Evaluation of Setting Times of Concrete Using Electro-Mechanical Impedance Sensing Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Materials
2.2. Penetration Resistance Test
2.3. EMI Measurement
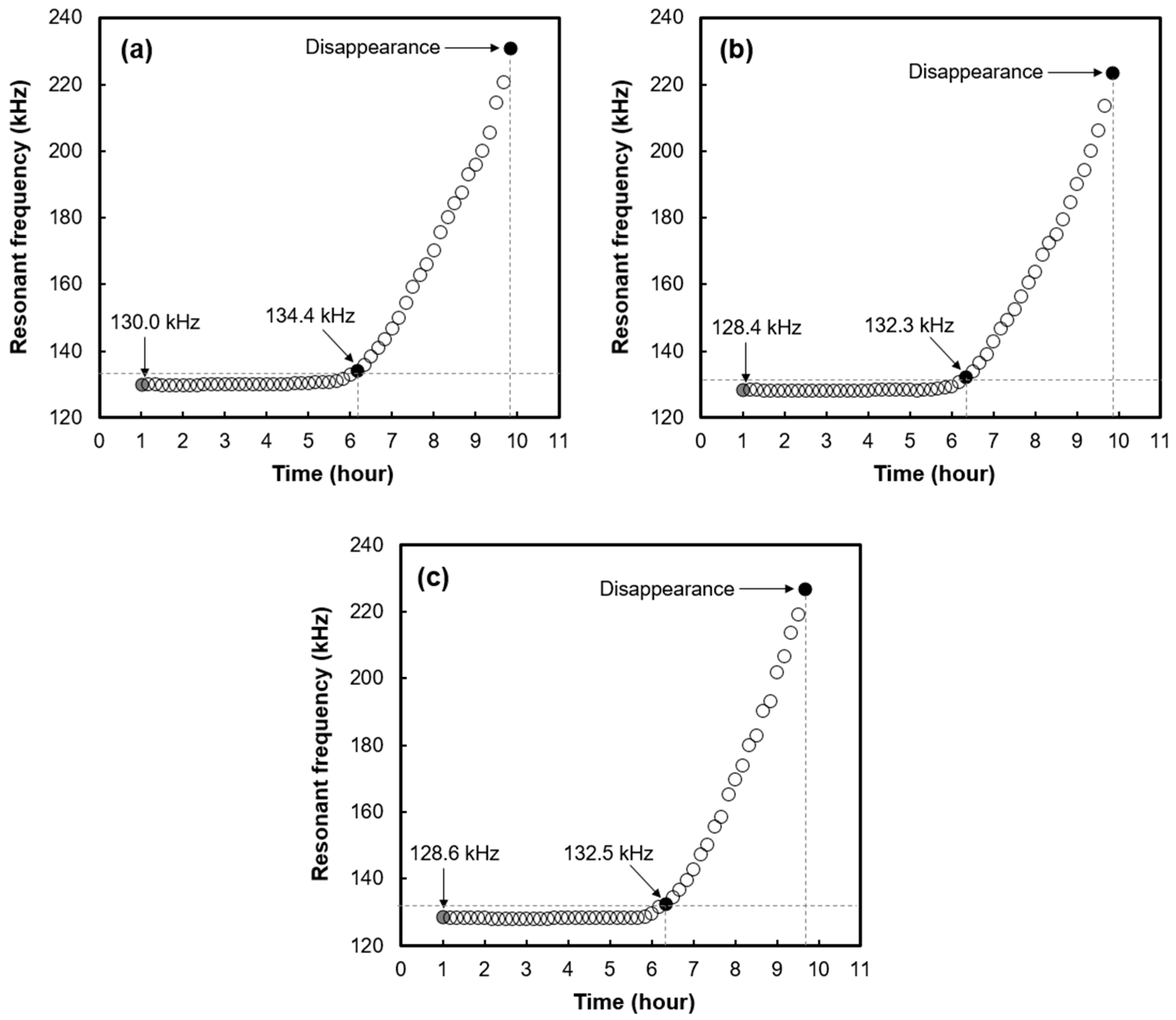
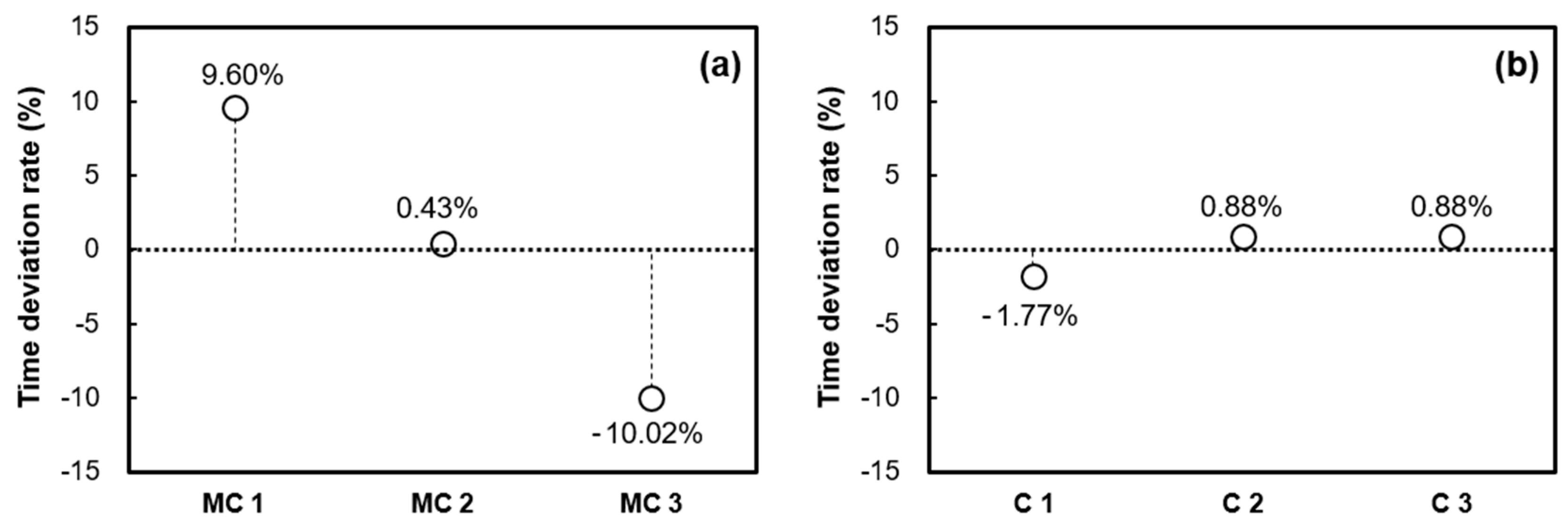
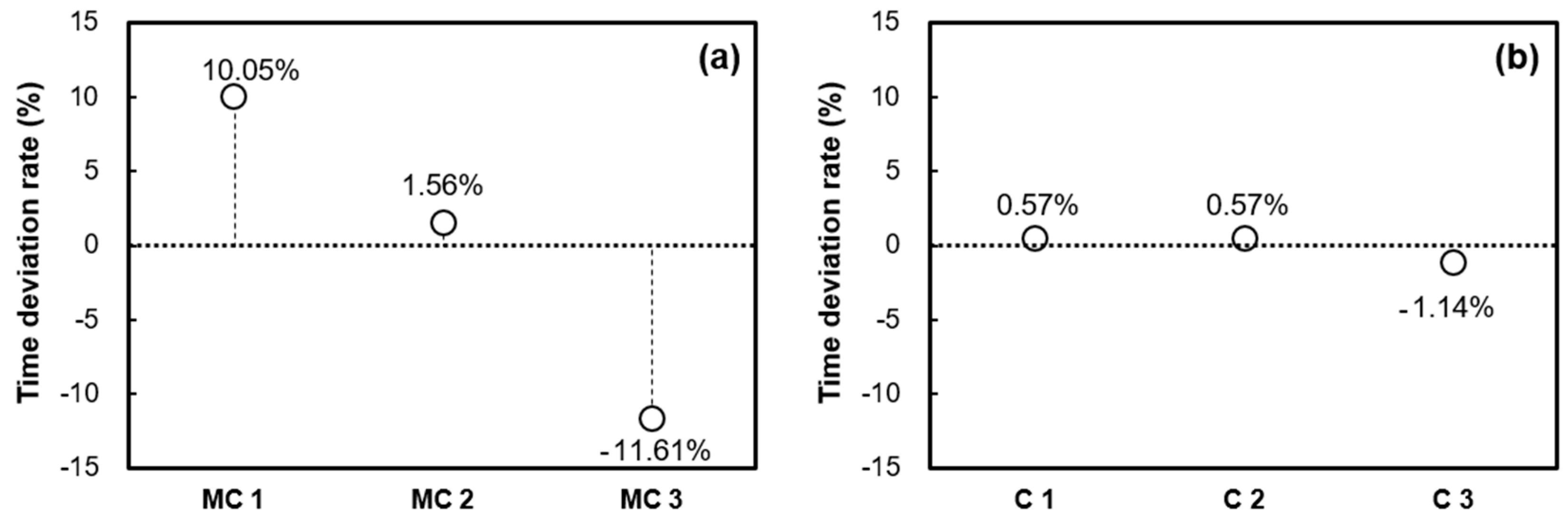
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mindess, S.; Young, J.F. Concrete; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C 191-21; Standard Test Method for Time of Setting of Hydraulic Cements by Vicat Needle. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- ASTMC403/C403M-21; Standard Test Method for Time of Setting of Concrete Mixtures by Penetration Resistance. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Misák, P.; Kucharczyková, B.; Kocáb, D.; Vymazal, T. Ultrasonic NDT determination of initial and final setting time of cement paste. MATEC Web Conf. 2020, 310, 00027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghoddousi, P.; Shirzadi Javid, A.A.; Sobhani, J.; Zaki Alamdari, A. A new method to determine initial setting time of cement and concrete using plate test. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 3135–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecskó, K.; Baranyi, A. Comparative Study of Setting Time and Heat of Hydration Development of Portland Cement According to EN 196-3. In Applications of Calorimetry; Intech Open: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.K.