Crosslinked Polydiallyldimethylammonium Chloride Adsorbent for the Selective Separation of Rhenium Ions from Pregnant Leach Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Synthesis of Crosslinked Poly DADMAC as Adsorbent
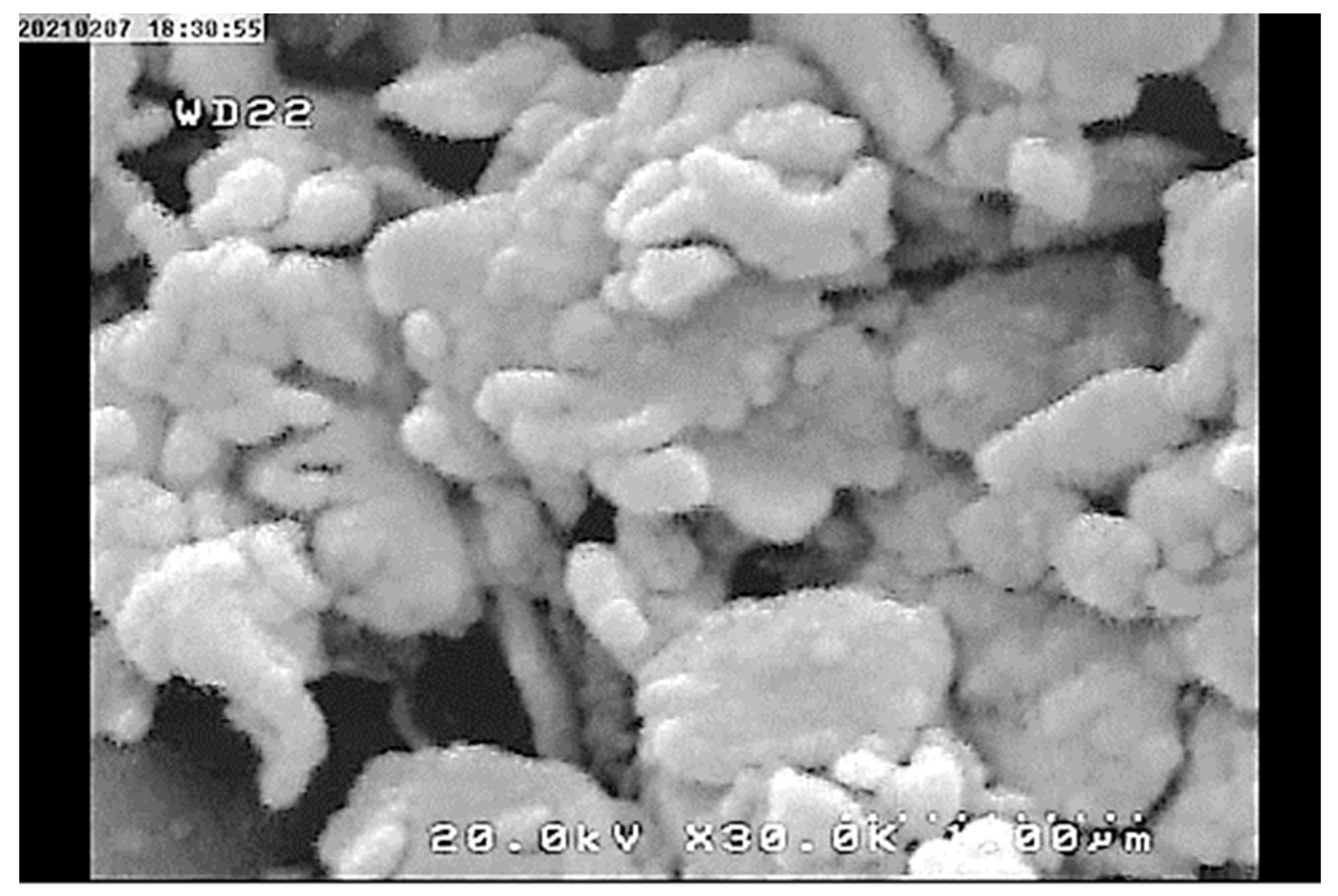
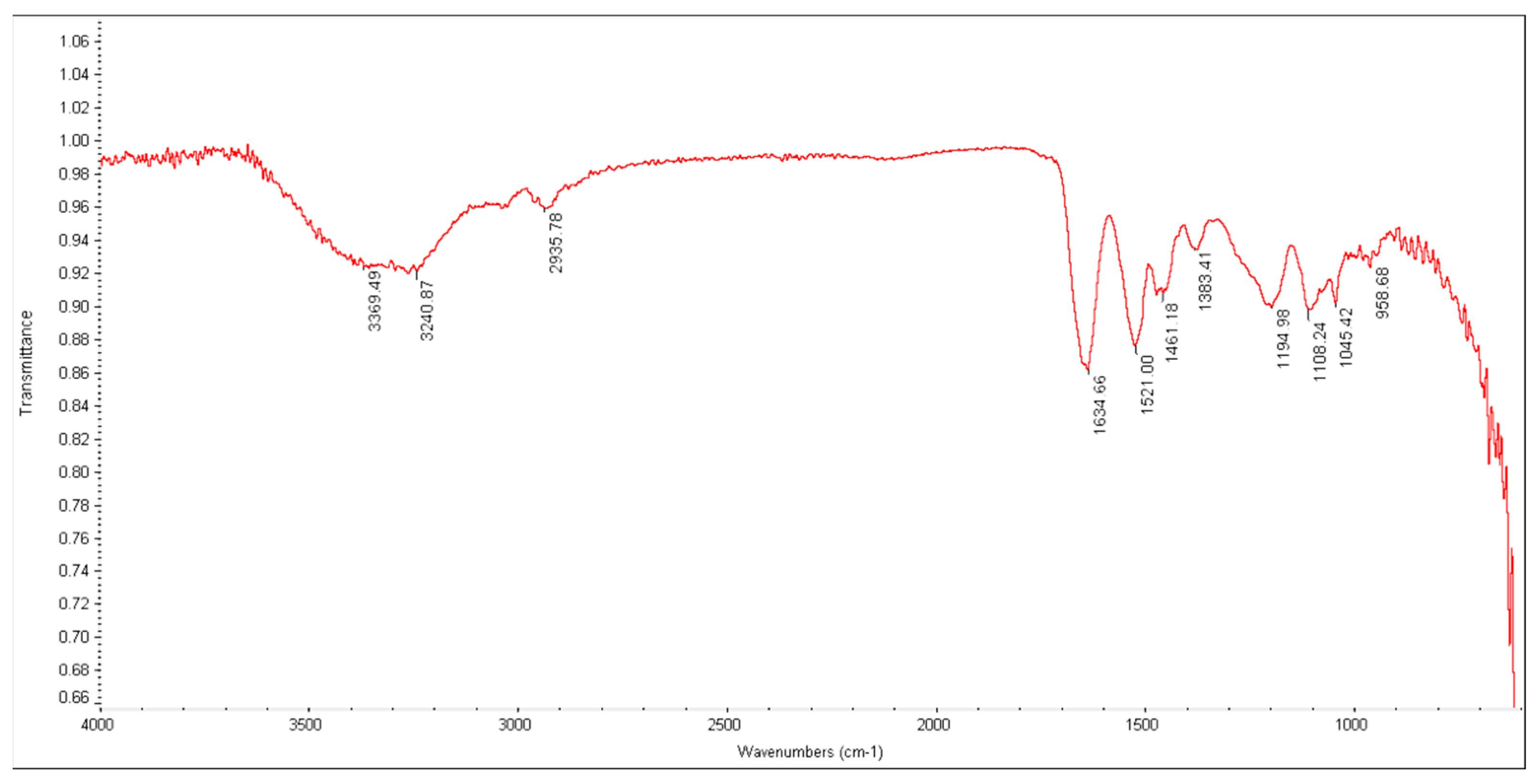
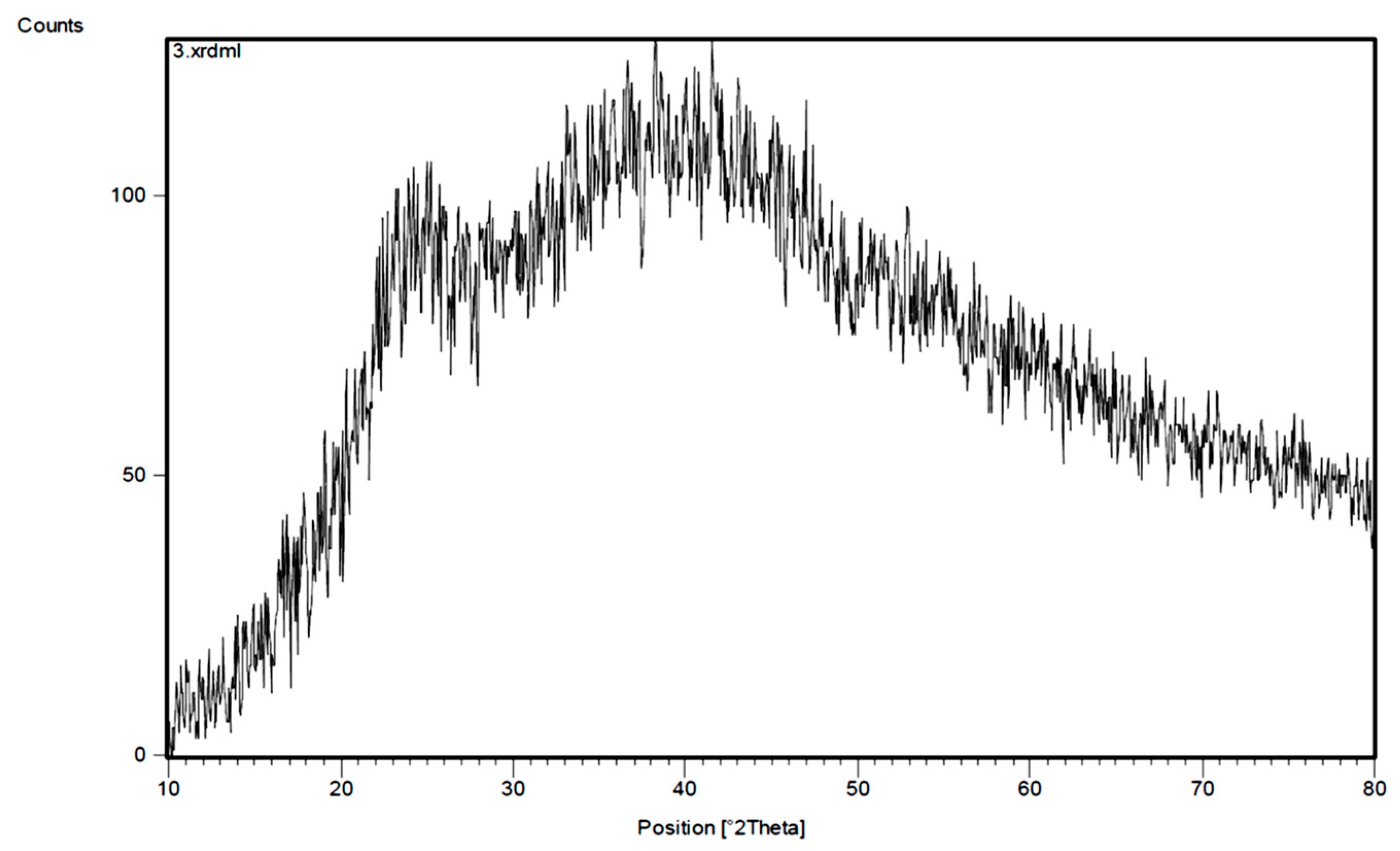
2.3. Characterization of the Synthesized Adsorbent (Poly-MADMAC)
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.5. Metal Sorption
2.5.1. Synthetic Solutions
2.5.2. Real Solutions
3. Results and Discussion
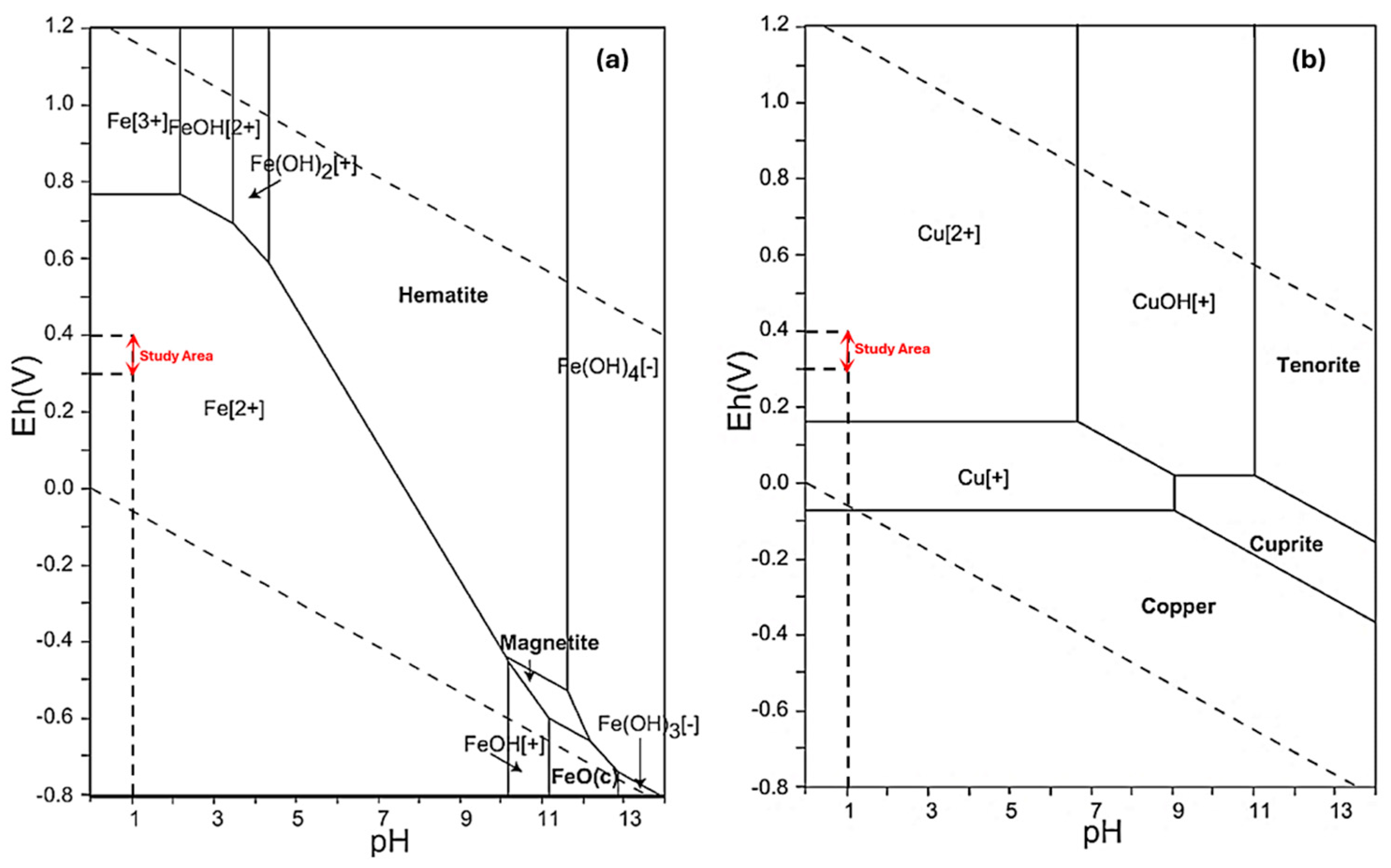
3.1. Resin Synthesis
3.2. Resin Uptake Tests
3.3. Selectivity of the Produced Resin toward Re Ions
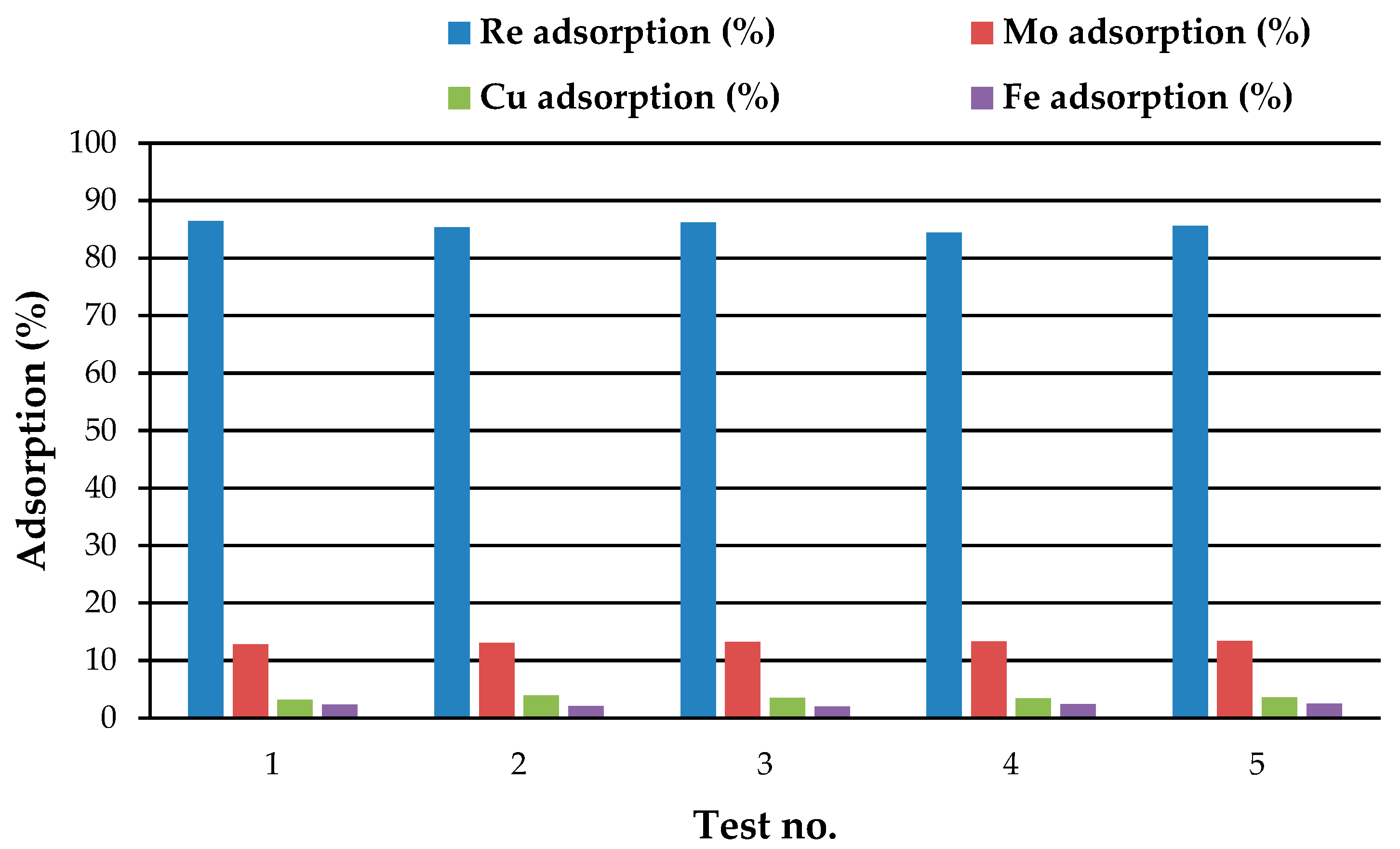
3.4. Adsorption Tests on Real Solutions
| Initial Conc. | Equilibrium Conc. | Adsorption (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Re (ppm) | Mo (g/L) | Fe (ppm) | Cu (ppm) | Re (ppm) | Mo (g/L) | Fe (ppm) | Cu (ppm) | Re | Mo | Fe | Cu |
| 54.6 | 5.2 | 460.5 | 312.2 | 18.4 | 4.4 | 445.7 | 300.7 | 66.3 | 16 | 3.2 | 3.7 |
| 56.1 | 5.3 | 461.4 | 340.4 | 19.4 | 4.4 | 450.7 | 322.4 | 65.4 | 16.3 | 2.3 | 5.3 |
| 50.4 | 5.3 | 430.4 | 316.3 | 18 | 4.4 | 412.4 | 302.3 | 64.3 | 16.7 | 4.2 | 4.4 |
| 52.1 | 7.4 | 480.4 | 341.7 | 19.7 | 6.2 | 464.2 | 324.5 | 62.2 | 17.2 | 3.4 | 5.0 |
| Bulk Solution | Elements | Resin | Efficiency | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Type | ||||
| Sulfate solutions | Re-Mo | IRA-67, A172 and 170 | Gel, gel, macroporous | 95.3% | [14] |
| Molybdenite calcine leaching solution | Re-Mo | D216 and 201X7 | Strong base, gel | 90% | [33] |
| Re-Mo solution with pH 2.6–6 | Re-Mo | Synthetic anion exchanger (4-amino-1,2,4-triazole) | Macroporous | βRe/Mo = 17.3 | [19] |
