Microstructural Characterization, Tribological and Corrosion Behavior of H111 Hot-Rolled AA5754 after Homogenization and Aging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
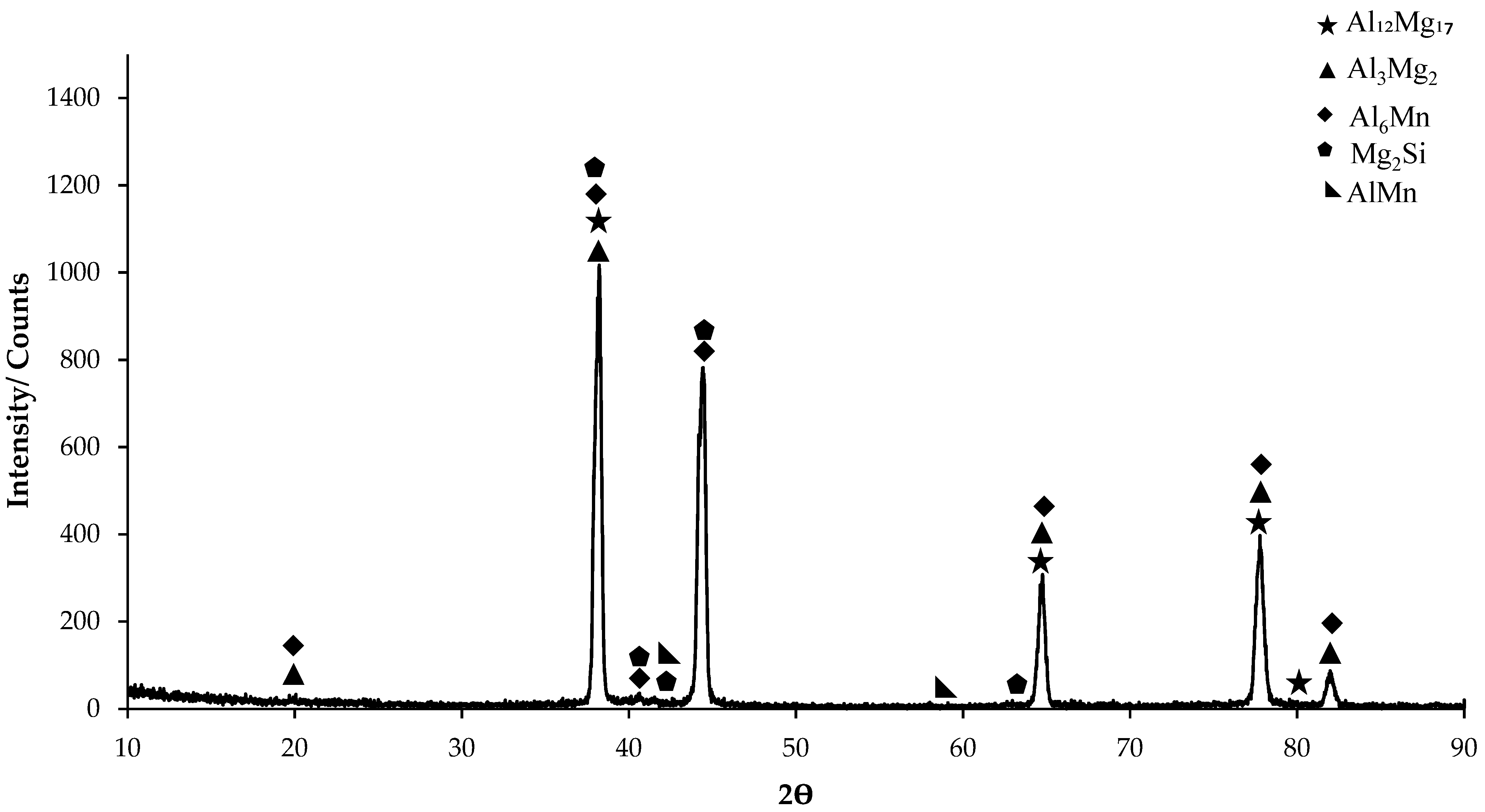
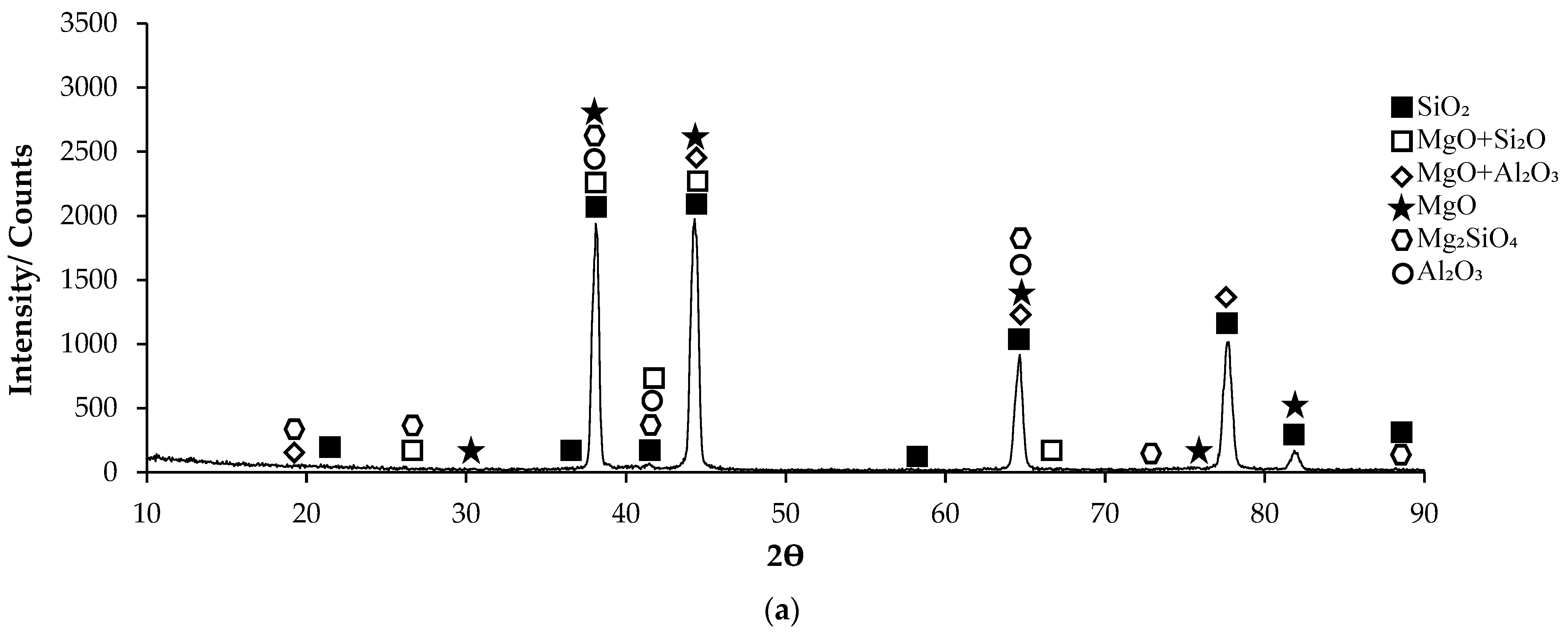
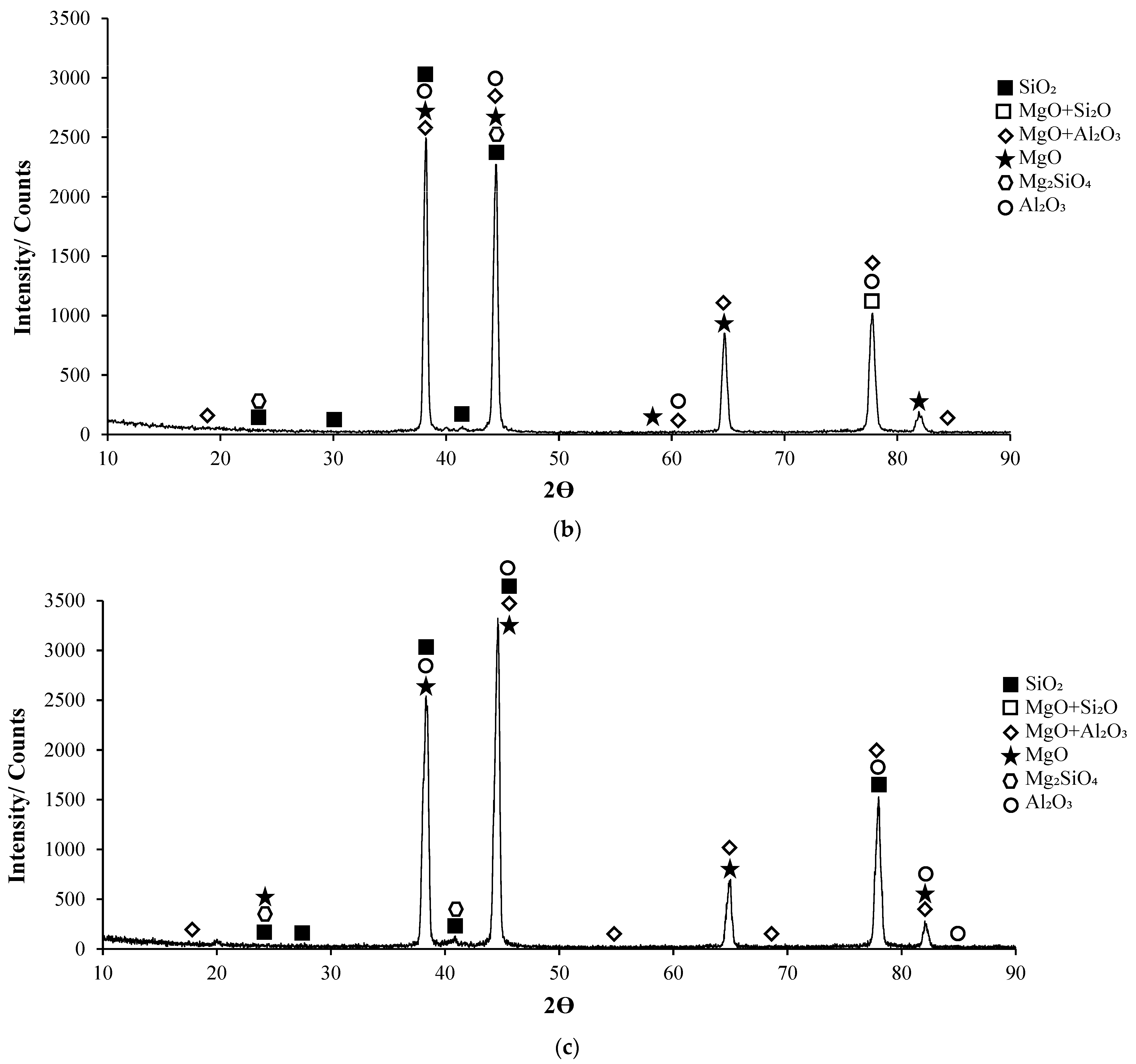
3.1. XRD Patterns
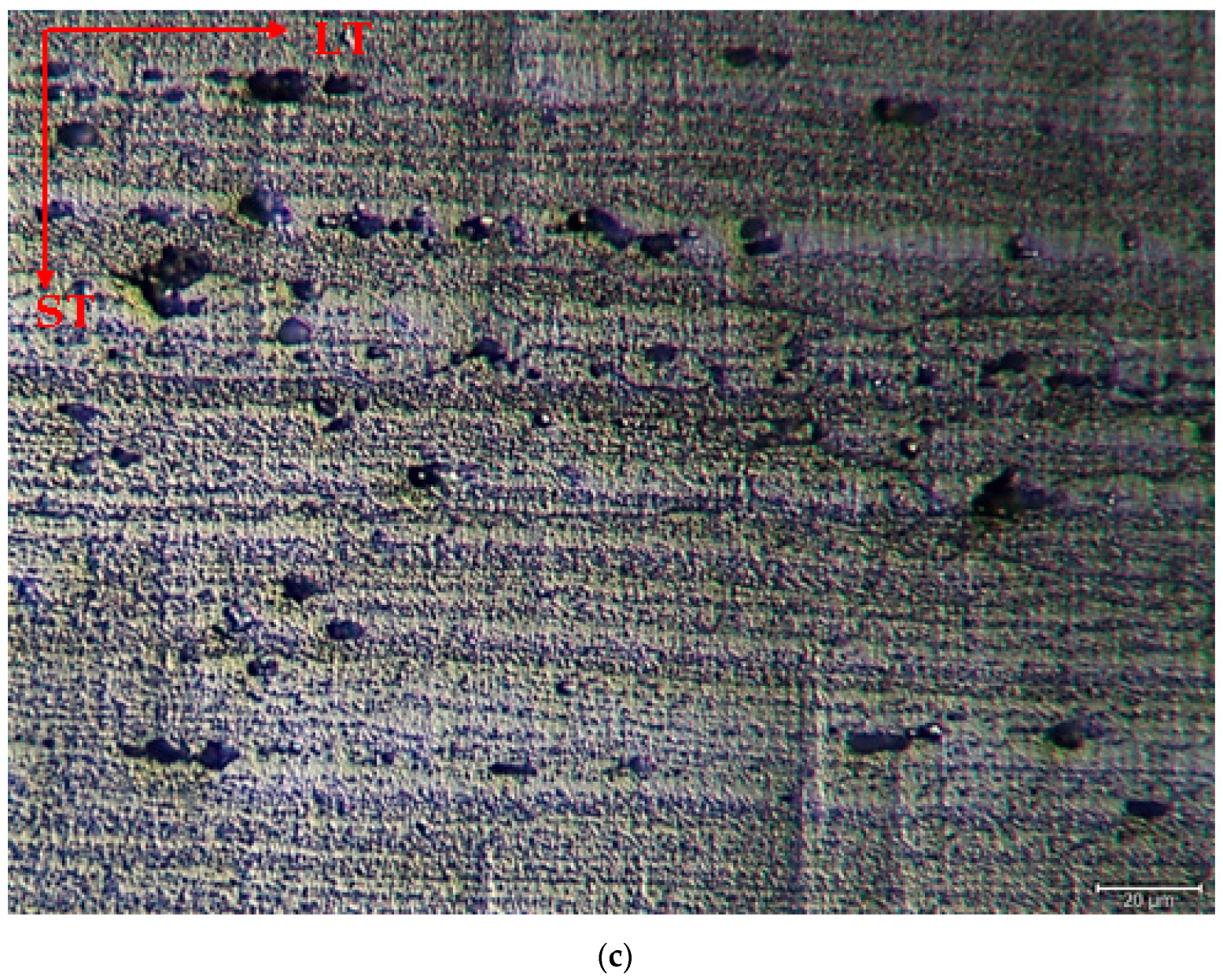
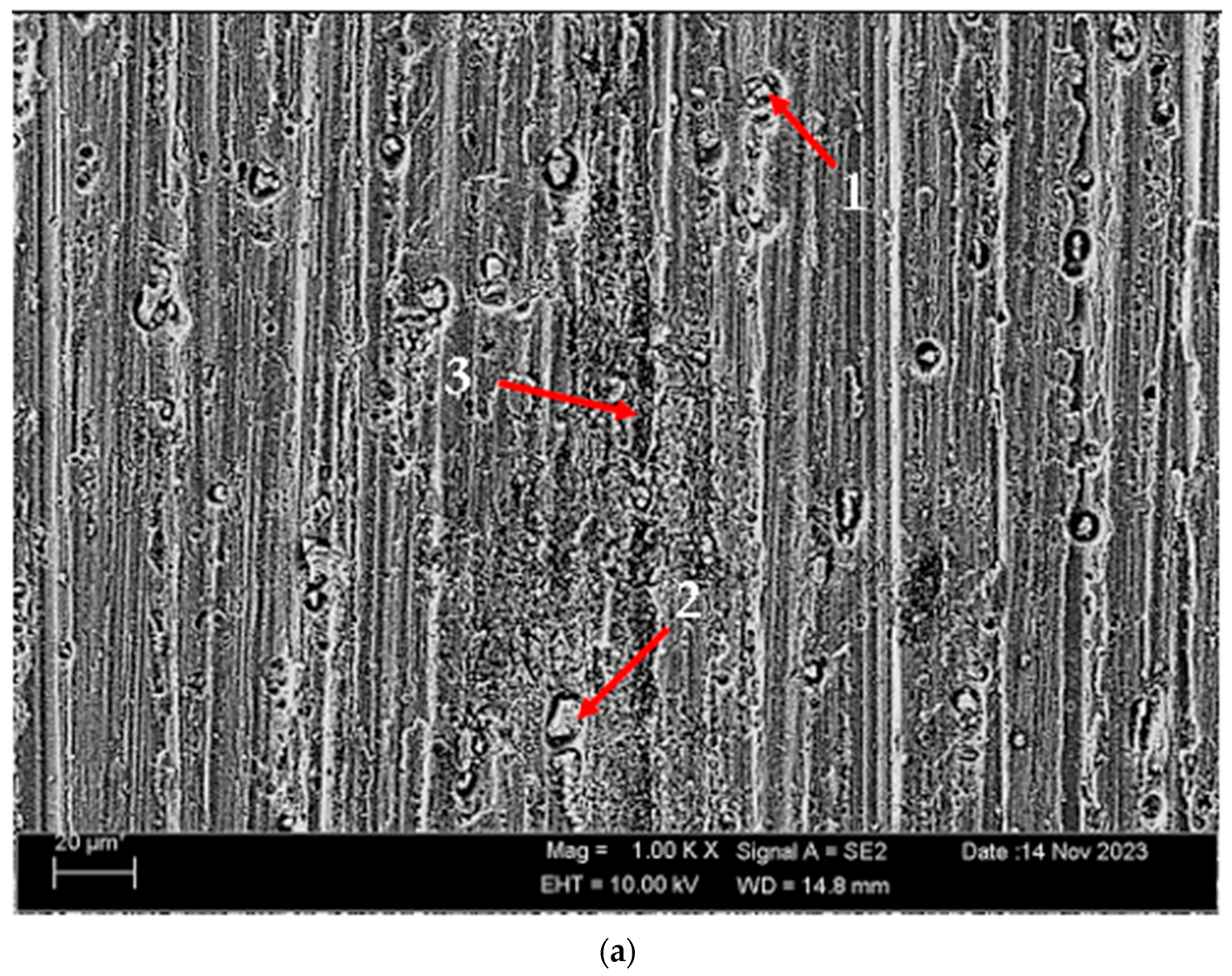
3.2. Microstructure
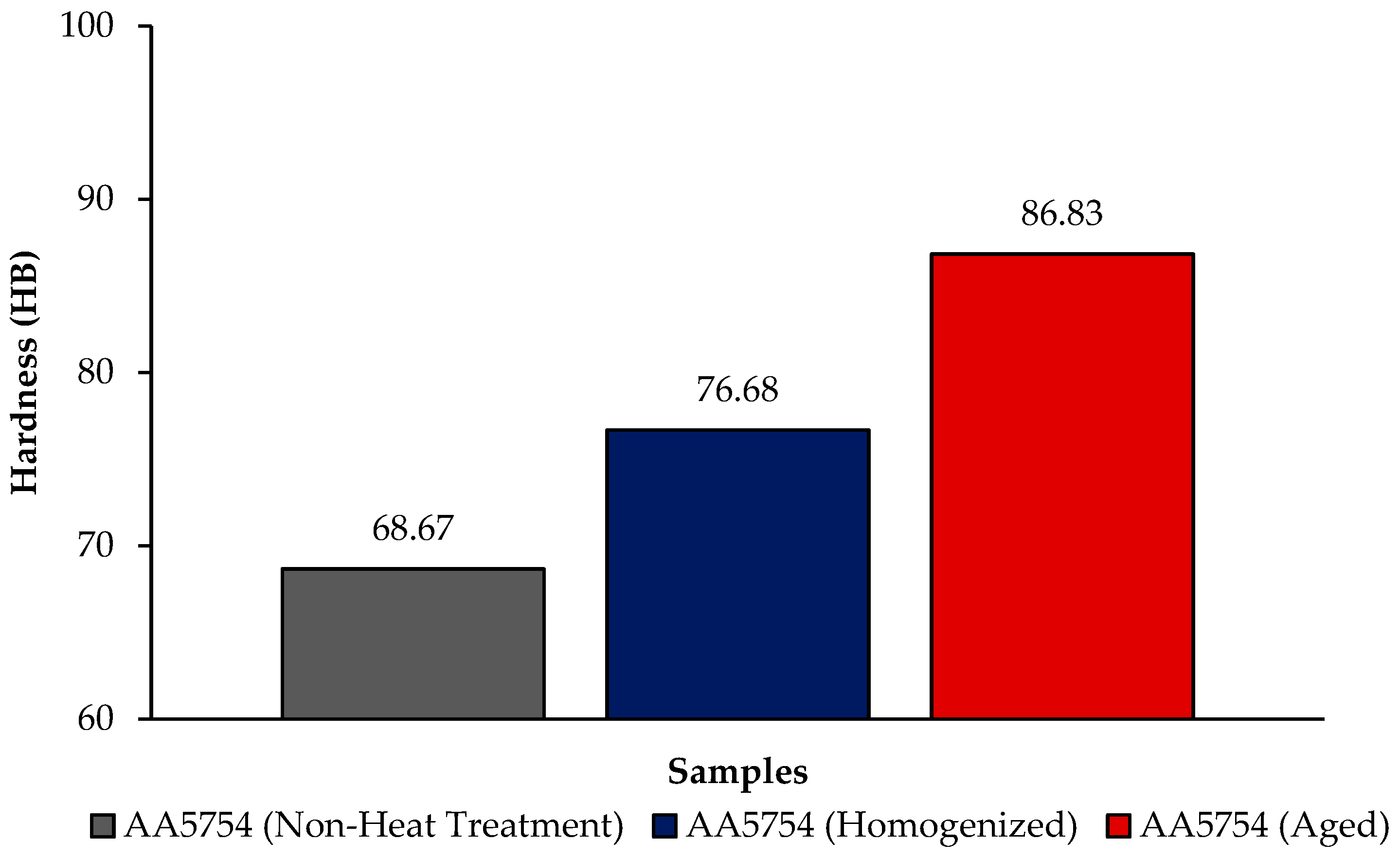
3.3. Hardness Test Results
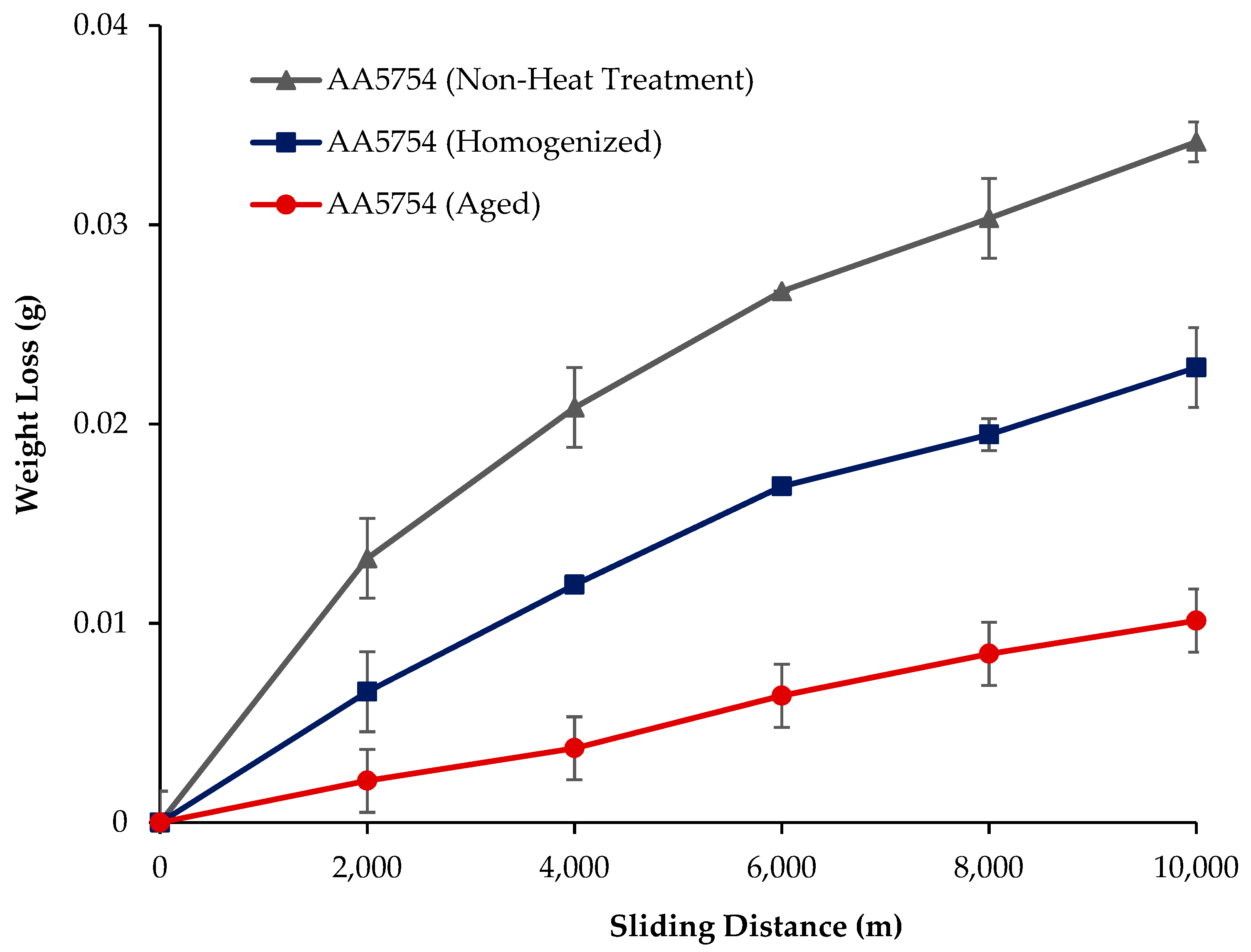
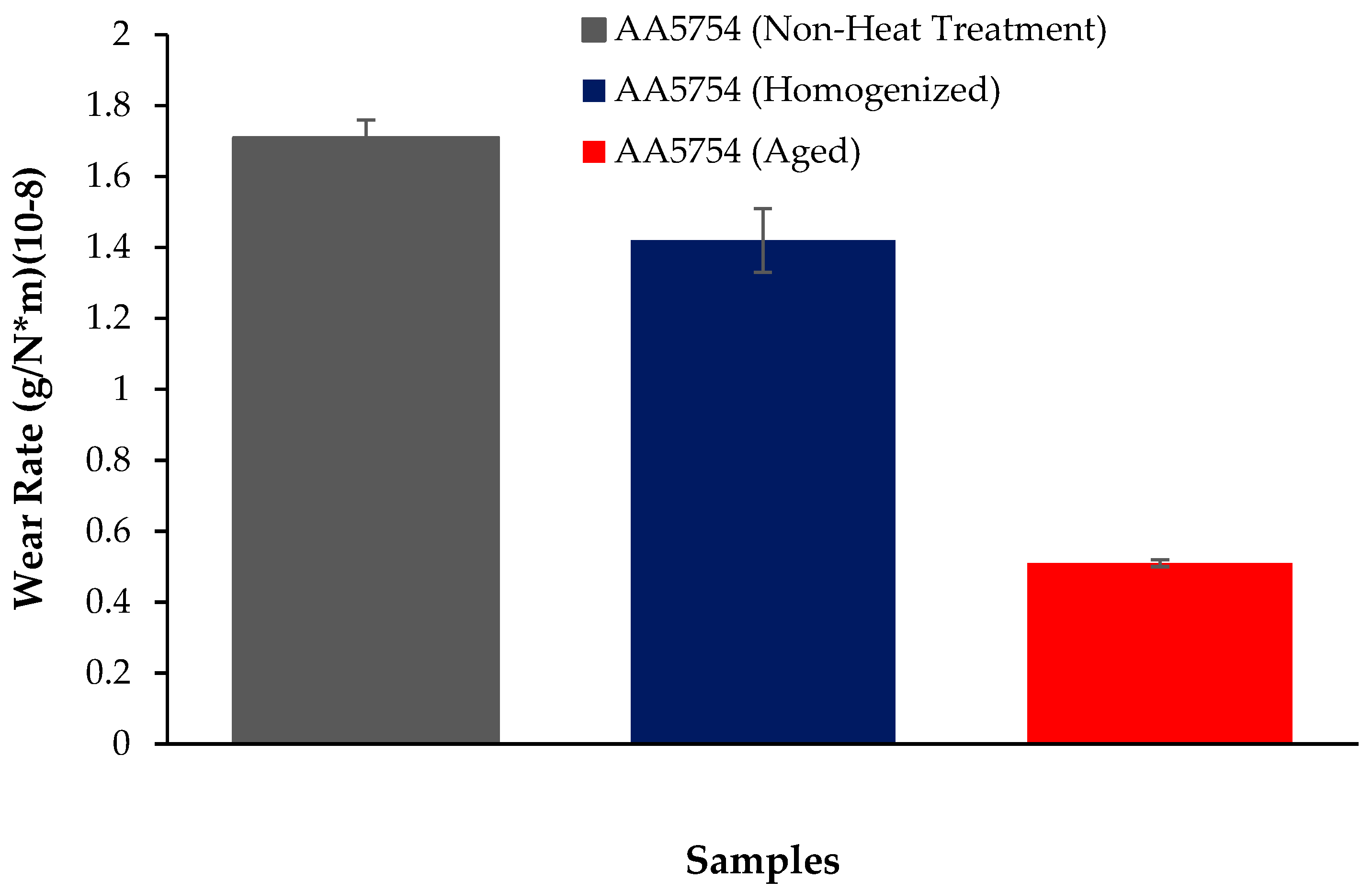
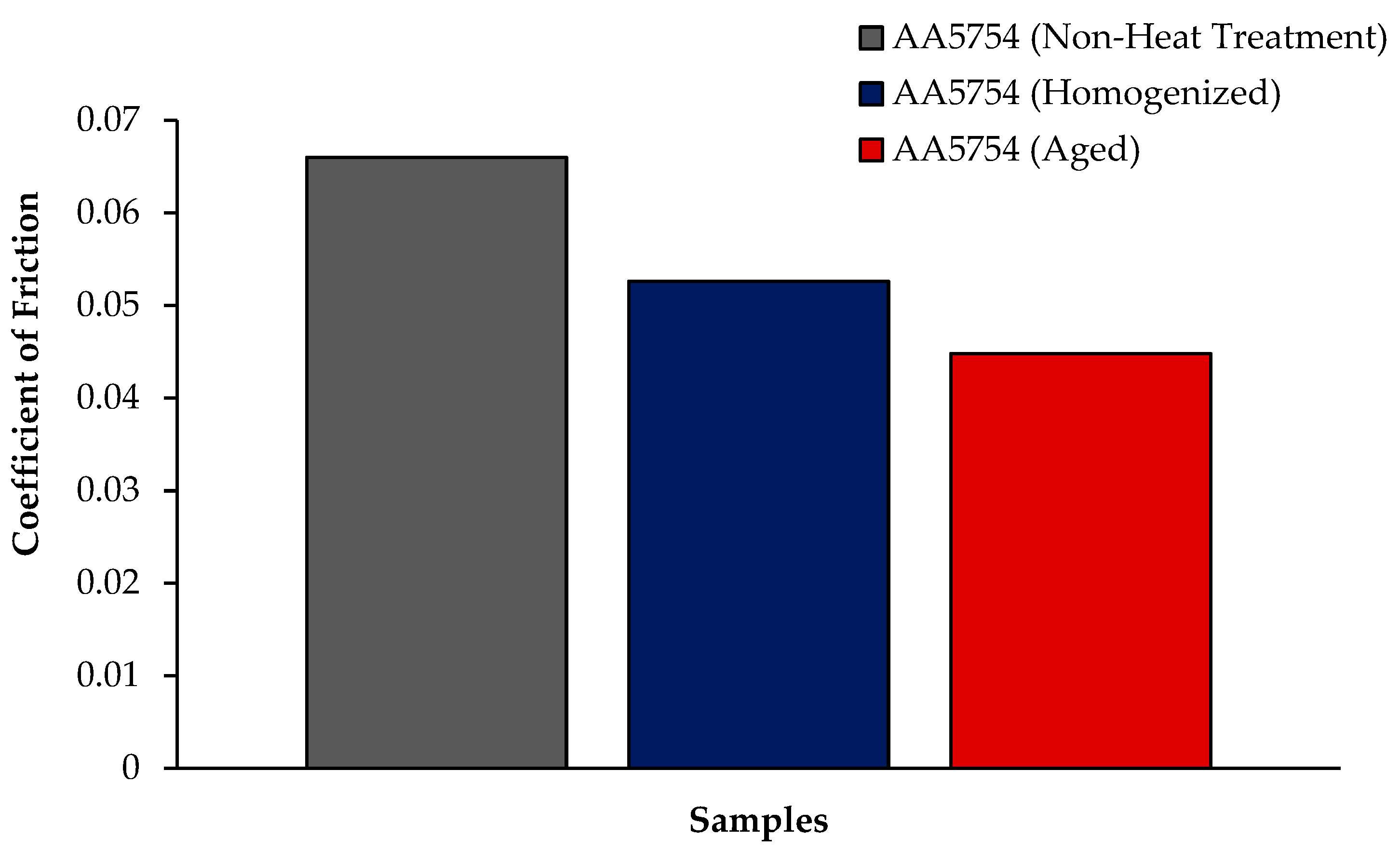
3.4. Wear Test Results
3.5. Corrosion Behavior
3.5.1. Immersion Test Results
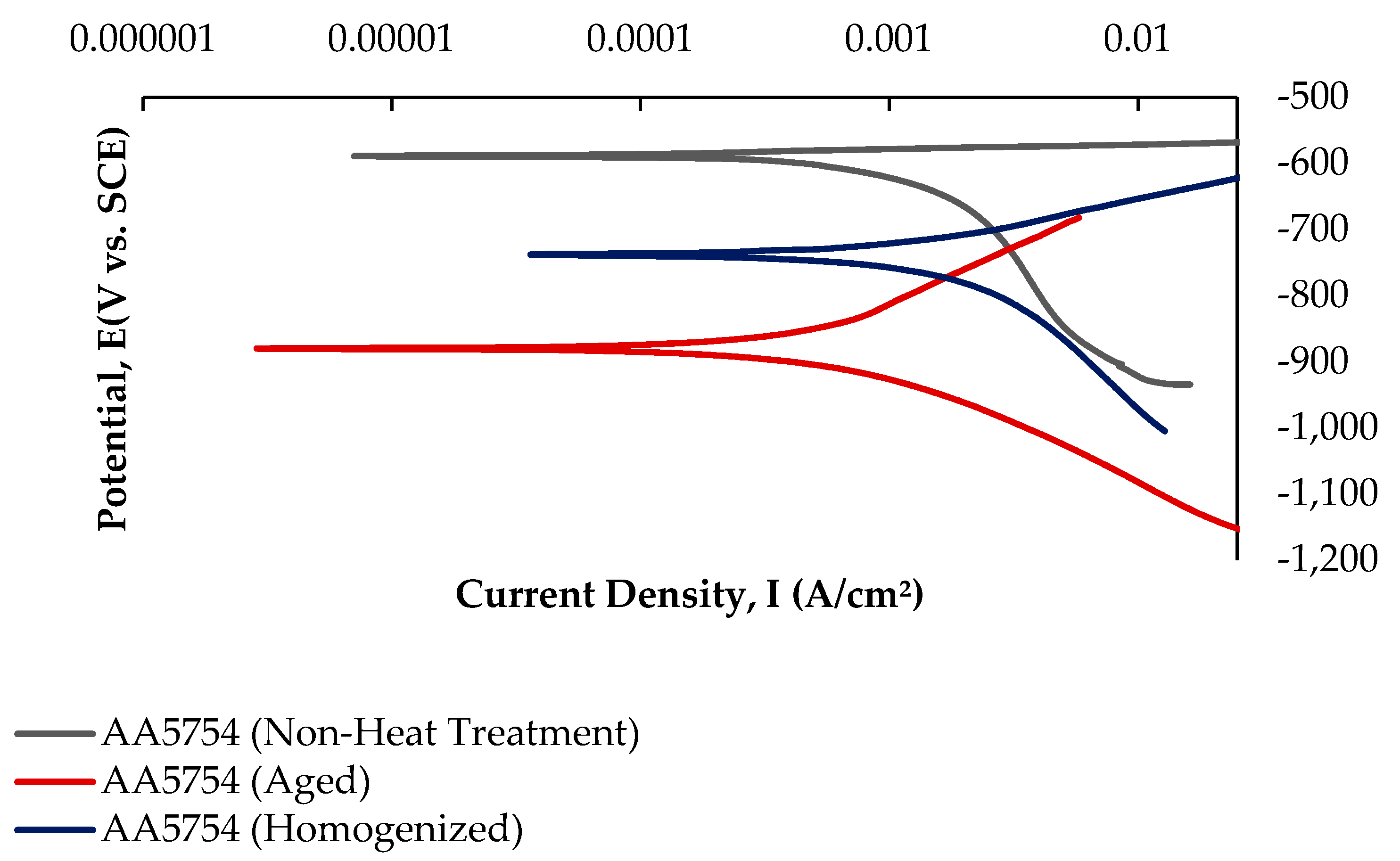
3.5.2. Potentiodynamic Polarization (PD) Tests
4. Conclusions
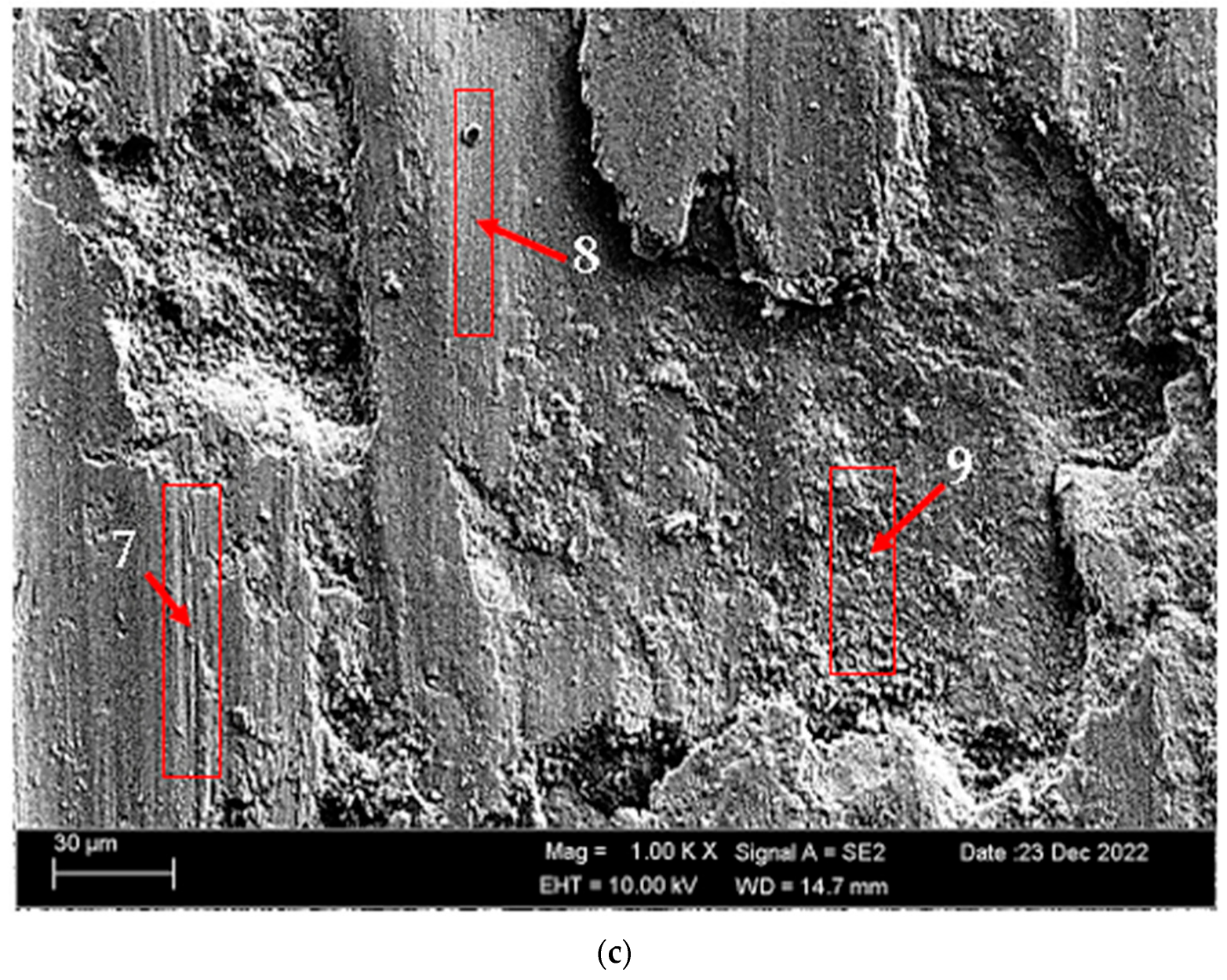
- The as-rolled material exhibits a dense pancake-shaped grain structure, which is typical of as-rolled material. Observation along the L-direction did not yield distinct demarcations among grains and there was no uniform distribution, with precipitates at the grain boundary. When they are aged, there is a parallel increase in fine and huge black and gray contrast particles in the zone. Therefore, it could be stated that the amount of fine grains increased due to the rise in the homogenization process. The rolled base metal with the grain orientation was found to be parallel to the rolling direction. On the other hand, the coarse grains were clearly observed in the aging heat-treatment condition. The grains have an elongated morphology consistent with the rolling process of the metal before the heat-treatment process.
- The aged alloy has the highest hardness with a value of 86.83 HB; the lowest hardness was seen in the alloy before heat treatment with a value of 68.67 HB.
- The weight loss and wear rate of this material at the end of 10,000 m are, respectively, 1.01 × 10−3 g and 5.07 × 10−9 g/Nm. It was observed that the alloy had the highest weight loss and worst wear resistance before heat treatment. Weight loss and wear rates at the end of 10,000 m are, respectively, 3.42 × 10−3 g and 17.08 × 10−9 g/Nm. According to these results, the friction coefficients during wear are parallel and the material with the lowest friction coefficient after aging is 0.045.
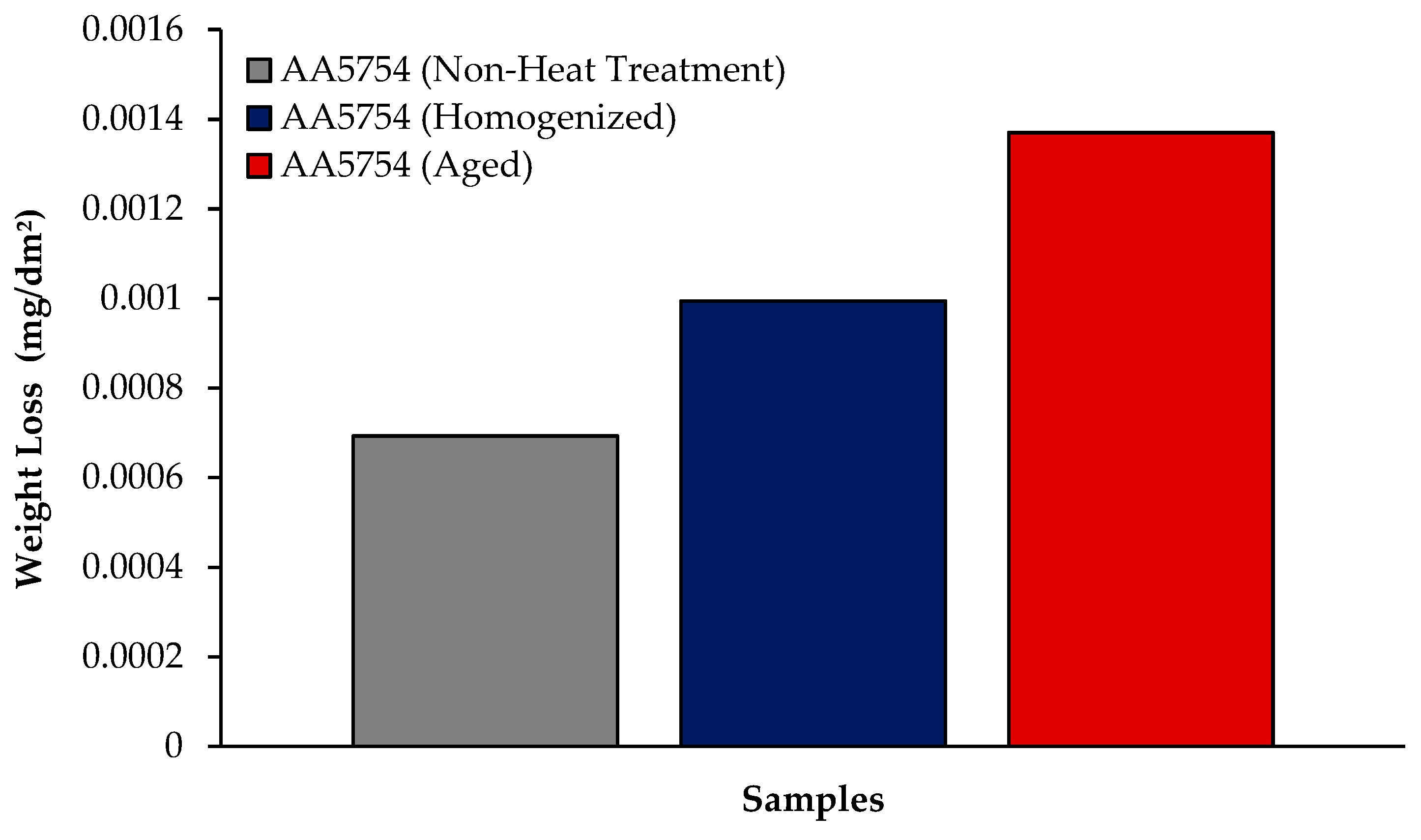
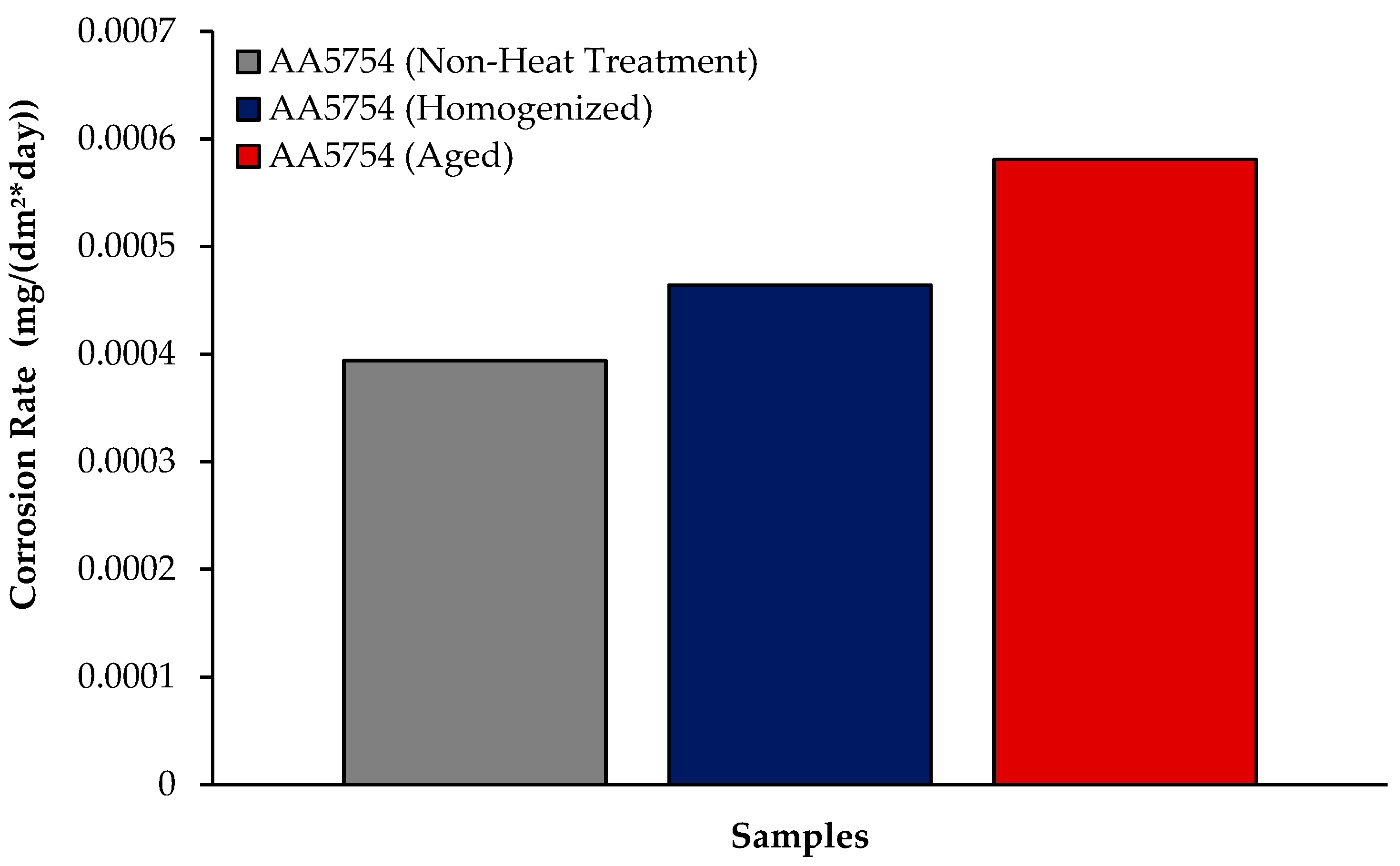
- While the alloys corroded after aging showed more weight loss, the alloys corroded before heat treatment exhibited better corrosion behavior. Among the alloys, the least weight loss after 24 h was observed in the alloy that was corroded before heat treatment and this value was 0.69 × 10−3 mg/dm2. The highest weight loss was observed in the aged alloy with a value of 1.37 × 10−3 mg/dm2. The alloy before heat treatment, which corroded after casting, showed the lowest corrosion rate with a value of 0.39 × 10−3 mg/(dm2·day) after 72 h.
