Aluminium Nitride Surface Characterization by Grinding with Laser–Ultrasonic Coupling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modelling on the Molecular Dynamics of LUAG
2.1. MD Simulation for Single Abrasive Grinding on Aluminium Nitride
2.2. Establishment of Multi-Field Processing Conditions
3. Results and Discussions
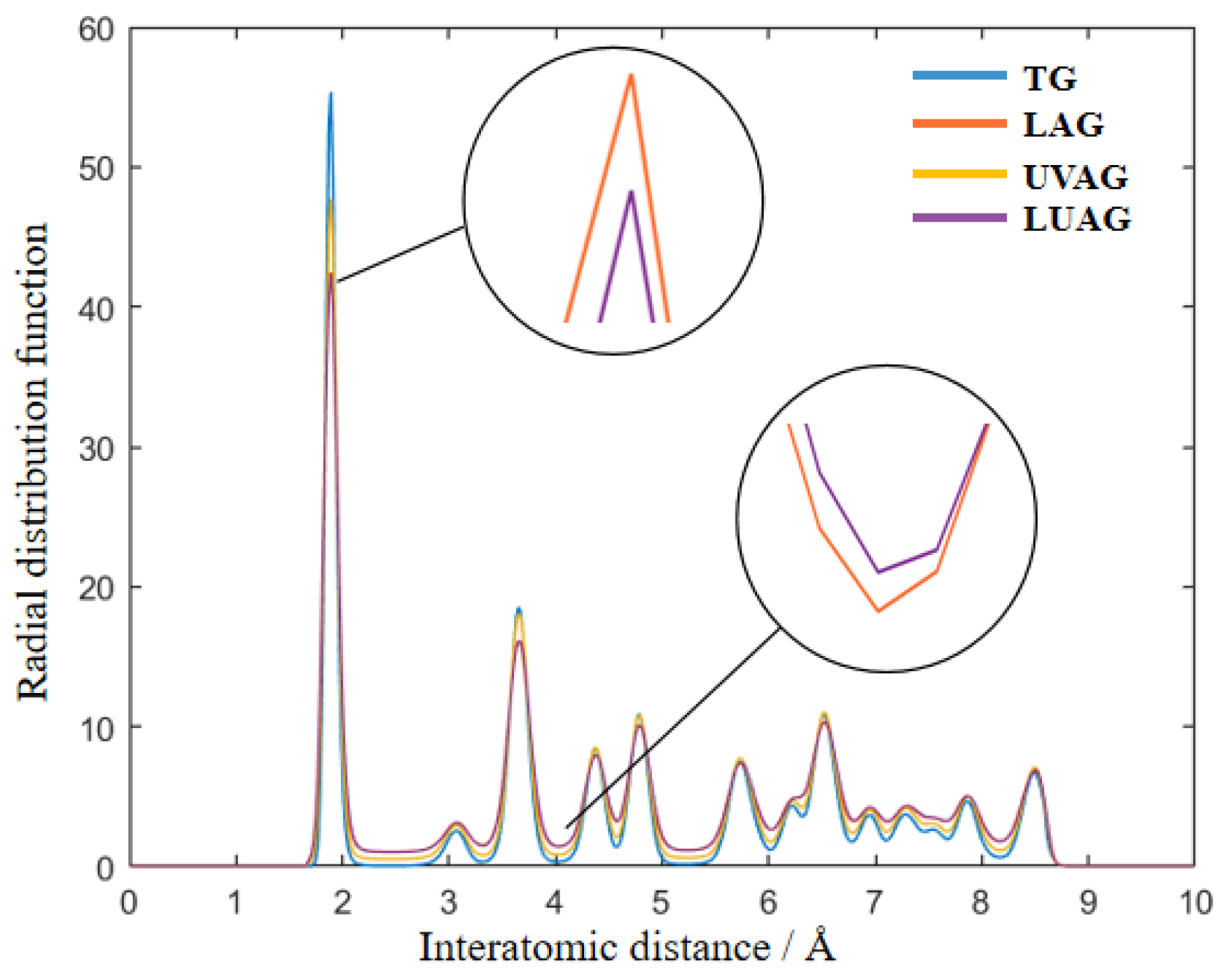
3.1. RDF Analysis of AlN Structure
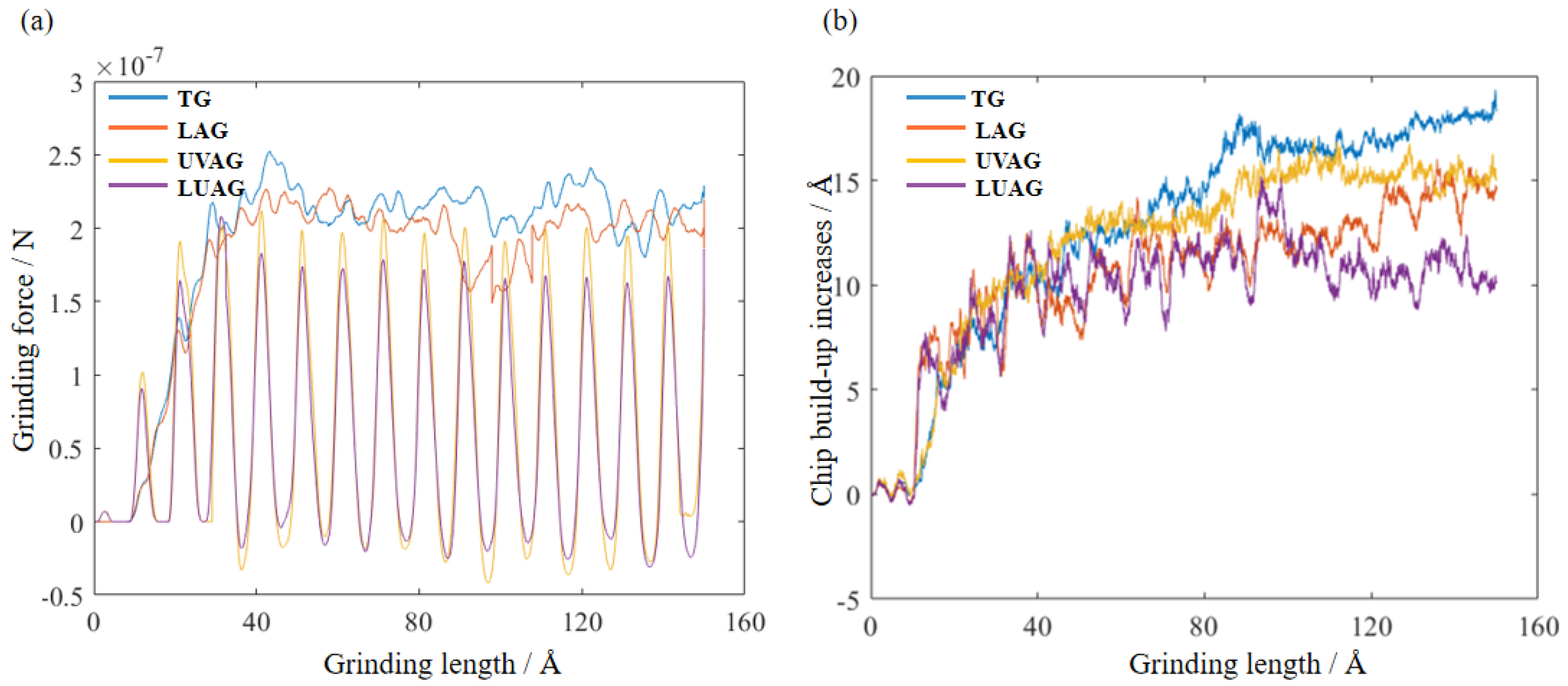
3.2. Analysis of the Grinding Force and Chip Build-Up Increases
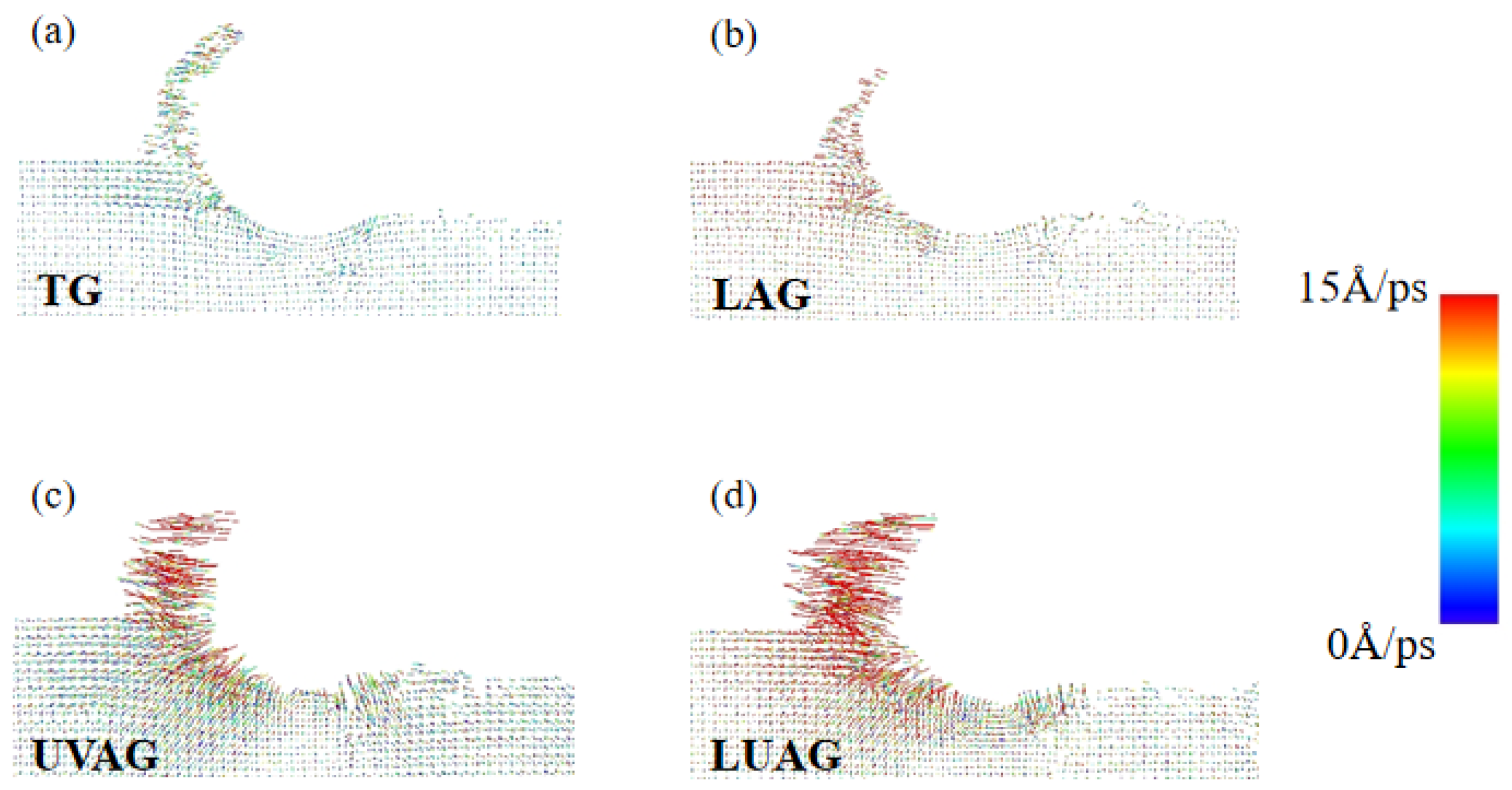
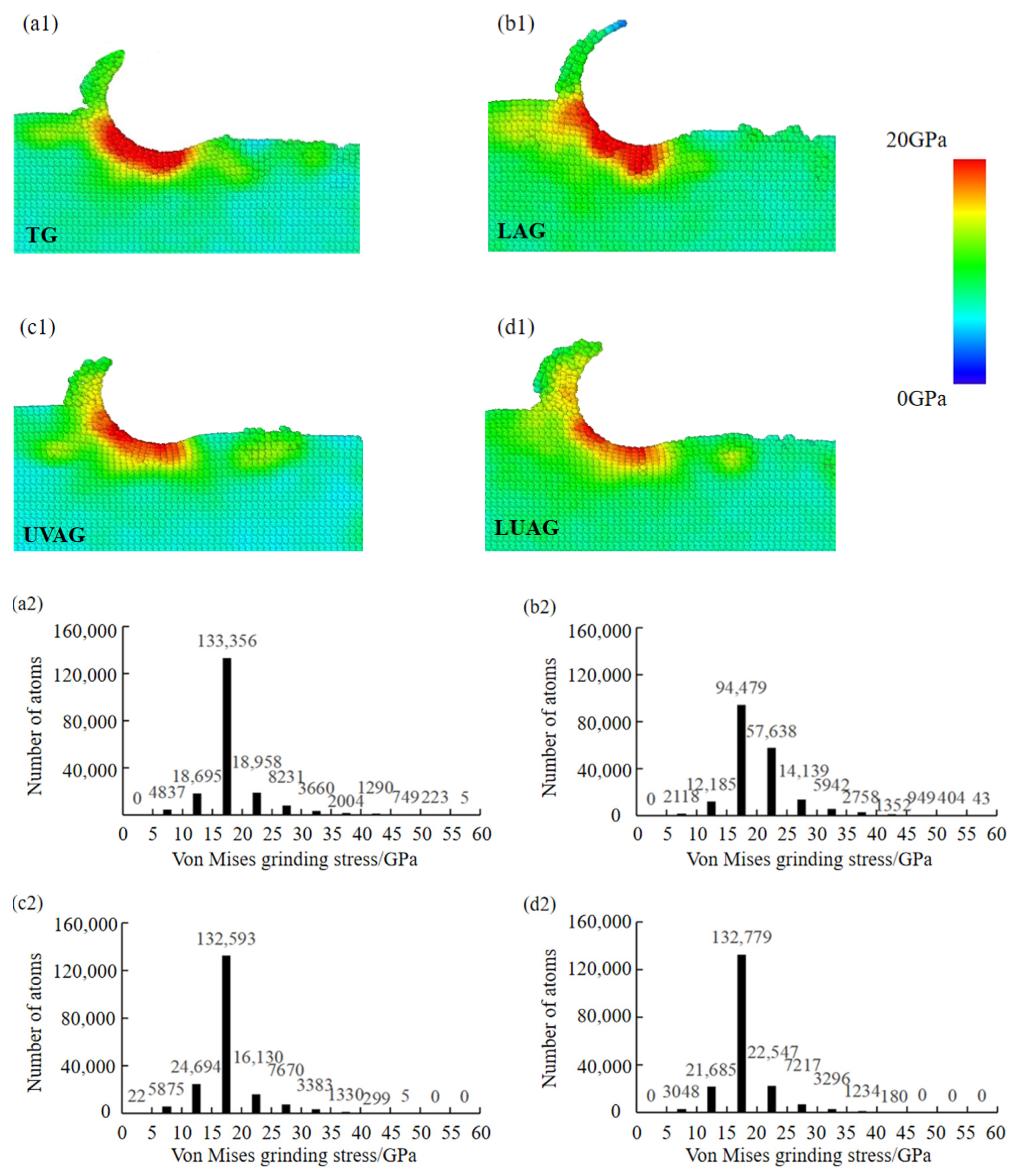
3.3. Analysis of the Atom Flow Field and Von Mises Shear Stress
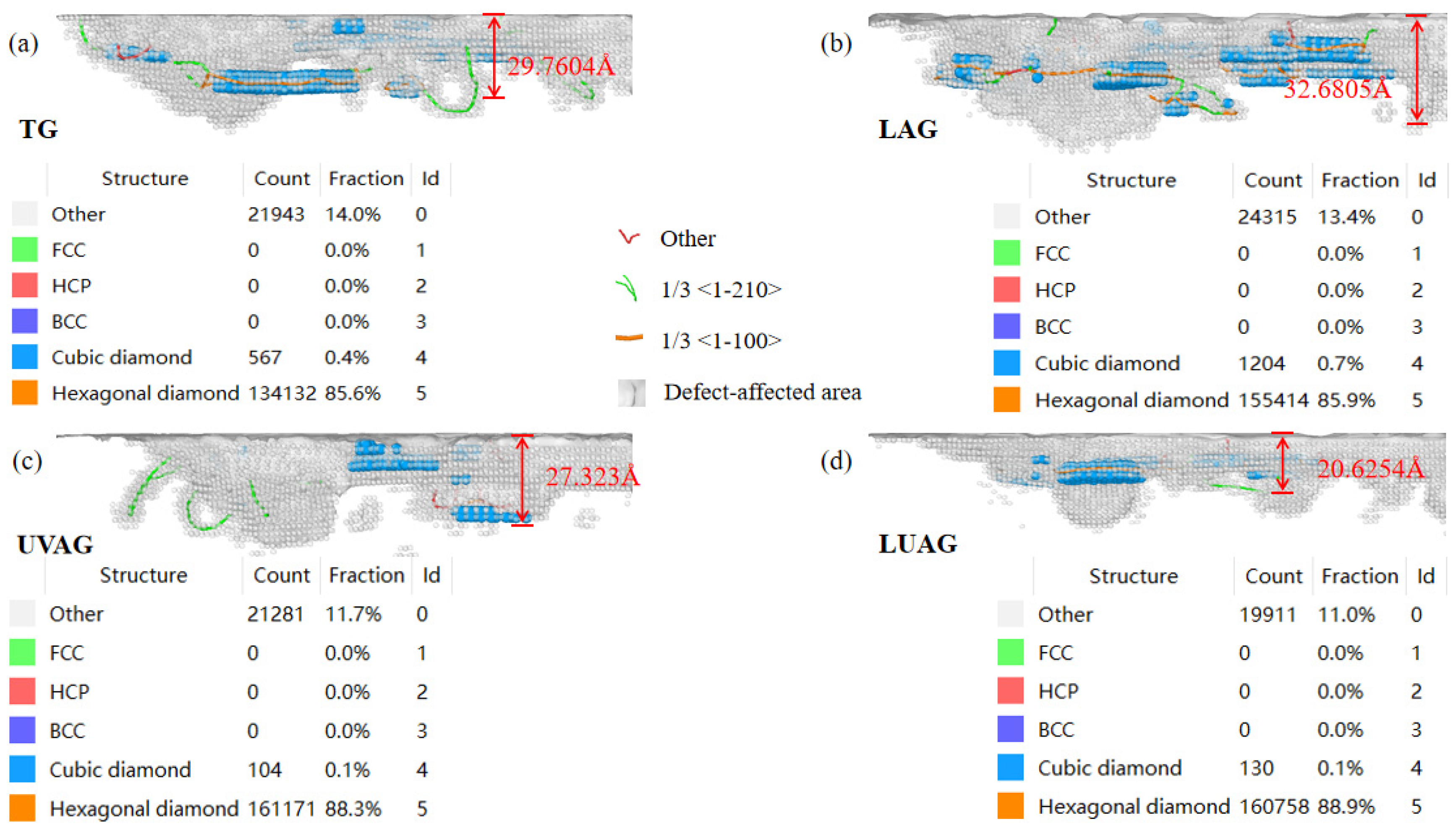
