Influence of Cyclic Heat Treatment Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 18Ni(C250) Maraging Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
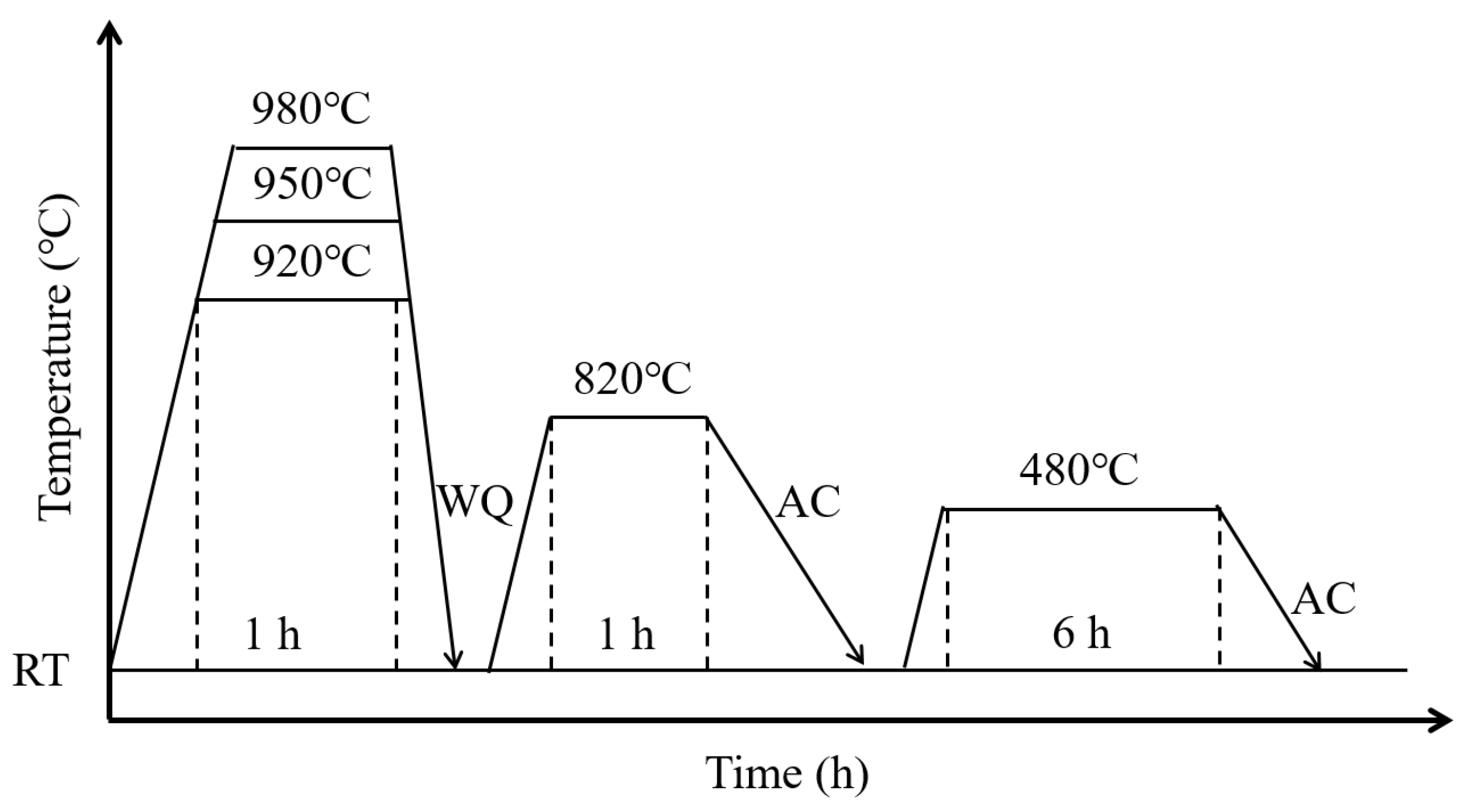
2.1. Materials and Heat Treatment Schedules
2.2. Material Tests
3. Results
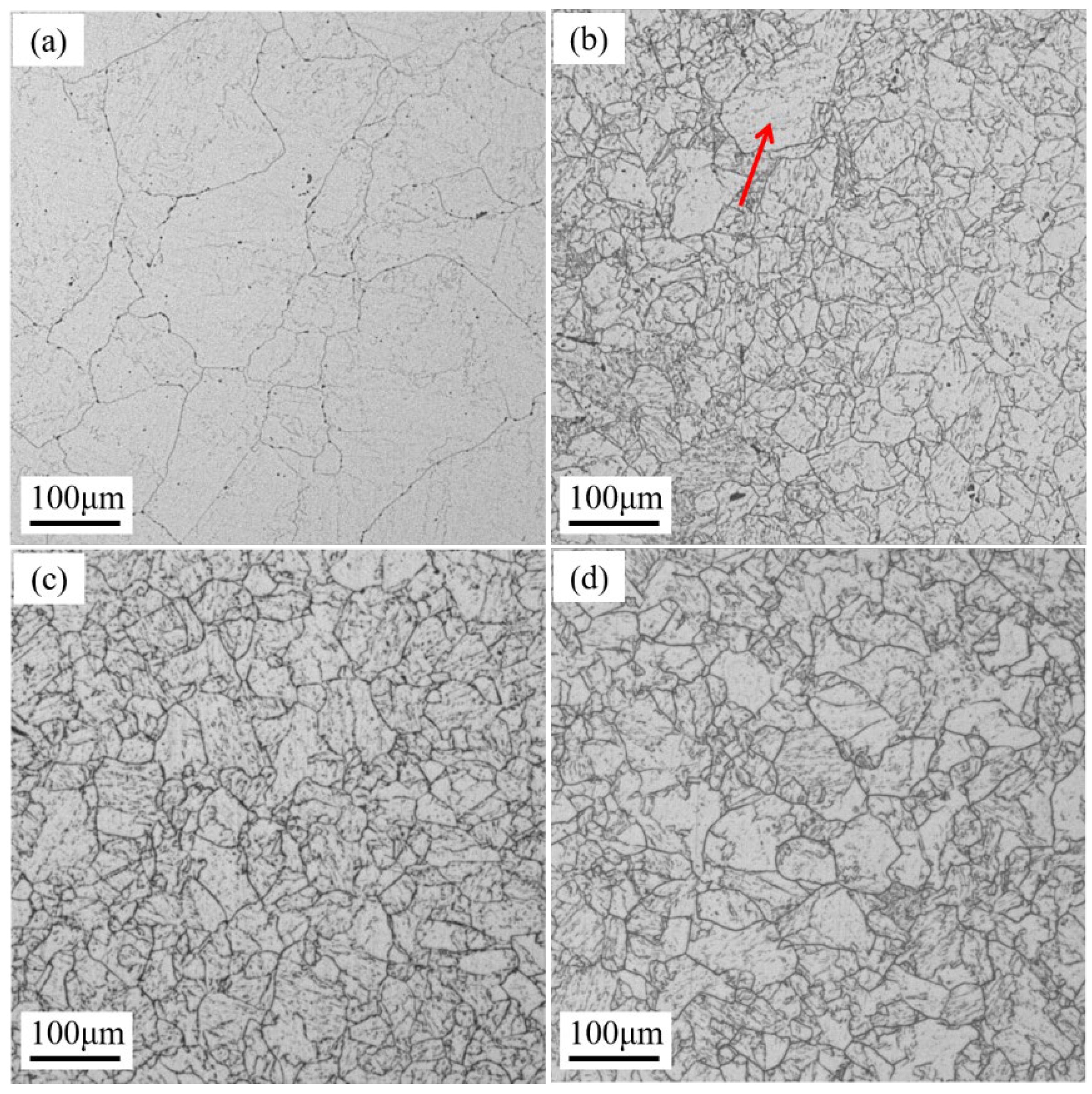
3.1. Analysis of Grain Morphology and Size
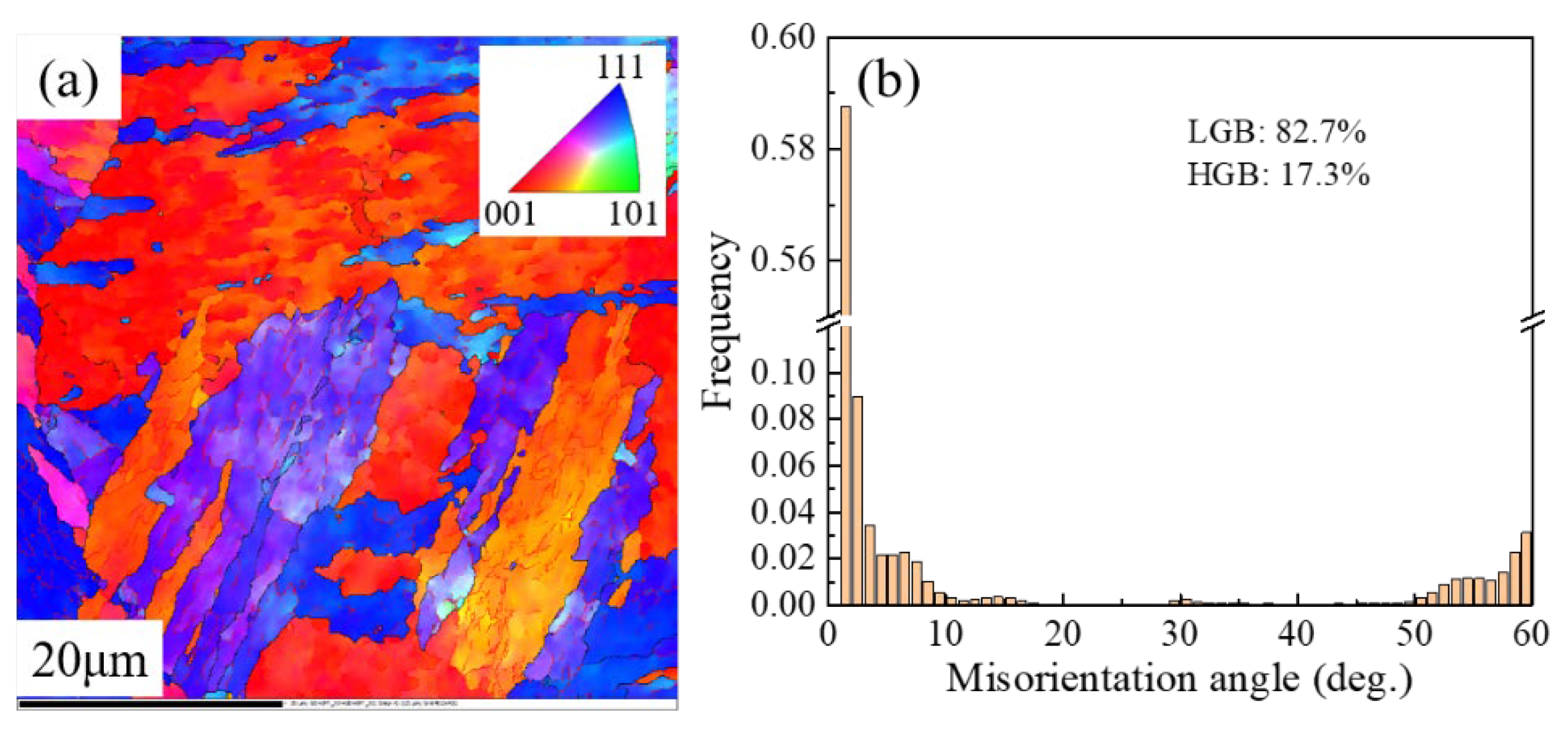
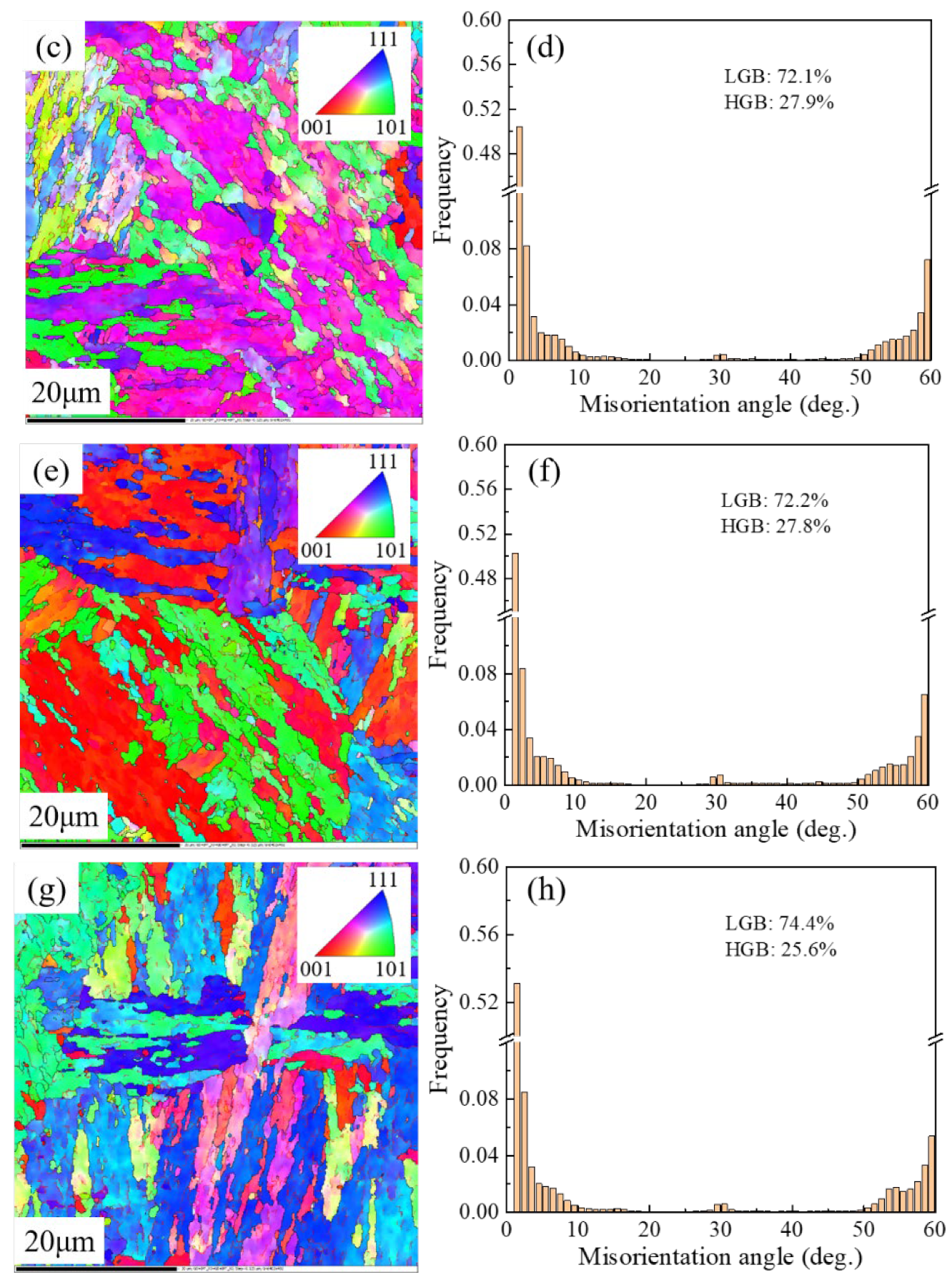
3.2. Evolution of Microstructure
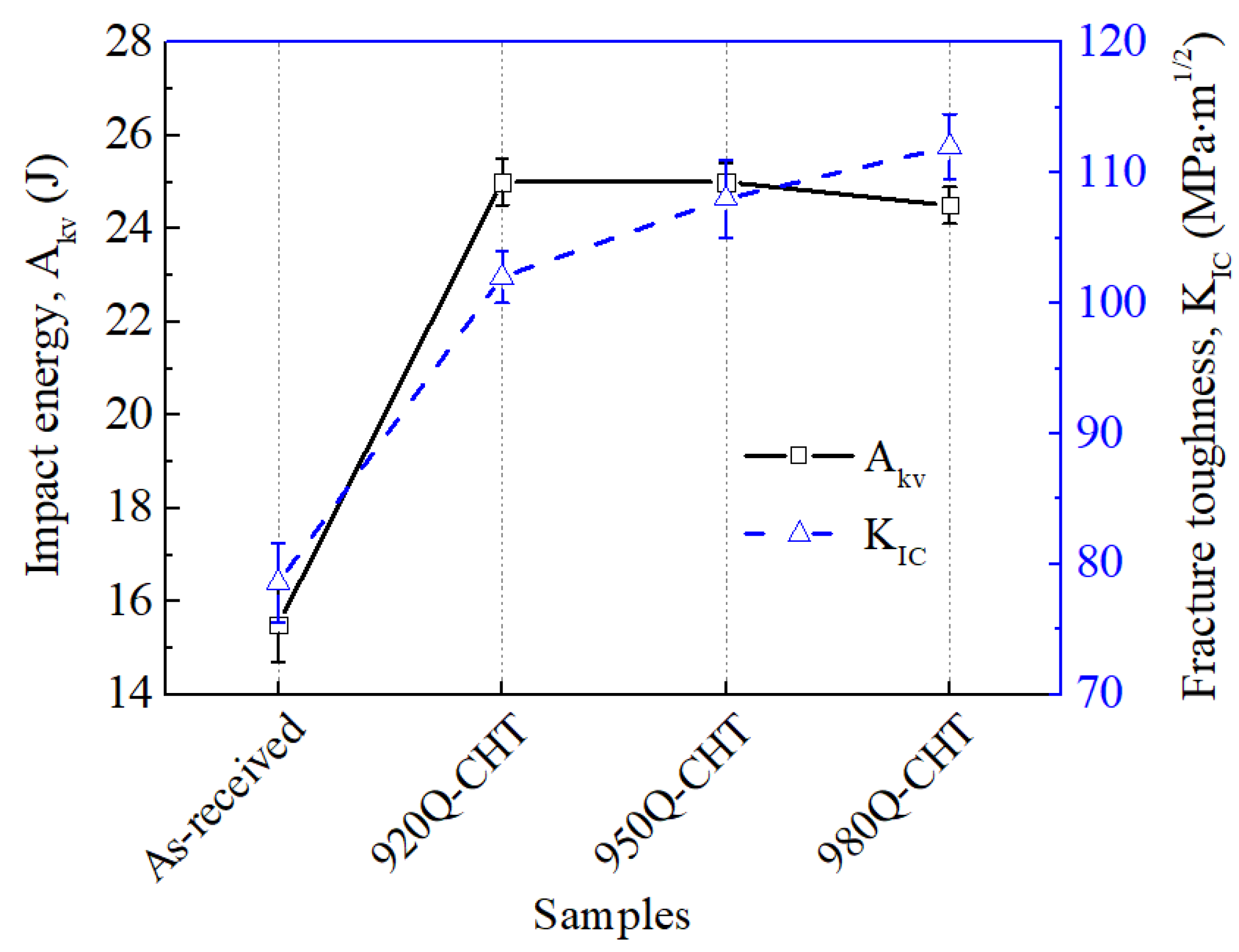
3.3. Analysis of Mechanical Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiss, B.Z. Maraging Steels-Structure, Properties and Applications. In Specialty Steels and Hard Materials; Pergamon Press Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1983; pp. 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.W., Jr. Making steel strong and cheap. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, P.; Duan, Q.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Optimizing the fatigue strength of 18Ni maraging steel through ageing treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 707, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Melero, E.; van Dijk, N.; Zhao, L.; Sietsma, J.; Offerman, S.; Wright, J.; van der Zwaag, S. Martensitic transformation of individual grains in low-alloyed TRIP steels. