Thermal Shock Behavior of Si3N4/BN Fibrous Monolithic Ceramics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
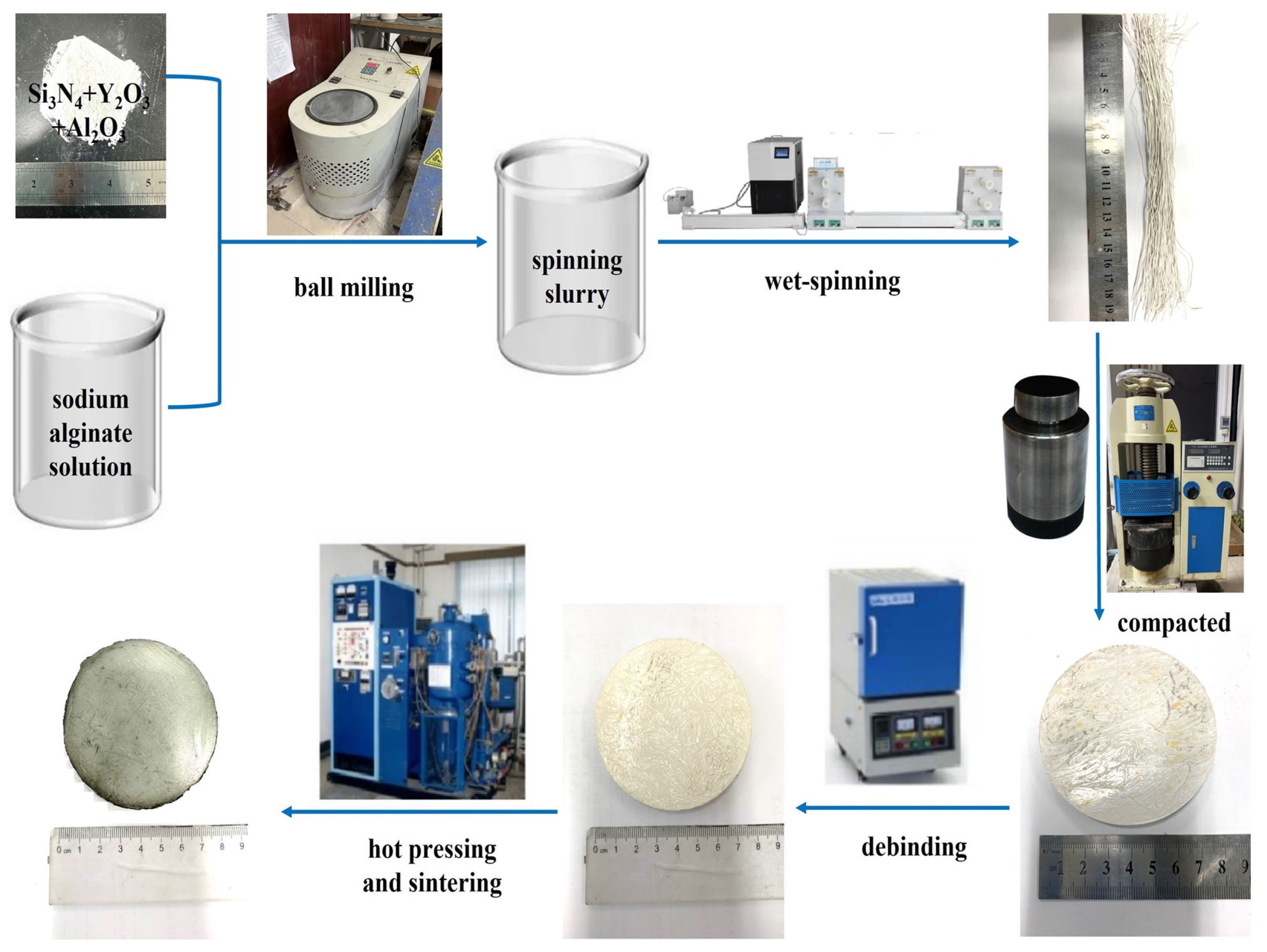
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
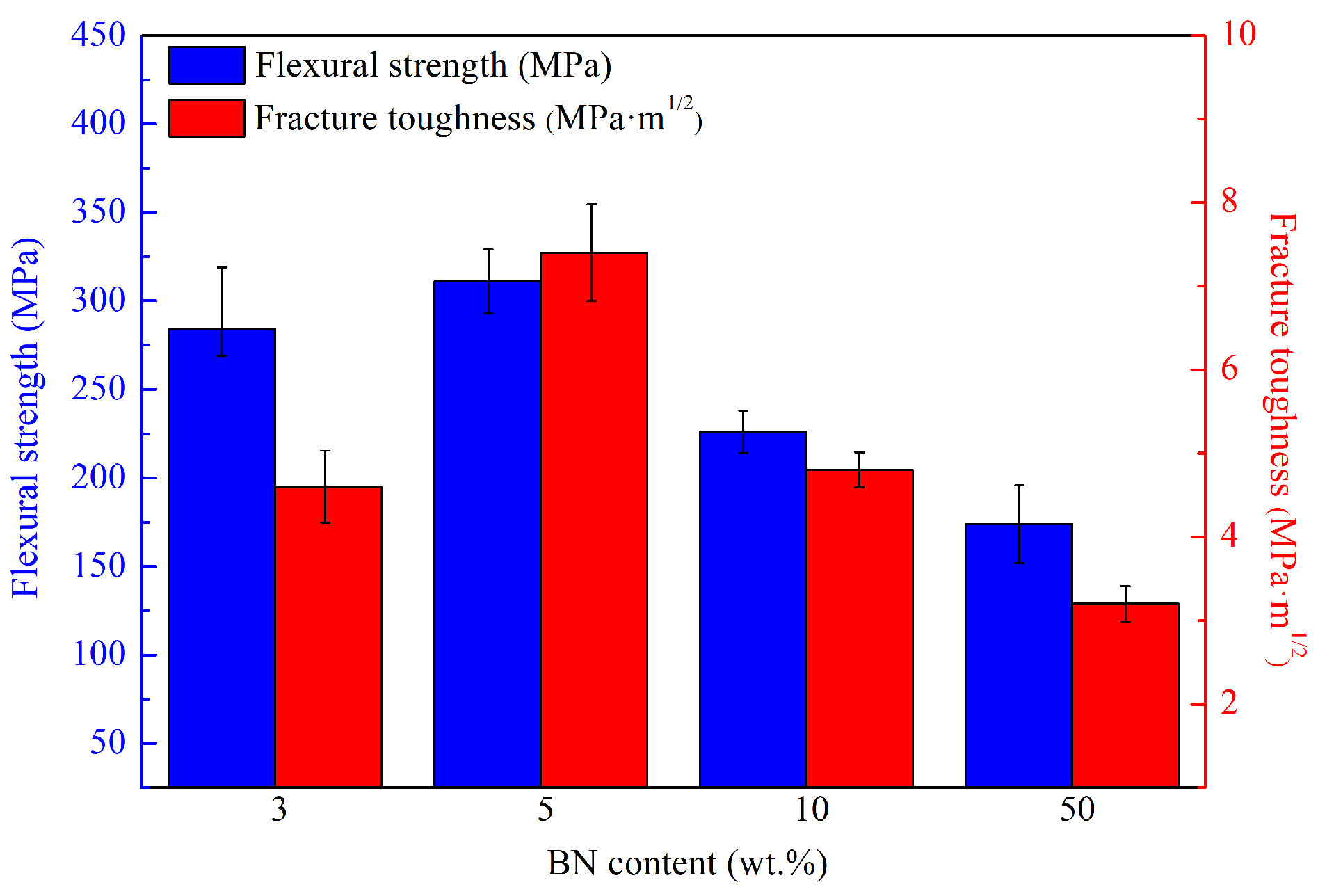
3.1. Mechanical Properties
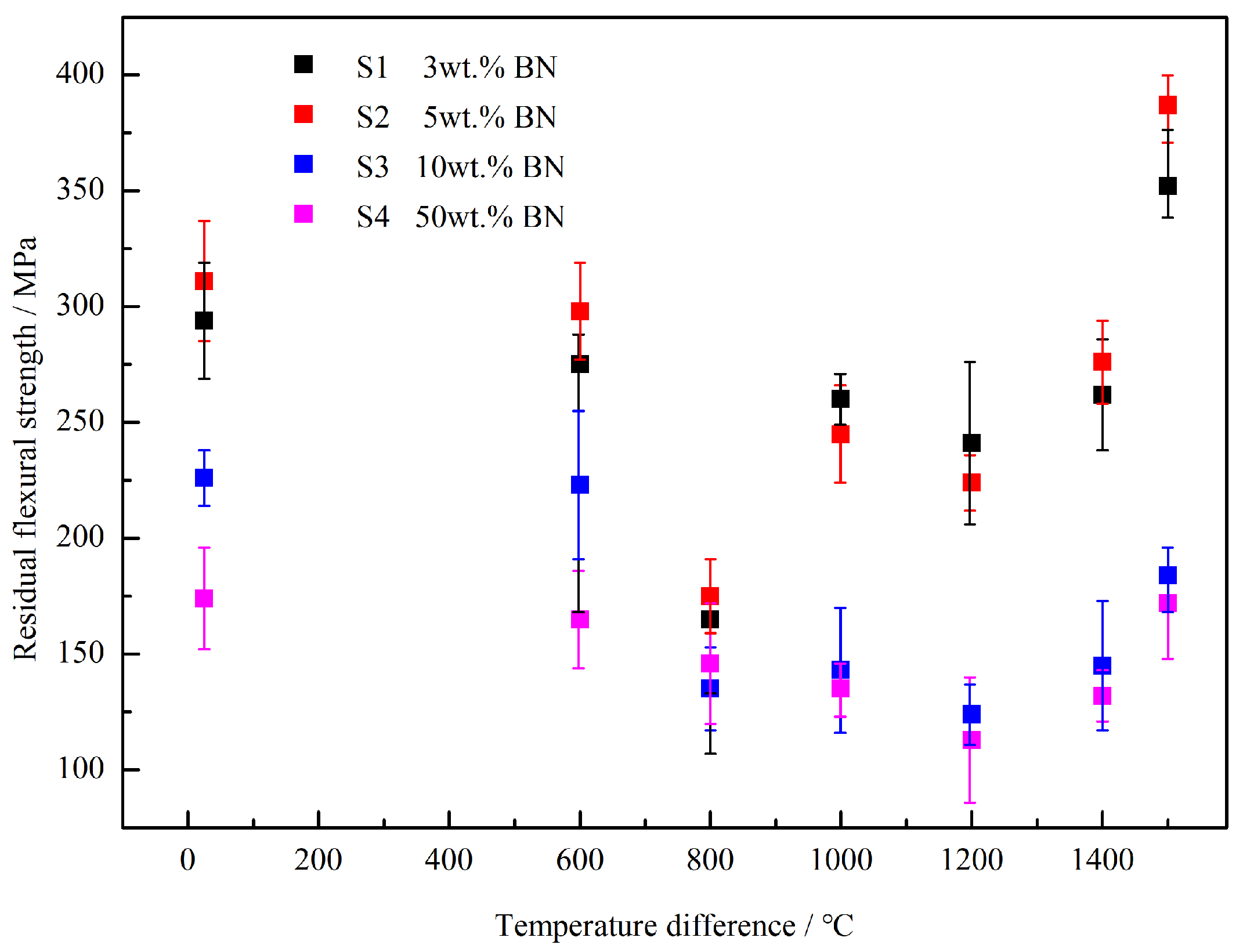
3.2. Residual Flexural Strength
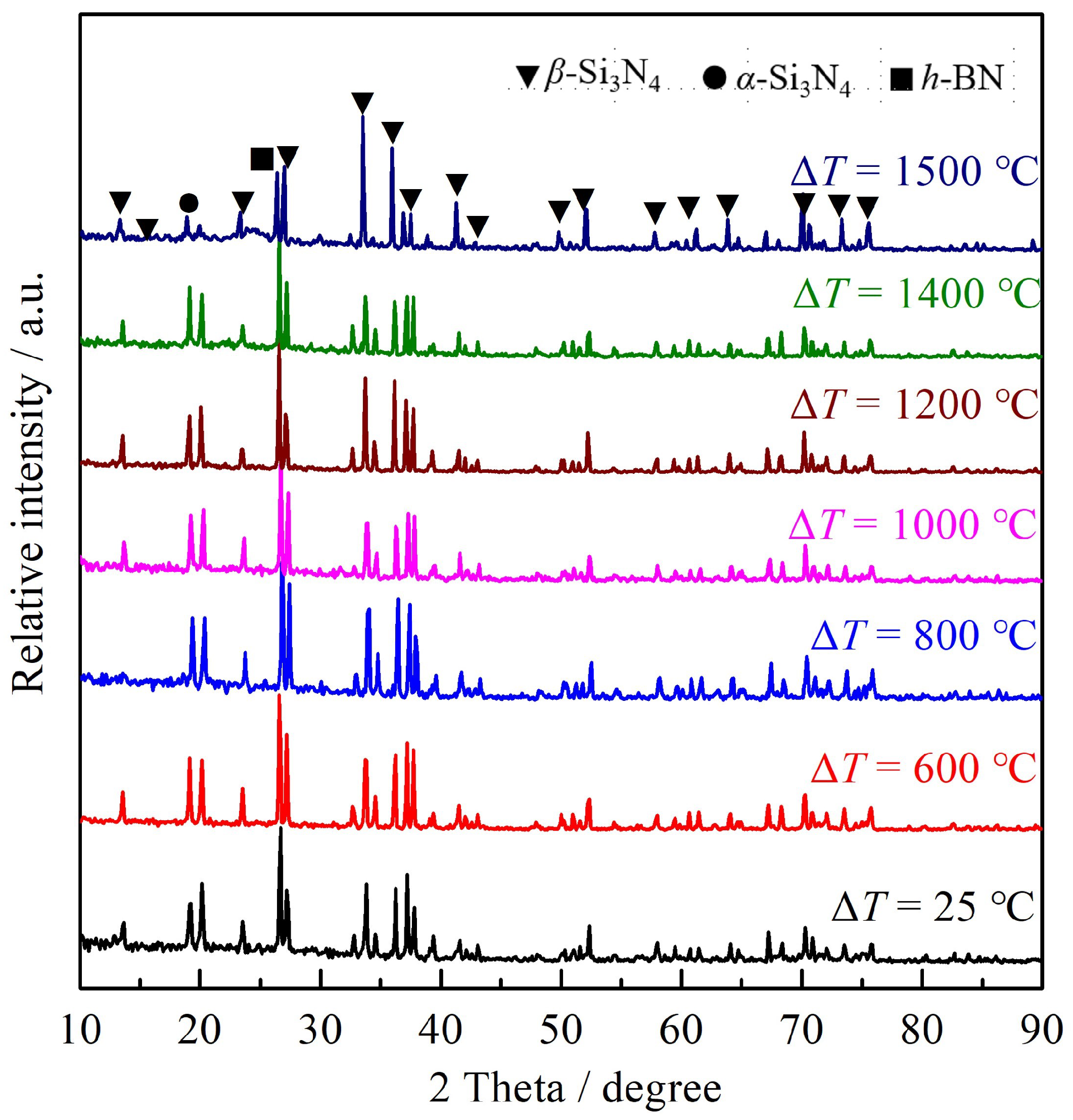
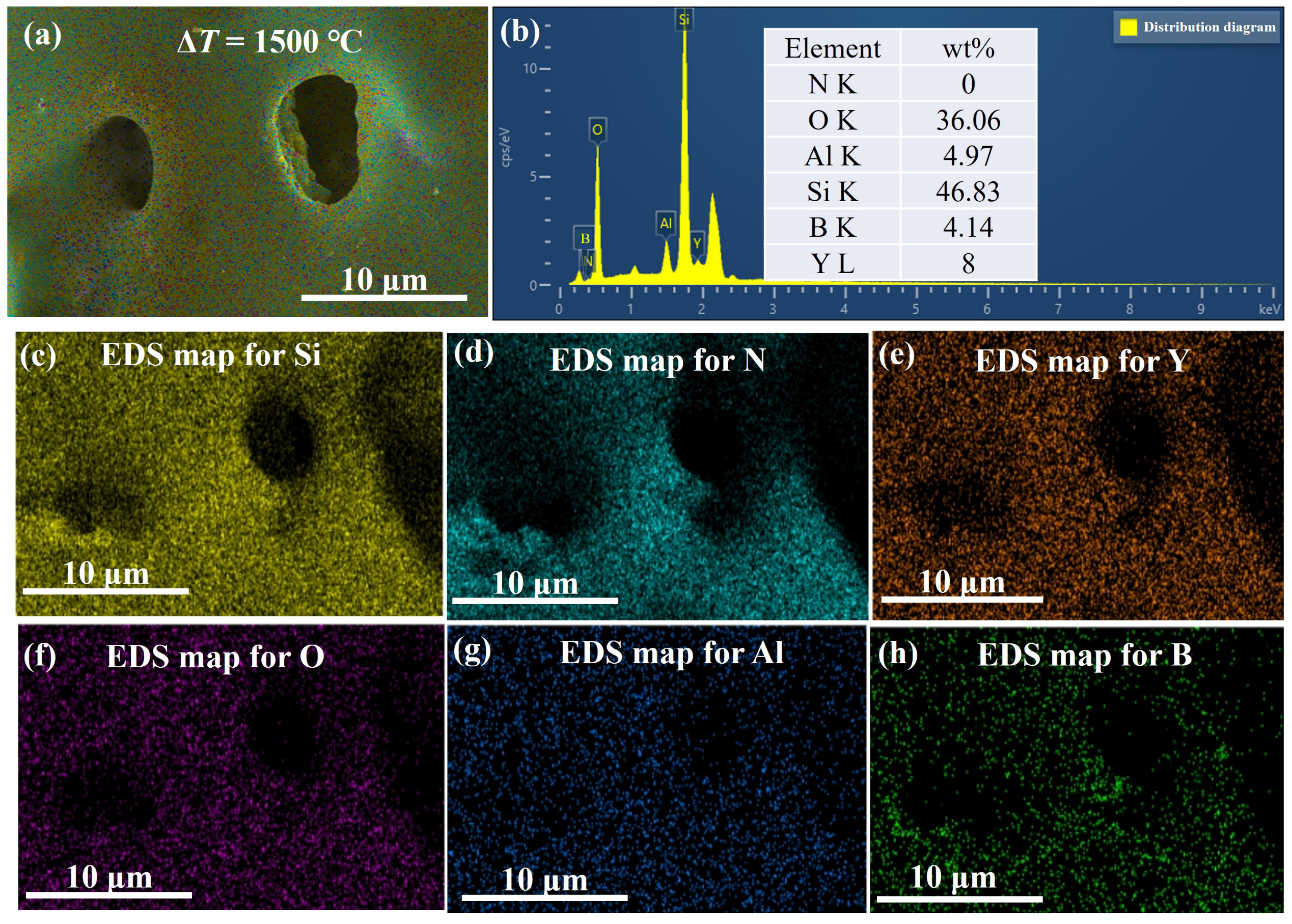
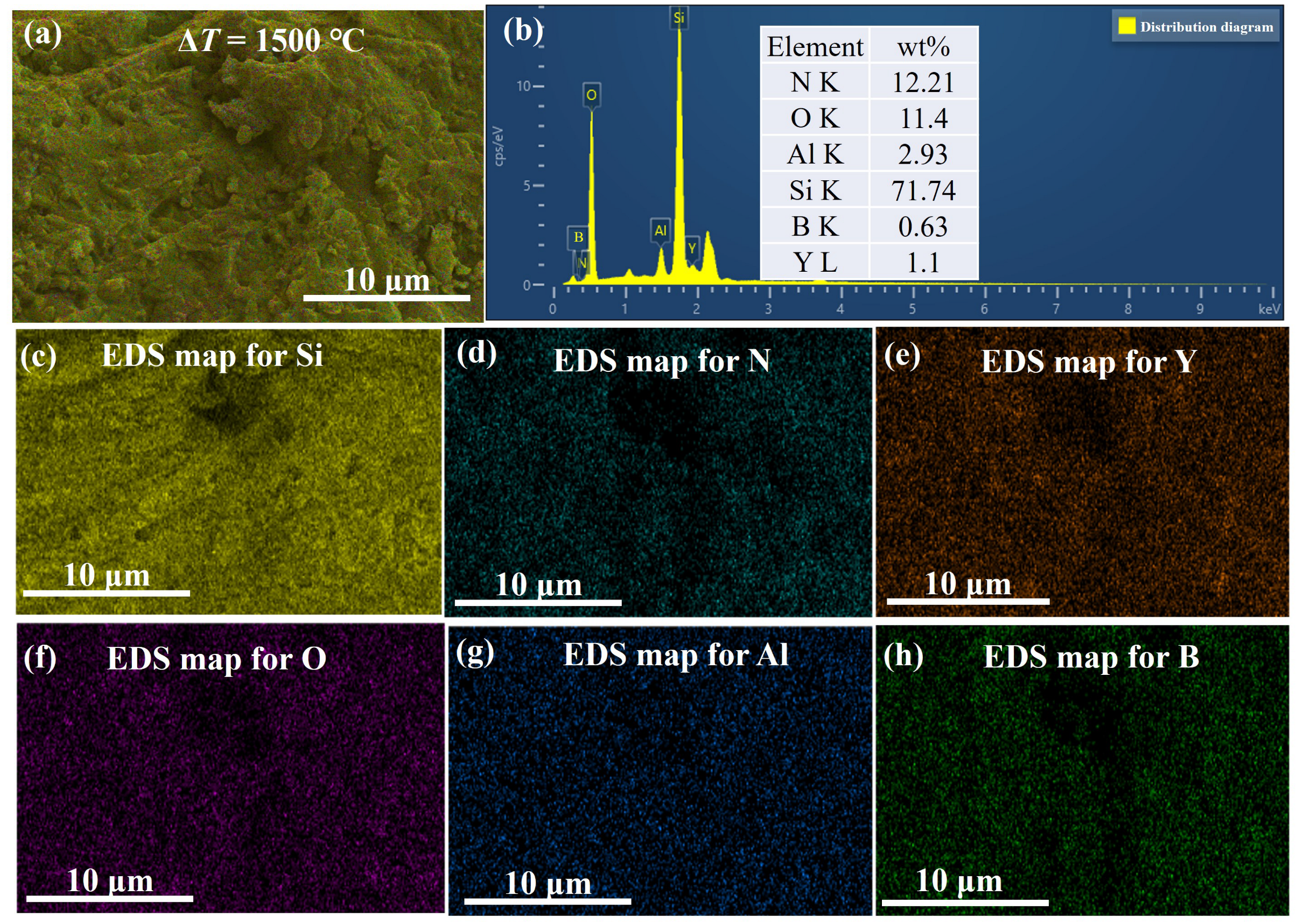
3.3. Surface Phase Composition
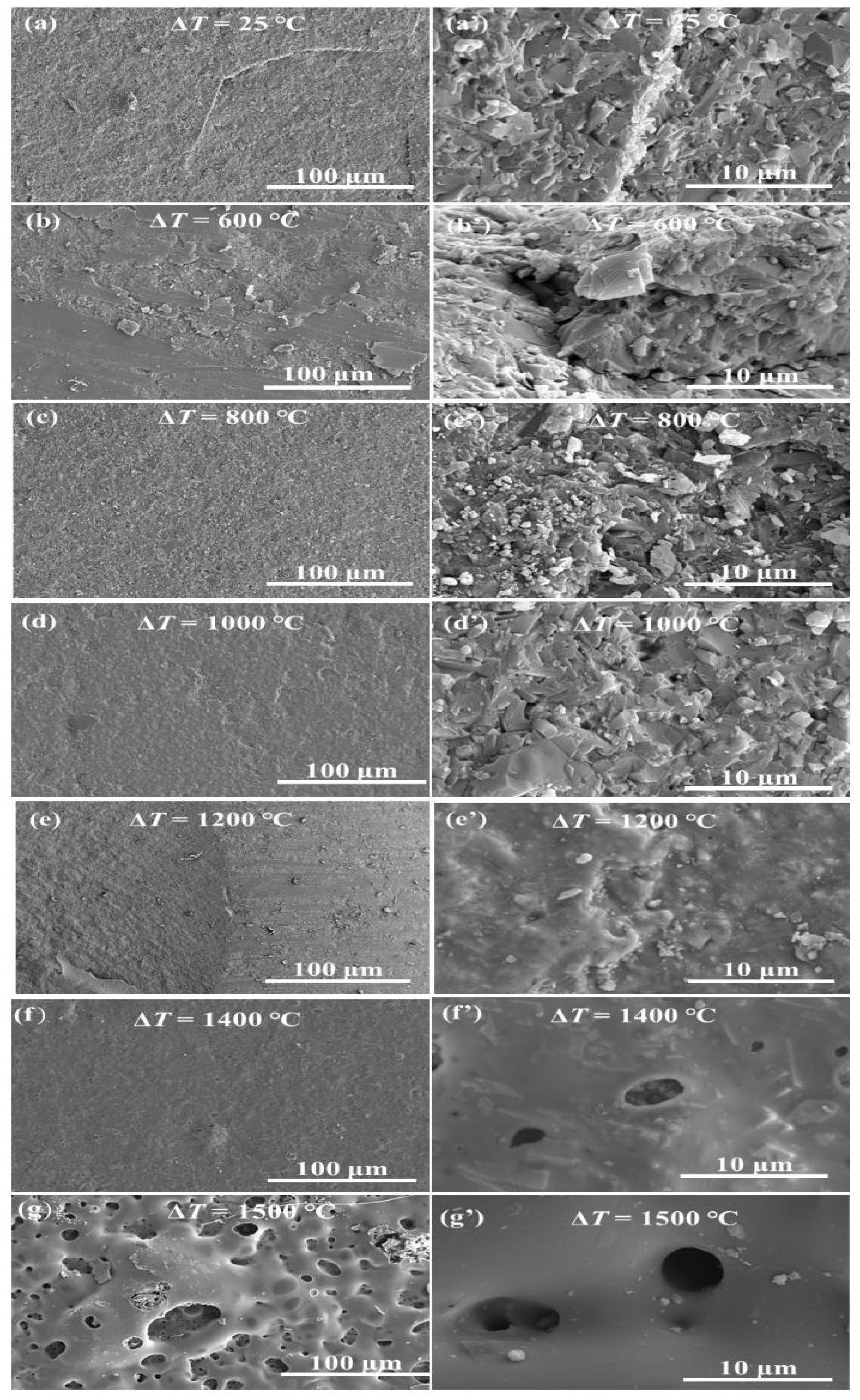
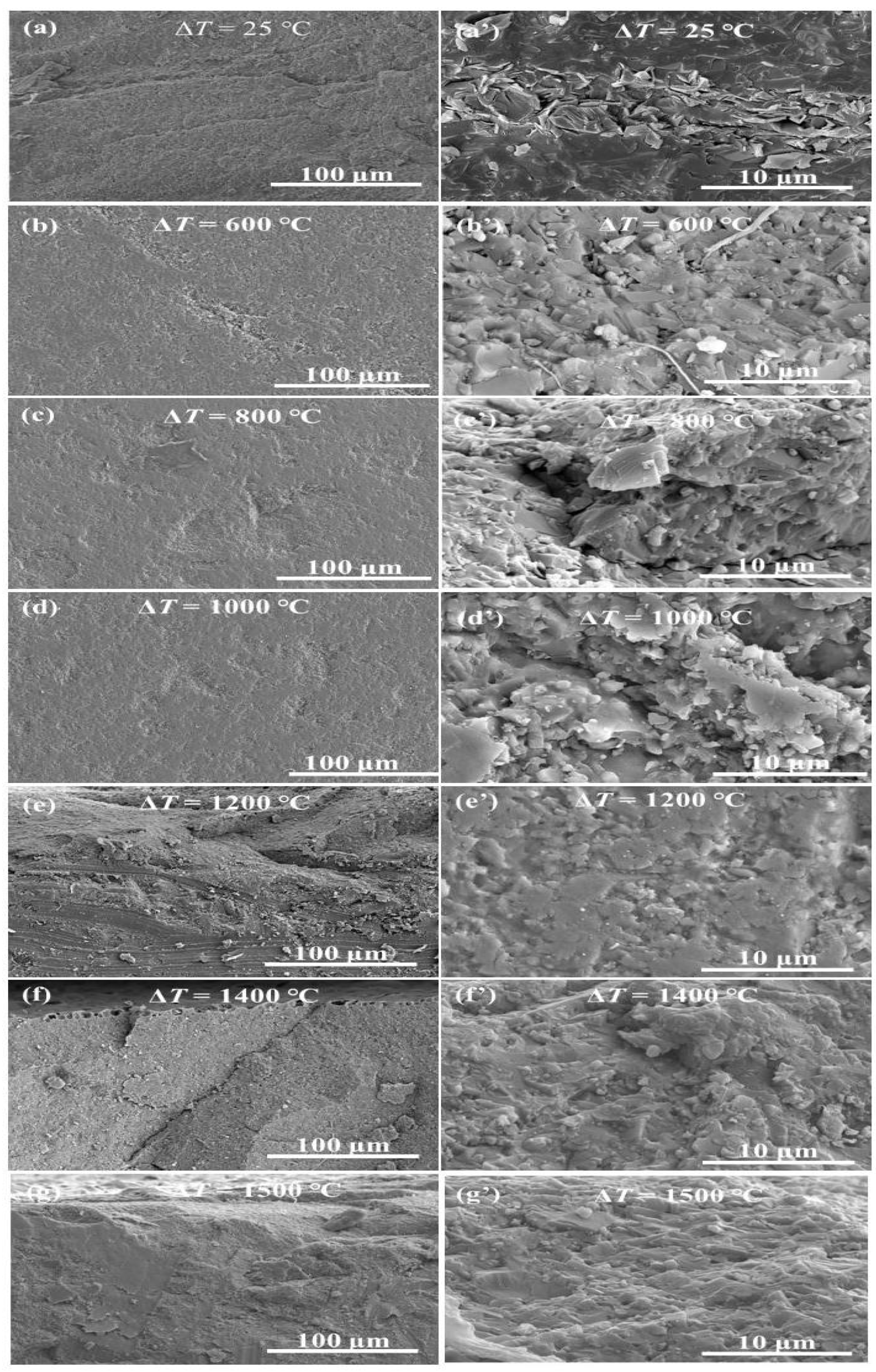
3.4. Surface Morphology
3.5. Fracture Morphology
4. Conclusions
- Residual flexural strength analysis: the flexural strength of SiN/BN fibrous monolithic ceramics first declines and then rises with an increasing thermal shock temperature differential. For thermal shock temperature differences below 800 °C, the material’s residual flexural strength reduces proportionally. However, when this difference surpasses 1000 °C, the strength begins to rise. Notably, all samples achieved their optimal residual strength after exposure to a 1500 °C temperature differential;
