Nozzle Wear in Abrasive Water Jet Based on Numerical Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A brief theoretical analysis of the fluid movement in the internal flow field of the nozzle using fluid dynamics, providing a theoretical basis for the process of numerical simulation.
- Using Fluent 6.3.26, a discrete phase model was used to analyze the erosion of the abrasive on the inner cavity of the jet polishing nozzle, and the effects of three parameters on the maximum erosion rate of the nozzle were analyzed and compared by changing the abrasive diameter, inlet pressure, and abrasive flow rate.
- Analysis of the simulation results of abrasive erosion on the inner cavity of the jet polishing nozzle and the prediction of the changes in the structure of the nozzle’s inner cavity based on existing data and references.
- Use of CFD to model and simulate the inner cavity of the nozzle before and after wear and compare the impact of structural changes on the nozzle jet and the impact of the jet on the target work piece after structural changes.
2. Erosion Mechanism
2.1. Numerical Simulation Calculation Model
- C1ε, C2ε, C3ε—The empirical constant in the k-ε model, where C1ε is 1.44, C2ε is 1.92, and C3ε is 0.09;
- ∂κ, ∂ε—the corresponding Prandtl number in k and ε, where ∂κ is 1.0 and ∂ε is 1.3;
- Sk,Sε—user defined source items;
- μt—turbulent eddy viscosity coefficient;
