Effect of Secondary Phase on Passivation Layer of Super Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S 32750: Advanced Safety of Li-Ion Battery Case Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
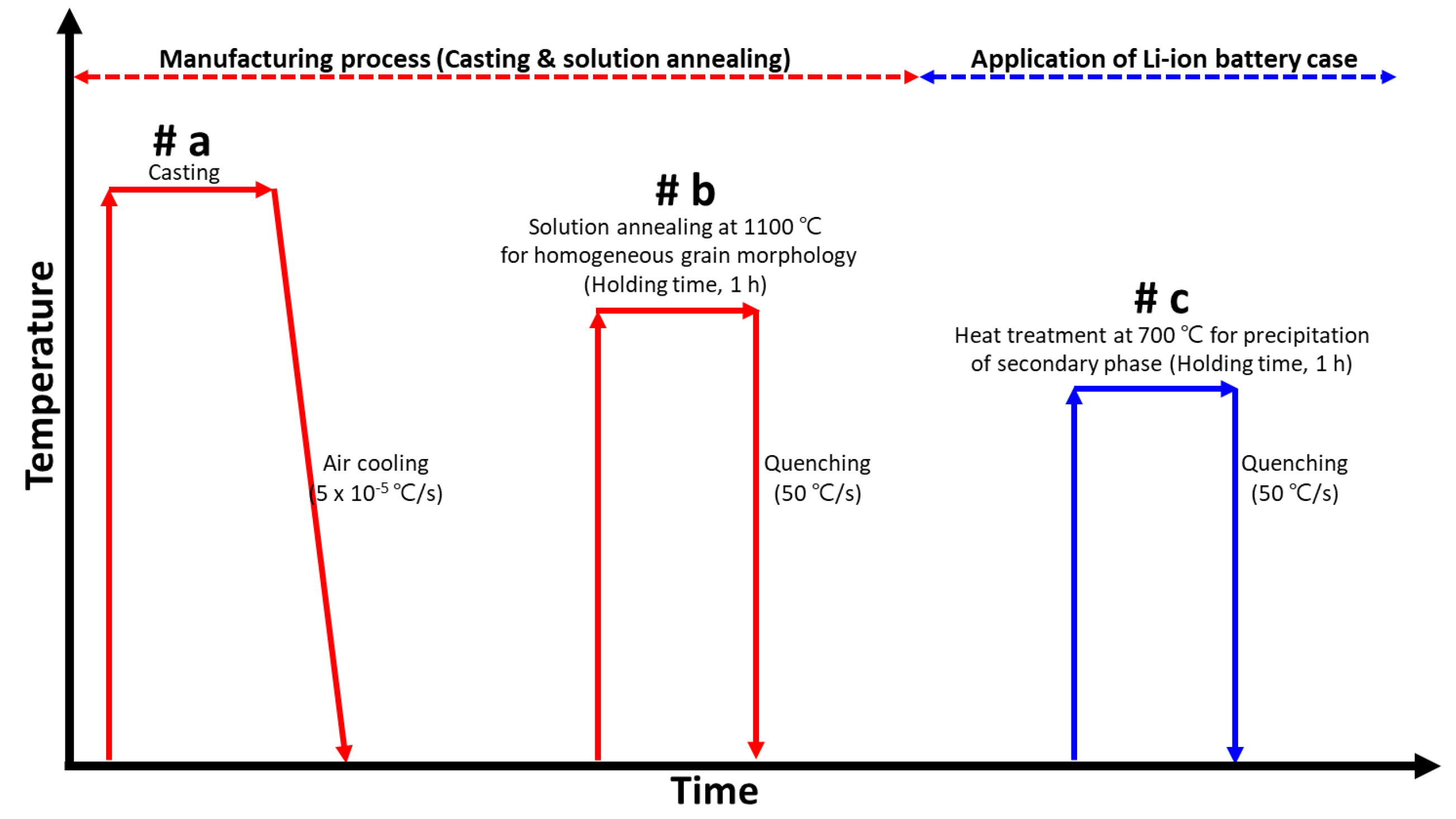
2.2. Heat Treatment
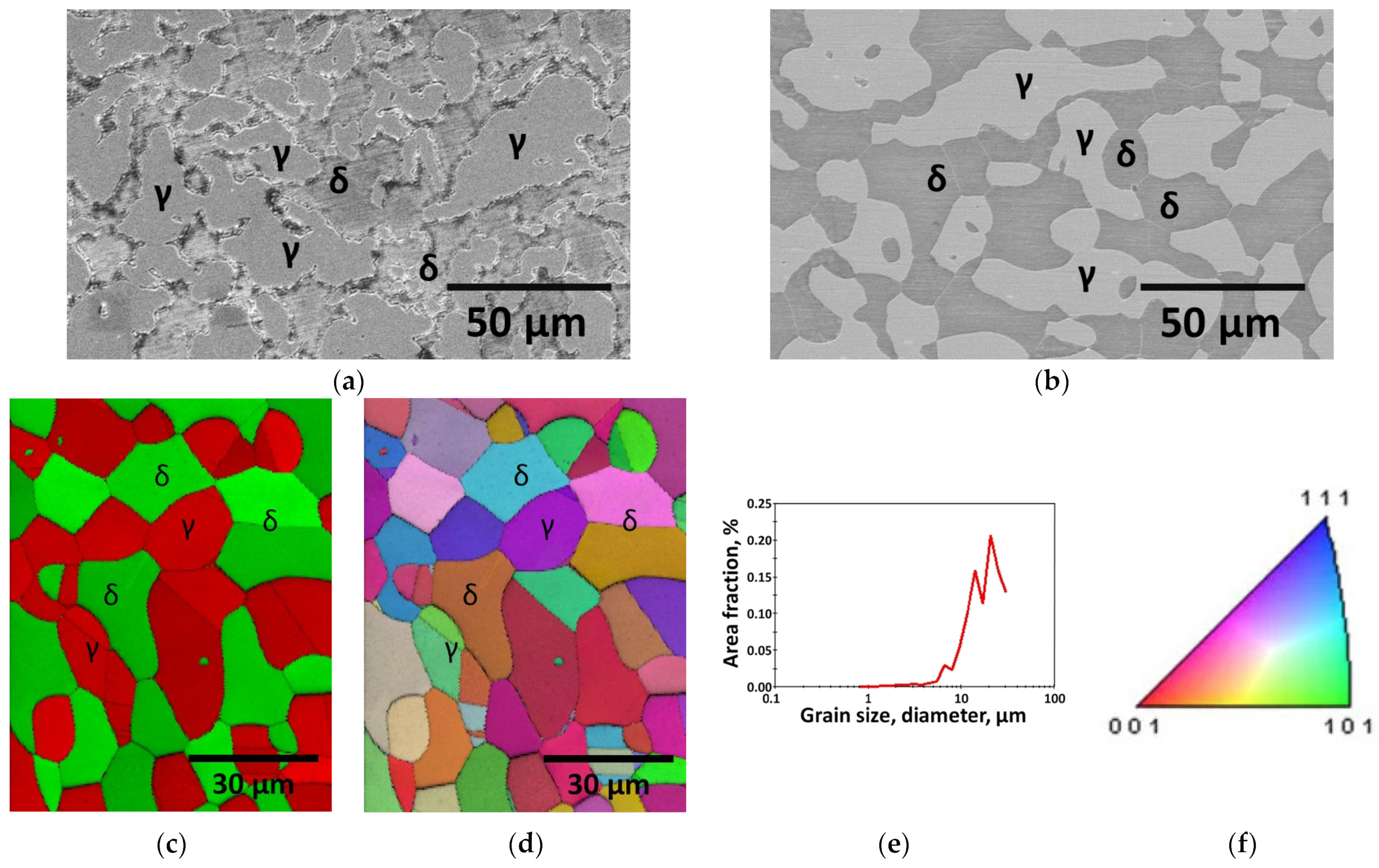