| Copper heap leaching solutions | Re | Purolite A170 | Macroporous | ~90% | [15] |
| Synthetic acidic solutions (Re-Mo) | Re-Mo | Synthesized anion exchanger | Macroporous | Re uptake: 46.3 mg/g | [4] |
| Synthetic solutions (Re/U) | Re | Ambersep A920U | Strong base | ~98.2% | [34] |
| Synthetic solutions (Re, U/alts) | Re | AN-21 | Weakly base | 33–99.2% | [16] |
| Different matrices (nitrate, chloride, sulfate) | Re | IRA-67, WP-1 | Gel, macroporous | Aimed for modelling | [17] |
| Copper leaching solutions | Re | Weak base resins ZS70 | Weak base | 97.13% | [18] |
| Acidified solutions (Re(VII), Mo(VI) and V(V), Cu(II)) | Re | Synthesized anion exchanger | Macroporous | Re uptake: 303 mg/g | [20] |
| Industrial wastewater | Re | Synthesized anion exchanger | Macroporous | 99.85% | [22] |
| Molybdenite concentrate leaching solutions | Re | Synthesized anion exchanger | Macroporous | 62.2–66.3% | This work |
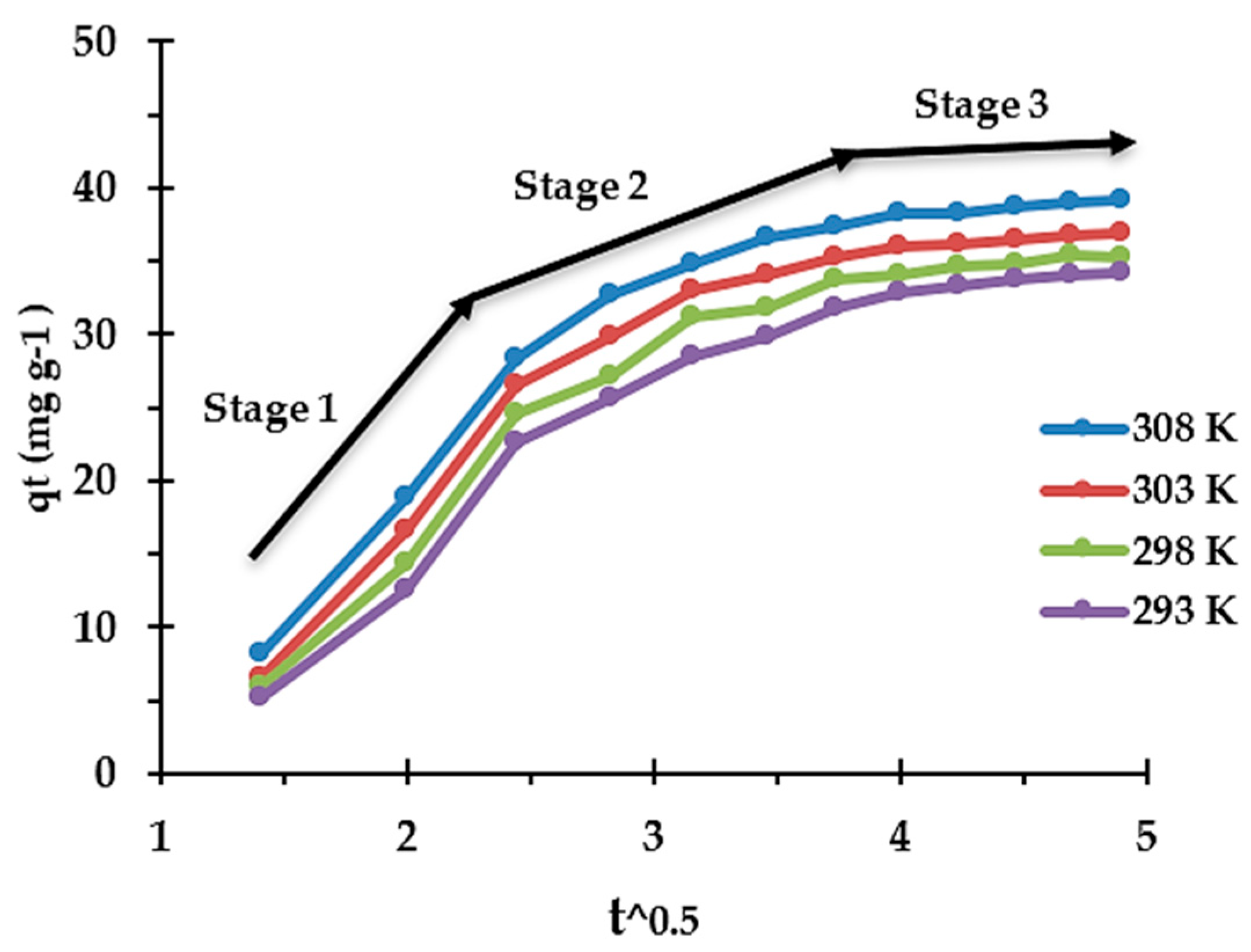
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, J.; Gao, B.; Guo, K.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Yue, Q. Insights into selective adsorption mechanism of copper and zinc ions onto biogas residue-based adsorbent: Theoretical calculation and electronegativity difference. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, R.; Yao, H.; Lu, X.; Yan, D.; Xin, J. Removal of Zn2+ from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) glycolytic monomers by sulfonic acid cation exchange resin. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Soldenhoff, K.; Ogden, M.D. Comparative study of the application of chelating resins for rare earth recovery. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.B.; Nasiri, M. Synthesis and characterization of modified resins and their selective sorption towards rhenium from binary (Re & Mo) solutions. