High Spin Magnetic Moments in All-3d-Metallic Co-Based Full Heusler Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Computational Details
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electronic Properties
3.2. Magnetic Properties
3.3. Slater–Pauling Behavior and Origin of the Pseudogap in the Lattice Structure
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOS | Density of States |
| f.u. | formula unit |
| FPLO | Full-potential nonorthogonal local-orbital minimum- basis band structure approach |
| GGA | Generalized gradient approximation |
| PBE | Perdew Burke Ernzerhof |
References
- Heusler, F. Über magnetische manganlegierungen. Verh. Dtsch. Phys. Ges. 1903, 12, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Heusler, F.; Take, E. The nature of the Heusler alloys. Phys. Z 1912, 13, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Ziebeck, K.R.A. Alloys and compounds of d-elements with main group elements. Part 2. In Landolt-Börnstein, New Series, Group III; Wijn, H.R.J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1988; Volume 19c, pp. 75–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ziebeck, K.R.A.; Neumann, K.-U. Magnetic Properties of metals. In Landolt-Börnstein, New Series, Group III; Wijn, H.R.J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Volume 32c, pp. 64–414. [Google Scholar]
- Graf, T.; Felser, C.; Parkin, S.S.P. Simple rules for the understanding of Heusler compounds. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2011, 39, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, I.; Dederichs, P.H.; Papanikolaou, N. Origin and Properties of the Gap in the Half-Ferromagnetic Heusler Alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 134428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, I.; Dederichs, P.H.; Papanikolaou, N. Slater-Pauling Behavior and Origin of the Half-Metallicity of the Full-Heusler Alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 174429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaftouros, S.; Özdoğan, K.; Şaşıoğlu, E.; Galanakis, I. Generalized Slater-Pauling rule for the inverse Heusler compounds. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 024420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdoğan, K.; Şaşıoğlu, E.; Galanakis, I. Slater-Pauling behavior in LiMgPdSn-type multifunctional quaternary Heusler materials: Half-metallicity, spin-gapless and magnetic semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 193903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsnelson, M.I.; Irkhin, V.Y.; Chioncel, L.; Lichtenstein, A.I.; de Groot, R.A. Half-metallic ferromagnets: From band structure to many-body effects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirohata, A.; Takanashi, K. Perspectives of Heusler compounds. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 193001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, I. Half-metallic alloys: Fundamentals and applications. In Lectures Notes in Physics; Galanakis, I., Dederichs, P.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; Volume 676. [Google Scholar]
- Felser, C.; Fecher, G.H. Spintronics. From Materials to Devices; Felser, C., Fecher, G.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ashby, M.F.; Jones, D.R.H. Half-metallic materials and their properties. In Series on Materials for Engineering; Fong, C.Y., Pask, J.E., Yang, L.H., Eds.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2013; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Heusler alloys: Properties, growth, applications. In Springer Series in Materials Science; Felser, C.; Hirohata, A. (Eds.) Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Volume 222. [Google Scholar]
- Galanakis, I.; Özdoğan, K.; Şaşıoğlu, E. Spin-filter and spin-gapless semiconductors: The case of Heusler compounds. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 055606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, M.; Şaşıoğlu, E.; Friedrich, C.; Blügel, S.; Galanakis, I. Design of L21-type antiferromagnetic semiconducting full-Heusler compounds: A first principles DFT+GW study. J. App. Phys. 2017, 121, 053903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, M.; Şaşıoğlu, E.; Friedrich, C.; Galanakis, I. A first-principles DFT+GW study of spin-filter and spin-gapless semiconducting Heusler compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 441, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillessen, M.; Dronskowski, R. A combinatorial study of full Heusler alloys by first-principles computational methods. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillessen, M.; Dronskowski, R. A combinatorial study of inverse Heusler alloys by first-principles computational methods. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Hegde, V.I.; Munira, K.; Xie, Y.; Keshavarz, S.; Mildebrath, D.T.; Wolverton, C.; Ghosh, A.W.; Butler, W.H. Computational investigation of half-Heusler compounds for spintronics applications. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 024411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; He, J.; Mazumdar, D.; Munira, K.; Keshavarz, S.; Lovorn, T.; Wolverton, C.; Ghosh, A.W.; Butler, W.H. Computational investigation of inverse Heusler compounds for spintronics applications. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 094410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanvito, S.; Oses, C.; Xue, J.; Tiwari, A.; Zic, M.; Archer, T.; Tozman, P.; Venkatesan, M.; Coey, M.; Curtarolo, S. Accelerated discovery of new magnets in the Heusler alloy family. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faleev, S.V.; Ferrante, Y.; Jeong, J.; Samant, M.G.; Jones, B.; Parkin, S.S.P. Unified explanation of chemical ordering, the Slater-Pauling rule, and half-metallicity in full Heusler compounds. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 045140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faleev, S.V.; Ferrante, Y.; Jeong, J.; Samant, M.G.; Jones, B.; Parkin, S.S.P. Origin of the Tetragonal Ground State of Heusler Compounds. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2017, 7, 034022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faleev, S.V.; Ferrante, Y.; Jeong, J.; Samant, M.G.; Jones, B.; Parkin, S.S.P. Heusler compounds with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and large tunneling magnetoresistance. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2017, 1, 024402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, I.; Özdoğan, K.; Şaşıoğlu, E. High-TC fully compensated ferrimagnetic semiconductors as spin-filter materials: The case of CrVXAl (X = Ti, Zr, Hf) Heusler compounds. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 086003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswara, Y.; Gupta, S.; Samatham, S.S.; Varma, M.R.; Enamullah; Suresh, K.G.; Alam, A. Competing magnetic and spin-gapless semiconducting behavior in fully compensated ferrimagnetic CrVTiAl: Theory and experiment. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 97, 054407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, H.; Liu, H.; Meng, F. Electronic structure, magnetic properties and martensitic transformation in all-d-metal Heusler alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Magn. 2018, 451, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.Y.; Liu, E.K.; Li, Y.; Han, X.L.; Du, Z.W.; Luo, H.Z.; Liu, G.D.; Xi, X.K.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, W.H.; et al. Magnetostructural martensitic transformations with large volume changes and magneto-strains in all-d-metal Heusler alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 071904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.Y.; Liu, E.K.; Chen, J.H.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.D.; Luo, H.Z.; Xi, X.K.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, W.H.; Wu, G.H. Realization of multifunctional shape-memory ferromagnets in all-d-metal Heusler phases. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 022406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Jiao, Y.; Meng, F.; Luo, H. Understanding the magnetic structural transition in all-d-metal Heusler alloy Mn2Ni1.25Co0.25Ti0.5. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 775, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mandal, K. Observation of giant exchange bias effect in Ni–Mn–Ti all-d-metal Heusler alloy. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2022, 34, 105801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aznar, A.; Gràcia-Condal, A.; Planes, A.; Lloveras, P.; Barrio, M.; Tamarit, J.-L.; Xiong, W.; Cong, D.; Popescu, C.; Manosa, L. Giant barocaloric effect in all-d-metal Heusler shape memory alloys. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019, 3, 044406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Ghosh, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Mandal, K. Large magnetocaloric effect and magnetoresistance in Fe-Co doped Ni_50-x(FeCo)_xNn_37Ti_13 all-d-metal Heusler alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 910, 164929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mandal, K. Large reversible magnetocaloric effect and magnetoresistance by improving crystallographic compatibility condition in Ni(Co)- Mn-Ti all-d-metal Heusler alloys. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2022, 6, 094411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shena, J.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xi, X.; Liu, E.; Wang, W.; Wu, G. Atomic configuration, unusual lattice constant change, and tunable ferromagnetism in all-d-metal Heusler alloys Fe2CrV-FeCr2V. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 492, 165661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, G. Magnetic phase transitions of all-d metal Heusler type model. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 153299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzim, M.F.; Fortunato, N.; Samathrakis, I.; Xie, R.; Opahle, I.; Gutfleisch, O.; Zhang, H. Giant Anomalous Hall and Nernst Conductivities in Magnetic All-d Metal Heusler Alloys. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, V.G.; Reis, M.S. All-d-Metal Full Heusler Alloys: A Novel Class of Functional Materials. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, M.; Herper, H.C. Exploration of all-3d Heusler alloys for permanent magnets: An ab initio based high-throughput study. Phys. Rev. B 2023, 107, 174402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nia, S.; Khenchoul, S.; Lefkaier, I.K.; Lagoun, B. DFT-based investigation of the structural, magnetic, electronic, half-metallicity and elastic properties in the all-d heusler compounds: The case of Co2VZn and CoVZn. Eur. Phys. J. B 2021, 94, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Jung, Y. Classifying Intermetallic Tetragonal Phase of All-d-Metal Heusler Alloys for Catalysis Applications. Today Catal. 2022, 65, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Shen, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Ding, B.; Xi, X.; Liu, E.; Wang, W.; Wu, G. Electronic behaviors during martensitic transformations in all-d-metal Heusler alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2019, 31, 425401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdoğan, K.; Maznichenko, I.V.; Ostanin, S.; Şaşıoğlu, E.; Ernst, A.; Mertig, I.; Galanakis, I. High spin polarization in all-3d-metallic Heusler compounds: The case of Fe2CrZ and Co2CrZ (Z=Sc,Ti,V). J. Phys. D Appl. Phys 2019, 52, 205003, Erratum in 2024, 57, 049501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, I. Slater–Pauling Behavior in Half-Metallic Heusler Compounds. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepernik, K.; Eschrig, H. Full-potential nonorthogonal local-orbital minimum-basis band-structure scheme. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopernik, K. Full Potential Local Orbital Minimum Basis Bandstructure Scheme User’s Manual. Available online: http://www.fplo.de/download/doc.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2023).