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereloma, E.; Shekhter, A.; Miller, M.; Ringer, S. Ageing behaviour of an Fe–20Ni–1.8Mn–1.6Ti–0.59Al (wt%) maraging alloy: Clustering, precipitation and hardening. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 5589–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiby, F.; Ul Haq, A.; Khan, A.Q. The properties and applications of 18% nickel maraging steels. Mater. Technology 1994, 9, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, V.K.; Kim, S.J.; Wayman, C.M. Precipitation reactions and strengthening behavior in 18 Wt Pct nickel maraging steels. Met. Trans. A 1990, 21, 2655–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.N. Progress in understanding the metallurgy of 18% nickel maraging steels. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 97, 1594–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Knowles, A.J.; Gong, P.; Rahman, K.M.; Rainforth, W.M.; Dye, D.; Galindo-Nava, E.I. Development of Ni-free Mn-stabilised maraging steels using Fe2SiTi precipitates. Acta Mater. 2019, 174, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhan, D.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Progress on improving strength-toughness of ultra-high strength martensitic steels for aerospace applications: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 172–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yu, B.; Misra, R.; Han, G.; Liu, S.; Shang, C. Strengthening of cobalt-free 19Ni3Mo1.5Ti maraging steel through high-density and low lattice misfit nanoscale precipitates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 715, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Qi, L.; Zhao, Y. Effect of austenitizing temperature on the mechanical properties of high-strength maraging steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 587, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzaki, K.; Maki, T. The Effect of Cooling Rate on the Morphology of Lath Martensite in Fe-Ni Alloys. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. Mater. 1981, 45, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morito, S.; Igarashi, R.; Kamiya, K.; Ohba, T.; Maki, T. Effect of Cooling Rate on Morphology and Crystallography of Lath Martensite in Fe-Ni Alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 638, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.M.; Wang, C.X. Study on grain refinement of18Ni maraging steel by cyclic transformation. Hot Work. Technol. 2012, 41, 194–199. [Google Scholar]
- Schnbauer, B.M.; Yanase, K.; Endo, M. The Influence of various types of small defects on the threshold behaviour of precipitation-hardened 17-4PH stainless steel. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2017, 87, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Yang, X.R.; Zhao, X.C.; Ma, W.Z. Influence of cyclic phase transformation on microstructure and properties of T250 maraging steel. Hot Work. Technol. 