Construction of Highly Conductive Cross-Linked Polybenzimidazole-Based Networks for High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
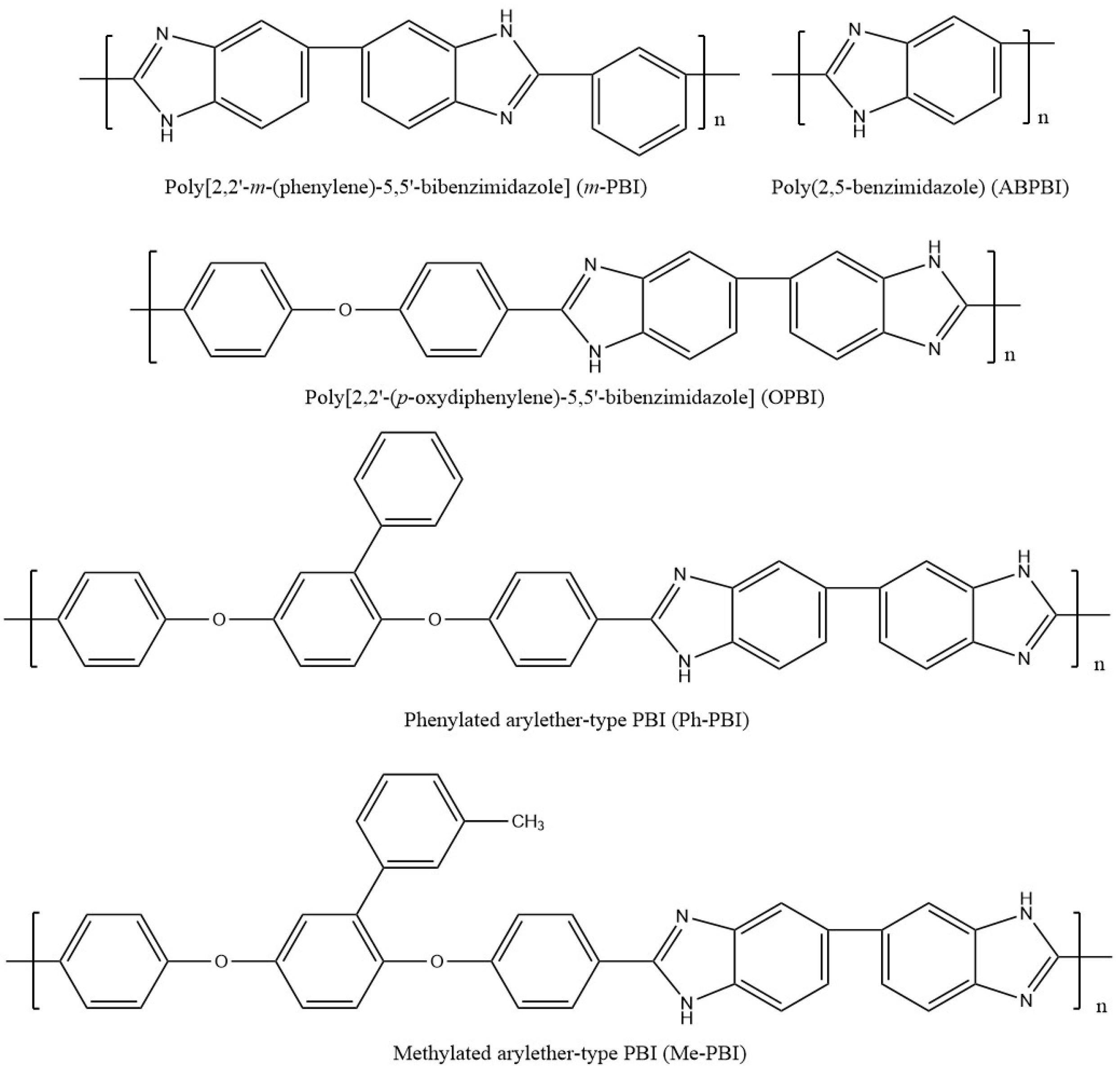
2. Polybenzimidazole-Based Membranes
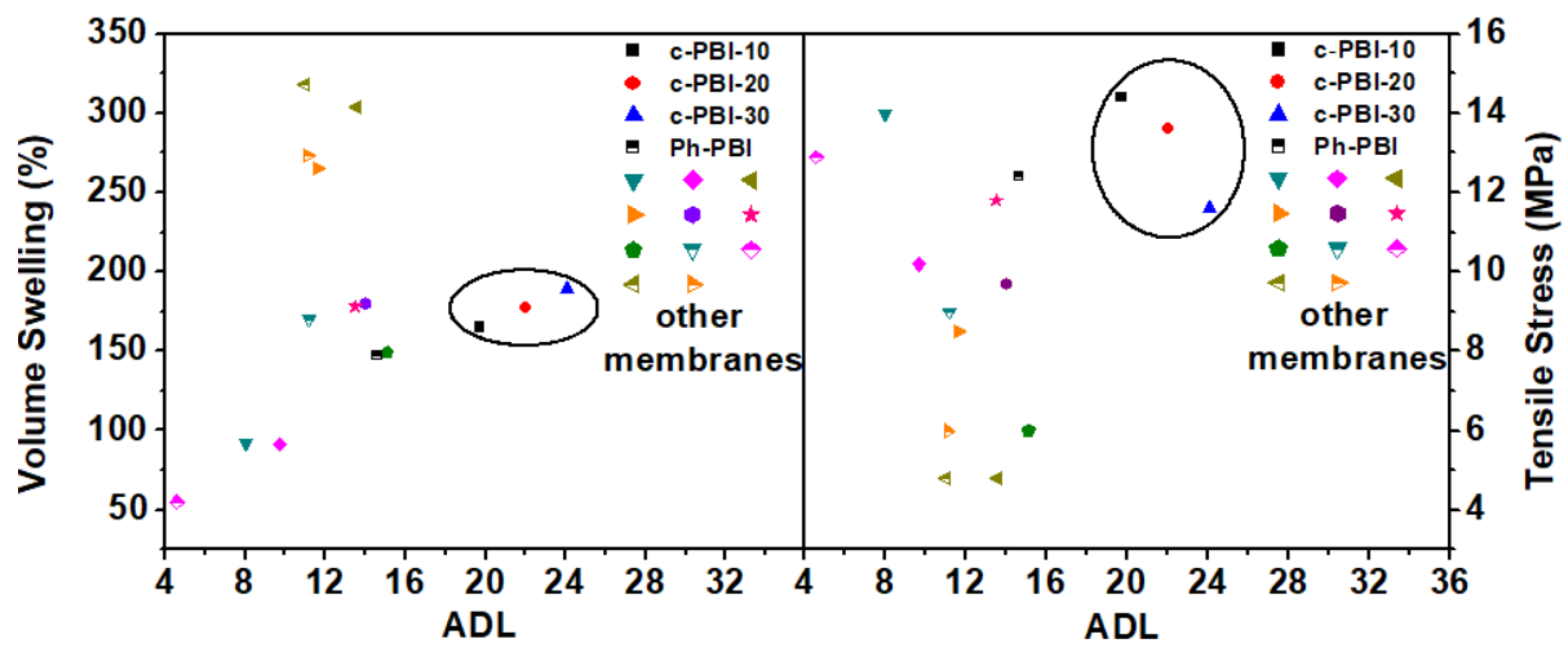
3. Cross-Linked Polybenzimidazole Membranes
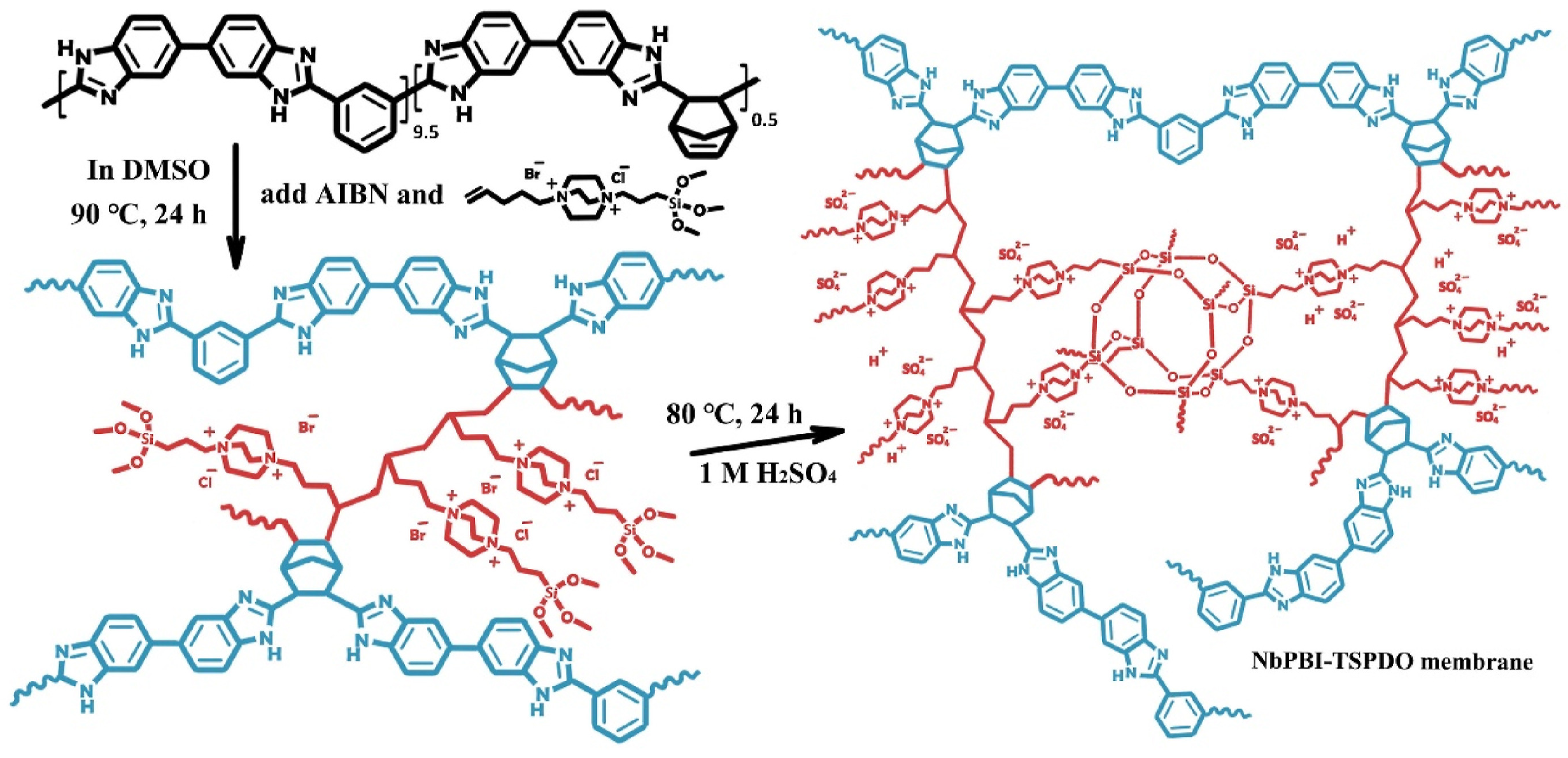
4. Cross-Linked Polybenzimidazole-Based Composite and Blend Membranes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krishnan, N.N.; Konovalova, A.; Aili, D.; Li, Q.; Park, H.S.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, H.-J.; Henkensmeier, D. Thermally crosslinked sulfonated polybenzimidazole membranes and their performance in high temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 588, 117218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Xuan, J.; Du, Q.; Bao, Z.; Xie, B.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, L.; Wang, H.; Hou, Z.; et al. Designing the next generation of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Nature 2021, 595, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araya, S.S.; Zhou, F.; Liso, V.; Sahlin, S.L.; Vang, J.R.; Thomas, S.; Gao, X.; Jeppesen, C.; Kaer, S.K. A comprehensive review of PBI-based high temperature PEM fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 21310–21344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalathil, A.; Raghavan, A.; Kandasubramanian, B. Polymer Fuel Cell Based on Polybenzimidazole Membrane: A Review. Polym-Plast. Tech. Mat. 2019, 58, 465–497. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, T.K.; Singh, J.; Majhi, J.; Ahuja, A.; Maiti, S.; Dixit, P.; Bhushan, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Chattopadhyay, S. Advances in polybenzimidazole based membranes for fuel cell applications that overcome Nafion membranes constraints. Polymer 2022, 255, 125151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Peng, J.; Shi, C.; Li, T.; Yang, J.; Shan, C.; Hu, W.; Liu, B. Construction of highly conductive PBI-based alloy membranes by incorporating PIMs with optimized molecular weights for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 659, 120790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Xiao, L.; Benicewicz, B.C. Durability studies of PBI-based high temperature PEMFCs. Fuel Cells 2008, 8, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, F.; Batool, R.; Gill, R.; Rehman, Z.U.; Majeed, H.; Ahmad, A.; Shafiq, M.; Dastan, D.; Abbas, G.; Jacob, K. Synthesis and electrochemical investigations of ABPBI grafted montmorillonite based polymer electrolyte membranes for PEMFC applications. Renew. Energ. 2021, 164, 709–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.L.; Wainright, J.S.; Litt, M.H.; Savinell, R.F. Conductivity of PBI membranes for high-temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, A8–A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheddie, D.; Munroe, N. Mathematical model of a PEMFC using a PBI membrane. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 1490–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.O.; Kwon, K.; Cho, M.D.; Hong, S.G.; Kim, T.Y.; Yoo, D.Y. Role of Binders in High Temperature PEMFC Electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, B675–B681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Simonsen, S.C.; Norby, T.; Chatzitakis, A. Composite Membranes for High Temperature PEM Fuel Cells and Electrolysers: A Critical Review. Membranes 2019, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quartarone, E.; Angioni, S.; Mustarelli, P. Polymer and Composite Membranes for Proton-Conducting, High-Temperature Fuel Cells: A Critical Review. Materials 