A Robust Strontium Coordination Polymer with Selective and Sensitive Fluorescence Sensing Ability for Fe3+ Ions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
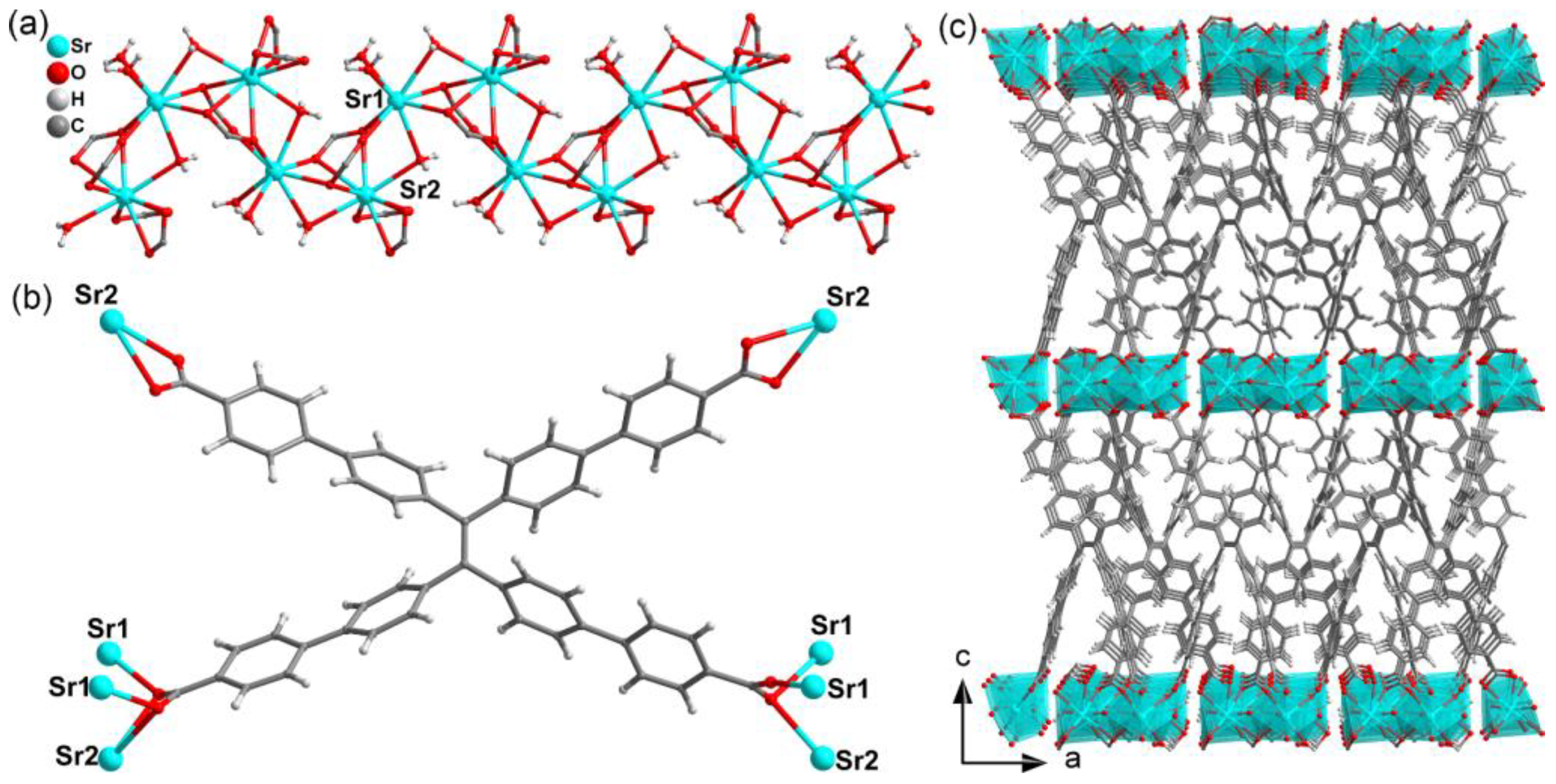
3.1. Crystal Structure Analysis
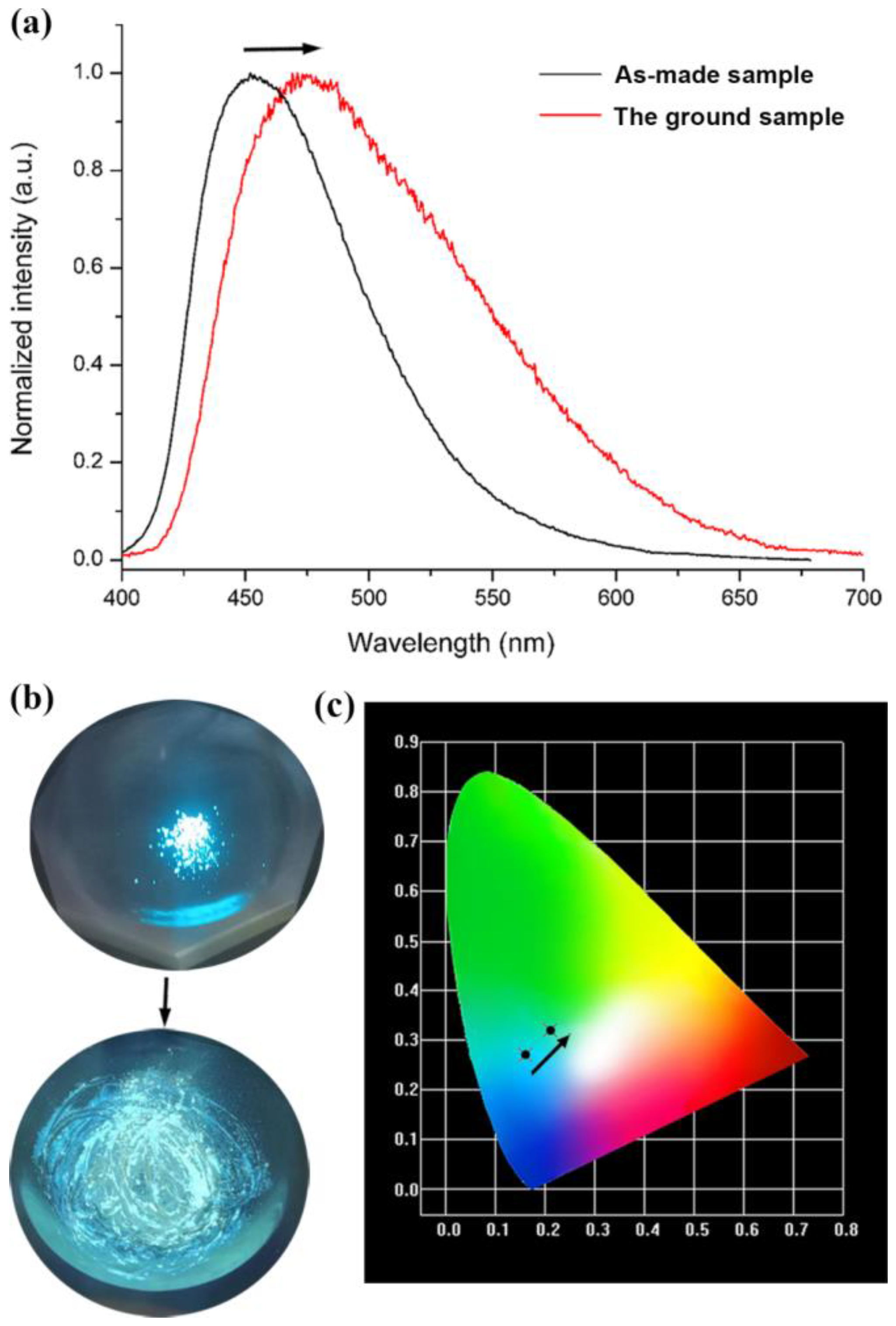
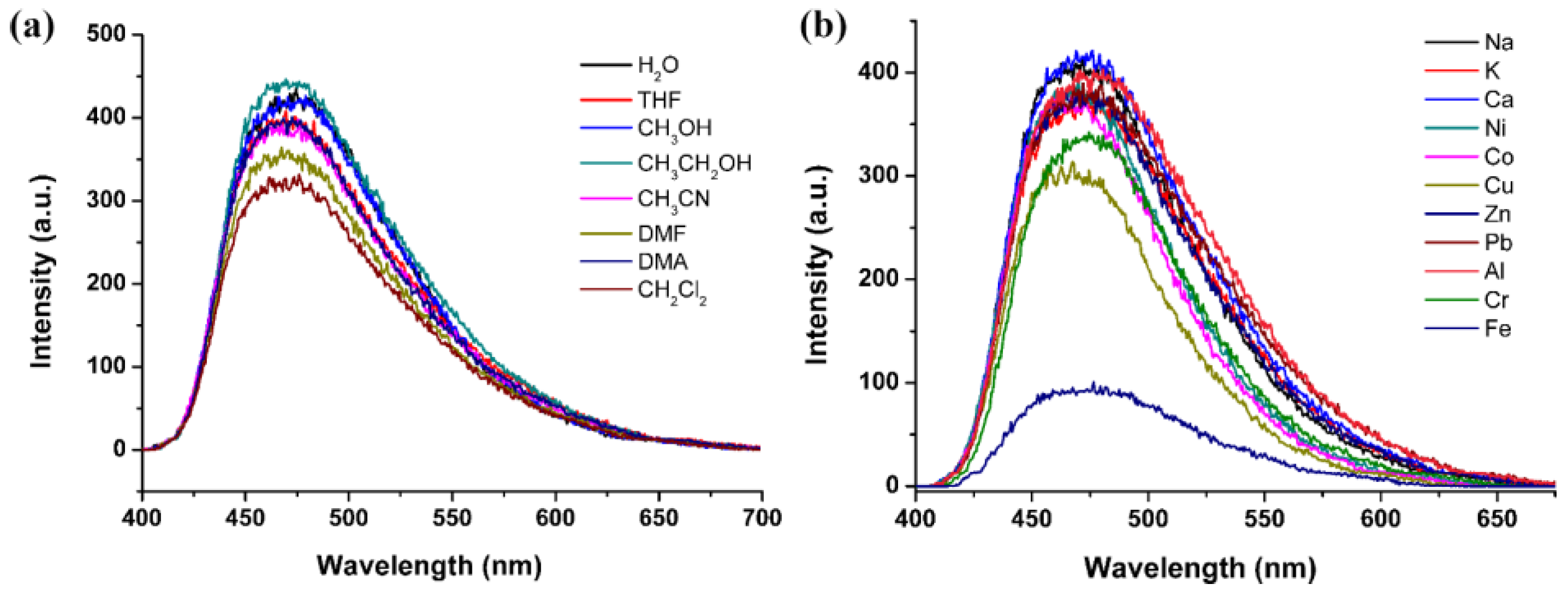
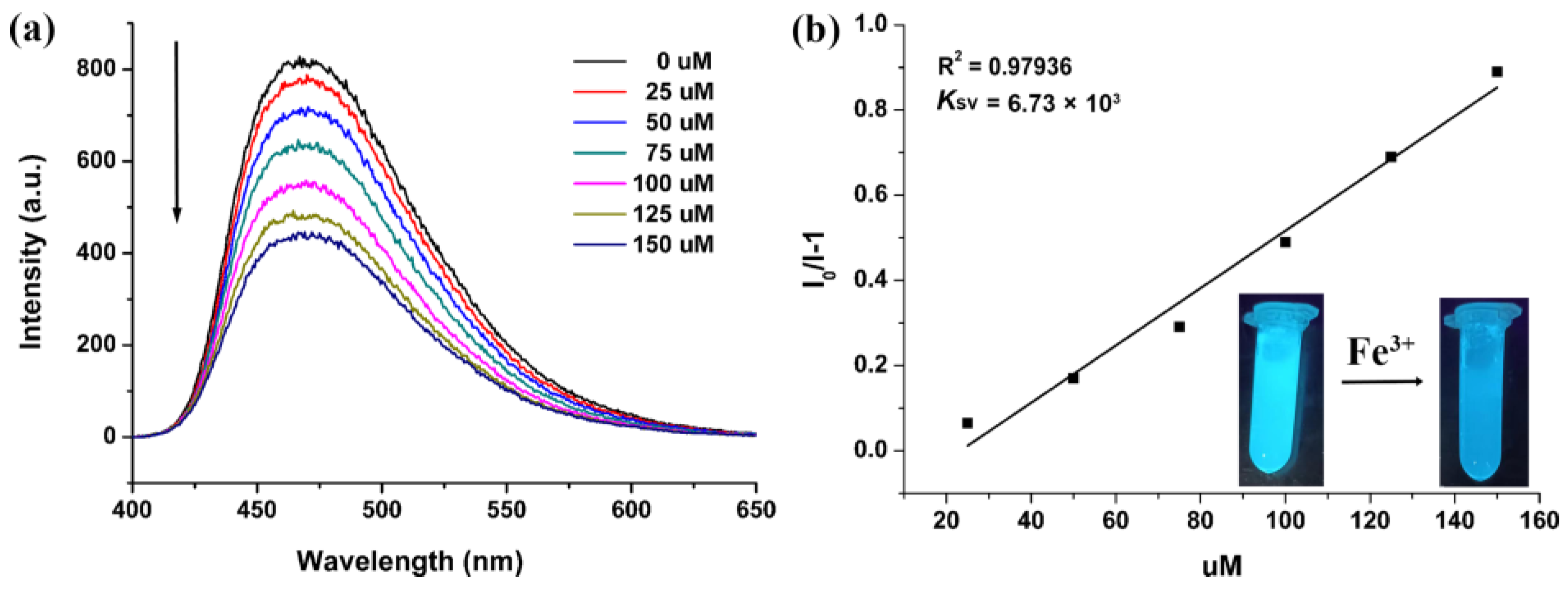
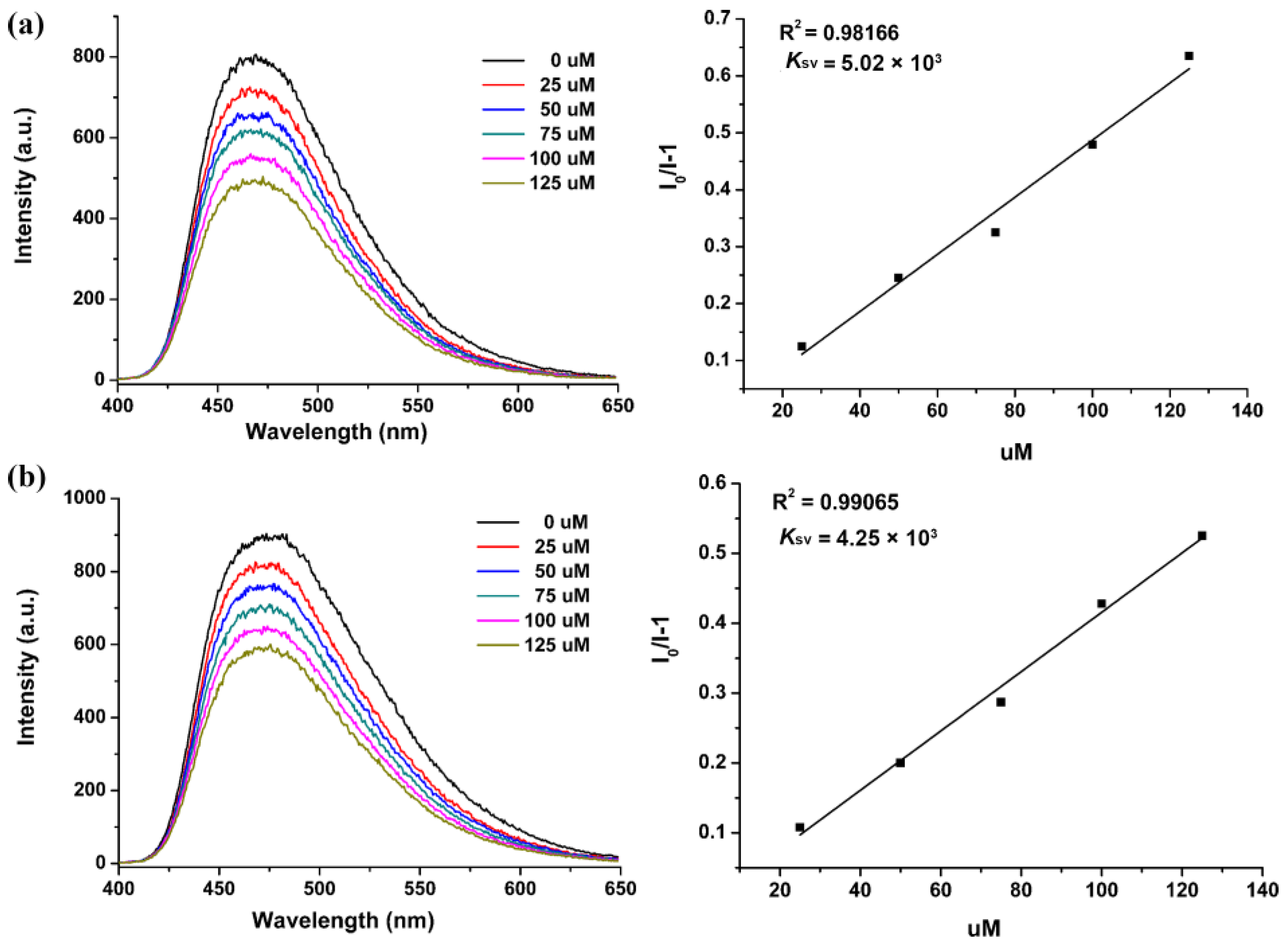
3.2. FL Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chowdhury, M.A. Metal-organic-frameworks for biomedical applications in drug delivery, and as MRI contrast agents. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 105, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastug, E.; Kursunlu, A.N.; Güler, E. A fluorescent clever macrocycle: Deca-bodipy bearing a pillar [5]arene and its selective binding of asparagine in half-aqueous medium. J. Lumin. 2020, 225, 117343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taner, B.; Kursunlu, A.N.; Güler, E. The example of calix[4]pyrrole derivative containing Bodipy unit: Fluorometric and colorimetric sensor for F− ion. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 118, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, W.P.; Mukherjee, S.; Rudd, N.D.; Desai, A.V.; Li, J.; Ghosh, S.K. Metal–organic frameworks: Functional luminescent and photonic materials for sensing applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3242–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.F.; Figueira, F.; Leite, J.P.; Gales, L.; Almeida Paz, F.A. Metal–organic frameworks: A future toolbox for biomedicine? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 9121–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allendorf, M.D.; Bauer, C.A.; Bhakta, R.K.; Houk, R.J.T. Luminescent metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1330–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, W.P.; Li, J. Luminescent metal–organic frameworks and coordination polymers as alternative phosphors for energy efficient lighting devices. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 373, 116–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, D. Lanthanide-functionalized metal–organic frameworks as ratiometric luminescent sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 12739–12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, B.; Qian, G. Lanthanide metal-organic frameworks for luminescent sensing and light-emitting applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 273–274, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Nakanishi, T. Luminescent lanthanide coordination polymers for photonic applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.; Carlos, L.D.; Paz, F.A.A.; Ananias, D. Luminescent multifunctional lanthanides-based metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B. Luminescence response mode and chemical sensing mechanism for lanthanide-functionalized metal–organic framework hybrids. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 201–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-F.; Tan, B.; Lustig, W.P.; Velasco, E.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.-Y.; Li, J. Magnesium based coordination polymers: Syntheses, structures, properties and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 399, 213025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Chen, C.; Lin, J.; Peng, X.; Kumar, A.; Liu, D.; Liu, J. Alkali /alkaline earth-based metal–organic frameworks for biomedical applications. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 17438–17454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, Y.; Li, L.-K.; Zang, S.-Q. Recent development on the alkaline earth MOFs (AEMOFs). Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 440, 213955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hureau, C. Coordination of redox active metal ions to the amyloid precursor protein and to amyloid-β peptides involved in Alzheimer disease. Part 1: An overview. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 2164–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, H.; Luczkowski, M.; Remelli, M.; Valensin, D. Copper, zinc and iron in neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and prion diseases). Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 2129–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yue, Y.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. Luminescent Functional Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1126–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Deibert, B.J.; Li, J. Luminescent metal–organic frameworks for chemical sensing and explosive detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5815–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lustig, W.P.; Li, J. Sensing and capture of toxic and hazardous gases and vapors by metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4729–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, W.P.; Shen, Z.; Teat, S.J.; Javed, N.; Velasco, E.; O’Carroll, D.M.; Li, J. Rational design of a high-efficiency, multivariate metal–organic framework phosphor for white LED bulbs. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 1814–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.-H.; Luo, P.; Wei, Z.; Li, Y.-Y.; Huang, R.-W.; Dong, X.-Y.; Li, K.; Zang, S.-Q.; Tang, B.Z. Guest-triggered aggregation-induced emission in silver chalcogenolate cluster metal–organic frameworks. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-F.; Velasco, E.; Shan, C.; Tan, K.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Hu, Q.-Q.; Xing, K.; Huang, X.-Y.; Li, J. Robust fluorescent calcium coordination polymers as Cu2+ sensors with high sensitivity and fast response. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 6820–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.-H.; Bi, C.; Zou, H.-H.; Feng, G.; Xu, S.; Tang, B.Z. Smart tetraphenylethene-based luminescent metal–organic frameworks with amide-assisted thermofluorochromics and piezofluorochromics. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-H.; Wang, X.-S.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.-B.; Cao, R. Highly selective sensing of Fe3+ by an anionic metal–organic framework containing uncoordinated nitrogen and carboxylate oxygen sites. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 3452–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-H.; Xie, A.D.; Chen, W.-C.; Shen, D.; Zhang, D.-E.; Tong, Z.-W.; Lee, C.-S. Multifunctional anionic indium–organic frameworks for organic dye separation, white-light emission and dual-emitting Fe3+ sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 14897–14903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Z. A luminescent terbium MOF containing uncoordinated carboxyl groups exhibits highly selective sensing for Fe3+ ions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 55252–55255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-F.; Huang, X.-Y. A series of Mg–Zn heterometallic coordination polymers: Synthesis, characterization, and fluorescence sensing for Fe3+, CS2, and nitroaromatic compounds. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 12597–12604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Liu, Y.-E.; Yang, L.-B.; Dou, A.-N.; Hou, C.-F.; Xu, Q.-Q.; Huang, B.; Zhu, A.-X. Novel alkaline earth metal–organic frameworks with thiophene groups for selective detection of Fe3+. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 5970–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Li, G.; Meng, X. Two luminescent transition-metal–organic frameworks with a predesigned ligand as highly sensitive and selective iron(iii) sensors. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 6839–6847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, N.; Ge, C.; Luo, X.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, Q.; Liu, R. A luminescent sensor based on a Zn (II) coordination polymer for selective and sensitive detection of NACs and Fe3+ ion. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Biswas, S. A multi.-responsive carbazole-functionalized Zr (IV)-based metal-organic framework for selective sensing of Fe (III), cyanide and p-nitrophenol. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2017, 250, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Biswas, S.; Trivedi, V.; Biswas, S. Extraordinary sensitivity for H2S and Fe (III) sensing in aqueous medium by Al-MIL-53-N3 metal–organic framework: In vitro and in vivo applications of H2S sensing. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, B.B.; Vittal, J.J. Water stable Zn (II) metal–organic framework as a selective and sensitive luminescent probe for Fe (III) and chromate ions. Inorg. Chem., 2020, 59, 8818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.-Y.; Nie, H.-J.; Li, J.-M.; Shi, Z.-F. Luminescent Zn (II)/Cd (II) coordination polymers based on 1-(tetrazol-5-H)-3, 5-bis (1-triazole) benzene for sensing Fe3+, Cr2O72−, and CrO42− in water. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 287, 121342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Fu, L.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.-H.; Dong, G.-Y. Three water-stable luminescent Zn (II) coordination polymers for highly sensitive and selective sensing of acetylacetone and Fe3+ ions. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 286, 121265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mi, X.; Lu, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Dou, J.; Li, D. From 2D→ 3D interpenetration to packing: N coligand-driven structural assembly and tuning of luminescent sensing activities towards Fe3+ and Cr2O72− ions. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-J.; Wang, M.-J.; Zhang, K.-L. A novel photoluminescent Cd (II)–organic framework exhibiting rapid and efficient multi-responsive fluorescence sensing for trace amounts of Fe3+ ions and some NACs, especially for 4-nitroaniline and 2-methyl-4-nitroaniline. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 11404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Empirical formula | Sr2C54H40O12 |
