The Abrasive Effect of Moon and Mars Regolith Simulants on Stainless Steel Rotating Shaft and Polytetrafluoroethylene Sealing Material Pairs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Shaft and Sealing Materials
2.2. Mars and Moon Soil Simulants Selected for Abrasion Tests
- Mineralogical form and particle shape of the simulant are more critical than chemical composition;
- Simulant should represent the landing site and resemble the actual samples as closely as possible;
- Level of mineralogical fidelity: particle shape relevant to the abrasion test, allowing good representativity of the test with real lunar/Martian regolith;
- Particle size distribution.
2.3. Testing and Measurement Methods
- Pin material: natural PTFE (Ln) as 8 × 8 × 8 mm cube;
- Rotating disc (n = 0.6 1/s) material: stainless steel 1.4404 (Ss)
- Sliding speed on the pin’s centre line: v = 0.1 m/s, on 25 mm sliding path radius
- Stress from normal load: 0.2 MPa;
- Ambient temperature: 22–24 °C;
- Relative humidity RH: 40–50%;
- Start: in clean contact;
- Sliding path: covered with abrasive simulants;
- Type of regolith applied: LHS-1, LMS-1, MGS-1, JEZ-1.
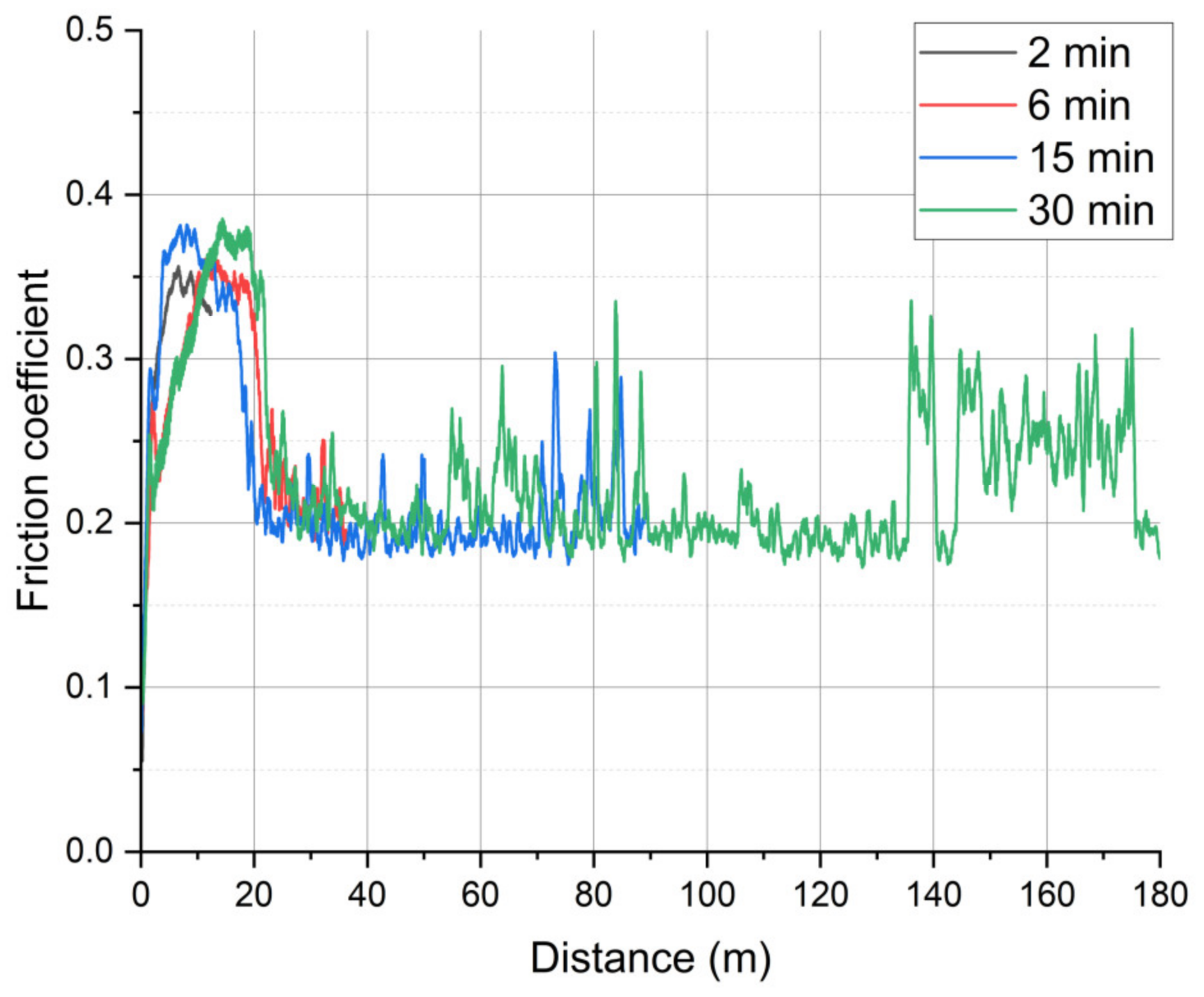
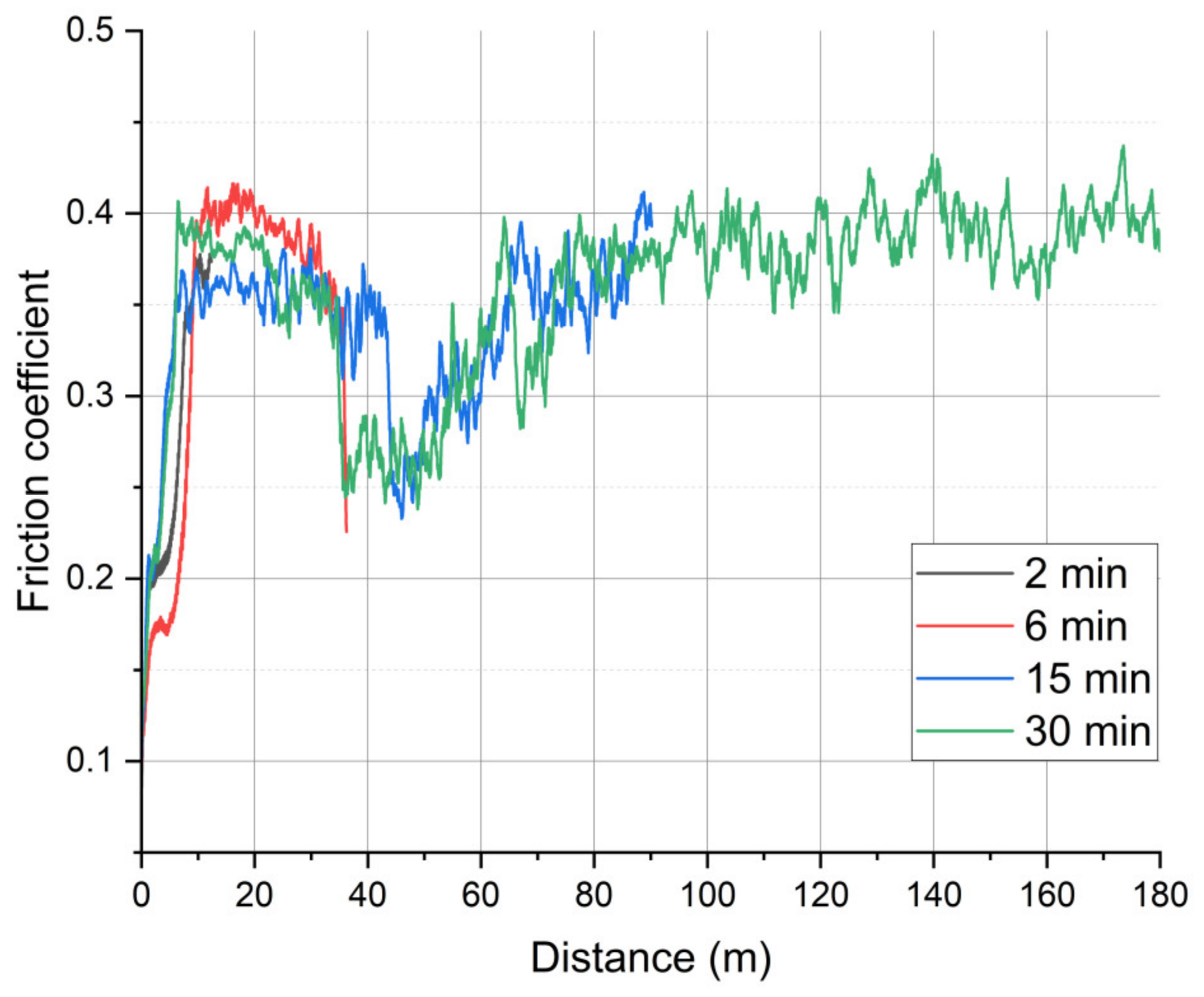
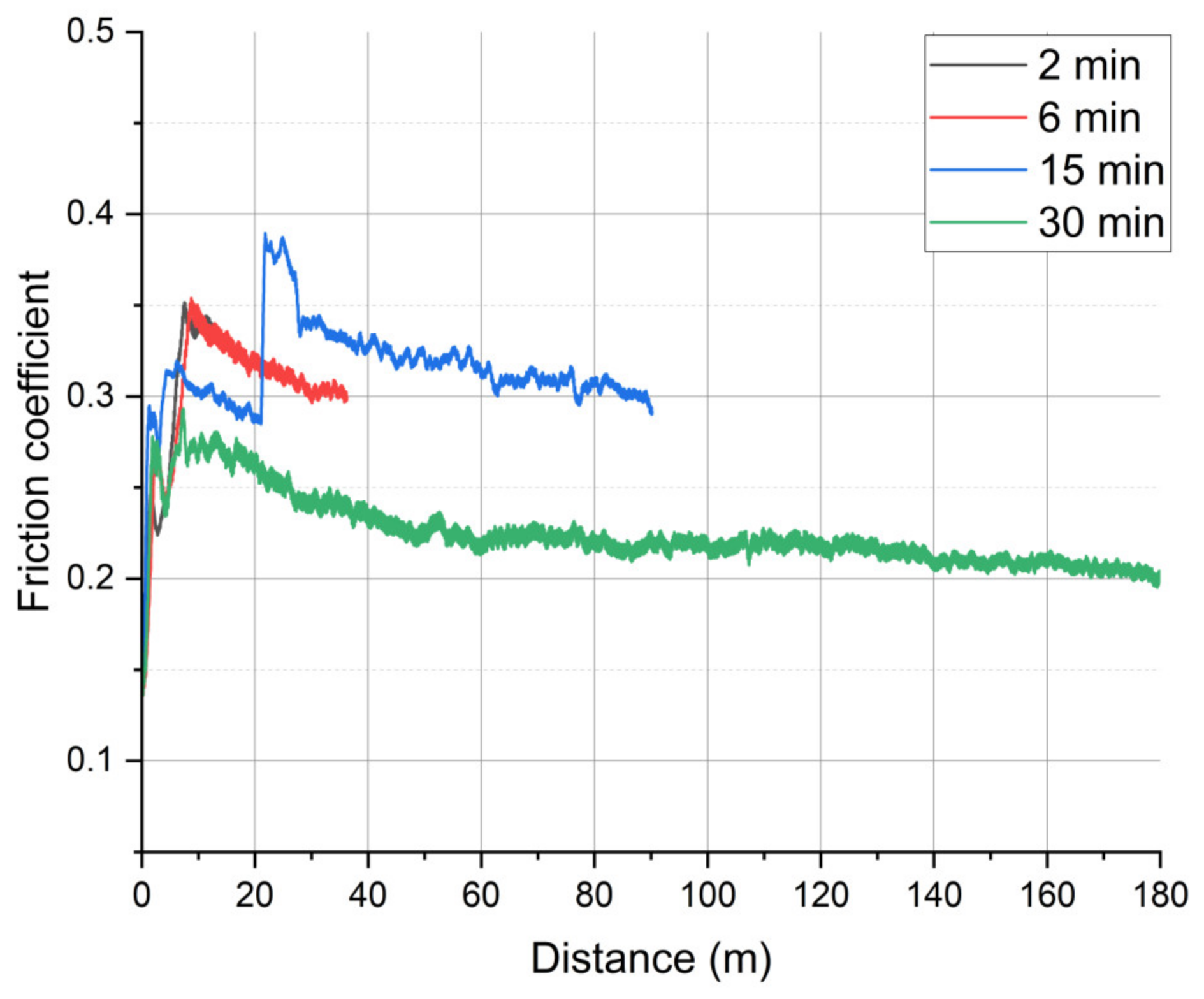
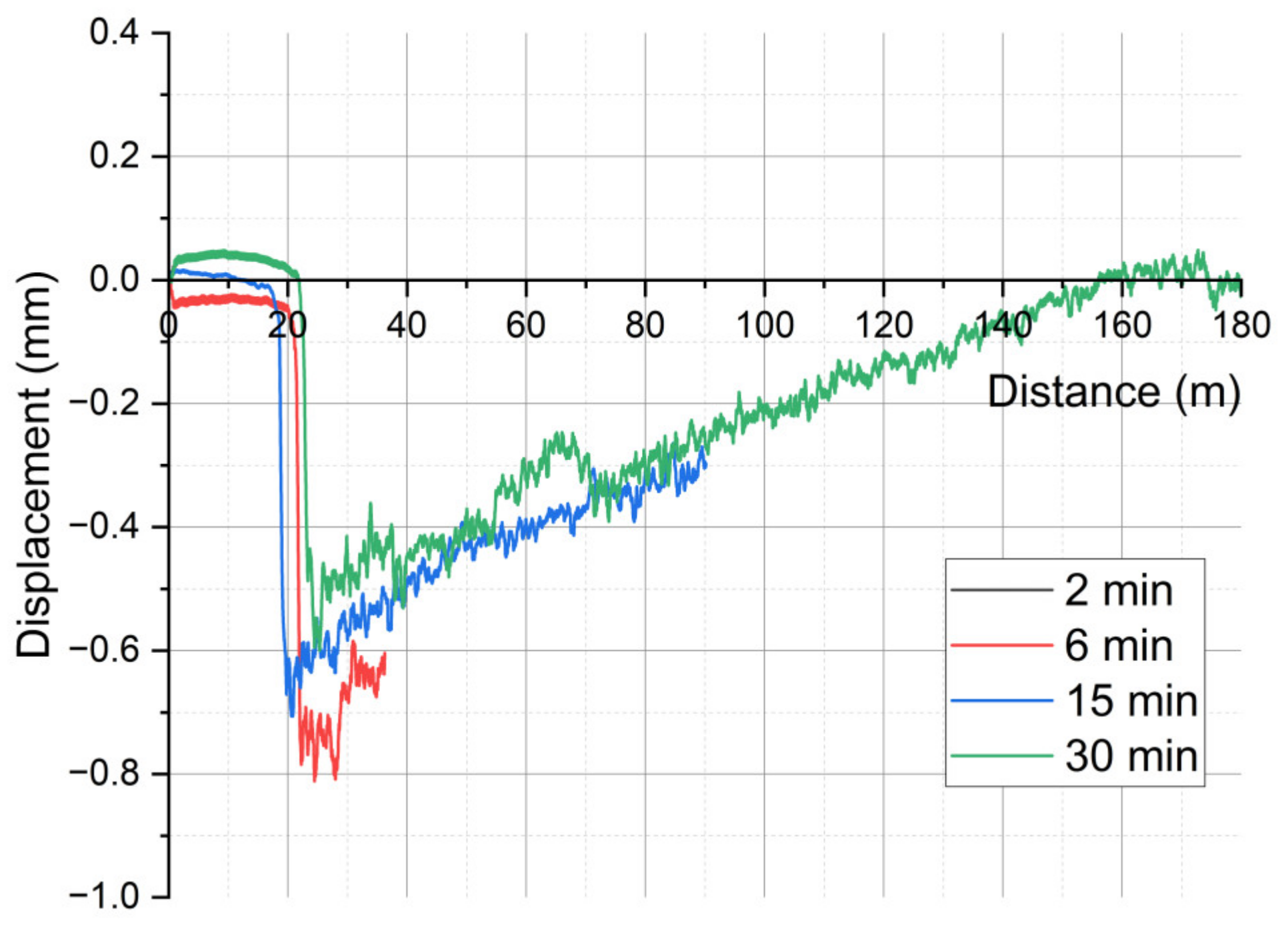
3. Results
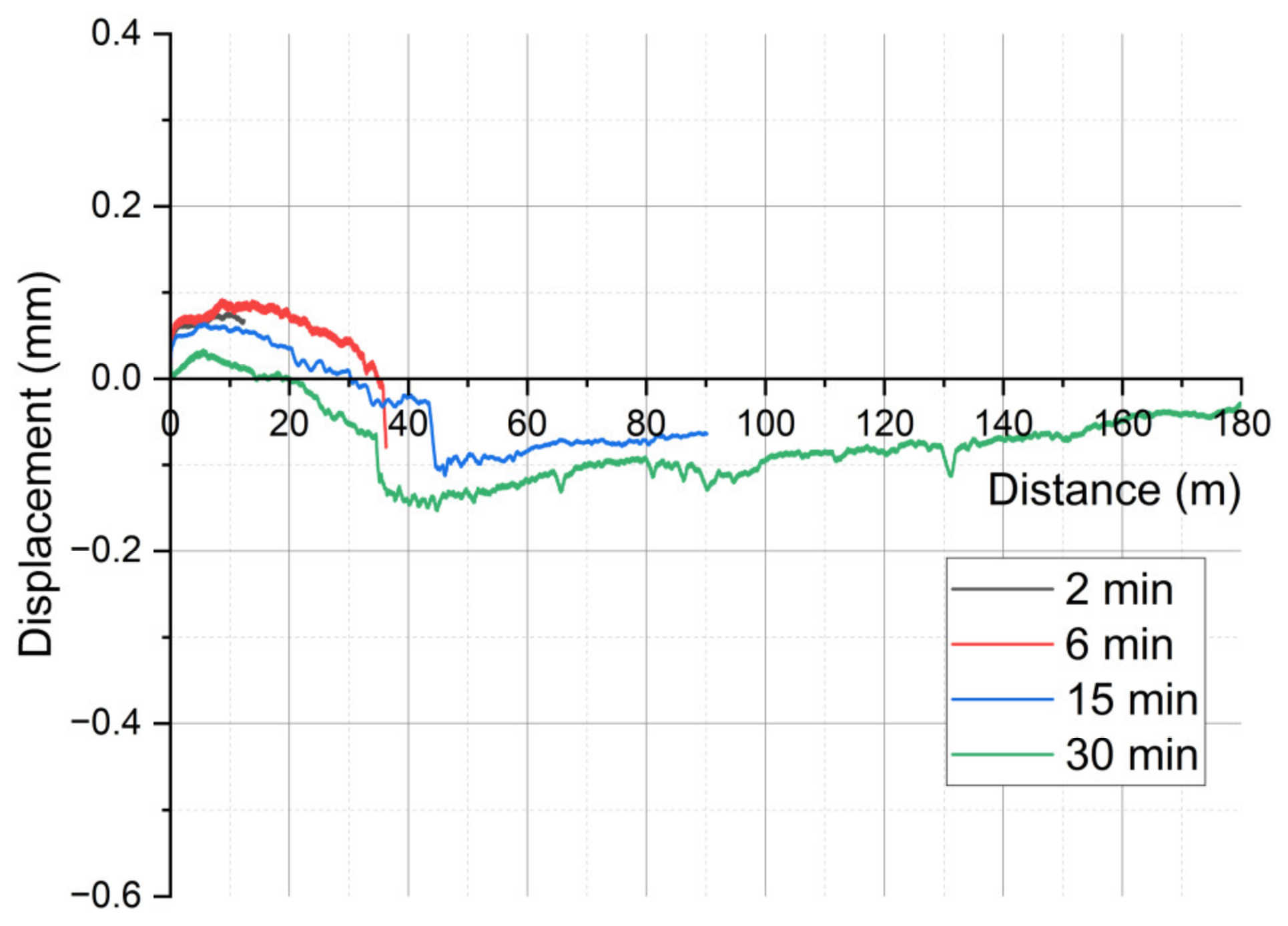