2.3. Microstructure and Phase
2.4. Chemical Composition
2.5. Electrochemical Analysis Behavior
3. Results
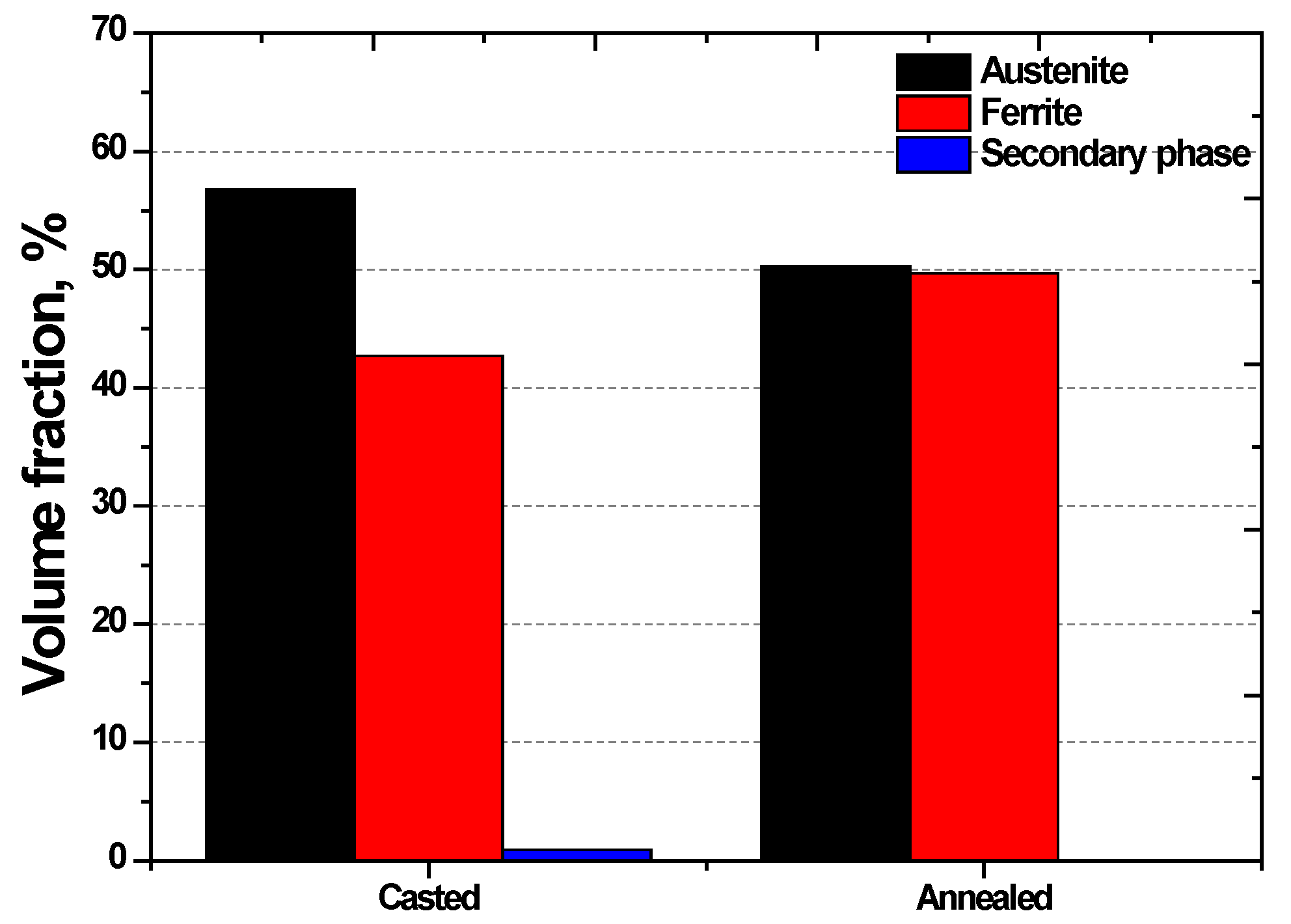
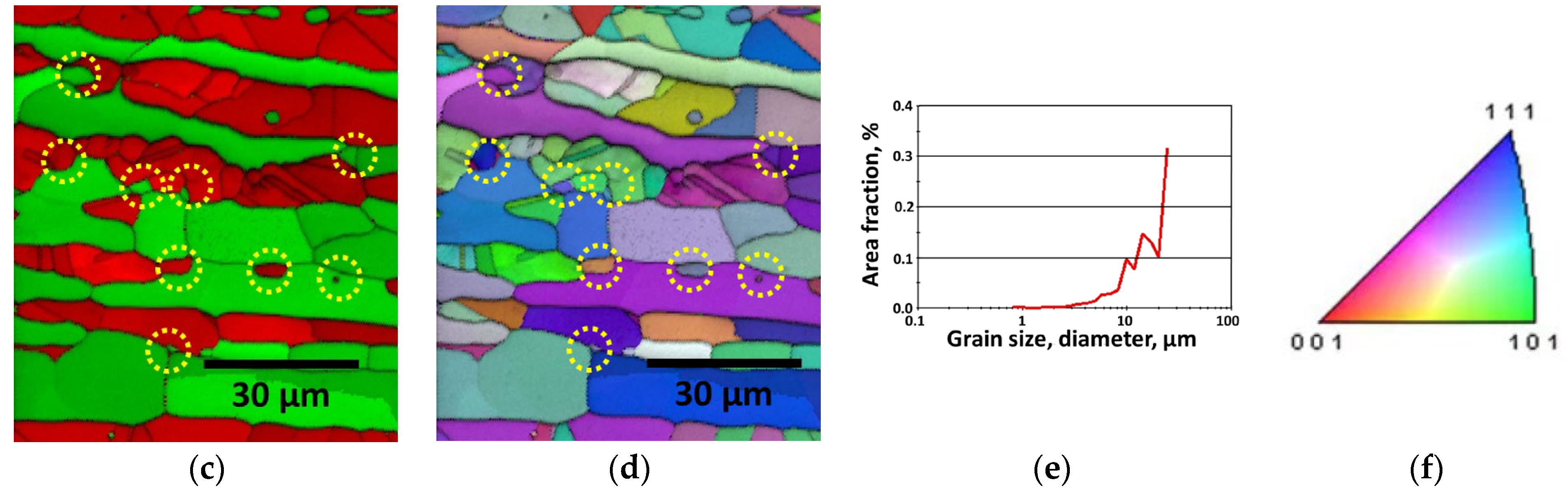
3.1. Effect of Manufacturing Process
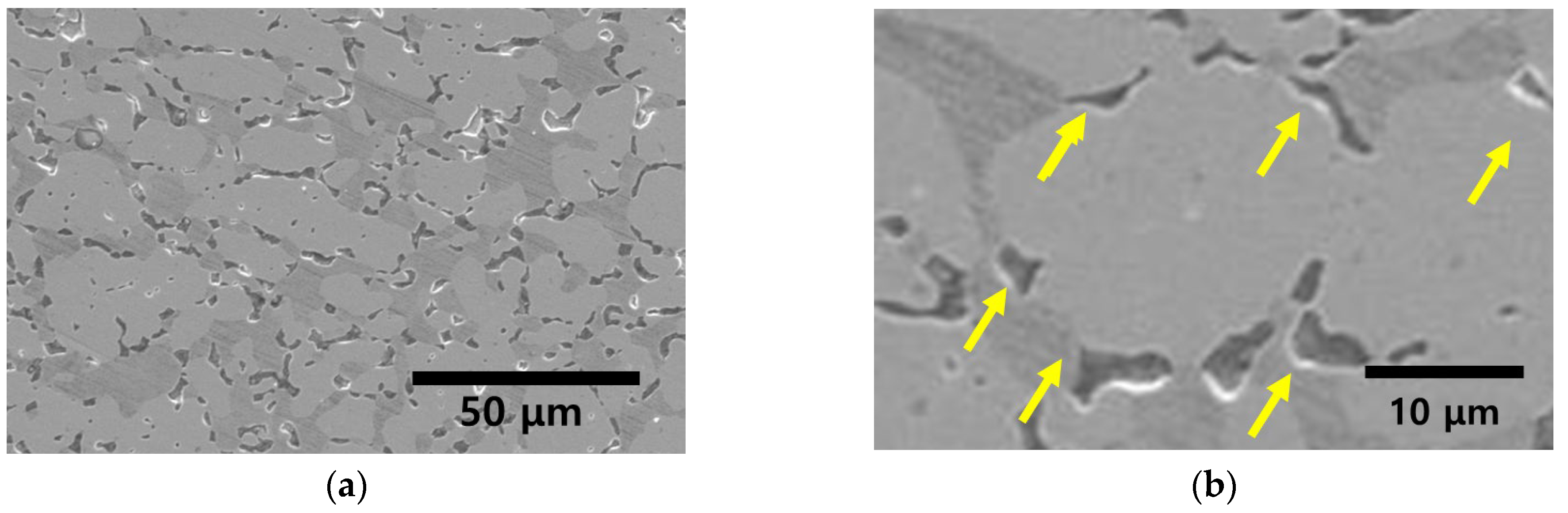
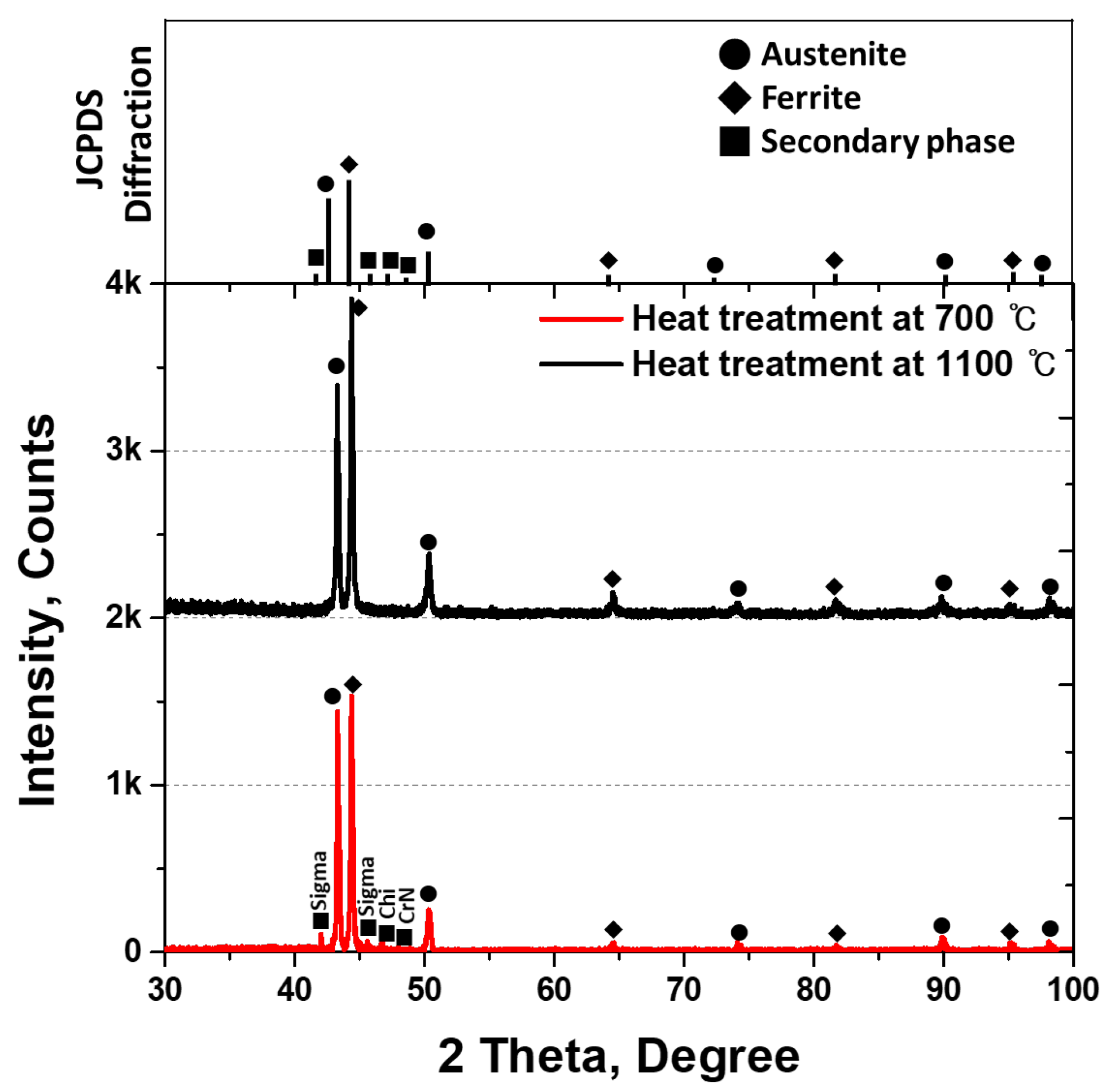