- The alloy that was corroded before heat treatment showed the best corrosion behavior by creating a corrosion potential of 1.04 ± 1.5 V at a current density of −586 ± 0.04 μA/cm2. However, after aging, the corroded alloy showed the worst corrosion behavior with a corrosion potential of 5.16 ± 3.3 V at a current density of −880 ± 0.01 μA/cm2.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gedikli, H.; Cora, Ö.N.; Koç, M. Comparative Investigations on Numerical Modeling for Warm Hydroforming of AA5754-O Aluminum Sheet Alloy. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2650–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverdlin, A. Aluminium Physıcal Metallurgy And Analytıcal Technıques: Properties of Pure Aluminum. In Handbook of Aluminum: Vol. 1: Physical Metallurgy and Processes; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 33–77. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, H.; Greze, R.; Oliveira, M.; Menezes, L.; Manach, P.Y.; Alves, J.L. Numerical Study of Springback Using the Split-Ring Test for an AA5754 Aluminum Alloy. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2010, 46, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Friedman, P.; Chen, M.; Gao, L. Warm Forming Behavior of High Strength Aluminum Alloy AA7075. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Panda, S.; Deep, N.; Das, L.; Priyadarshini, M. A Study on Mechanical and Tribological Behaviour of Alumina Filled AA5754 Composites Using Taguchi Experimental Design. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 5130–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, D.Y. Improvement in the Resistance of Aluminum with Yttria Particles to Sliding Wear in Air and in a Corrosive Medium. Wear 2001, 251, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Baydoğan, M.; Çimenoğlu, H. The Effect of Deformation before Ageing on the Wear Resistance of an Aluminium Alloy. Mater. Lett. 1999, 38, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutkiewicz, J.; Litynska, L. The Effect of Plastic Deformation on Structure and Properties of Chosen 6000 Series Aluminium Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 324, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Fujiwara, J. Surface Modification of Aluminium Alloys. MSF 2006, 519–521, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, M.M.; Fazal, M.A.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A.; Yusof, F.; Masjuki, H.H.; Arslan, A. Laser-Based Surface Modifications of Aluminum and Its Alloys. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2016, 41, 106–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimura, K.; Sugawara, T.; Jibiki, T.; Ito, S.; Shima, M. Surface Modification of Aluminum Alloy to Improve Fretting Wear Properties. Tribol. Int. 2016, 93, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiletov, A.; Kuznetsov, Y.I. Surface Modification of Aluminum Alloy 6063 with Trialkoxysilane Solutions. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2022, 11, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, A.; Nieh, T. Evaluating Abrasive Wear of Amorphous Alloys Using Nanoscratch Technique. Intermetallics 2004, 12, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbery, P.; Nutt, S.; Lavernia, E. Multi-Scale Al 5083 for Military Vehicles with Improved Performance. JOM 2006, 58, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Baer, D.; Danielson, M.; Vetrano, J. Role of Mg in the Stress Corrosion Cracking of an Al-Mg Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 32, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Vetrano, J.; Windisch, C. Stress Corrosion Cracking of Al-Mg and Mg-Al Alloys. Corrosion 2004, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, Ş.Y.; Delikanlı, Y.E. AA 2024 Alüminyum Alaşımında Çökelme Sertleşmesinin Mekanik Özelliklere Etkisi. Tek. Bilim. Derg. 2012, 2, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.