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://oqmd.org (accessed on 3 December 2023).
- Şaşıoğlu, E.; Sandratskii, L.M.; Bruno, P.; Galanakis, I. Exchange interactions and temperature dependence of magnetization in half-metallic Heusler alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 184415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiles, D. Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
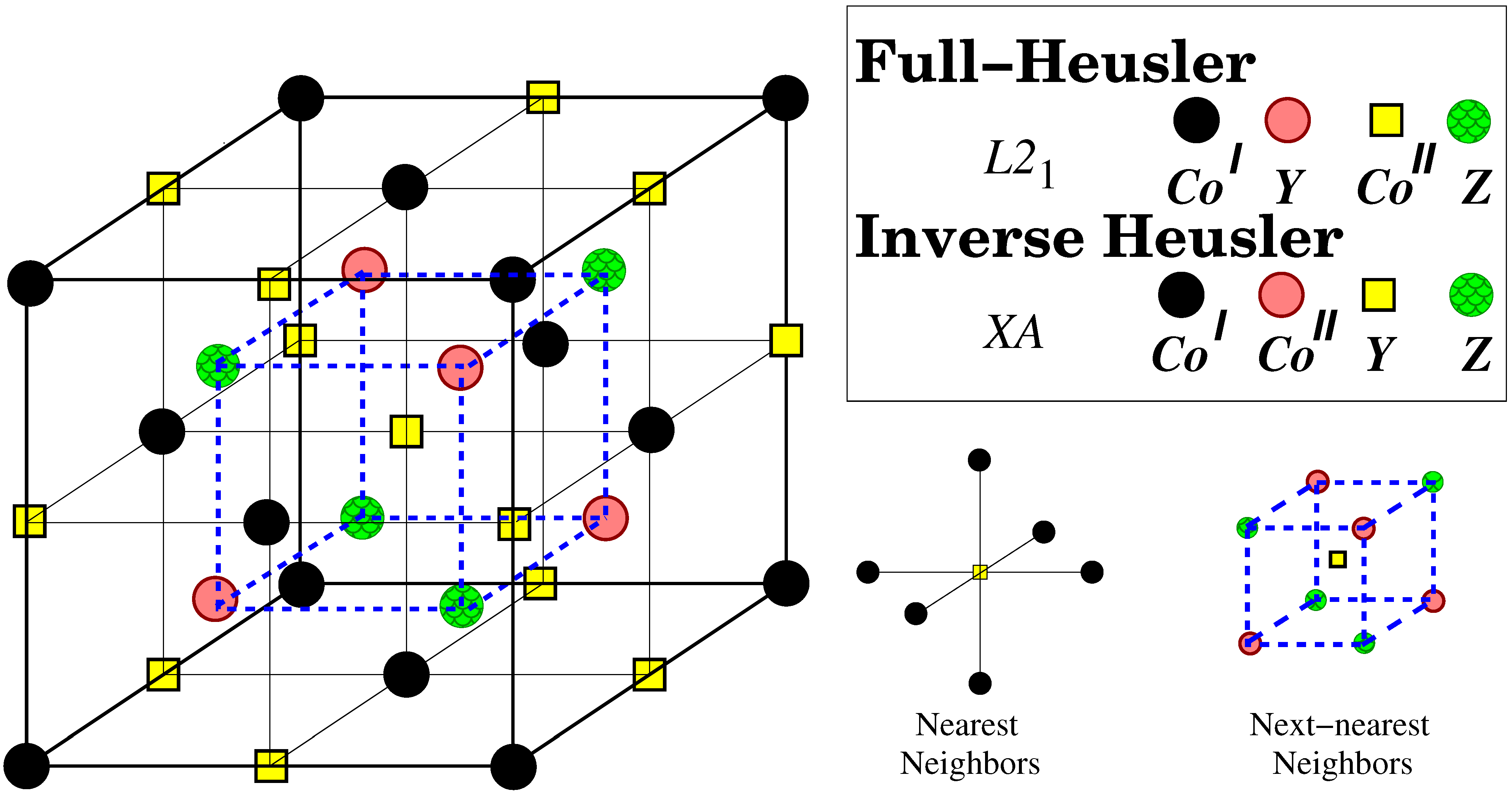
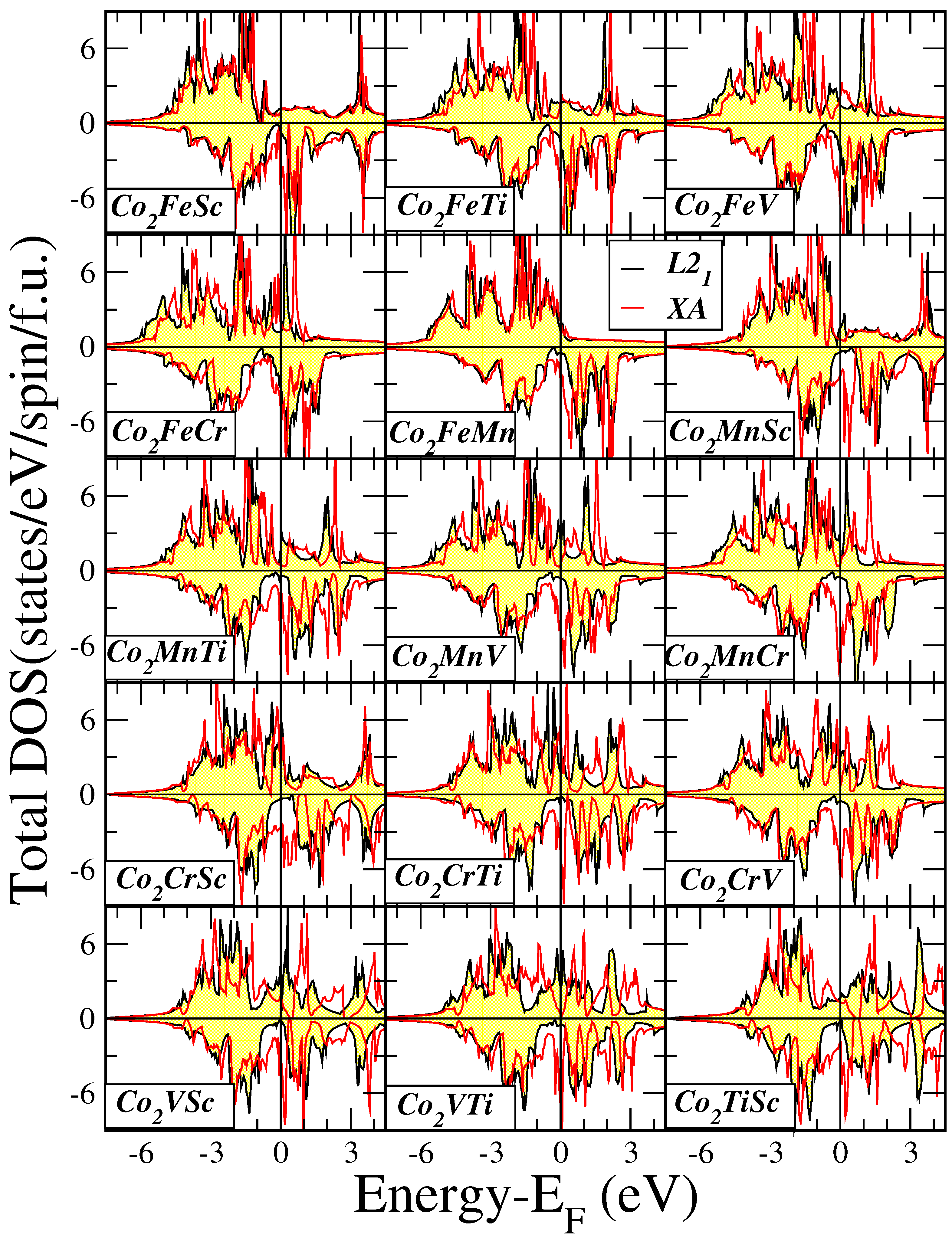
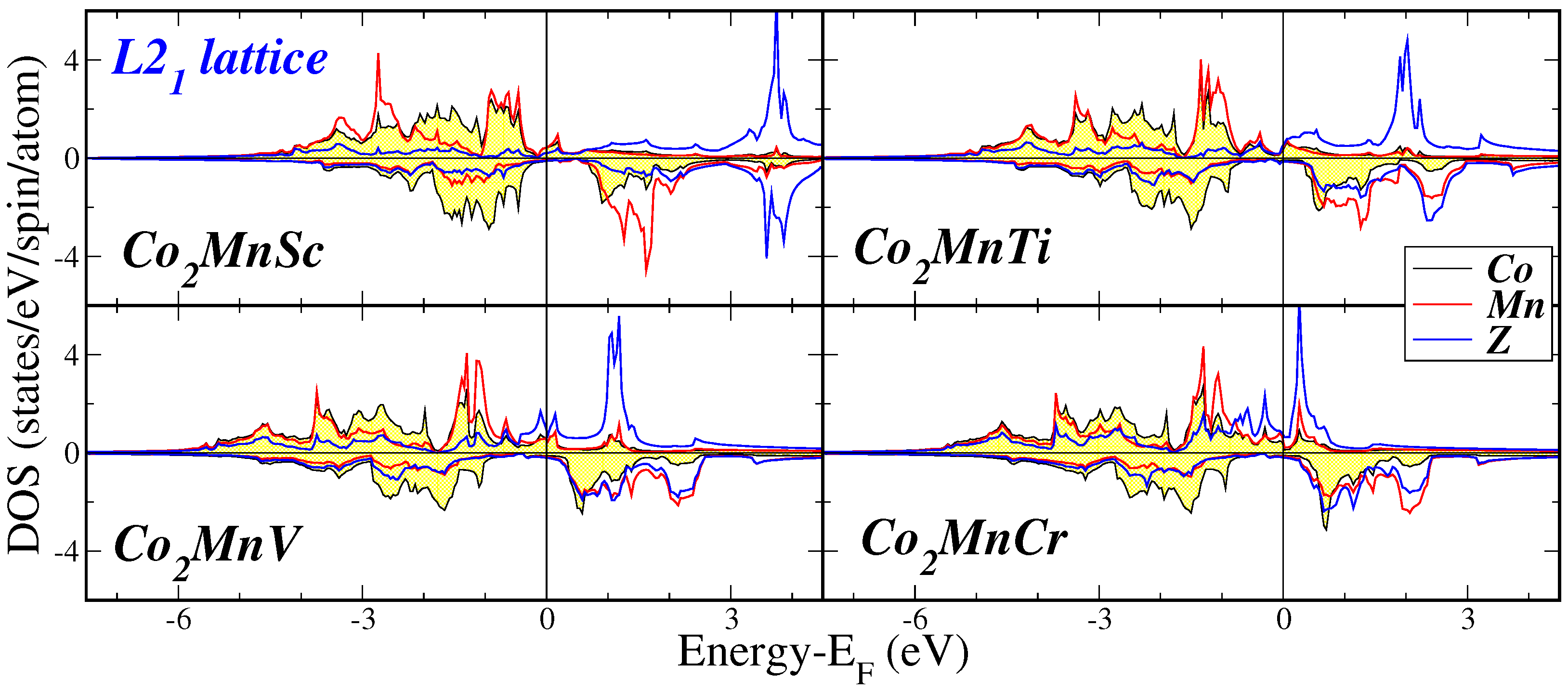

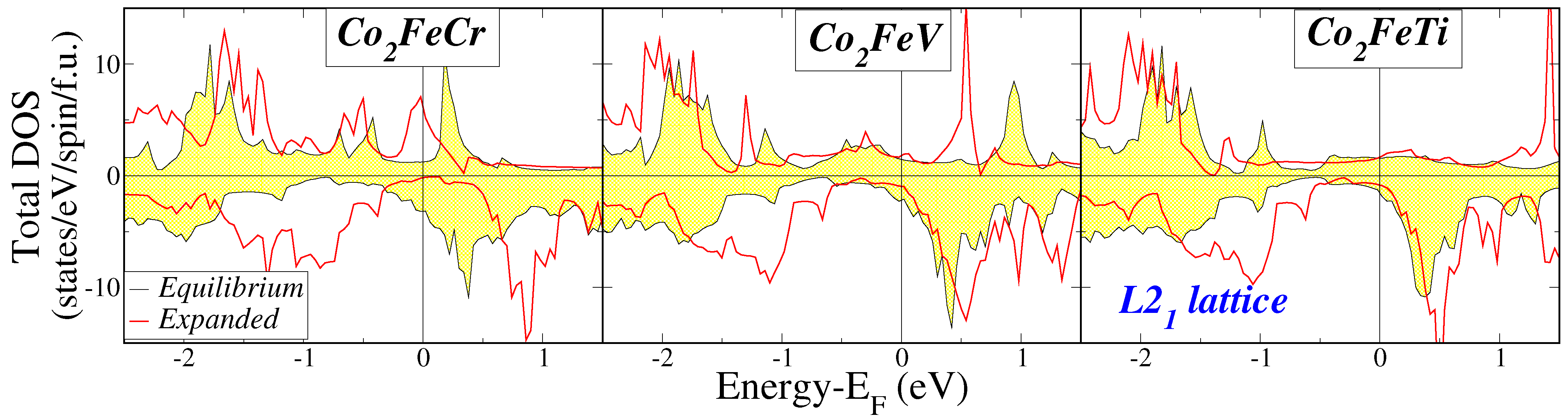
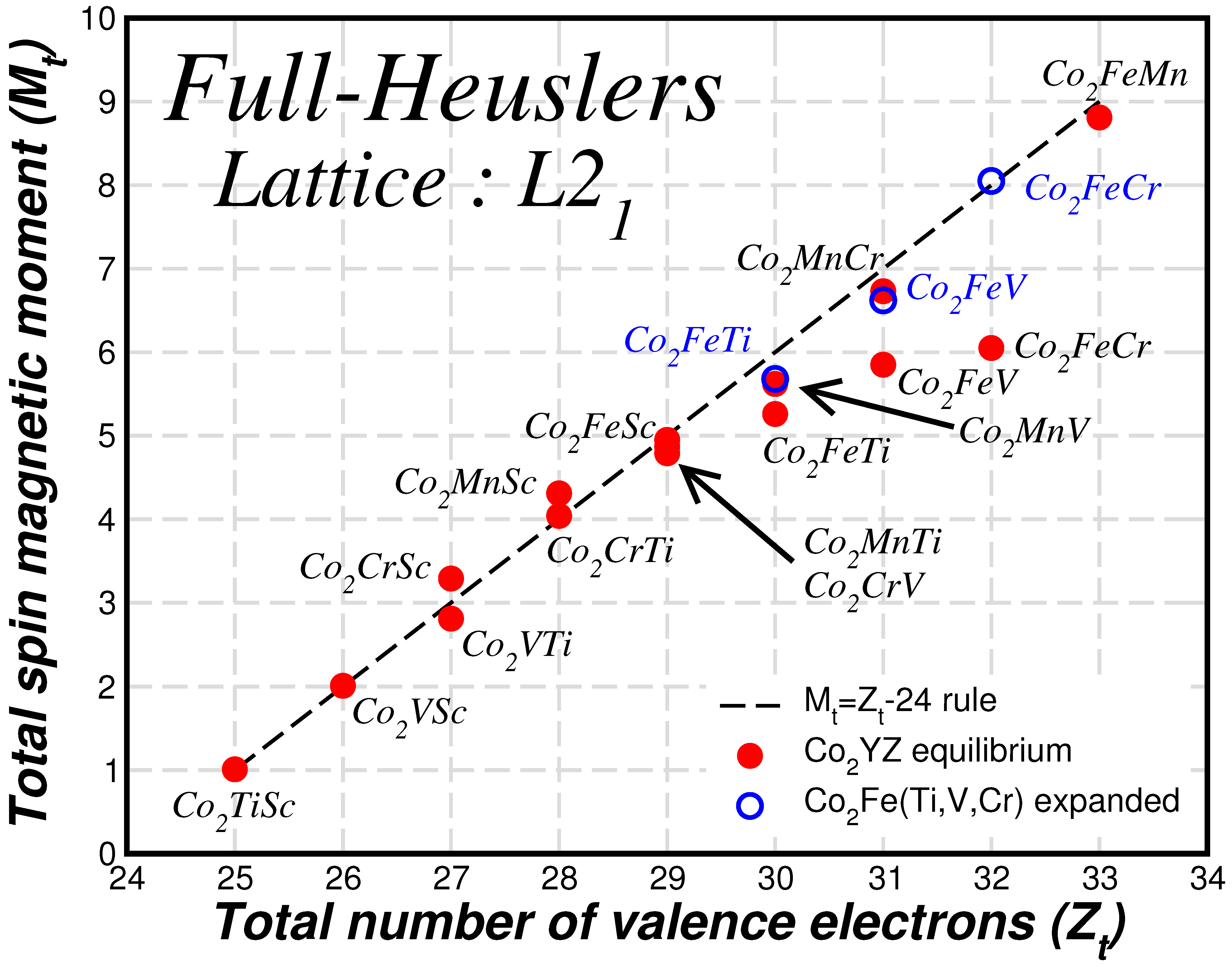
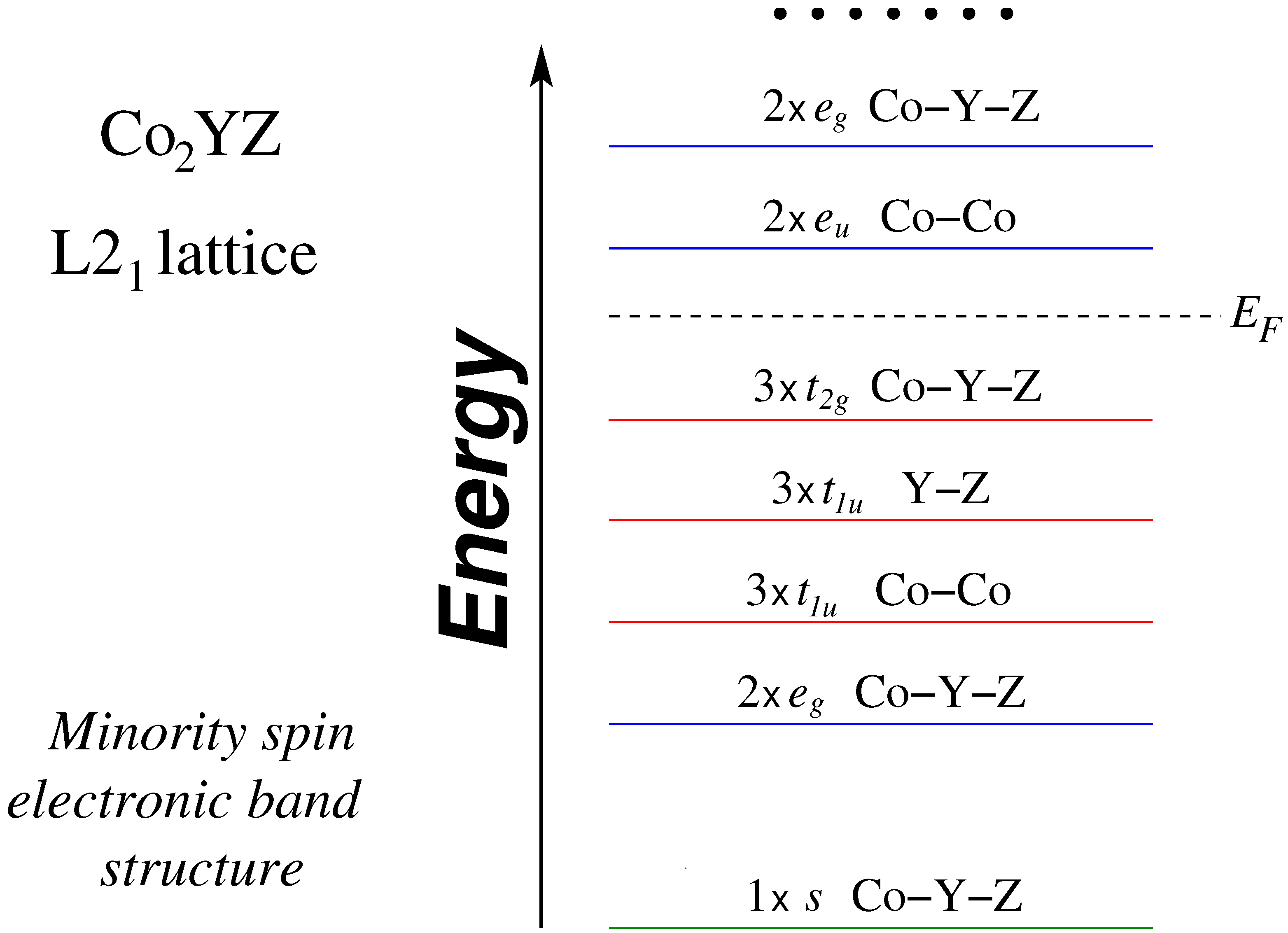
| XYZ | Structure | (Å) | (eV/atom) | (eV/atom) | (eV/f.u.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoFeSc | 5.884 | −0.153 | 0.123 | −0.499 | |
