The Synergistic Effect of Trace Ag and Hot Extruding on the Microstructure and Properties of a Biodegradable Mg-Zn-Sr-Ag Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Hot Extrusion Treatment
2.3. Charaterization
2.4. Properties
2.4.1. Mechanical Properties
2.4.2. Degradation Properties
3. Results and Discussion
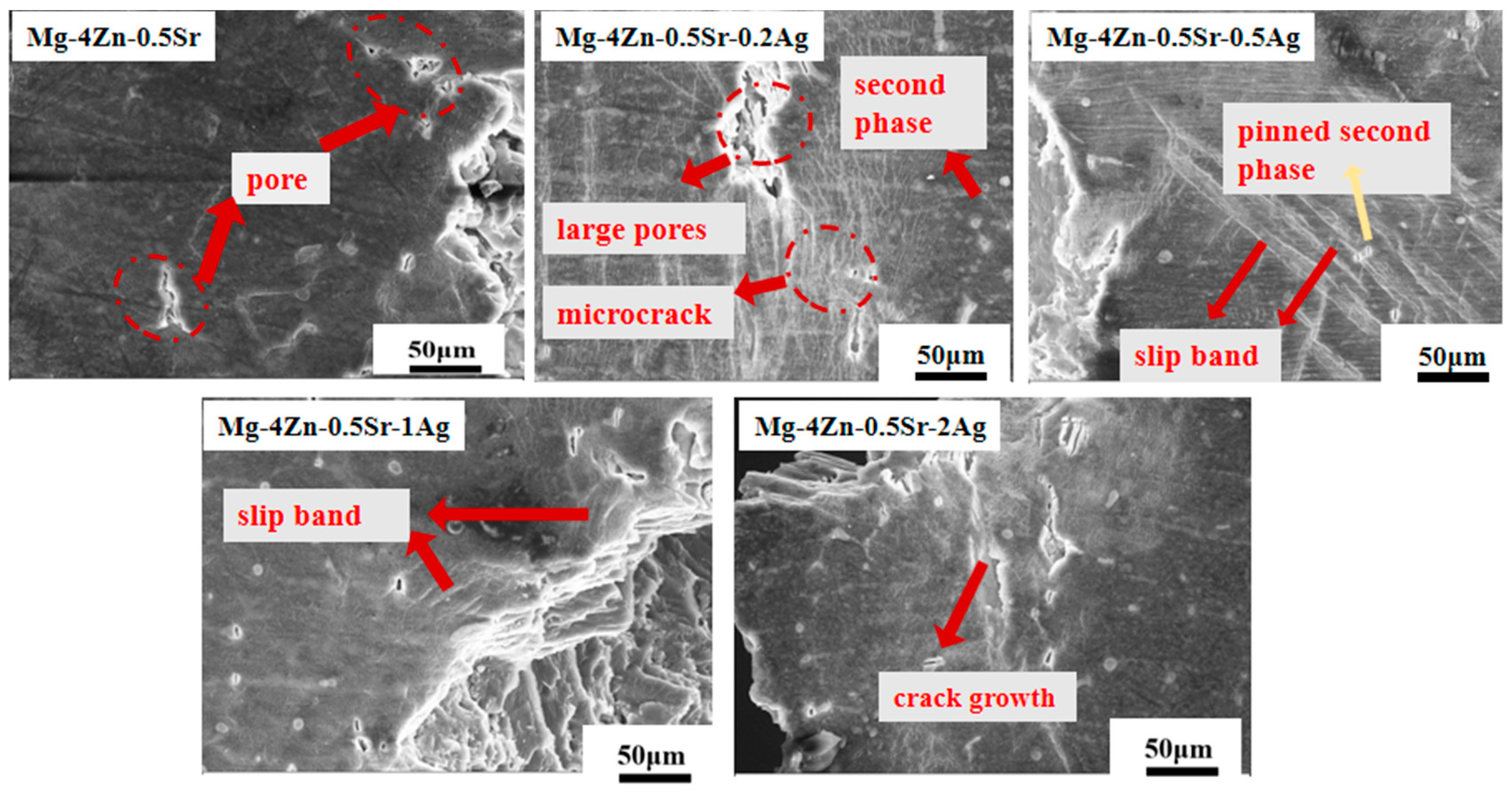
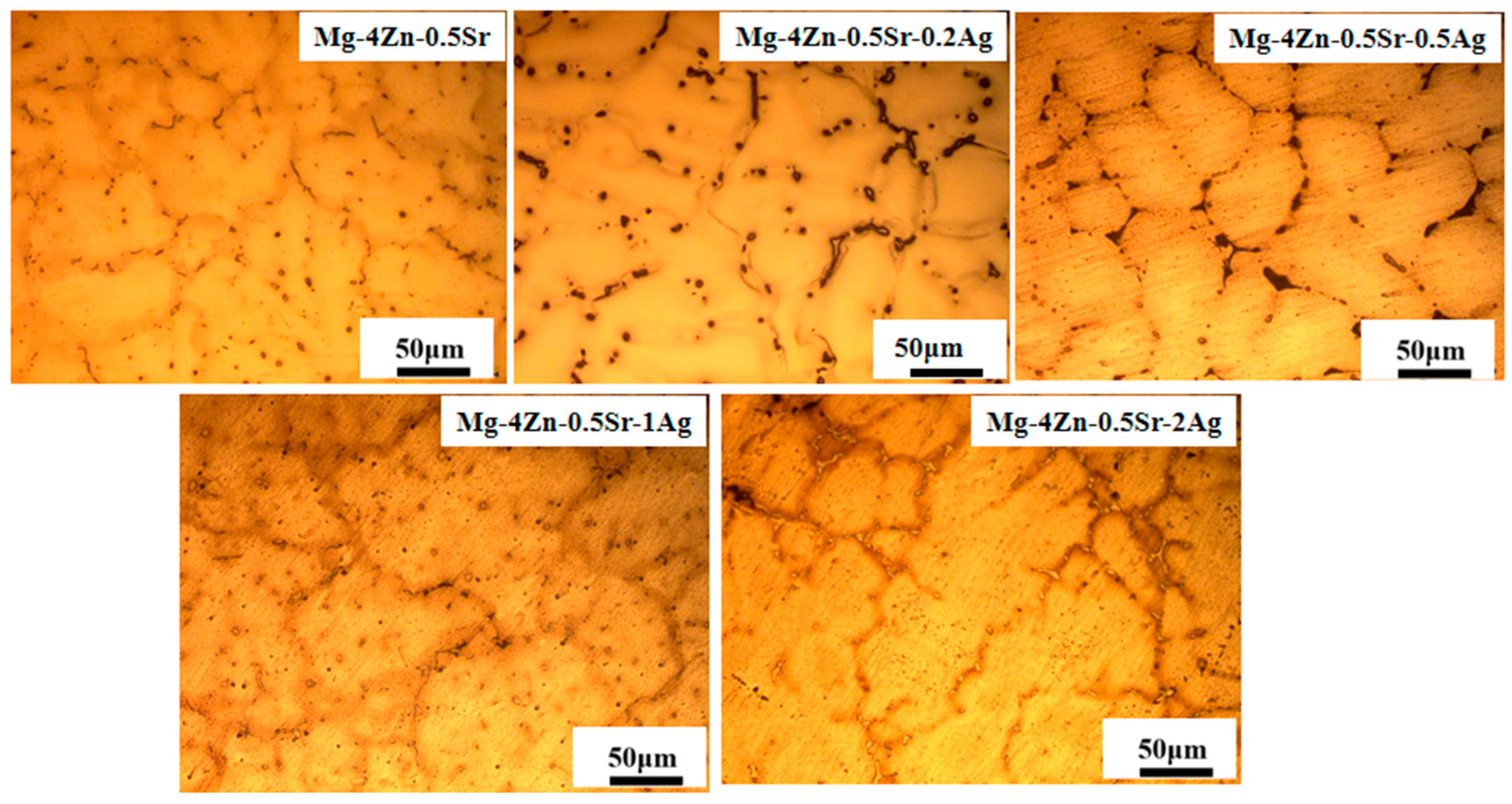
3.1. The Microstruture and Mechanical Properties of Casted Mg-Zn-Sr-xAg
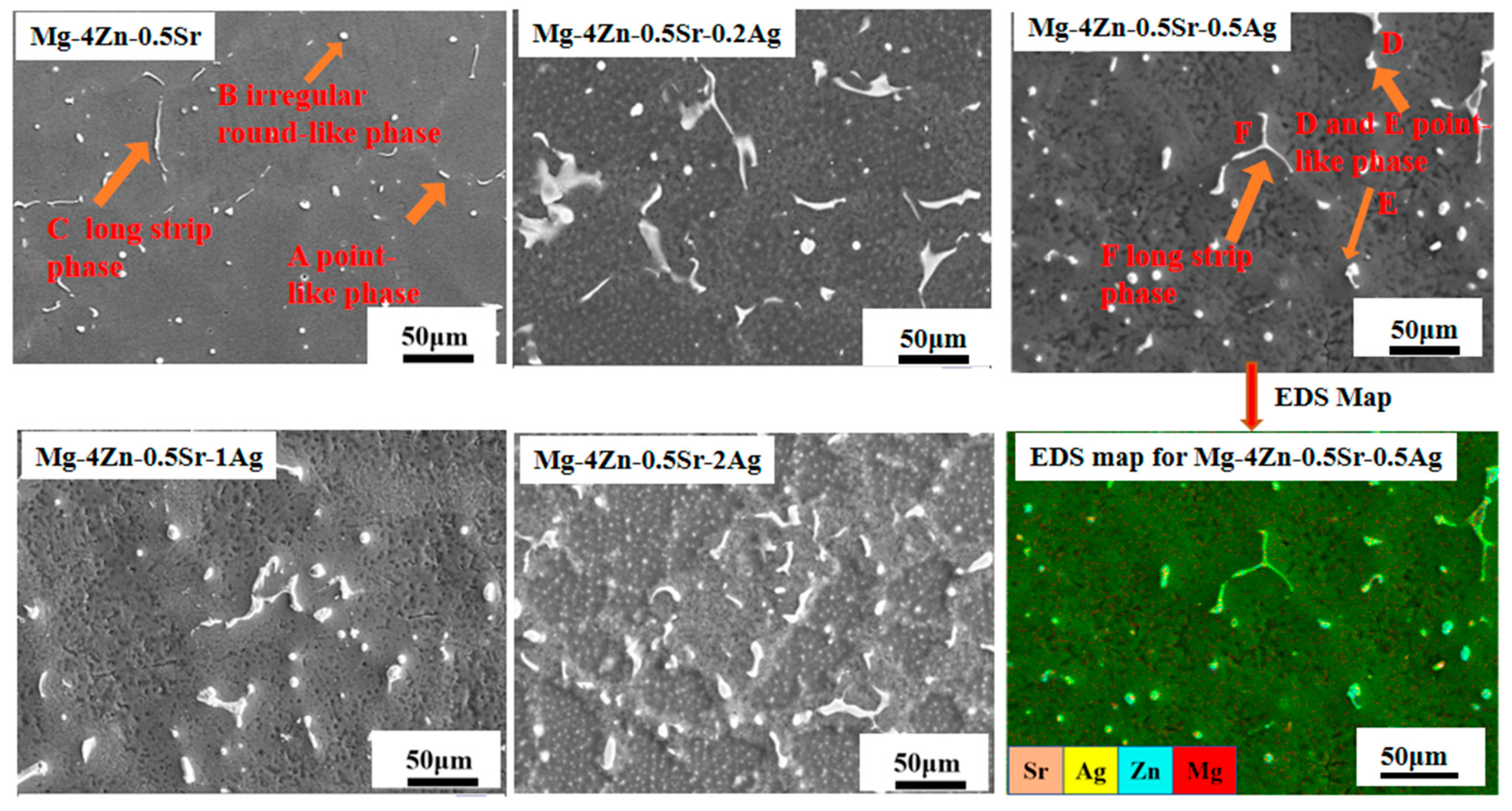
- Microstructure and Composition of Casted Mg-Zn-Sr-xAg
- 2.