- Ui—turbulence coefficient at coordinate i;
- Xi—coordinate component;
- Gb—generation term of k due to buoyancy;
- YM—pulsation expansion term in compressible turbulence;
- Gk—stress source term caused by velocity gradient.


2.2. Discrete Phase Model and Solution Condition Settings
- and —the normal velocity of solid particles before and after impacting the wall surface;
- , —tangential velocity of solid particles before and after impacting the wall;
- θ—the angle between the trajectory of solid particles and the wall surface.
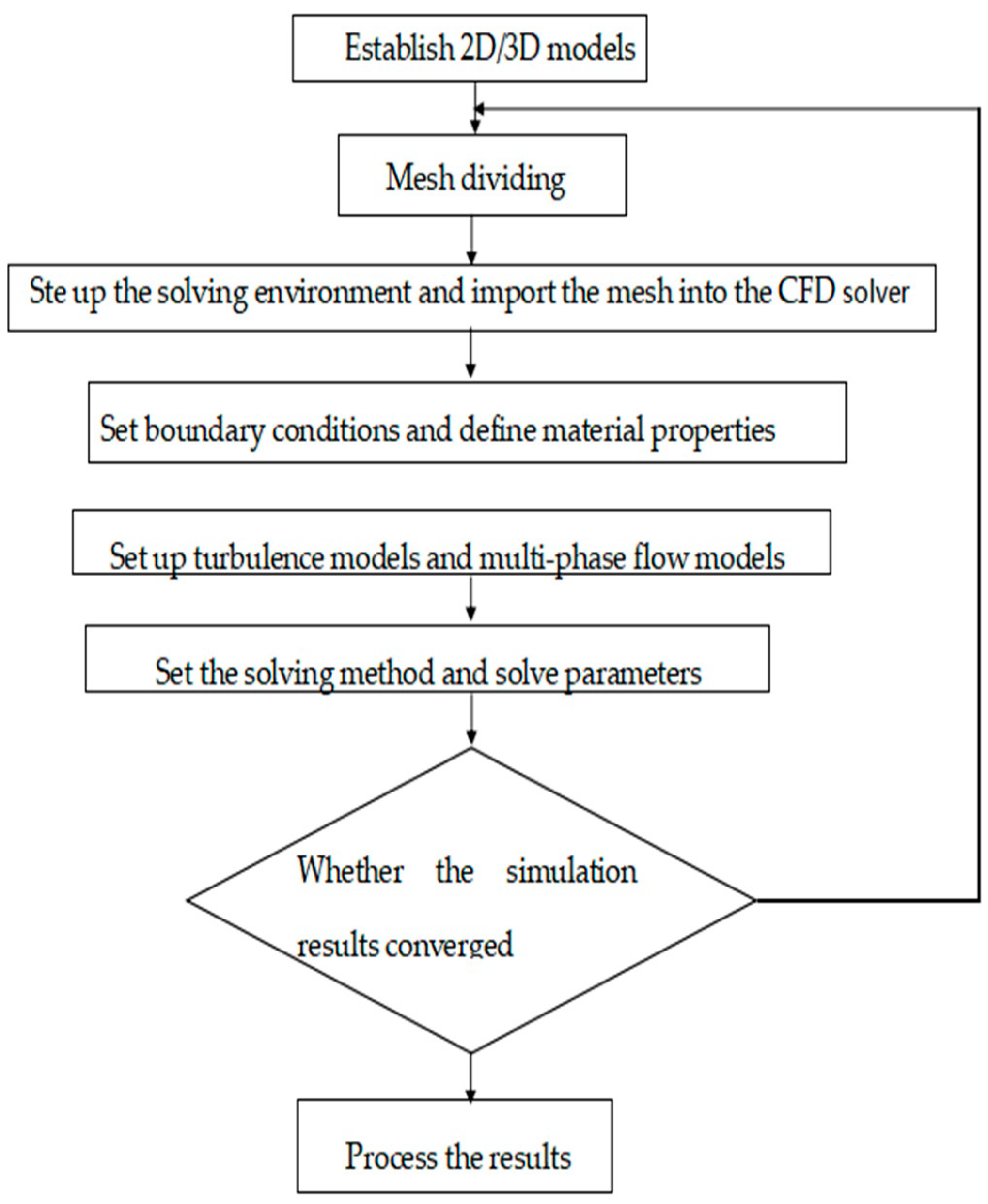
2.3. Mesh Generation
3. Simulation Results of Nozzle Cavity Erosion
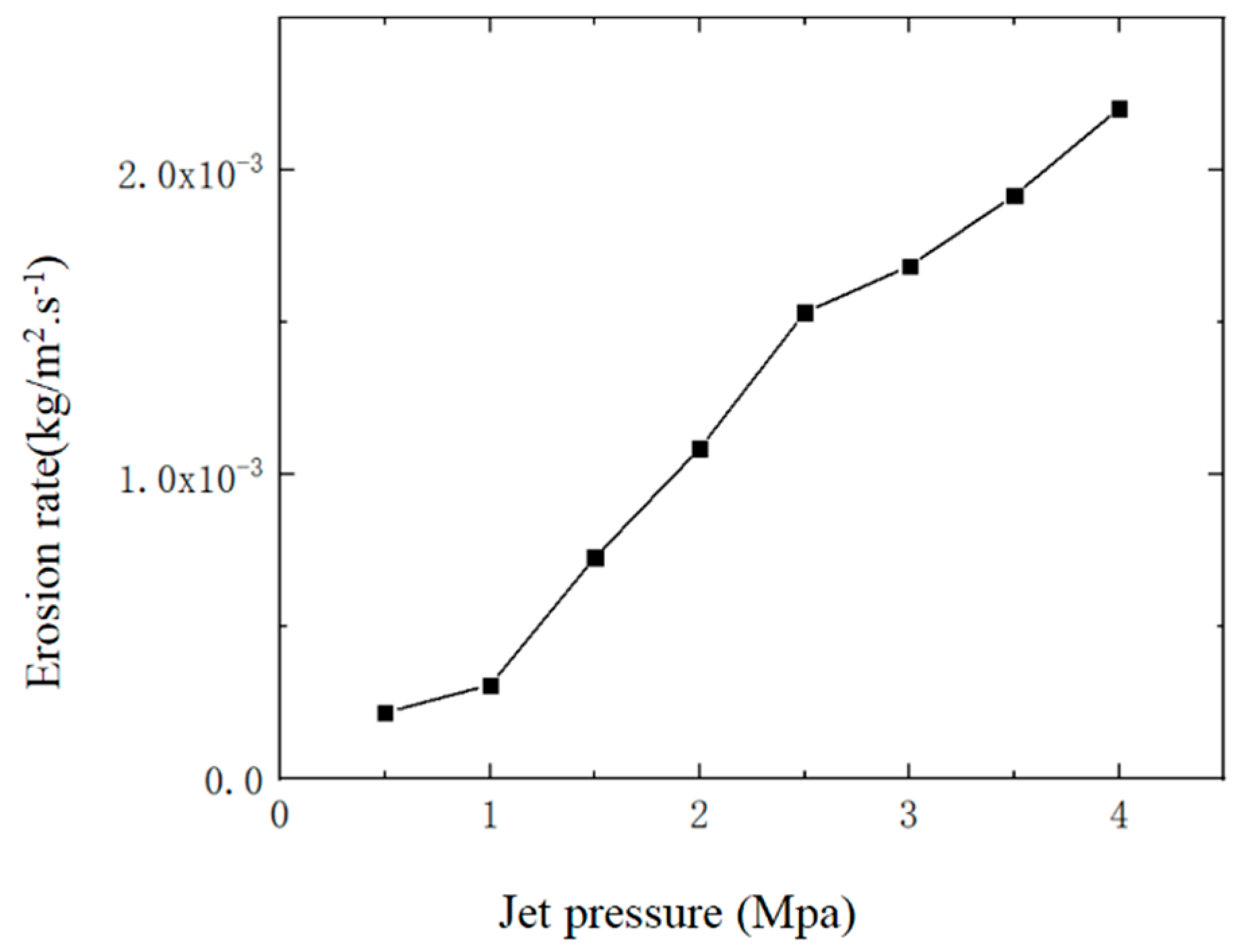