3.4. Analysis of the Subsurface Damage Depth
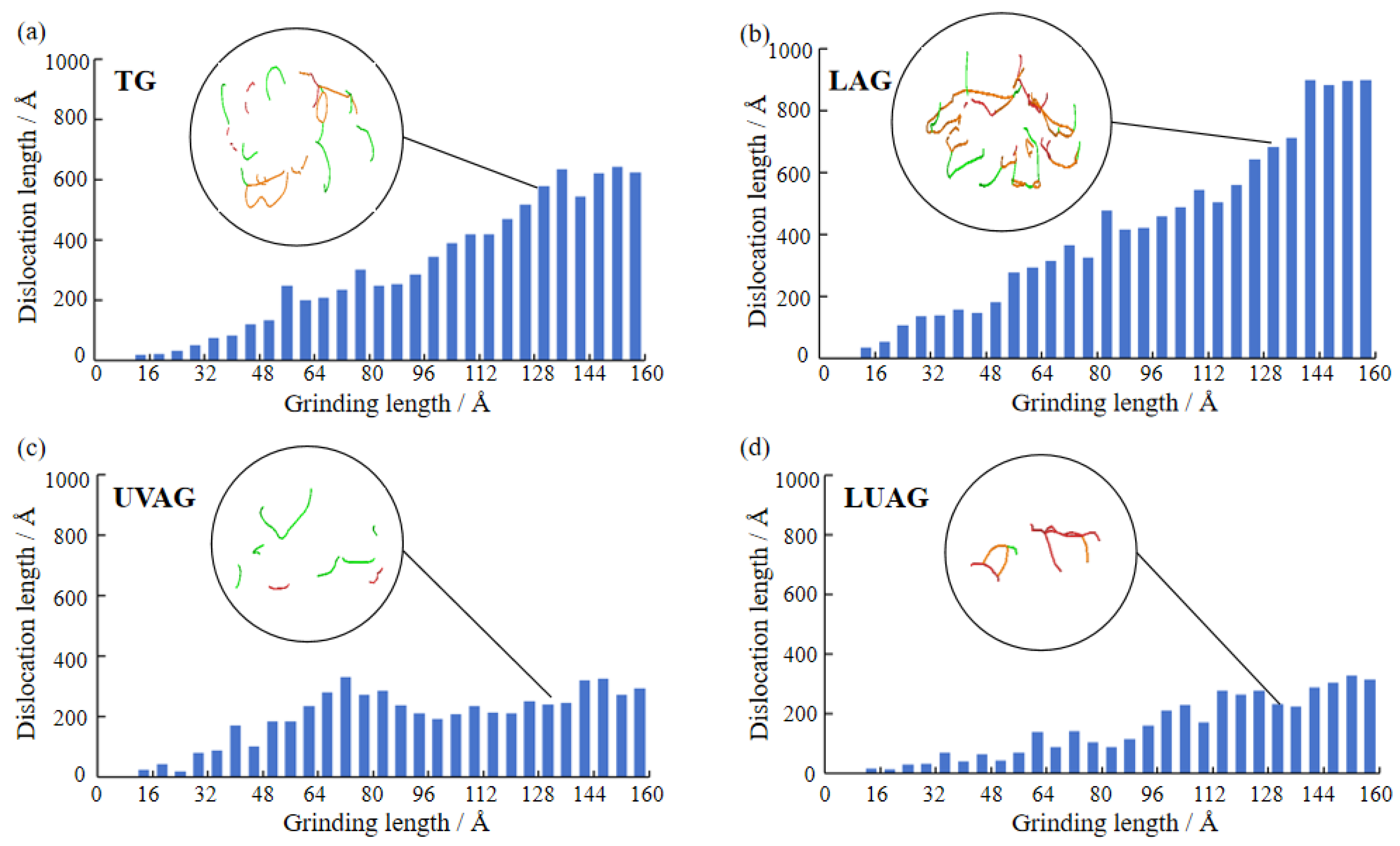
3.5. Analysis of the Dislocation Properties
4. Experimental Characteristics and Validation
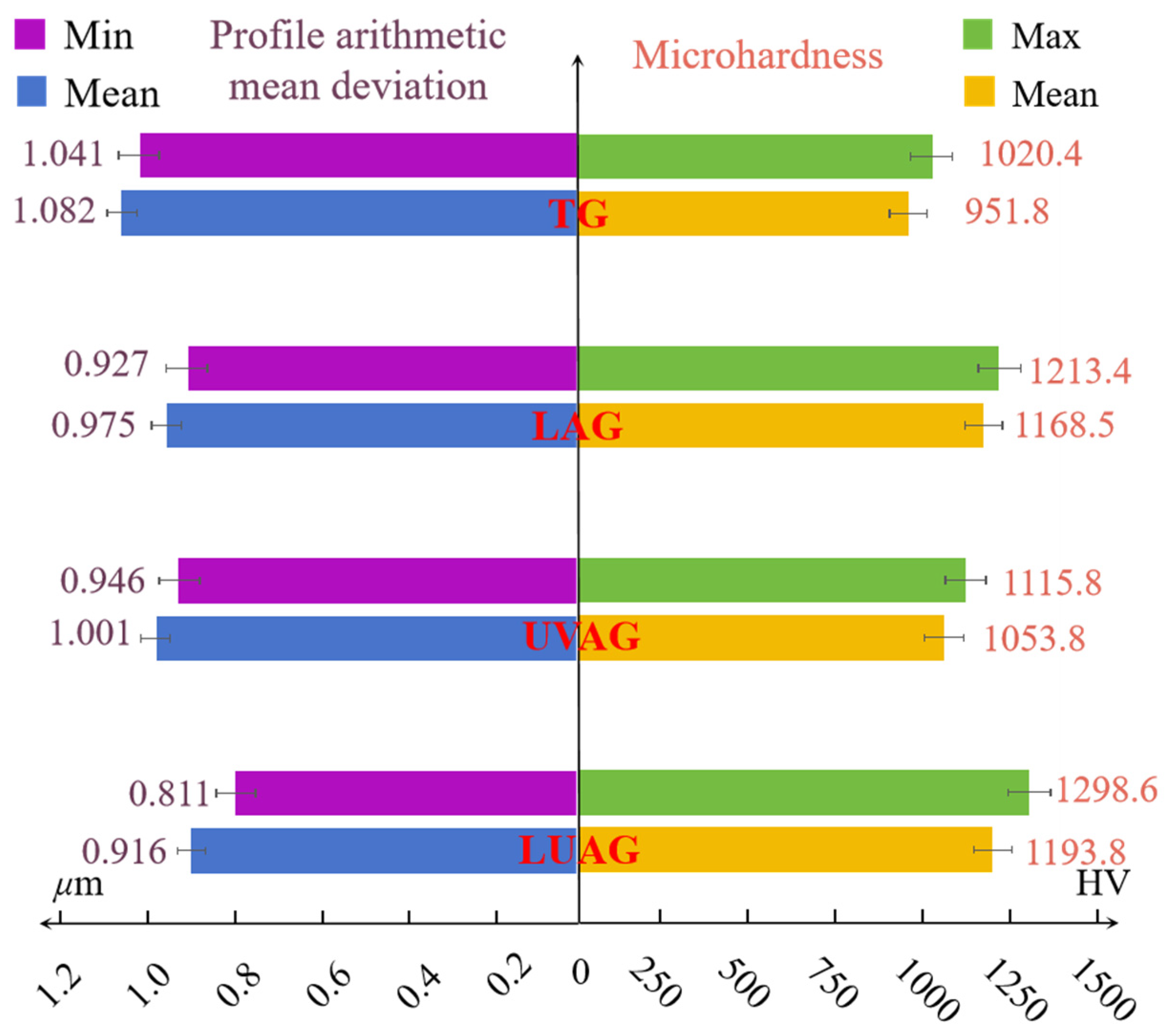
4.1. Microhardness and Surface Roughness of the AlN
4.2. Grinding Forces during Machining
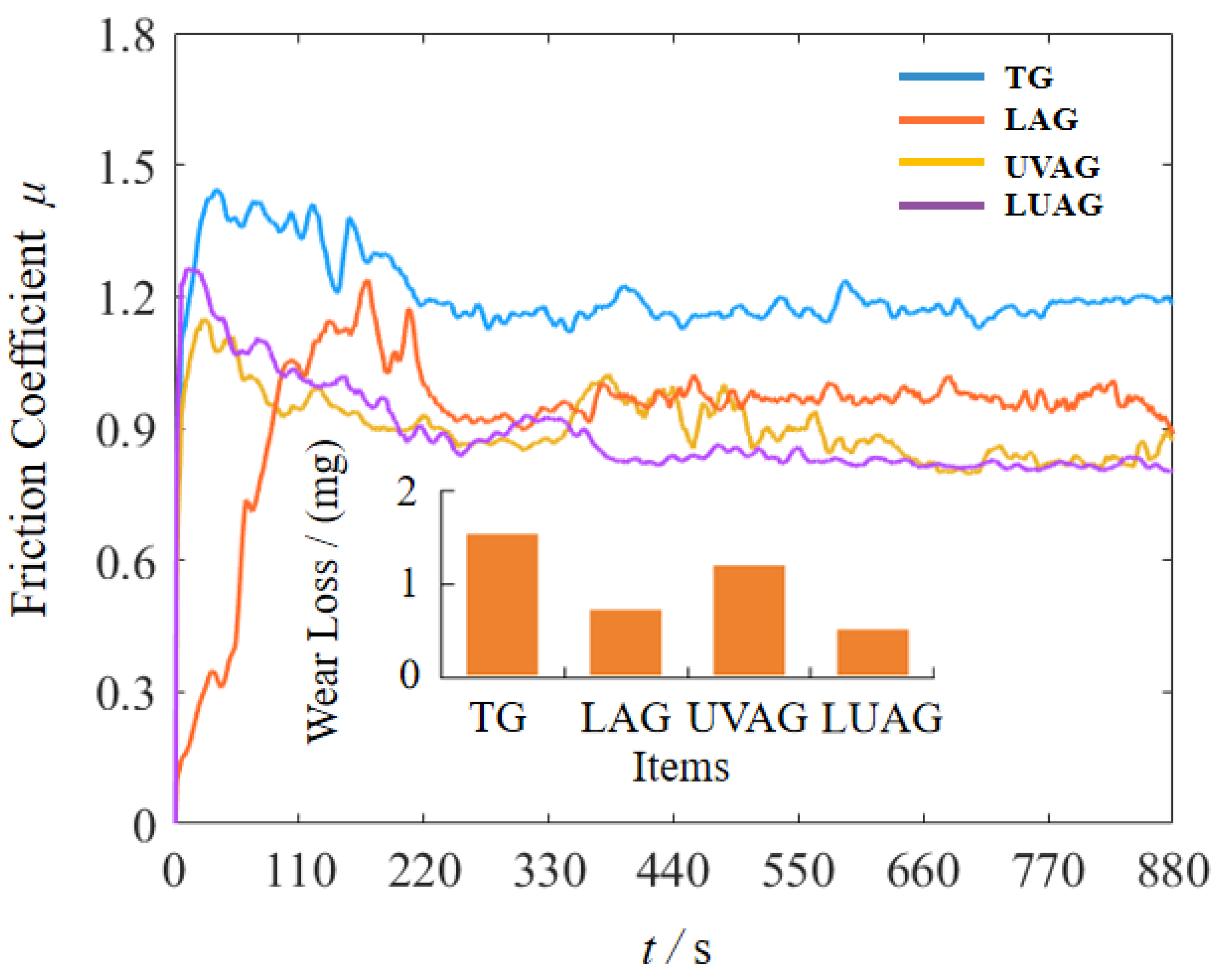
