Silicon-Based Superslippery/Superhydrophilic Striped Surface for Highly Efficient Fog Harvesting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Fabrication
2.1. Materials
2.2. Solution Preparation
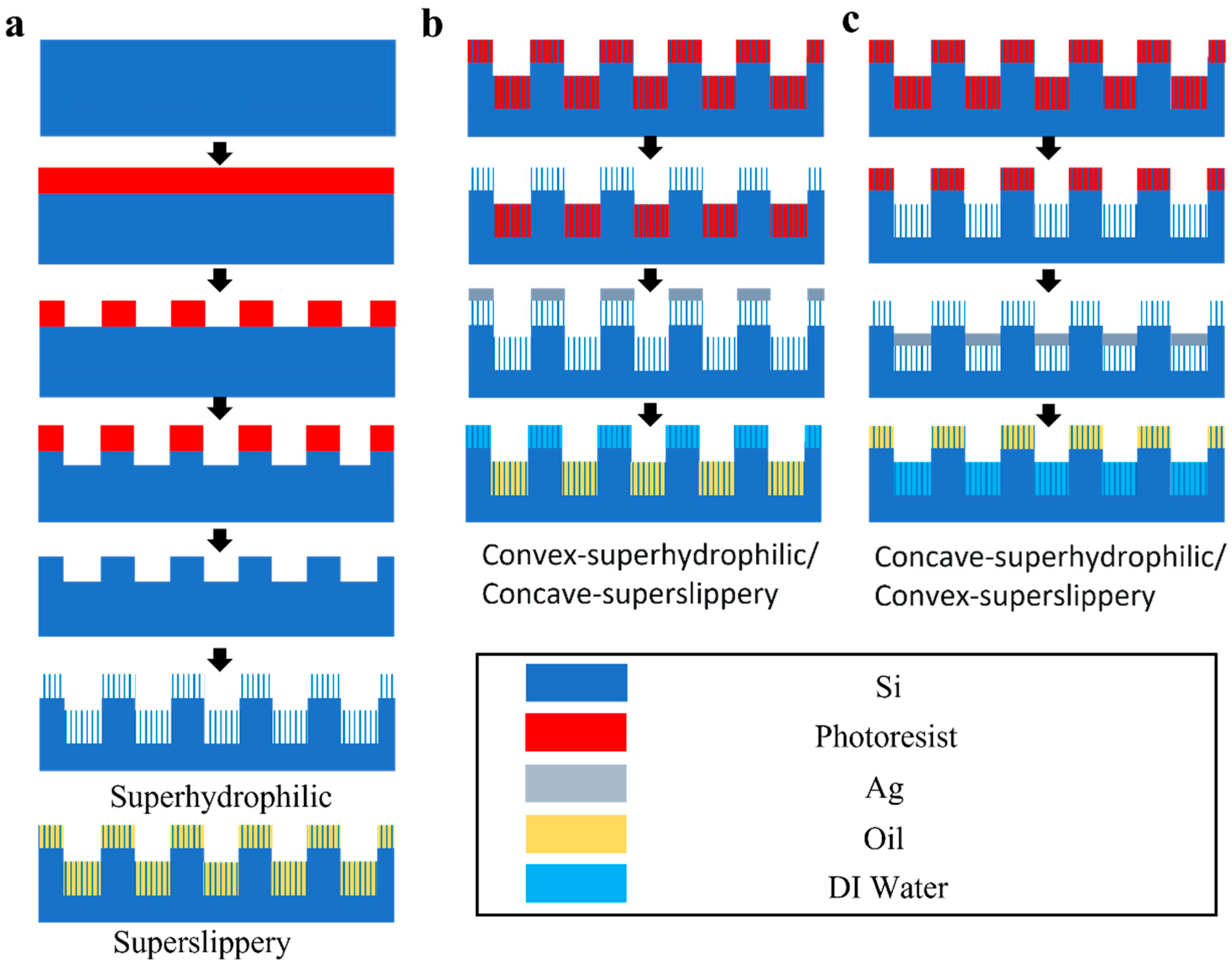
2.3. Fabrication of Homogeneous Striped Superhydrophilic and Superslippery Samples
2.4. Fabrication of Superslippery/Superhydrophilic Striped Surface
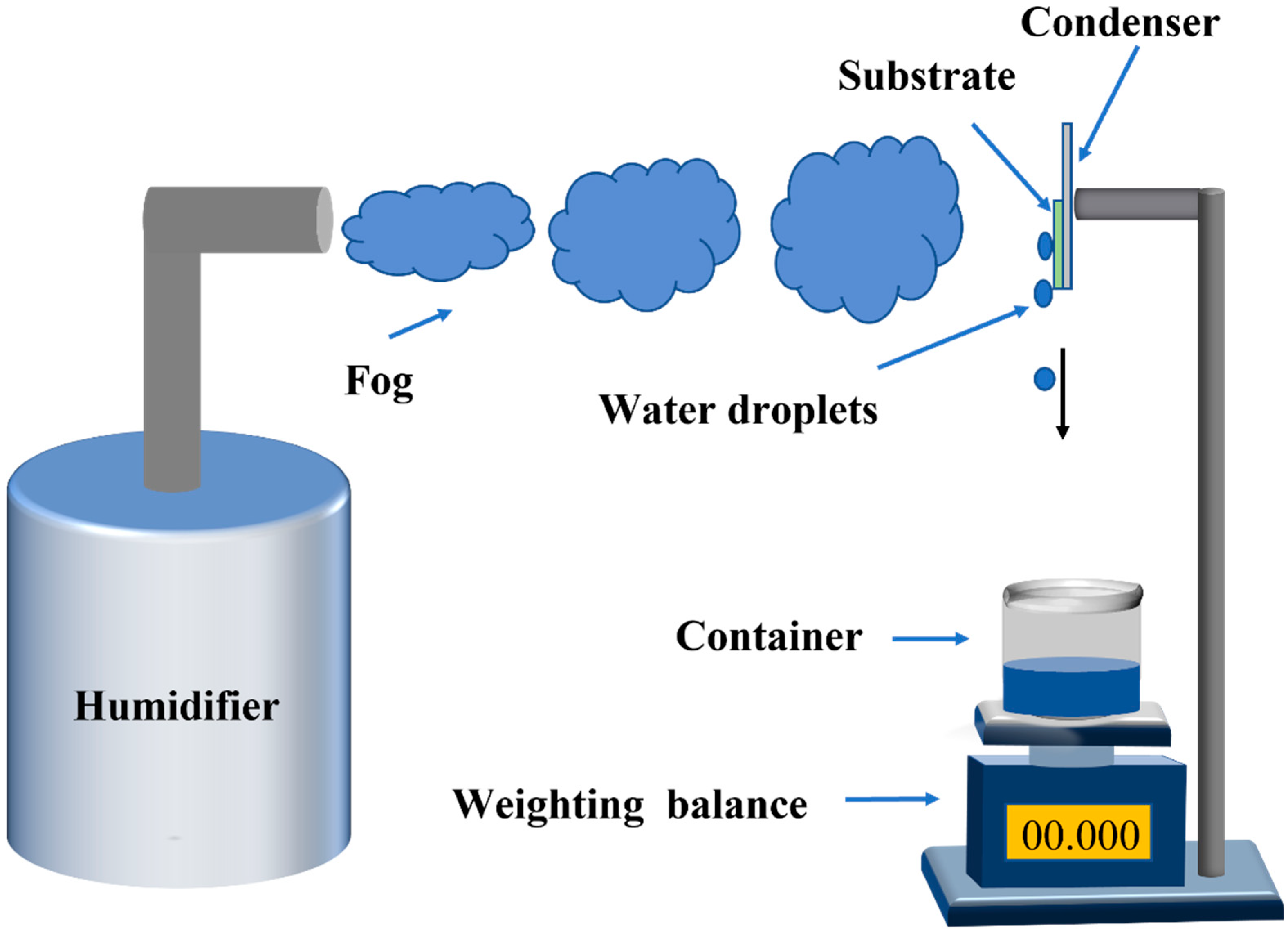
2.5. Fog Harvest
2.6. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
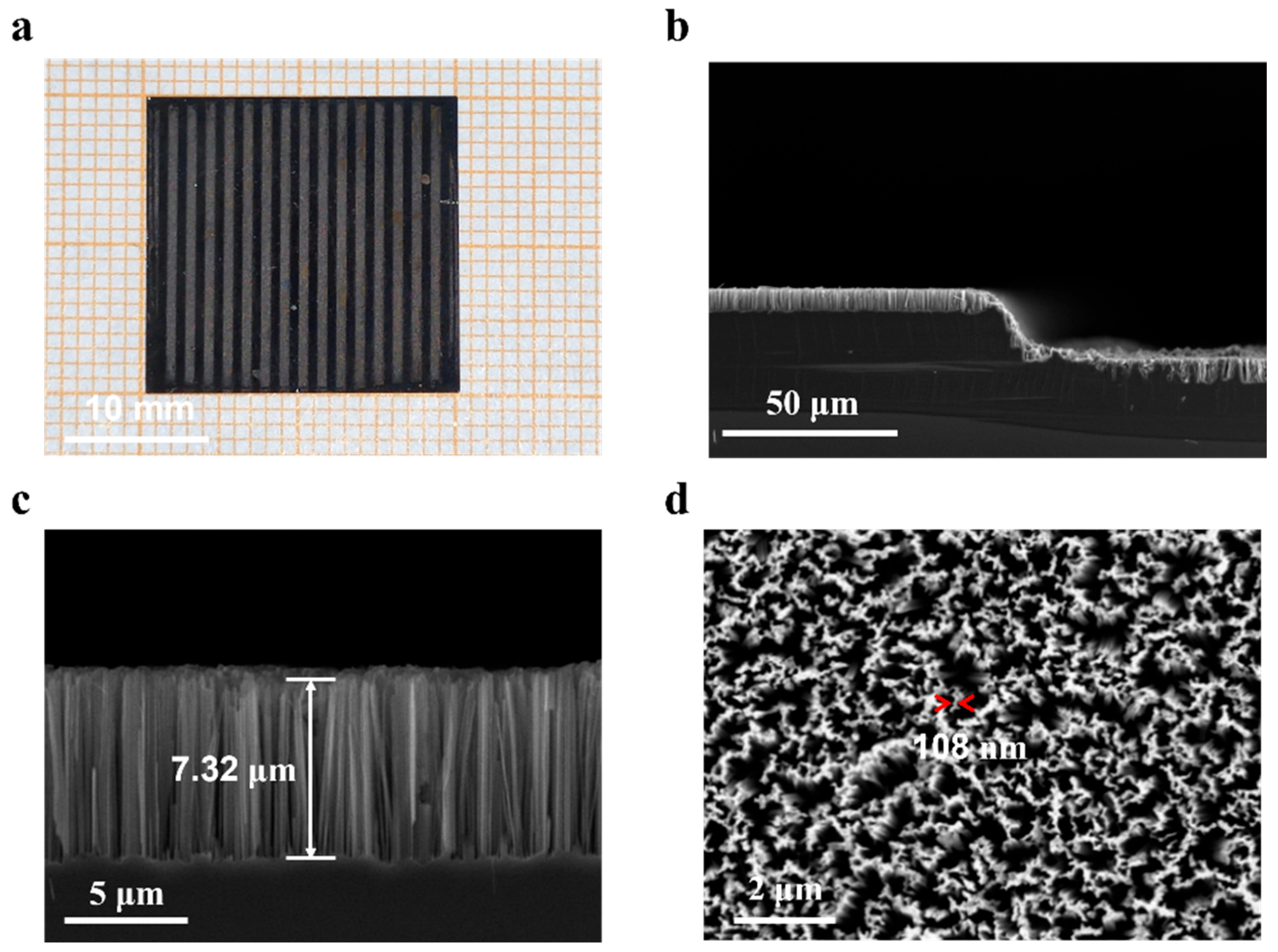
3.1. Morphological Features
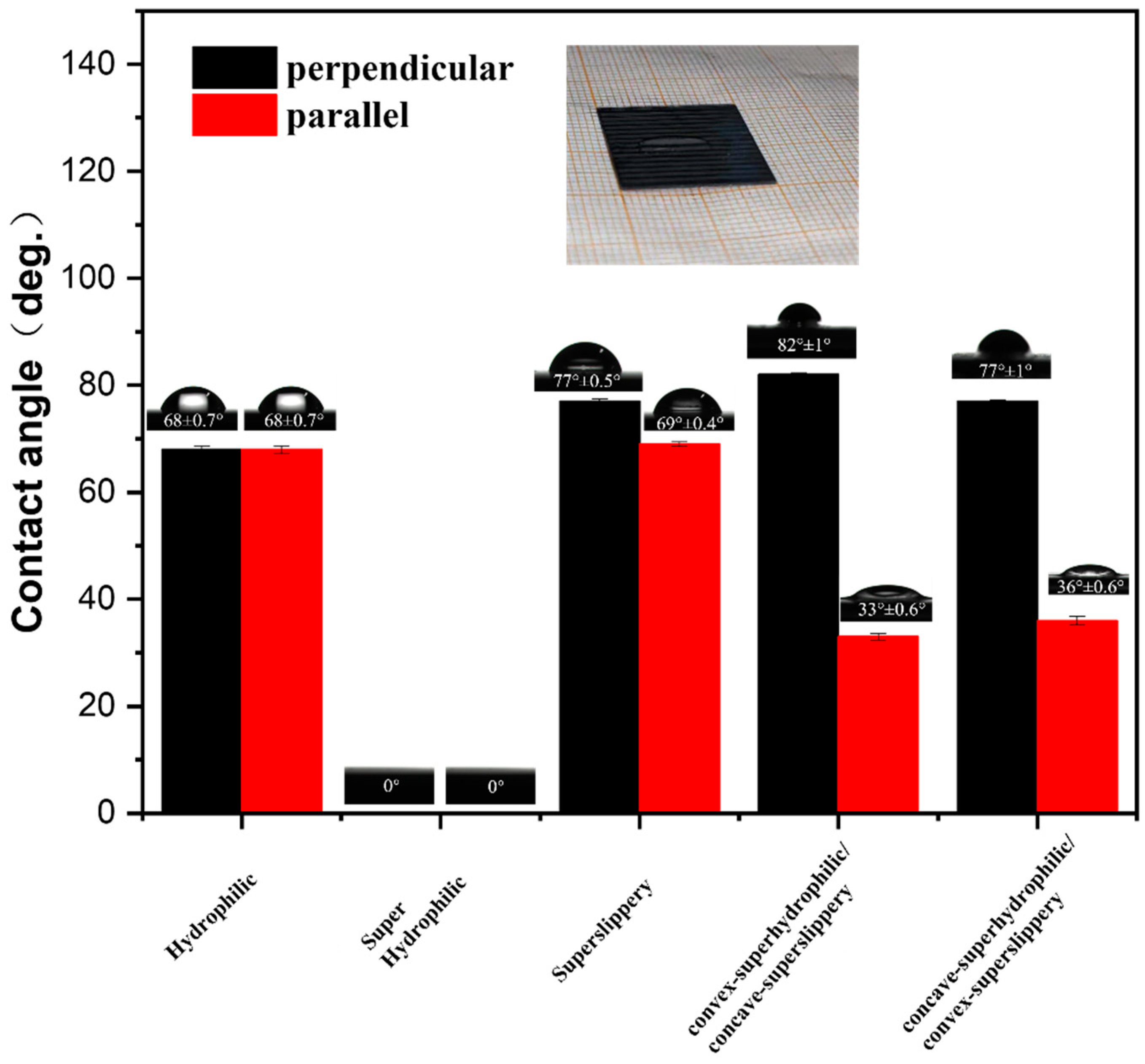
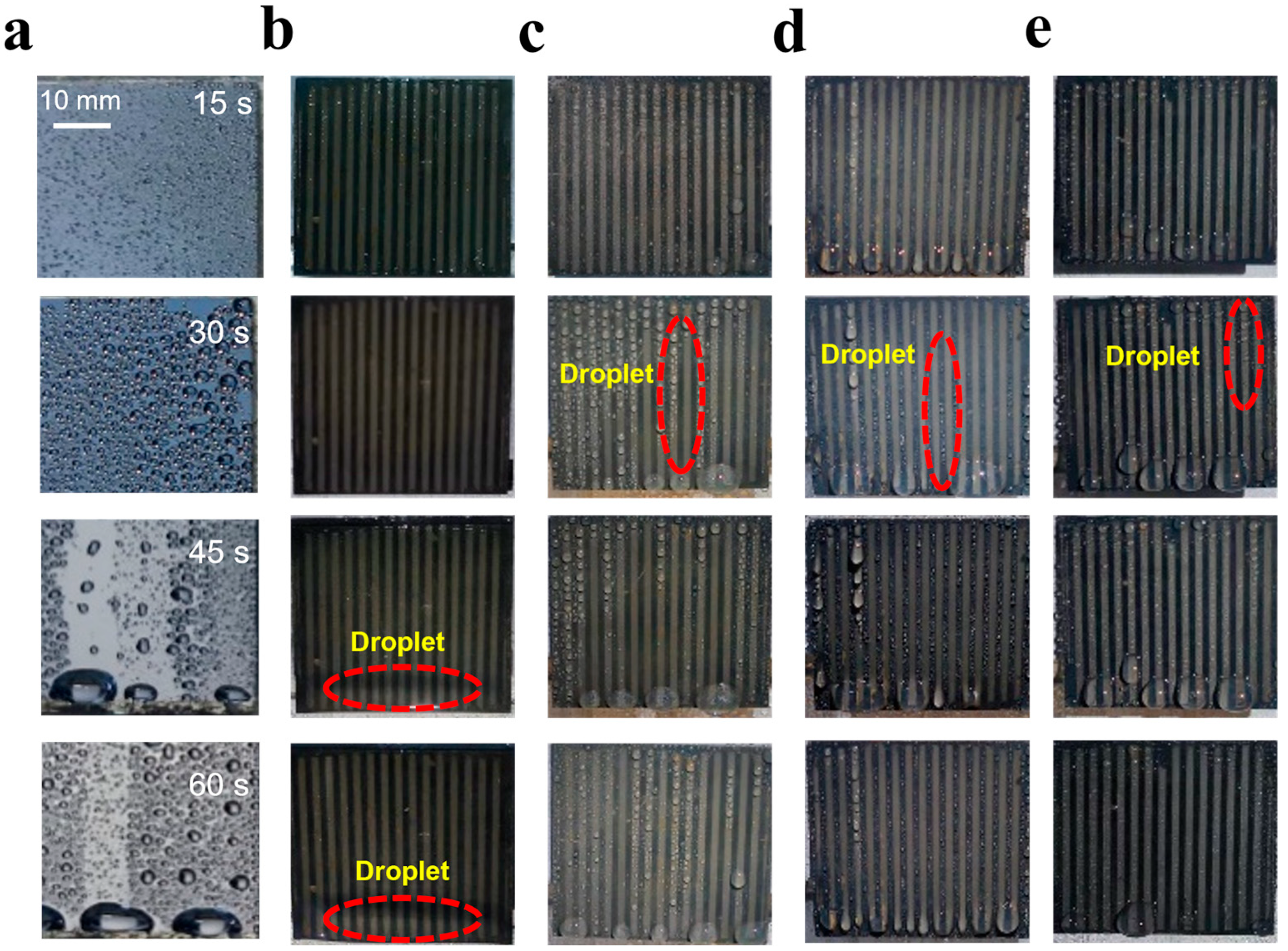
3.2. Surface Wettability of Different Samples and the Behavior of Water Droplets
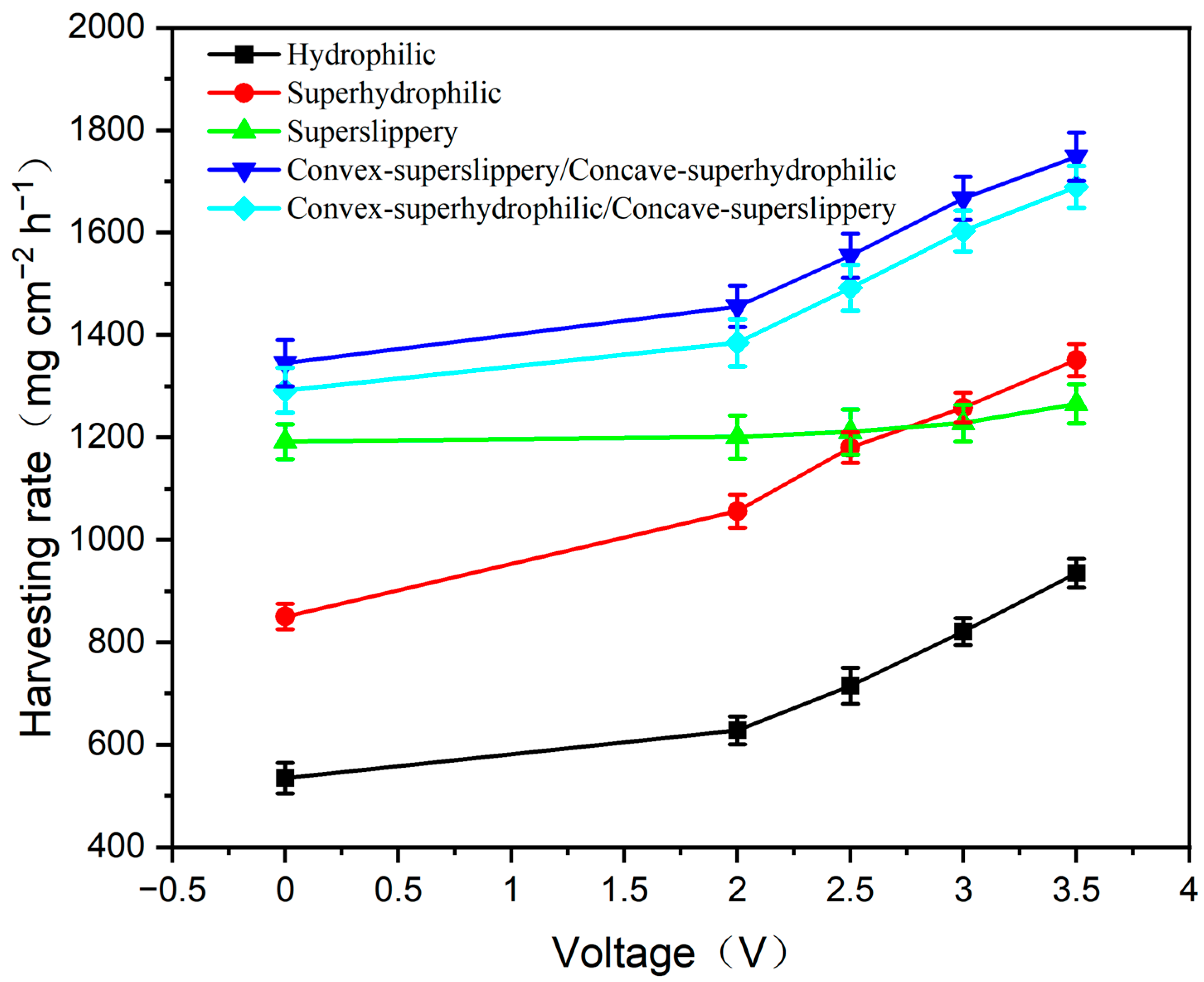
3.3. Fog Harvest
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhai, Y. Slippery surface with honeycomb structures for enhancing chemical durability of aluminum. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Ganguly, R. Fog harvesting from cooling towers using metal mesh: Effects of aerodynamic, deposition, and drainage efficiencies. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2020, 234, 994–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yu, C.; Zhou, S.