2017, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yusoff, Y.N.; Loh, K.S.; Wong, W.Y.; Daud, W.R.W.; Lee, T.K. Sulfonated graphene oxide as an inorganic filler in promoting the properties of a polybenzimidazole membrane as a high temperature proton exchange membrane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 27510–27526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopalan, G.; Chang, K.; Nijoka, J.; Livingston, S.; Geise, G.M.; Arges, C.G. Stable and Highly Conductive Polycation-Polybenzimidazole Membrane Blends for Intermediate Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. ACS. Appl. Energ. Mater. 2020, 3, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, J.; Olvera-Mancilla, J.; Alexandrova, L.; del Castillo, L.F.; Compan, V. Recent Progress in the Development of Composite Membranes Based on Polybenzimidazole for High Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seland, F.; Berning, T.; Borresen, B.; Tunold, R. Improving the performance of high-temperature PEM fuel cells based on PBI electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2006, 160, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Kuila, T.; Thi Xuan Lien, N.; Kim, N.H.; Lau, K.-T.; Lee, J.H. Polymer membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell: Recent advances and challenges. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 813–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jung, J.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, H.-J.; Cho, E.A.; Henkensmeier, D.; Kim, J.Y.; Yoo, S.J.; et al. Effect of Membrane Electrode Assembly Fabrication Method on the Single Cell Performances of Polybenzimidazole-Based High Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Macromol. Res. 2014, 22, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liang, M.; Cao, K.; Liu, Z.; Wang, P.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B. Fabrication of Cross-Linked Anion Exchange Membranes Using a Pillar 5 arene Bearing Multiple Alkyl Bromide Head Groups as Cross-Linker. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liang, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, P.; Shi, C.; Hu, W.; Liu, B. Poly(arylene ether sulfone) crosslinked networks with pillar 5 arene units grafted by multiple long-chain quaternary ammonium salts for anion exchange membranes. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Peng, J.; Cao, K.; Shan, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, P.; Hu, W.; Liu, B. Multiply quaternized poly(phenylene oxide)s bearing beta-cyclodextrin pendants as “assisting moiety” for high-performance anion exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 660, 120881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, H.; Lee, H.; Jung, N.; Bae, B.; Shin, D. Electrochemical Method for Measurement of Hydroxide Ion Conductivity and CO2 Poisoning Behavior of Anion Exchange Membrane. J. Korean Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 25, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Z.; Liang, M.; Wang, P.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B. Highly conductive and stable anion-exchange membranes based on crosslinked poly(arylene ether sulfone)-block-poly(phenylene oxide) Networks. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Peng, J.; Shan, C.; Liu, Z.; Liang, M.; Wang, L.; Hu, W.; Liu, B. Beneficial use of hyperbranched polymer in cross-linked anion exchange membranes for fuel cells. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 24395–24407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Song, Y.; Hu, W.; Li, X.; Jiang, Z.; Guiver, M.D.; Liu, B. SPAEK-based binary blends and ternary composites as proton exchange membranes for DMFCs. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Liu, C.; Ren, D.; Jing, L.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B. Fluorinated/non-fluorinated sulfonated polynaphthalimides as proton exchange membranes. Macromol. Res. 2013, 21, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cao, X.; Liang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Qi, Y.; Hu, W.; Li, K.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B. Sulfonated polyimides and their polysilsesquioxane hybrid membranes for fuel cells. Solid State Ionics 2014, 258, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, P.; Hu, W.; Liu, B. Preparation and Properties of Hybrid Silane-crosslinked Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether ketone)s as Proton Exchange Membranes. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2019, 35, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jin, Y.; Liang, Q.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B. Novel sulfonated polyimides containing multiple cyano groups for polymer electrolyte membranes. J. Power Sources 2013, 238, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, X.; Shi, C.; Liu, B.; Cao, K.; Shan, C.; Hu, W.; Liu, B. Fabrication of PBI/SPOSS hybrid high-temperature proton exchange membranes using SPAEK as compatibilizer. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Peng, J.; Li, H.; Shi, C.; Wang, P.; Liu, B. High-temperature Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Cross-linked Polybenzimidazole/hyperbranched-polymer Blends. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2021, 42, 2049–2055. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, M.; Wang, P.; Li, H.; Li, T.; Cao, K.; Peng, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, B. Preparation of High-temperature Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Semi-interpenetrating Polymer Networks. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2020, 41, 2845–2850. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, P.; Liu, Z.; Peng, J.; Shi, C.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B. Arylether-type polybenzimidazoles bearing benzimidazolyl pendants for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2018, 393, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Peng, J.; Hu, W.; Liu, B. Toward enhanced conductivity of high-temperature proton exchange membranes: Development of novel PIM-1 reinforced PBI alloy membranes. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 6491–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiti, P.; Minutoli, M.; Hocevar, S. Membranes based on phosphotungstic acid and polybenzimidazole for fuel cell application. J. Power Sources 2000, 90, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, S.; Higier, A.; Liu, H. The effects of excess phosphoric acid in a Polybenzimidazole-based high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, S.; Aravi, I.; Sanli, L.I.; Menceloglu, Y.Z.; Ozden-Yenigun, E. Fabrication and optimization of proton conductive polybenzimidazole electrospun nanofiber membranes. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Ven, E.; Chairuna, A.; Merle, G.; Benito, S.P.; Borneman, Z.; Nijmeijer, K. Ionic liquid doped polybenzimidazole membranes for high temperature Proton Exchange Membrane fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2013, 222, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Kim, D.-H.; Ahn, M.-K.; Min, C.-M.; Lee, S.-B.; Byun, J.; Pak, C.; Lee, J.