3.1. Effect of Different Abrasive Water Jet Inlet Pressures on Nozzle Cavity Wear
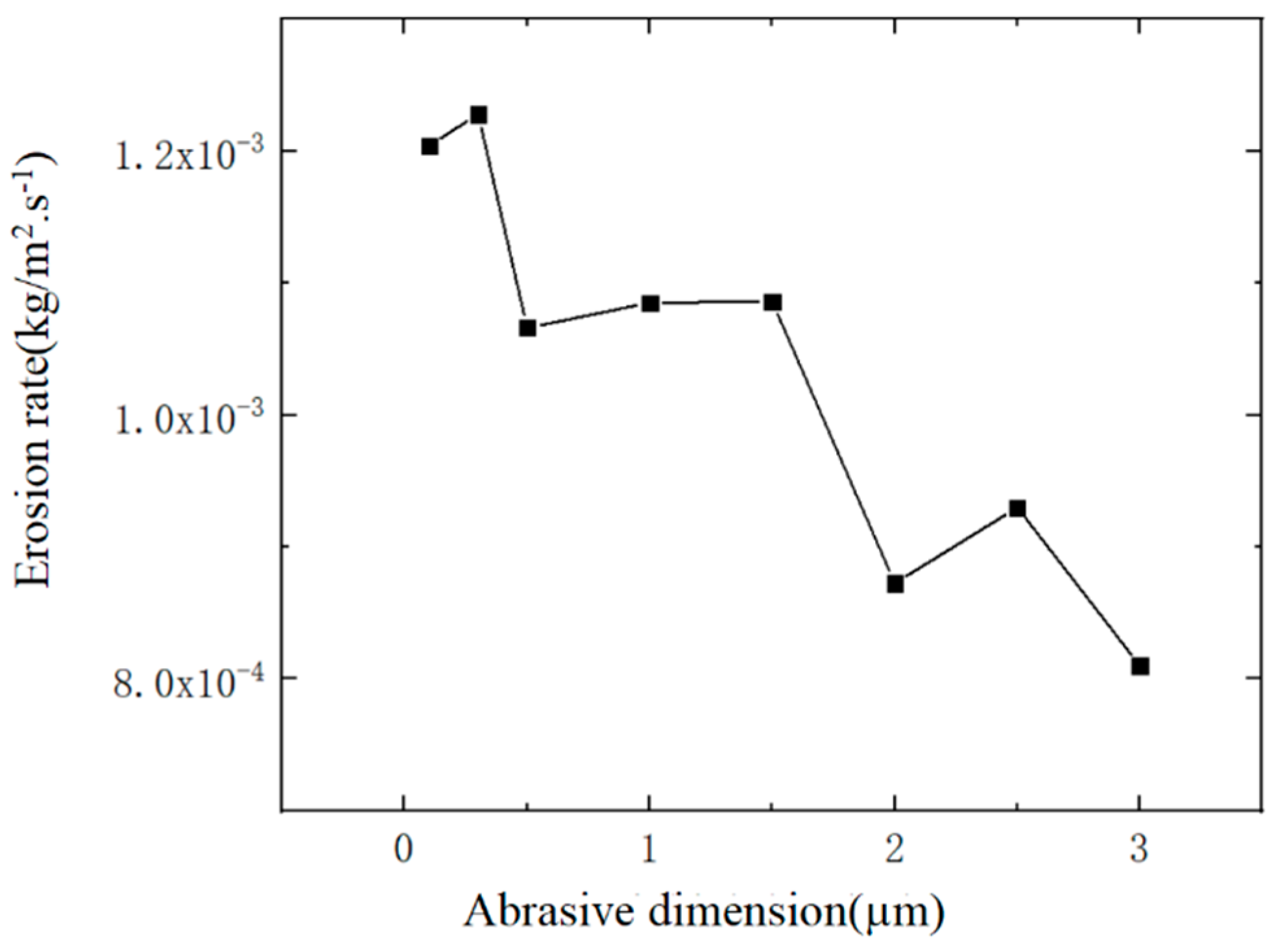
3.2. Effect of Different Abrasive Diameters on Nozzle Cavity Wear
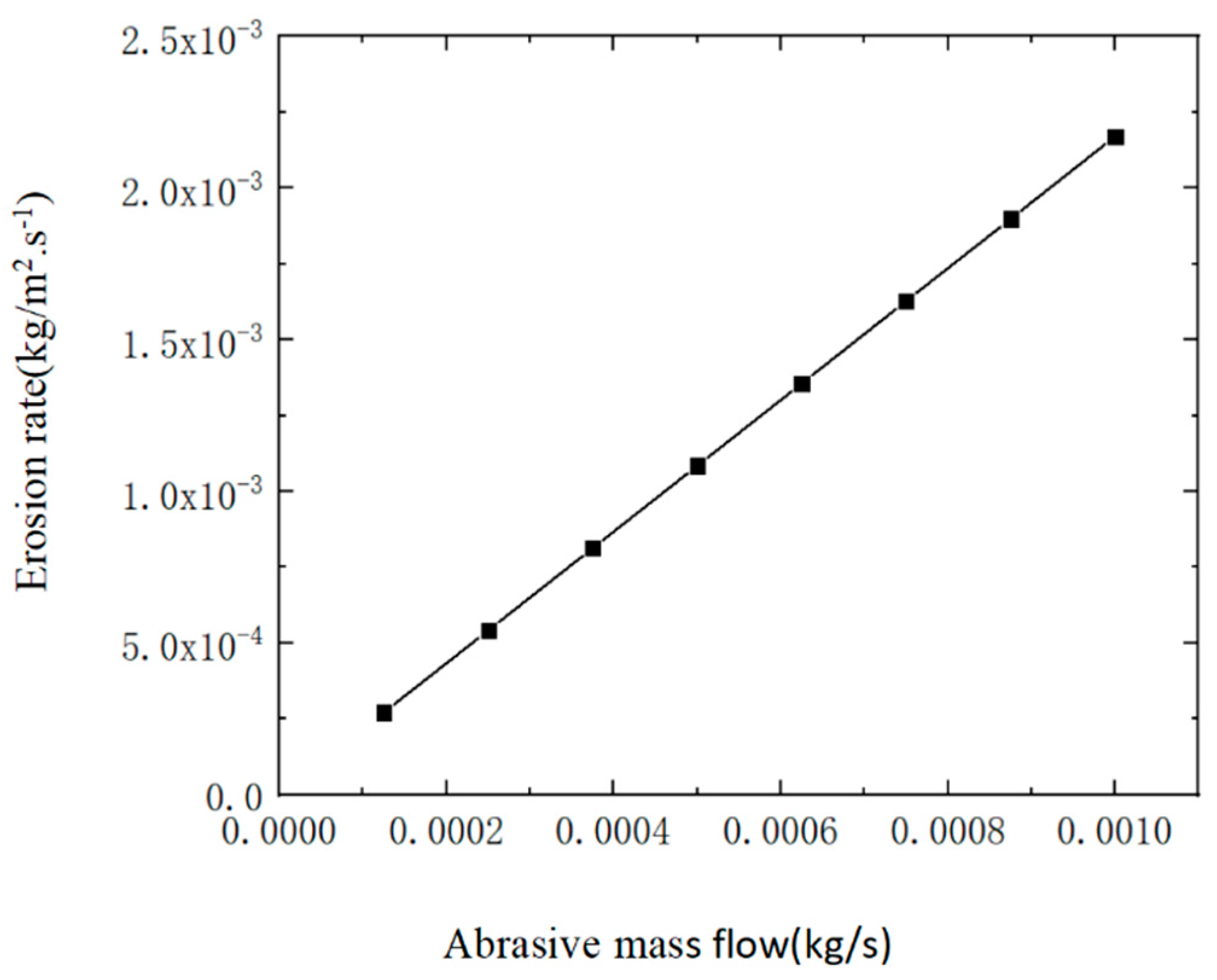
3.3. Effect of Different Abrasive Mass Flow Rates on Nozzle Cavity Wear
4. Numerical Simulation Analysis of Structural Changes in Nozzle Wear
4.1. Numerical Simulation Solution Process
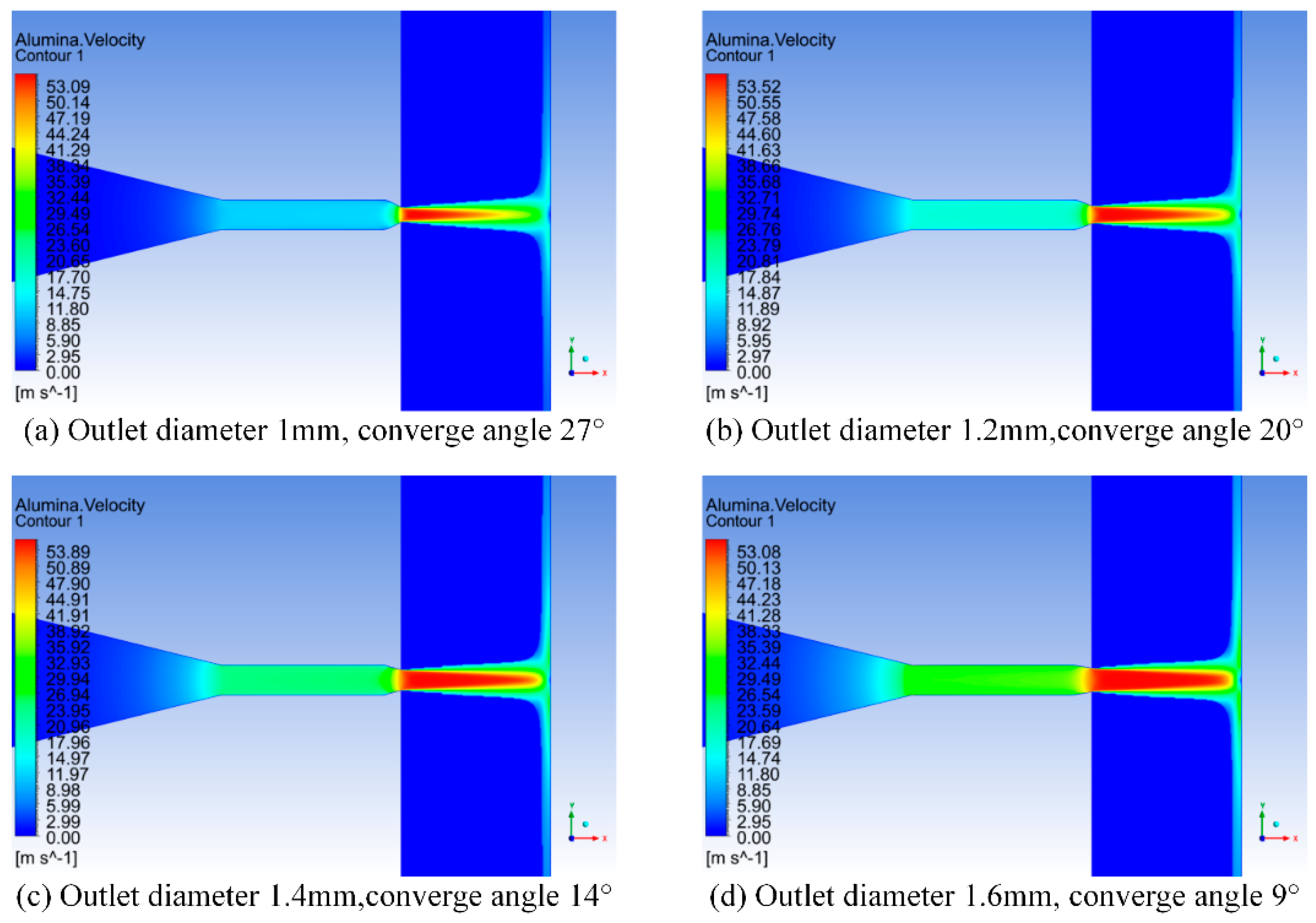
4.2. Analysis of Jet Velocity in the Internal and External Flow Fields of Nozzles with Different Degrees of Wear
4.3. Analysis of the Impact of Jet Flow from Nozzles with Different Degrees of Wear on the Work Piece
5. Conclusions and Outlook
- The maximum erosion rate of the nozzle inner cavity is mainly affected by the jet pressure, abrasive particle diameter and abrasive mass flow rate. When the jet pressure and abrasive mass flow rate are higher, the maximum erosion rate caused by abrasive water on the nozzle inner cavity is greater. Abrasive diameter is inversely proportional to erosion rate.
- Through the analysis of the velocity distribution at the nozzle axis, as the degree of wear at the nozzle outlet increases, the pressure of abrasive water on the work piece also increases significantly. When the diameter of the outlet is worn to 1.6 mm, the pressure on the work piece caused by the abrasive water jet increases by more than twice compared to the non-worn nozzle.