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. (IJCCE) 2023, 42, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Mohebbi, A.; Abolghasemi Mahani, A.; Izadi, A. Ion exchange resin technology in recovery of precious and noble metals. In Applications of Ion Exchange Materials in Chemical and Food Industries; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 193–258. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Ning, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Yin, X. Preparation of ion-exchange resin via in-situ polymerization for highly selective separation and continuous removal of palladium from electroplating wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 258, 117670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badsha, M.A.; Khan, M.; Wu, B.; Kumar, A.; Lo, I.M. Role of surface functional groups of hydrogels in metal adsorption: From performance to mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makvandi, P.; Iftekhar, S.; Pizzetti, F.; Zarepour, A.; Zare, E.N.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Agarwal, T.; Padil, V.V.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Sillanpaa, M. Functionalization of polymers and nanomaterials for water treatment, food packaging, textile and biomedical applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 583–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdzy, K.; Chen, Y.-G.; Lv, G.-Y.; Chen, S.-H.; Kołodyńska, D. Application of Ion Exchangers with the N-Methyl-D-Glucamine Groups in the V (V) Ions Adsorption Process. Materials 2022, 15, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Tesfaye, F.; Li, X.; Lindberg, D.; Taskinen, P. Review of rhenium extraction and recycling technologies from primary and secondary resources. Miner. Eng. 2021, 161, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shan, W.; Lou, Z.; Cui, J.; Yu, H. Superior adsorption of Re (VII) by anionic imprinted chitosan-silica composite: Adsorption performance, selectivity and mechanism study. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 108, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, R.; Okabe, T.H. Rhenium and its smelting and recycling technologies. Int. Mater. Rev. 2024, 69, 142–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorov, A.; Negmatov, S.; Erniyozov, N.; Subanova, Z.; Sultonova, I. Investigation of the sorption method of processing molybdenum-containing raw materials to extract rare metals. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 401, 03045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virolainen, S.; Laatikainen, M.; Sainio, T. Ion exchange recovery of rhenium from industrially relevant sulfate solutions: Single column separations and modeling. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 158, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebeker, N.; Hiskey, J.B. Recovery of rhenium from copper leach solution by ion exchange. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 125, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorodnyaya, A.; Abisheva, Z.; Sharipova, A.; Sadykanova, S.; Akcil, A. Regularities of rhenium and uranium sorption from mixed solutions with weakly basic anion exchange resin. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2015, 36, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laatikainen, M.; Virolainen, S.; Paatero, E.; Sainio, T. Recovery of ReO4− by weakly basic anion exchangers: Modeling of sorption equilibrium and rate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 153, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, H.