| 5.911 | −0.033 | 0.243 | |||
| CoFeTi | 5.727 | −0.225 | 0.039 | −0.275 | |
| 5.748 | −0.167 | 0.097 | |||
| CoFeV | 5.630 | −0.033 | 0.130 | −0.114 | |
| 5.644 | −0.019 | 0.145 | |||
| CoFeCr | 5.509 | 0.377 | 0.414 | 0.098 | |
| 5.598 | 0.170 | 0.207 | |||
| CoFeMn | 5.563 | −0.002 | 0.040 | −0.372 | |
| 5.616 | 0.087 | 0.129 | |||
| CoMnSc | 5.902 | −0.169 | 0.102 | −0.735 | |
| 5.964 | 0.005 | 0.276 | |||
| CoMnTi | 5.759 | −0.289 | 0.010 | −0.587 | |
| 5.799 | −0.154 | 0.144 | |||
| CoMnV | 5.603 | 0.196 | 0.365 | −0.143 | |
| 5.669 | −0.035 | 0.134 | |||
| CoMnCr | 5.614 | 0.093 | 0.122 | −0.216 | |
| 5.628 | 0.129 | 0.158 | |||
| CoCrSc | 5.928 | −0.014 | 0.258 | −0.898 | |
| 5.971 | 0.206 | 0.477 | |||