-S. Phosphoric acid doped triazole-containing cross-linked polymer electrolytes with enhanced stability for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainright, J.S.; Wang, J.T.; Weng, D.; Savinell, R.F.; Litt, M. Acid-Doped Polybenzimidazoles: A New Polymer Electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, L121–L123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jensen, J.O.; Savinell, R.F.; Bjerrum, N.J. High temperature proton exchange membranes based on polybenzimidazoles for fuel cells. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 449–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Highly Conductive Polybenzimidazole Membranes at Low Phosphoric Acid Uptake with Excellent Fuel Cell Performances by Constructing Long-Range Continuous Proton Transport Channels Using a Metal-Organic Framework (UIO-66). ACS. Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 41350–41358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escorihuela, J.; Garcia-Bernabe, A.; Montero, A.; Sahuquillo, O.; Gimenez, E.; Compan, V. Ionic Liquid Composite Polybenzimidazol Membranes for High Temperature PEMFC Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hooshyari, K.; Javanbakht, M.; Adibi, M. Novel composite membranes based on dicationic ionic liquid and polybenzimidazole mixtures as strategy for enhancing thermal and electrochemical properties of proton exchange membrane fuel cells applications at high temperature. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 10870–10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, R.; Wen, Y.; Ma, Z.-F.; Wilkinson, D.P.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; Song, S.; Zhang, J. High temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells: Progress in advanced materials and key technologies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 1138–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wannek, C.; Konradi, I.; Mergel, J.; Lehnert, W. Redistribution of phosphoric acid in membrane electrode assemblies for high-temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 9479–9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, J.; Canizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Ubeda, D.; Javier Pinar, F. A novel titanium PBI-based composite membrane for high temperature PEMFCs. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshyari, K.; Rezania, H.; Vatanpour, V.; Salarizadeh, P.; Askari, M.B.; Beydaghi, H.; Enhessari, M. High temperature membranes based on PBI/sulfonated polyimide and doped-perovskite nanoparticles for PEM fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Seo, K.; Ghorpade, R.V.; Nam, K.-H.; Han, H. High temperature anhydrous proton exchange membranes based on chemically-functionalized titanium/polybenzimidazole composites for fuel cells. Mater. Lett. 2020, 263, 127167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Che, Q.; Sun, B. The acid doping behavior of polybenzimidazole membranes in phosphoric acid for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Fiber. Polym. 2008, 9, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Geng, K.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; You, W.; Yan, F.; Guiver, M.D.; Li, N. Fuel cells with an operational range of −20 °C to 200 °C enabled by phosphoric acid-doped intrinsically ultramicroporous membranes. Nat. Energy 2022, 7, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Tian, X.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Mao, T.; Liu, G. Ethyl phosphoric acid grafted amino-modified polybenzimidazole with improved long-term stability for high-temperature proton exchange membrane applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 3176–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, R.; Kumar, P.; Unnikrishnan, L.