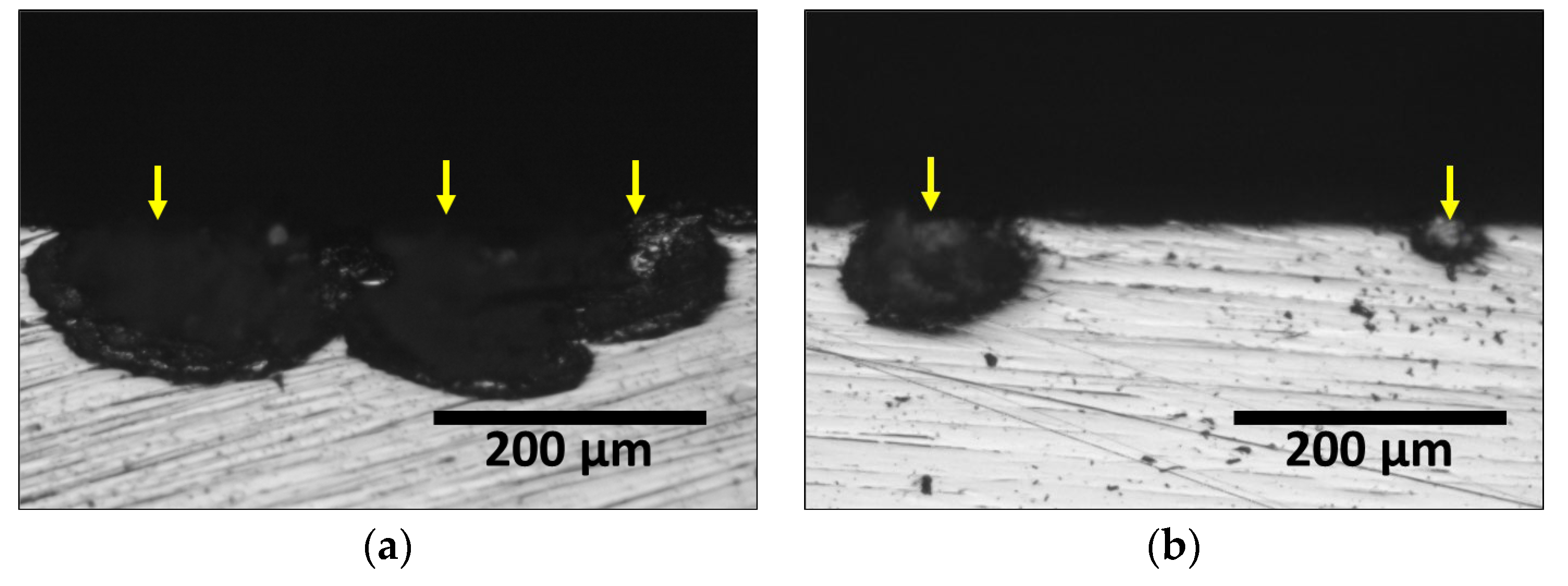
3.2. Precipitation of Secondary Phase
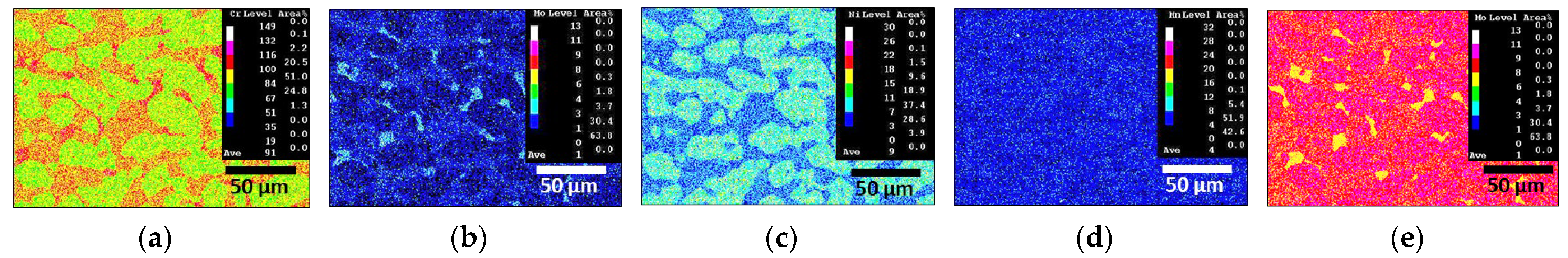
3.3. Chemical Composition of Secondary Phase
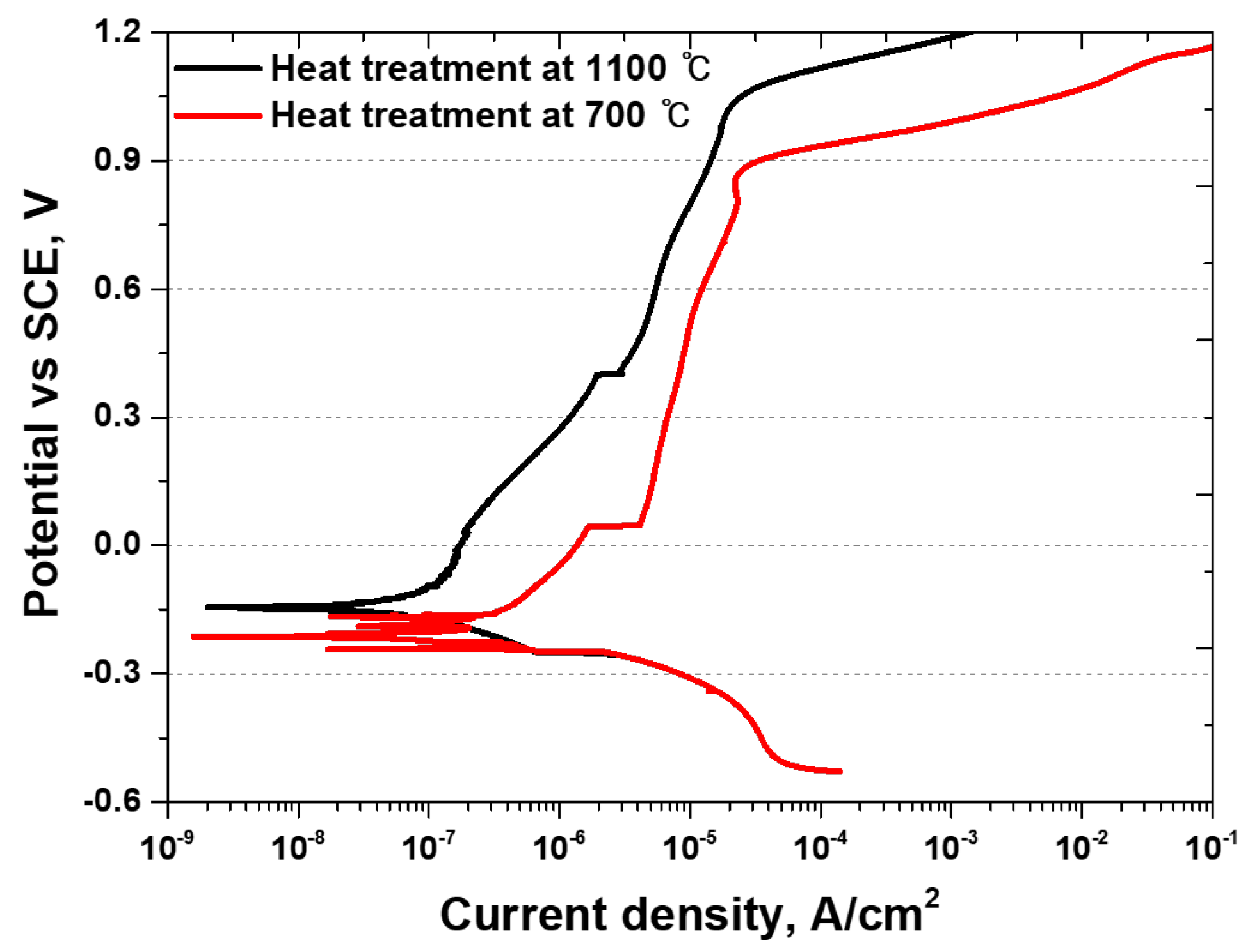
3.4. Electrochemical Behavior
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
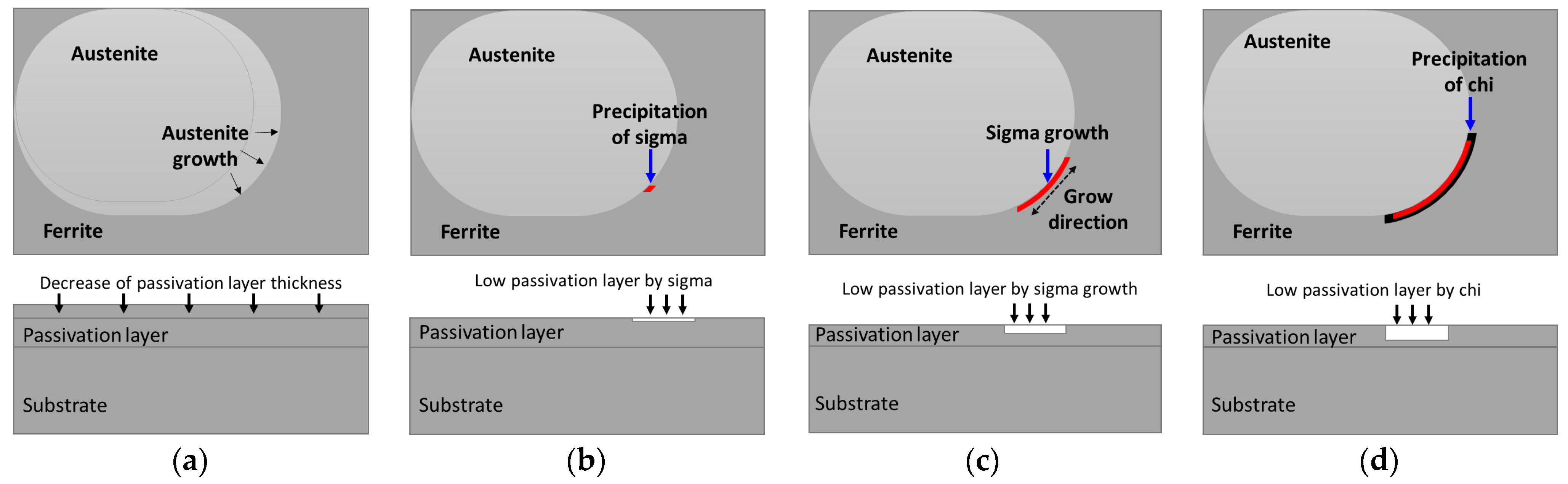
- SDSS SAF2507 exhibited precipitation of the secondary phase at 700 °C. The precipitation of the secondary phase began at the boundaries of austenite when ferrite transformed into austenite. The ferrite had a high Cr content of 26.6 wt%, whereas austenite had a lower Cr content of 23.3%. As a result, during the transformation from ferrite to austenite, over 3% of the Cr from ferrite was transferred to austenite. Owing to the precipitation of undissolved Cr and Mo at the austenite boundaries, the secondary phase also undergoes precipitation. The precipitated secondary phase grew along the austenite boundaries.
