Influences of Ultrafine Ti(C, N) on the Sintering Process and Mechanical Properties of Micron Ti(C, N)-Based Cermets
Abstract
1. Introduction
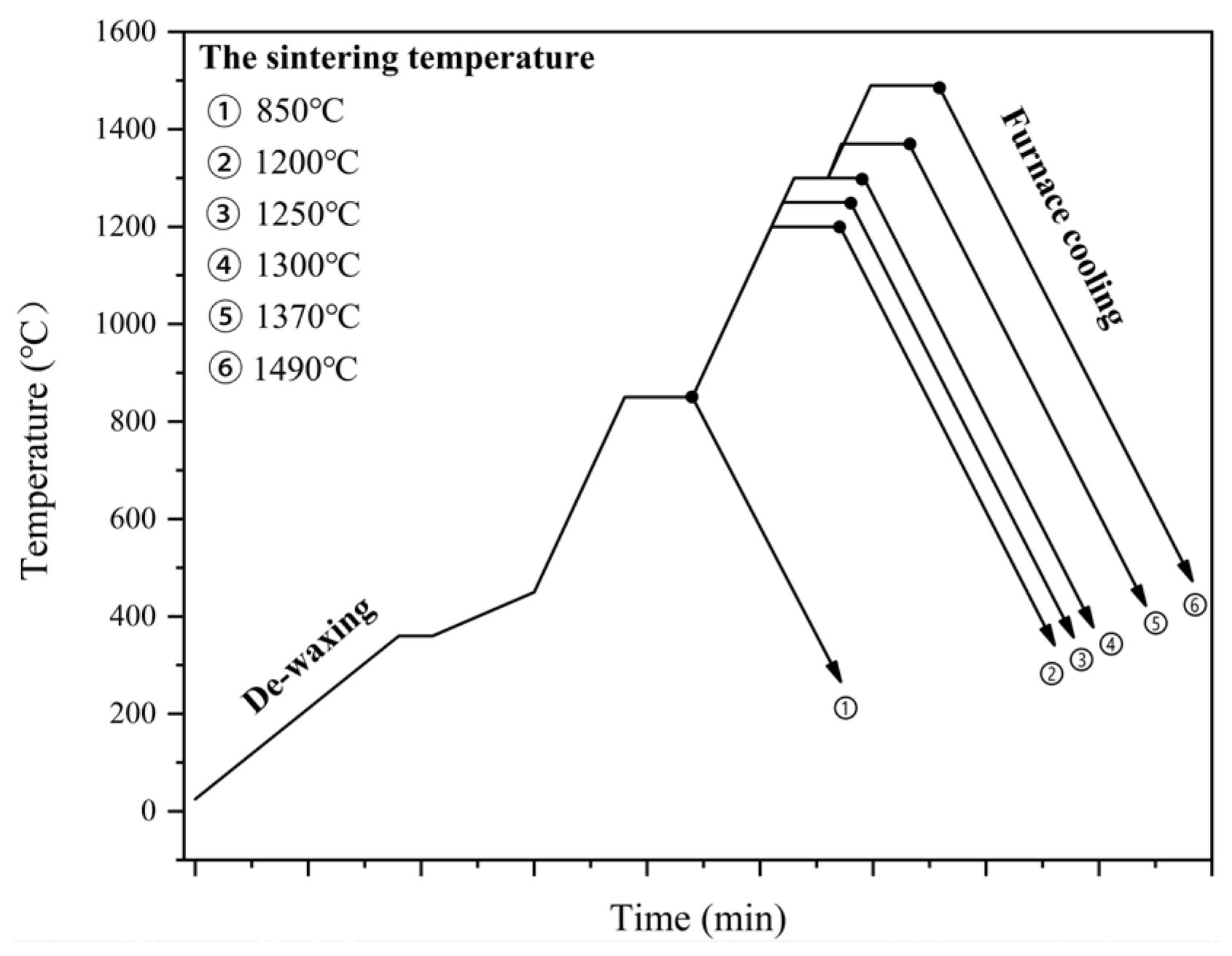
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
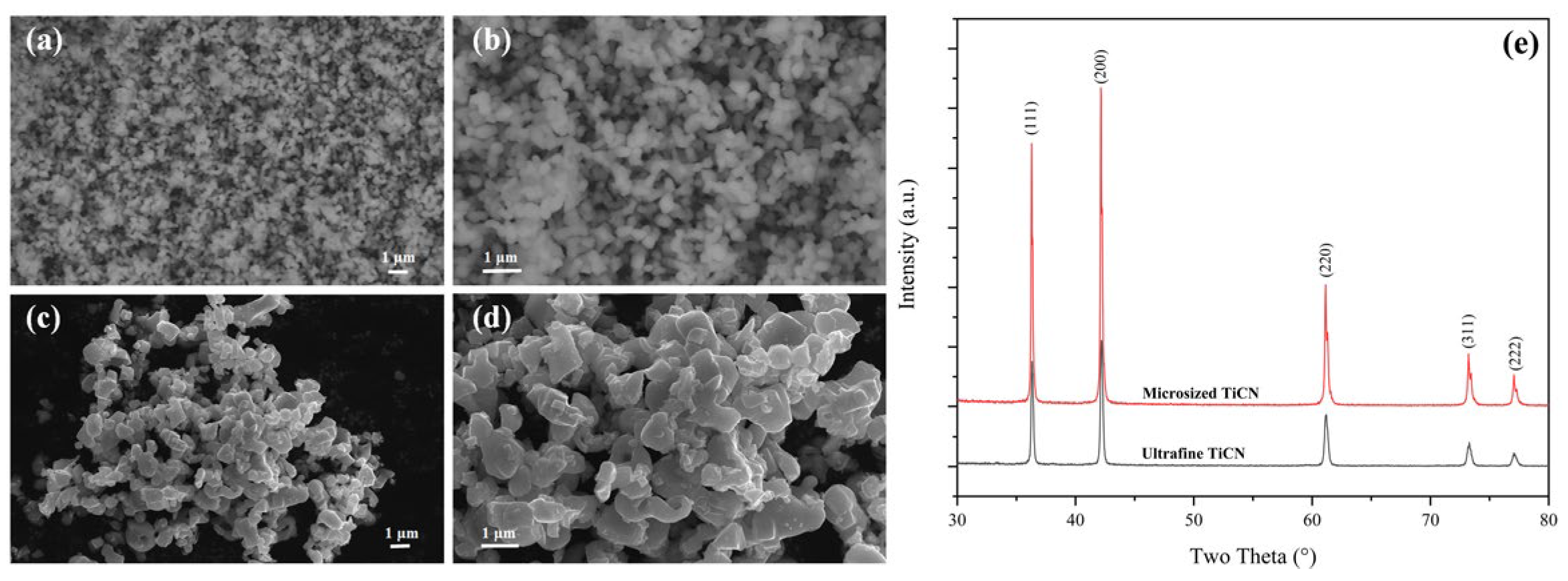
3.1. Ultrafine TiCN Powders
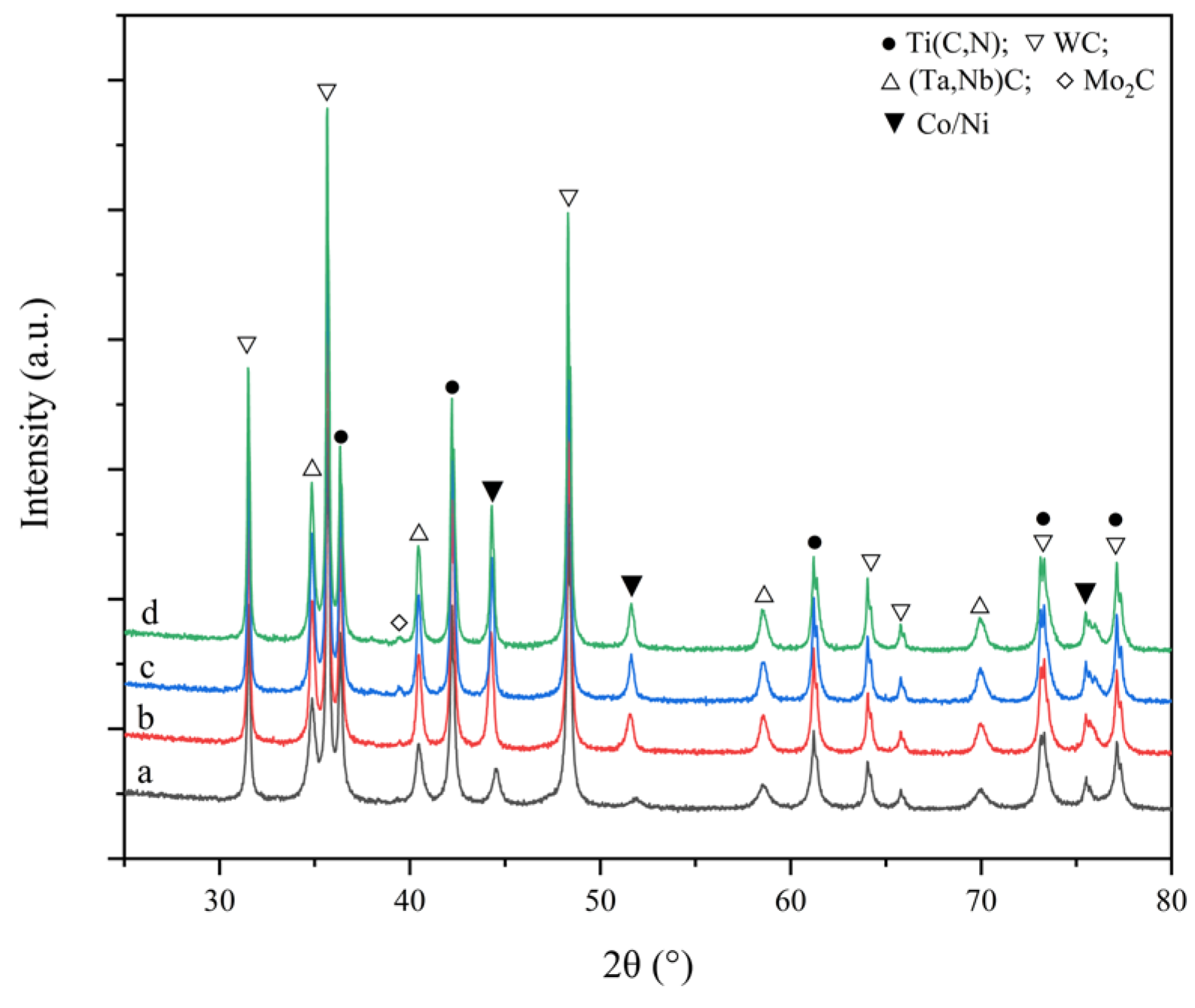
3.2. Function of Ultrafine Ti(C, N) in Densification Behaviors of TiCN-Based Cermets
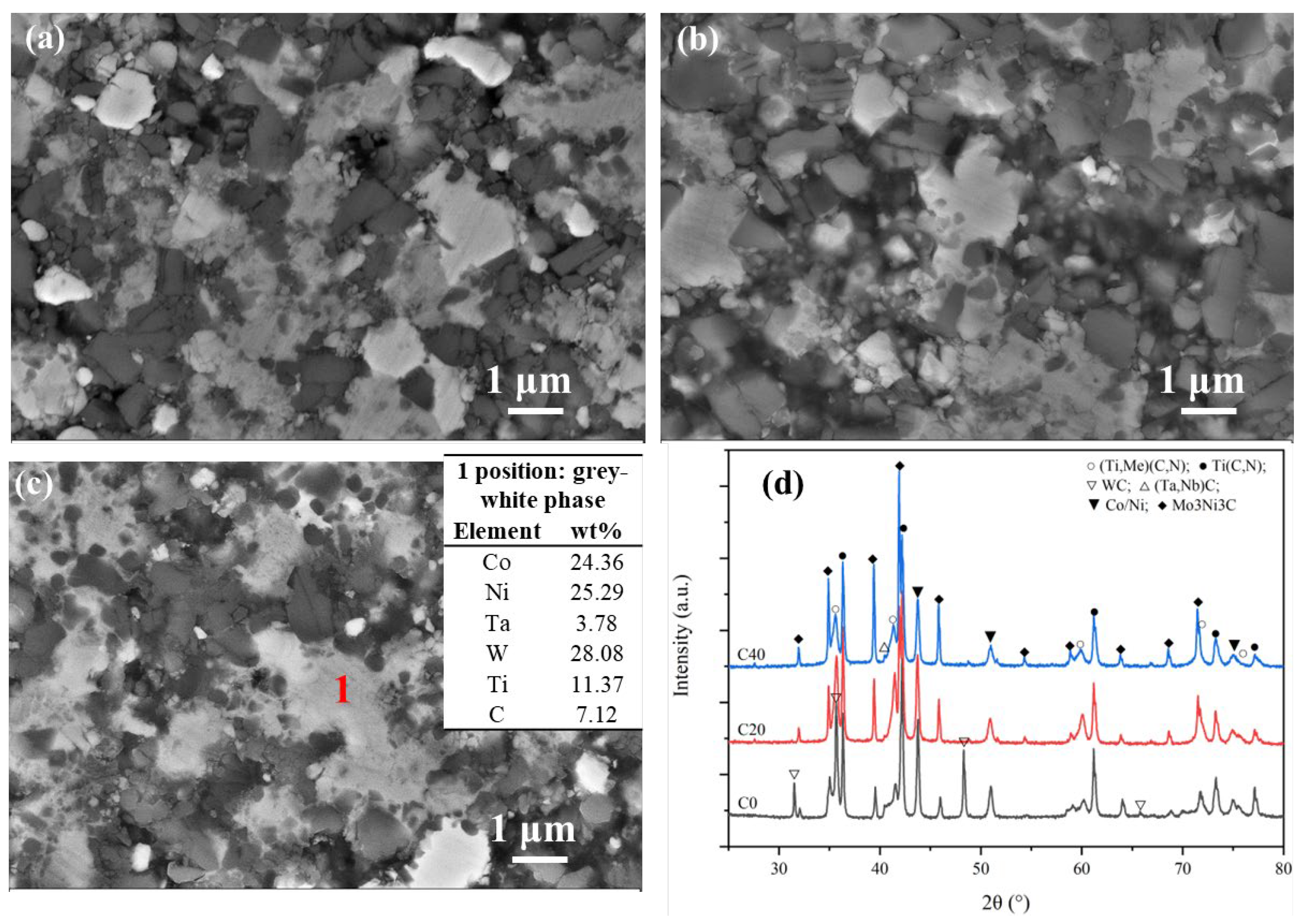
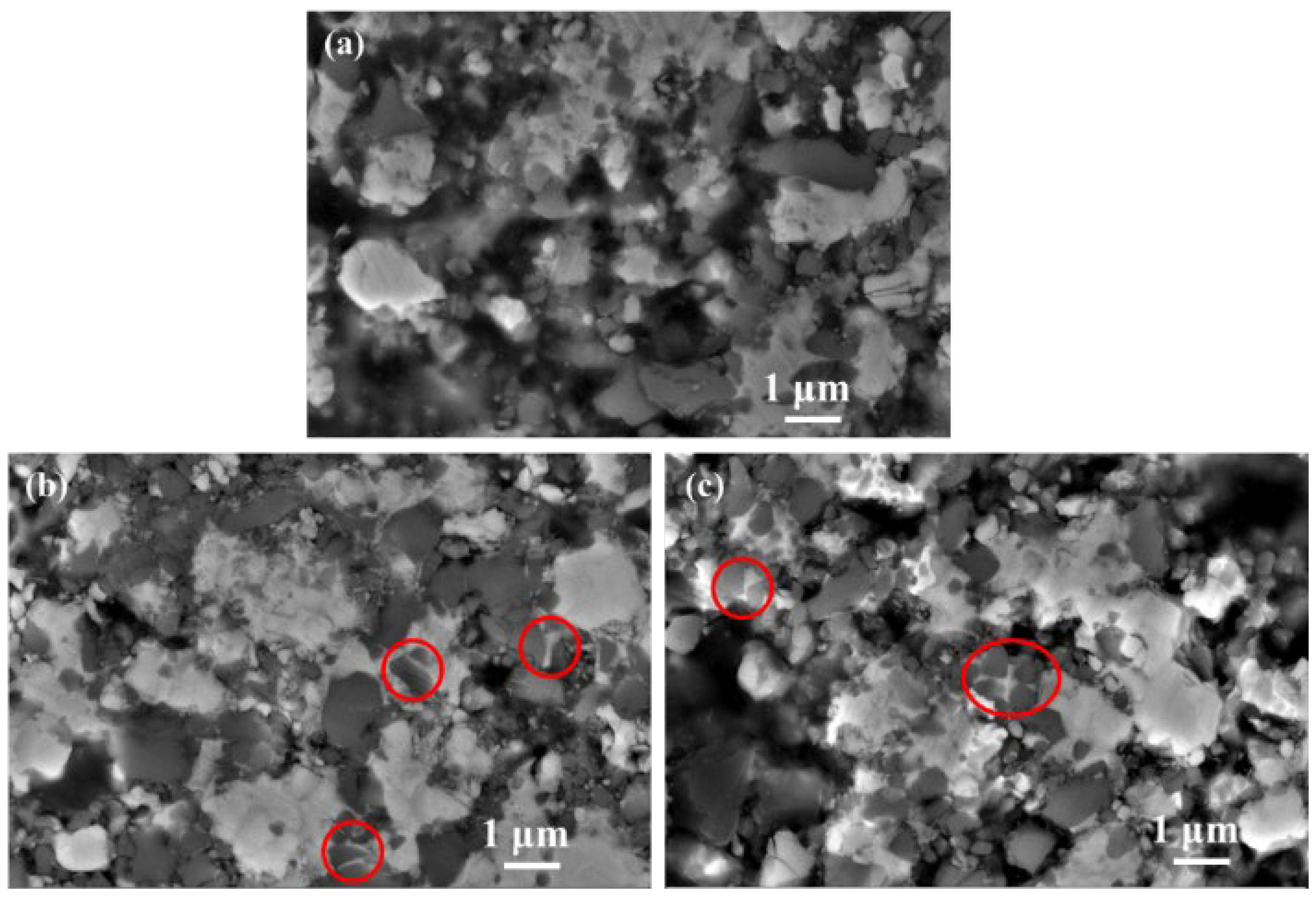
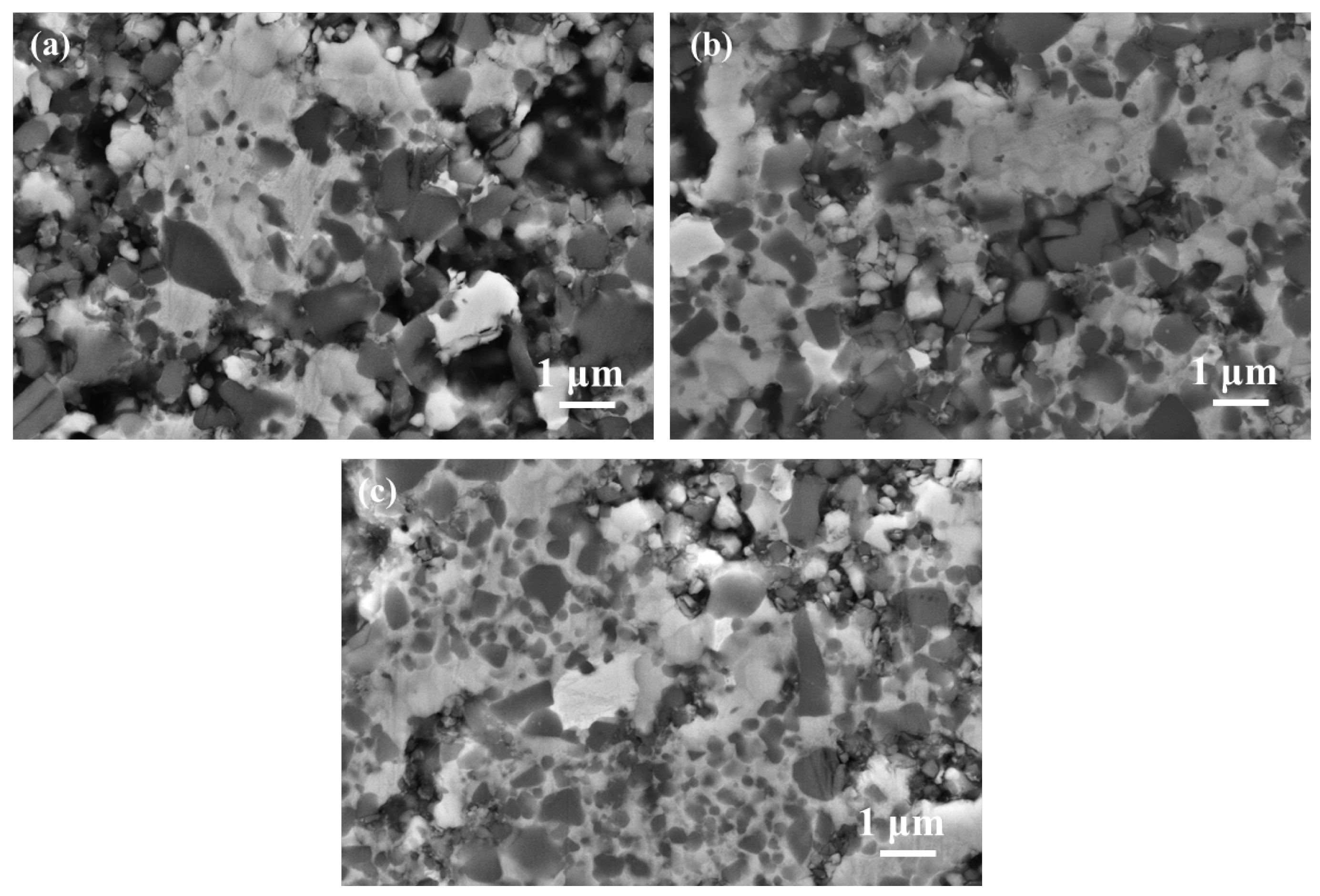
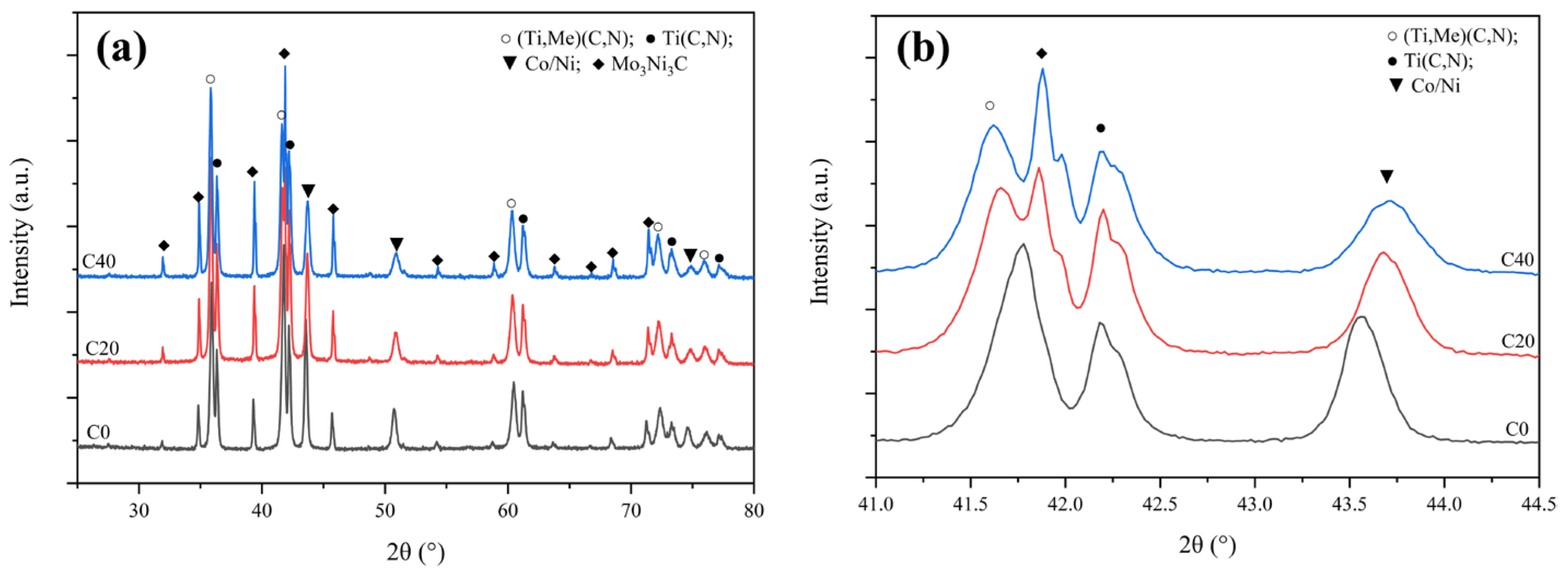
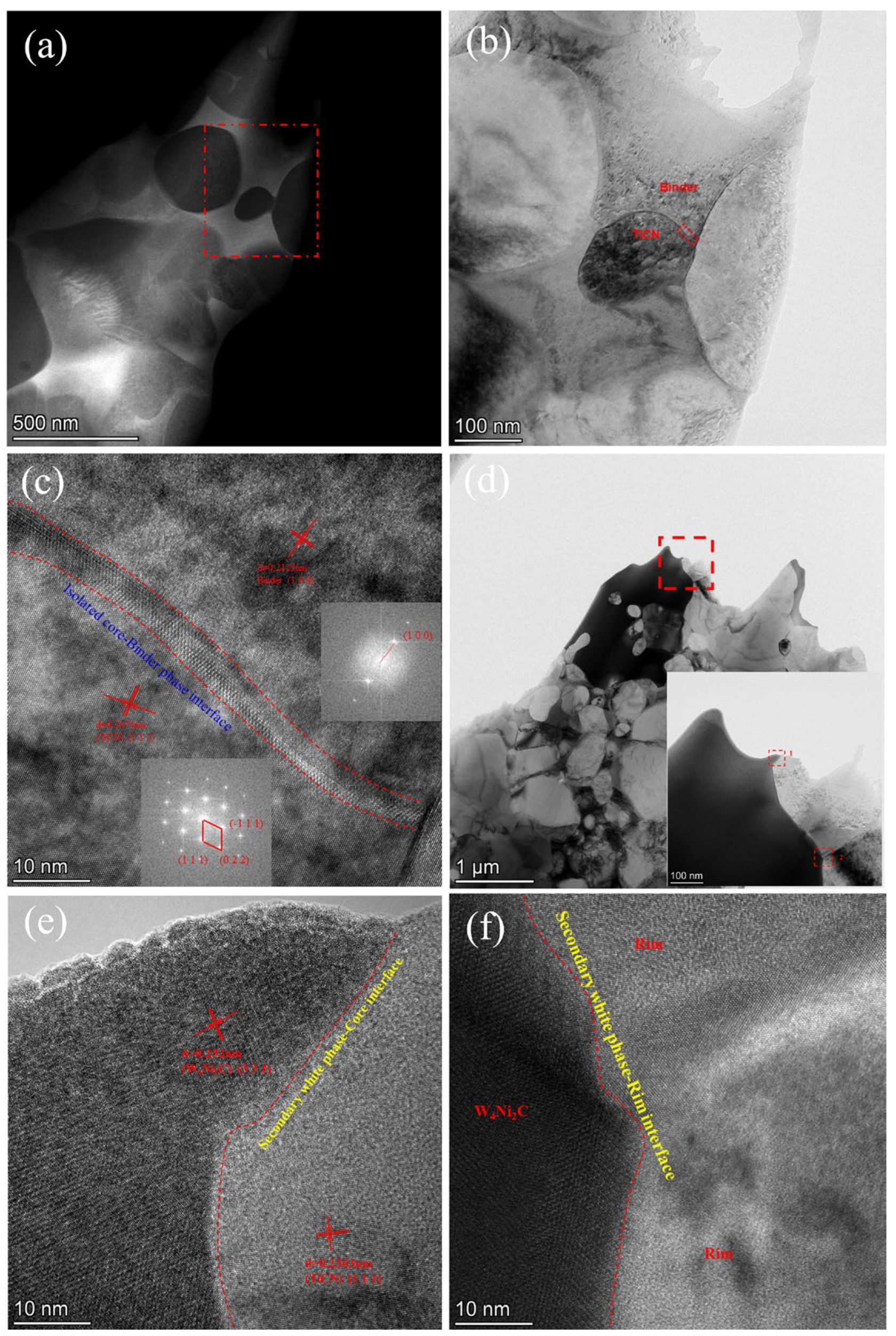
3.3. Function of Ultrafine TiCN in Microstructure and Phase Evolution during the Solid-State Stage
3.4. Role of Ultrafine TiCN in Cermet Morphology and Mechanical Performance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Adding ultrafine Ti(C, N) accelerates the cermets’ shrinkage rate, especially for the solid-state sintering process.
- (2)
- Adding ultrafine Ti(C, N) improves the diffusion of heavy elements such as W, Ta, Nb into the binder phase and Ti(C, N) at 1200 °C. As the sintering temperature further elevates, the heavy-element (W, Mo Ta, and