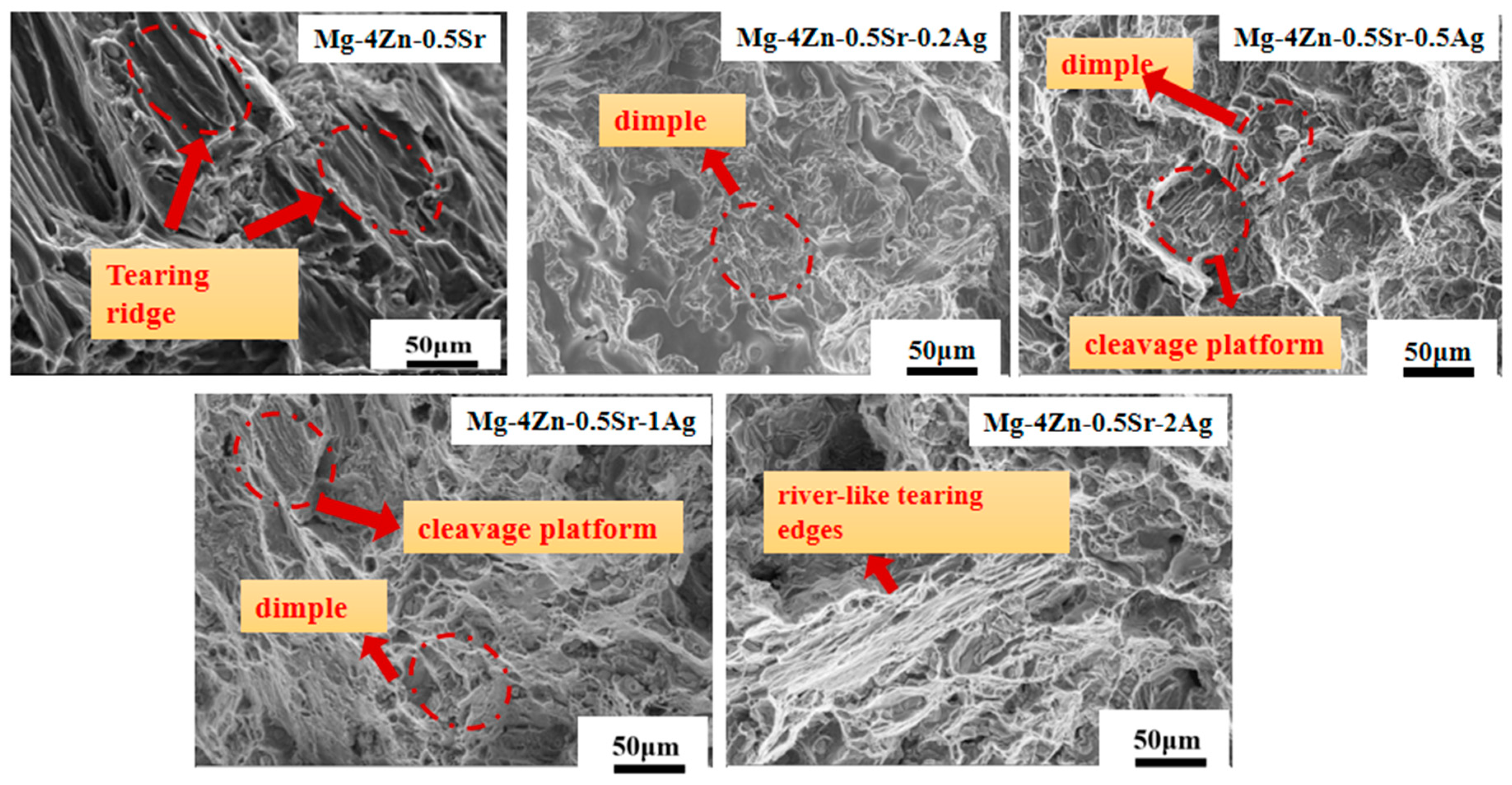
- Mechanical Properties of Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-xAg
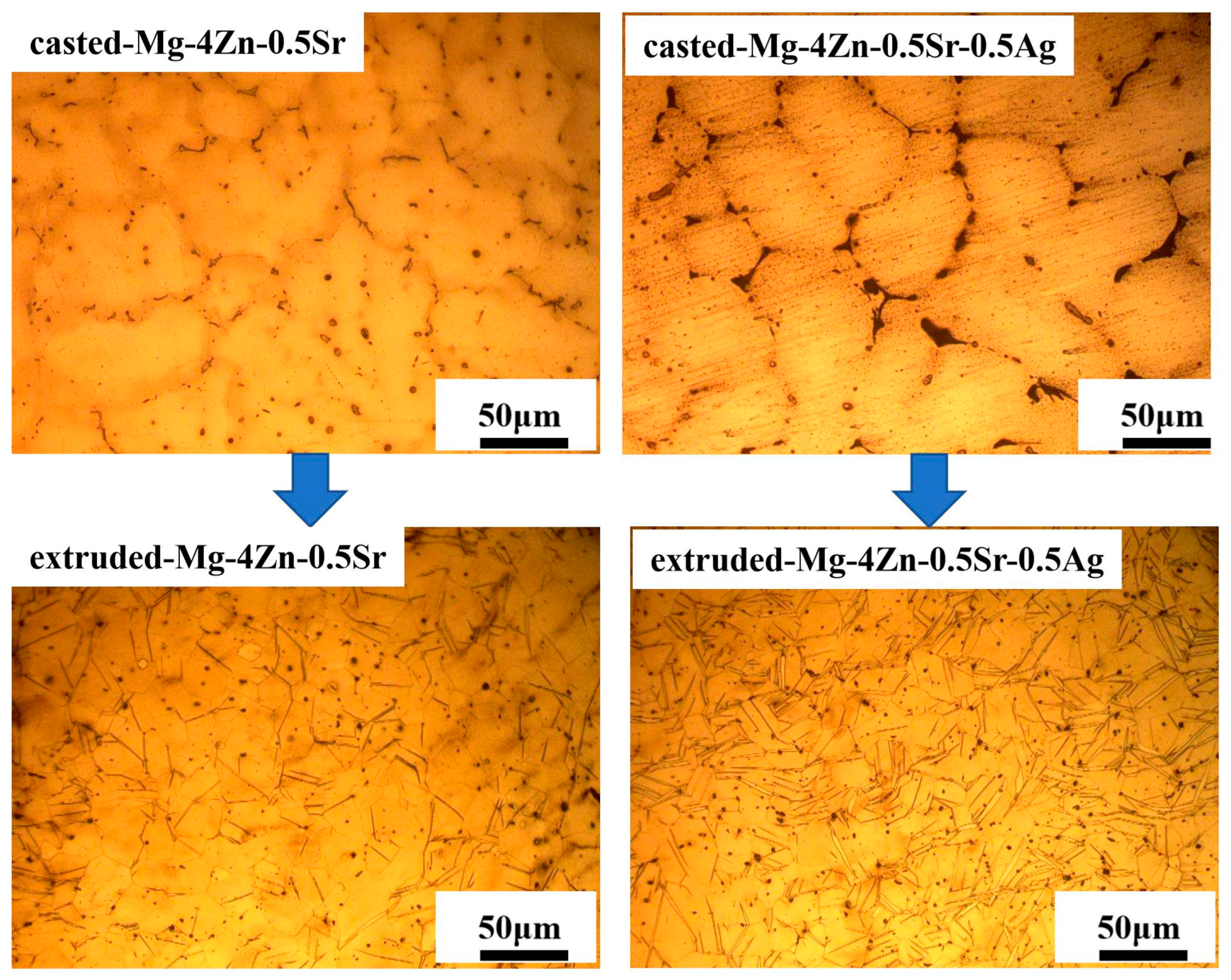
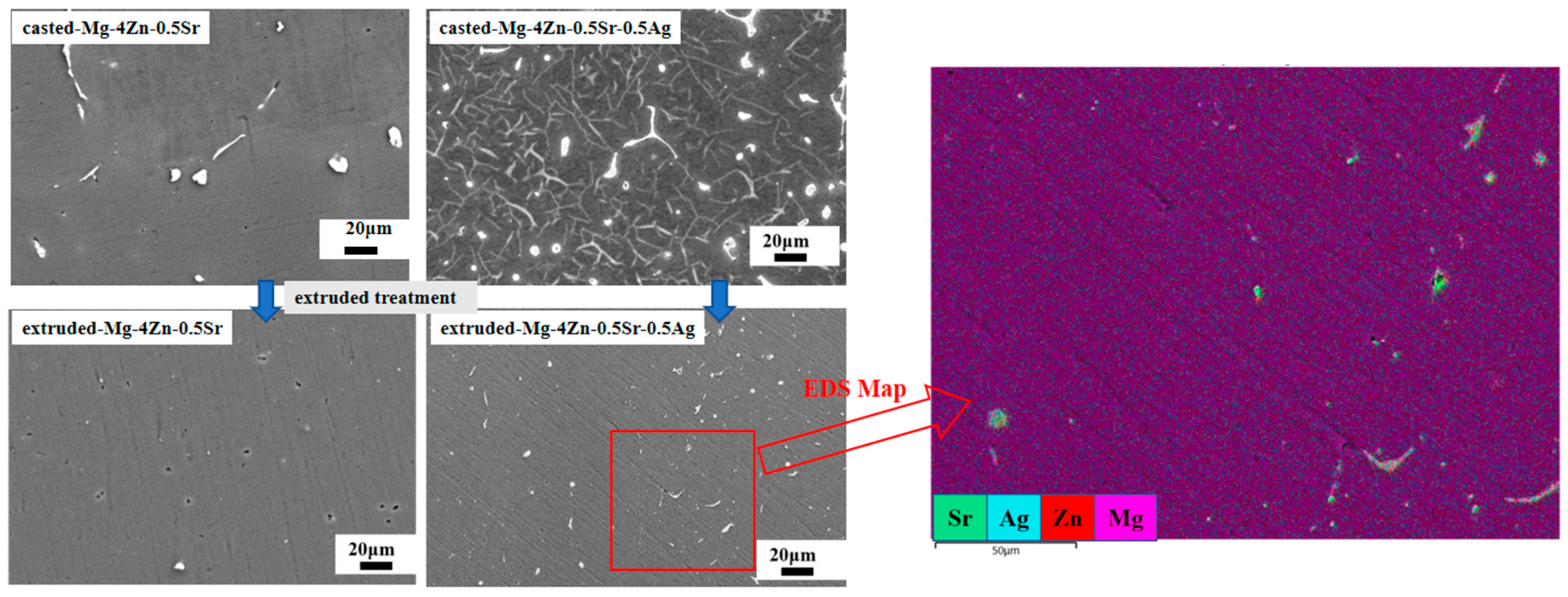
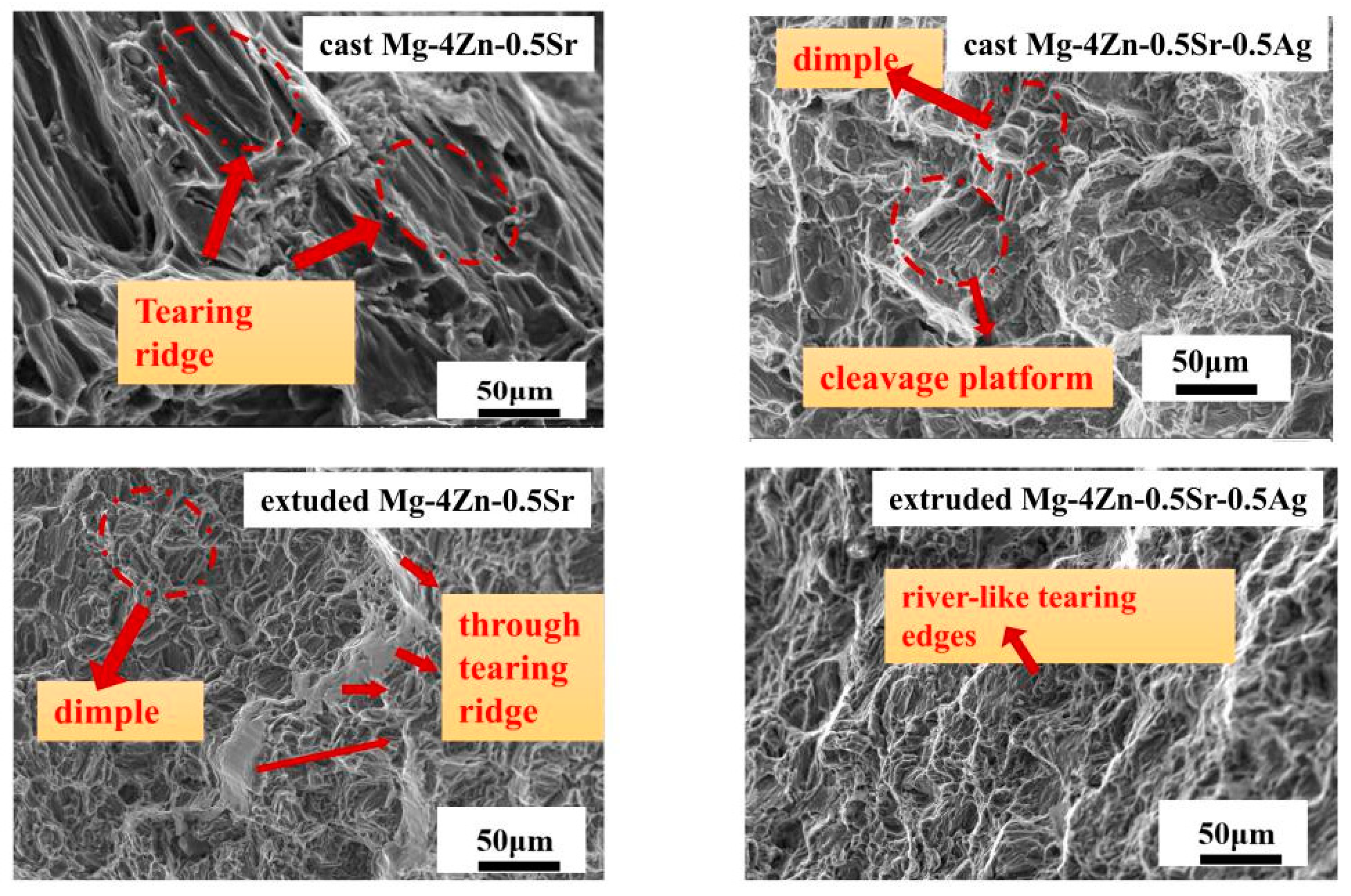
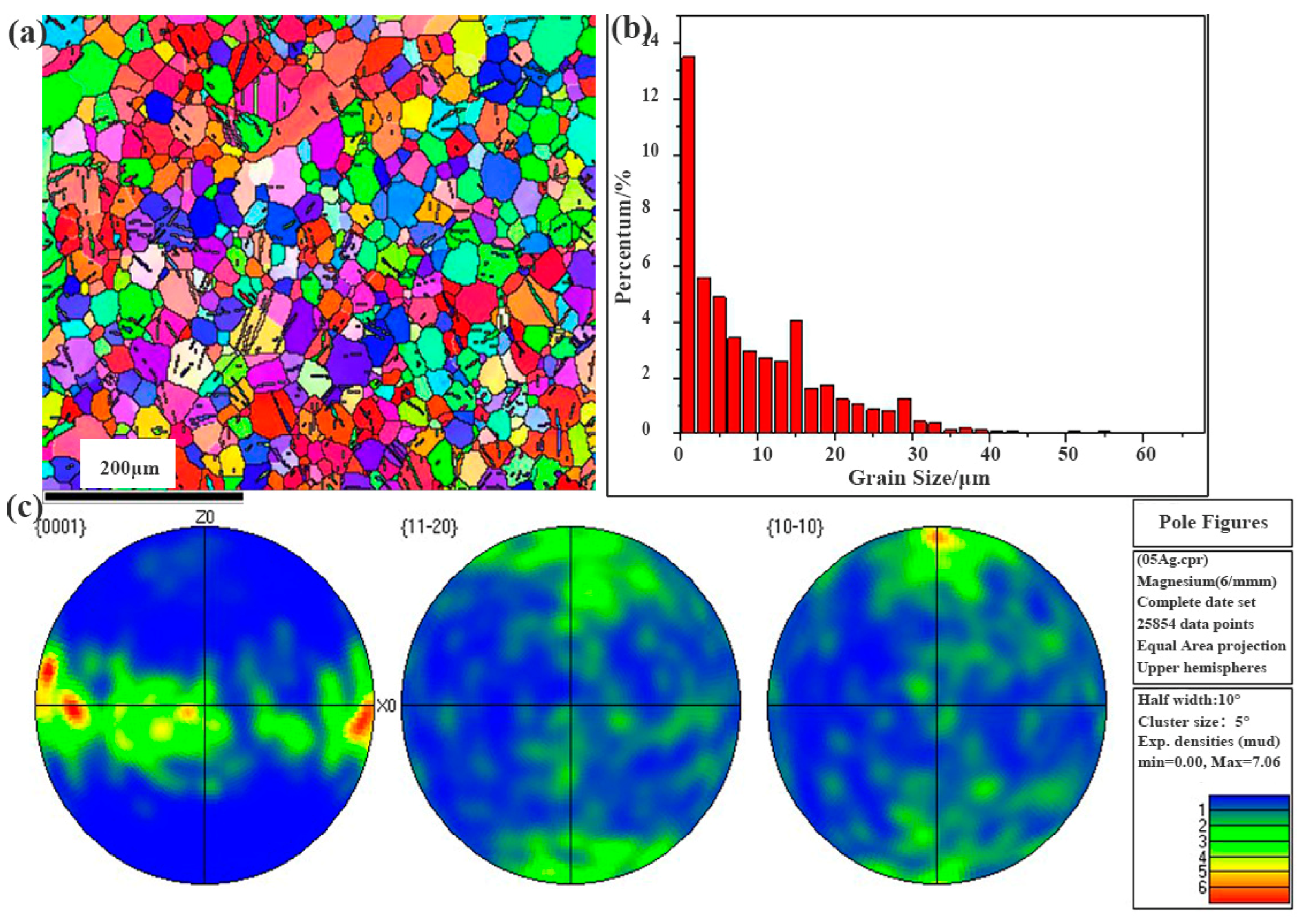
