Influence of Braking Speed on the Friction and Wear Characteristics of High-Speed Railway Braking Materials under High Ambient Humidity Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Test
2.1. Braking Materials
2.2. Test Equipment
2.3. Test Process and Details
3. Test Results of Braking Materials
3.1. Friction Coefficient Analysis
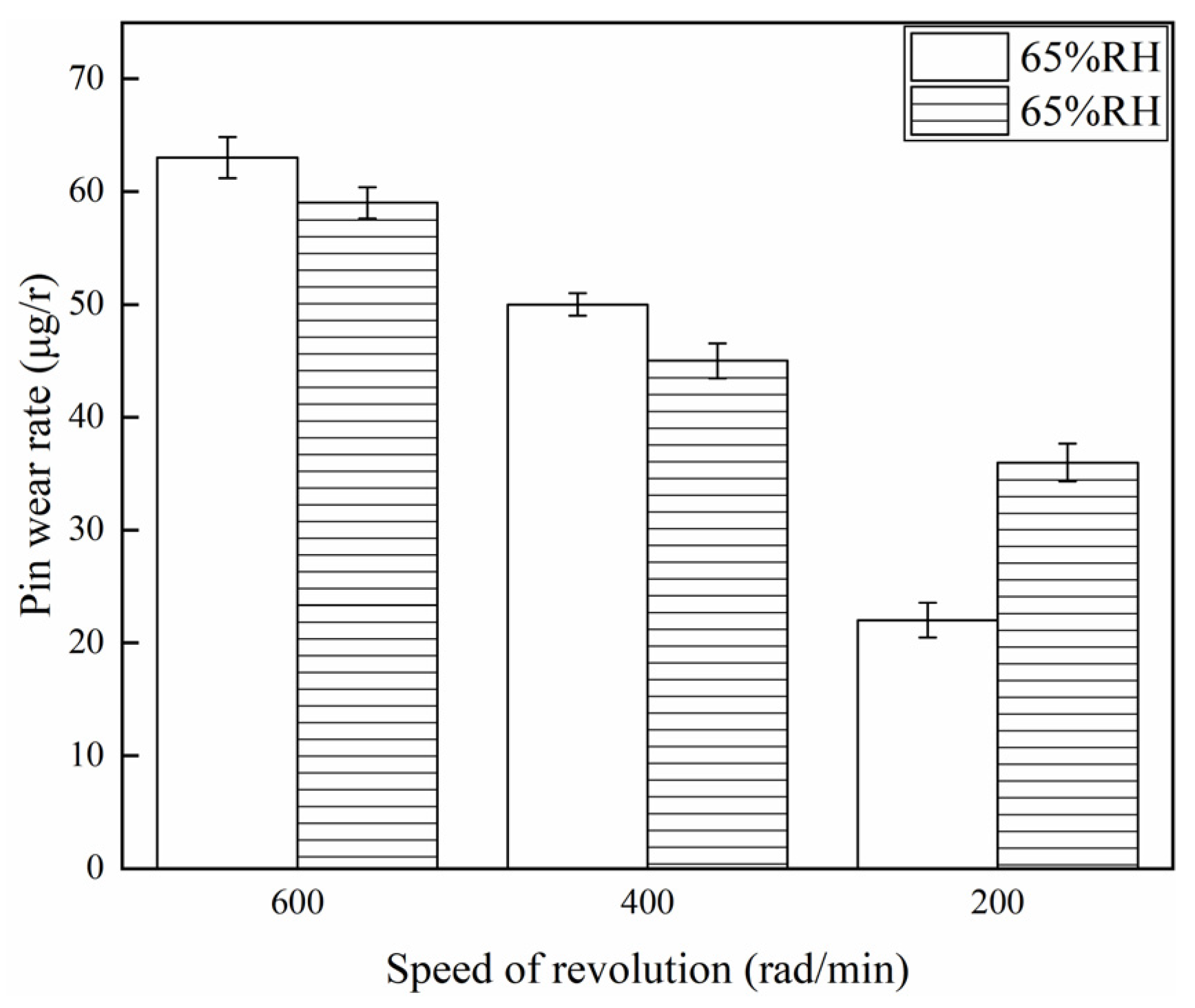
3.2. Wear Rate
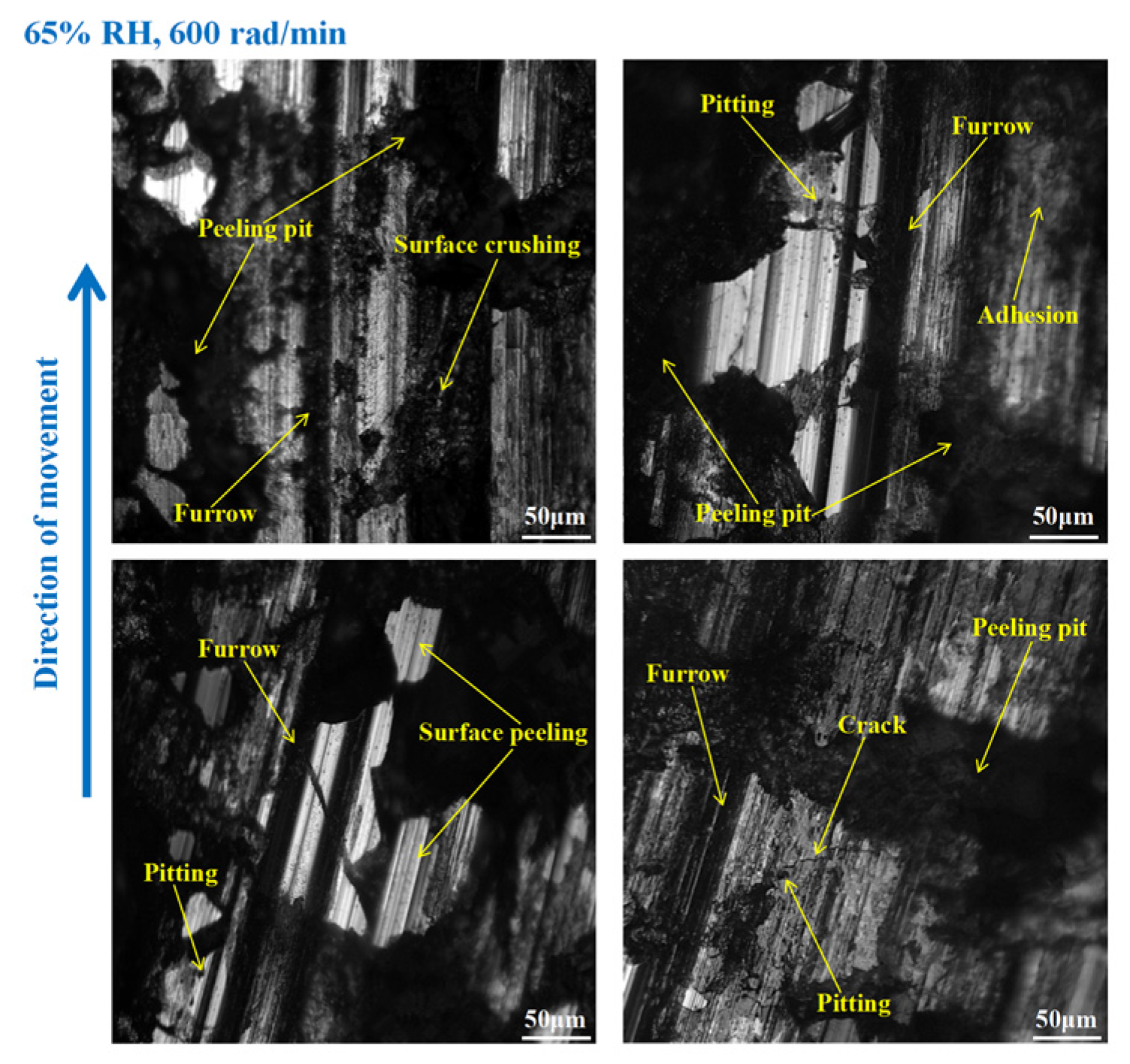
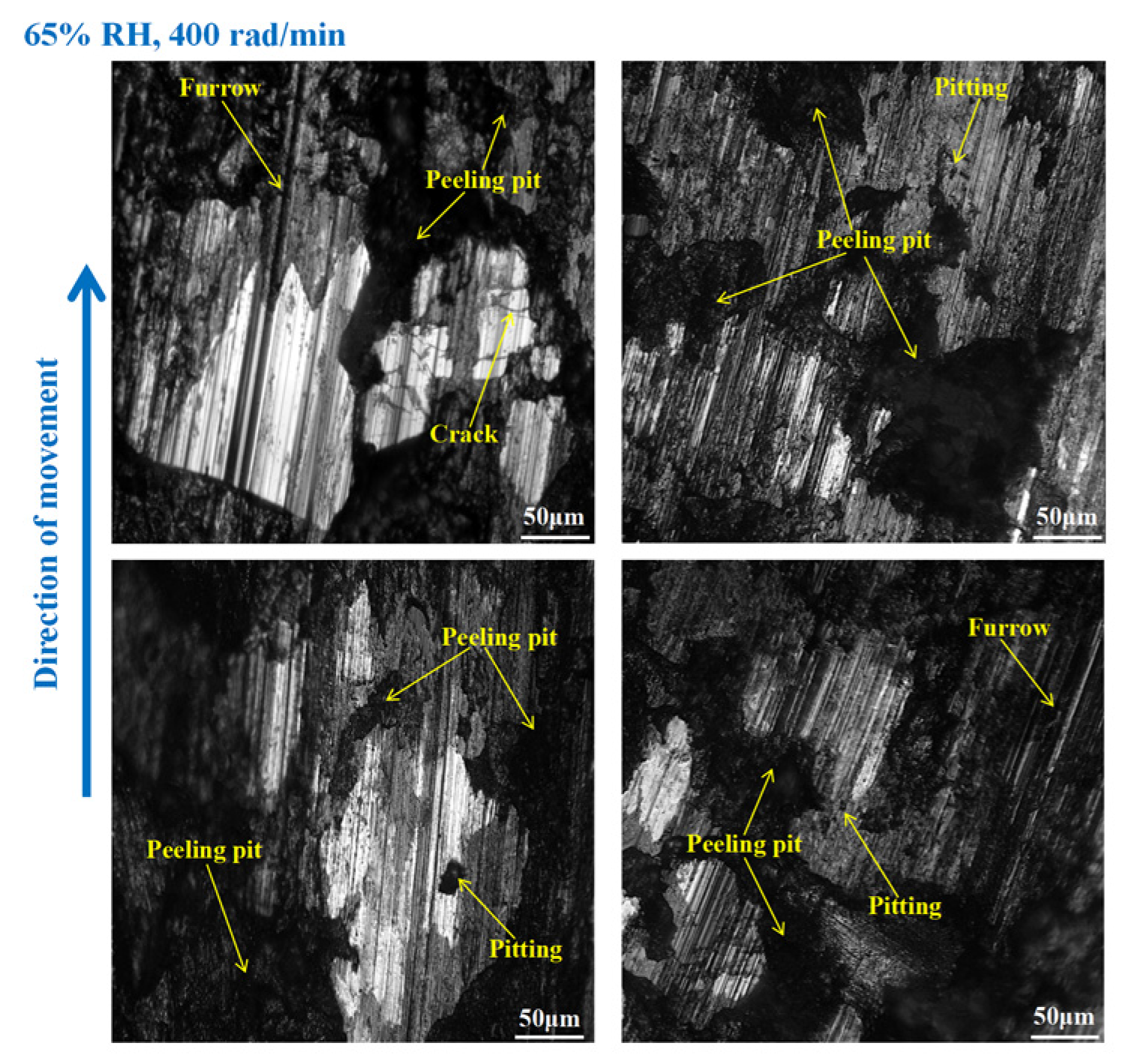
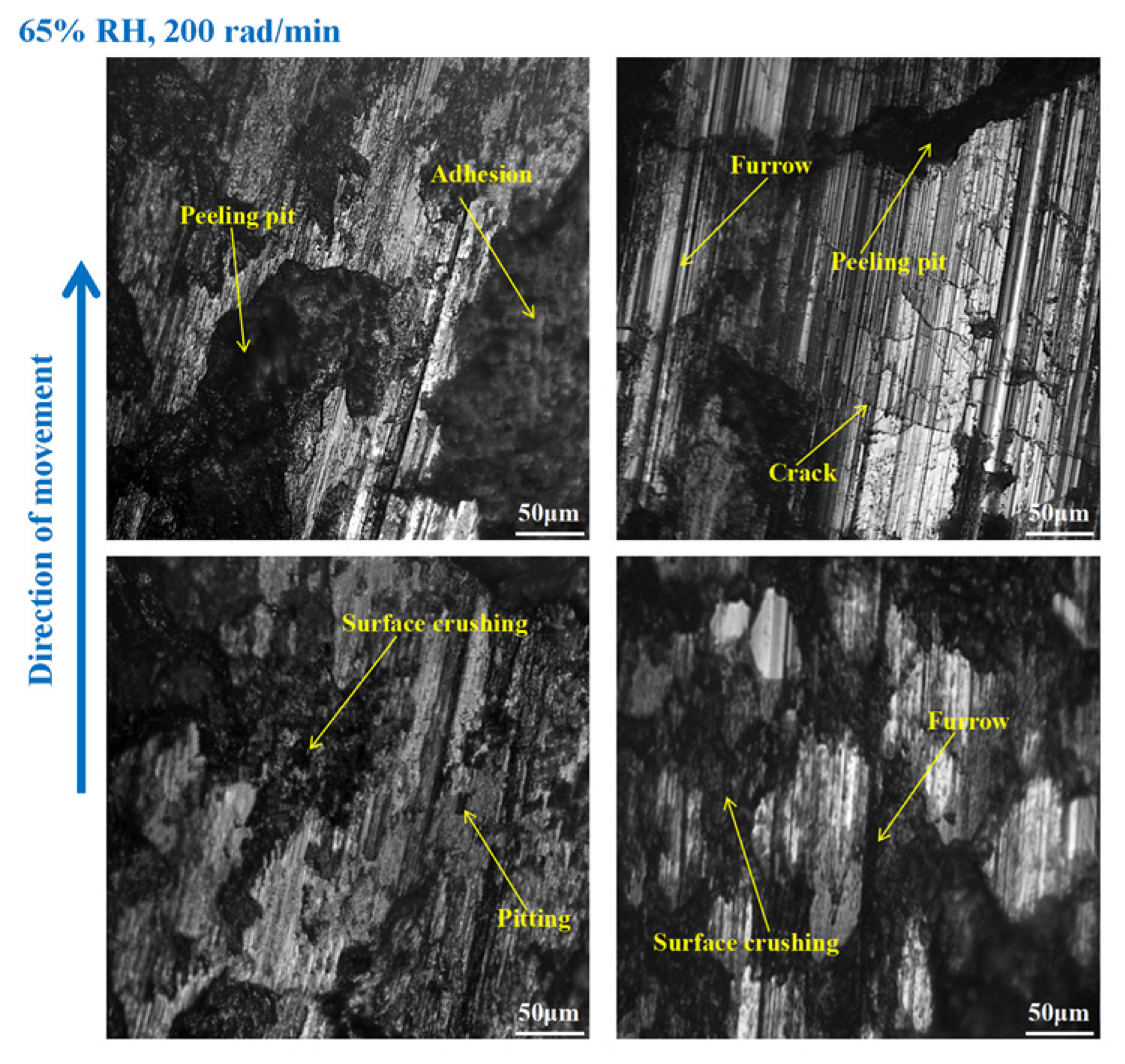
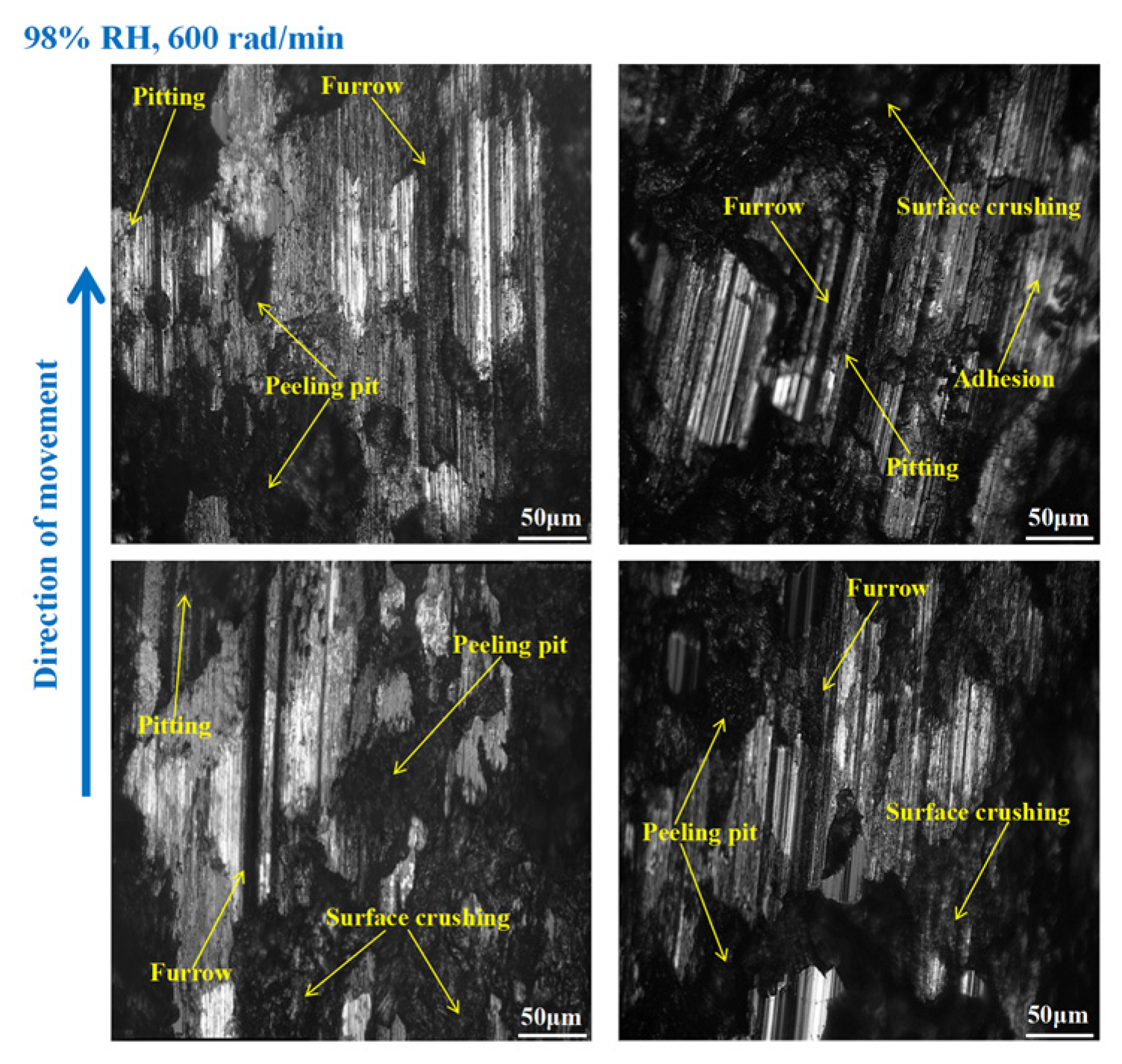
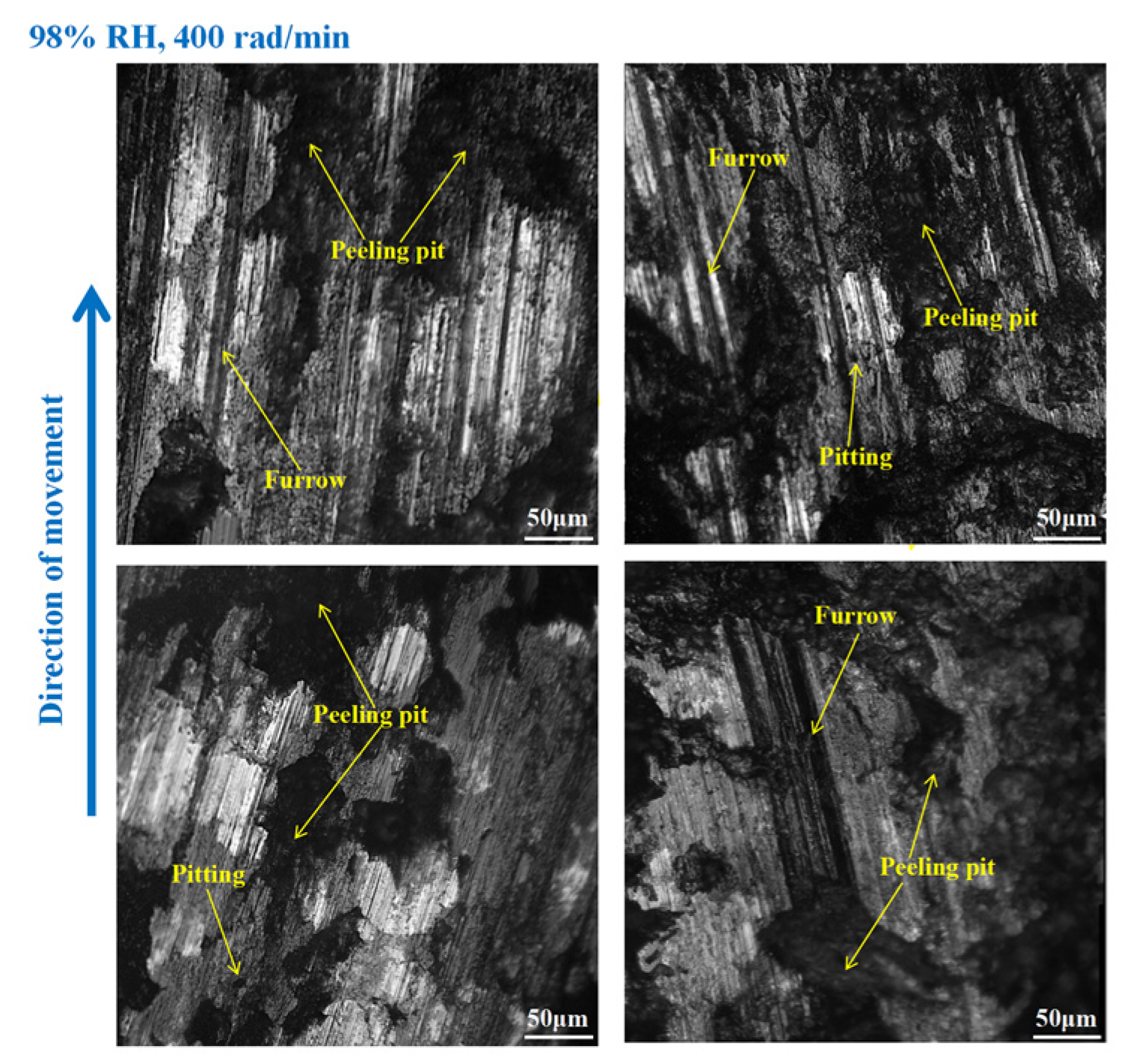
