Prolonging Campaign Life of Blast Furnace Trough by Water Cooling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
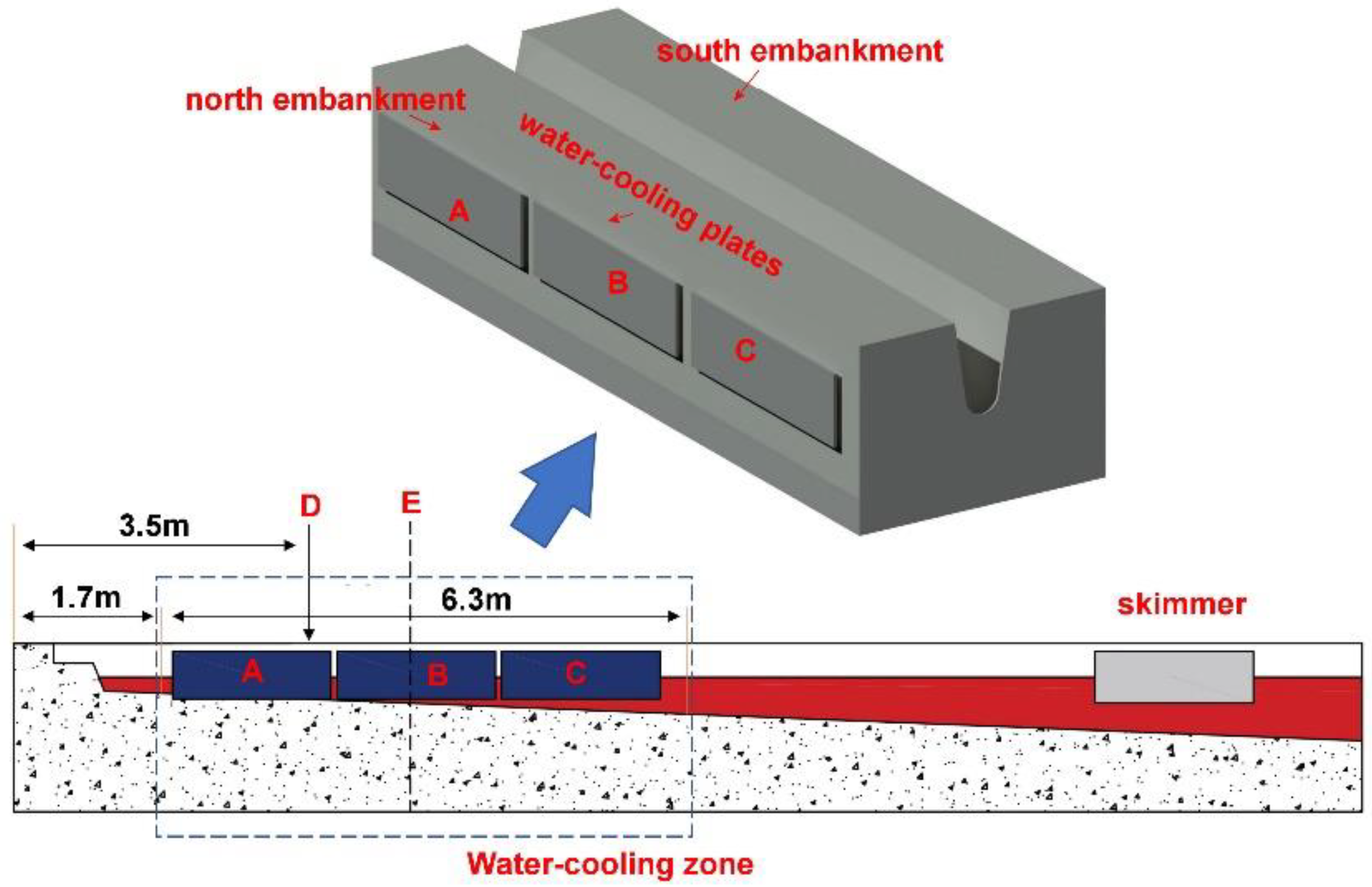
2. Design of Water Cooling Device and Industrial Tests
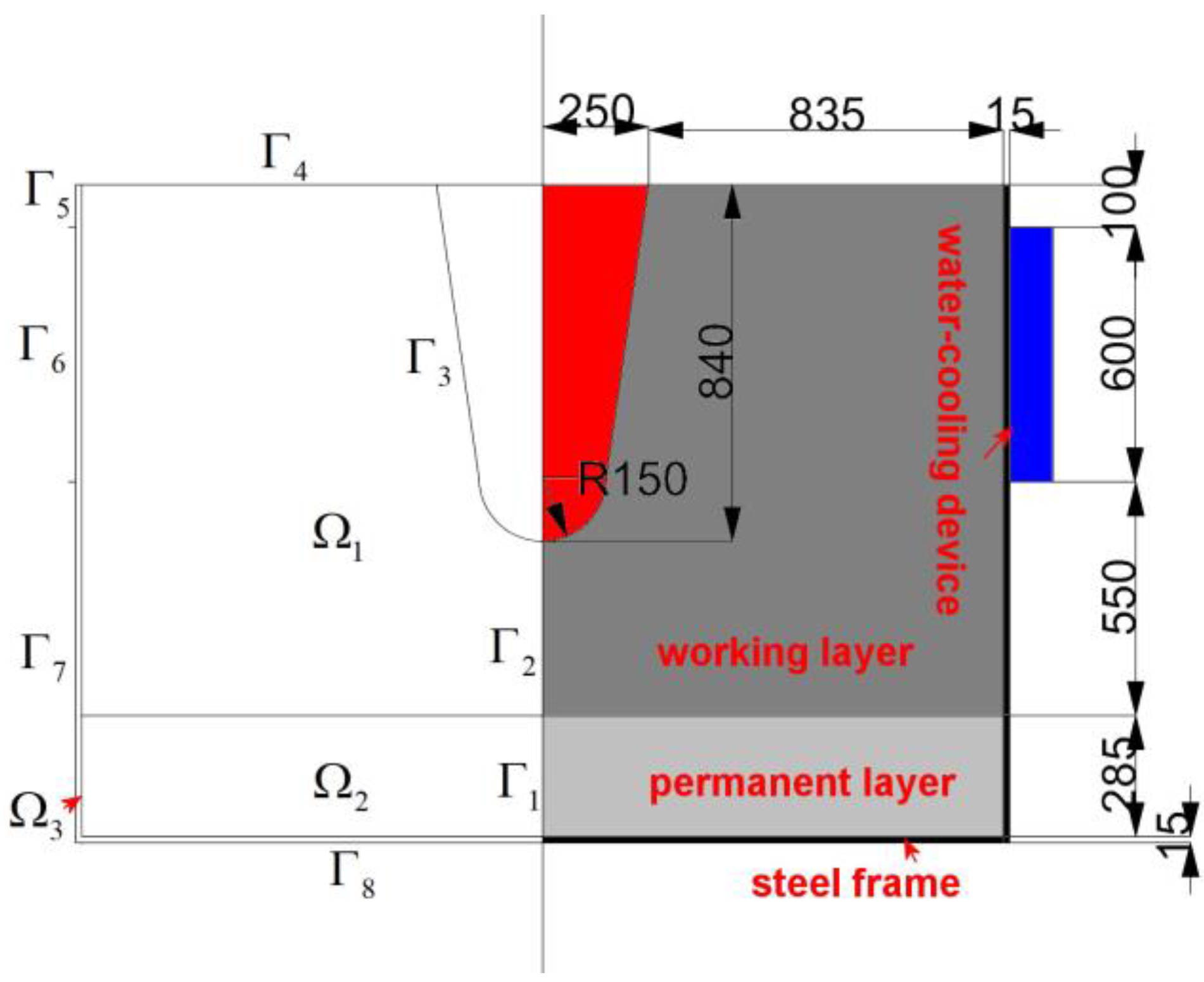
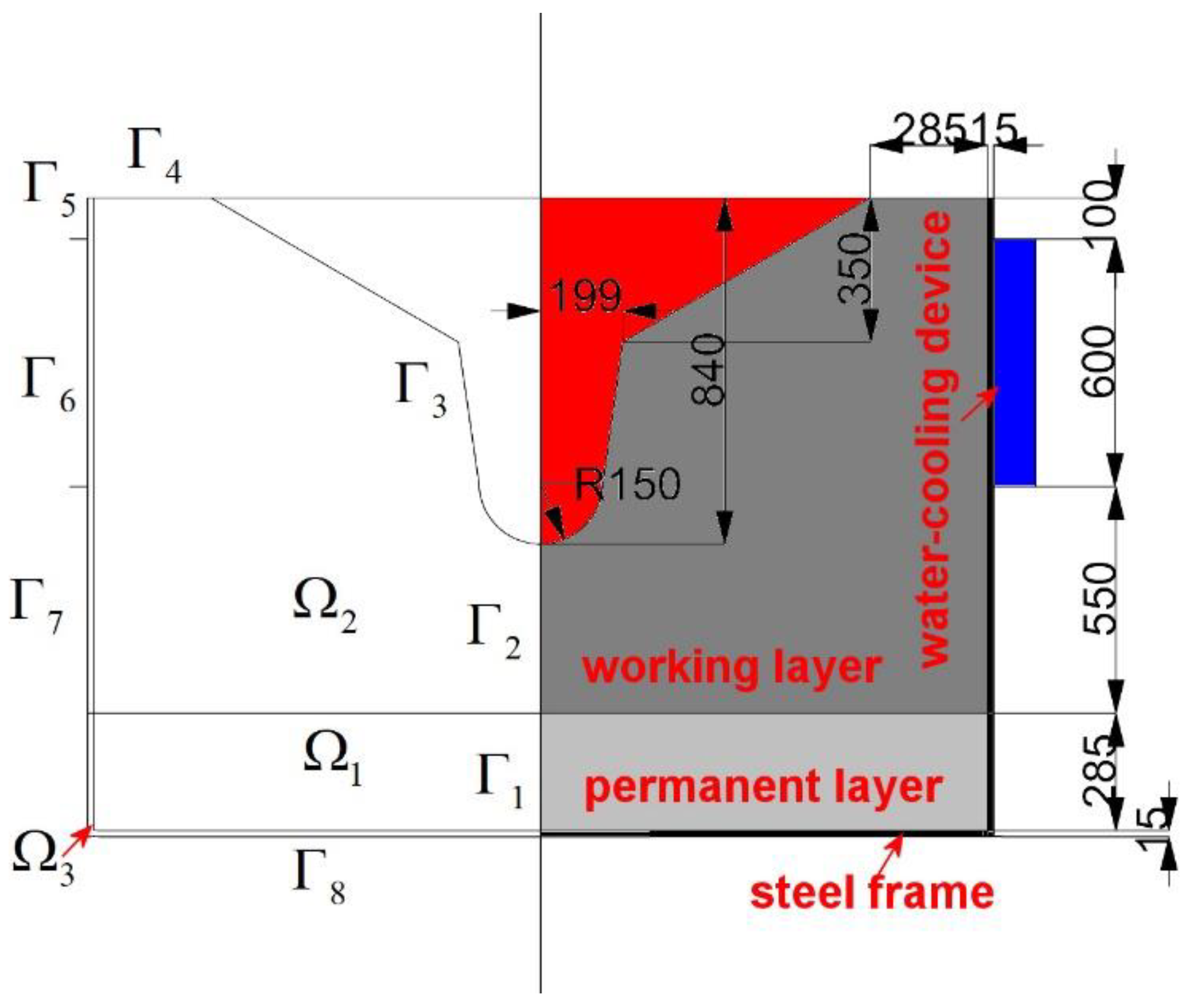
3. Numerical Simulation
4. Results and Discussion
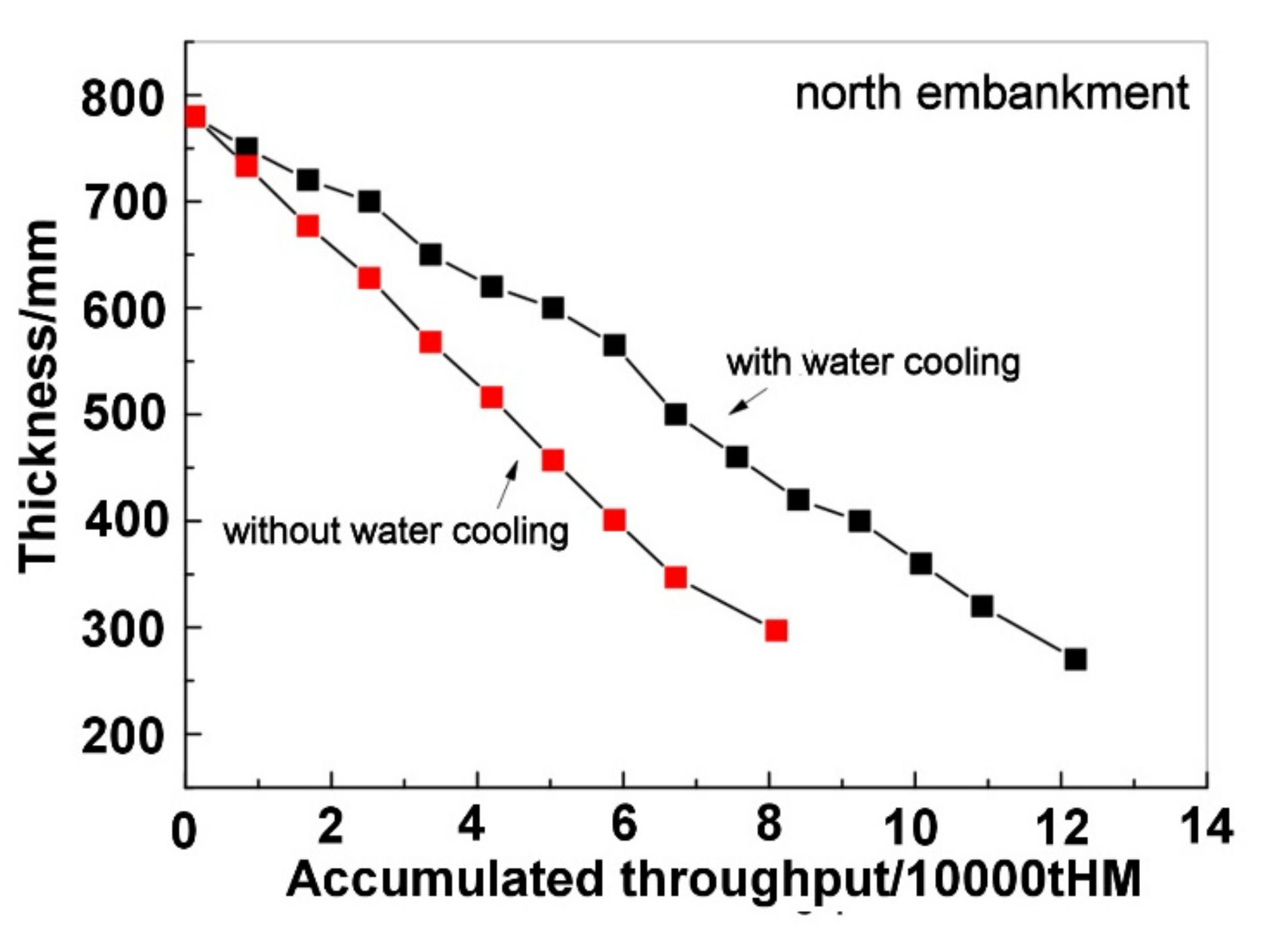
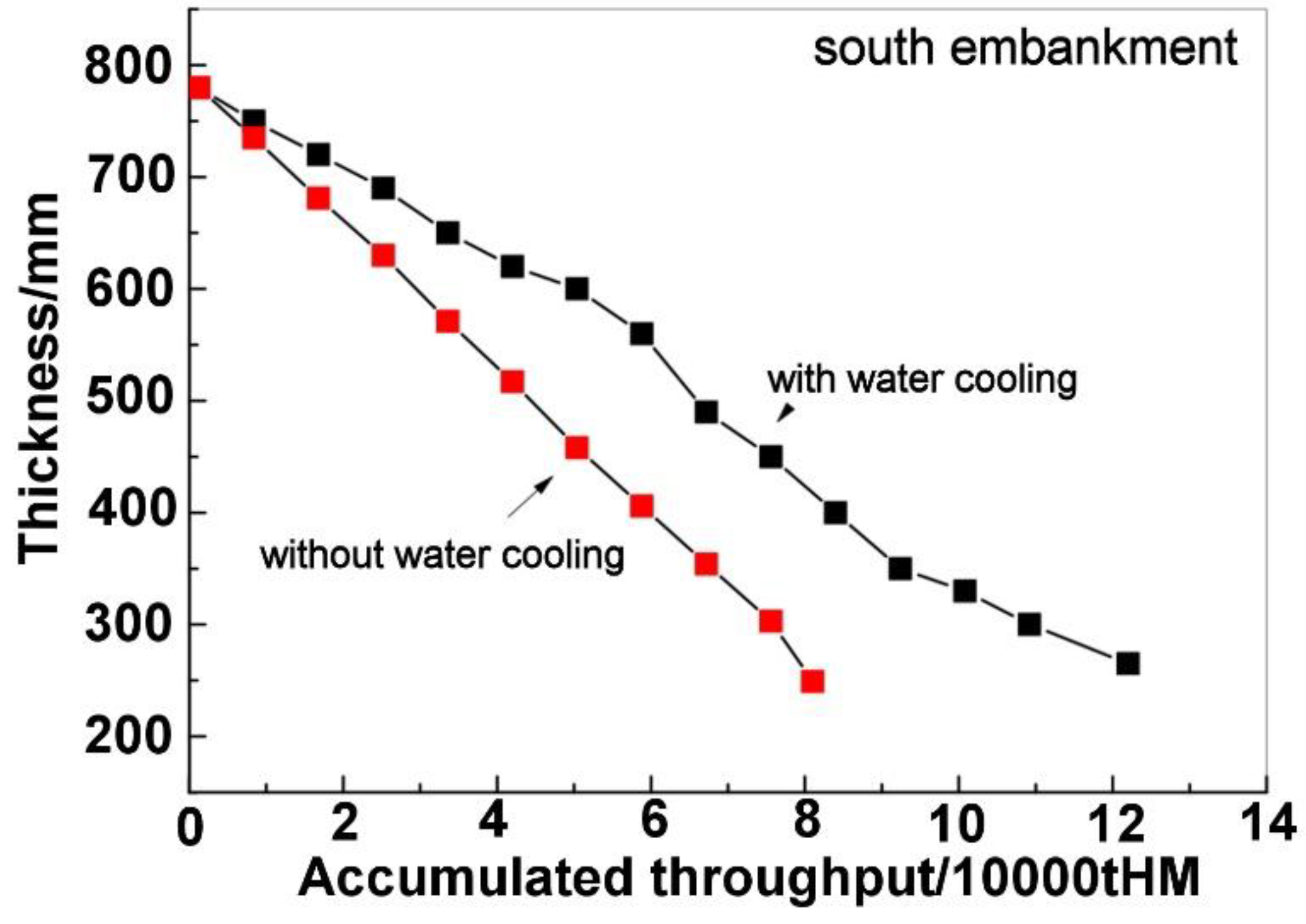
4.1. Results of Industrial Tests
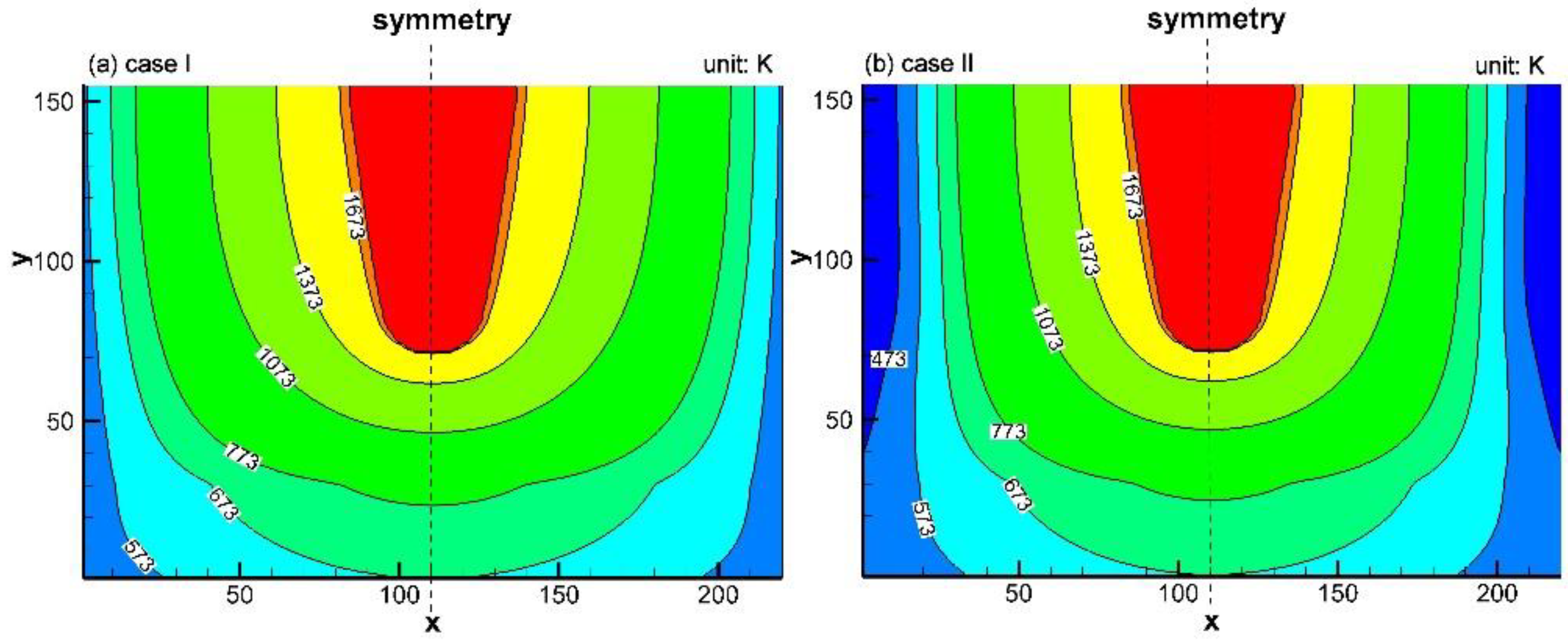
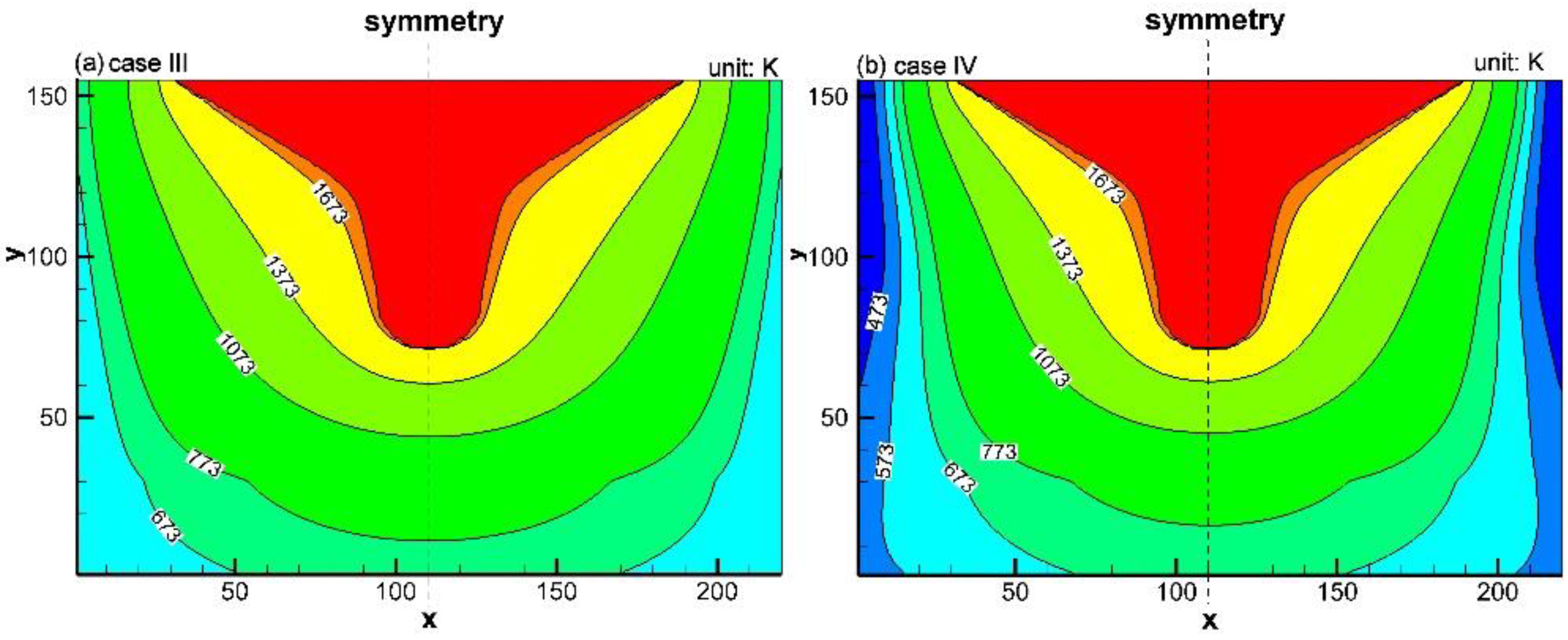
4.2. Effect of Water Cooling on Temperature Field in Trough Refractories
4.3. Mechanism
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The industrial tests showed that, after installing the water cooling device, the throughput of the main trough increased from 80,000 tons to 120,000 tons, and its unit campaign life increased from 66 days to 100 days.
- (2)
- The simulation results disclosed that the influence of the water cooling device on the temperature distribution in the refractory material of the trough gradually develops