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Yim, H.; Bae, D.B. Ultrasonic in-situ monitoring of setting process of high-performance concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.W.; Suraneni, P.; Popovics, J.S.; Struble, L.J. Setting time measurement using ultrasonic wave reflection. ACI Mater. J. 2012, 109, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q.; Liao, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, S.; Zhang, D. Intelligent monitoring and assessment on early-age hydration and setting of cement mortar through an EMI-integrated neural network. Measurement 2022, 203, 111984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Panda, G.P.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Vipulanandan, C.; Song, G. Monitoring early-age hydration and setting of portland cement paste by piezoelectric transducers via electromechanical impedance method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 120348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.F.; Han, G.; Amran, A.; Nantung, T.; Lu, N. Instantaneous monitoring the early age properties of cementitious materials using PZT-based electromechanical impedance (EMI) technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawie, R.; Lee, H.K. Characterization of cement-based materials using a reusable piezoelectric impedance-based sensor. Smart Struct. Syst. 2011, 20, 085023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.J.; Lee, J.C.; Shin, S.W.; Kim, W.J. Investigation of setting process of cementitious materials using electromechanical impedance of embedded piezoelectric patch. J. Korea Inst. Build. Constr. 2012, 12, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.C.; Shin, S.W.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, C.J. Electro-mechanical impedance based monitoring for the setting of cement paste using piezoelectricity sensor. Smart Struct. Syst. 2016, 17, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Lee, C.J. Electro-Mechanical Impedance Technique for Assessing the Setting Time of Steel-Fiber-Reinforced Mortar Using Embedded Piezoelectric Sensor. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Yi, C.Y. Setting Process Monitoring of Cement Paste Using Electromechanical Impedance of Piezoelectric Patch. Materials 2022, 15, 8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, T. Fundamentals of Piezoelectricity; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Crawley, E.F.; Luis, J. Use of Piezoelectric Actuators as Elements of Intelligent Structures. AIAA J. 1987, 25, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Sun, F.P.; Rogers, C.A. An impedance method for dynamic analysis of active material systems. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1997, 8, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KSL5201; Portland Cement. Korean Agency for Technology and Standards: Chungbuk, Republic of Korea, 2021.