- BN concentration influence: When the BN mass fraction is 5 wt.%, the residual strength after a thermal shock at a temperature difference of 1500 °C is 387 ± 19 MPa, which is 124% higher than the original strength of the sample that did not undergo thermal shock (25 °C, 311 ± 18 MPa);
- Oxide film in oxygen-rich environments: When SiN/BN ceramics encounter an oxygen-abundant atmosphere during thermal shocks, they generate a compact YO-AlO-BO oxide film on their surface, which significantly augments the ceramic’s thermal shock resistance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Jia, D.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y. Principles, design, structure and properties of ceramics for microwave absorption or transmission at high-temperatures. Int. Mater. Rev. 2022, 67, 266–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonenko, E.; Simonenko, N.; Gordeev, A.; Kolesnikov, A.; Papynov, E.; Shichalin, O.; Tal’skikh, K.Y.; Gridasova, E.; Avramenko, V.; Sevastyanov, V.; et al. Impact of a supersonic dissociated air flow on the surface of HfB2-30 vol% SiC UHTC produced by the Sol–Gel method. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 63, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonenko, E.; Gordeev, A.; Simonenko, N.; Vasilevskii, S.; Kolesnikov, A.; Papynov, E.; Shichalin, O.; Avramenko, V.; Sevastyanov, V.; Kuznetsov, N. Behavior of HfB2-SiC (10, 15, and 20 vol%) ceramic materials in high-enthalpy air flows. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 61, 1203–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevastyanov, V.; Simonenko, E.; Gordeev, A.; Simonenko, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Papynov, E.; Shichalin, O.; Avramenko, V.; Kuznetsov, N. HfB2-SiC (10–20 vol%) ceramic materials: Manufacture and behavior under long-term exposure to dissociated air streams. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 59, 1361–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevastyanov, V.; Simonenko, E.; Gordeev, A.; Simonenko, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Papynov, E.; Shichalin, O.; Avramenko, V.; Kuznetsov, N. HfB2-SiC (45 vol%) ceramic material: Manufacture and behavior under long-term exposure to dissociated air jet flow. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 59, 1298–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonenko, E.; Simonenko, N.; Gordeev, A.; Papynov, E.; Shichalin, O.; Kolesnikov, A.; Avramenko, V.; Sevastyanov, V.; Kuznetsov, N. Study of the thermal behavior of wedge-shaped samples of HfB2-45 vol% SiC ultra-high-temperature composite in a high-enthalpy air flow. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 63, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, A.H.; Golczewski, J.A.; Bill, J.; Navrotsky, A. Effect of boron on the thermodynamic stability of amorphous polymer-derived Si (B) CN ceramics. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 4514–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, T. Thermal shock resistance of SiC whisker reinforced Si3N4 ceramic composites. Ceram. Int. 1996, 22, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kašiarová, M.; Tatarko, P.; Burik, P.; Dusza, J.; Šajgalík, P. Thermal shock resistance of Si3N4 and Si3N4–SiC ceramics with rare-earth oxide sintering additives. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 3301–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, N.N.; Bi, J.Q.; Wang, W.L.; Du, M.; Bai, Y.J. Mechanical properties and microstructure of porous BN-Si N2–Si3N4 composite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Meng, Q.; Jia, D. Mechanical and tribological properties of hot-pressed h-BN/Si3N4 ceramic composites. Ceram. Int. 2006, 32, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnyakov, L.; Maznaya, A.; Tomila, T.; Pereselentseva, L. Effect of mechanical activation on the in situ synthesis of aluminosilicates in the BN- Al2O3- SiO2- Si3N4 system. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 2008, 47, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenot, F.; Doche, C.; Mongeot, H.; Guilhon, F.; Miele, P.; Cornu, D.; Bonnetot, B. Boron nitride obtained from molecular precursors: Aminoboranes used as a BN source for coatings, matrix, and Si3N4–BN composite ceramic preparation. J. Solid State Chem. 1997, 133, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Jin, C.H.; Hwang, W.S.; Cho, W.S. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Si3N4/h-BN Composites Prepared by Hot-Pressing Using Nitrided Si3N4 Powders. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications, Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2007; Volume 544–545, pp. 415–418. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, S.K.; Li, C.W.; Wang, C.A.; Zan, Q.F. Flexure creep behaviors of Si3N4/BN laminated ceramic composites produced by rolling. Key Eng. Mater. 