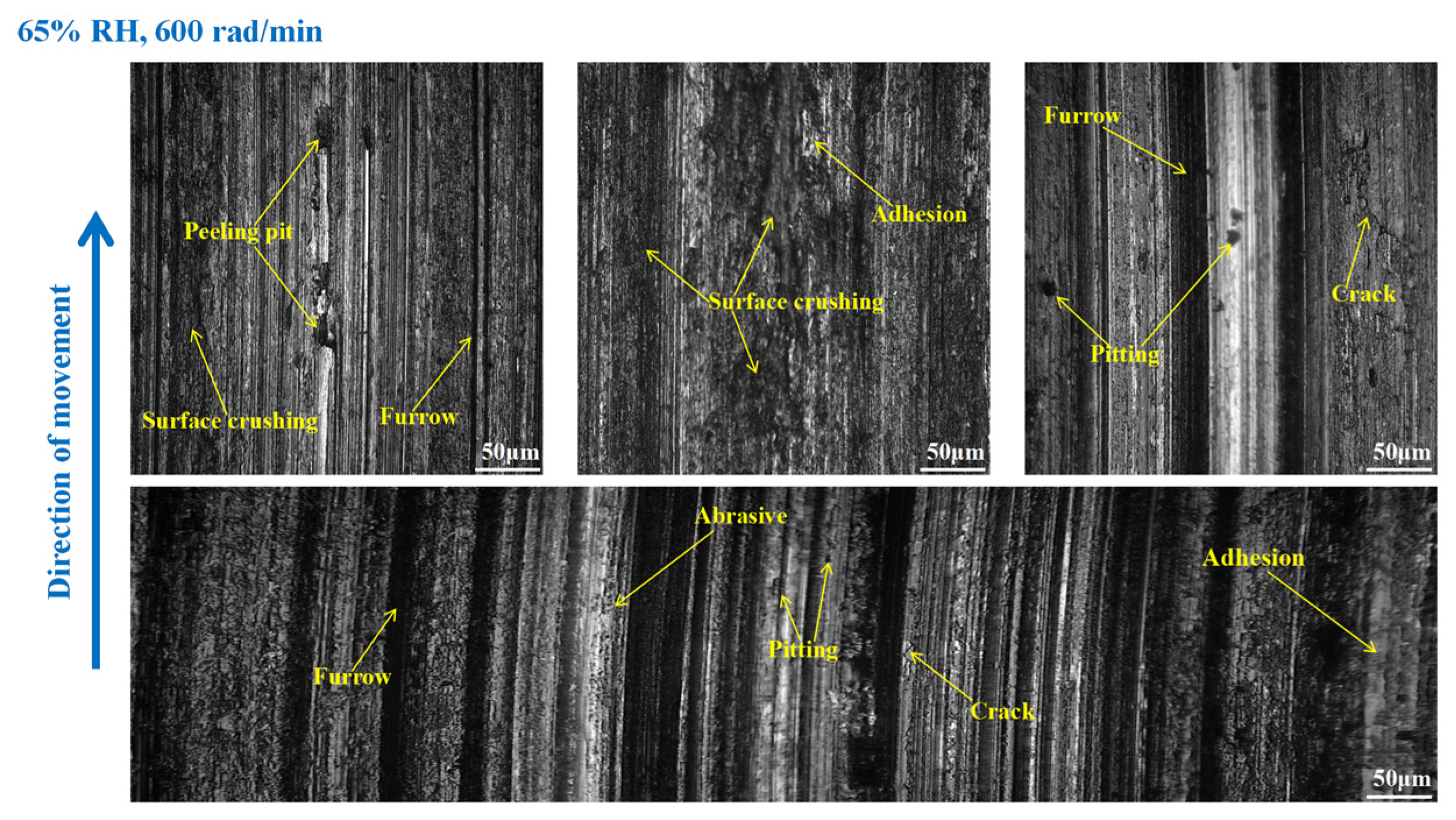
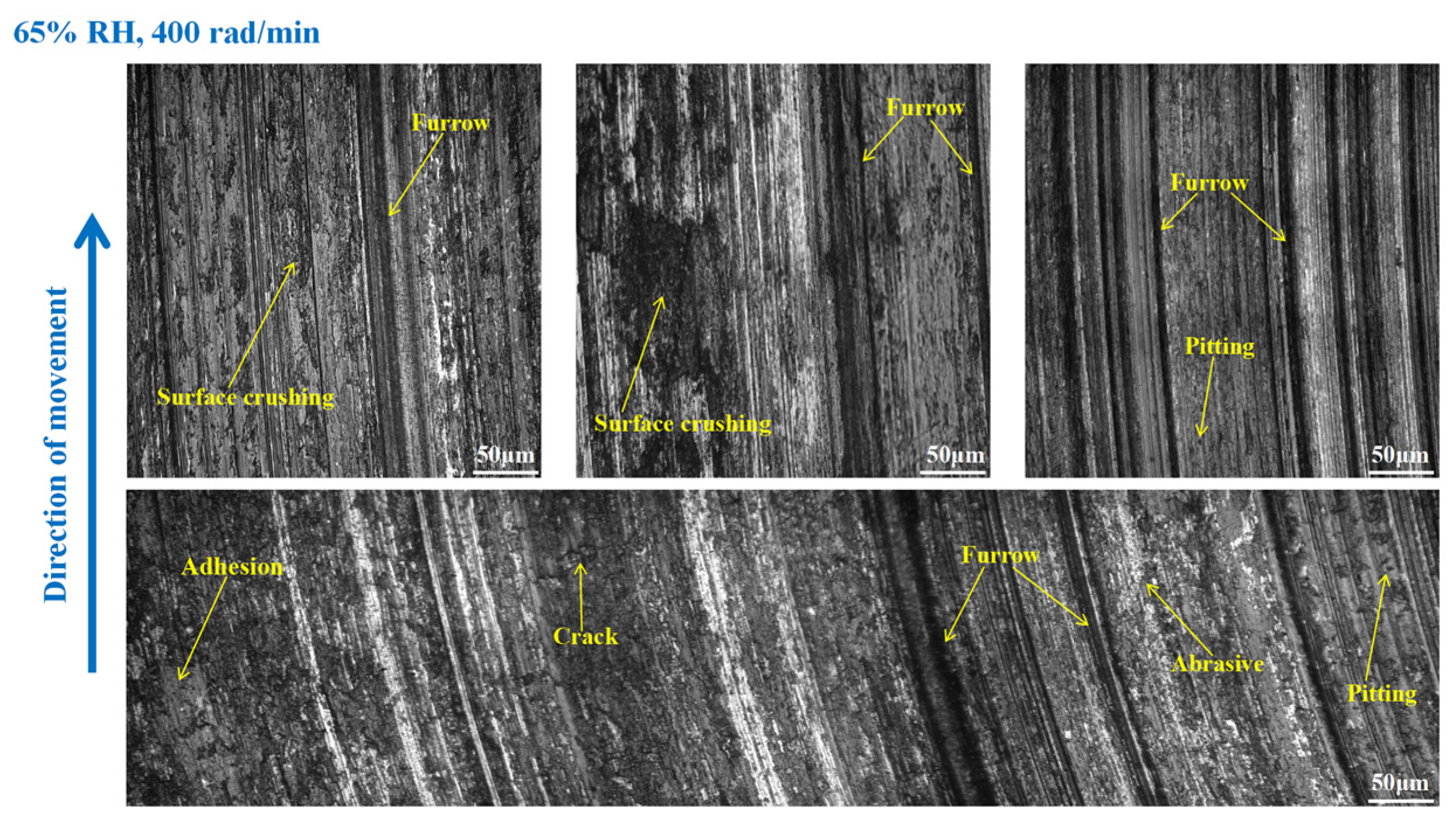
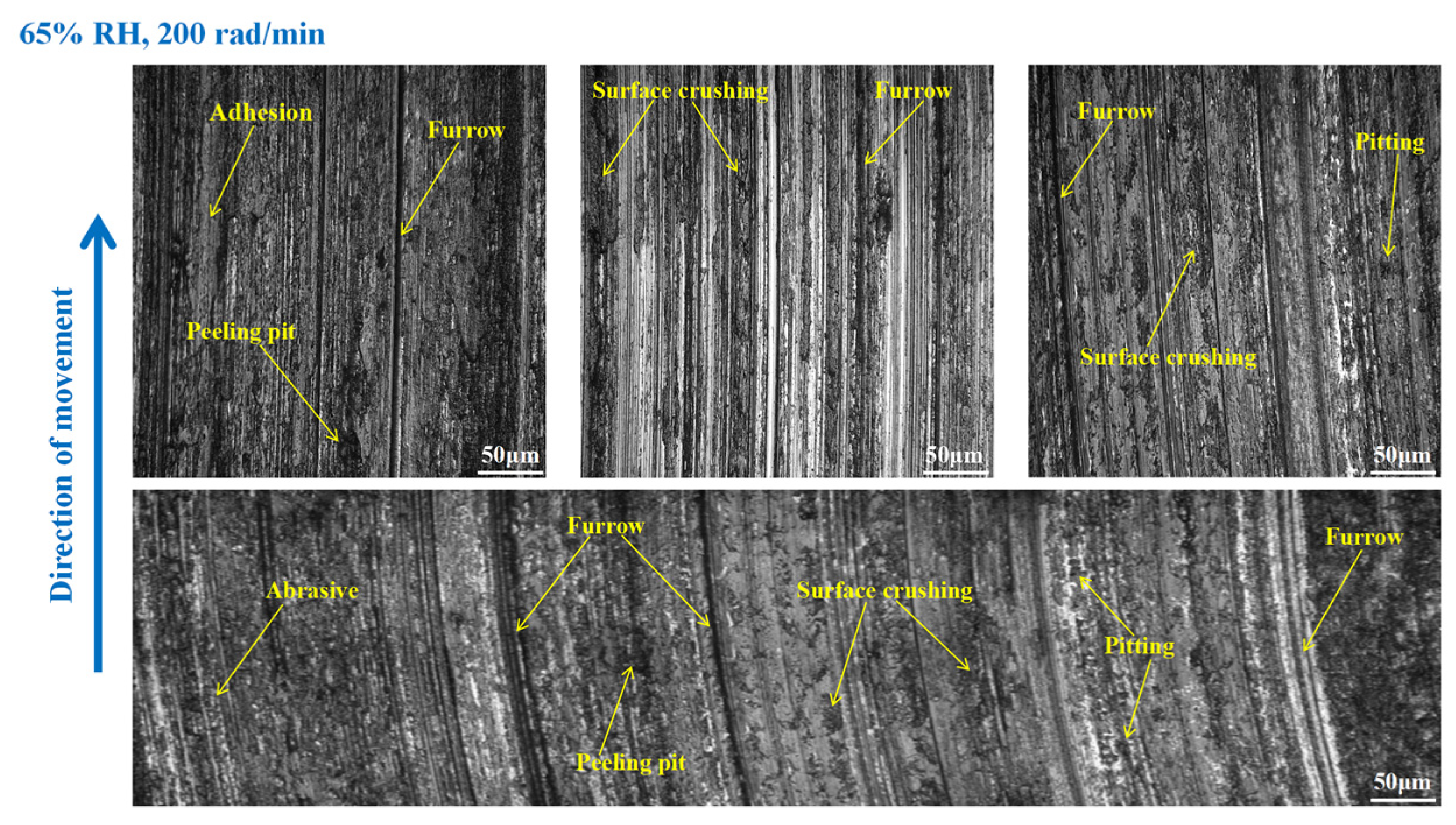
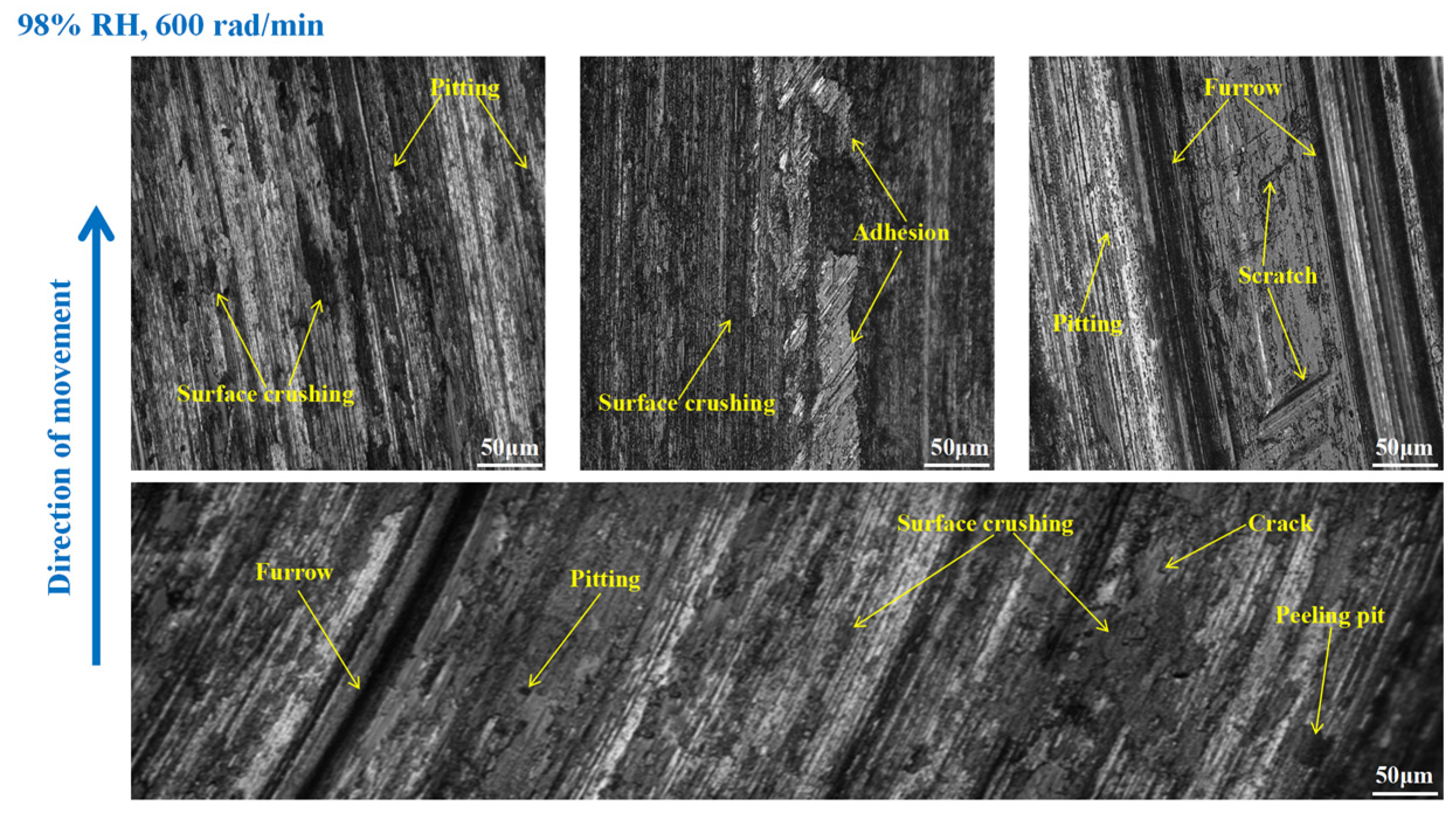
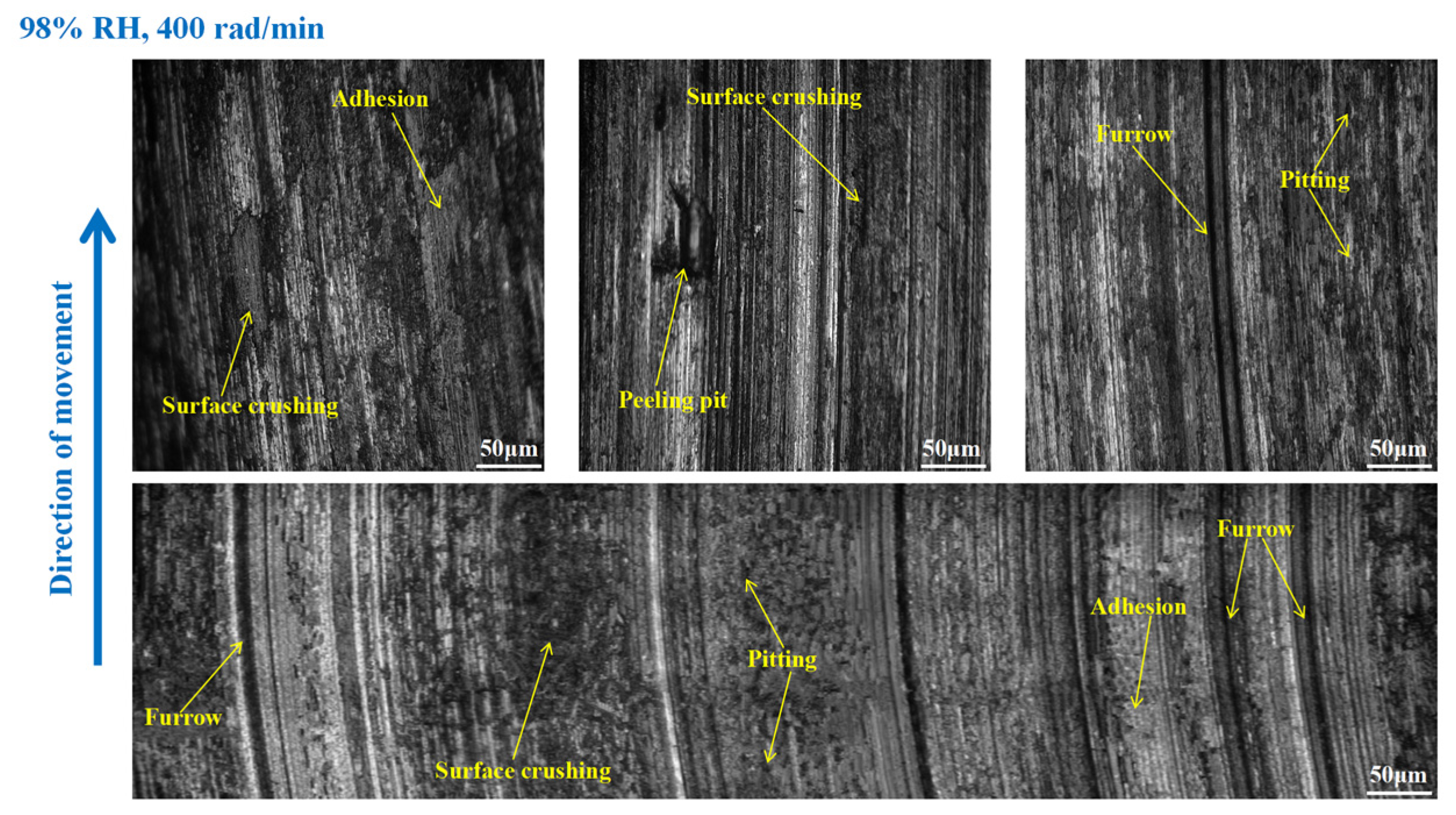
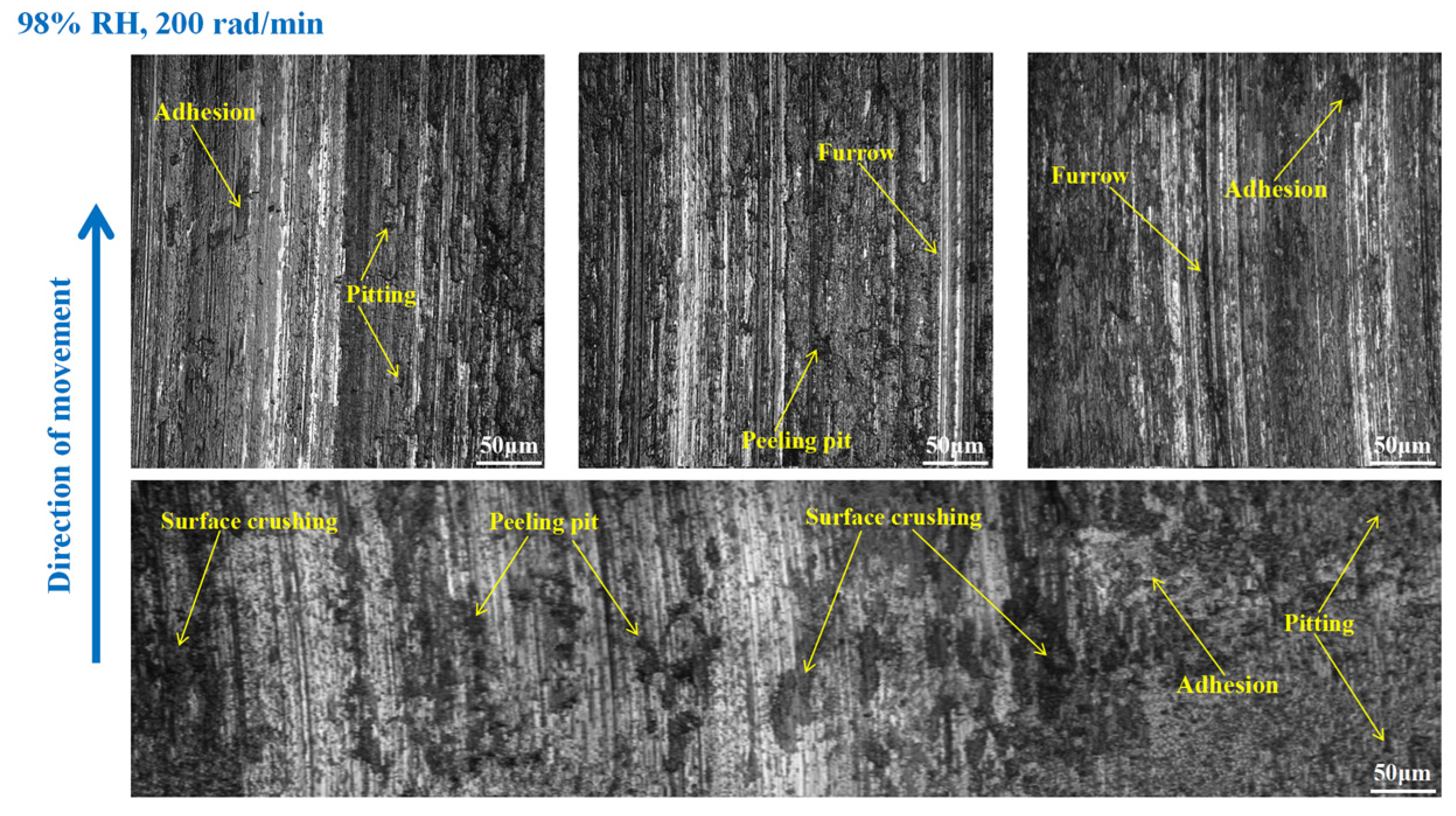
3.3. Wear Morphology