-Z.; Wang, W.; Gao, Z.-G.; Cao, Y.-H. Recovery of rhenium from copper leach solutions using ion exchange with weak base resins. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 173, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Yao, C.; Wu, X. Adsorption of rhenium (VII) on 4-amino-1, 2, 4-triazole resin. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 90, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyganowski, P.; Cierlik, A.; Leśniewicz, A.; Pohl, P.; Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D. Separation of Re (VII) from Mo (VI) by anion exchange resins synthesized using microwave heat. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyganowski, P.; Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D. Experimental review of microwave-assisted methods for synthesis of functional resins for sorption of rhenium (vii). Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2018, 36, 420–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ma, Z.; Li, D.; Tian, Q.; Xu, Z. Recovery of Re (VII) from aqueous solutions with coated impregnated resins containing ionic liquid Aliquat 336. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 190, 105149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawierucha, I.; Nowik-Zajac, A.; Girek, T.; Lagiewka, J.; Ciesielski, W.; Pawlowska, B.; Biczak, R. Arsenic (V) removal from water by resin impregnated with cyclodextrin ligand. Processes 2022, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwuozor, K.O.; Ighalo, J.O.; Emenike, E.C.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Adeniyi, A.G. Do adsorbent pore size and specific surface area affect the kinetics of methyl orange aqueous phase adsorption? J. Chem. Lett. 2021, 2, 188–198. [Google Scholar]