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, L. Liquid harvesting and transport on multiscaled curvatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 23436–23442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, H.; Ran, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, G. High-Efficient Fog Harvest from a Synergistic Effect of Coupling Hierarchical Structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 33993–34001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Huang, W.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Design of a Venation-like Patterned Surface with Hybrid Wettability for Highly Efficient Fog Harvesting. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 3104–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, X. Tunable Wetting Patterns on Superhydrophilic/Superhydrophobic Hybrid Surfaces for Enhanced Dew-Harvesting Efficacy. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 1901683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Bhushan, B. Enhancement of water collection and transport in bioinspired triangular patterns from combined fog and condensation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 557, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Orejon, D.; Takata, Y.; Krishnan, V.; Harish, S. Gladiolus dalenii Based Bioinspired Structured Surface via Soft Lithography and Its Application in Water Vapor Condensation and Fog Harvesting. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6981–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-Hydrophobic Surfaces: From Natural to Artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, J.-N.; Wu, S.-Z.; Chen, Q.-D.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H.-B.; Jiang, L. Three-Level Biomimetic Rice-Leaf Surfaces with Controllable Anisotropic Sliding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 2927–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.; Lee, C.; Nam, Y. Influence of Geometric Patterns of Microstructured Superhydrophobic Surfaces on Water-Harvesting Performance via Dewing. Langmuir 2014, 30, 15468–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wier, K.A.; McCarthy, T.J. Condensation on ultrahydrophobic surfaces and its effect on droplet mobility: Ultrahydrophobic surfaces are not always water repellant. Langmuir 2006, 22, 2433–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-T.; Rodak, D.E. Is the lotus leaf superhydrophobic? Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 144101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouaghi, S.; Six, T.; Bellayer, S.; Moradi, S.