The Effect of Long-Term Aging on the Microstructure and Properties of a Novel Nickel-Based Powder Superalloy FGH4113A
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure Evolution of Alloy after Long-Term Aging
3.1.1. Grain Structure and γ′ Phase
3.1.2. Carbides
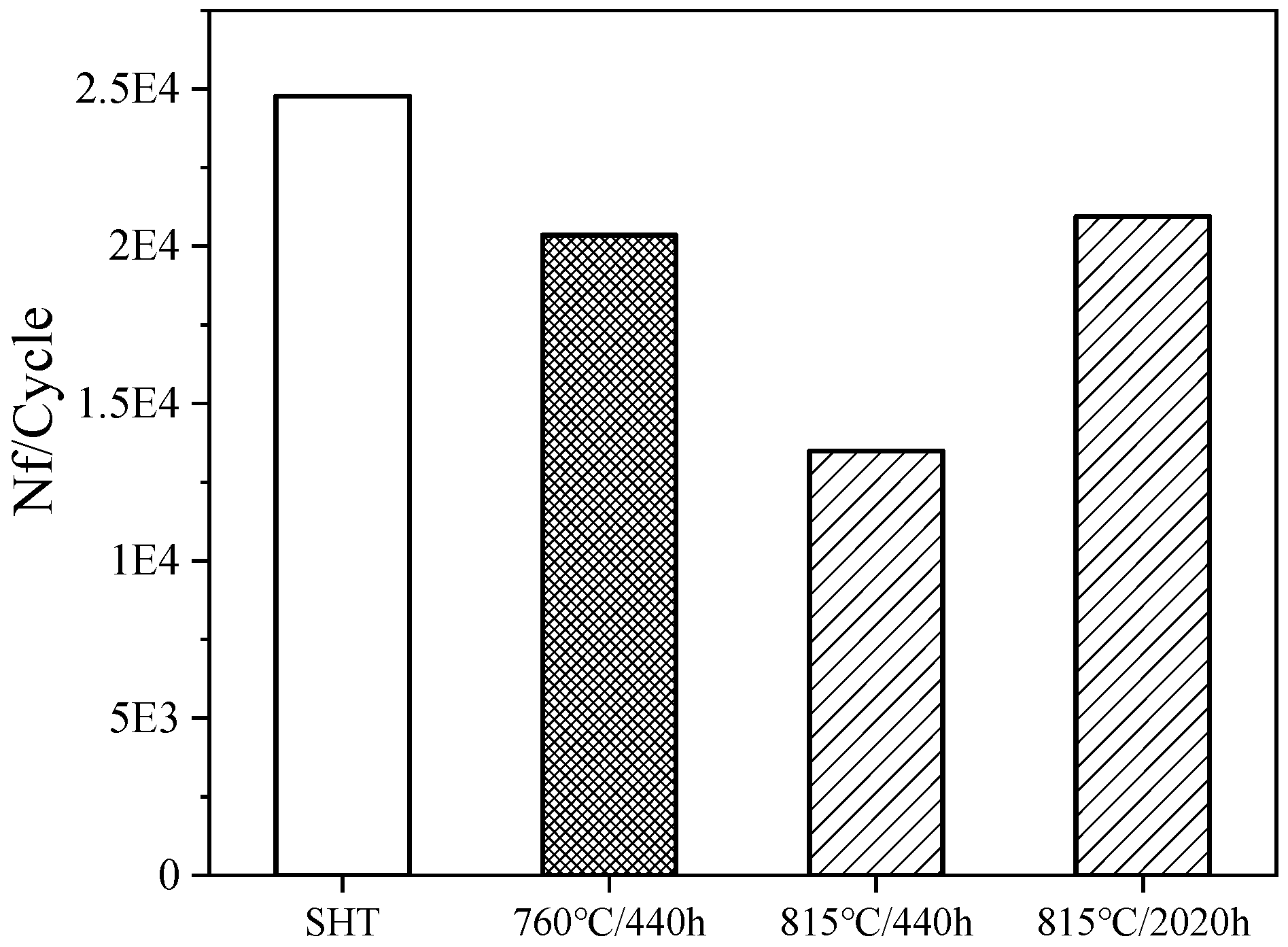
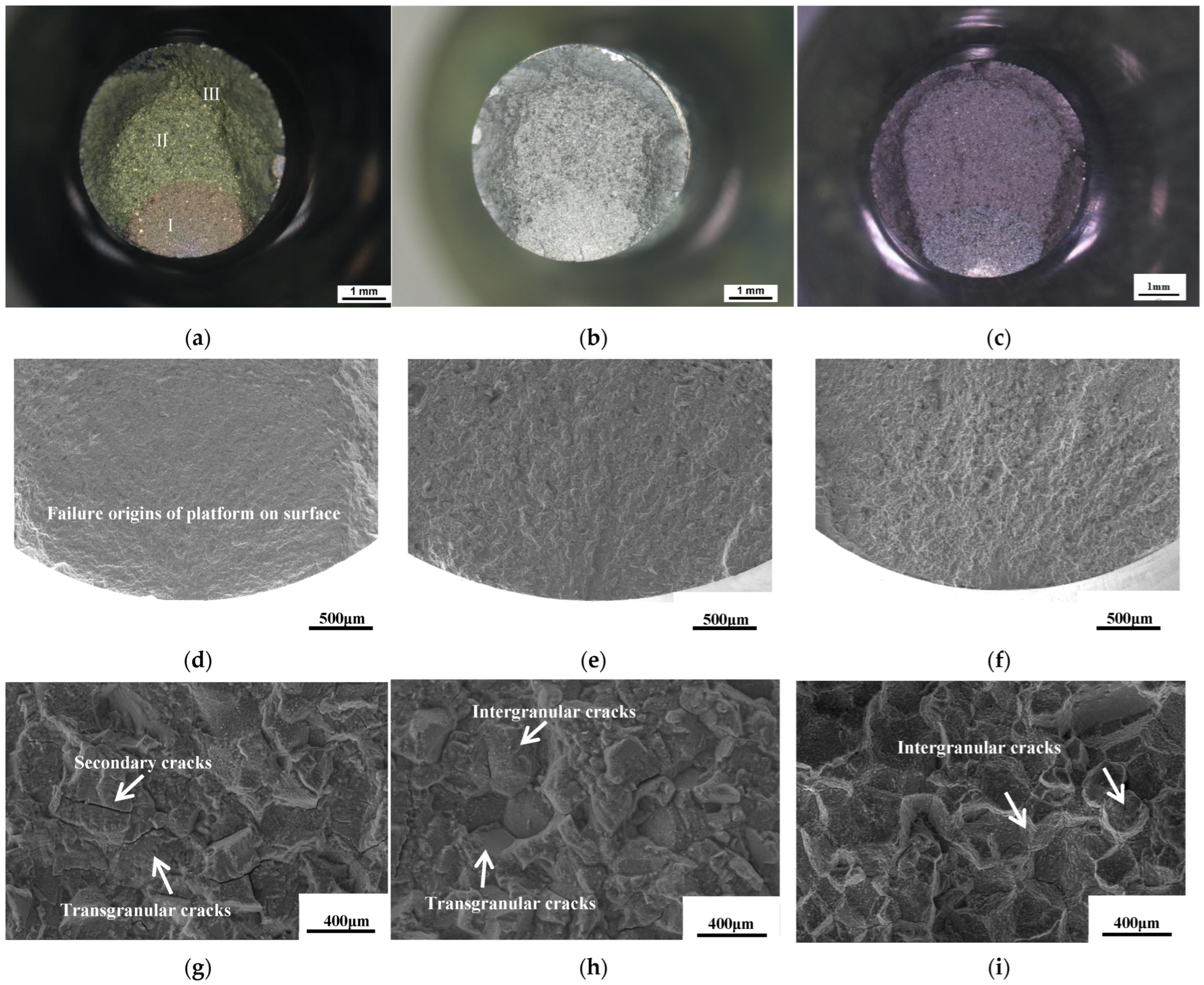
3.2. Low-Cycle Fatigue Properties
4. Discussion
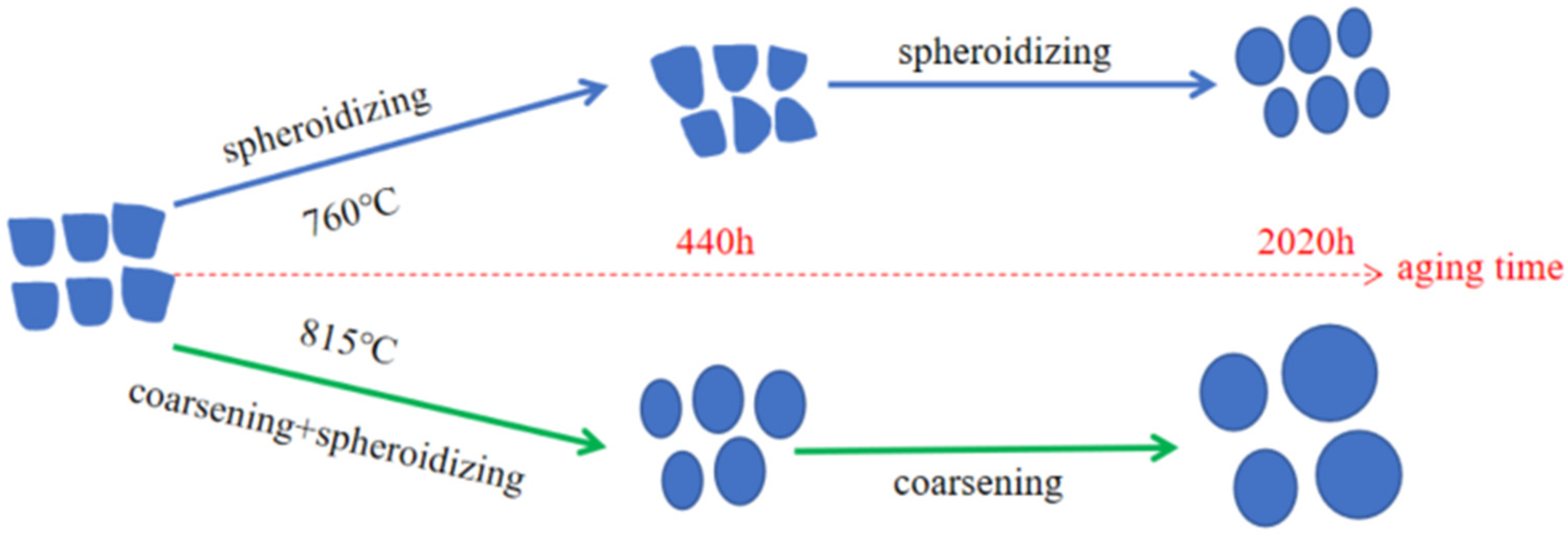