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Current Scenario of Poly (2,5-Benzimidazole) (ABPBI) as Prospective PEM for Application in HT-PEMFC. Polym. Rev. 2020, 60, 267–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.F.; He, R.H.; Jensen, J.O.; Bjerrum, N.J. Approaches and recent development of polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cells operating above 100 °C. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 4896–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berber, M.R.; Nakashima, N. Bipyridine-based polybenzimidazole membranes with outstanding hydrogen fuel cell performance at high temperature and non-humidifying conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, J.A.; Benicewicz, B.C. Sulfonated Polybenzimidazoles for High Temperature PEM Fuel Cells. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6706–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, H.; Shen, Y.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B.; Guiver, M.D. Dimensionally-stable phosphoric acid-doped polybenzimidazoles for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2016, 336, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Hu, M.; Liu, D.; Xie, H.; Xiang, X.; Wang, L. Synthesis and properties of highly branched polybenzimidazoles as proton exchange membranes for high-temperature fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 4814–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Pan, C.; Jensen, J.O.; Noye, P.; Bjerrum, N.J. Cross-linked polybenzimidazole membranes for fuel cells. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Zhu, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lew, C.M.; Na, H. Cross-linked polybenzimidazole with enhanced stability for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2187–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerres, J.; Atanasov, V. Cross-linked PBI-based high-temperature membranes: Stability, conductivity and fuel cell performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 14723–14735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, Y.; Ozkan, N.; Devrim, Y. Fabrication and Characterization of Cross-linked Polybenzimidazole Based Membranes for High Temperature PEM Fuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 245, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossiander, T.; Perchthaler, M.; Heinzl, C.; Scheu, C. Influence of thermal post-curing on the degradation of a cross-linked polybenzimidazole-based membrane for high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2014, 267, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, Z.; Peng, J.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B.; Guiver, M.D. Highly Conductive and Mechanically Stable Imidazole-Rich Cross-Linked Networks for High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, T.; Neelakandan, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y. Cross-linked polybenzimidazoles containing hyperbranched cross-linkers and quaternary ammoniums as high-temperature proton exchange membranes: Enhanced stability and conductivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 593, 117435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Yong, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liang, D.; Wang, Z. Novel double cross-linked membrane based on poly (ionic liquid) and polybenzimidazole for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2021, 515, 230637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, G.; Cui, Y.; Liang, D.; Wang, X.; Yong, Z.; Wang, Z. Multifunctional poly(ionic liquid)s cross-linked polybenzimidazole membrane with excellent long-term stability for high temperature-proton exchange membranes fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2021, 494, 229732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Ni, H.; Wang, Z. Benzimidazole grafted polybenzimidazole cross-linked membranes with excellent PA stability for high-temperature proton exchange membrane applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 465, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Peng, J.; Yin, B.; Fu, X.; Wang, L.; Luo, J.