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G.; Dargent, T.; Thomy, V.; Coffinier, Y.; André, C.; Delaplace, G.; et al. Antifouling Biomimetic Liquid-Infused Stainless Steel: Application to Dairy Industrial Processing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26565–26573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatopoulos, C.; Hemrle, J.; Wang, D.; Poulikakos, D. Exceptional Anti-Icing Performance of Self-Impregnating Slippery Surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10233–10242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, X.; Chen, F. Silicone Oil-Infused Slippery Surfaces Based on Sol-Gel Process-Induced Nanocomposite Coatings: A Facile Approach to Highly Stable Bioinspired Surface for Biofouling Resistance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34810–34819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, T.; Zhang, D. Fabrication of non-wetting surfaces on zinc surface as corrosion barrier. Corros. Sci. 2017, 128, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Paxson, A.T.; Dhiman, R.; Smith, J.D.; Varanasi, K.K. Enhanced Condensation on Lubricant-Impregnated Nanotextured Surfaces. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 10122–10129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhuang, K.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X. Creation of Topological Ultraslippery Surfaces for Droplet Motion Control. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 2589–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Luo, Y.; Luan, L.; Wang, Z.; Wu, T. Inkjet printing of patterned ultra-slippery surfaces for planar droplet manipulation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, K.-C.; Kim, P.; Grinthal, A.; He, N.; Fox, D.; Weaver, J.C.; Aizenberg, J. Condensation on slippery asymmetric bumps. Nature 2016, 531, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Ma, H.; Li, Z.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.; Yu, C.; Cao, M.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Pressure-Tolerant Asymmetric Slippery Surface for Continuous Self-Transport of Gas Bubbles in Aqueous Environment. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 2048–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Gutierrez, E.; Guan, J.H.; Xu, B.; McHale, G.; Wells, G.G.; Ledesma-Aguilar, R. Energy Invariance in Capillary Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 218003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, J.H.