| Formula weight | 1056.10 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21 |
| T/K | 298(2) |
| λ/Å | 0.71073 |
| a/Å | 10.0613(2) |
| b/Å | 9.8710(2) |
| c/Å | 22.7537(3) |
| β/º | 90.0016(11) |
| V/Å3 | 2259.79(7) |
| Z | 2 |
| Dc/Mg·m−3 | 1.552 |
| μ/mm−1 | 2.428 |
| F(000) | 1072 |
| Measured refls. | 50,879 |
| Independent refls. | 11,257 |
| Rint | 0.0504 |
| No. of parameters | 638 |
| GOF | 1.038 |
| Flack parameter | 0.401(10) |
| aR1, bwR2 [I > 2σ(I)] | 0.0490, 0.1226 |
| aR1, bwR2 (all data) | 0.0516, 0.1238 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.-W.; Tan, B.; Wu, Z.-F.; Huang, X.-Y. A Robust Strontium Coordination Polymer with Selective and Sensitive Fluorescence Sensing Ability for Fe3+ Ions. Materials 2023, 16, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020577
Li Z-W, Tan B, Wu Z-F, Huang X-Y. A Robust Strontium Coordination Polymer with Selective and Sensitive Fluorescence Sensing Ability for Fe3+ Ions. Materials. 2023; 16(2):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020577
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zi-Wei, Bin Tan, Zhao-Feng Wu, and Xiao-Ying Huang. 2023. "A Robust Strontium Coordination Polymer with Selective and Sensitive Fluorescence Sensing Ability for Fe3+ Ions" Materials 16, no. 2: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020577
APA StyleLi, Z.-W., Tan, B., Wu, Z.-F., & Huang, X.-Y. (2023). A Robust Strontium Coordination Polymer with Selective and Sensitive Fluorescence Sensing Ability for Fe3+ Ions. Materials, 16(2), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020577