-F. Precipitation and Hardening in Magnesium Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 3891–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, N.; Liu, K.; Zhao, G.; Zuo, L. Study of the Portevin-Le Chatelier (PLC) Characteristics of a 5083 Aluminum Alloy Sheet in Two Heat Treatment States. Materials 2018, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Xie, J.; Sun, S.; Wang, L.; Qian, Y.; Meng, Y.; Wei, Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Aluminum 5083 Weldments by Gas Tungsten Arc and Gas Metal Arc Welding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 549, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehrnia, R.; Ebrahimi, A.; Abbasi, S.; Yazdipour, A. The Effect of Harmonic Vibration with a Frequency below the Resonant Range on the Mechanical Properties of AA-5083-H321 Aluminum Alloy GMAW Welded Parts. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 736, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corigliano, P.; Crupi, V.; Pei, X.; Dong, P. DIC-Based Structural Strain Approach for Low-Cycle Fatigue Assessment of AA 5083 Welded Joints. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2021, 116, 103090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Lai, R.; Qin, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Yi, D. Effect of Weld Reinforcement on Tensile and Fatigue Properties of 5083 Aluminum Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welded Joint: Experiments and Numerical Simulations. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 144, 106046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Obikawa, T.; Nishizaki, I.; Enomoto, M.; Fang, Z. Friction Stir Welding of Non-Heat-Treatable High-Strength Alloy 5083-O. Metals 2018, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Han, L.; Chrysanthou, A.; O’Sullivan, J. Fretting Wear in Self-Piercing Riveted Aluminium Alloy Sheet. Wear 2003, 255, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; He, X.; Xing, B.; Lu, Y.; Gu, F.; Ball, A. Influence of Sheet Thickness on Fatigue Behavior and Fretting of Self-Piercing Riveted Joints in Aluminum Alloy 5052. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, H.Q. An Overview of Self-Piercing Riveting Process with Focus on Joint Failures, Corrosion Issues and Optimisation Techniques. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 34, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Andrés, M.; Conde, A.; de Damborenea, J.; Garcia, I. Wear Behavior of Aluminum Alloys at Slow Sliding Speeds. Tribol. Trans. 