- Shin, S.W.; Qureshi, A.R.; Lee, J.Y.; Yun, C.B. Piezoelectric sensor based nondestructive active monitoring of strength gain in concrete. Smart Struct. Syst. 2008, 17, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
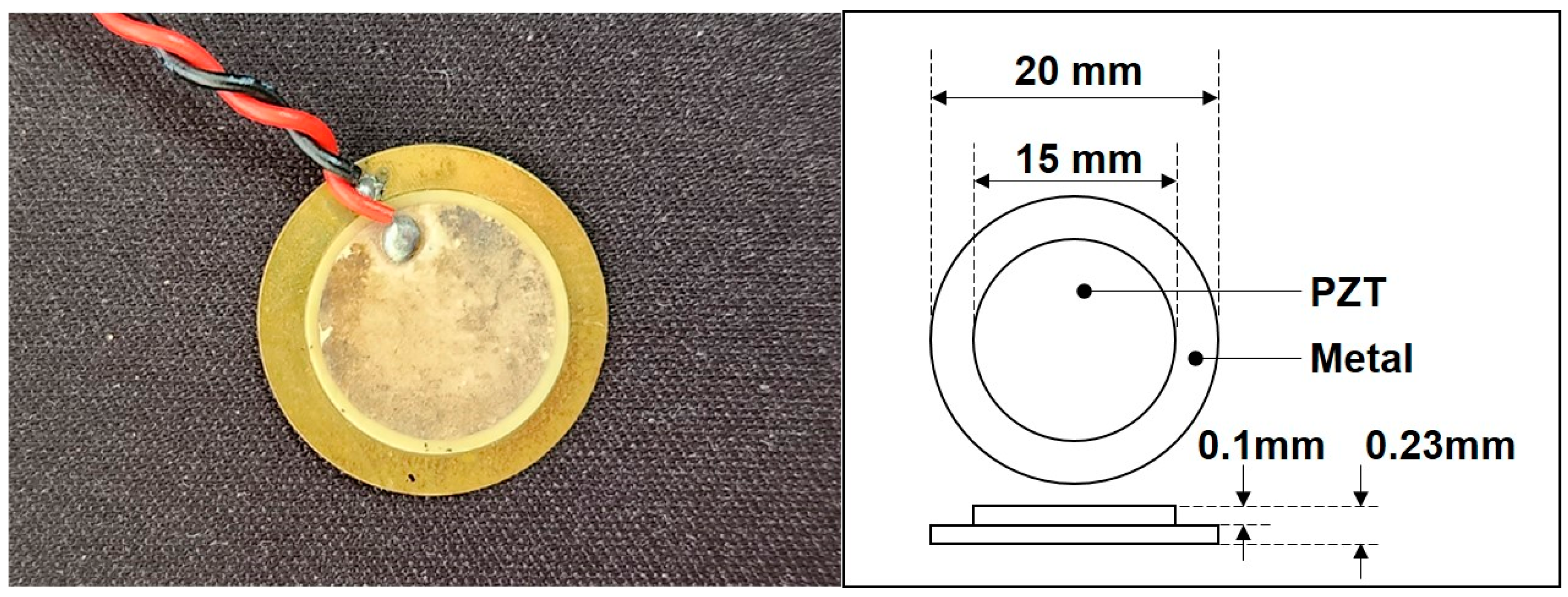
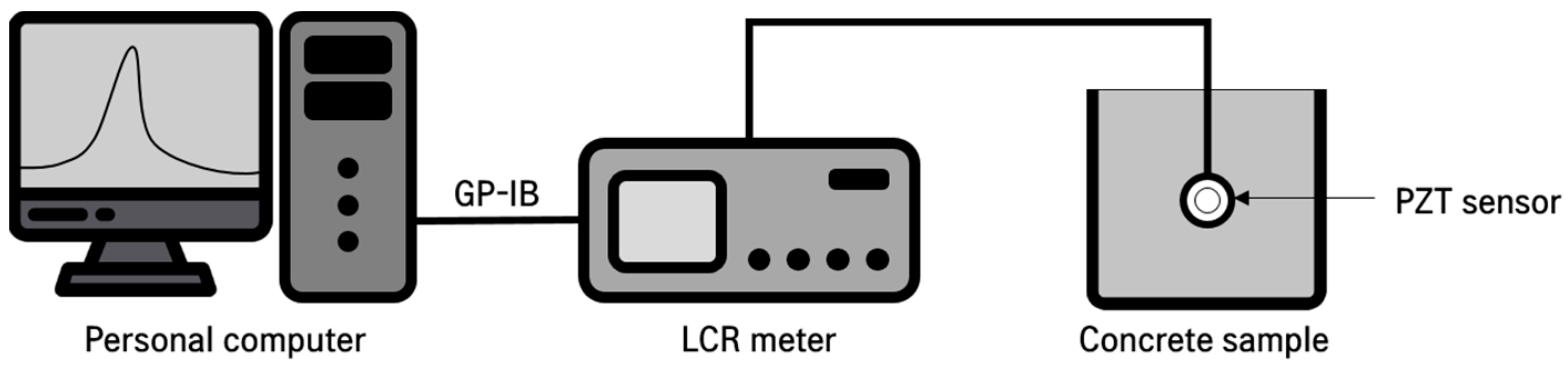

| Type | Specific Gravity | Maximum Size (mm) | Unit Weight (kg/m3) | Water Absorption (%) | Fineness Modulus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine aggregate | 2.60 | 4.75 | 1564 | 1.05 | 2.63 |
| Coarse aggregate | 2.65 | 25.00 | 1569 | 0.9 | 6.49 |
| W/C (%) | S/a (%) | Unit Weight (kg/m3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | Fine Aggregate | Coarse Aggregate | ||
| 50 | 37.9 | 388 | 663 | 1088 |
| Frequency (kHz) | Resonant Resistance (Ω) | Capacity (pF) | Metal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.5 ± 0.5 | 350 | 30,000 ± 30 | Brass |
| Designation | Initial Setting Time (min) | Final Setting Time (min) | Time Gap between the Initial Set and Final Set (min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mortar sample extracted from the same batch of concrete | MC 1 | 430 | 635 | 205 |
| MC 2 | 394 | 586 | 192 | |
| MC 3 | 353 | 510 | 157 | |
| Pure mortar | 373 | 576 | 203 | |
| Designation | Initial Setting Time (min) | Final Setting Time (min) | Time Gap between the Initial Set and Final Set (min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete sample from the same concrete batch | C 1 | 370 | 590 | 220 |
| C 2 | 380 | 590 | 210 | |
| C 3 | 380 | 580 | 200 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-C. Evaluation of Setting Times of Concrete Using Electro-Mechanical Impedance Sensing Technique. Materials 2023, 16, 5618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165618
Lee J-C. Evaluation of Setting Times of Concrete Using Electro-Mechanical Impedance Sensing Technique. Materials. 2023; 16(16):5618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165618
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jun-Cheol. 2023. "Evaluation of Setting Times of Concrete Using Electro-Mechanical Impedance Sensing Technique" Materials 16, no. 16: 5618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165618
APA StyleLee, J.-C. (2023). Evaluation of Setting Times of Concrete Using Electro-Mechanical Impedance Sensing Technique. Materials, 16(16), 5618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165618