4.3. Friction and Wear Characteristics of Machined Surfaces
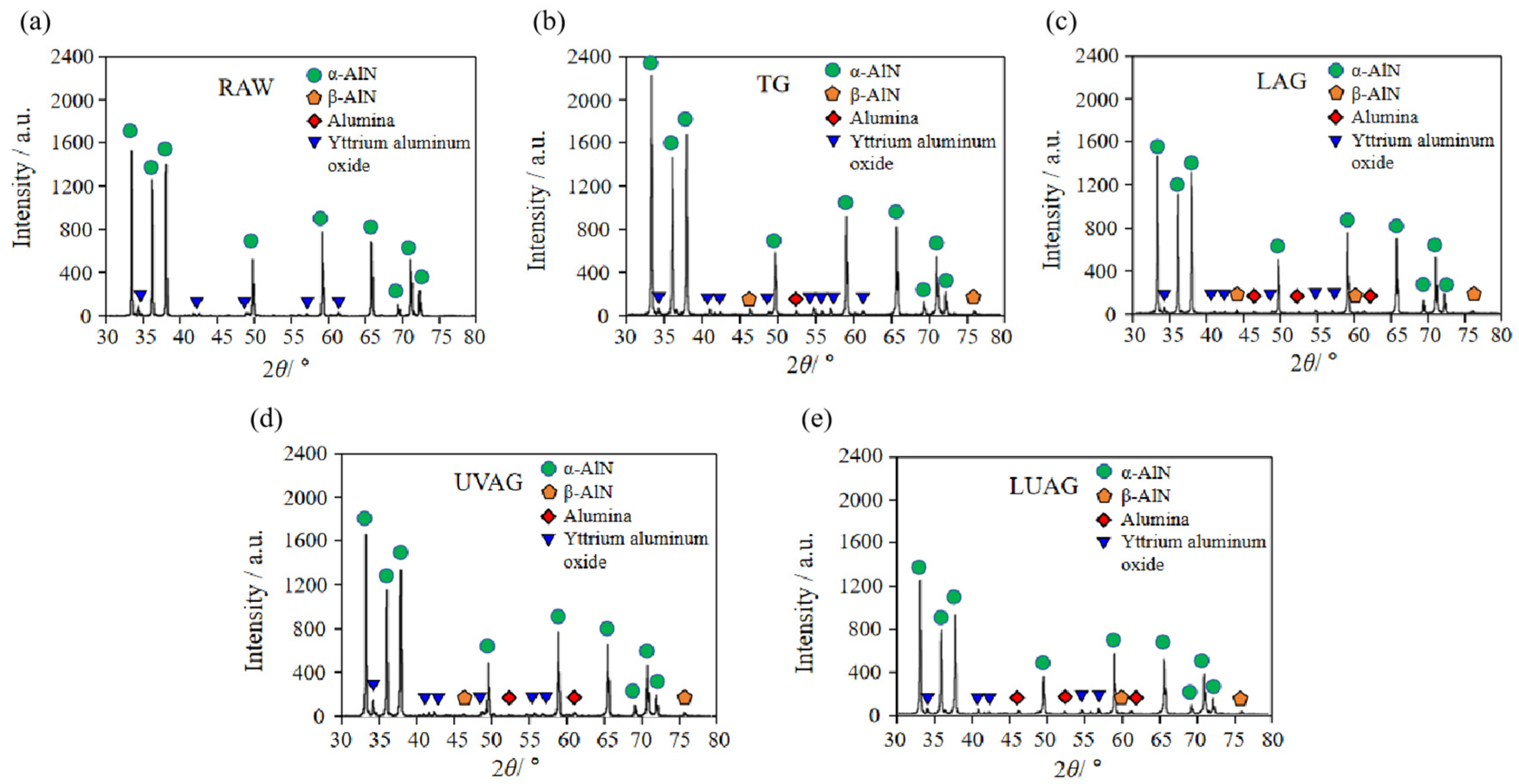
4.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Spectrum Analysis
5. Conclusions
- The structural phase change and dislocation migration occurred in all materials when aluminium nitride is processed via grinding. Among them, the aluminium nitride under the LUAG process has the smallest subsurface affected zone and the shortest total length of dislocation lines. As a result, the hardness of the aluminium nitride surface affected by the coupling effect can reach 1236.9 HV, which is 26.7% harder than TG. The machined surface quality was significantly improved under this process, and the material’s friction coefficient was reduced by nearly 42.6%.
- LUAG makes the surface of aluminium nitride have a better stress state. The residual stress layer on the machined surface is smaller and uniform, while the stress in the affected area in front of the abrasive grain during the grinding process is obviously lower than that in the conventional grinding process.