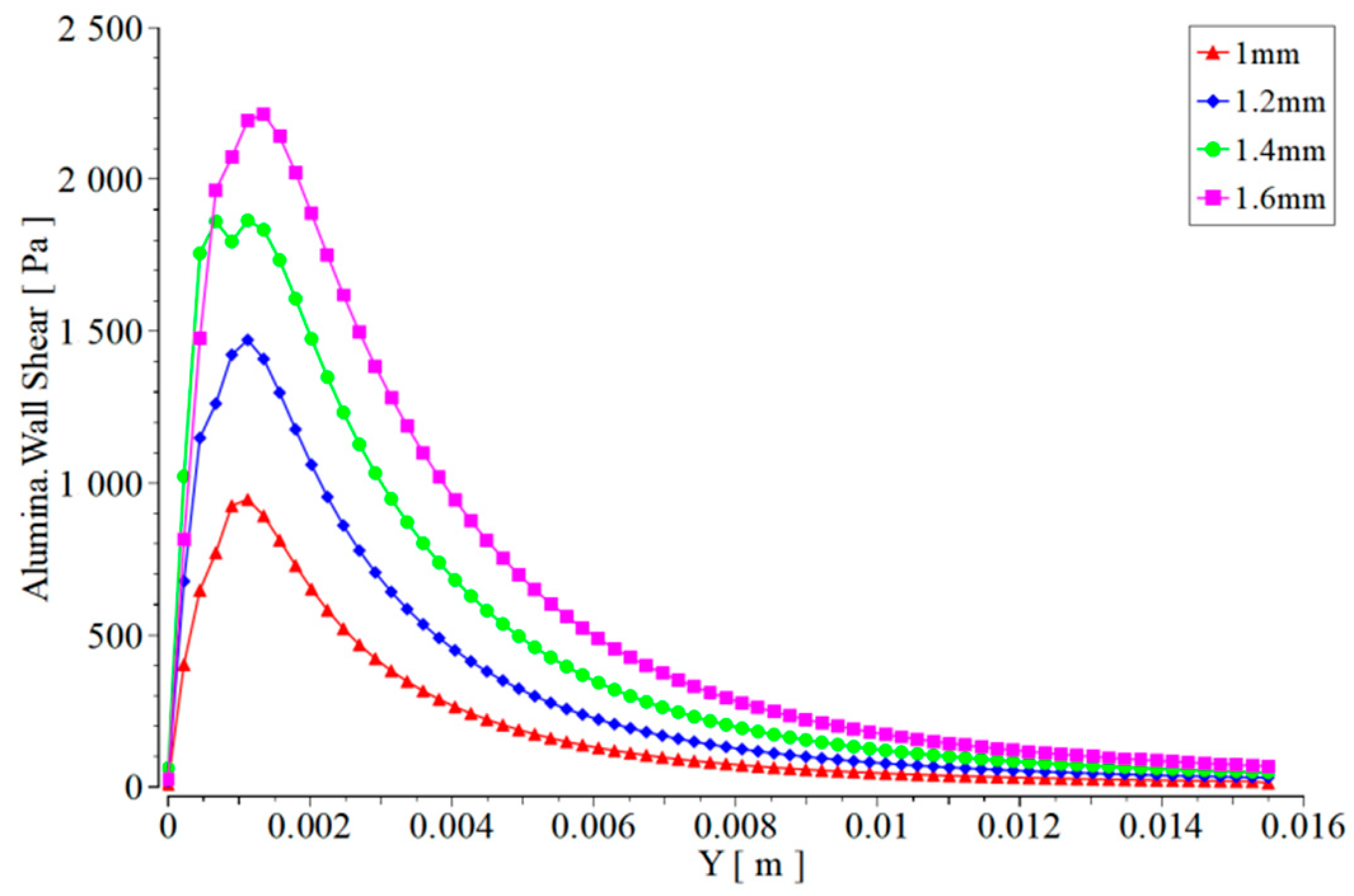
- From the pressure distribution and transverse shear force distribution curves caused by the jet on the surface of the work piece, both the pressure caused by the jet on the work piece and the transverse shear force will increase with the increase of wear at the nozzle outlet. when the diameter of the nozzle outlet is worn to 1.6 mm, the shear force is 2.5 times higher than the shear force when the diameter is 1.0, which means that the jet force is divergent when the diameter is 1.6 mm, and the damage to the work piece is very serious. The increase of jet pressure and transverse shear force will have an impact on the processing quality of the work piece surface.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Dai, Q. Recent Advances and Status of Abrasive Jet Machining Technology. Surf. Technol. 2022, 51, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanduri, M.; Taggart, D.G.; Kim, T.J. The effects of system and geometric parameters on abrasive water jet nozzle wear. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2002, 42, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantin, G.; Aleksander, P.; Anastasia, K. Determination of the wear limit value, the optimal operating time, and the consumption of jet-forming elements made of different materials when implementing water jet technologies. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 57, 210–219. [Google Scholar]
- Kamarudin, N.H.; Mebrahitom, A.; Azhari, A. Assembly meshing of abrasive waterjet nozzle erosion simulation. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 290, p. 012069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzetti, G.; Peters, B. A numerical approach for the evaluation of particle-induced erosion in an abrasive water jet focusing tube. Powder Technol. 2018, 333, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Z.; Wu, M.; Miao, X.; Sawhney, R. CFD research on particle movement and nozzle wear in the abrasive water jet cutting head. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 95, 4091–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syazwani, H.; Mebrahitom, G.; Azmir, A. A review on nozzle wear in abrasive water jet machining application. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2016; Volume 114, p. 