3.3.1. Wear Morphology to the Brake Disc
3.3.2. Wear Morphology to the Brake Pin
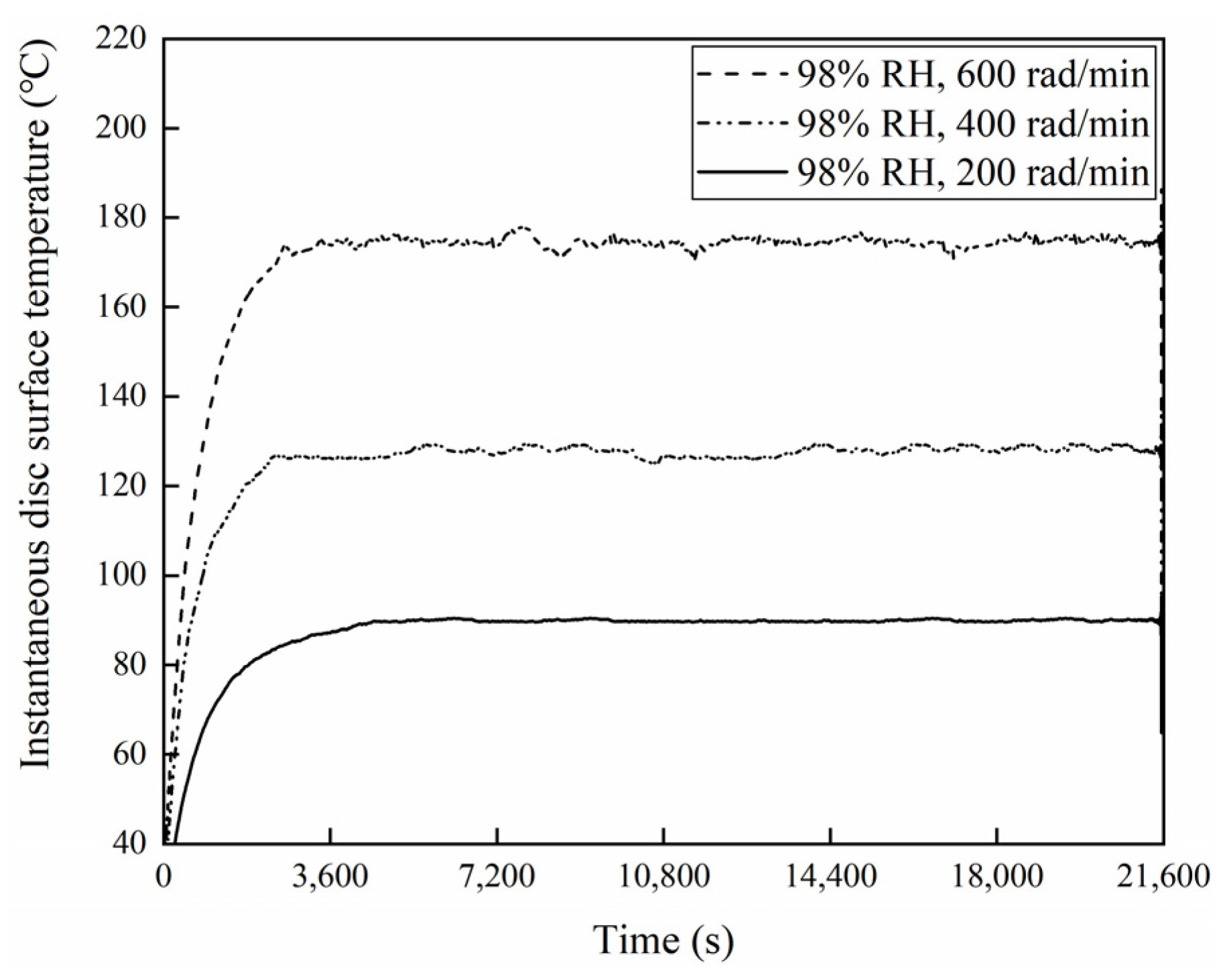
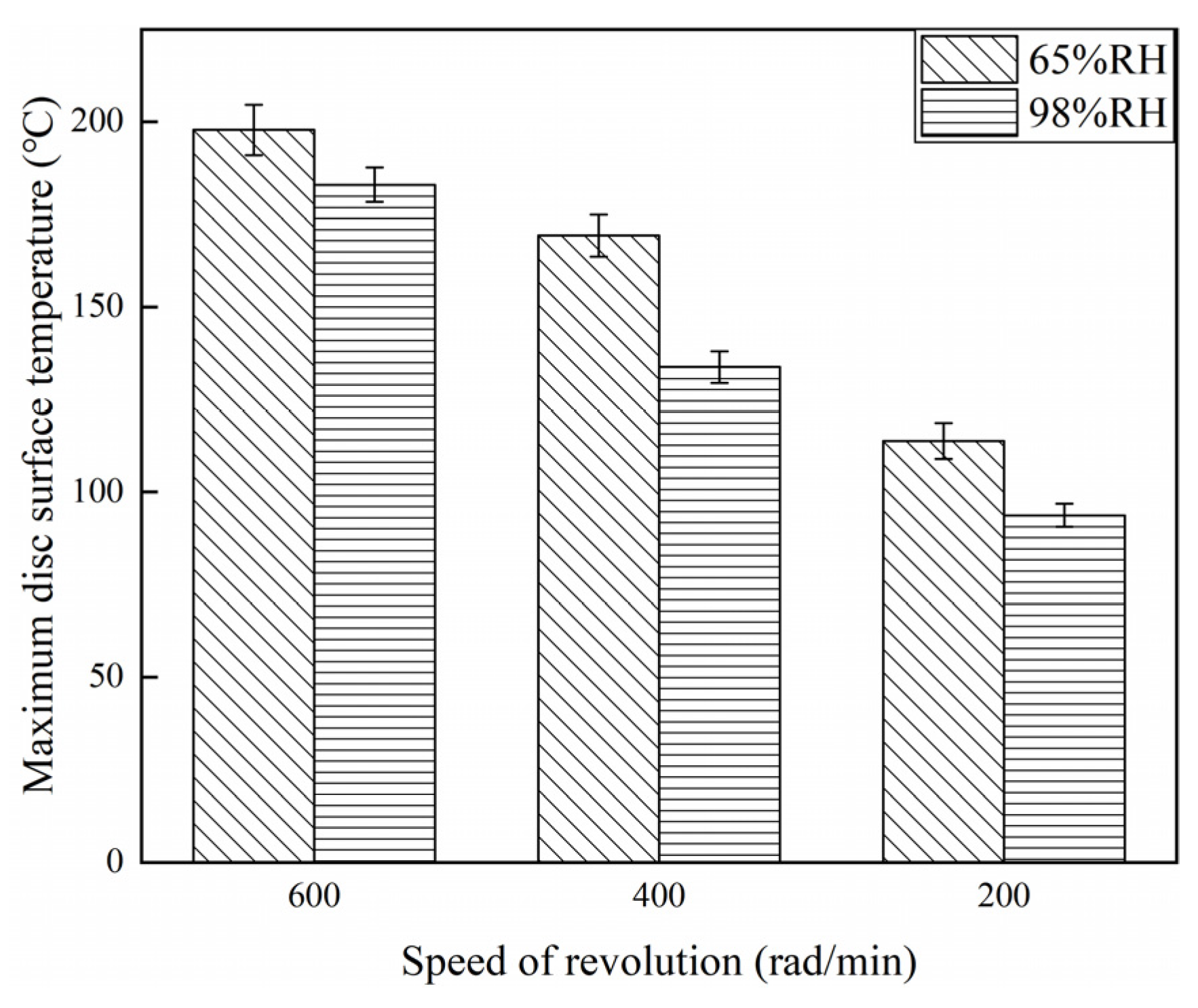
3.4. Disc Surface Temperature Analysis
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
- Under certain ambient humidity conditions, the friction coefficient, wear rate, wear damage, and the disc surface temperature of the braking materials reduce with a decrease in the braking speed.
- Under certain braking speed conditions, the friction coefficient to the braking materials at 98% RH is smaller compared to that at 65% RH. However, at 200 rad/min, the wear rate to the braking materials at 98% RH is larger than that at 65% RH.
- Considering both the braking speed and ambient humidity comprehensively, at a high braking speed, the effect of high humidity on the braking materials is small but significant at low braking speeds.