from the low-temperature zone to the high-temperature zone in a unit campaign cycle, inhibiting the expansion of the high-temperature zone in the working layer.
- (3)
- Theoretical analysis indicated that the water cooling device inhibited the dissolution of the castable and retarded the chemical erosion from molten slag and the atmosphere.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.; Ozturk, B.; Fruehan, R.J. Slag-metal separation in the blast furnace trough. ISIJ Int. 1998, 38, 43–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro de Oliveira, M.J.; Rodrigues, G.F.R.; Silva, I.A.; Peixoto, J.J.M.; Silva, C.A.D. Modeling of two-phase flow in blast furnace trough. Steel Res. Int. 2021, 92, 2000485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Chen, H.; Ge, Y.; Wei, H.; Li, Y.; Saxén, H.; Wang, B.; Yu, Y. Numerical analysis on erosion and optimization of a blast furnace main trough. Materials 2021, 14, 4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Evans, G.; Zulli, P.; Tanzil, F.; Lee, B. Flow characteristics in a blast furnace trough. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kou, M.; Yao, S.; Wu, S.; Zhou, H.; Xu, J. Effects of blast furnace main trough geometry on the slag-metal separation based on numerical simulation. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1800383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ajmani, S.K.; Pal, A.R. Optimal configuration of blast furnace slag runner to reduce fluid flow stresses at wall using mathematical modeling. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2010, 37, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prompt, N.; Ouedraogo, E. High-temperature mechanical characterization of an alumina refractory concrete for Blast Furnace main trough: Part I. General context. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 2859–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, E.; Prompt, N. High-temperature mechanical characterization of an alumina refractory concrete for Blast Furnace main trough: Part II. Material behavior. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 2867–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Khan, S.A.; Biswas, S.; Pal, A. Strategic steps towards longer and reliable blast furnace trough campaign–Tata Steel experience. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2010, 37, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, S.K.; Zhang, S.H.; Liu, X.F.; Zhu, L. Development on long service life design of blast furnace trough. Sichan Metall. 2009, 31, 56–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan, S.; Mazumdar, D.; Chakraborty, I.N.; Sinha, S.; Sarkar, R. Review and analysis of metallurgical processes in blast furnace main trough and trough performances. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2022, 75, 589–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thethwayo, B.M.; Steenkamp, J.D. A review of carbon-based refractory materials and their applications. J. S. Afr. I. Min. Metall. 2020, 120, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Fernández, S.; Pieiga, A.G.; Lausín-Gónzalez, C.; Quintela, P. Mathematical modeling and numerical simulation of the heat transfer in a trough of a blast furnace. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 137, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, P.; Pérez-Pérez, L.J.; Quintela, P. Numerical simulation of the transient heat transfer in a blast furnace main trough during its complete campaign cycle. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 173, 107349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Zhang, J.L.; Zuo, H.B.; Yang, T.J. Recent progress on long service life design of Chinese blast furnace hearth. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, A.B.; Zulli, P. Three-dimensional modeling of the wall heat transfer in the lower stack region of a blast furnace. ISIJ Int. 1997, 37, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qie, Y.N.; Zhang, S.H.; Lv, Q.; Zhang, L.H. Simulation on flow field and temperature field in water cooling tuyere of blast furnace. Adv. Mat. Res. 2013, 753, 2709–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.H.; Zeng, S.L.; Nong, W.J.; Chen, F.; Chen, Q.Z.; Ruan, F.X.; Huang, K.; Xie, Q.R. Research on condensing lining