- (2)
- The secondary phase, Sigma, precipitated primarily because of the segregation of Cr and Mo, was followed by the formation of the Chi phase because of deficiencies in Cr and Mo. Additionally, N, which remains unincorporated into Sigma and Chi, precipitated as CrN. The precipitation of the secondary phase, which was influenced by the segregation of Cr and Mo, led to differences in the PREN. These differences in the PREN contributed to galvanic corrosion and reduced corrosion resistance. The galvanic corrosion resulted from compositional variations. Therefore, if ignition occurs and the secondary phase precipitates during the use of Li-ion batteries, this may lead to a decrease in corrosion resistance due to galvanic corrosion.
- (3)
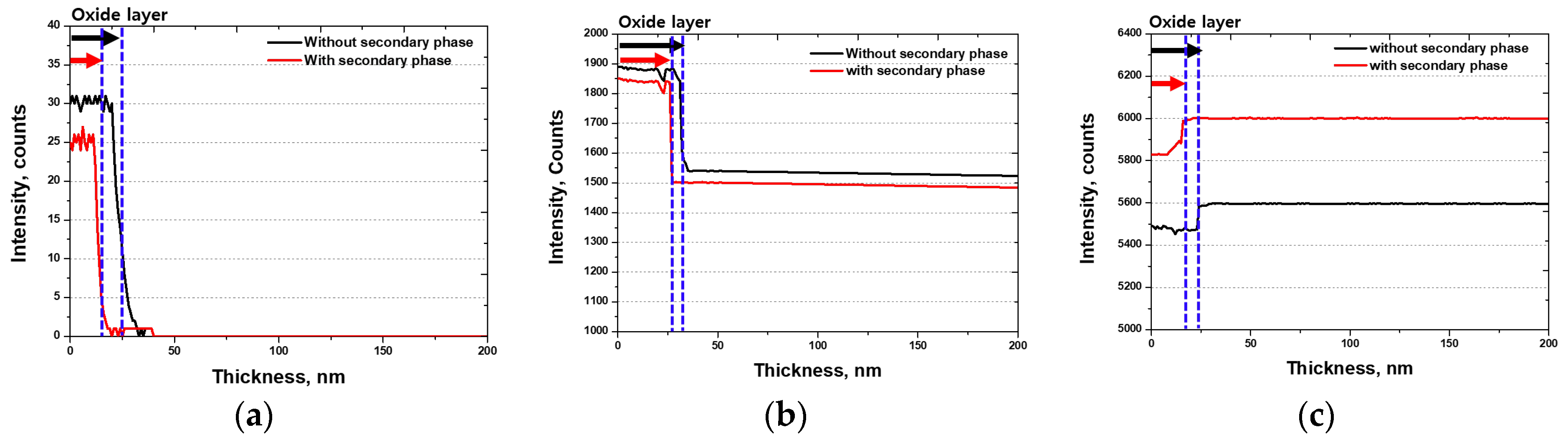
- The secondary phase affected the thickness and chemical composition of the passivation layer. After the solution heat treatment, the depth of the passivation layer was 30 nm, whereas after the precipitation of the secondary phase, it decreased to 25 nm. The precipitation of Cr in the secondary phase decreased the thickness of the passivation layer. This decrease in the thickness of the passivation layer reduces the corrosion resistance and may shorten the lifespan of Li-ion batteries. Therefore, applying SDSS UNS S 32750 as a material for Li-ion battery cases can enhance stability. However, if recycled, it must undergo solution heat treatment without failure because of the secondary phase.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, J.; Fatima, S.A. A DFT Study of TiC3 as Anode Material for Li-Ion Batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 638, 158024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-S.; Park, C.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-U.; Jeong, G.; Sohn, H.-J. Quartz (SiO2): A New Energy Storage Anode Material for Li-Ion Batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6895–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizeray, A.M.; Howey, D.A.; Monroe, C.W. Resolving a Discrepancy in Diffusion Potentials, with a Case Study for Li-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, E223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Lin, X. Li-Ion Battery Individual Electrode State of Charge and Degradation Monitoring Using Battery Casing through Auto Curve Matching for Standard CCCV Charging Profile. Appl. Energy 2022, 321, 119367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudoroiu, R.-E.; Zaheeruddin, M.; Tudoroiu, N.; Radu, S.M.; Chammas, H. Investigations of Different Approaches for Controlling the Speed of an Electric Motor with Nonlinear Dynamics Powered by a Li-Ion Battery-Case Study; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, M.; Prada, E.; Sauvant-Moynot, V. Development of an Empirical Aging Model for Li-Ion Batteries and Application to Assess the Impact of Vehicle-to-Grid Strategies on Battery Lifetime. Appl. Energy 2016, 172, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klink, J.; Hebenbrock, A.; Grabow, J.; Orazov, N.; Nylén, U.; Benger, R.; Beck, H.-P. Comparison of Model-Based and Sensor-Based Detection of Thermal Runaway in Li-Ion Battery Modules for Automotive Application. Batteries 2022, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, S.; Heredia, W.G.B.; Ghatpande, O.A. Resilience Metrics for Building-Level Electrical Distribution Systems with Energy Storage. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Sustainability (SusTech), Corona, CA, USA, 21–23 April 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- 9Banaszczyk, J.; De Mey, G.; Anca, A.; Schwarz, A.; Van Langenhove, L. Contact Resistance Investigation between Stainless Steel Electroconductive Yarns. In Proceedings of the 2009 MIXDES-16th International Conference Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits & Systems, Lodz, Poland, 25–27 June 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 417–419. [Google Scholar]
- Koleva, M.; Shi, Y.; McKenna, K.; Craig, M.; Nagarajan, A. Optimal Strategies for Hybrid Battery Storage Systems Design. Energy Technol. 2023, 11, 2300115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoosain, S.E.; Tshabalala, L.C.; Skhosana, S.; Freemantle, C.; Mndebele, N. Investigation of the Properties of Direct Energy Deposition Additive Manufactured 304 Stainless Steel. S. Afr. J. Ind. Eng. 2021, 32, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.-R.; Choi, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-S. Effect of Laser Peening on the Corrosion Properties of 304L Stainless Steel. Materials 2023, 16, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharyya, S.G.; Khandelwal, A.; Kain, V.; Kumar, A.; Samajdar, I. Surface Working of 304L Stainless Steel: Impact on Microstructure, Electrochemical Behavior and SCC Resistance. Mater. Charact. 2012, 72, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speidel, M.O. Nitrogen Containing Austenitic Stainless Steels. Mater. Werkst. Entwickl. Fert. Prüfung Eig. Anwendungen Tech. Werkst. 2006, 37, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fande, A.W.; Taiwade, R.V. Welding of Super Duplex Stainless Steel and Austenitic Stainless Steel:# Xd; Influence and Role of Bicomponent Fluxes. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2023, 38, 434–448. [Google Scholar]