2003, 249, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L. Dielectric, electromagnetic interference shielding and absorption properties of Si3N4–PyC composite ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Qiao, R.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L. Fabrication and thermal shock resistance of β-Si3N4-based environmental barrier coating on porous Si3N4 ceramic. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 14222–14227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.J.; Guo, W.M.; Sun, S.K.; Lin, H.T. Design strategy of phase and microstructure of Si3N4 ceramics with simultaneously high hardness and toughness. J. Adv. Ceram. 2023, 12, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan, L.; Rajavel, R.; Venkataramanan, K.; Srinivasan, V. Experimental investigation on surface morphology and recasting layer of Si3N4-TiN composites machined by die-sinking and rotary EDM. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 8487–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Zhao, D.; Guo, T.; Fan, X.; Xue, J.; Ye, F.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, L. Oxidation behaviors of carbon fiber reinforced multilayer SiC- Si3N4 matrix composites. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, H.E. Mechanical properties of fibrous monolithic Si3N4/BN ceramics with different cell boundary thicknesses. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, H.E.; Halloran, J.W. Thermal shock resistance of fibrous monolithic Si3N4/BN ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 2339–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T1965-1996; Test Method for Cross-Bending Strength of Porous Ceramics. China Standard Press: Zibo, China, 1997.
- GB/T 23806-2009; Fine Ceramics (Advanced Ceramics Advanced Technical Ceramics)—Test Method for Fracture Toughness of Monolithic Ceramics at Room Temperature by Single Edge Precracked Beam (SEPB) Method. China Standard Press: Zibo, China, 2009.
- GB/T 16536-1996; Test Methods for Thermal Shock Resistance of High Performane Ceramics. China Standard Press: Zibo, China, 1997.
- GB/T 10700-2006; Test Methods for Elastic Moduli of Fine Ceramics (Advanced Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics)—Bending Method. China Standard Press: Zibo, China, 2006.