structure of large scale submerged-arc furnace for ferronickel production. Adv. Mat. Res. 2013, 815, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenkamp, J.D.; Reynolds, Q.G.; Erwee, M.W.; Swanepoel, S. Freeze-lining formation in submerged arc furnaces producing ferrochrome alloy in South Africa. In TMS 2019 148th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1161–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabandeh, E.; Ghaderi, M.; Afzalabadi, A.; Rouboa, A.; Salarifard, A. Parametric study of heat transfer in an electric arc furnace and cooling system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 123, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombeni, A.G.; Hajidavalloo, E.; Behbahani-Nejad, M. Transient simulation of conjugate heat transfer in the roof cooling panel of an electric arc furnace. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 98, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.L.; Kong, X.Q.; Chen, S.N. Computational Heat Transfer; University of Science and Technology of China Press: Hefei, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, P.R.; Nagomi, H.; Yagi, J. A mathematical model for blast furnace reaction analysis based on the four-fluid model. ISIJ Int. 1997, 37, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Hu, J. Thermodynamic Data Manual of Inorganics; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Sun, C.; Song, S.; Wang, Q. Influences of Al2O3 and TiO2 content on viscosity and structure of CaO–8%MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–TiO2–5%FeO blast furnace primary slag. Metals 2019, 9, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamalloa, M.; Ma, D.; Ta, U. Oxidation rates of industrial cokes with CO2 and air. ISIJ Int. 1995, 35, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Component | SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | MgO | MnO | S | FeO | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 32 | 37 | 13 | 8 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.62 | 1.86 |
| Component | SiC (98) | Corundum | Alumina Powder | Silica Fume | Cement (70) | Additive | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | Working layer | 35 | 47.5 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 2.5 |
| Permanent layer | 7 | 75.5 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 2.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Ding, F.; Tang, H. Prolonging Campaign Life of Blast Furnace Trough by Water Cooling. Materials 2023, 16, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16030891
Li Z, Wang H, Ding F, Tang H. Prolonging Campaign Life of Blast Furnace Trough by Water Cooling. Materials. 2023; 16(3):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16030891
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhiyuan, Haifei Wang, Fengshou Ding, and Huiqing Tang. 2023. "Prolonging Campaign Life of Blast Furnace Trough by Water Cooling" Materials 16, no. 3: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16030891
APA StyleLi, Z., Wang, H., Ding, F., & Tang, H. (2023). Prolonging Campaign Life of Blast Furnace Trough by Water Cooling. Materials, 16(3), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16030891