4.1. The Evolution of the γ′ Phase
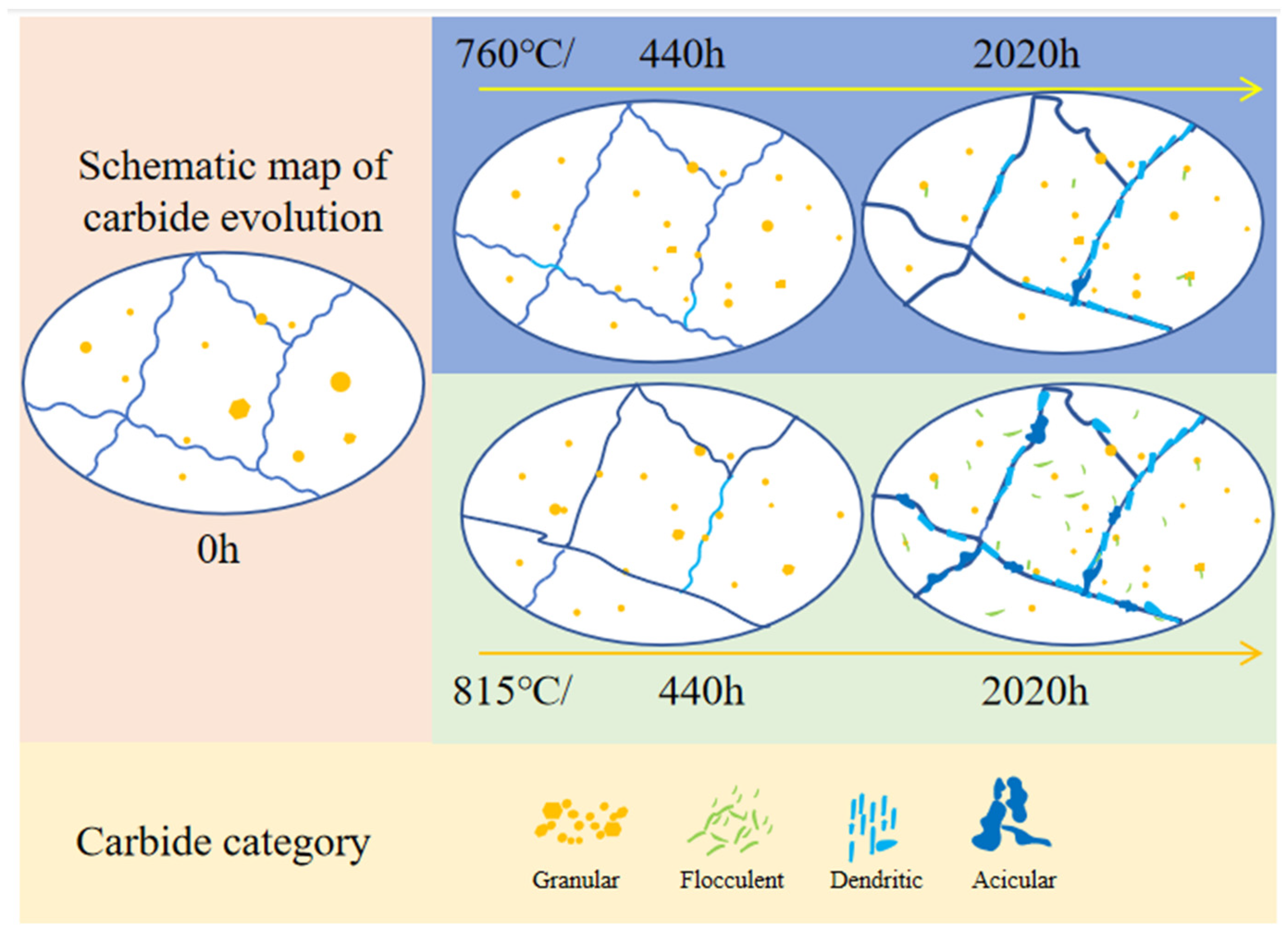
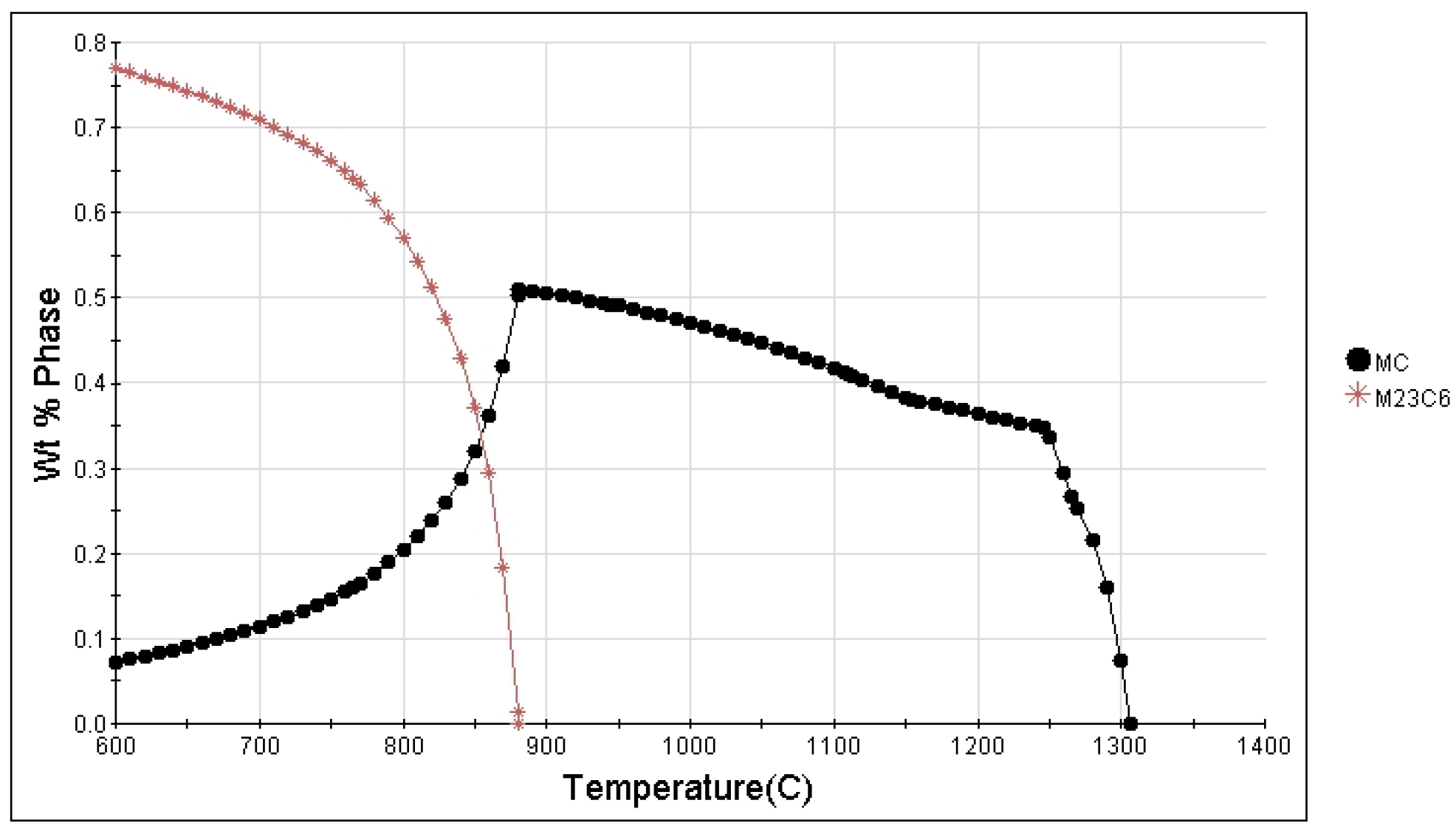
4.2. The Evolution of Carbides
4.3. Effect of Long Term Aging on the Fatigue Properties
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The long-term aging at 760 °C or 815 °C up to 2020 h revealed no effect on the grain size of the alloy, which maintained unchanged at about ASTM 7.5.
