Amorphous BN-Based Synaptic Device with High Performance in Neuromorphic Computing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
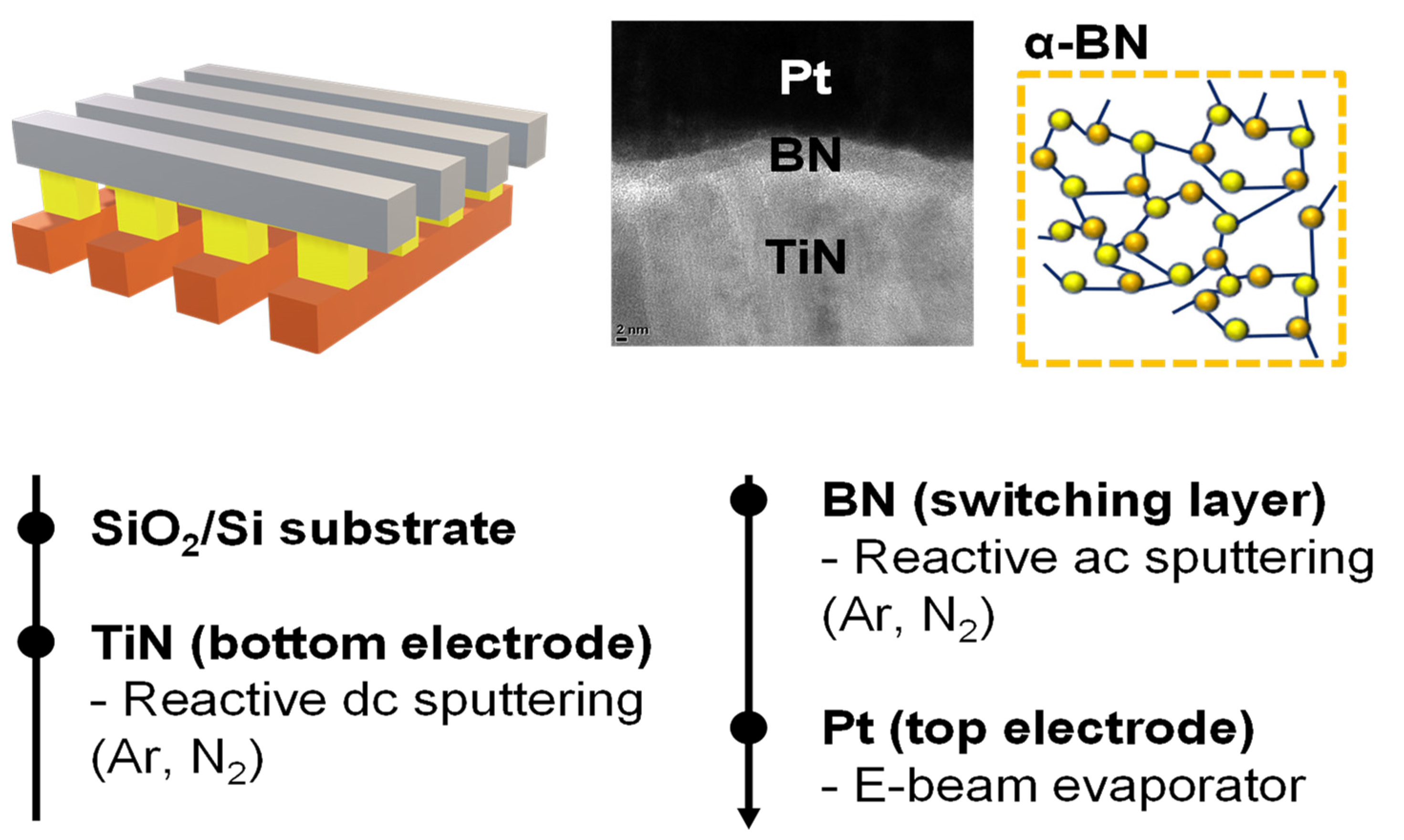
2. Materials and Methods
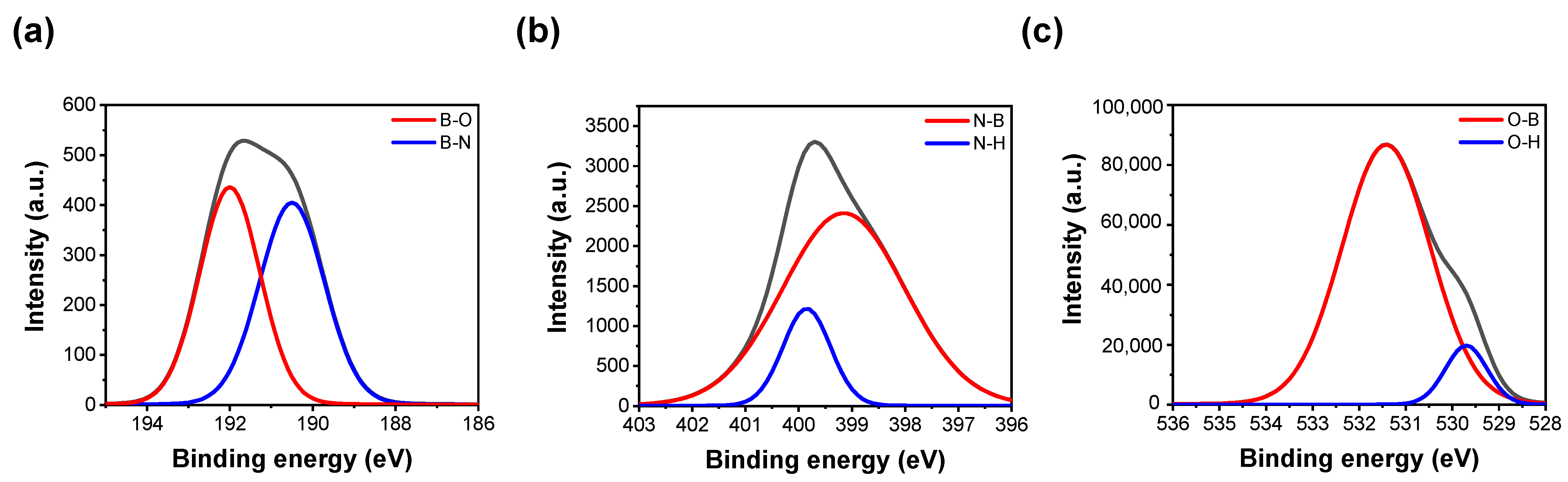
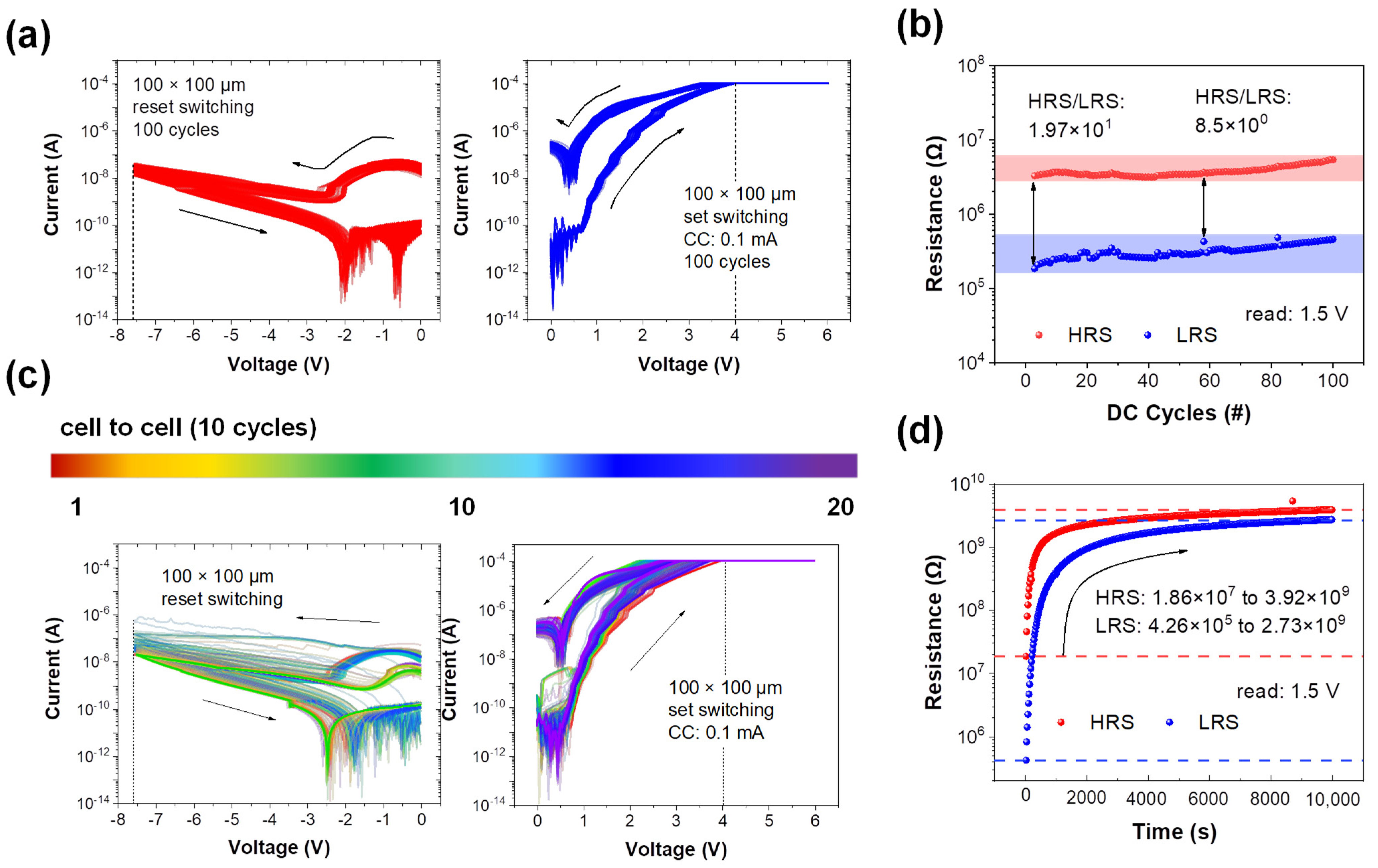
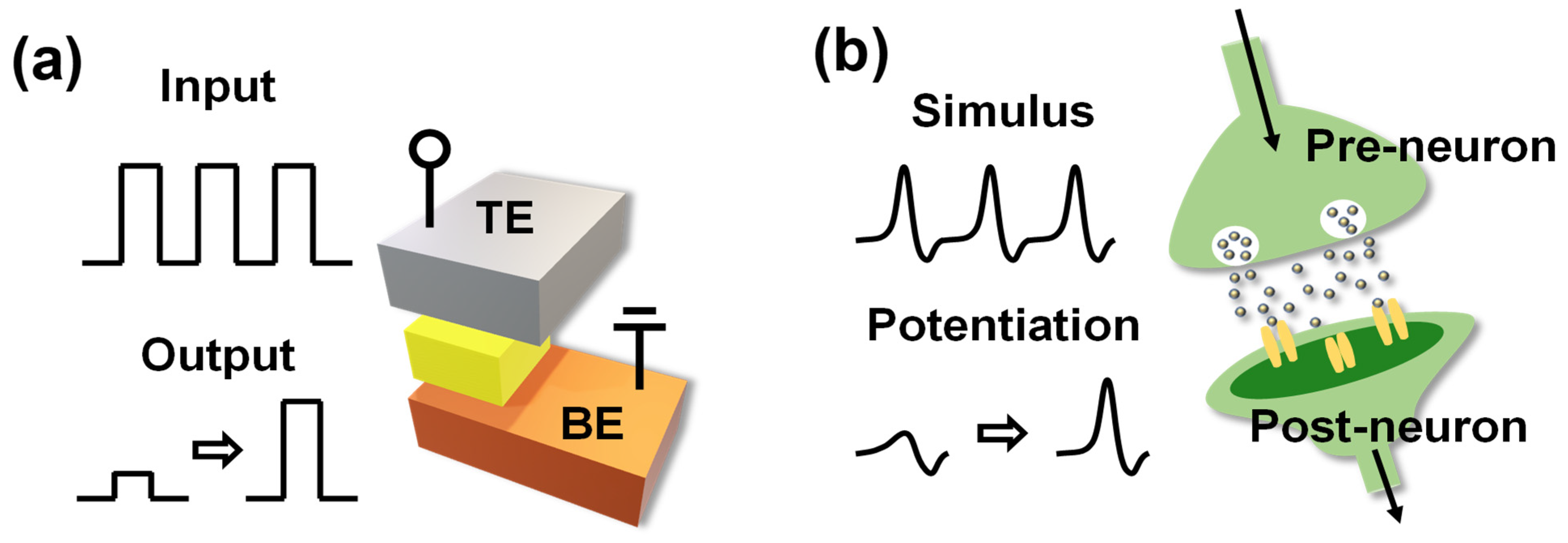
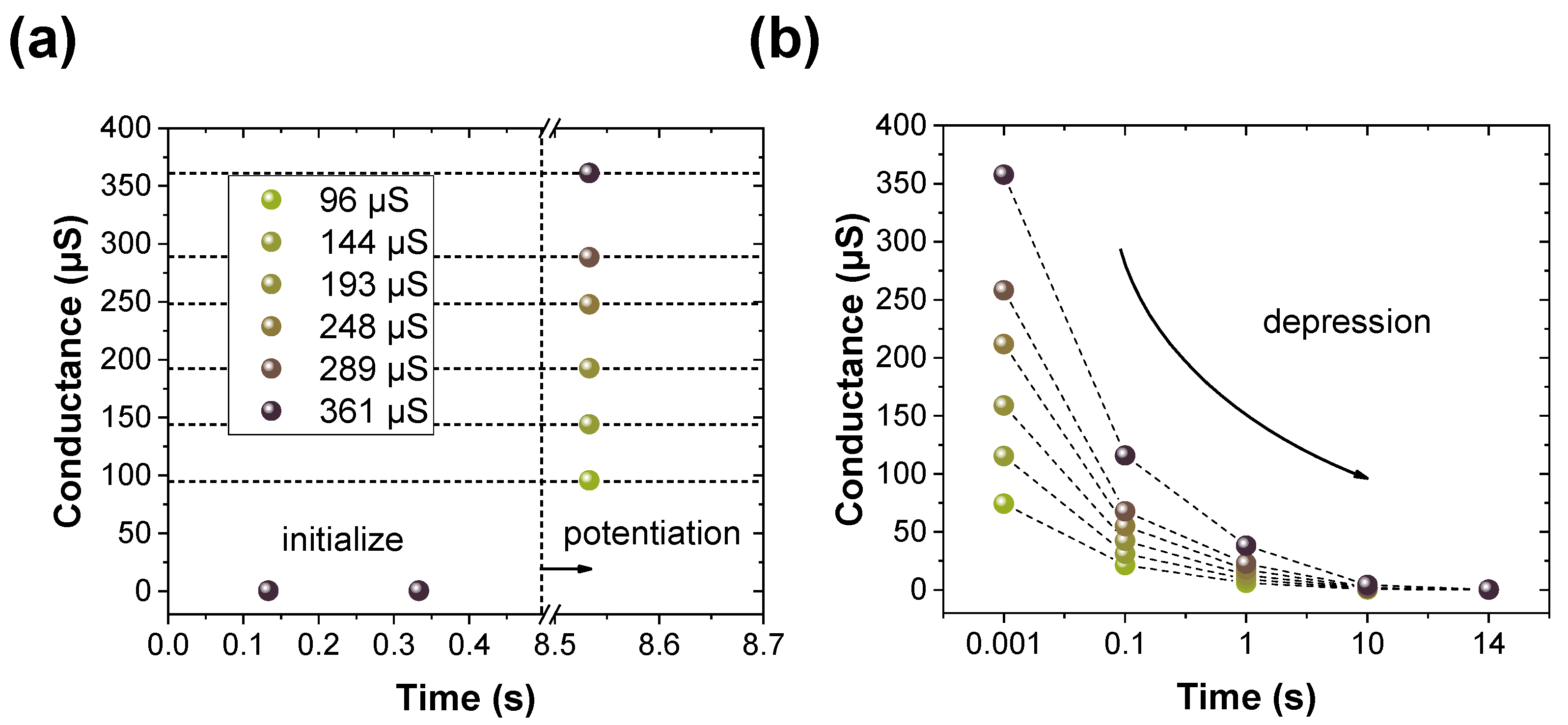
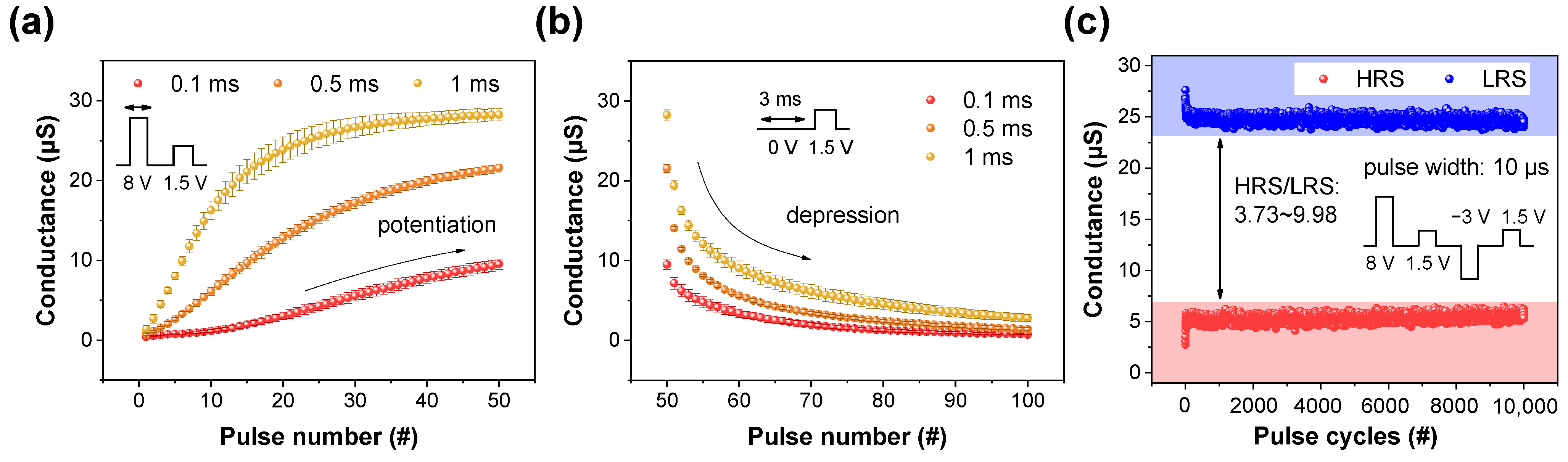
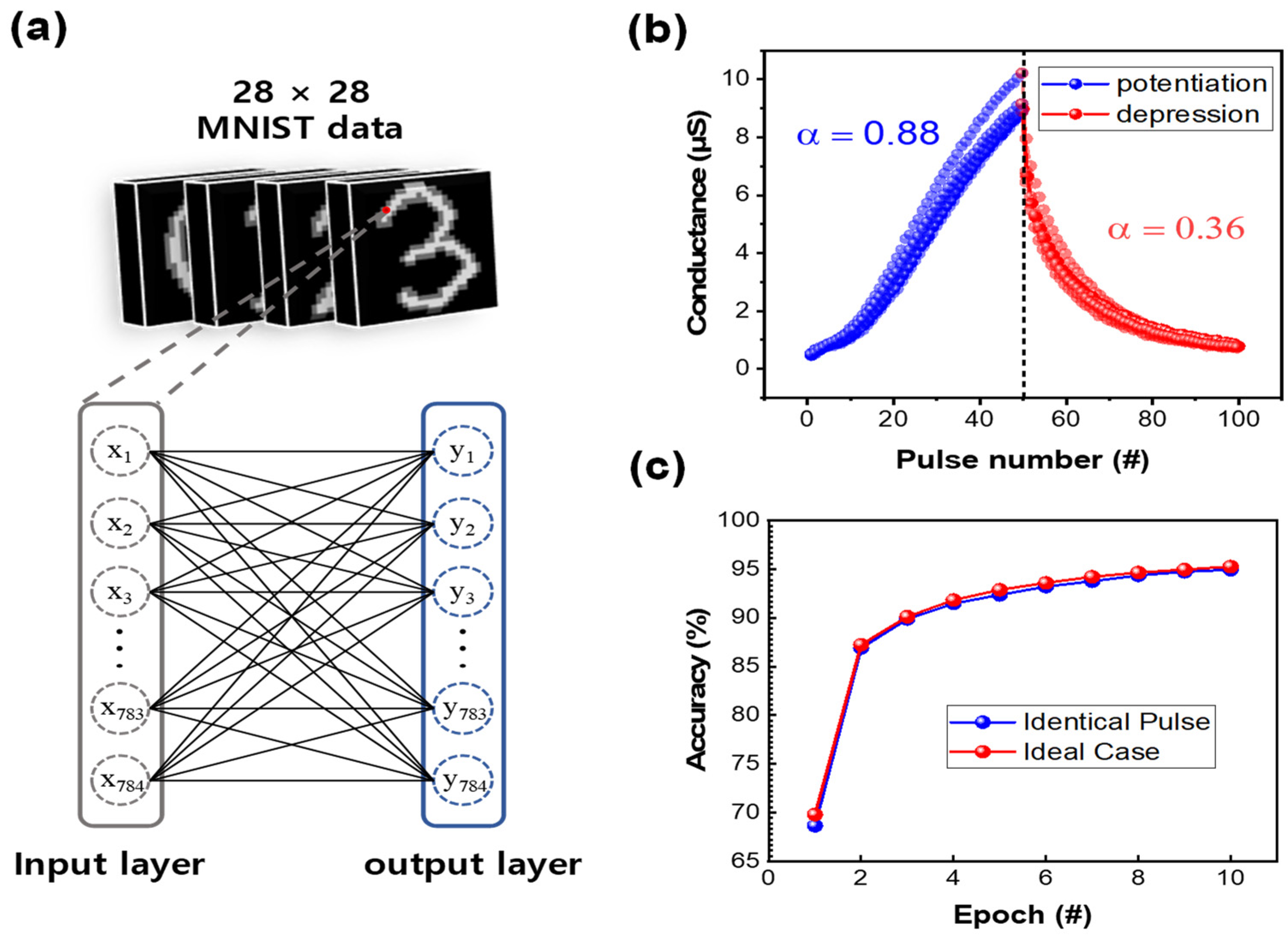
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.H.; Yoon, S.M. Improvement in Energy Consumption and Operational Stability of Electrolyte-Gated Synapse Transistors Using Atomic-Layer-Deposited HfO2 Thin Films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2023, 153, 107182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Burr, G.W.; Hwang, C.S.; Wang, K.L.; Xia, Q.; Yang, J.J. Resistive switching materials for information processing. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.R.; Zhou, L.; Mao, J.Y.; Ren, Y.; Yang, J.Q.; Yang, G.H.; Zhu, X.; Han, S.T.; Roy, V.A.L.; Zhou, Y. Artificial Synapse Emulated by Charge Trapping-Based Resistive Switching Device. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.-T.; Gao, B.; Wu, D.; Tang, J.-S.; Qian, H.; Wu, H.-Q. Trends and Challenges in the Circuit and Macro of RRAM-Based Computing-in-Memory Systems. Chip 2022, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Wu, W.; Zhang, W.; Gao, B.; Zhao, M.; Qian, H.; Lin, Y.; Wu, H. Intelligent Computing with RRAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Memory Workshop (IMW), Monterey, CA, USA, 12–15 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Sun, B.; Ren, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, C.; Wu, B.; Li, P.; Yao, Y.; Duan, S. Resistive switching behaviors and memory logic functions in single MnOx nanorod modulated by moisture. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 9915–9918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talati, N.; Ben-Hur, R.; Wald, N.; Haj-Ali, A.; Reuben, J.; Kvatinsky, S. MMPU—A Real Processing-in-Memory Architecture to Combat the von Neumann Bottleneck. In Springer Series in Advanced Microelectronics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 63, pp. 191–213. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Kim, H.; Choo, M.; Noh, J.; Sheri, A.; Jung, S.; Seo, K.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, W.; et al. RRAM-based synapse for neuromorphic system with pattern recognition function. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–13 December 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Burr, G.W.; Breitwisch, M.J.; Franceschini, M.; Garetto, D.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Jackson, B.; Kurdi, B.; Lam, C.; Lastras, L.A.; Padilla, A.; et al. Phase Change Memory Technology. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2010, 28, 223–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.; Kim, K. Recent advances in high density phase change memory (PRAM) Daewon. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Symposium on VLSI Technology, Systems and Applications (VLSI-TSA), Hsinchu, Taiwan, 23–25 April 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwara, H. Ferroelectric Random Access Memories. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 7619–7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.F.; Ross, F.M.; Paz De Araujo, C.A.; Scott, M.C.; Huffman, M. Structure and Device Characteristics of SrBi2Ta2O9-Based Nonvolatile Random-Access Memories. Mrs Bull. 1996, 21, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaki, Y.; Ishiwara, H. Ferroelectric Thin Film Depositions for Various Types of FeRAMs (Ferroelectric Random Access Memories). MRS Online Proc. Libr. (OPL) 2004, 830, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Chen, P.S.; Wu, T.Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Wang, C.C.; Tzeng, P.J.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, F.; Lien, C.H.; Tsai, M.-J. Low Power and High Speed Bipolar Switching with A Thin Reactive Ti Buffer Layer in Robust HfO2 Based RRAM. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–17 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hosoi, Y.; Tamai, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Ishihara, K.; Shibuya, T.; Inoue, Y.; Yamazaki, S.; Nakano, T.; Ohnishi, S.; Awaya, N.; et al. High Speed Unipolar Switching Resistance RAM (RRAM) Technology. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–13 December 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.R.; Kim, Y.-B.; Chang, M.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, C.B.; Hur, J.H.; Park, G.-S.; Lee, D.; Lee, M.-J.; Kim, C.J.; et al. Multi-level switching of triple-layered TaOx RRAM with excellent reliability for storage class memory. In Proceedings of the 2012 Symposium on VLSI Technology (VLSIT), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–14 June 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, J.; Yu, S. Impact of Selector Devices in Analog RRAM-Based Crossbar Arrays for Inference and Training of Neuromorphic System. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2019, 27, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.; Fumarola, A.; Sidler, S.; Jang, J.; Narayanan, P.; Shelby, R.M.; Burr, G.W.; Hwang, H. Bidirectional Non-Filamentary RRAM as an Analog Neuromorphic Synapse, Part I: Al/Mo/Pr0.7Ca0.3MnO3 Material Improvements and Device Measurements. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2018, 6, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.X.; Huo, J.Q.; Qiu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, R.X.; Chen, Y.; Wong, C.M.; Yau, H.M.; Dai, J.Y. Thickness-Dependent Bipolar Resistive Switching Behaviors of NiOx Films. In Proceedings of the Materials Science Forum, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 23–27 October 2016; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 847, pp. 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, A.; Deleruyelle, D.; Song, J.; Bocquet, M.; Hwang, H. Resistance Controllability and Variability Improvement in a TaOx-Based Resistive Memory for Multilevel Storage Application. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 233104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Kim, S.I.; Lee, C.B.; Yin, H.; Ahn, S.-E.; Kang, B.S.; Kim, K.H.; Park, J.C.; Kim, C.J.; Song, I.; et al. Low-temperature-grown transition metal oxide based storage materials and oxide transistors for high-density non-volatile memory. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magyari-Köpe, B.; Tendulkar, M.; Park, S.-G.; Lee, H.D.; Nishi, Y. Resistive switching mechanisms in random access memory devices incorporating transition metal oxides: TiO2, NiO and Pr0.7Ca0.3MnO3. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 254029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, S.; Park, B.G. Improved Rectification Characteristics by Engineering Energy Barrier Height in TiOx-Based RRAM. Microelectron. Eng. 2021, 237, 111498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Li, X.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Zheng, X.; Gao, B.; Qian, H.; Wu, H. Investigation of Resistive Switching Mechanisms in Ti/TiOx/Pd-Based RRAM Devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2022, 8, 2100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, S. Self-Compliance and High Performance Pt/Hfox/Ti RRAM Achieved through Annealing. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Xie, W.; Zhang, W.; Yin, Z.; Wei, S.; Qu, D.; Li, Y.; Qin, F.; Zhou, D.; Wang, D. Conduction Mechanism and Impedance Analysis of HfOx-Based RRAM at Different Resistive States. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 600, 154084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Jung, S.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, S.; Park, B.G. Tuning Resistive Switching Parameters in Si3N4-Based RRAM for Three-Dimensional Vertical Resistive Memory Applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 663, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cho, S.; Ryoo, K.-C.; Park, B.-G. Effects of Conducting Defects on Resistive Switching Characteristics of SiNx-Based Resistive Random-Access Memory with MIS Structure. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2015, 33, 062201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Park, J.; Cho, Y.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S. Enhanced Resistive Switching and Synaptic Characteristics of ALD Deposited AlN-Based RRAM by Positive Soft Breakdown Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, M.M.; Rehman, H.M.M.U.; Gul, J.Z.; Kim, W.Y.; Karimov, K.S.; Ahmed, N. Decade of 2D-Materials-Based RRAM Devices: A Review. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2020, 21, 147–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, H.D. Effect of Hydrogen Annealing on Performances of BN-Based RRAM. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Lee, S.C. Graphene/h-BN Heterostructures for Vertical Architecture of RRAM Design. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khot, A.C.; Dongale, T.D.; Nirmal, K.A.; Sung, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Nikam, R.D.; Kim, T.G. Amorphous Boron Nitride Memristive Device for High-Density Memory and Neuromorphic Computing Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 10546–10557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Jian, X.C.; Wang, F.; Han, Y.M.; Tian, Y.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, H.Z.; Zhang, K.L. Resistive Switching Characteristic and Uniformity of Low-Power HfOx-Based Resistive Random Access Memory with the BN Insertion Layer. Chin. Phys. B 2016, 25, 107302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milo, V.; Anzalone, F.; Zambelli, C.; Perez, E.; Mahadevaiah, M.K.; Ossorio, O.G.; Olivo, P.; Wenger, C.; Ielmini, D. Optimized Programming Algorithms for Multilevel RRAM in Hardware Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium Proceedings, Virtual Conference, 21–24 March 2021; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, J.; Moon, K.; Song, J.; Kwak, M.; Park, J.; Hwang, H. Optimized Programming Scheme Enabling Linear Potentiation in Filamentary HfO2 RRAM Synapse for Neuromorphic Systems. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2016, 63, 5064–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.W.; Shin, M.C.; Schweitz, M.A.; Oh, J.M.; Koo, S.M. Influence of Gas Annealing on Sensitivity of Aln/4h-Sic-Based Temperature Sensors. Materials 2021, 14, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Liu, S.; Yan, W.; Wang, J. Highly Efficient Preparation of Hexagonal Boron Nitride by Direct Microwave Heating for Dye Removal. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 8852–8859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari-Esfahlan, S.M.; Kim, H.G.; Hyun, S.H.; Choi, J.H.; Hwang, H.S.; Kim, E.T.; Park, H.G.; Lee, J.H. Low-Temperature Direct Growth of Amorphous Boron Nitride Films for High-Performance Nanoelectronic Device Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 7274–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, C.; Du, M.; Wu, Y.; Ren, C.; Ding, K.; Song, M.; Huang, C. Porous Hexagonal Boron Nitride Sheets: Effect of Hydroxyl and Secondary Amino Groups on Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 4566–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, F.; Azni Zulkifli, T.Z.; Khanday, F.A. Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM): An Overview of Materials, Switching Mechanism, Performance, Multilevel Cell (Mlc) Storage, Modeling, and Applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Electron Devices Society; Gakkai, Ō.B. Proceedings of the Digest of Technical Papers/2014 Symposium on VLSI Technology (VLSI-Technology), Honolulu, HI, USA, 9–12 June 2014; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA; ISBN 9781479933327.