Nb) transfer behavior from the binder phase is enhanced effectively to form the solid-solution (Ti, Me)CN phase through ultrafine Ti(C, N), advancing phase and morphology evolution.
- (3)
- Adding ultrafine Ti(C, N) also benefits microstructure and mechanical performance, which provides a solution for achieving cermets with excellent mechanical performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.Y. Titanium carbonitride-based cermets: Processes and properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1993, 163, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettmayer, P.; Kolaska, H.; Lengauer, W.; Dreyer, K. Ti (C, N) cermets—Metallurgy and properties. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 1995, 13, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Miao, H.Z.; Peng, Z.J. Development of TiCN-based cermets: Mechanical properties and wear mechanism. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2013, 39, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demoly, A.; Lengauer, W.; Veitsch, C.; Rabitsch, K. Effect of submicron Ti (C, N) on the microstructure and the mechanical properties of Ti (C, N)-based cermets. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2011, 29, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, J.J.; Huang, Q.; Xiong, W.H. Effect of carbon addition on the densification behavior, microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of Ti (C, N)-based cermets. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 5487–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Fischer, T.E.; Gallois, B. Microstructure, hardness and toughness of nanostructured and conventional WC-Co composites. Nanostruct. Mater. 1998, 10, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yin, W.H.; Zhu, L.W. Effect of TiC/TiN powder size on microstructure and properties of Ti (C, N)-based cermets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 445, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.X.; Xiong, J.; Yang, M.; Xiong, S.J.; Liu, P.; Chen, J.Z. Preparation and characterization of Ti (C, N)-based nano-cermets. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 5983–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.A.; Fu, M.; Ma, L.; Gu, S.Y.; Liu, J.W.; Chen, Y. Fabrication and Properties of (Ti, W, Mo, Nb, Ta)(C, N)-Co-Ni Cermets. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 7198–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengauer, W.; Scagnetto, F. Ti (C, N)-based cermets: Critical review of achievements and recent developments. Solid State Phenom. 2018, 274, 53–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Zheng, Z.P.; Zhao, L.B.; Ma, C.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, Y.H. Influences of ultrafine Ti (C, N) additions on microstructure and properties of micron Ti (C, N)-based cermets. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 230, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Zou, B.; Wang, J. Effects of sintering temperature and nano Ti (C, N) on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti (C, N) cermets cutting tool materials with low Ni-Co. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 705, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.W.; Wen, Y.; Gan, X.P.; Li, Z.Y.; Chai, L.Y. Influence of coarse TiCN content on the morphology and mechanical properties of ultrafine TiCN-based cermets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 682, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, D.K.; Wright, I.G.; Mincer, P.N.; Clauer, A.H. Indentation fracture of WC-Co cermets. J. Mater. Sci. 1985, 20, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Xiong, W.H.; Zhang, G.P.; Huang, B. Grain growth in Ti (C, N)–based cermets during liquid—Phase sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 98, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.Q.; Yang, W.; Xiang, X.; Huang, B.; Xiong, H.W.; Zhang, L.; Shi, K.H. Microstructural evolution and phase transition mechanism of Ti (C, N)-based cermets during vacuum sintering process. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 8020–8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zackrisson, J.; Andrén, H.O.; Rolander, U. Development of cermet microstructures during sintering. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 32, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.P.; Ye, J.W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.J.; Yu, H.J. Study on the formation of core–rim structure in Ti (CN)-based cermets. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2012, 35, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, J.M.; Chicardi, E.; Gotor, F.J. Liquid-phase sintering of Ti (C, N)-based cermets. The effects of binder nature and content on the solubility and wettability of hard ceramic phases. J. Alloys Comp. 2013, 559, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Xie, D.