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, E.; Xu, B.B.; Wood, D.; McHale, G.; Ledesma-Aguilar, R.; Wells, G.G. Drop transport and positioning on lubricant-impregnated surfaces. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 3404–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, K.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, X. Architecture-Driven Fast Droplet Transport without Mass Loss. Langmuir 2021, 37, 12519–12528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Sun, N.; Nielsen, S.O.; Stogin, B.B.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Wong, T.-S. Hydrophilic directional slippery rough surfaces for water harvesting. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaaq0919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, X. Ultraslippery/hydrophilic patterned surfaces for efficient fog harvest. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 640, 128398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Song, F.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-Z. A Quadruple-Biomimetic surface for spontaneous and efficient fog harvesting. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, K.; Das, A.; Dhar, M.; Manna, U. Synergistic chemical patterns on a hydrophilic slippery liquid infused porous surface (SLIPS) for water harvesting applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 25040–25046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nioras, D.; Ellinas, K.; Constantoudis, V.; Gogolides, E. How Different Are Fog Collection and Dew Water Harvesting on Surfaces with Different Wetting Behaviors? ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48322–48332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Lu, Y.; Yin, S.; Huang, S.; Song, J.; Chen, F.; Chen, F.; Carmalt, C.J.; Parkin, I.P. Robust platform for water harvesting and directional transport. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 5635–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, A.; Beaini, S.; Zhang, B.J.; Ganguly, R.; Megaridis, C.M. Enhancing Dropwise Condensation through Bioinspired Wettability Patterning. Langmuir 2014, 30, 13103–13115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettlemoyer, A.C. Nucleation; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Varanasi, K.K.; Hsu, M.; Bhate, N.; Yang, W.; Deng, T. Spatial control in the heterogeneous nucleation of water. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 094101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, X.; Lan, Z.; Song, T.; Ji, J. Experimental investigation of enhancement of dropwise condensation heat transfer of steam-air mixture: Falling droplet effect. J. Enhanc. Heat Transf. 2007, 14, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, X.; Shuai, S.; Liu, S.; Weng, Y.; Zheng, F. Silicon-Based Superslippery/Superhydrophilic Striped Surface for Highly Efficient Fog Harvesting. Materials 2023, 16, 5423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155423
Ji X, Shuai S, Liu S, Weng Y, Zheng F. Silicon-Based Superslippery/Superhydrophilic Striped Surface for Highly Efficient Fog Harvesting. Materials. 2023; 16(15):5423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155423
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Xiang, Shunxu Shuai, Shuai Liu, Yuyan Weng, and Fengang Zheng. 2023. "Silicon-Based Superslippery/Superhydrophilic Striped Surface for Highly Efficient Fog Harvesting" Materials 16, no. 15: 5423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155423
APA StyleJi, X., Shuai, S., Liu, S., Weng, Y., & Zheng, F. (2023). Silicon-Based Superslippery/Superhydrophilic Striped Surface for Highly Efficient Fog Harvesting. Materials, 16(15), 5423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155423