3.2. The Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Extruded Mg-Zn-Sr-0.5Ag
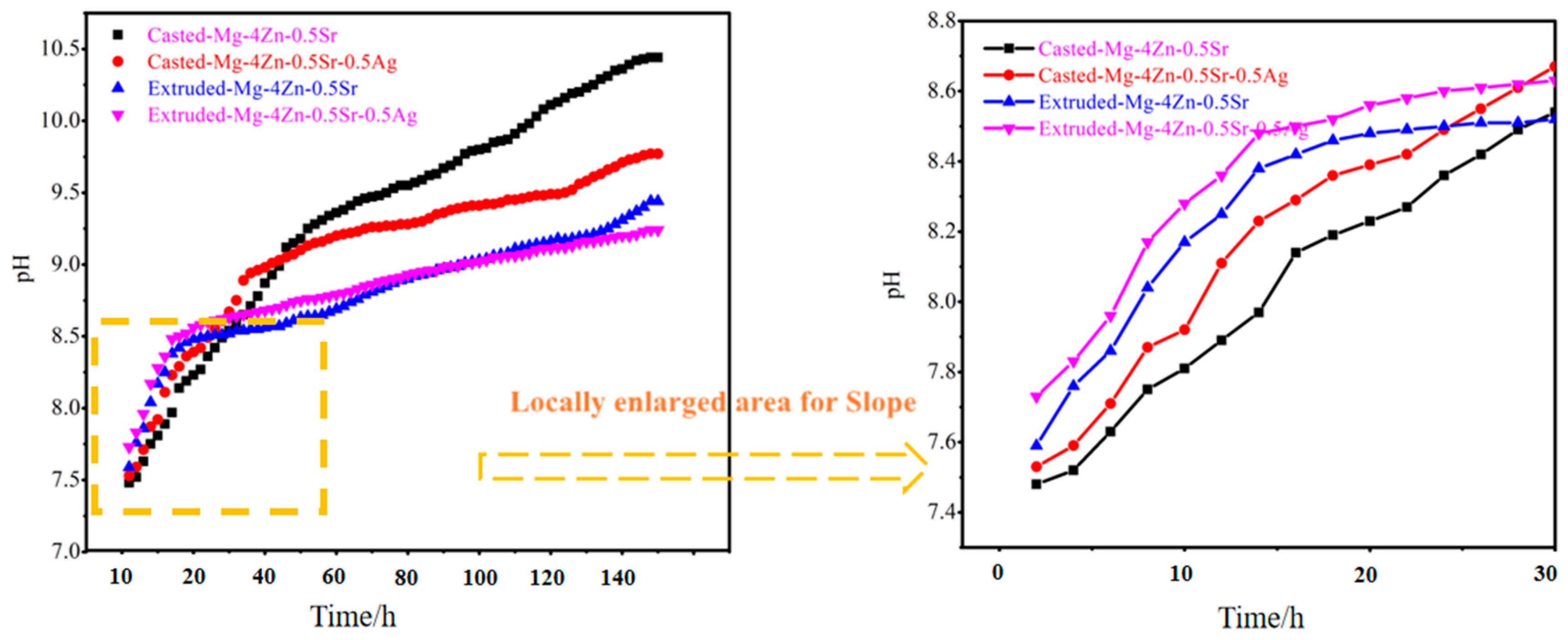
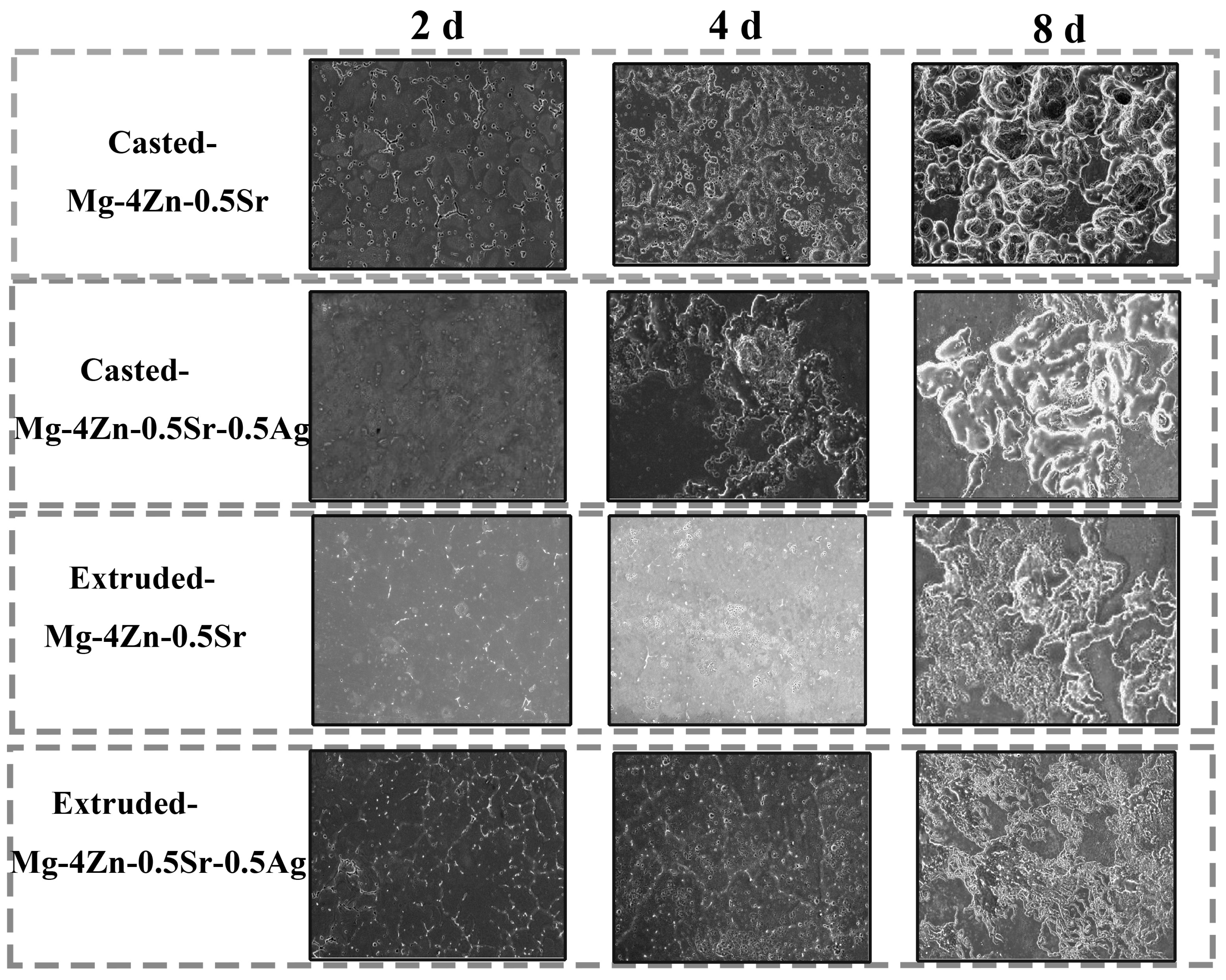
3.3. Corrosion Property of Extruded Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.5Ag Alloy
3.4. Discussion
4. Conclusions
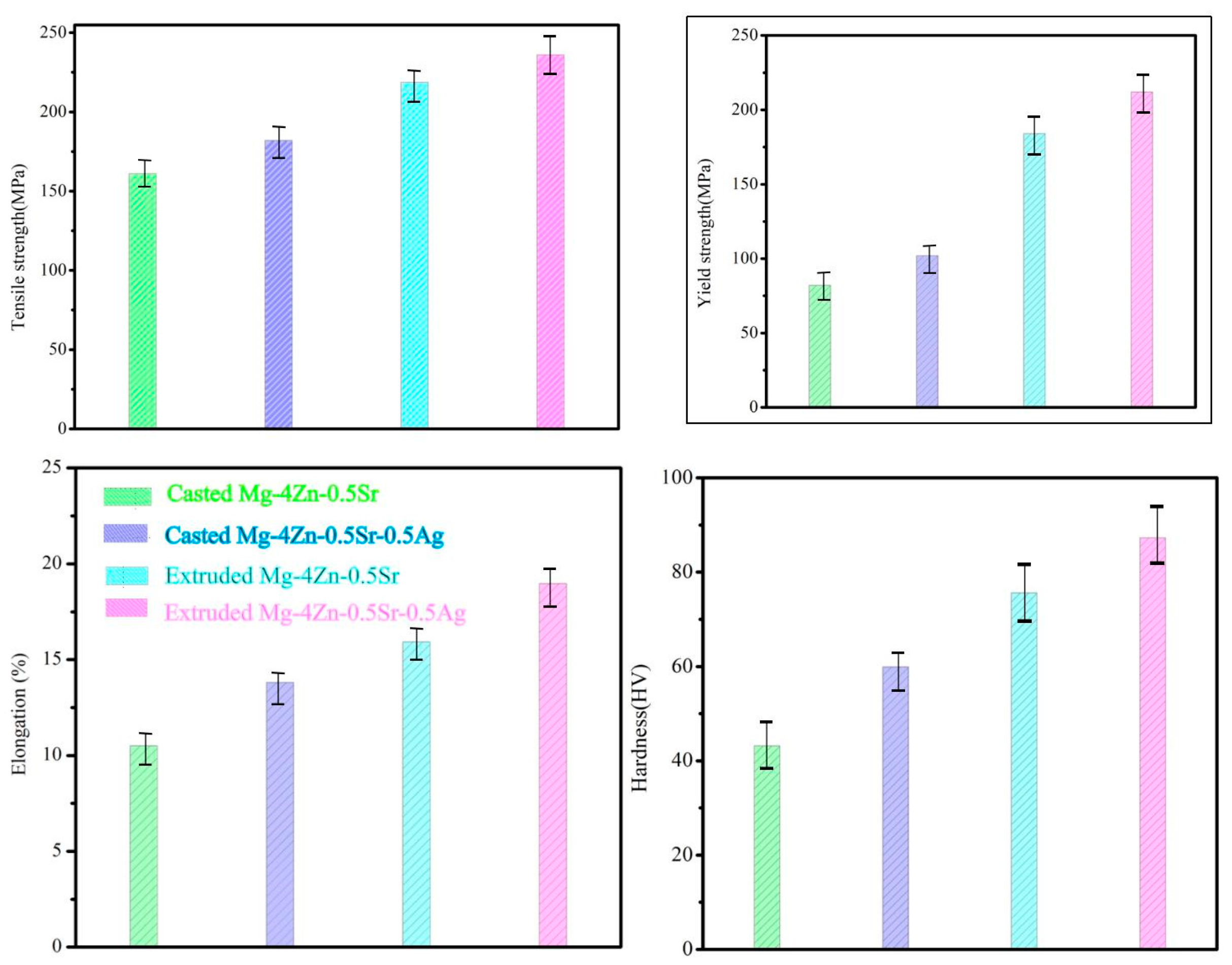
- The appropriate amount of the Ag element in cast Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr alloy could make the grain of the alloy refined; when the Ag content is 0.5 wt.%, the obtained Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.5Ag alloy has a minimal grain size, that is, 83.28 μm, and the comprehensive properties of the cast Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.5Ag alloy is the best. The average tensile strength (σb), yield strength (σs), elongation (ε), and hardness of the cast Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.5Ag alloy are 168.00 MPa, 88.00 MPa, 12.20%, and 59.90 HV, respectively.