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, K.; Xiong, H. Ti (C, N)-based cermets by vacuum sintering using commercial composite powders: Morphology evolution, composition and related properties. Vacuum 2019, 170, 108983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kang, S. Effect of ultra-fine powders on the microstructure of Ti (CN)–xWC–Ni cermets. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.K.; Lee, H.C. Microstructural evolution during the sintering of a Ti (C, N) Mo2CNi alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 209, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.W.; Chu, S.L.; Lei, P.F.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhou, K.C. Ti (C, N)-based cermets containing uniformly dispersed ultrafine rimless grains: Effect of VC additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 19904–19911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J.W.; Ma, S.Q.; Pang, J. The fabrication of multi-core structure cermets based on (Ti, W, Ta) CN and TiCN solid-solution powders. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 64, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cermets | Microsized-TiCN | Ultrafine-TiCN | WC | Mo2C | TaNbC | Co | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | 50 | 0 | 25 | 1 | 10 | 7 | 7 |
| C20 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 1 | 10 | 7 | 7 |
| C40 | 30 | 20 | 25 | 1 | 10 | 7 | 7 |
| (Ti, Me) CN (Å) | TiCN (Å) | Co/Ni (Å) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | 4.329 | 4.278 | 3.596 |
| C20 | 4.337 | 4.279 | 3.585 |
| C40 | 4.338 | 4.277 | 3.580 |
| Element | wt.% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Black Core | 3 Grey Rim around Black Core | 4 White Core | 5 Grey Rim around White Core | 6 Eta Phase | |
| Co | 0.68 | 0.26 | 0.53 | 1.17 | 10.34 |
| Ni | 0.52 | 0.05 | 0.56 | 0.89 | 6.25 |
| Ta | 3.48 | 9.30 | 12.50 | 12.27 | 0.59 |
| W | 6.98 | 20.70 | 32.13 | 24.57 | 72.07 |
| Ti | 62.14 | 43.65 | 23.27 | 34.15 | 1.90 |
| Mo | 0.05 | 0.79 | 1.98 | 0.23 | 1.60 |
| Nb | 0.50 | 2.88 | 3.99 | 3.01 | 0.16 |
| C | 17.98 | 18.61 | 23.93 | 21.11 | 6.39 |
| N | 7.67 | 3.68 | 1.12 | 2.57 | 0.69 |
| Cermet | HV30 | K IC/MPa·m1/2 | TRS/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | 1530 | 7.86 | 1180 |
| C20 | 1520 | 7.80 | 1140 |
| C40 | 1540 | 8.00 | 1440 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Gu, S.; Zhang, H. Influences of Ultrafine Ti(C, N) on the Sintering Process and Mechanical Properties of Micron Ti(C, N)-Based Cermets. Materials 2023, 16, 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083175
Ma L, Zhao Z, Wu Y, Sun J, Gu S, Zhang H. Influences of Ultrafine Ti(C, N) on the Sintering Process and Mechanical Properties of Micron Ti(C, N)-Based Cermets. Materials. 2023; 16(8):3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083175
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Lili, Zaiyang Zhao, Yurong Wu, Jingjing Sun, Siyong Gu, and Houan Zhang. 2023. "Influences of Ultrafine Ti(C, N) on the Sintering Process and Mechanical Properties of Micron Ti(C, N)-Based Cermets" Materials 16, no. 8: 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083175
APA StyleMa, L., Zhao, Z., Wu, Y., Sun, J., Gu, S., & Zhang, H. (2023). Influences of Ultrafine Ti(C, N) on the Sintering Process and Mechanical Properties of Micron Ti(C, N)-Based Cermets. Materials, 16(8), 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083175