- Yuan, B.; Li, H.X.; Wang, G.; Yu, J.B.; Ma, W.K.; Liu, L.F.; Liu, Y.S.; Shen, Z.J. Preparation and properties of porous silicon carbide based ceramic filter. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 684, 613–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, M.; Nakamura, K.; Hirao, K.; Toriyama, M.; Kanzaki, S. Factors affecting mechanical properties of silicon oxynitride ceramics. Ceram. Int. 1997, 23, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.S.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, M.W.; Lee, E.S.; Park, D.S.; Munir, Z. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Silicon Nitride/h-BN Based Machinable Ceramics. Key Eng. Mater. 2005, 287, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iengo, P.; Di Serio, M.; Solinas, V.; Gazzoli, D.; Salvio, G.; Santacesaria, E. Preparation and properties of new acid catalysts obtained by grafting alkoxides and derivatives on the most common supports. Part II: Grafting zirconium and silicon alkoxides on γ-alumina. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1998, 170, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordia, R.K.; Kang, S.J.L.; Olevsky, E.A. Current understanding and future research directions at the onset of the next century of sintering science and technology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 2314–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, N.S.; Morscher, G.N.; Bryant, D.R.; Tressler, R.E. High-temperature oxidation of boron nitride: II, boron nitride layers in composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.B.; Li, H.J.; Fu, Q.G.; Hui, X.; Sun, G.L. Fabrication and tribological properties of B2O3 as friction reducing coatings for carbon-carbon composites. New Carbon Mater. 2007, 22, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
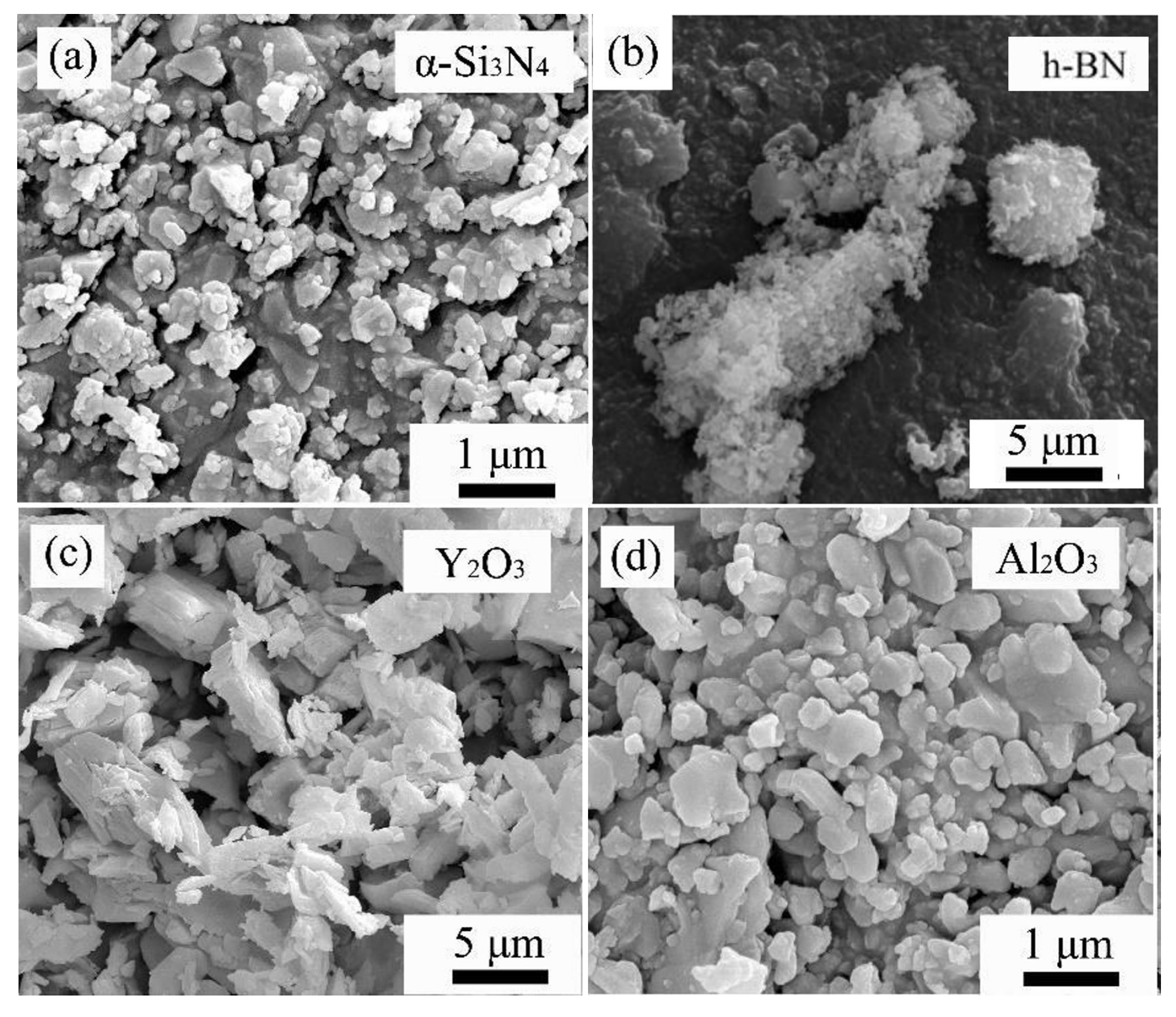





| -SiN (wt.%) | (wt.%) | AlO (wt.%) | Deionized Water (wt.%) | (CHNO) (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 47.5 | 1.78 | 0.72 | 48.75 | 1.25 |
| Composites | BN ( wt.%) |
|---|---|
| S1 | 3 |
| S2 | 5 |
| S3 | 10 |
| S4 | 50 |
| Composites | Theoretical Density g·cm | Actual Density g·cm | Relative Density % | Apparent Porosity % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 3.33 | 3.27 | 98.3 | 0.93 |
| S2 | 3.26 | 3.15 | 96.8 | 1.25 |
| S3 | 3.17 | 2.96 | 93.5 | 1.88 |
| S4 | 2.67 | 2.24 | 83.8 | 3.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Ying, G. Thermal Shock Behavior of Si3N4/BN Fibrous Monolithic Ceramics. Materials 2023, 16, 6377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196377
Chen Q, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Li D, Ying G. Thermal Shock Behavior of Si3N4/BN Fibrous Monolithic Ceramics. Materials. 2023; 16(19):6377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196377
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qingqing, Yuan Zhang, Yu Zhou, Daxin Li, and Guobing Ying. 2023. "Thermal Shock Behavior of Si3N4/BN Fibrous Monolithic Ceramics" Materials 16, no. 19: 6377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196377
APA StyleChen, Q., Zhang, Y., Zhou, Y., Li, D., & Ying, G. (2023). Thermal Shock Behavior of Si3N4/BN Fibrous Monolithic Ceramics. Materials, 16(19), 6377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196377