- After further extruding treatment on the cast Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.5Ag alloy, the grain size of the alloy was significantly refined to 9 μm; at the same time, fine second phases were formed and evenly distributed in the matrix. And then, the mechanical properties of the alloy are significantly enhanced due to the effect of fine crystal strengthening and dispersion strengthening. The σb, σs, λ, and hardness value of the extruded Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.5Ag alloy are 236.00 MPa, 212.00 MPa, 18.97%, and 65.42 HV, respectively.
- Under the synergistic action of adding the Ag element and extrusion treatment, the grain size of the alloy was significantly refined and the coarse second phase in the alloy became refined to disperse in the matrix, which benefits the formation of electric couples characterized as small cathode–large anode between the second phase and Mg matrix. During full immersion, corrosion products covered on the large anode surface could reduce the galvanic corrosion tendency. Therefore, the degradation resistance of the Mg alloy was further increased by the synergistic action of adding the Ag element and extrusion treatment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zan, R.; Shen, S.; Huang, Y.D.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.H.; Yang, S.; Zheng, B.H.; Gong, Z.J.; Wang, W.H.; Zhang, X.N.; et al. Research hotspots and trends of biodegradable magnesium and its alloys. Smart Mater. Med. 2023, 4, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, N.; Evis, Z.; Kayhan, S.M.; Tahmasebifar, A.; Koç, M. Review of magnesiumbased biomaterials and their applications. J. Magnes. Alloys 2018, 6, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Smith, C.; Sankar, J. Recent advances on the development of magnesium alloys for biodegradable implants. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4561–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Thouas, G.A. Metallic implant biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2015, 87, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Dutta, N.K.; Choudhury, R.N. Magnesium alloys with tunable interfaces as bone implant materials. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2020, 8, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.W.; Jian, K.X.; Hopkins, C.; Chow, D.H.; Qin, L. Biodegradable magnesium-based implants in orthopedics—A general review and perspectives. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902443. [Google Scholar]
- Eivani, A.R.; Tabatabaei, F.; Khavandi, A.R.; Tajabadi, M.; Mehdizade, M.; Jafarian, H.R. The effect of addition of hardystonite on the strength, ductility and corrosion resistance of WE43 magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, G.; Mao, L.; Niu, J.; Ding, W. Biocorrosion properties of as-extruded Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy compared with commercial AZ31 and WE43 alloys. Mater. Lett. 2012, 66, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.Q.; Duan, W.C.; Liu, W.H.; Wu, L.; Yu, J.M.; Zhao, Z.L.; Liu, M.; Wang, P.; Cui, J.Z.; Zhang, Z.Q. Influence of specific second phases on corrosion behaviors of Mg-Zn-Gd-Zr alloys. Corros. Sci. 2020, 166, 108419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.N.; Xie, X.H.; Li, N.; Zheng, Y.F.; Qin, L. In vitro and in vivo studies on a Mg-Sr binary alloy system developed as a new kind of biodegradable metal. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2360–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, L.; Chen, M.F.; Li, W.; Zheng, H.R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, D.B.; Feng, J. The synergistic effect of trace Sr and Zr on the microstructure and properties of a biodegradable Mg-Zn-Zr-Sr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 702, 290–302. [Google Scholar]
- Aschner, M.; Guilarte, T.R.; Schneider, J.S.; Zheng, W. Manganese: Recent advances in understanding its transport and neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 221, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, C.A.; Petrik, M.S. Aluminum hydroxide injections lead to motor deficits and motor neuron degeneration. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyerabend, F.; Fischer, J.; Holtz, J.; Witte, F.; Willumeit, R.; Drücker, H. Evaluation of short-term effects of rare earth and other elements used in magnesium alloys on primary cells and cell lines. Acta. Biomater. 2010, 6, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhong, S.; Xi, T. In vitro corrosion and biocompatibility of binary magnesium alloys. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornapour, M.; Mahjoubi, H.; Vali, H.; Shum-Tim, D.; Cerruti, M.; Pekguleryuz, M. Surface characterization, in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of Mg-0.3Sr-0.3Ca for temporary cardiovascular implant. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 67, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignesh, R.; Sakthinathan, G.; Raja, V.; Seeram, R. An in-vitro evaluation study on the effects of surface modification viaphysical vapor deposition on the degradation rates of magnesium-based biomaterials. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 411, 126972. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, A.Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, S.G. Study of Electroless-Deposited Zn on the Surface of Mg-Li Alloy. Materials 2023, 16, 5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darothi, B.; Sumantra, M. A comprehensive review on biocompatible Mg-based alloys as temporary orthopaedic implants: Current status, challenges, and future prospects. J. Magnes. Alloys 2022, 10, 627–669. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Pan, F. Microstructure, electromagnetic shielding effectiveness and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloys. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, R.S.; Tang, W.N. Influence of texture and grain size on the roomtemperature ductility and tensile behavior in a Mg–Gd–Zn alloy processed by rolling and forging. Mater. Des. 2012, 41, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Ma, N.; Fang, D.; Li, H.; Liu, R.; Tian, Y. Microstructures, aging behaviour and mechanical properties in hydrogen and chloride media of backward extruded Mg-Y based biomaterials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 17, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Chen, M.; Bi, Y.; Liu, D. In vivo comparative property study of the bioactivity of coated Mg-3Zn-0.8Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3263–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Xiao, W.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. Influences of Gd on the microstructure and strength of Mg-4.5Zn alloy. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wu, Y.Q.; Qiu, X.; Tian, Z.; Meng, J.; Wan, P.; Li, C.; Dong, B.X.; Qiu, F. Remarkably enhancing mechanical and degradation performance of cast MgZn1.2 alloys via small amount addition of zirconium combined with hot extrusion for orthopedic applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Bai, Z.X.; Wang, Z.Z.; He, X.C.; Shen, C.; Wang, Q. Influence of silver addition on microstructure and corrosion behavior of Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr alloysfor biomedical application. Mater. Lett. 2013, 100, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Davies, C.H.J.; Nie, J.F.; Birbilis, N. The influence of composition and processing on the corrosion of magnesium alloys containing binary and ternary additions of zinc and strontium. Corrosion 2015, 71, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dou, J.; Pang, Z.F.; Zheng, Z.Q.; Yu, H.J.; Chen, C.Z. Ag-containing antibacterial self-healing micro-arc oxidation coatings on Mg-Zn-Sr alloys. Surf. Eng. 2021, 37, 926–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, B.; Ren, Y.P.; Qin, G.W. Experimental evidence of the Mg7 (Zn, Ag) 3 continuous solid solution in Mg-rich corner of Mg-Zn-Ag ternary system at 335 °C. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 789, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryła, K.; Horky, J.; Krystian, M.; Dobrzynska, L.L.; Mingler, B. Microstructure, mechanical properties, and degradation of Mg-Ag alloy after equal-channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Blawert, C.; Yang, H. Microstructure-corrosion behaviour relationship of micro-alloyed Mg-0.5 Zn alloy with the addition of Ca, Sr, Ag, In and Cu. Mater. Des. 2020, 195, 108980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.H.; Xie, J.S.; Liu, S.J. Toward the development of Mg alloys with simultaneously improved strength and ductility by refining grain size via the deformation process. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2021, 28, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Li, X.; Ma, N.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H. Effects of backward extrusion on mechanical and degradation properties of Mg-Zn biomaterial. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 10, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, D.; Guan, R.G.; Liu, H.N.; Chen, M.F.; Ulasevich, S.A.; Skorb, E.V.; Torres, P.H.; Lu, X.P.; Hort, N. In vivo degradability and biocompatibility of a rheo-formed Mg–Zn–Sr alloy for ureteral implantation. J. Magnes. Alloys 2022, 10, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.G.; Zhang, H.L.; Krishnan, P.; Hale, C.; Kecskes, L.J.; Yarmolenko, S. Non-conventional hot rolling for improvement of mechanical properties in binary Mg-alloys. Mech. Mater. 2022, 164, 104111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.C.; Yu, B.Y.; Jiang, L.; Hao, J.F.; Zhu, H.W.; Jin, P.; Zheng, L.; Li, R.X. Research on the effect of Sr and Zr on microstructure and properties of Mg-4Zn alloy. Int. J. Metalcast. 2021, 4, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.N.; Hudon, P.; Chartrand, P.; Jung, I.H.; Medra, M. Experimental study of the crystal structure of the Mg15-xZnxSr3 ternary solid solution in the Mg–Zn–Sr ternary system at 300 °C. Mater. Des. 2015, 86, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Du, Y.B.; Li, W.D.; Chai, Y.T.; Huang, W.G. Effects of Ag content on the solid-solution and age-hardening behavior of a Mg-5Sn alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 696, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Elements (wt.%) | Mg | Zn | Sr | Ag | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloys | Theo. | Par. | Theo. | Par. | Theo. | Par. | Theo. | Par. | |
| Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr | 95.50 | 95.69 | 4.00 | 3.86 | 0.50 | 0.42 | - | - | |
| Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.2Ag | 95.30 | 95.00 | 4.00 | 4.25 | 0.50 | 0.44 | 0.20 | 0.18 | |
| Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.5Ag | 95.00 | 95.00 | 4.00 | 4.18 | 0.50 | 0.36 | 0.50 | 0.44 | |
| Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-1.0Ag | 94.50 | 94.70 | 4.00 | 4.03 | 0.50 | 0.34 | 1.00 | 0.92 | |
| Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-2.0Ag | 93.50 | 94.30 | 4.00 | 3.47 | 0.50 | 0.38 | 2.00 | 1.82 | |
| Samples | Casted-MZS | Casted-MZS-0.2Ag | Casted-MZS-0.5Ag | Casted-MZS-1Ag | Casted-MZS-2Ag | Extruded-MZS | Extruded-MZS-0.5Ag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grain size /μm | 103.62 | 102.67 | 83.28 | 102.32 | 110.43 | 20 | 9 |
| Element | Mg | Zn | Sr | Ag | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point | wt.% | at% | wt.% | at% | wt.% | at% | wt.% | at% | |
| Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr | A | 26.50 | 49.22 | 73.50 | 50.78 | - | - | - | - |
| B | 35.31 | 59.65 | 62.90 | 39.52 | 1.79 | 0.84 | - | - | |
| C | 36.95 | 62.06 | 53.99 | 33.72 | 9.06 | 4.22 | - | - | |
| Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.5Ag | D | 47.44 | 72.82 | 36.87 | 21.05 | 8.90 | 3.79 | 6.79 | 2.35 |
| E | 61.29 | 82.91 | 21.44 | 10.79 | 14.76 | 5.54 | 2.51 | 0.77 | |
| F | 43.62 | 68.74 | 47.74 | 27.98 | 2.60 | 1.14 | 6.04 | 2.14 | |
| Alloy | Tensile Strength (σb) (MPa) | Yield Strength (σs) (MPa) | Elongation (ε) (%) | Hardness (HV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr | ~161.00 | ~82.00 | ~10.30 | ~43.15 |
| Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.2Ag | ~173.00 | ~97.00 | ~12.31 | ~52.90 |
| Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.5Ag | ~182.00 | ~102.00 | ~13.81 | ~59.90 |
| Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-1.0Ag | ~175.00 | ~85.00 | ~13.12 | ~51.60 |
| Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-2.0Ag | ~129.00 | ~70.50 | ~6.67 | ~49.50 |
| Immersion Time | 2 | 4 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloys | ||||
| Casted Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr | 1.05 | 0.86 | 0.71 | |
| Casted Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.5Ag | 0.90 | 0.68 | 0.54 | |
| Extruded Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr | 0.95 | 0.75 | 0.67 | |
| Extruded Mg-4Zn-0.5Sr-0.5Ag | 0.44 | 0.34 | 0.25 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Q.; Wu, H.; Gao, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, R. The Synergistic Effect of Trace Ag and Hot Extruding on the Microstructure and Properties of a Biodegradable Mg-Zn-Sr-Ag Alloy. Materials 2023, 16, 6423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196423
Shi Q, Wu H, Gao Z, Wang D, Wang J, Yang Y, Li R. The Synergistic Effect of Trace Ag and Hot Extruding on the Microstructure and Properties of a Biodegradable Mg-Zn-Sr-Ag Alloy. Materials. 2023; 16(19):6423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196423
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Qifeng, Huishu Wu, Zhixian Gao, Dongsheng Wang, Jingwen Wang, Youwen Yang, and Runxia Li. 2023. "The Synergistic Effect of Trace Ag and Hot Extruding on the Microstructure and Properties of a Biodegradable Mg-Zn-Sr-Ag Alloy" Materials 16, no. 19: 6423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196423
APA StyleShi, Q., Wu, H., Gao, Z., Wang, D., Wang, J., Yang, Y., & Li, R. (2023). The Synergistic Effect of Trace Ag and Hot Extruding on the Microstructure and Properties of a Biodegradable Mg-Zn-Sr-Ag Alloy. Materials, 16(19), 6423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196423