-L.; Peng, X. Phosphoric acid-doped polybenzimidazole with a leaf-like three-layer porous structure as a high-temperature proton exchange membrane for fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 26345–26353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Mao, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z. Cross-Linkable Polymeric Ionic Liquid Improve Phosphoric Acid Retention and Long-Term Conductivity Stability in Polybenzimidazole Based PEMs. ACS. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 16352–16362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Kim, T.-H.; Ko, T.; Lee, J.-C. Cross-linked poly(2,5-benzimidazole) consisting of wholly aromatic groups for high-temperature PEM fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 373, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harilal; Nayak, R.; Ghosh, P.C.; Jana, T. Cross-Linked Polybenzimidazole Membrane for PEM Fuel Cells. ACS. Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 3161–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Fu, X.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Peng, X. Constructing novel cross-linked polybenzimidazole network for high-performance high-temperature proton exchange membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 643, 120037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Mao, T.; Wang, Z. The impact of poly (ionic liquid) on the phosphoric acid stability of polybenzimidazole-base HT-PEMs. Renew. Energ. 2021, 163, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, F.; Chuluunbandi, K.; Freiberg, A.T.S.; Kormanyos, A.; Sit, F.; Cherevko, S.; Kerres, J.; Thiele, S.; Bohm, T. Performance of Quaternized Polybenzimidazole-Cross-Linked Poly(vinylbenzyl chloride) Membranes in HT-PEMFCs. ACS. Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 56584–56596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, F.; Zhou, L.L.; Yin, B.; Wang, P.; Wang, L. Achieving high power density and excellent durability for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells based on crosslinked branched polybenzimidazole and metal-organic frameworks. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 630, 119288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Z.; Lv, Y.; Pei, H.; Sun, P.; Zhang, L.; Cui, W.; Yin, X.; Hui, H. Monolithic Macromolecule Membrane Based on Polybenzimidazole: Achieving High Proton Conductivity and Low Fuel Permeability through Multiple Cross-Linking. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 2021, 4, 8969–8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Mao, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z. Novel cross-linked membranes based on polybenzimidazole and polymeric ionic liquid with improved proton conductivity for HT-PEMFC applications. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 95, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-W.; Park, J.O.; Pak, C.; Choi, K.H.; Lee, J.-C.; Chang, H. Design and Synthesis of Cross-Linked Copolymer Membranes Based on Poly(benzoxazine) and Polybenzimidazole and Their Application to an Electrolyte Membrane for a High-Temperature PEM Fuel Cell. Polymers 2013, 5, 77–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, P.; Li, Z.; Guo, H.; Pei, H.; Yin, X. High performance polymer electrolyte membrane with efficient proton pathway over a wide humidity range and effective cross-linking network. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 161, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Yin, X. Performance enhancement of polybenzimidazole based high temperature proton exchange membranes with multifunctional crosslinker and highly sulfonated polyaniline. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Tian, X.; Chen, H.; Mao, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z. Cage-like cross-linked membranes with excellent ionic liquid retention and elevated proton conductivity for HT-PEMFCs. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 283, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Sun, P.; Pei, H.; Yin, X. Preparation and Properties of Covalently Crosslinked Polybenzimidazole High Temperature Proton Exchange Membranes Doped with High Sulfonated Polyphosphazene. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 104517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, Z.; Peng, J.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, B. Construction of High-Performance, High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membranes through Incorporating SiO2 Nanoparticles into Novel Cross-linked Polybenzimidazole Networks. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 30735–30746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Membrane | Fuel Cell Type | Test Temperature (C) | Proton Conductivity (S·cm) | Peak Power Density (mW·cm) | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES-P5-1.2 [20] | AEMFC | 20–80 | 0.053 (80 C) | 135 (60 C) |  |
| PES-P5-12 [21] | AEMFC | 20–80 | 0.093 (80 C) | 105 (60 C) | 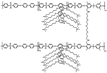 |
| PPO-30-15CD [22] | AEMFC | 20–80 | 0.099 (80 C) | 154 (60 C) | 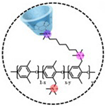 |
| Orion TM1 [23] | AEMFC | 20–80 | 0.125 (50 C) | - | 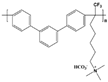 |
| c-PES-12.8-PPO-20 [24] | AEMFC | 20–80 | 0.126 (80 C) | - | 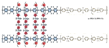 |
| PPO-HVBC-100 [25] | AEMFC | 25–80 | 0.136 (80 C) | 71 (60 C) | 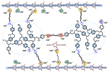 |
| PAM/SPAEK/POSS [26] | LT-PEMFC | 20–80 | 0.031 (80 C) | - | 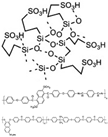 |
| CF3-SPI-0 [27] | LT-PEMFC | 20–100 | 0.085 (80 C) | - |  |
| SP-SPI/POSS [28] | LT-PEMFC | 20–100 | 0.144 (100 C) | - |  |
| SC-SPAEK/TiO2-4 [29] | LT-PEMFC | 20–100 | 0.147 (100 C) | - |  |
| CN-SPI-4 [30] | LT-PEMFC | 20–100 | 0.149 (100 C) | - |  |
| Nafion 117 [30] | LT-PEMFC | 20–100 | 0.156 (100 C) | - | 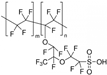 |
| PBI/SPAEK-SPOSS-1% [31] | HT-PEMFC | 100–200 | 0.126 (200 C) | 300 (160 C) | 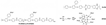 |
| OPBI/H-VBC-QA-1 [32] | HT-PEMFC | 100–200 | 0.152 (200 C) | - | 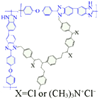 |
| PBI/Allyl-SPAEK-10% [33] | HT-PEMFC | 100–200 | 0.206 (200 C) | - | 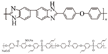 |
| g-PBI-20 [34] | HT-PEMFC | 100–200 | 0.212 (200 C) | 443 (160 C) |  |
| OPBI [35] | HT-PEMFC | 100–200 | 0.25 (200 C) | 161 (160 C) | 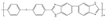 |
| OPBI/PIM-1(10%) [35] | HT-PEMFC | 100–200 | 0.313 (200 C) | 438 (160 C) |  |
| Membrane | Cross-Linking Method | Proton Conductivity (S·cm) | Peak Power Density (mW·cm) | Chemical Structure of PBI and Cross-Linker |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QOPBI-15 [66] | N-substitution reactions | 0.049 (160 C) | 260 (160 C) | 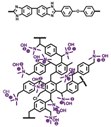 |
| NbPBI-TSPDO30 [67] | Acid-base interactions | 0.061 (170 C) | 159 (120 C) | 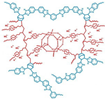 |