2015, 58, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luri, R.; Luis, C.; Leon, J.; Fuertes, J.P.; Salcedo, D.; Puertas, I. Analysis of Fatigue and Wear Behaviour in Ultrafine Grained Connecting Rods. Metals 2017, 7, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, F.; Tichelaar, F.D.; Glenn, M.; Taheri, P.; Sababi, M.; Terryn, H.; Mol, J.M.C. Improved Corrosion Resistance of Aluminum Brazing Sheet by a Post-Brazing Heat Treatment. Corrosion 2016, 73, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Helal, K.; Patel, J.; Scamans, G.M.; Fan, Z. Melt Conditioned Direct Chill (MC-DC) Casting and Extrusion of AA5754 Aluminium Alloy Formulated from Recycled Taint Tabor Scrap. Materials 2020, 13, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Ataya, S.; El-Sayed Seleman, M.; Mahdy, A.; Alsaleh, N.; Ahmed, E. Heat Input and Mechanical Properties Investigation of Friction Stir Welded AA5083/AA5754 and AA5083/AA7020. Metals 2020, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Hayden, M.; Gao, X. An Investigation of the Strain Rate and Temperature Effects on the Plastic Flow Stress and Ductile Failure Strain of Aluminum Alloys 5083-H116, 6082-T6 and a 5183 Weld Metal. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2013, 227, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G. Microstructure and Its Influence on the Welding Quality of 6063 Aluminum Alloy Porthole Die Extrusion. Materials 2021, 14, 6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayvaz, M. Determination of the Effect of Artificial Aging Parameters on Dry Sliding Wear Resistance of 6013 Aluminum Alloy (Al-Mg-Si-Cu). Int. Adv. Res. Eng. J. 2021, 5, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C.; Krause, A.; Dunand, D.; Seidman, D. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a 5754 Aluminum Alloy Modified by Sc and Zr Additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 338, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, M.; Shankar, G. On the Role of Precipitates in Controlling Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ag and Sn Added 7075 Alloys during Artificial Ageing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 738, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, G.; Ilyas, M.; Lemopi Isidore, B.B.; Khan, W.A. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Evolution in Incremental Forming of AA5754 and AA6061 Aluminum Alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.M.; Han, Z.Q.; Luo, A.A.; Liu, B.C. Microstructure Characteristics and Effect of Aging Process on the Mechanical Properties of Squeeze-Cast AZ91 Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 641, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, O.; Liu, Z.; Kuhnke, K. Impact of Homogenization on Particles in the Al–Mg–Mn Alloy AA 5454—Experiment and Simulation. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 560, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, O.; Miller-Jupp, S. Control of Second-Phase Particles in the Al-Mg-Mn Alloy AA 5083. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 689, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, O.; Kuhnke, K.; Hasenclever, J. Development of Intermetallic Particles during Solidification and Homogenization of Two AA 5xxx Series Al-Mg Alloys with Different Mg Contents. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 728, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Cheng, G.