- LUAG enables ductility removal of aluminium nitride, which reduces plastic damage such as dislocations and lamination caused by mechanical stress. Meanwhile, compared with the TG process, the AlN substrate’s subsurface damage depth and surface roughness are reduced by 33% and 28.4%, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, R.; Liu, G.; Wang, G.; Chen, C.; Xu, M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, T.; Yu, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, L. Ultrawide-bandgap semiconductor AlN crystals: Growth and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 1852–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.; Lin, C.; Chuang, K.; Chang, Y.; Wu, C.; Hu, S. Failure and stress analysis of through-aluminum-nitride-via substrates during thermal reliability tests for high power LED applications. Microelectron. Reliab. 2016, 67, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Hong, Y.; Xiu, S. Influence of the abrasive shape-position characteristic on the grinding thermo-mechanical coupling. Surf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Z.; Yuan, J.L.; Lv, B.H. Study on the finishing process for the aluminum nitride substrates. Adv. Mater. Res. 2009, 69, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Piao, Y.; Hou, N.; Hu, K.J. Characterization of surface and subsurface defects induced by abrasive machining of optical crystals using grazing incidence X-ray diffraction and molecular dynamics. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 36, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Huang, H. Deformation mechanism and force modelling of the grinding of YAG single crystals. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2019, 143, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, X.; Mu, D.; Lawn, B. Science and art of ductile grinding of brittle solids. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2021, 161, 103675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Lang, H.; Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Kang, R. Atomic understanding of elastic-plastic deformation and crack evolution for single crystal AlN during nanoscratch. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 35357–35367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Guo, X.; Gao, S.; Li, Z.; Kang, R. Material removal mechanism and deformation characteristics of AlN ceramics under nanoscratching. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 20545–20554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, H.; Kang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z. Effect of strain rate on the deformation characteristic of AlN ceramics under scratching. Micromachines 2021, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, S.; Kang, R.; Huang, J.; Dong, Z. The Deformation Pattern of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics Under Nanoscratching. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Nanomanufacturing (nanoMan2021), Xi’an, China, 17–19 November 2021; pp. 285–297. [Google Scholar]
- Abedinzadeh, R.; Norouzi, E.; Toghraie, D. Experimental investigation of machinability in laser-assisted machining of aluminum-based nanocomposites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 3481–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Wang, J.; Zhu, S.; He, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y. A review of research on material removal mechanisms for laser-assisted machining of difficult-to-machine materials. Surf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.a.; Pi, J.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Yang, G.; Shen, Z. A novel method for effecting flexible guided wave propagation in elliptical vibration cutting. Precis. Eng. 2021, 72, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Cao, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y. Analysis on the tool wear behavior of 7050-T7451 aluminum alloy under ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting. Wear 2021, 466-467, 203538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, A. Developments in the non-traditional machining of particle reinforced metal matrix composites. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2014, 86, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Geng, Y.; Meng, B. Molecular dynamics simulation of laser assisted grinding of GaN crystals. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 239, 107856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, T. Effects of laser-assisted grinding on surface integrity of zirconia ceramic. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Qu, S.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T. A grinding force predictive model and experimental validation for the laser-assisted grinding (LAG) process of zirconia ceramic. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 302, 117492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Luo, X.; Chang, W.; Cai, Y.; Zhong, W.; Ding, F. Material removal mechanism of laser-assisted grinding of RB-SiC ceramics and process optimization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 39, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Lai, Z.; Zhu, J.; Xu, X.; Peng, Q. Processing and machining mechanism of ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding on sapphire. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 142, 106470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, P.; Zhang, J. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted scratch-induced characteristics of C-plane sapphire with a spherical indenter. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2013, 64, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Hartmaier, A. Atomistic investigation of machinability of monocrystalline 3C–SiC in elliptical vibration-assisted diamond cutting. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 2358–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, A.; Veiga, F.; Polvorosa, R.; Artaza, T.; Holmberg, J.; De Lacalle, L.N.L.; Wretland, A. Surface integrity and fatigue of non-conventional machined Alloy 718. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 48, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.; Cong, W. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted (UV-A) manufacturing processes: State of the art and future perspectives. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 51, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Piao, Y.; Meng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, F. Anisotropy dependence of material removal and deformation mechanisms during nanoscratch of gallium nitride single crystals on (0001) plane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 578, 152028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishta, P.; Kalia, R.K.; Nakano, A.; Rino, J. Interaction potential for aluminum nitride: A molecular dynamics study of mechanical and thermal properties of crystalline and amorphous aluminum nitride. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G.; Ni, C.; Lin, B. Review of ultrasonic vibration-assisted machining in advanced materials. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2020, 156, 103594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tsang, K.S.; Liu, Y.; Pang, J.H.L. Finite element and experimental study on multiaxial fatigue analysis of rail clip failures. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2020, 43, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, F.; Yu, W.; Bai, Y.; Liu, Z.J.M. Microstructural characteristics and subsequent soften mechanical response in transverse direction of wrought AZ31 with elevated compression temperature. Materials 2021, 14, 4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhen, L.; Yang, L.; Shao, W.; Zhang, B.J. Deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of 7050 aluminum alloy during high temperature deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 488, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, K.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, J.; Tweedle, T.; Carpenter, D.; Zheng, G. Femtosecond laser fabrication of nanograting-based distributed fiber sensors for extreme environmental applications. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2021, 3, 025401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnikov, V.S.; Mayer, A.E. Dislocation dynamics in aluminum containing θ’phase: Atomistic simulation and continuum modeling. Int. J. Plast. 2019, 119, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cao, M.; Chen, R.; Feng, Z.; Poprawe, R.; Schleifenbaum, J.H.; Ziegler, S.J. Effect of δ phase on high temperature mechanical performances of Inconel 718 fabricated with SLM process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 767, 138327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Piao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, F. Modelling and experimental investigation of temperature field during fly-cutting of KDP crystals. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 210, 106751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, C.; Hong, Y.; Deng, Y.; Ma, L. Aluminum nitride surface modification mechanism by laser ultrasonic-assisted grinding. Tribol. Int. 2024, 196, 109718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, X.; Lu, J.; Zhu, J. An investigation into mechanics and tribology of SnAgCu and MoO3 containing in 20CrMnTi based composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 831, 154858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Cai, X.; Li, Z.; Dong, Z.; Ma, G.; Bao, Y.; Kang, R.; Niu, F. Cf/C-SiC Abla-tive Behavior and Feasibility of Laser Assisted Ultrasonic Grinding. Surf. Technol. 2024, 53, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
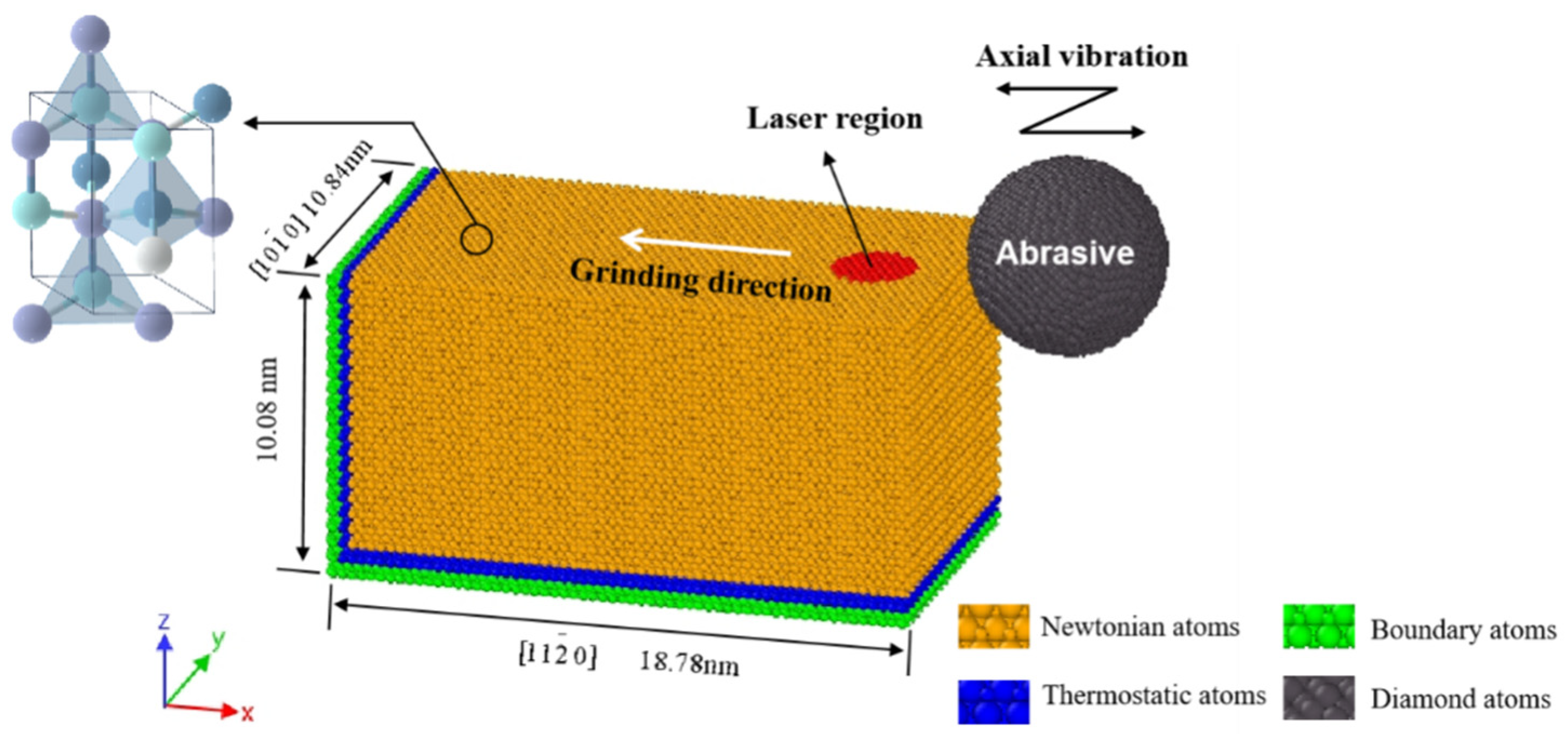


| Machining Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Material structure | fibrillated zincite structure |
| Newtonian layer size (nm3) | 18.1 × 10.8 × 7.0 |
| Abrasive radius (nm) | 3 |
| Grinding depth (nm) | 2 |
| Grinding speed (m/s) | 50 |
| Vibration frequency (GHz) | 0.1 |
| Amplitude (nm) | 0.8 |
| Grinding distance (nm) | 16 |
| Laser heating temperature (K) | 800 |
| Initial temperature (K) | 300 |
| Potential function | Vashishta, Tersoff, Lennard-Jones |
| Relaxation system | NVT |
| Processing system | NVE |
| Items | Laser Power (J/s) | Ultrasound Amplitude (µm) | Ultrasound Frequency (KHz) | Grinding Depth (mm) | Wheel Grit | Grinding Width (mm) | Feed Rate (mm/s) | Wheel Speed (rad/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | - | 0.02 | 320# | 13 | 2 | 2500 |
| 2 | 500 | - | - | |||||
| 3 | - | 8 | 20 | |||||
| 4 | 500 | 8 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Sun, C.; Hong, Y.; Deng, Y.; Ma, L. Aluminium Nitride Surface Characterization by Grinding with Laser–Ultrasonic Coupling. Materials 2024, 17, 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153772
Zhang H, Sun C, Hong Y, Deng Y, Ma L. Aluminium Nitride Surface Characterization by Grinding with Laser–Ultrasonic Coupling. Materials. 2024; 17(15):3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153772
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, He, Cong Sun, Yuan Hong, Yansheng Deng, and Liang Ma. 2024. "Aluminium Nitride Surface Characterization by Grinding with Laser–Ultrasonic Coupling" Materials 17, no. 15: 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153772
APA StyleZhang, H., Sun, C., Hong, Y., Deng, Y., & Ma, L. (2024). Aluminium Nitride Surface Characterization by Grinding with Laser–Ultrasonic Coupling. Materials, 17(15), 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153772