- Under 65% RH conditions, at 600, 400, and 200 rad/min, the wear mechanisms to the braking materials principally include adhesive wear and abrasive wear. And under 98%, RH conditions principally involve abrasive wear, adhesive wear, and surface fatigue wear.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.N.; Chen, Y.B.; Zuo, L.L.; Zhao, H.Y.; Ma, N.S. Evaluation of thermal fatigue life and cracks morphology in brake discs of low-alloy steel for high-speed trains. Materials 2022, 15, 6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.M.; Zhang, H.Q.; Chen, B.S.; Zhao, H.Y.; Yang, X.H.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.D. Safety assessment and life prediction model of brake discs for fast trains. J. Tsinghua Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2021, 38, 609–612. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.L.; Ma, T.H.; Tian, C.; Yang, J.; Chen, M.L. Discussion on the development trend of train braking technology. China Railw. Sci. 2019, 40, 134–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Wu, J.; Su, B.L.; Cui, B.; Teng, F.; An, S.; Bai, Y.Z. Thermo-mechanical-abrasive coupling analysis of solid rubber tire under high-speed rolling. Wear 2023, 512, 204546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, A.; Lemos, G.V.B.; Gasparin, A.L. Effects and interactions between service brake temperature, lining contact pressure, and vehicle speed. J. Eng. Tribol. 2022, 236, 2468–2476. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Jiang, Z.S.; Niu, M.Y.; Sun, Y.H.; Zhang, X.H. Tribological behavior of CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy against 304, Al2O3 and Si3N4 counterparts. Wear 2022, 508, 204471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gu, J.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, G.H. Study on laser cladding process and friction characteristics of friction pairs of copper-based powder metallurgy materials. Tribol. Int. 2022, 177, 107953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.M.; Zhao, C.F. Frontiers and Challenges of Modern Rail Transit Engineering Science and Technology. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2016, 51, 209–226. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, W.; Feng, Y.H.; Fu, S.H.; Wu, Y.L. Experimental study on brake disc wear tracking of high-speed rolling stock under wind and sand environment. J. Wuyi Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 34, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.X.; Li, J.Q.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.P.; Huangfu, L.Z.; Xiong, G.Y.; Shen, M.X. Study on the response behavior of warm and wet air flow to wheel-rail interface adhesion and damage at different service temperatures. Tribology 2023, 43, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.B. Effect of train passing weight on rail damage of Beijing-Guangzhou railway. China Railw. 2020, 4, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.Q.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhong, W.G.; Wen, Y.Y.; Yan, Q.Z. The wet braking and recovery behaviors of the P/M pad mated with C/C-SiC disc for high-speed trains. Wear 2021, 468, 203609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.S. Study on Stress Intensity Factor of Brake Disc Cracks of High-Speed Train. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Jianzhu University, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.X.; Shi, H.B.; Ding, S.Y.; Ma, L. Influence of braking speed on the wear property and simulation analysis of high-speed railway braking materials at low temperature. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2023, 75, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Yan, Q.Z.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhuang, Y. Role of titanium carbide and alumina on the friction increment for Cu-based metallic brake pads under different initial braking speeds. Friction 2021, 9, 1543–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Study on Wear and Friction Braking Behavior of EMU Brake Disc/Pad under Low Temperature Environment. Master’s Thesis, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Han, J.M.; Domblesky, J.P.; Li, Z.A.; Fan, X.G.; Liu, X.L. Cracks propagation and microstructural transformation on the friction surface of a high-speed railway brake disc. Wear 2019, 428, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D. Experimental Study on the Effect of Water and Snow on the Friction Coefficient of Brake Friction Pair. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou Jiaotong University, Lanzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, Y.Z.; Bergseth, E.; Wahlstrom, J. A pin-on-disc study on the tribology of cast iron, sinter and composite railway brake blocks at low temperatures. Wear 2019, 424, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djafri, M.; Bouchetara, M.; Busch, C.; Weber, S. Effects of humidity and corrosion on the tribological behaviour of the brake disc materials. Wear 2015, 321, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gu, K.K.; Wang, W.J.; Liu, Q.Y.; Zhu, M.H. Study on braking tribological behaviors of brake shoe material under the wet condition. Wear 2015, 342, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Shin, M.W.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, H.; Cho, M.H. The influence of humidity on the sliding friction of brake friction material. Wear 2013, 302, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.C.; Wu, S.Z.; Qiao, Q.F.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.H. Friction performance of brake discs and blocks for high-speed EMU trains in cold, rainy, and snowy weather. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2017, 52, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Q.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, S.H.; Yin, W. Research progress of friction properties of copper-based powder metallurgical friction materials for high-speed trains. Hot Work. Technol. 2020, 49, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Belhocine, A.; Omar, W.Z.W. Three-dimensional finite element modeling and analysis of the mechanical behavior of dry contact slipping between the disc and the brake pads. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 17, 761–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.X.; Ou, Y.D.; Yuan, H.B.; Pan, J.L.; Ma, L. Simulation experiment study on friction and wear of materials under high humidity conditions. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2023, 75, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.Y.; Zhang, M.X.; Ou, Y.D.; Ma, L. Study on the influence of friction and wear properties of high-speed rail brake materials under humidity environment and temperature conditions. Materials 2023, 16, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.Z.; Qiu, M.; Li, X.J. Study on friction and wear properties of steel/copper pairs in different humidity environment. Lubr. Seal. 2010, 35, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.; Fang, J.; Yang, Y.H. Analysis of influence of different temperature and humidity on wheel wear of high-speed train. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 54, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
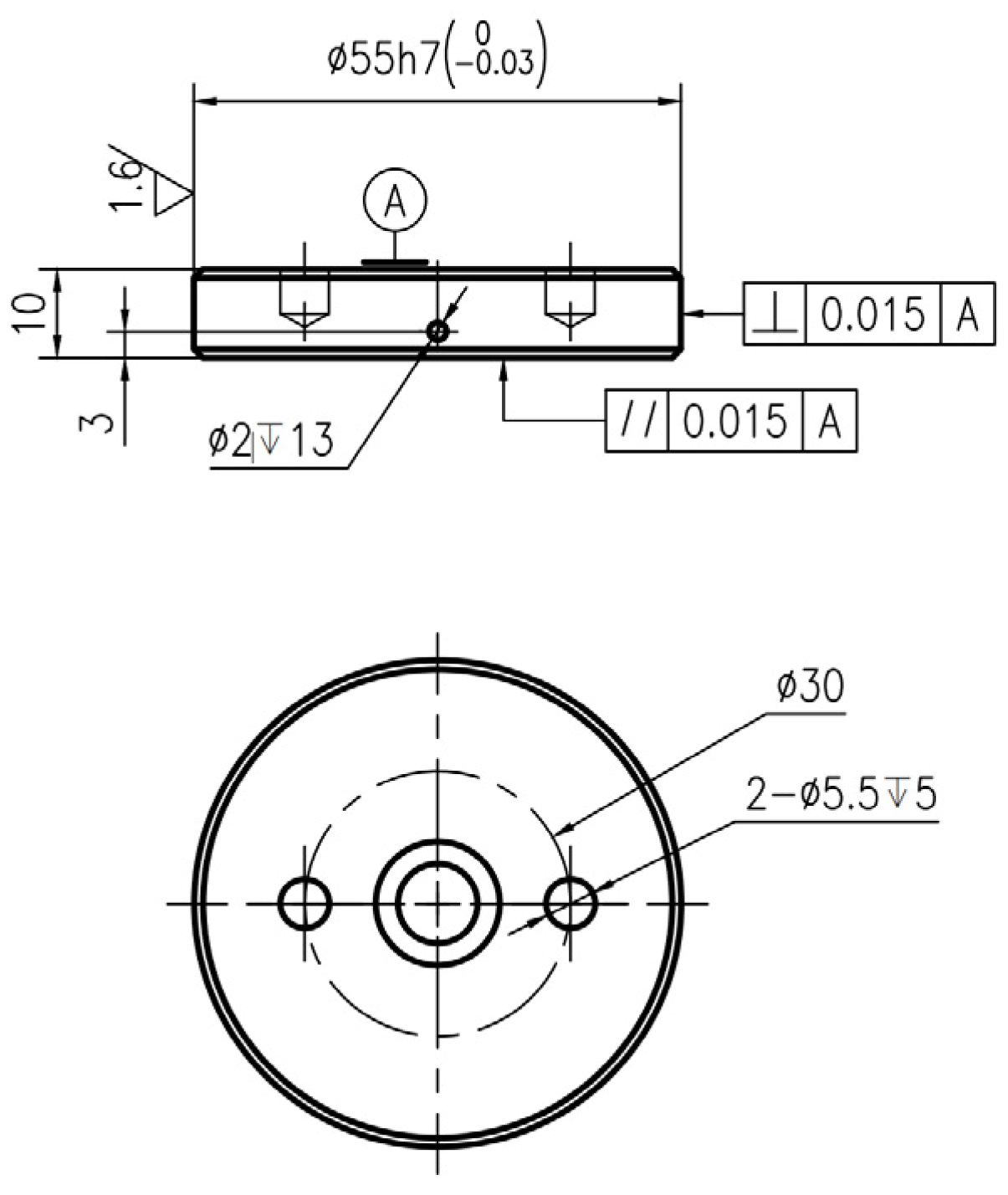
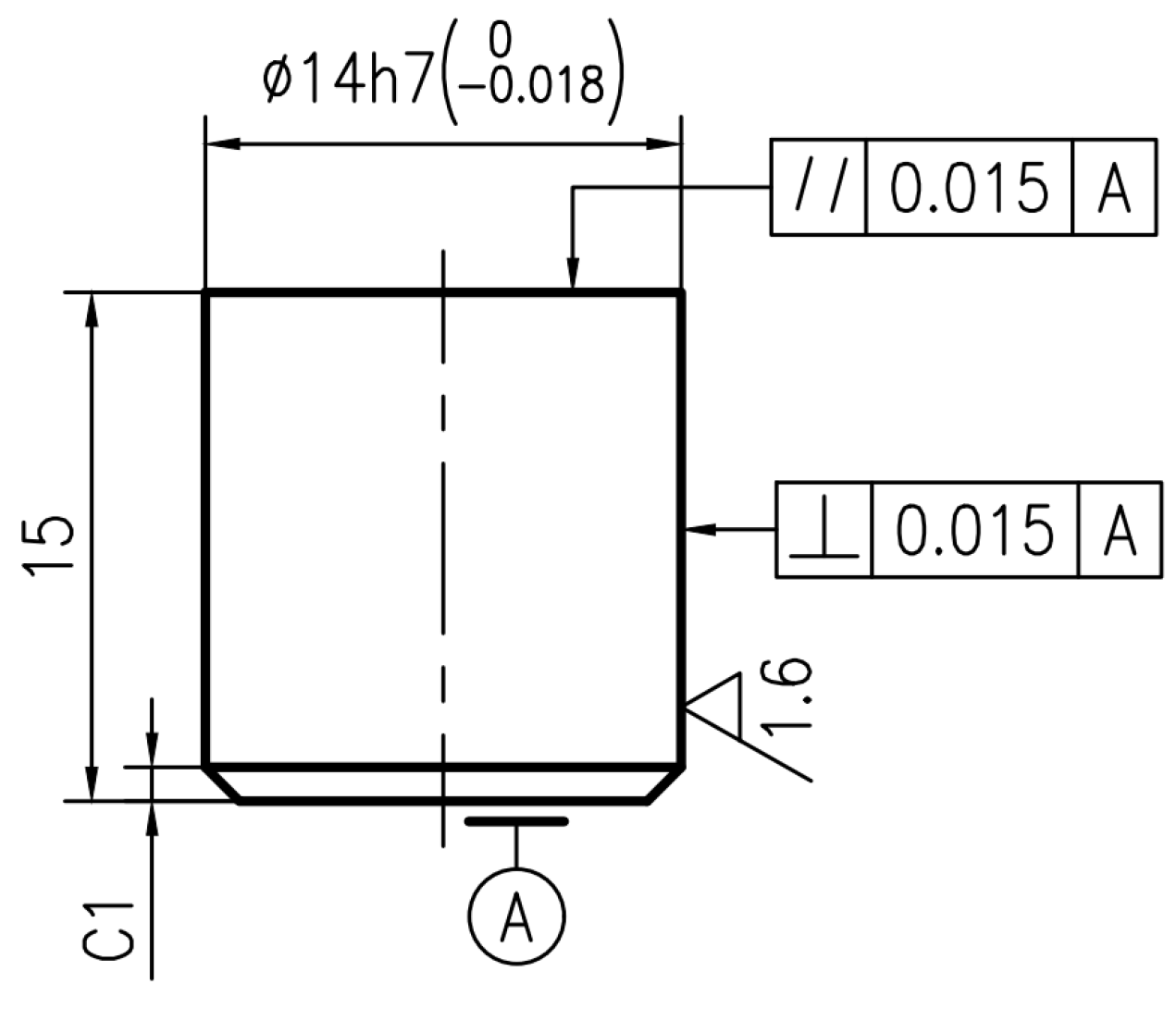
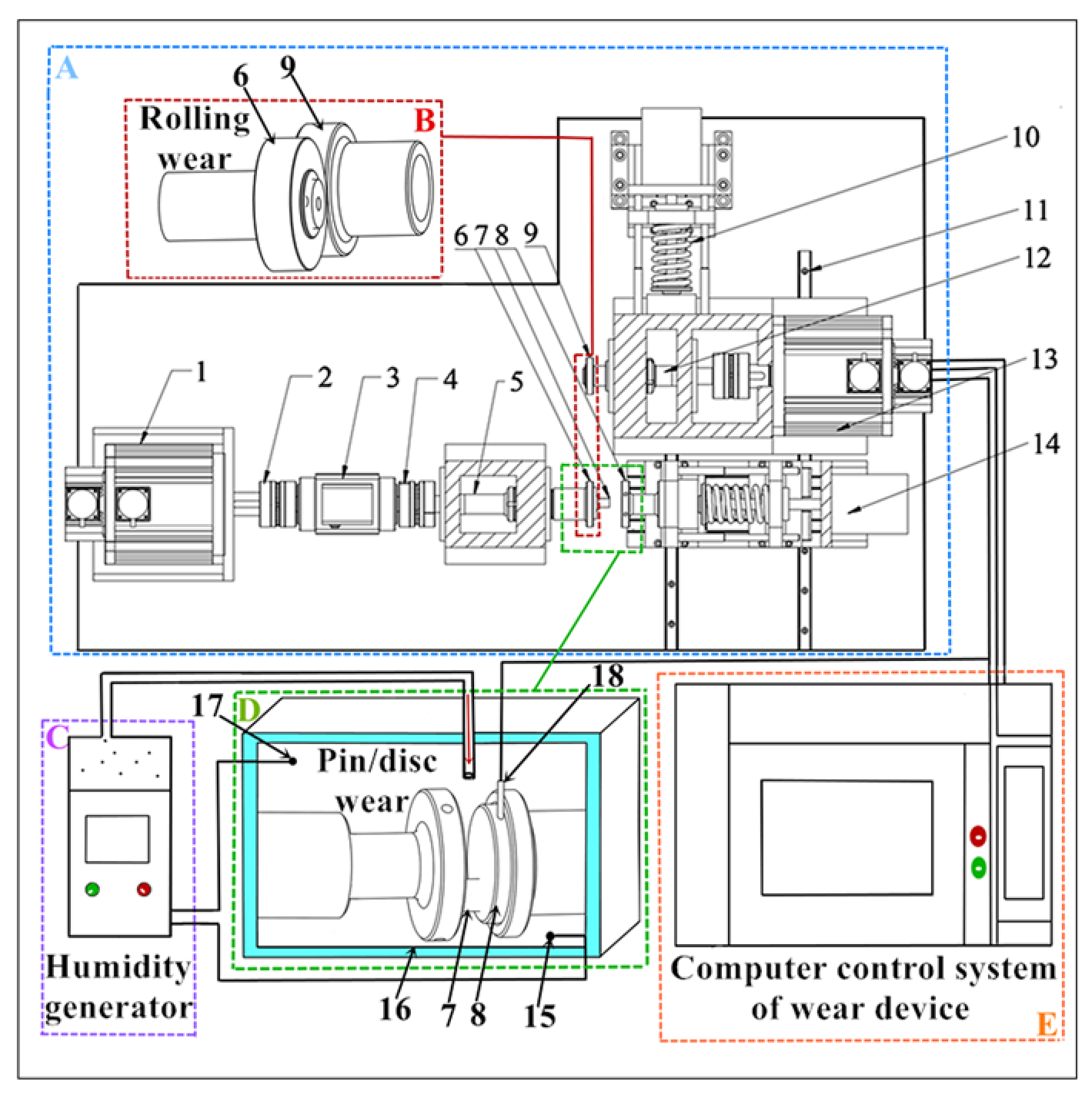











| Element | Mn | C | Cr | Cu | Si | Ni | O | Fe | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brake disc sample | 1.02 | 0.42 | 0.70 | - | 0.54 | 0.08 | - | Bal | - |
| Brake pin sample | - | 6.75 | 3.47 | 38.85 | - | - | 20.31 | Bal | 1.18 |
| Number | Braking Speeds/(rad/min) | Test Humidities/(%) | Test Force/(N) | Loading Speed/(m/s) | Ambient Temperature/(°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 600 | 65 | 100 | 0.5 | 20 |
| 2 | 400 | ||||
| 3 | 200 | ||||
| 4 | 600 | 98 | |||
| 5 | 400 | ||||
| 6 | 200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, L.; Zhang, M.; Ding, S.; Ou, Y. Influence of Braking Speed on the Friction and Wear Characteristics of High-Speed Railway Braking Materials under High Ambient Humidity Conditions. Materials 2023, 16, 6026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16176026
Ma L, Zhang M, Ding S, Ou Y. Influence of Braking Speed on the Friction and Wear Characteristics of High-Speed Railway Braking Materials under High Ambient Humidity Conditions. Materials. 2023; 16(17):6026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16176026
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Lei, Meixian Zhang, Siyuan Ding, and Yiding Ou. 2023. "Influence of Braking Speed on the Friction and Wear Characteristics of High-Speed Railway Braking Materials under High Ambient Humidity Conditions" Materials 16, no. 17: 6026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16176026
APA StyleMa, L., Zhang, M., Ding, S., & Ou, Y. (2023). Influence of Braking Speed on the Friction and Wear Characteristics of High-Speed Railway Braking Materials under High Ambient Humidity Conditions. Materials, 16(17), 6026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16176026