- Astam, M.O.; Zhan, Y.; Slot, T.K.; Liu, D. Active Surfaces Formed in Liquid Crystal Polymer Networks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 22697–22705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piai, L.; Dykstra, J.E.; Adishakti, M.G.; Blokland, M.; Langenhoff, A.A.; van der Wal, A. Diffusion of hydrophilic organic micropollutants in granular activated carbon with different pore sizes. Water Res. 2019, 162, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, M.B.; Rezai, B.; Alamdari, E.K.; Alorro, R.D. Mechanism and equilibrium modeling of Re and Mo adsorption on a gel type strong base anion resin. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 90, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajmohammadi, H.; Jafari, A.H.; Eskandari Nasab, M. Adsorption of Scandium and Yttrium from Aqueous Solutions by Purolite C100Na Resin: Equilibrium and Kinetic Modeling. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2021, 40, 1132–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Takeno, N. Atlas of Eh-pH diagrams. Geol. Surv. Jpn. Open File Rep. 2005, 419, 102. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Qi, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Fujita, T.; Wang, G.; Ma, S.; Yang, W.; Gan, J. Highly selective separation of germanium from sulfuric solution using an anion exchange D201× 7 resin with tartaric acid. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 224, 106230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Christodoulatos, C.; Braida, W. Adsorption of molybdate and tetrathiomolybdate onto pyrite and goethite: Effect of pH and competitive anions. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.N.; Warren, J.P.; Krieger, S.P.; Vestal, B.L.; Harrison, R.G. Separation and preconcentration of perrhenate from ionic solutions by ion exchange chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1631, 461588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorodnyaya, A.; Abisheva, Z.; Sharipova, A.; Sadykanova, S.; Bochevskaya, Y.G.; Atanova, O. Sorption of rhenium and uranium by strong base anion exchange resin from solutions with different anion compositions. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 131, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Rethinking of the intraparticle diffusion adsorption kinetics model: Interpretation, solving methods and applications. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Liang, S.; Song, Y. Recovery of rhenium from molybdenite calcine by a resin-in-pulp process. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 82, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


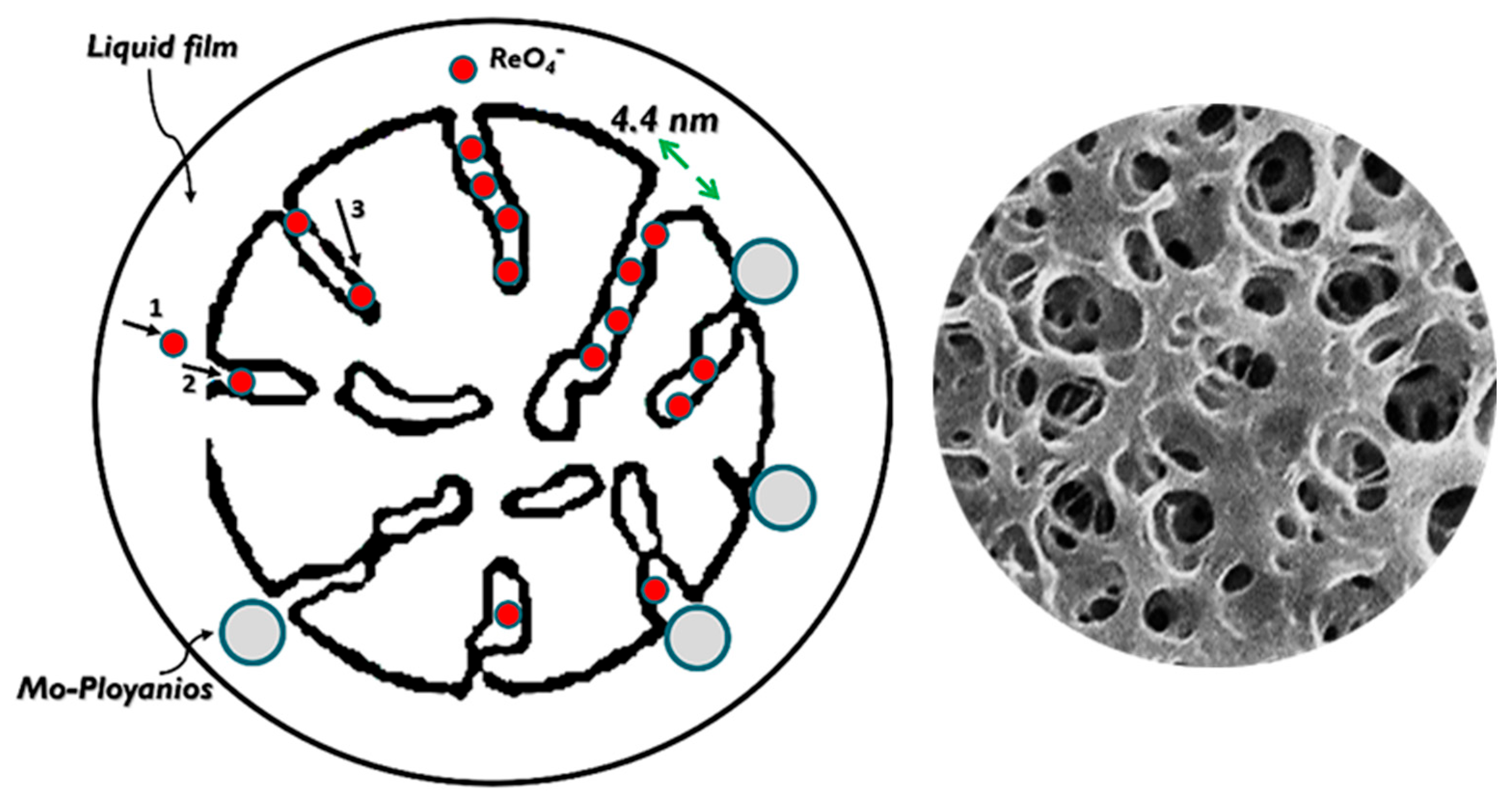
| Ion Concentration (ppm) | Test No. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Re | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 |
| Mo | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 |
| Cu | 520 | 1040 | 1560 | 2080 | 2600 |
| Fe | 600 | 1200 | 1800 | 2400 | 3000 |
| Sample/Element | Re (ppm) | Mo (g/L) | Fe (ppm) | Cu (ppm) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56.6 | 5.2 | 460.5 | 312.2 | 0.6 |
| 2 | 56.1 | 5.3 | 461.4 | 340.4 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 50.4 | 5.3 | 430.4 | 316.3 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 52.1 | 7.4 | 480.4 | 341.6 | 0.5 |
| Adsorbate | Test No. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Re (single system) (%) | 92.1 | 93.8 | 94.3 | 94.2 | 94.4 |