| CoCrTi | 5.786 | −0.152 | 0.096 | −0.703 | |
| 5.734 | 0.014 | 0.262 | |||
| CoCrV | 5.698 | 0.029 | 0.172 | −0.236 | |
| 5.632 | 0.072 | 0.213 | |||
| CoVSc | 5.960 | −0.133 | 0.180 | −0.852 | |
| 5.944 | 0.077 | 0.390 | |||
| CoVTi | 5.806 | −0.223 | 0.085 | −0.460 | |
| 5.794 | −0.125 | 0.182 | |||
| CoTiSc | 6.041 | −0.367 | 0.028 | −1.287 | |
| 6.052 | −0.004 | 0.390 |
| XYZ | Structure | () | () | () | () | () | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoFeSc | 1.24 | 1.24 | 2.88 | −0.40 | 4.95 | 29 | |
| 1.19 | 1.68 | 2.20 | −0.47 | 4.61 | |||
| CoFeTi | 1.33 | 1.33 | 2.89 | −0.29 | 5.26 | 30 | |
| expanded | 1.61 | 1.61 | 3.20 | −0.74 | 5.68 | ||
| 1.02 | 1.61 | 1.95 | −0.63 | 3.95 | |||
| CoFeV | 1.42 | 1.42 | 2.79 | 0.22 | 5.85 | 31 | |