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, L. Effects of Al Content on Friction and Wear Behavior of Weld Surfacing Mg-Al-Zn Alloy. Met. Mater. 2020, 58, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, G.; Tao, K. Cerium Addition Improved the Dry Sliding Wear Resistance of Surface Welding AZ91 Alloy. Materials 2018, 11, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamdi, Z.; Shipway, P.; Voisey, K.; Sturgeon, A. Abrasive Wear Behaviour of Conventional and Large-Particle Tungsten Carbide-Based Cermet Coatings as a Function of Abrasive Size and Type. Wear 2011, 271, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, L.; Bruzzaniti, P.; Proverbio, E. Pitting Corrosion of Aluminum Alloys in Anhydrous Ethanol. Mater. Corros. 2018, 69, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqerzadeh Chehreh, A.; Grätzel, M.; Bergmann, J.; Walther, F. Effect of Corrosion and Surface Finishing on Fatigue Behavior of Friction Stir Welded EN AW-5754 Aluminum Alloy Using Various Tool Configurations. Materials 2020, 13, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Gu, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Ma, P. The Microstructure and Properties of an Al-Mg-0.3Sc Alloy Deposited by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. Metals 2020, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-J.; Kim, S.J. Electrochemical Characteristics of Aluminum Alloys in Sea Water for Marine Environment. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2019, 135, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Birbilis, N.; Knight, S.; Holtz, R.; Goswami, R.; Davies, C. A Survey of Sensitization in 5xxx Series Aluminum Alloys. Corrosion 2015, 72, 150903122215004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenberber Dumanlı, F.T.; Yildirim Ozen, M.; Asensio, M.; Yuksel, S.; Kıpçak, A.S.; Derun, E. Characteristic, Electrical and Optical Properties of Potassium Borate (KB5O8·4H2O) Hydrothermally Synthesized from Different Boron Sources. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2021, 47, 5353–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, A.; Komura, Y.; Kanaya, M.; Narita, T.; Kondo, A.; Misutani, T. Preparation of Nanocrystalline Silicon Carbide Thin Films by Hot-Wire Chemical Vapor Deposition at Various Filament Temperature. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2006 IEEE 4th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, WCPEC-4, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 7–12 May 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjari, D.; Patil, A.P.; Singh, S.K.; Ullah, I.; Shukla, S. Study of Strain Induced Martensite and Its Reversal on Sensitization Behaviour of Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steel. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 2022, 69, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, X.; Leach, G. Shape Control of Electrodeposited Copper Films and Nanostructures through Additive Effects. Langmuir 2014, 30, 3589–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezuber, H.; El-Houd, A.; El-Shawesh, F. A Study on the Corrosion Behavior of Aluminum Alloys in Seawater. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yan, L.; Kang, S.; Qi, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, P. Corrosion Behavior and Electrochemical Corrosion of a High Manganese Steel in Simulated Marine Splash Zone. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 126507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Ye, L.; Deng, Y.; Guo, X. Effect of the Oxidation Reaction Interface on the Accelerated Corrosion Behaviour of Al–Mg–Si Alloy. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.D.; Liu, H.; Suebka, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Guo, W.; Cheng, Y.M.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, L. Corrosion Behaviour of Laser-Cleaned AA7024 Aluminium Alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 435, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, S.; Cheng, W.; Wang, G.; Liu, W.; Ren, Y. Investigation on the Surface Properties of 5A12 Aluminum Alloy after Nd: YAG Laser Cleaning. Coatings 2019, 9, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genevieve, B.; Blanc, C.; Keddam, M.; Pebere, N. Local Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Applied to the Corrosion Behavior of an AZ91 Magnesium Alloy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, B488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Kaiser, M. Electrochemical Corrosion Performance of Eutectic Al-Si Automotive Alloy in 0.1 M and 0.2 M NaCl Solution. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1248, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falak, A.; Amjad, A.; Grzegorz, M.; Yasir, M.; Al-Mansour, A.; Khan, M.; Alam, S.; Shahbaz, M.; Zia, A.; Ejaz, A. Long-Term Potentiodynamic Testing and Tribometric Properties of Amorphous Alloy Coatings under Saline Environment. Molecules 2022, 27, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, J.M.; Guan, L.; Wang, G. pH-Dependent Electrochemical Behaviour of Al3Mg2 in NaCl Solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467–468, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.-H.; Oh, M.-S. Effects of the Mg Content on Microstructural and Corrosion Characteristics of Hot-Dip Al–Si–Mg Alloy-Coated Steel Sheets. Materials 2023, 16, 5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Liu, S.; Zeng, G.; Li, X.; Lei, T.; Li, Y.; Du, Y. Effect of Manganese on Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of the Mg-3Al Alloys. Metals 2019, 9, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, M.; Jasionowski, R. The Role of Microstructure on the Corrosion Behaviour of as Cast AlCu4MgSi and MgAl2Si Alloys. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2018, 18, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlatci, H. Production and Corrosion Behaviours of the Al–12Si–XMg Alloys Containing in Situ Mg2Si Particles. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 503, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasakau, K.A.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Lamaka, S.V.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Role of Intermetallic Phases in Localized Corrosion of AA5083. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 7651–7659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, C.; Ball, J. The Oxidation of Rolled and Heat Treated Al-Mg Alloys. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1984, 17, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.-O.; Ha, S.-H.; Kim, B.-H.; Lim, H.; Kim, S.K. Experimental Investigation of MgAl2O4 Spinel Formation in Oxidation of Al–Mg Alloys. In Light Metals 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 460–464. ISBN 978-3-030-36407-6. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, B.; Almanza, J.M.; Rodríguez, J.L.; Cortes, D.A.; Escobedo, J.C.; Gutiérrez, E.J. Corrosion Mechanisms of Al2O3/MgAl2O4 by V2O5, NiO, Fe2O3 and Vanadium Slag. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 2973–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, M. Advantages and Challenges of Implementing Lightweight Materials in Automobiles: A Review. Int. J. Sci. Res. (IJSR) 2023, 13, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, R.; Arun, S.G.; Adepu, R. Design and Development of Fuel Tank for High Mobility Military Vehicle. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Automotive Materials and Manufacturing AMM 2023, Florence, Italy, Online; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2023-28-1342/ (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Macwan, A.; Mirza, F.A.; Bhole, S.D.; Chen, D.L. Similar and Dissimilar Ultrasonic Spot Welding of 5754 Aluminum Alloy for Automotive Applications. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 877, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.S.; Zhuang, L.; Bottema, J.; Wittebrood, A.J.; De Smet, P.; Haszler, A.; Vieregge, A. Recent Development in Aluminium Alloys for the Automotive Industry. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 280, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, D.J.; Evans, D.; Pelow, C.; Nolan, P.; Jain, M. Bending in Aluminium Alloys AA 6111 and AA 5754 Using the Cantilever Bend Test. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2002, 18, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
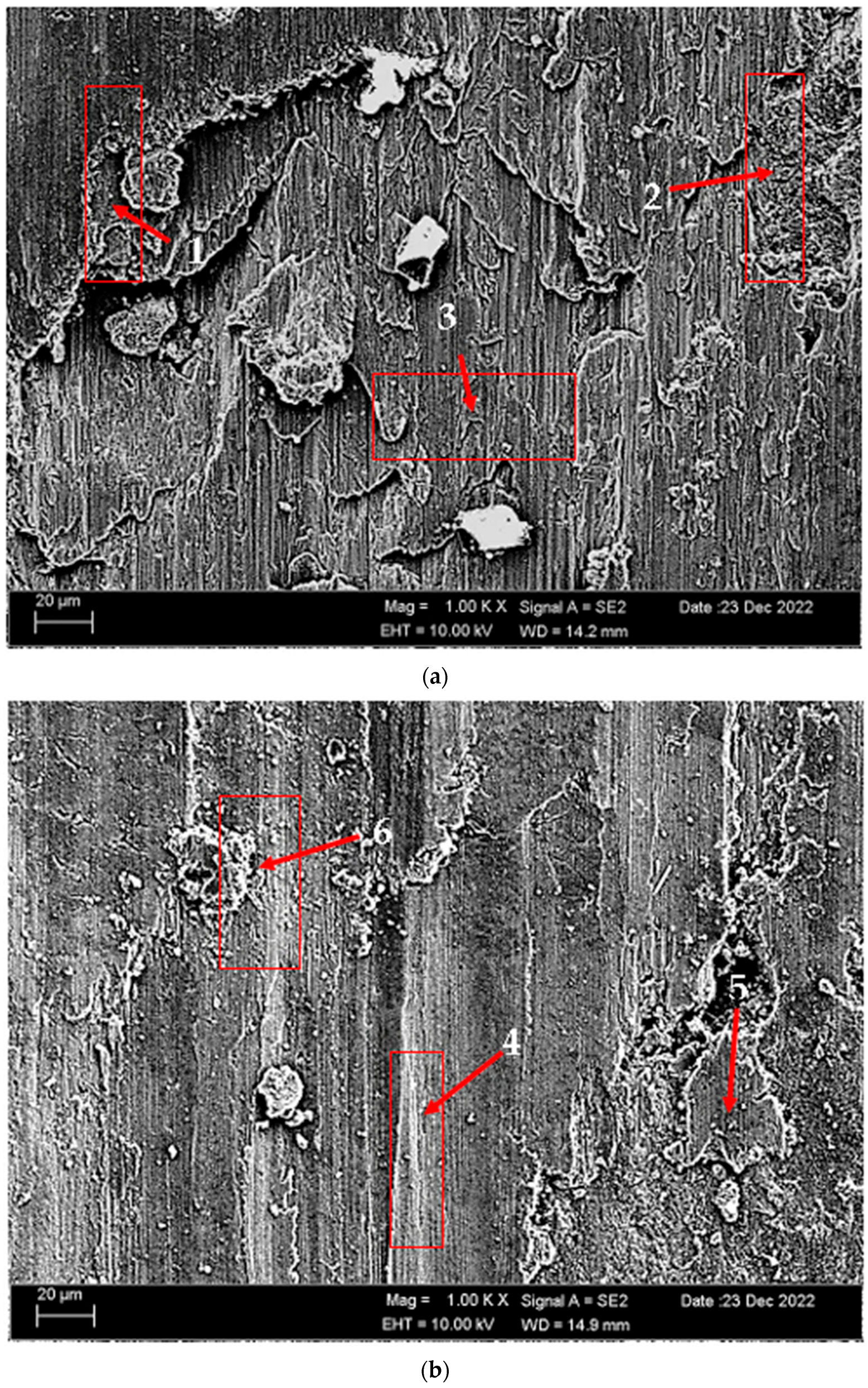
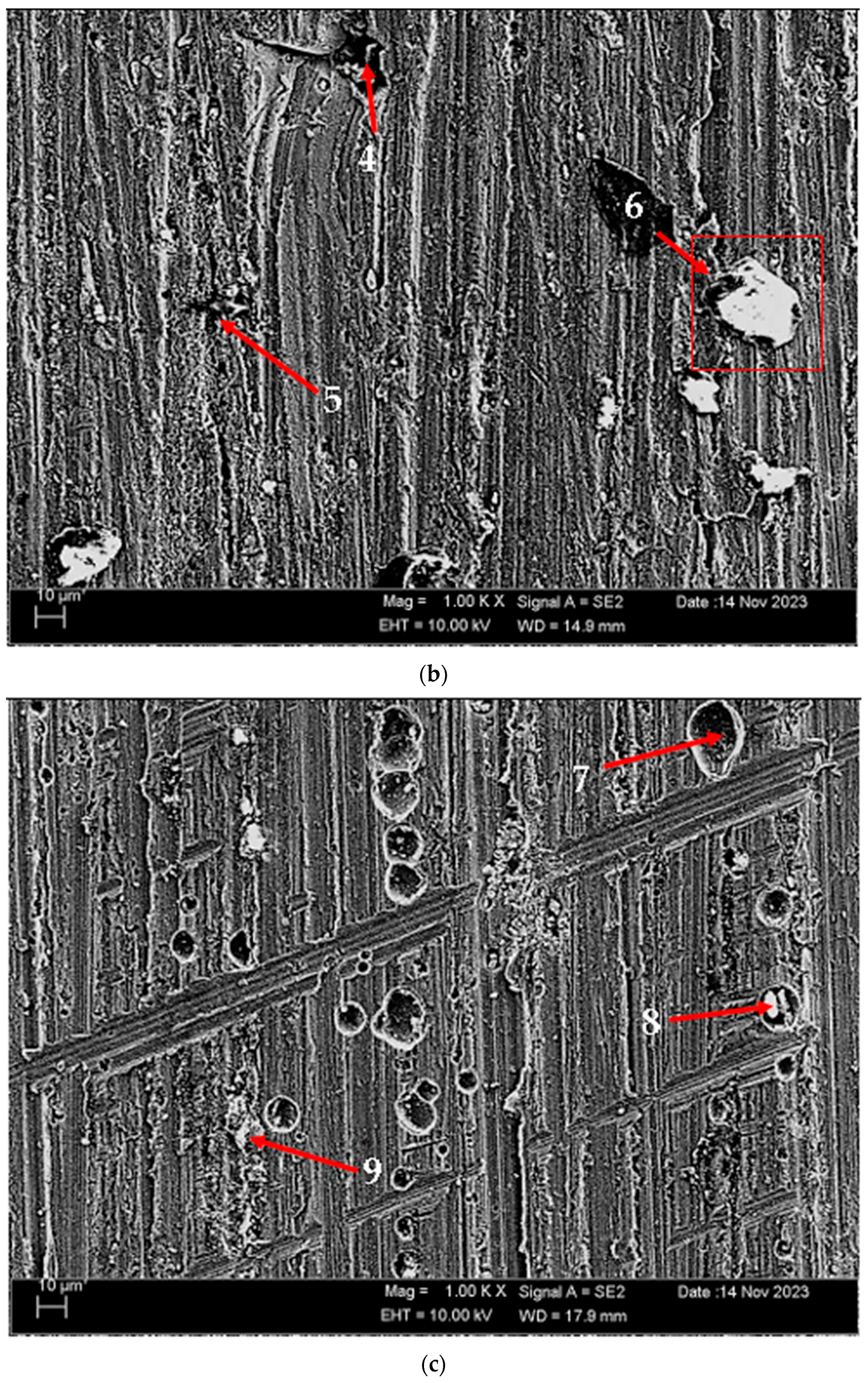
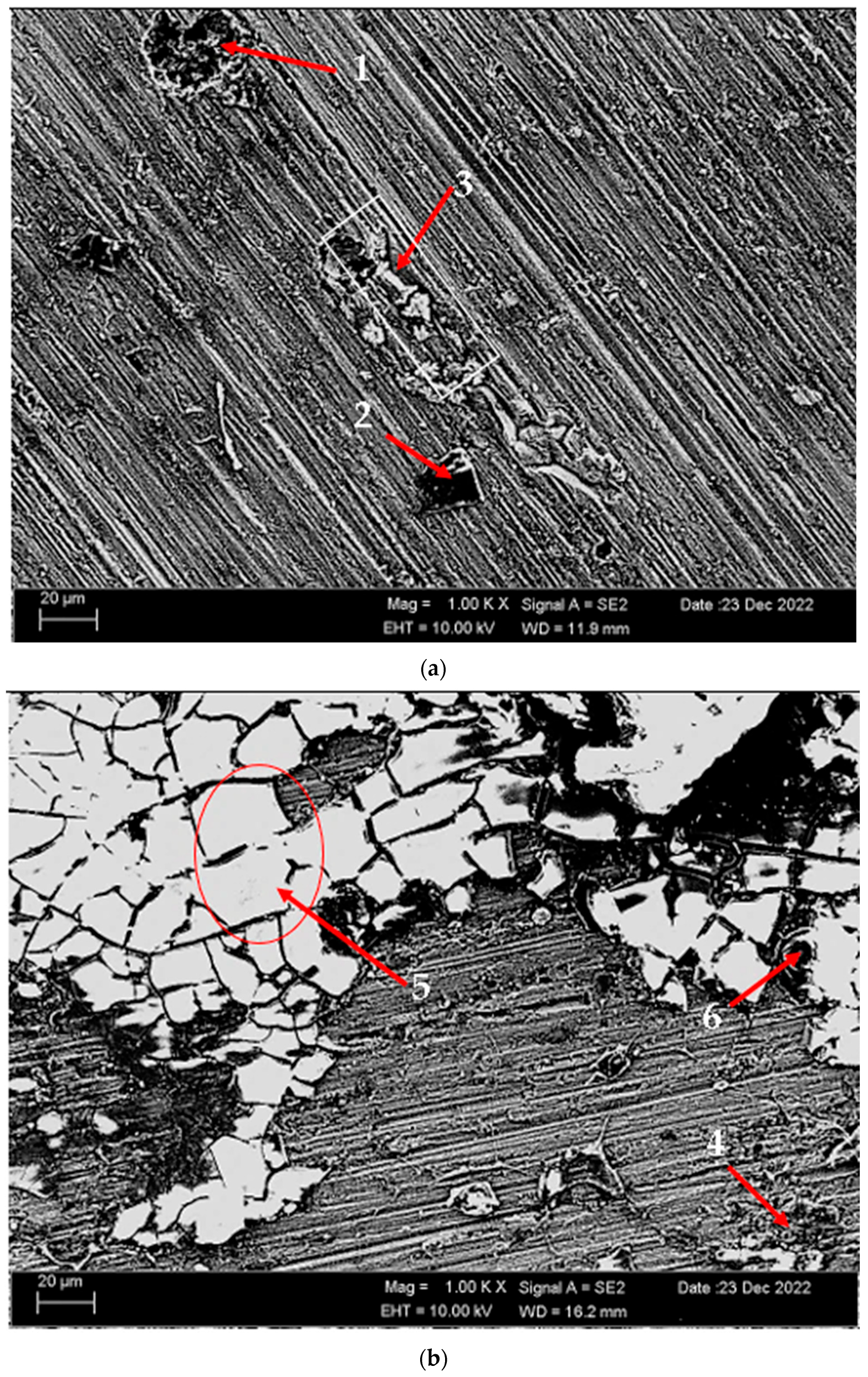
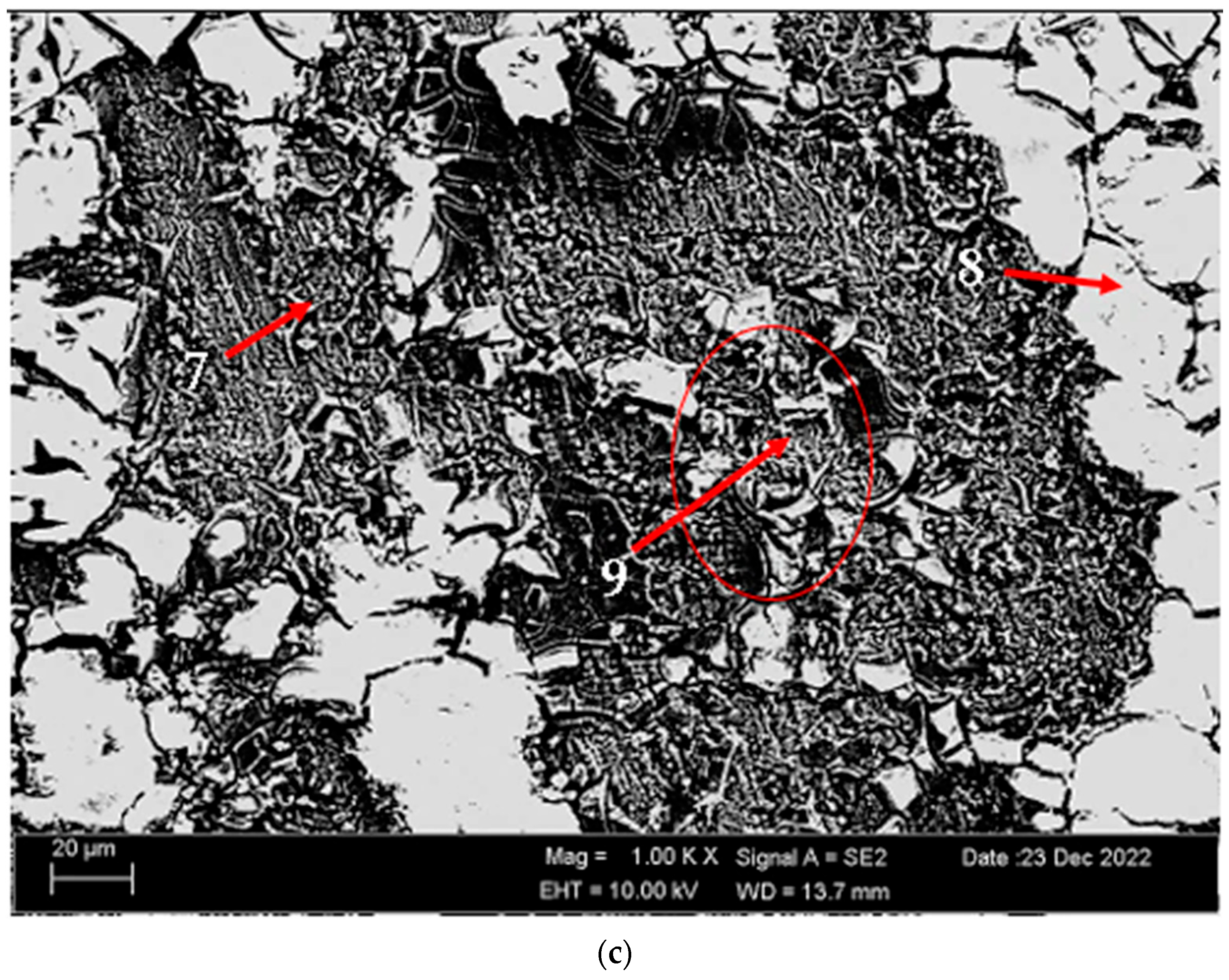





| Alloy | Chemical Composition (wt.%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Mn | Si | Fe | Cr | Al | |
| AA5754 | 3.650 | 0.526 | 0.349 | 0.348 | 0.122 | Bal. |
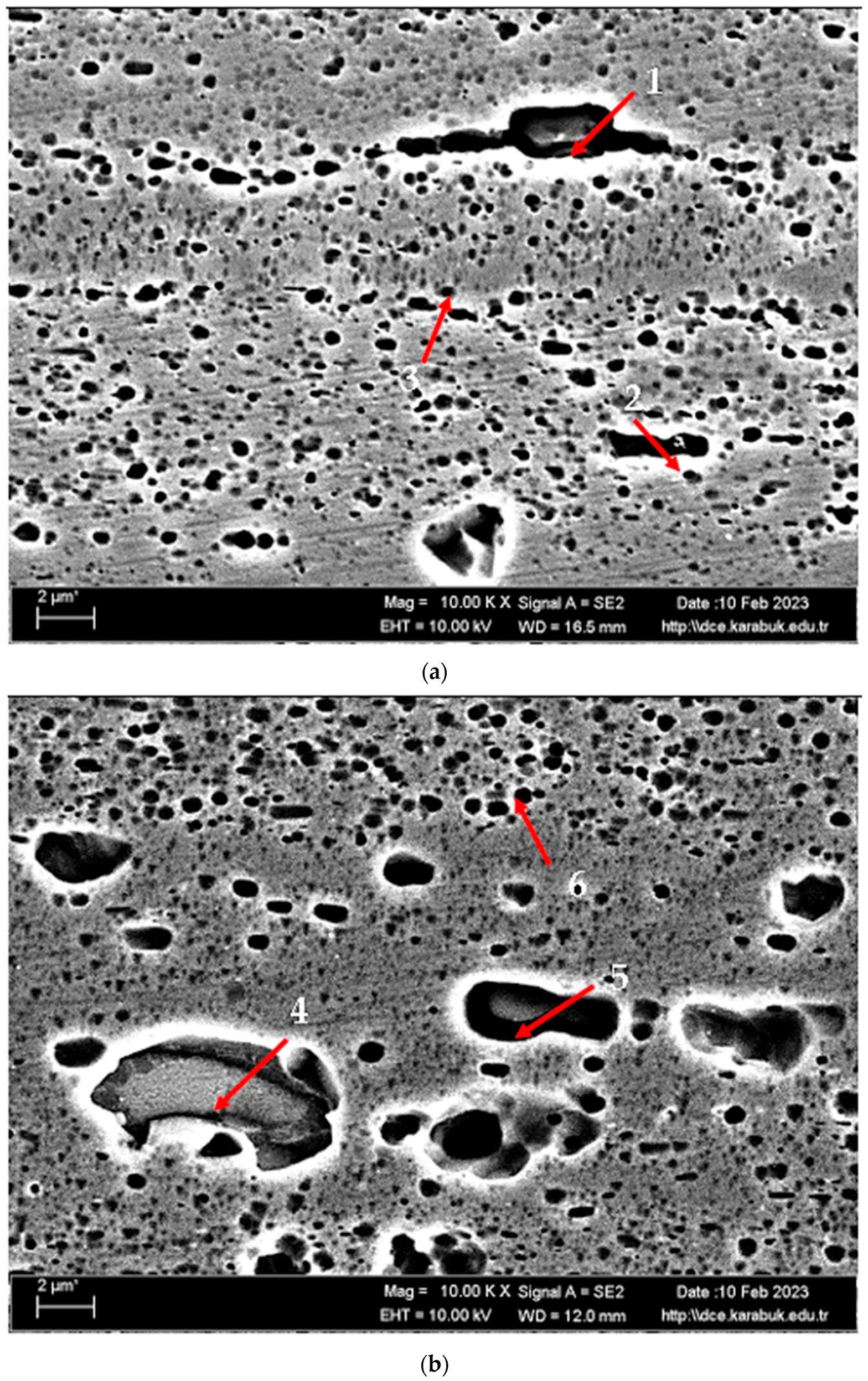
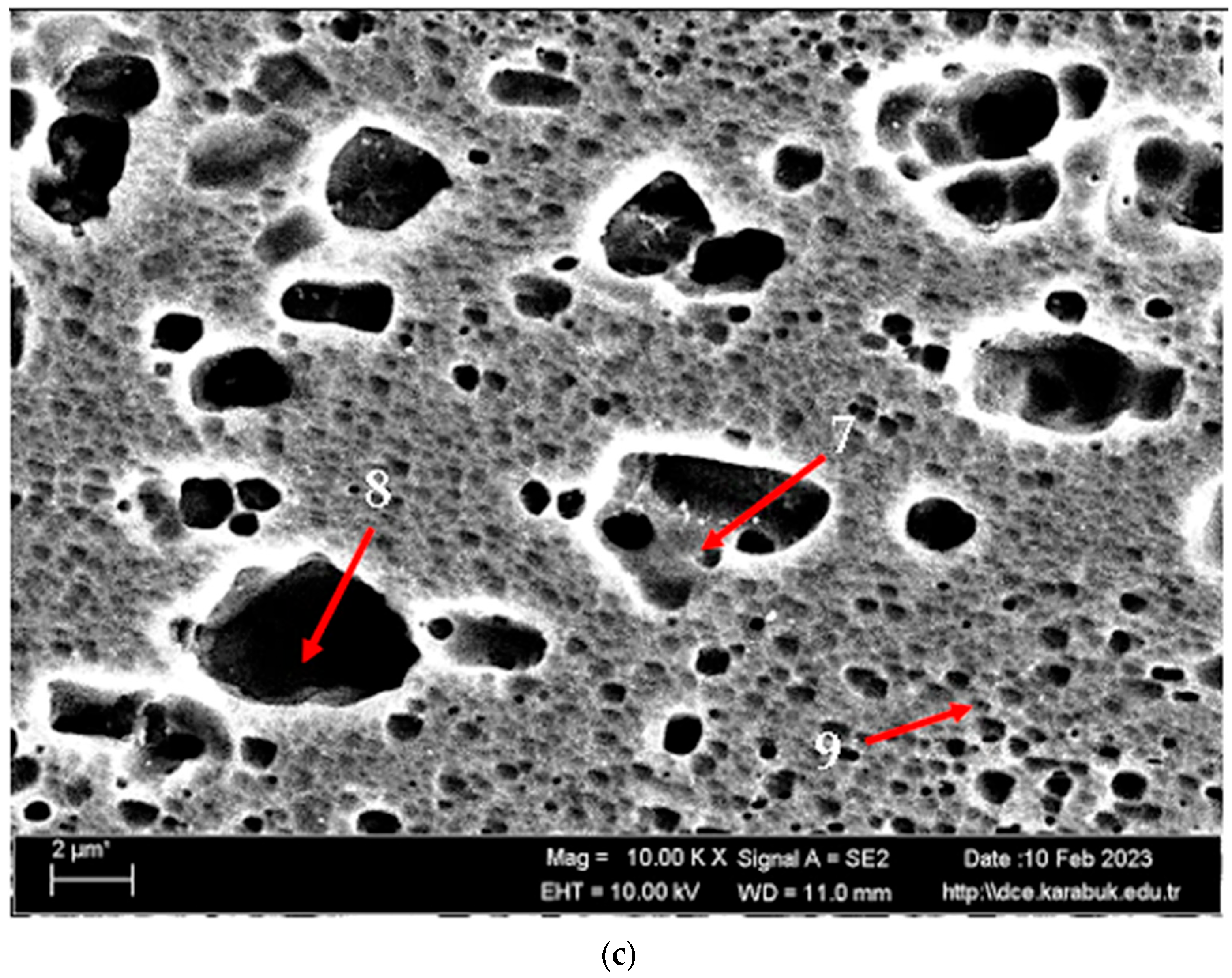
| Points | Mg | Al | Si | Cr | Mn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.50 | 93.00 | - | - | 1.21 | 1.29 |
| 2 | 5.05 | 94.30 | - | 0.15 | - | 0.50 |
| 3 | 4.88 | 93.78 | 0.44 | 0.15 | - | 0.63 |
| 4 | 1.21 | 69.43 | 4.60 | 0.46 | 7.22 | 17.08 |
| 5 | 4.76 | 93.53 | 1.29 | 0.09 | - | 0.32 |
| 6 | 4.86 | 94.44 | - | - | 0.71 | - |
| 7 | 2.06 | 33.29 | 63.76 | 0.28 | 0.61 | - |
| 8 | 4.96 | 94.34 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.28 |
| 9 | 4.22 | 91.49 | 0.51 | - | 1.37 | 2.42 |
| Points | C | O | Mg | Al | Si | Mn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.685 | 23.795 | 3.815 | 66.53 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 1.785 |
| 2 | 5.21 | 37.57 | 3.11 | 53.94 | 0.17 | - | - |
| 3 | 5.04 | 6.08 | 4.74 | 82.35 | 0.24 | 0.69 | 0.85 |