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perec, A.; Pude, F.; Grigoryev, A.; Kaufeld, M.; Wegener, K. A study of wear on focusing tubes exposed to corundum-based abrasives in the waterjet cutting process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 104, 2415–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofa, M.G.; Kil, K.Y.; Hwan, A.J. Computational fluid analysis of abrasive waterjet cutting head. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Fu, L.; Wu, L.; Zuo, W. Research on Multiphase Flow and Nozzle Wear in a High-Pressure Abrasive Water Jet Cutting Head. Machines 2023, 11, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Study on Abrasive Jet Polishing Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Defense Science and Technology, Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Deng, S.; Guan, J.; Hua, W. Experiment and simulation research on abrasive water jet nozzle wear behavior and anti-wear structural improvement. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2017, 39, 2023–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Wang, H.; Dong, H.; Guo, Y.; Ke, Y. Numerical research on multi-particle movements and nozzle wear involved in abrasive waterjet machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 117, 2845–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yao, S.; Yun, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y. Simulation and Optimization of the Nozzle Section Geometry for a Suspension Abrasive Water Jet. Machines 2022, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Liu, L.; Zhao, J.; Sun, J. Erosion wear of laminated ceramic nozzles. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2007, 25, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zohoor, M.; Nourian, S.H. Development of an algorithm for optimum control process to compensate the nozzle wear effect in cutting the hard and tough material using abrasive water jet cutting process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 61, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.; Tabakoff, W. Erosion Prediction in Turbomachinery Resulting from Environmental Solid Particles. J. Aircr. 1975, 12, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baha, V.; Mižáková, J.; Pavlenko, I. An Increase in the Energy Efficiency of Abrasive Jet Equipment Based on the Rational Choice of Nozzle Geometry. Energies 2023, 16, 6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Reuterfors, E.P.; Mclaury, B.S.; Rybicki, E.F. Comparison of Computed and Measured Particle Velocities and Erosion in Water and Air Flows. Wear 2007, 263, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mclaury, B.S.; Shirazi, S.A. CFD Simulation and 2-D Modeling of Solid Particle Erosion in Annular Flow. In Proceedings of the 10th North American Conference on Multi Phase Technology, Banff, AB, Canada, 8–10 June 2016. BHR-2016-433. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H. Simulation and Analysis of Erosion Characteristics in Flushing Oil Pipeline with Liquid-Solid Phase Fluids. Tribology 2016, 36, 695–702. [Google Scholar]



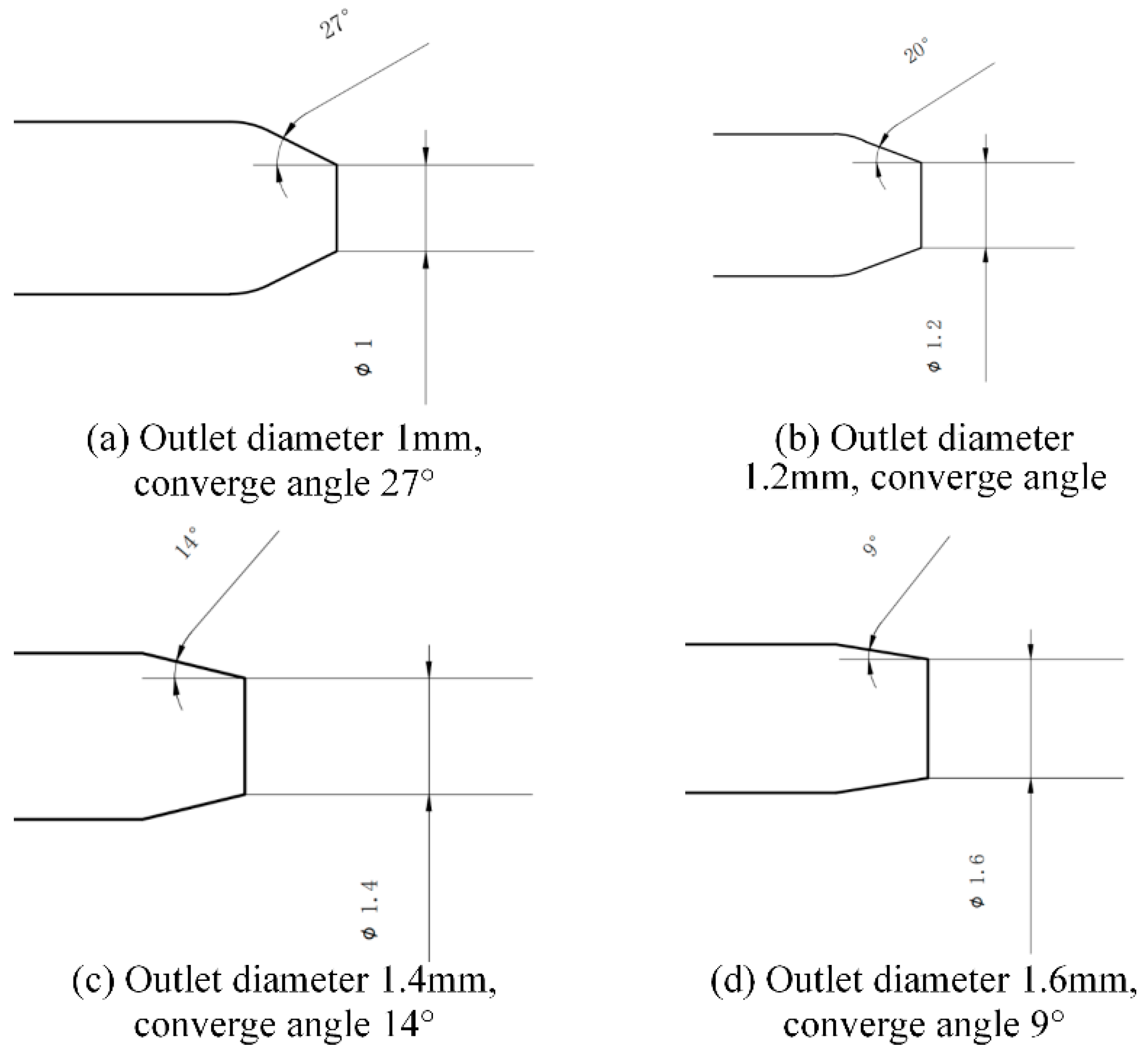


| Inlet Pressure of Abrasive Water (MPa) | Abrasive Particle Diameter (μm) | Abrasive Mass Flow Rate (kg/s) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.000125 |
| 1 | 0.3 | 0.00025 |
| 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.000375 |
| 2 | 1 | 0.0005 |
| 2.5 | 1.5 | 0.000625 |
| 3 | 2 | 0.00075 |
| 3.5 | 2.5 | 0.000875 |
| 4 | 3 | 0.001 |
| Current Density (kg/m3) | Water Flow Viscosity (kg/m·s−1) | Abrasive Grain Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| 998.2 | 0.001003 | 3500 |
| Parameters | Values Tested | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Polishing pressure (MPa) | 2 | 0.5–4 |
| Abrasive flow rate (L/M) | 4 | 3–5 |
| Abrasive solid garnet | (#80) Garnet | (#80–#150) |
| Orifice diameter (mm) (before wear) | 1 | 0.6–3 |
| Orifice diameter (mm) (after wear) | 1.2, 1.4, 1.6 | N/A (not available) |
| Particle inlet diameter (mm) | 3 | 3–5 |
| Particle inlet position (mm) | Low, mid, high | N/A (not available) |
| Particle inlet angle (°) | 0 | 0, 30, 45 |
| Converging part angle (before wear) | 27 | N/A (not available) |
| Converging part angle (after wear) | 20, 14, 9 | N/A (not available) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Pan, H.; Chen, L.; You, H.; Liang, X. Nozzle Wear in Abrasive Water Jet Based on Numerical Simulation. Materials 2024, 17, 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17143585
Chen X, Yu H, Pan H, Chen L, You H, Liang X. Nozzle Wear in Abrasive Water Jet Based on Numerical Simulation. Materials. 2024; 17(14):3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17143585
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xuhong, Hongji Yu, Haihong Pan, Lin Chen, Hui You, and Xubin Liang. 2024. "Nozzle Wear in Abrasive Water Jet Based on Numerical Simulation" Materials 17, no. 14: 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17143585
APA StyleChen, X., Yu, H., Pan, H., Chen, L., You, H., & Liang, X. (2024). Nozzle Wear in Abrasive Water Jet Based on Numerical Simulation. Materials, 17(14), 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17143585