| expanded | 1.63 | 1.63 | 3.18 | 0.18 | 6.62 | ||
| 0.98 | 1.50 | 1.90 | −0.86 | 3.52 | |||
| CoFeCr | 1.37 | 1.37 | 2.50 | 0.81 | 6.05 | 32 | |
| expanded | 1.33 | 1.33 | 3.05 | 2.34 | 8.05 | ||
| 1.47 | 1.57 | 2.23 | −0.29 | 4.99 | |||
| CoFeMn | 1.47 | 1.47 | 2.83 | 3.05 | 8.81 | 33 | |
| 1.60 | 1.76 | 2.37 | 2.75 | 8.49 | |||
| CoMnSc | 0.82 | 0.82 | 3.12 | −0.44 | 4.31 | 28 | |
| 1.23 | 1.56 | 2.95 | −0.42 | 5.31 | |||
| CoMnTi | 1.05 | 1.05 | 3.23 | −0.45 | 4.87 | 29 | |
| 1.20 | 1.61 | 2.45 | −0.65 | 4.61 | |||
| CoMnV | 1.15 | 1.15 | 3.07 | 0.25 | 5.62 | 30 | |
| 1.12 | 1.52 | 2.14 | −0.93 | 3.85 | |||
| CoMnCr | 1.23 | 1.23 | 2.95 | 1.32 | 6.73 | 31 | |
| 0.76 | 1.53 | 2.32 | −1.71 | 2.89 | |||
| CoCrSc | 0.70 | 0.70 | 2.21 | −0.032 | 3.29 | 27 | |