2015, 44, 190–194, 197. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wan, Q.; Yang, C. Effect of forging ratio on microstructure and properties of 18Ni(250) maraging steel. Forg. Stamp. Technol. 2020, 45, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E112-2013 Standard; Standard Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- ASTM A307-21 Standard; Standard Specification for Carbon Steel Bolts, Studs, and Threaded Rod 60000 psi Tensile Strength. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. Available online: https://infinitalab.com/astm/astm-a307-21/ (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- ASTM E399-2022 Standard; Standard Test Method for Linear-Elastic Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022. Available online: https://cdn.standards.iteh.ai/samples/112806/b586dccbd5764a10a5c5720781607a6e/ASTM-E399-22.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Chen, J.; Tang, S.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Wang, G.-D. Microstructural characteristics with various cooling paths and the mechanism of embrittlement and toughening in low-carbon high performance bridge steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 559, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvergaard, V. Material failure by void growth to coalescence. Adv. Appl. Mech. 1990, 27, 83–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzerga, A.A.; Leblond, J.B. Ductile fracture by void growth to coalescence. Adv. Appl. Mech. 2010, 44, 169–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-Z.; Wu, J.-J.; Huang, X.-F.; Hong, X.-F. SLM-manufactured 30CrMnSiA alloy: Mechanical properties and microstructural effects of designed heat treatment. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 107, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumofen, L.; Kirchheim, A.; Dennig, H.J. Laser powder bed fusion of 30CrNiMo8 steel for quenching and tempering: Examination of the processability and mechanical properties. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 5, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, T.H.; Kumar, P.; Ramamurty, U. Fracture and fatigue in additively manufactured metals. Acta Mater. 2021, 219, 117240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rack, H. The role of prior austenite grain size on the tensile ductility and fracture toughness of 18Ni maraging steels. Scr. Met. 1979, 13, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.; Kumar, B.R.; Datta, G.; Ranganath, V. Effect of microstructure and grain size on the fracture toughness of a micro-alloyed steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Gan, X.; Ma, G.; Luo, F.; Zou, H. The development of Ti-alloyed high strength microalloy steel. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 2891–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahed, M.; Bengtsson, S.; Boniardi, M.; Casaroli, A.; Casati, R.; Vedani, M. An investigation on the plane-strain fracture toughness of a water atomized 4130 low-alloy steel processed by laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 855, 143941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z. Short fatigue crack growth behavior in 18Ni marageing steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 807, 140844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, T.; Ischia, G.; Naclerio, F.; Ipek, R.; Molinari, A. Effect of a direct aging heat treatment on the microstructure and the tensile properties of a 18Ni-300 maraging steel produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 872, 144921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ye, Q.-B.; Zhao, T.; Hu, J.; Gao, X.-H.; Wang, Z.-D. Strengthening and toughening mechanisms in Ni-alloyed steel: Enhancing the integral stability of retained austenite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 852, 143703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Element | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | 0.0045 | <0.05 | <0.01 | 0.0022 | 0.0004 | 0.019 | 18.01 | <0.01 | 4.92 |
| Element | Ti | AI | As | Bi | Co | Fe | |||
| wt% | 0.40 | 0.12 | 0.0022 | 0.00003 | 7.72 | Remainder |
| Heat Treatment States | Grain Size (μm) | Grain-Size Number |
|---|---|---|
| As-received state | 91.8 | 3.5 ± 0.5 |
| 920 °C × 1 hWQ + 820 °C × 1 hAC | 24.5 | 7.5 ± 0.5 |
| 950 °C × 1 hWQ + 820 °C × 1 hAC | 22.3 | 8 ± 0.5 |
| 980 °C × 1 hWQ + 820 °C × 1 hAC | 25.0 | 7.5 ± 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, K.; Han, S.; Li, Z.; Geng, R.; Han, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Influence of Cyclic Heat Treatment Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 18Ni(C250) Maraging Steel. Materials 2024, 17, 2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17122796
Xiao K, Han S, Li Z, Geng R, Han G, Li Y, Wang C. Influence of Cyclic Heat Treatment Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 18Ni(C250) Maraging Steel. Materials. 2024; 17(12):2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17122796
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Kai, Shun Han, Zhixin Li, Ruming Geng, Gaoyang Han, Yong Li, and Chunxu Wang. 2024. "Influence of Cyclic Heat Treatment Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 18Ni(C250) Maraging Steel" Materials 17, no. 12: 2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17122796
APA StyleXiao, K., Han, S., Li, Z., Geng, R., Han, G., Li, Y., & Wang, C. (2024). Influence of Cyclic Heat Treatment Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 18Ni(C250) Maraging Steel. Materials, 17(12), 2796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17122796