- (2)
- After the long-term aging at 760 °C for 2020 h, the size of the secondary γ′ phase showed no significant change, holding at about 130 nm. But the morphology of the γ′ phase changed from the rounded squares to nearly spherical shapes. After aging at 815 °C for 440 h, the secondary γ′ phase coarsening and spheroidizing took place. The size of the γ′ phase increased to about 200 nm after 2020 h, and the morphology also changed to a near-spherical shape.
- (3)
- After long-term aging at 760 °C for 2020 h, dispersed MC carbides transformed into high-Mo flocculent M6C carbides and noncontinuous M6C. In the same time, M23C6 carbides began to enrich at the grain boundaries. After aging at 815 °C for 440 h, flocculent carbides started precipitating within the grains. The amount of flocculent carbides within the grains kept on growing, and the grain boundary carbides became coarser after 2020 h.
- (4)
- Compared to the SHT heat treatment state, the 760 °C LCF life of the alloy decreased after long-term aging. The reductions in fatigue life after aging 760 °C for 440 h and 815 °C for 2020 h showed no significant difference. The maximum reduction in LCF life is less than 20% for the conditions in this study. The little reduction in fatigue life after long-term aging is associated with the insignificant coarsening of the γ′ phase and the enrichment of carbides at the grain boundaries.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, W.M.; Song, P.S.; Wu, J.T.; Zhang, F.G.; Yang, C.; Zang, Y.W.; Chen, S.D. Development and prospects of power metallurgy superalloys. Powder Metall. Ind. (Chin. Ed.) 1999, 2, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Liu, J.T. Development in powder metallurgy superalloy. Mater. China (Chin. Ed.) 2013, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findley, K.O.; Saxena, A. Low cycle fatigue in rene 88DT at 650 °C: Crack nucleation mechanisms and modeling. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayda, J.; Gabb, T.P.; Kantzos, P.T. The Effect of Dual Microstructure Heat Treatment on an Advanced Nickel-Base Disk Alloy. In Proceedings of the Superalloys 2004, Champion, PA, USA, 19–23 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Raisson, G. Evolution of PM nickel base superalloy processes and products. Powder Metall. 2008, 51, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Chi, Y.; Liu, J.T. Recent development of new type powder metallurgy superalloys in Russia. Powder Metall. Ind. (Chin. Ed.) 2015, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.Y.; Zhu, L.H.; Xiao, L.; Guo, J.Z.; Ji, H.J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of new third-generation Nickel-based powder superalloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. (Chin. Ed.) 2022, 51, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabb, T.P.; Sudbrack, C.K.; Draper, S.L.; MacKay, R.A.; Telesman, J. Effects of Long Term Exposures on PM Disk Superalloys; NASA/TM-2013-216614; NASA: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2013; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, T.; Hao, Z.B.; Li, X.G.; Jia, C.L.; Peng, S.H.; Zhu, Q. Influence of aging treatment on microstructure and properties of a novel spray formed powder metallurgy superalloy FGH100L. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 830, 154699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Zhao, X.B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Pei, Y.L.; Li, S.S.; Gong, S.K. Application of a modified Ostwald ripening theory in coarsening of γ′ phases in Ni based single crystal superalloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 632, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Dong, J.X.; Zhang, Y.W. Effect of long time aging treatment on the γ′ phase evolution of FGH97 P/M supperalloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. (Chin. Ed.) 2014, 43, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.L.; Sun, N.R.; Feng, G.J. Effect of long-term aging on microstructure stability of two kinds of Ni-Base superalloy. Hot Work. Technol. (Chin. Ed.) 2019, 48, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.R.; Xiong, J.Y.; Yang, J.L.; Feng, G.J. Research on the stability of microstructure of new Nickel-based superalloys during heat-treatment and long-time aging. Foundry (Chin. Ed.) 2017, 66, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Q.; Xie, Y.; Sun, S.S.; Xue, P.J.; Long, A.P.; Wu, T.G.; Cai, C.; Guo, J.Z.; Wei, Q.S. Understanding on processing temperature-metallographic microstructure-tensile property relationships of third-generation nickel-based superalloy WZ-A3 prepared by hot isostatic pressing. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 909, 164668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.M.; Lin, Y.C.; Zhao, W.W.; Liu, G.; Chen, Z.J.; Zhu, J.C.; Chen, M.S.; Qiu, Y.L. Formation and elimination mechanisms of prior particle boundaries in a new powder metallurgy superalloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 8037–8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.L.; Tang, X.F.; Jin, J.S.; Cai, C.; Yang, H.Y.; Teng, Q.; Wei, Q.S.; Wang, X.Y.; Zheng, C.W.; He, Y.J.; et al. Effect of extrusion ratios on microstructure evolution and strengthening mechanisms of a novel P/M nickel-based superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 847, 143356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.Y.; Yin, C.; Wang, C.; Guo, J.Z. Study on microstructure long-term stability of powder metallurgy superalloy FGH4113A. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. (Chin. Ed.) 2023, 52, 2885–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 15248; The Test Method for Axial Loading Constant-Amplitude Low-Cycle Fatigue of Metallic Materials. Beijing Institute of Aeronautical Materials: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Wood, W.A. Formation of fatigue cracks. Philos. Mag. 1958, 3, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, F.; Jahazi, M.; Shahriari, D.; Cormier, J. Coarsening and dissolution of γ′ precipitates during solution treatment of AD730 Ni-based superalloy: Mechanisms and kinetics models. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 658, 981–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Wakatsuki, T. The effect of elastic interaction energy on the morphology of γ′ precipitates in nickel-based alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1984, 67, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Prasath Babu, R.; Slater, T.J.A.; Bai, M.W.; Robert Mitchell, R.; Ciuca, O.; Preuss, M.; Haigh, S.J. An investigation of diffusion-mediated cyclic coarsening and reversal coarsening in an advanced Ni-based superalloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 110, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachaturyan, A.G.; Semenovskaya, S.V.; Morris Jr, J.W. Theoretical analysis of strain-induced shape changes in cubic precipitates during coarsening. Acta Metall. 