 1170.97 | <0.0001 |
| AB | 0.9409 | 1 | 0.9409 | 2.02 | 0.2279 |
| A2 | 0.0211 | 1 | 0.0211 | 0.0453 | 0.8419 |
| B2 | 0.2315 | 1 | 0.2315 | 0.4980 | 0.5193 |
| Residual | 1.86 | 4 | 0.4649 | -- | -- |
| Lack of fit | 1.86 | 3 | 0.6198 | -- | -- |
| Pure error | 0.0000 | 1 | 0.0000 | -- | -- |
| Total | 660.19 | 9 | -- | -- | -- |
| Model: quadratic; R2: 0.9971; R2 adjusted: 0.9937; R2 predicted: 0.9736; adequate precision: 52.4867; S.D: 0.6818; CV: 2.83. | |||||
| Source (CS-MD) | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
| Model | 1976.70 | 5 | 395.34 | 93.94 | 0.0003 a |
| A | 1198.03 | 1 | 1198.03 | 284.66 | <0.0001 |
| B | 690.37 | 1 | 690.37 | 164.04 | 0.0002 |
| AB | 13.32 | 1 | 13.32 | 3.17 | 0.1498 |
| A2 | 71.52 | 1 | 71.52 | 16.99 | 0.0146 |
| B2 | 0.1803 | 1 | 0.1803 | 0.0428 | 0.8461 |
| Residual | 16.83 | 4 | 4.21 | -- | -- |
| Lack of fit | 16.33 | 3 | 5.44 | 10.89 | 0.2183 b |
| Pure error | 0.5000 | 1 | 0.5000 | -- | -- |
| Total | 1993.53 | 9 | -- | -- | -- |
| Model: quadratic; R2: 0.9915; R2 adjusted: 0.9809; R2 predicted: 0.9134; adequate precision: 31.2851; S.D: 2.0514; CV: 5.1897. | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben Amor, I.; Hemmami, H.; Laouini, S.E.; Zeghoud, S.; Benzina, M.; Achour, S.; Naseef, A.; Alsalme, A.; Barhoum, A. Use of Insect-Derived Chitosan for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Wastewater: Process Optimization Using a Central Composite Design. Materials 2023, 16, 5049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145049
Ben Amor I, Hemmami H, Laouini SE, Zeghoud S, Benzina M, Achour S, Naseef A, Alsalme A, Barhoum A. Use of Insect-Derived Chitosan for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Wastewater: Process Optimization Using a Central Composite Design. Materials. 2023; 16(14):5049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145049
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen Amor, Ilham, Hadia Hemmami, Salah Eddine Laouini, Soumeia Zeghoud, Mourad Benzina, Sami Achour, Abanoub Naseef, Ali Alsalme, and Ahmed Barhoum. 2023. "Use of Insect-Derived Chitosan for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Wastewater: Process Optimization Using a Central Composite Design" Materials 16, no. 14: 5049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145049
APA StyleBen Amor, I., Hemmami, H., Laouini, S. E., Zeghoud, S., Benzina, M., Achour, S., Naseef, A., Alsalme, A., & Barhoum, A. (2023). Use of Insect-Derived Chitosan for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Wastewater: Process Optimization Using a Central Composite Design. Materials, 16(14), 5049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145049