| Re (binary system) (%) | 87.3 | 86.8 | 86.6 | 85.1 | 86. |
| Re (multicomponent) (%) | 86.4 | 85.3 | 86.2 | 84.4 | 85.6 |
| Mo (binary system) (%) | 13.2 | 13.5 | 13.8 | 13.7 | 13.8 |
| Mo (multicomponent) (%) | 12.8 | 13.1 | 13.2 | 13.3 | 13.4 |
| Cu (multicomponent) (%) | 3.2 | 3.9 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 3.6 |
| Fe (multicomponent) (%) | 2.3 | 2.1 | 2 | 2.4 | 2.5 |
| qe (single) (mg/g) | 9.2 | 18.8 | 28.3 | 37.7 | 47 |
| qe,mix (binary) (mg/g) | 8.7 | 17.4 | 26 | 34 | 43 |
| qe,mix (multicomponent) (mg/g) | 8.6 | 17.1 | 25.9 | 33.8 | 43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fathi, M.; Mahmoudian, M.; Alorro, R.D.; Chegini, M. Crosslinked Polydiallyldimethylammonium Chloride Adsorbent for the Selective Separation of Rhenium Ions from Pregnant Leach Solutions. Materials 2024, 17, 2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112737
Fathi M, Mahmoudian M, Alorro RD, Chegini M. Crosslinked Polydiallyldimethylammonium Chloride Adsorbent for the Selective Separation of Rhenium Ions from Pregnant Leach Solutions. Materials. 2024; 17(11):2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112737
Chicago/Turabian StyleFathi, Mohammadbagher, Mehdi Mahmoudian, Richard Diaz Alorro, and Mostafa Chegini. 2024. "Crosslinked Polydiallyldimethylammonium Chloride Adsorbent for the Selective Separation of Rhenium Ions from Pregnant Leach Solutions" Materials 17, no. 11: 2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112737
APA StyleFathi, M., Mahmoudian, M., Alorro, R. D., & Chegini, M. (2024). Crosslinked Polydiallyldimethylammonium Chloride Adsorbent for the Selective Separation of Rhenium Ions from Pregnant Leach Solutions. Materials, 17(11), 2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112737