| NbPBI-MPIm [68] | Acid-base interactions | 0.074 (170 C) | 375 (160 C) |  |
| CPBIm-5 [69] | N-substitution reactions | 0.092 (180 C) | - | 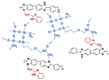 |
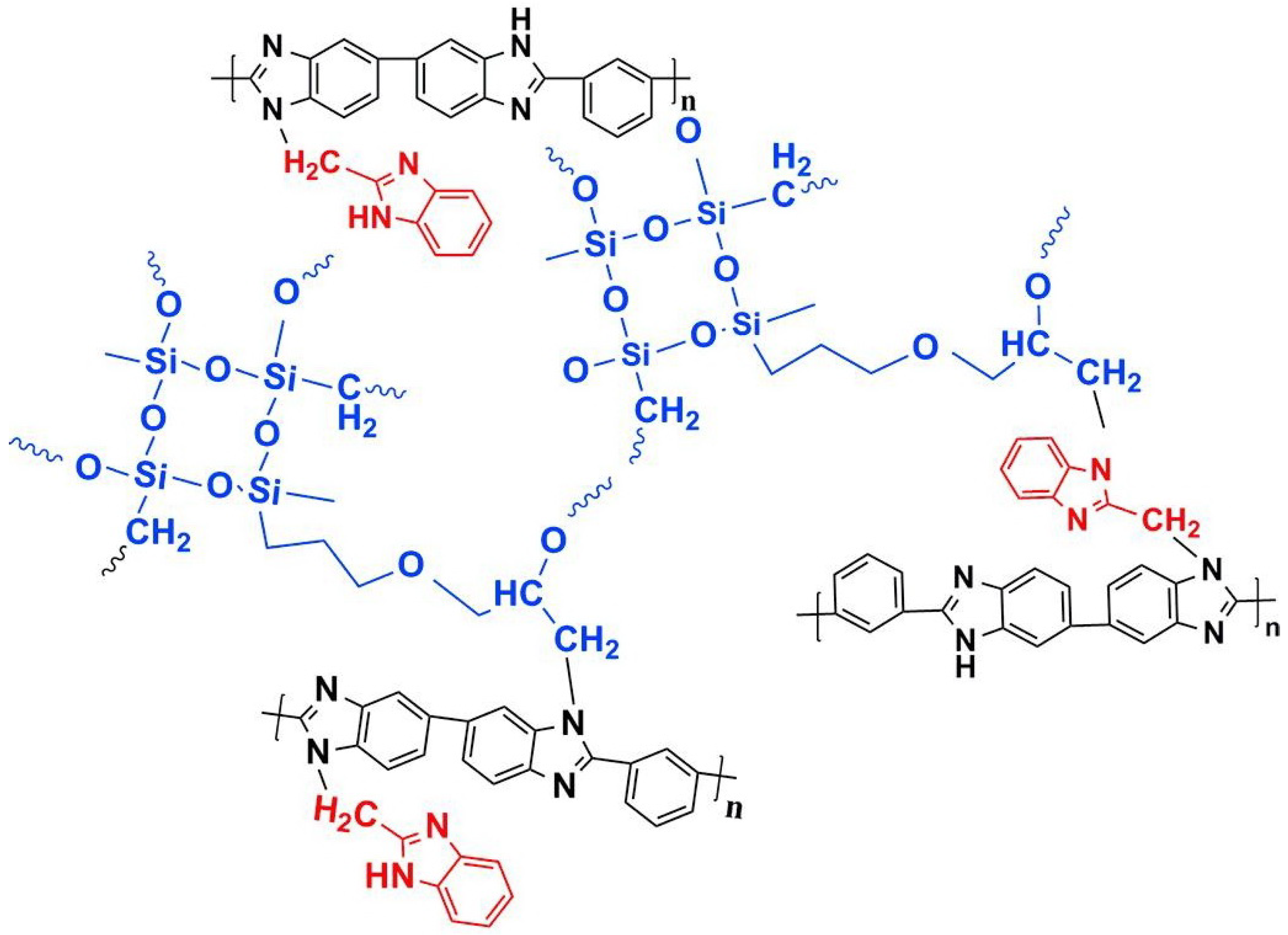
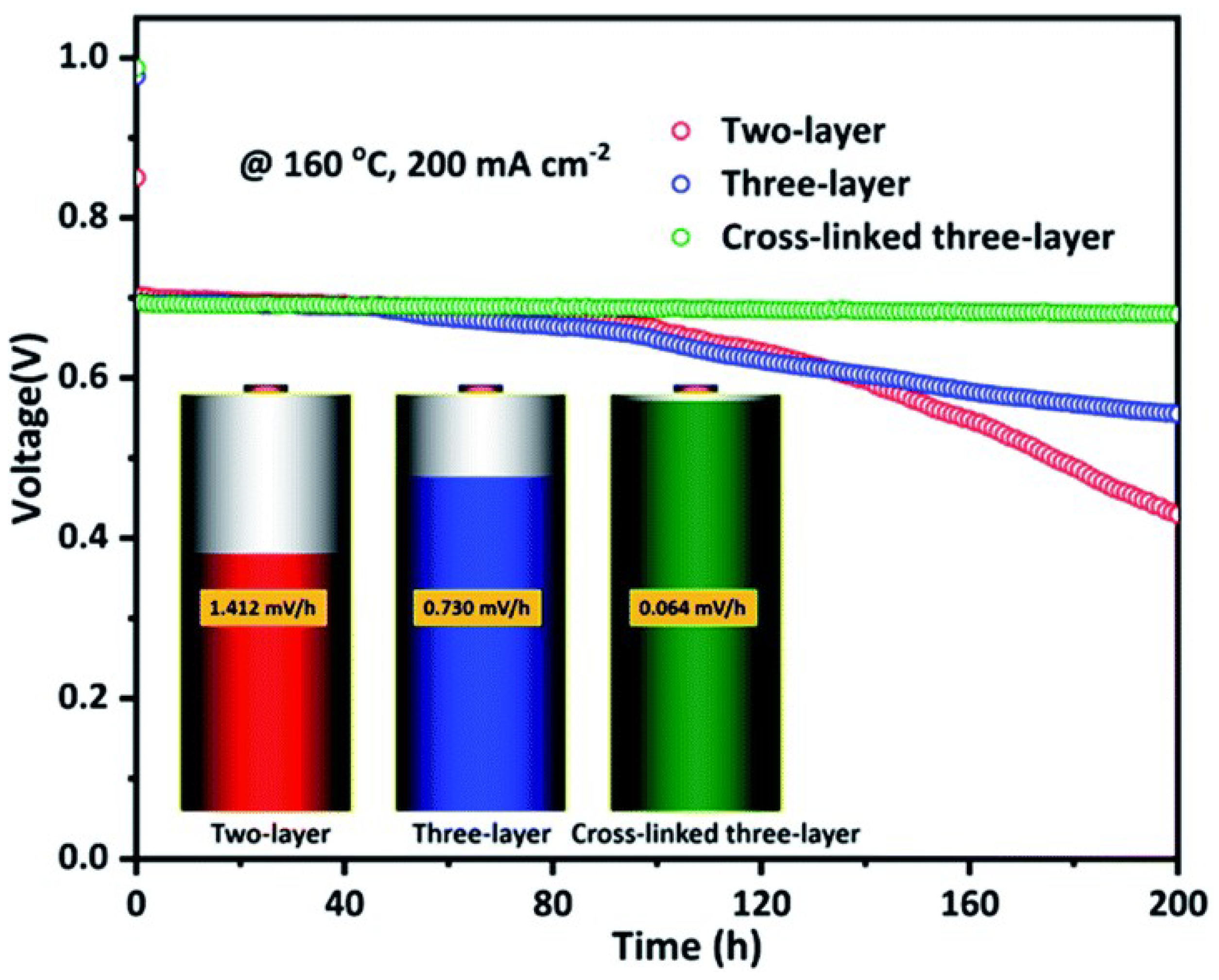
| Cross-linked three-layer [70] | N-substitution reactions | 0.101 (200 C) | 605 (160 C) | 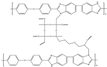 |
| 6FPBI-cPIL20 [71] | N-substitution reactions | 0.106 (170 C) | - |  |
| C-ABPBI-50 [72] | Covalent cross-linking | 0.12 (150 C) | - | 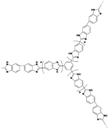 |
| P1 [73] | N-substitution reactions | 0.123 (180 C) | 289 (160 C) |  |
| PBI/DBpX [63] | N-substitution reactions | 0.151 (180 C) | 106 (165 C) | 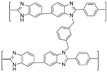 |
| 1%-OPBI [74] | N-substitution reactions | 0.168 (160 C) | 598 (160 C) | 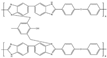 |
| c-PBI-30 [65] | N-substitution reactions | 0.253 (200 C) | 533 (160 C) | 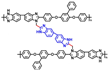 |
| Membrane | Cross-Linking Method | Proton Conductivity (S·cm) | Peak Power Density (mW·cm) | Chemical Structure of PBI and Cross-Linker |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60-40-Q [76] | Covalent and ionic cross-linking | 0.092 (180 C) | 530 (180 C) | 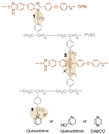 |
| CBOPBI@MOF 40% [77] | N-substitution reactions | 0.1 (160 C) | 607 (160 C) | 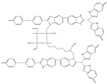 |
| mPBI-CMPEI(20)-TTPSA(30) [78] | N-substitution reactions and covalent cross-linking | 0.113 (180 C) | - |  |
| cPBI-BF4-40 [79] | N-substitution reactions | 0.117 (170 C) | - | 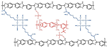 |
| P(pBUa-co-BI)-65 [80] | Covalent cross-linking | 0.121 (150 C) | 410 (150 C) | 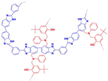 |
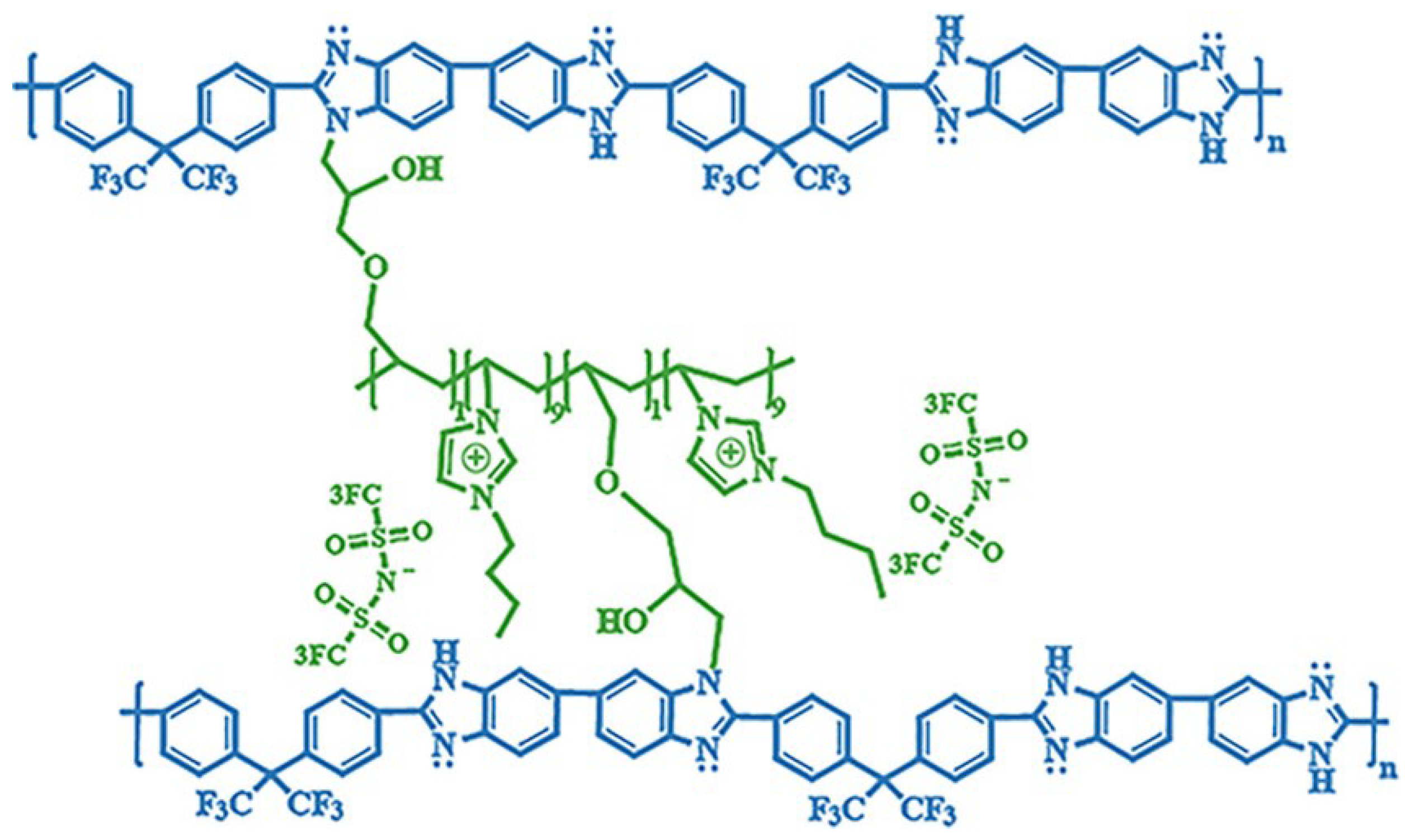
| mPBI-TGDDM (5%)/ZrSP (50%) [81] | N-substitution reactions and covalent cross-linking | 0.127 (180 C) | - | 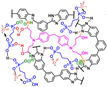 |
| PBI-TGIC(5%)/SPAN(50%) [82] | N-substitution reactions | 0.13 (180 C) | - |  |
| cPBI-IL 8 [83] | Covalent cross-linking | 0.133 (160 C) | - | 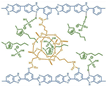 |
| mPBI-TGIC (5%)/SPOP (50%) [84] | N-substitution reactions | 0.143 (180 C) | - |  |
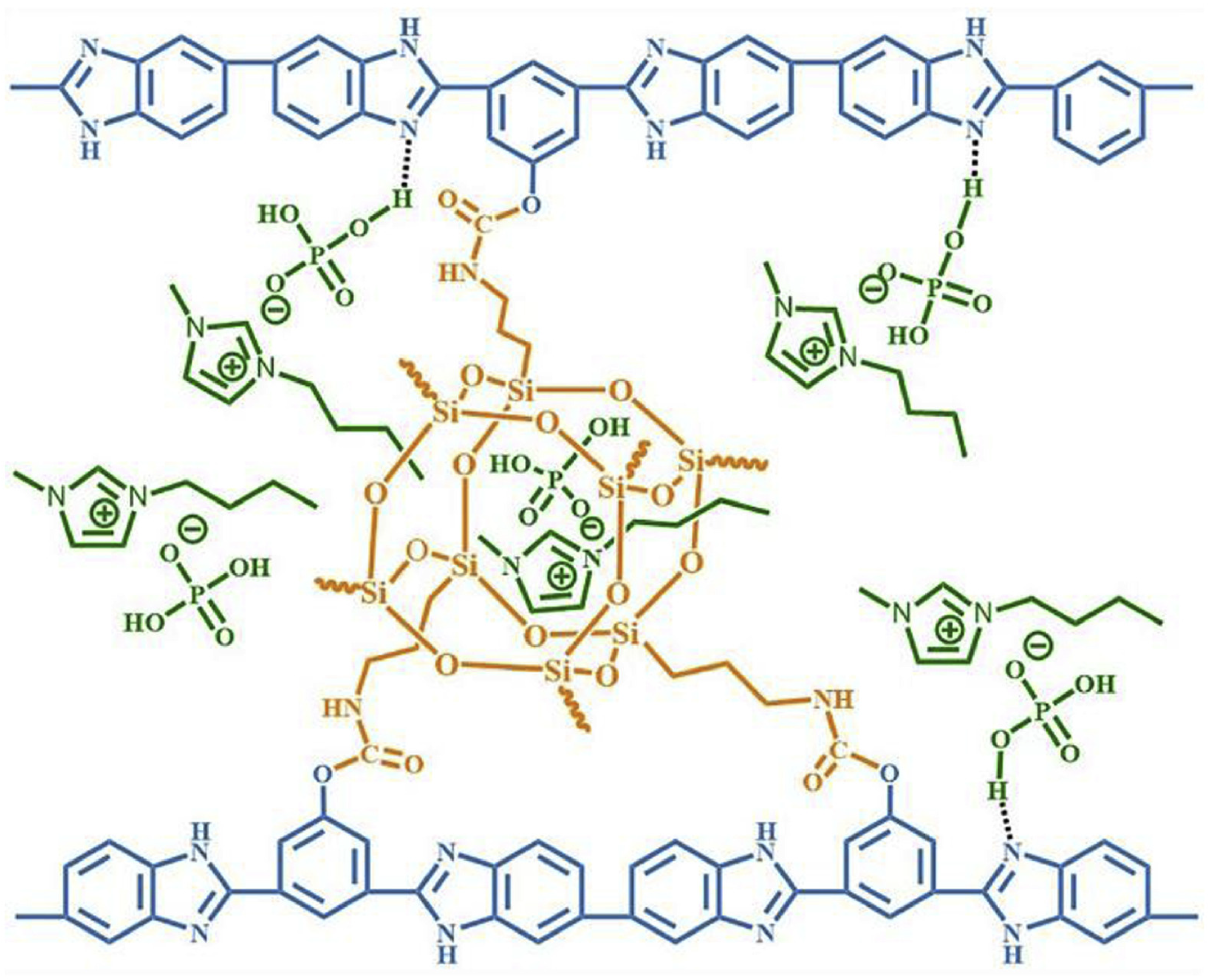
| c-PBI-20-SiO2-2 [85] | N-substitution reactions | 0.244 (200 C) | 497 (160 C) | 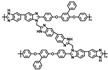 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Yang, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Hu, W.; Liu, B. Construction of Highly Conductive Cross-Linked Polybenzimidazole-Based Networks for High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Materials 2023, 16, 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051932
Li T, Yang J, Chen Q, Zhang H, Wang P, Hu W, Liu B. Construction of Highly Conductive Cross-Linked Polybenzimidazole-Based Networks for High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Materials. 2023; 16(5):1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051932
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tianyang, Jiayu Yang, Qingxin Chen, Hui Zhang, Peng Wang, Wei Hu, and Baijun Liu. 2023. "Construction of Highly Conductive Cross-Linked Polybenzimidazole-Based Networks for High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells" Materials 16, no. 5: 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051932
APA StyleLi, T., Yang, J., Chen, Q., Zhang, H., Wang, P., Hu, W., & Liu, B. (2023). Construction of Highly Conductive Cross-Linked Polybenzimidazole-Based Networks for High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Materials, 16(5), 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051932