1988, 36, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Tao, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhang, G.D.; Qu, J.L. Evolution of γ′ phases of the fourth generation powder metallurgy superalloy FGH4102 during long-term aging. Powder Metall. Ind. (Chin. Ed.) 2020, 30, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Banerjee, R.; Wang, Y. Formation of split patterns of γ′ precipitates in NiAl via particle aggregation. Scr. Mater. 1999, 41, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.Y. Retarded coarsening phenomenon of γ′ particles in Ni-based alloy. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 4969–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Дцгрoва, T.Д. Mat. Metall. 1972, 33, 297–302. (In Russian)
- Guo, J.T. Materials Science and Engineering for Superalloy; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 368–373. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.R.; Jin, T.; Zhao, N.R.; Sun, X.F.; Guan, H.R.; Hu, Z.Q. Formation of carbides and their effects on stress rupture of a Ni-base single crystal superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 361, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Q.; Zhou, Z.J.; Cui, C.Y.; Zhang, R.; Shi, Z.W.; Wang, X.G.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Sun, X.F. Formation and evolution behavior of M6C carbide in a Ni-W-Cr superalloy. Mater. Charact. 2023, 204, 113211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.X.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, X.F.; Guan, H.; Hu, Z.S. Topologically close-packed phase precipitation in a nickel-base superalloy during thermal exposure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 465, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.H.; Li, J.S.; Hu, R.; Zhang, T.B.; Kou, H.C.; Fu, H.Z. Effect of thermal exposure on the stability of carbides in Ni–Cr–W based superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 2339–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zeng, C.; Hou, J.S.; Qin, X.Z.; Guo, J.T.; Zhou, L.Z. The decomposition behaviour of primary MC carbide in Nickel base directionally solidified superalloy DZ444. Acta Metall. Sin. (Chin. Ed.) 2014, 50, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.Z.; Guo, J.T.; Yuan, C.; Hou, J.S.; Ye, H.Q. Precipitation and thermal instability of M23C6 carbide in cast Ni-base superalloy K452. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Zhu, X.M.; Xiong, J.Y.; Chen, Q.; Guo, J.Z. Effect of inclusion size and distribution on low cycle fatigue properties of an FGH97 superalloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. (Chin. Ed.) 2020, 49, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhang, N.; Liu, M.D.; Liu, J.T. Fracture character of low cycle fatigue of P/M superalloy FGH97. Acta Metall. Sin. (Chin. Ed.) 2010, 46, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Dong, J.X.; Zhang, M.N. Microstructures’ effects on high temperature fatigue failure behavior of typical superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 587, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torster, F.; Baumeister, G.; Albrecht, J.; Lütjering, G.; Helm, D.; Daeubler, M.A. Influence of grain size and heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the nickel-base superalloy U 720 LI. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1997, 234–236, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-S’Anchez, A.; Hernandez-Rodríguez, Y.M.; Casas-Espínola, J.L.; Cigarroa-Mayorga, O.E. Nanostructural modulation of Schottky barrier in Au/α-MoO3 heterojunction via Au nanoparticle size control. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 670, 160624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigarroa-Mayorga, O.E. Enhancement of photocatalytic activity in ZnO NWs array due to Fe2O3 NPs electrodeposited on the nanowires surface: The role of ZnO-Fe2O3 interface. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Dong, J.S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.T.; Lou, L.H.; Zhang, J. Effect of long-term thermal exposure on microstructure and stress rupture properties of GH3535 superalloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nai, Q.L.; Dong, J.X.; Zhang, M.C.; Yao, Z.H. Influence of multi-microstructure interaction on fatigue crack growth rate of GH4738 alloy. Acta Metall. Sin. (Chin. Ed.) 2016, 52, 151–160. [Google Scholar]



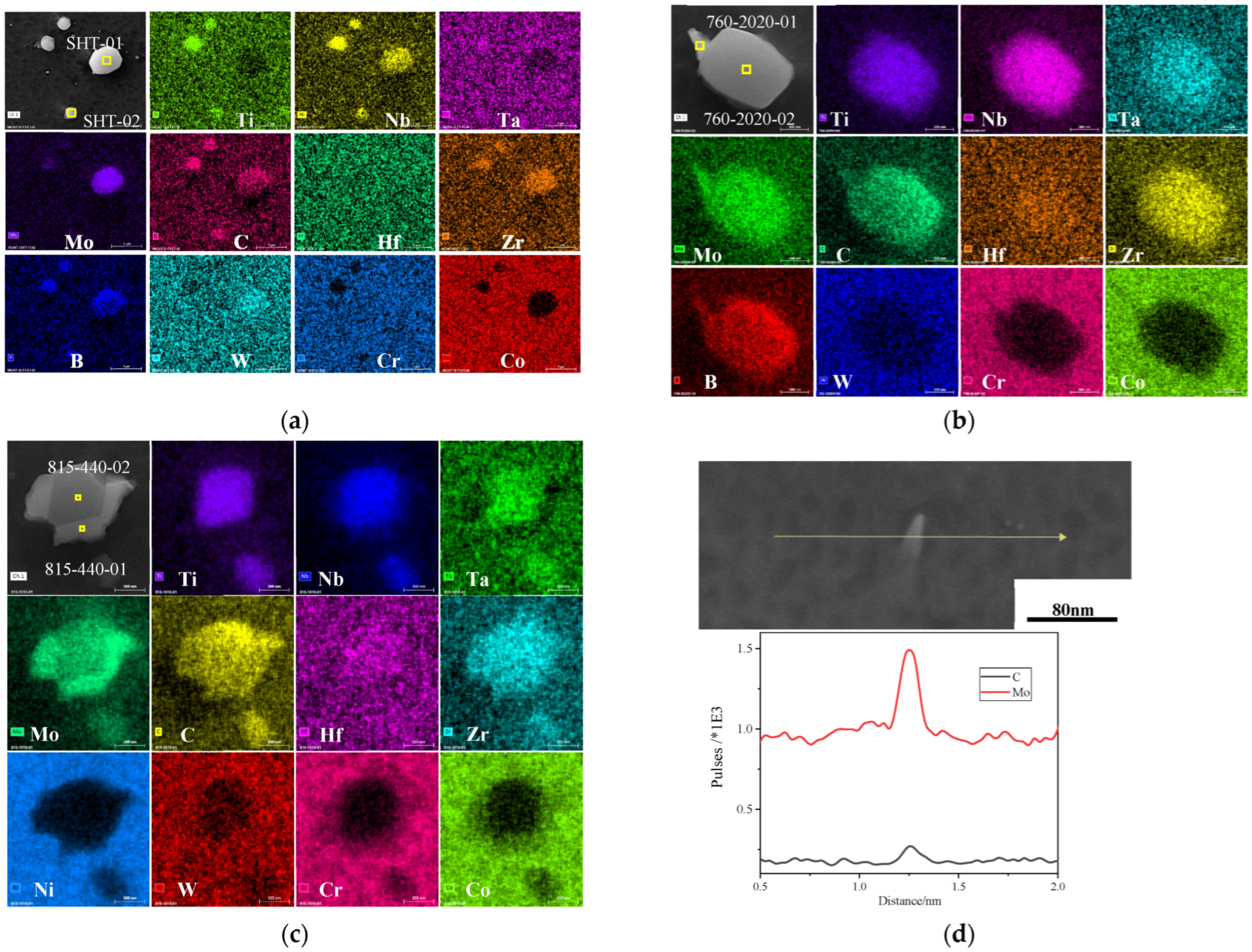
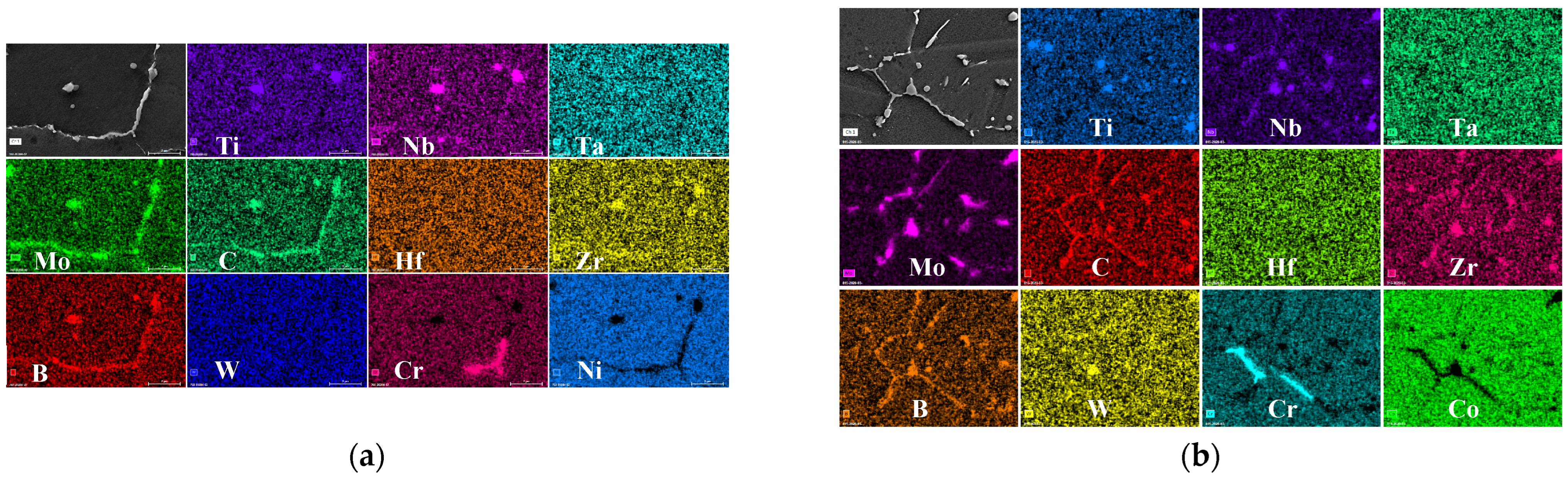

| Alloy Status | Al | Ti | Cr | Co | Ni | Zr | Nb | Mo | Hf | Ta | W | Ti, Nb, Hf, Ta | W, Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHT-01 | 1.4 | 3.4 | 16.2 | 9.3 | 21.9 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 24.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 18.6 | 6.9 | 42.7 |
| SHT-02 | 2.8 | 8.5 | 11.0 | 16.1 | 40.7 | 0.5 | 6.6 | 3.8 | 0.5 | 6.0 | 3.4 | 21.7 | 7.2 |
| 760-2020-01 | 2.7 | 5.6 | 12.6 | 18.7 | 39.3 | 0.4 | 3.3 | 8.4 | 0.3 | 2.0 | 6.8 | 11.2 | 15.1 |
| 760-2020-02 | 1.5 | 15.9 | 7.8 | 10.7 | 25.8 | 1.1 | 13.3 | 2.9 | 2.5 | 15.4 | 3.1 | 47.1 | 6.0 |
| 815-440-01 | 2.0 | 5.5 | 12.3 | 17.9 | 31.6 | 0.5 | 4.0 | 11.9 | 0.7 | 3.1 | 10.6 | 13.3 | 22.5 |
| 815-440-02 | 1.5 | 14.5 | 8.1 | 11.3 | 26.8 | 0.9 | 12.3 | 5.5 | 1.7 | 13.5 | 3.9 | 42.0 | 9.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, J.; Yin, C.; Wang, C.; Feng, G.; Guo, J. The Effect of Long-Term Aging on the Microstructure and Properties of a Novel Nickel-Based Powder Superalloy FGH4113A. Materials 2024, 17, 4175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174175
Xiong J, Yin C, Wang C, Feng G, Guo J. The Effect of Long-Term Aging on the Microstructure and Properties of a Novel Nickel-Based Powder Superalloy FGH4113A. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174175
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Jiangying, Chao Yin, Chong Wang, Ganjiang Feng, and Jianzheng Guo. 2024. "The Effect of Long-Term Aging on the Microstructure and Properties of a Novel Nickel-Based Powder Superalloy FGH4113A" Materials 17, no. 17: 4175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174175
APA StyleXiong, J., Yin, C., Wang, C., Feng, G., & Guo, J. (2024). The Effect of Long-Term Aging on the Microstructure and Properties of a Novel Nickel-Based Powder Superalloy FGH4113A. Materials, 17(17), 4175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174175