- Paulraj, P.; Garg, R. Effect of Intermetallic Phases on Corrosion Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Duplex Stainless Steel and Super-Duplex Stainless Steel. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2015, 9, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhdoom, M.A.; Ahmad, A.; Kamran, M.; Abid, K.; Haider, W. Microstructural and Electrochemical Behavior of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Weldments. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 9, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.-Y.; Jang, M.-H.; Lee, T.-H.; Moon, J. Interpretation of the Relation between Ferrite Fraction and Pitting Corrosion Resistance of Commercial 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel. Corros. Sci. 2014, 89, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadchi, A.; Hosseini, V.A.; Valiente Bermejo, M.A.; Axelsson, B.; Harati, E.; Högström, M.; Karlsson, L. Wire Laser Metal Deposition of 22% Cr Duplex Stainless Steel: As-Deposited and Heat-Treated Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 9556–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeriano, L.d.C.; Correa, E.O.; Mariano, N.A.; Robin, A.L.M.; Machado, M.A.G. Influence of the Solution-Treatment Temperature and Short Aging Times on the Electrochemical Corrosion Behaviour of Uns S32520 Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, e20180774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.-H.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Ok, J.-W.; Kim, D.-I.; Yoon, J.-H. Study of Electroless Nickel Plating on Super Duplex Stainless Steel for Lithium-Ion Battery Cases: Electrochemical Behaviour and Effects of Plating Time. Metals 2024, 14, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.; Shin, B.-H.; Chung, W. Effect of Heat Energy Input on Electrochemical Properties of Solution-Annealed Super-Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S 32750 Laser Welding. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 220339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, L.N.; Lee, D. The Characteristics of Laser Welding of a Thin Aluminum Tab and Steel Battery Case for Lithium-Ion Battery. Metals 2020, 10, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beziou, O.; Hamdi, I.; Boumerzoug, Z.; Brisset, F.; Baudin, T. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Welded Joint of X70 Steel Joined to Duplex Stainless Steel by Gas Tungsten Arc Welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 127, 2799–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignal, V.; Delrue, O.; Heintz, O.; Peultier, J. Influence of the Passive Film Properties and Residual Stresses on the Micro-Electrochemical Behavior of Duplex Stainless Steels. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 7118–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, H.; Yıldız, Ç.; Arshad, A.; Arıcı, M.; Choukairy, K.; El Alami, M. Passive Thermal Management Strategy for Cooling Multiple Portable Electronic Components: Hybrid Nanoparticles Enhanced Phase Change Materials as an Innovative Solution. J. Energy Storage 2023, 70, 108087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, K.; Kim, D.-I.; Chung, W.; Shin, B.-H. The Effect of Surface Roughness on Re-Passivation and Pitting Corrosion of Super Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S 32760. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2023, 18, 100351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topolska, S.; Łabanowski, J. Effect of Microstructure on Impact Toughness of Duplex and Superduplex Stainless Steels. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2009, 36, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, J.-O. Super Duplex Stainless Steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1992, 8, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linton, V.M.; Laycock, N.J.; Thomsen, S.J.; Klumpers, A. Failure of a Super Duplex Stainless Steel Reaction Vessel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2004, 11, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatsuka, S.; Nishimoto, M.; Muto, I.; Kawamori, M.; Takara, Y.; Sugawara, Y. Micro-Electrochemical Insights into Pit Initiation Site on Aged UNS S32750 Super Duplex Stainless Steel. NPJ Mater. Degrad. 2023, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.O.; Wilson, A. Influence of Isothermal Phase Transformations on Toughness and Pitting Corrosion of Super Duplex Stainless Steel SAF 2507. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1993, 9, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Kim, D.-I.; Shin, B.-H.; Yoon, J.-H. Effects of Passivation with Cu and W on the Corrosion Properties of Super Duplex Stainless Steel PRE 42. Metals 2024, 14, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehovnik, F.; Arzensek, B.; Arh, B.; Skobir, D.; Pirnar, B.; Zuzek, B. Microstructure Evolution in SAF 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Mater. Technol. 2011, 45, 339–345. [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson, N.; Pettersson, R.F.A.; Wessman, S. Precipitation of Chromium Nitrides in the Super Duplex Stainless Steel 2507. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.; Kim, K.; Chung, W.; Shin, B.-H. Electrochemical Properties of UNS S 32750 and UNS S 32760 Annealed Super Duplex Stainless Steels. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 220526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente Bermejo, M.A.; Thalavai Pandian, K.; Axelsson, B.; Harati, E.; Kisielewicz, A.; Karlsson, L. Microstructure of Laser Metal Deposited Duplex Stainless Steel: Influence of Shielding Gas and Heat Treatment. Weld. World 2021, 65, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, F.N.U.M.; Shakil, S.I.; Shaha, S.K.; Kacher, J.; Nasiri, A.; Haghshenas, M.; Hadadzadeh, A. Study of Direct Aging Heat Treatment of Additively Manufactured PH13–8Mo Stainless Steel: Role of the Manufacturing Process, Phase Transformation Kinetics, and Microstructure Evolution. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 3772–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.; Casteletti, L.C. Sigma Phase Morphologies in Cast and Aged Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E 1245; Standard Practice for Determining the Inclusion or Second-Phase Constituent Content of Metals by Automatic Image Analysis. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Maurya, A.K.; Pandey, C.; Chhibber, R. Effect of Filler Metal Composition on Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization of Dissimilar Welded Joint of Nitronic Steel and Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2022, 22, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, K.U.; Kumar, R.; Mahapatra, M.M.; Mulik, R.S.; Świerczyńska, A.; Fydrych, D.; Pandey, C. Wire Arc Additive Manufactured Mild Steel and Austenitic Stainless Steel Components: Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Residual Stresses. Materials 2022, 15, 7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlina, J.; Reboun, J.; Simonovsky, M.; Syrovy, T.; Janda, M.; Hamacek, A. Study of New Nitrogen-Fireable Copper-Nickel Thick Film Paste Formulation Compatible with Thick Printed Copper. Materials 2022, 15, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G61; Standard Test Method for Conducting Cyclic Potentiodynamic Polarization Measurements for Localized Corrosion Susceptibility of Iron-, Nickel-, or Cobalt-Based Alloys. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Kannan, A.R.; Shanmugam, N.S.; Rajkumar, V.; Vishnukumar, M. Insight into the Microstructural Features and Corrosion Properties of Wire Arc Additive Manufactured Super Duplex Stainless Steel (ER2594). Mater. Lett. 2020, 270, 127680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhoud, A.M.; Renton, N.C.; Deans, W.F. Hydrogen Embrittlement of Super Duplex Stainless Steel in Acid Solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 6455–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.-Y.; Lee, T.-H.; Bae, J.-H.; Chun, D.W. Molybdenum Effects on Pitting Corrosion Resistance of FeCrMnMoNC Austenitic Stainless Steels. Metals 2018, 8, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybalka, K.V.; Beketaeva, L.A.; Davydov, A.D. Electrochemical Behavior of Stainless Steel in Aerated NaCl Solutions by Electrochemical Impedance and Rotating Disk Electrode Methods. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2006, 42, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, E.; Cristiani, P.; Grattieri, M.; Santoro, C.; Li, B.; Trasatti, S. Electrochemical Behavior of Stainless Steel Anodes in Membraneless Microbial Fuel Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 161, H62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Elements | C | N | Mn | Ni | Cr | Mo | Fe | PREN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical composition (wt%) | 0.01 | 0.27 | 0.8 | 6.8 | 25.0 | 3.8 | Bal | 42.0 |
| Phase | C | N | Mn | Ni | Cr | Mo | Fe | PREN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Casted | Austenite | 0.01 | 0.55 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 7.8 ± 0.5 | 22.8 ± 1.1 | 3.0 ± 0.4 | Bal | 41.4 |
| Ferrite | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 5.6 ± 0.5 | 27.2 ± 1.1 | 4.5 ± 0.4 | Bal | 42.9 | |
| Annealed | Austenite | 0.01 | 0.51 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 7.9 ± 0.5 | 23.3 ± 1.2 | 3.2 ± 0.4 | Bal | 42.0 |
| Ferrite | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.5 | 26.6 ± 1.2 | 4.4 ± 0.4 | Bal | 42.1 |
| Phase | Cr | Mo | Ni | Mn | Fe | PREN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma | 31.0 ± 1.4 | 9.1 ± 1.1 | 4.5 ± 0.8 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 56.3 ± 3.1 | 61.0 |
| Chi | 22.0 ± 0.9 | 2.1 ± 0.5 | 9.5 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 65.2 ± 2.4 | 28.9 |
| Heat Treatment | Ecorr | Icorr | Epit |
|---|---|---|---|
| At 700 °C | −270 mV | 2 × 10−7 A/cm2 | 890 mV |
| At 1100 °C | −150 mV | 1 × 10−9 A/cm2 | 1040 mV |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, B.-H.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Ok, J.-W.; Kim, D.; Yoon, J.-H. Effect of Secondary Phase on Passivation Layer of Super Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S 32750: Advanced Safety of Li-Ion Battery Case Materials. Materials 2024, 17, 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112760
Shin B-H, Kim S, Park J, Ok J-W, Kim D, Yoon J-H. Effect of Secondary Phase on Passivation Layer of Super Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S 32750: Advanced Safety of Li-Ion Battery Case Materials. Materials. 2024; 17(11):2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112760
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Byung-Hyun, Seongjun Kim, Jinyong Park, Jung-Woo Ok, Dohyung Kim, and Jang-Hee Yoon. 2024. "Effect of Secondary Phase on Passivation Layer of Super Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S 32750: Advanced Safety of Li-Ion Battery Case Materials" Materials 17, no. 11: 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112760
APA StyleShin, B.-H., Kim, S., Park, J., Ok, J.-W., Kim, D., & Yoon, J.-H. (2024). Effect of Secondary Phase on Passivation Layer of Super Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S 32750: Advanced Safety of Li-Ion Battery Case Materials. Materials, 17(11), 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112760