- Shen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Qi, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Mitrovic, I.Z.; Yang, L.; Zhao, C. Advances of RRAM Devices: Resistive Switching Mechanisms, Materials and Bionic Synaptic Application. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garshin, A.P.; Shvaiko-Shvaikovskii, V.E. Theoretical Analysis of Defect Formation In Silicon Nitride Processes. Refract. Ind. Ceram. 1998, 39, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vil’k, Y.N.; Chupov, V.D.; Shvaiko-Shvaikovskii, V.E.; Garshin, A.P. A Theoretical Analysis of the Formation of Nonstoichiometric Defects in Hexagonal Boron Nitride. Refract. Ind. Ceram. 2001, 42, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kwak, M.; Moon, K.; Woo, J.; Lee, D.; Hwang, H. TiOx-Based RRAM Synapse With 64-Levels of Conductance and Symmetric Conductance Change by Adopting a Hybrid Pulse Scheme for Neuromorphic Computing. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 1559–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Aluguri, R.; Chand, U.; Tseng, T.-Y. High Performance Bipolar Resistive Switching Characteristics in SiO2/ZrO2/SiO2 Tri-Layer Based CBRAM Device. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits (EDSSC), Hsinchu, Taiwan, 18–20 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, D.; Simanjuntak, F.M.; Tseng, T.Y. Temperature Induced Complementary Switching in Titanium Oxide Resistive Random Access Memory. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 075314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varun, I.; Bharti, D.; Raghuwanshi, V.; Tiwari, S.P. Multi-Temperature Deposition Scheme for Improved Resistive Switching Behavior of Ti/AlOx/Ti MIM Structure. Solid State Ion. 2017, 309, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Su, Y.K. Improvement of the Performance in Cr-Doped ZnO Memory Devices: Via Control of Oxygen Defects. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2941–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, F.M.; Larcher, L.; Pan, C.; Xiao, N.; Shi, Y.; Hui, F.; Lanza, M. 2D h-BN based RRAM devices. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 December 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Hu, K.; She, Y.; Song, S.; Song, Z.; Zhang, K. Improvement of Resistive Switching Performance in Sulfur-Doped Hfox-Based Rram. Materials 2021, 14, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-W.; Park, S.; Jeong, Y.-H.; Hwang, H. ReRAM-based synaptic device for neuromorphic computing. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Melbourne, Australia, 1–5 June 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014. ISBN 9781479934324. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, B.; Hussain, F.; Mahata, C.; Sim, E.; Ismail, M.; Abbas, Y.; Abbas, H.; Lee, D.K.; et al. Synaptic Characteristics of Amorphous Boron Nitride-Based Memristors on a Highly Doped Silicon Substrate for Neuromorphic Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 33908–33916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No | Structure | Vset/Vreset | ON/OFF Ratio | Endurance (Cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cu/SiO2/ZrO2/SiO2/TiN | 1/−1 | 102 | 103 |
| 2 | ITO/WO3/ITO | 0.25/−0.42 | 102 | 108 |
| 3 | Ti/AlOx/Ti | 0.65/−1.15 | 103 | 75 |
| 4 | Pt/ZnO/IZO | 2.5/−2 | 9.12 × 102 | 105 |
| 5 | Ti/h-BN/CuNi | 0.7/−0.5 | 104 | 102 |
| 6 | Pt/a-BN/TiN | 4/−8 | 1.97 × 101 | 104 (In this work) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pyo, J.; Jang, J.; Ju, D.; Lee, S.; Shim, W.; Kim, S. Amorphous BN-Based Synaptic Device with High Performance in Neuromorphic Computing. Materials 2023, 16, 6698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16206698
Pyo J, Jang J, Ju D, Lee S, Shim W, Kim S. Amorphous BN-Based Synaptic Device with High Performance in Neuromorphic Computing. Materials. 2023; 16(20):6698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16206698
Chicago/Turabian StylePyo, Juyeong, Junwon Jang, Dongyeol Ju, Subaek Lee, Wonbo Shim, and Sungjun Kim. 2023. "Amorphous BN-Based Synaptic Device with High Performance in Neuromorphic Computing" Materials 16, no. 20: 6698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16206698
APA StylePyo, J., Jang, J., Ju, D., Lee, S., Shim, W., & Kim, S. (2023). Amorphous BN-Based Synaptic Device with High Performance in Neuromorphic Computing. Materials, 16(20), 6698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16206698