| 1.16 | 1.29 | 2.47 | −0.24 | 4.68 | |||
| CoCrTi | 0.99 | 0.99 | 2.38 | −0.32 | 4.04 | 28 | |
| 0.89 | 1.13 | 0.98 | −0.17 | 2.84 | |||
| CoCrV | 1.13 | 1.13 | 2.25 | 0.28 | 4.79 | 29 | |
| 0.76 | 1.01 | 0.56 | 0.09 | 2.42 | |||
| CoVSc | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.60 | −0.22 | 2.01 | 26 | |
| 1.20 | 1.39 | −0.98 | −0.19 | 1.41 | |||
| CoVTi | 1.02 | 1.02 | 0.83 | −0.05 | 2.81 | 27 | |
| 0.76 | 0.88 | −0.48 | −0.22 | 0.94 | |||
| CoTiSc | 0.78 | 0.78 | −0.32 | −0.22 | 1.01 | 25 | |
| 1.32 | 1.33 | −0.51 | −0.23 | 1.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tas, M.; Özdoğan, K.; Şaşıoğlu, E.; Galanakis, I. High Spin Magnetic Moments in All-3d-Metallic Co-Based Full Heusler Compounds. Materials 2023, 16, 7543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247543
Tas M, Özdoğan K, Şaşıoğlu E, Galanakis I. High Spin Magnetic Moments in All-3d-Metallic Co-Based Full Heusler Compounds. Materials. 2023; 16(24):7543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247543
Chicago/Turabian StyleTas, Murat, Kemal Özdoğan, Ersoy Şaşıoğlu, and Iosif Galanakis. 2023. "High Spin Magnetic Moments in All-3d-Metallic Co-Based Full Heusler Compounds" Materials 16, no. 24: 7543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247543
APA StyleTas, M., Özdoğan, K., Şaşıoğlu, E., & Galanakis, I. (2023). High Spin Magnetic Moments in All-3d-Metallic Co-Based Full Heusler Compounds. Materials, 16(24), 7543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247543