| 4 | 2.58 | 26.945 | 3.61 | 66.02 | 0.145 | - | 0.705 |
| 5 | 2.82 | 28.58 | 3.365 | 64.99 | 0.04 | 0.21 | - |
| 6 | 3.77 | 12.41 | 4.01 | 78.80 | - | 0.54 | 0.46 |
| 7 | 7.32 | 26.845 | 3.89 | 61.085 | 0.695 | - | 0.165 |
| 8 | 6.315 | 38.785 | 3.55 | 50.80 | 0.495 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| 9 | 9.12 | 25.73 | 3.99 | 60.60 | 0.54 | - | 0.03 |
| Points | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | Cl | Mn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.433 | 0.603 | 2.226 | 75.33 | 2.403 | 0.183 | 4.326 | 8.50 |
| 2 | 5.63 | 1.20 | 2.345 | 75.855 | 2.445 | 0.645 | 4.38 | 7.495 |
| 3 | 19.98 | 1.32 | 2.91 | 71.185 | 1.265 | 1.13 | 0.60 | 1.605 |
| 4 | 6.936 | 0.53 | 4.486 | 87.253 | 0.29 | 0.343 | 0.163 | - |
| 5 | 14.42 | 2.255 | 3.705 | 76.245 | 0.87 | 2.505 | - | - |
| 6 | 49.933 | 12.263 | 2.113 | 16.863 | 1.96 | 13.13 | 1.186 | 2.556 |
| 7 | 5.458 | 0.37 | 4.30 | 87.666 | 1.014 | 0.09 | 0.534 | 0.564 |
| 8 | 40.52 | 0.66 | 2.09 | 47.60 | 1.45 | 0.81 | 3.00 | 3.87 |
| 9 | 19.67 | 0.625 | 7.235 | 70.54 | 1.10 | 0.665 | 0.165 | - |
| Alloys | Ecorr (V) | Icorr (μA/cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| AA5754 (Non-Heat Treatment) | −586 ± 0.04 | 1.04 ± 1.5 |
| AA5754 (Homogenized) | −736 ± 0.01 | 2.04 ± 2.0 |
| AA5754 (Aged) | −880 ± 0.01 | 5.16 ± 3.3 |
| Points | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | Cl | Mn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35.43 | 3.25 | 8.65 | 43.32 | 8.02 | 0.84 | 0.50 | - |
| 2 | 43.33 | 9.24 | 4.43 | 30.71 | 2.42 | 5.53 | 1.39 | 2.96 |
| 3 | 24.18 | 1.70 | 2.49 | 52.48 | 4.09 | 0.40 | 5.36 | 9.30 |
| 4 | 40.85 | 0.63 | 3.18 | 38.82 | 14.85 | 1.19 | 0.37 | 0.12 |
| 5 | 62.15 | 1.70 | 4.47 | 21.63 | 7.99 | 0.89 | 1.18 | - |
| 6 | 44.87 | 0.70 | 4.40 | 49.11 | 0.07 | 0.45 | 0.08 | 0.32 |
| 7 | 14.76 | 0.56 | 4.18 | 80.15 | - | 0.01 | - | 0.35 |
| 8 | 59.13 | 0.71 | 3.72 | 26.92 | 0.26 | 7.74 | 0.51 | 1.00 |
| 9 | 39.77 | 0.51 | 3.80 | 52.87 | 0.48 | 1.96 | 0.48 | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abukhdair, O.F.M.; Esen, I.; Ahlatci, H.; Keskin, E. Microstructural Characterization, Tribological and Corrosion Behavior of H111 Hot-Rolled AA5754 after Homogenization and Aging. Materials 2024, 17, 3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133164
Abukhdair OFM, Esen I, Ahlatci H, Keskin E. Microstructural Characterization, Tribological and Corrosion Behavior of H111 Hot-Rolled AA5754 after Homogenization and Aging. Materials. 2024; 17(13):3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133164
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbukhdair, Otman Farj Mohammed, Ismail Esen, Hayrettin Ahlatci, and Esma Keskin. 2024. "Microstructural Characterization, Tribological and Corrosion Behavior of H111 Hot-Rolled AA5754 after Homogenization and Aging" Materials 17, no. 13: 3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133164
APA StyleAbukhdair, O. F. M., Esen, I., Ahlatci, H., & Keskin, E. (2024). Microstructural Characterization, Tribological and Corrosion Behavior of H111 Hot-Rolled AA5754 after Homogenization and Aging. Materials, 17(13), 3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133164