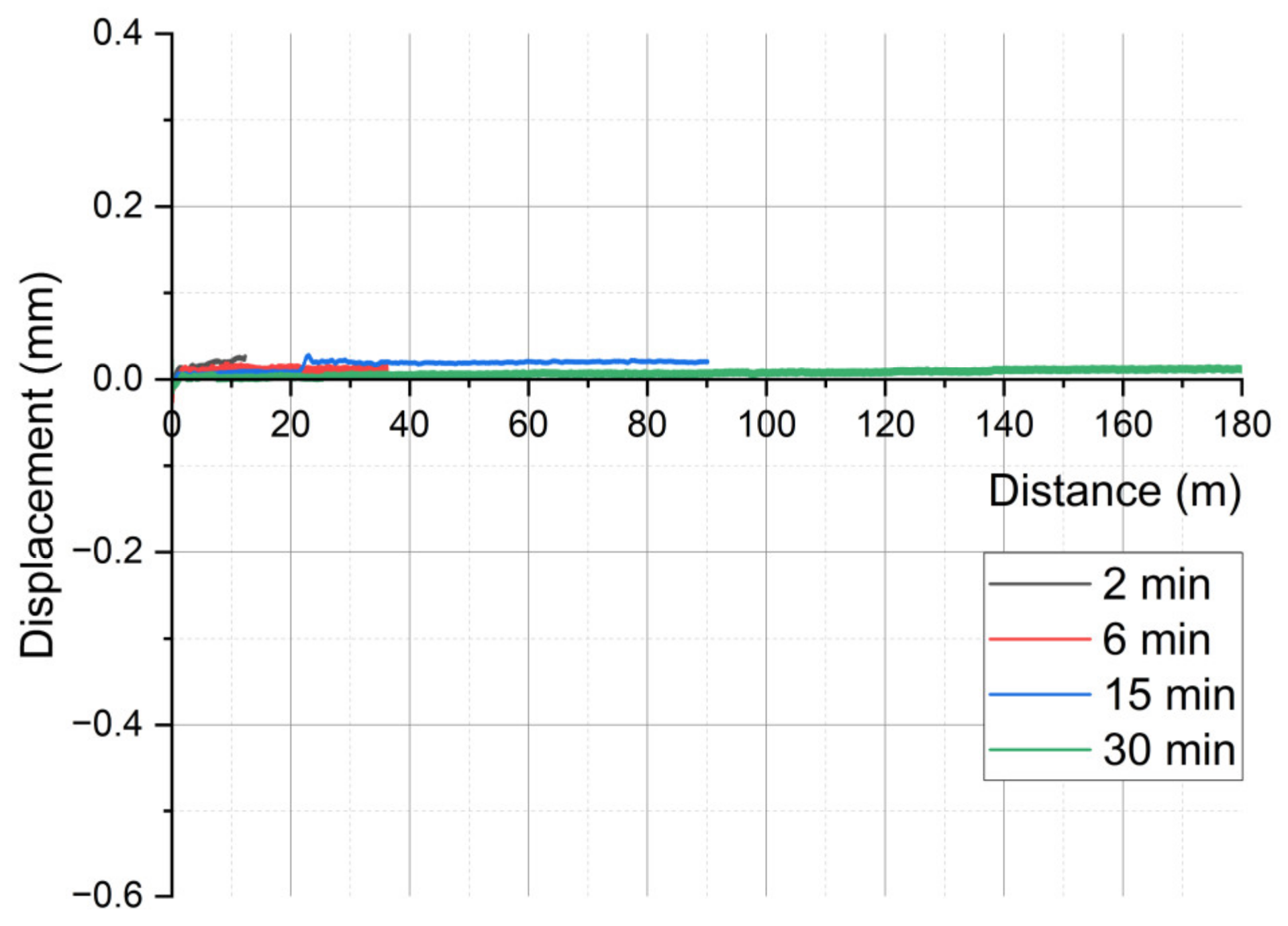
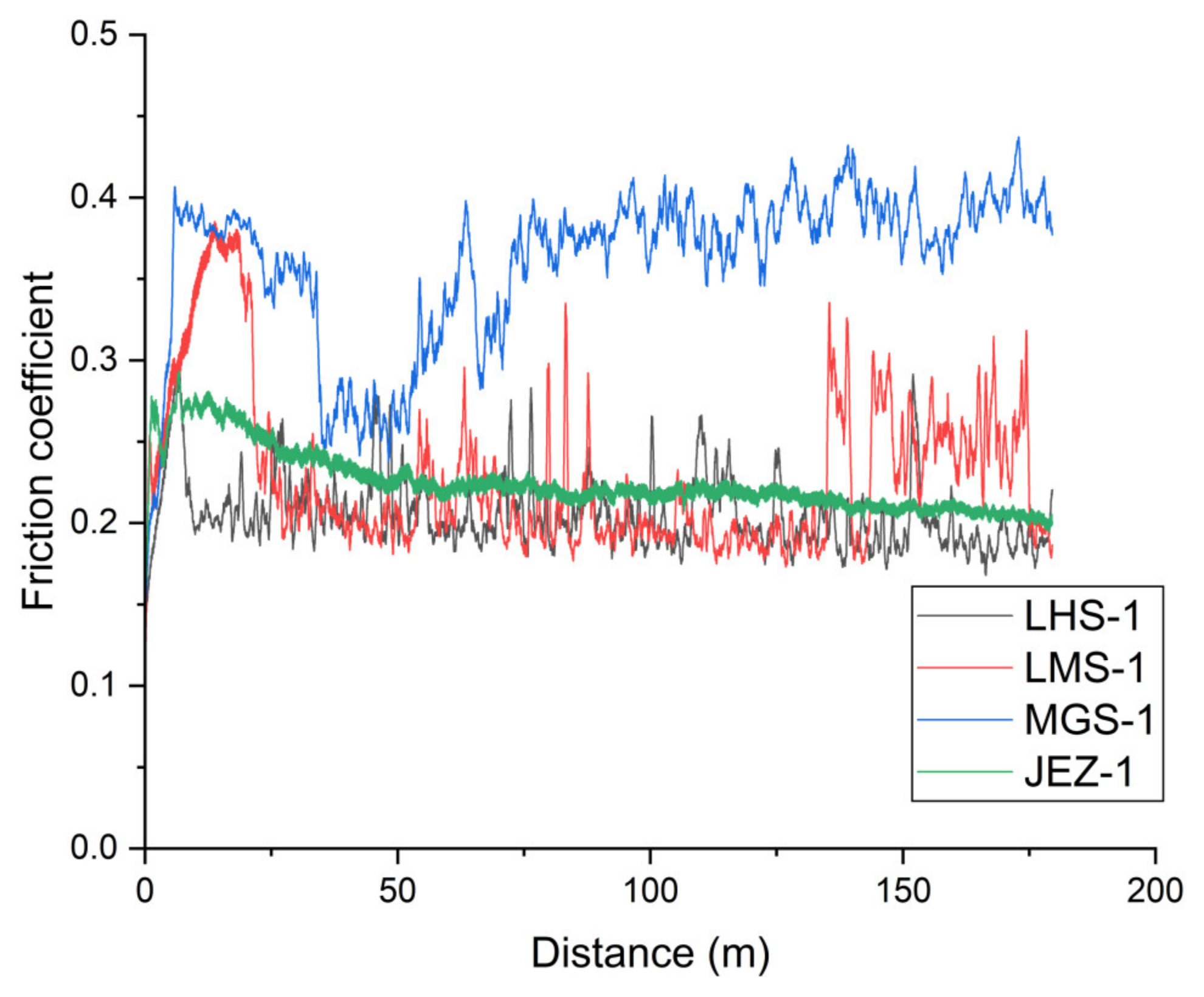
3.1. On-Line Friction and Wear
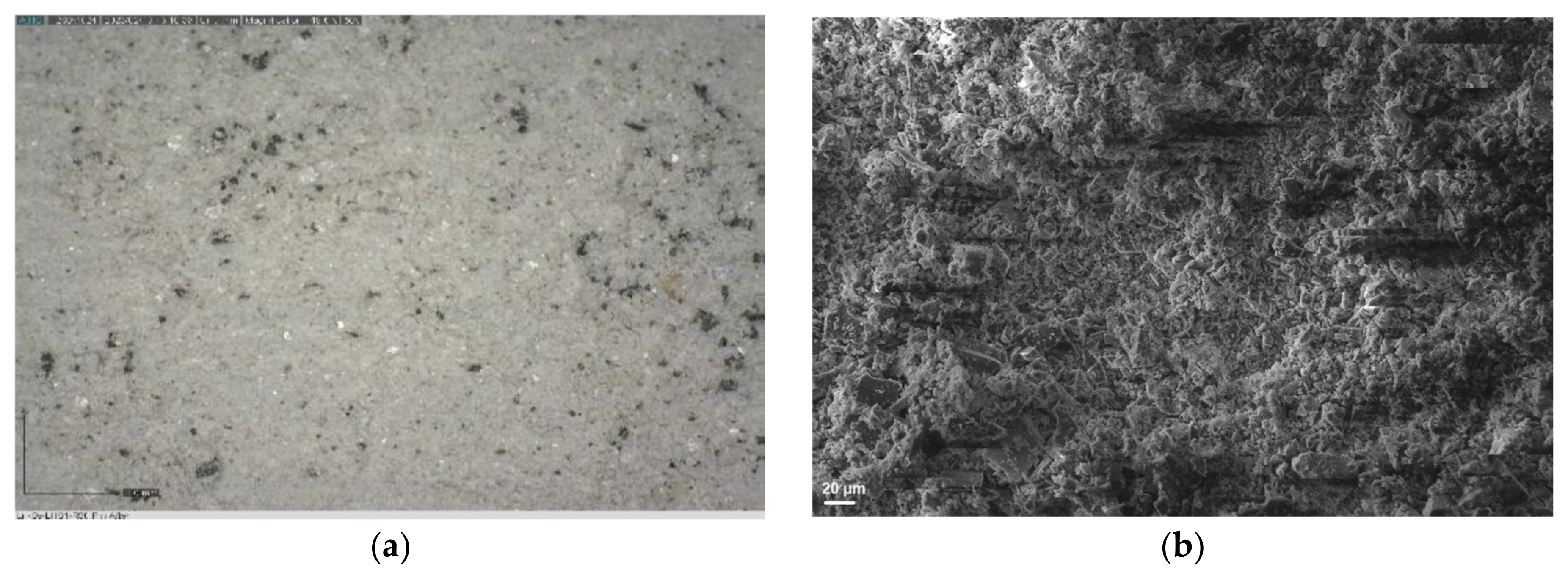
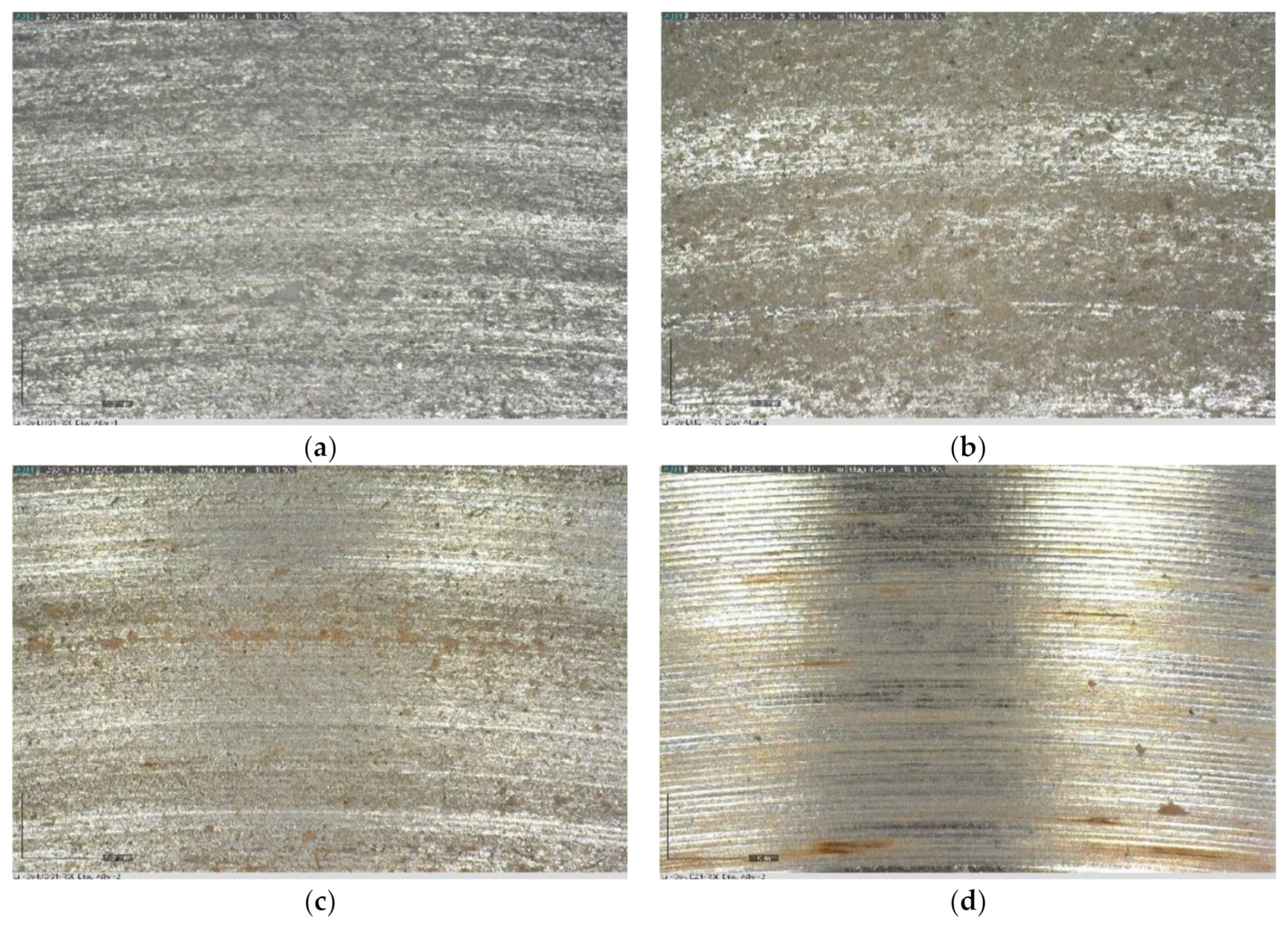
3.2. Surface Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Hill, E.; Mellin, M.J.; Deane, B.; Liu, Y.; Taylor, L.A. Apollo Sample 70051 and High- and low-Ti Lunar Soil Simulants MLS-1A and JSC-1A: Implications for Future Lunar Exploration. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2007, 112, E02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickman, D.; Street, K.W.; El-Genk, M.S. Some Expected Mechanical Characteristics of Lunar Dust: A Geological View. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2008; Volume 969, pp. 949–955. [Google Scholar]
- Catling, D.C.; Leovy, C. Mars Atmosphere: History and Surface Interactions. In Encyclopedia of the Solar System; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 301–314. ISBN 978-0-12-088589-3. [Google Scholar]
- Karl, D.; Cannon, K.M.; Gurlo, A. Review of Space Resources Processing for Mars Missions: Martian Simulants, Regolith Bonding Concepts and Additive Manufacturing. Open Ceram. 2022, 9, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delage, P.; Karakostas, F.; Dhemaied, A.; Belmokhtar, M.; Lognonné, P.; Golombek, M.; De Laure, E.; Hurst, K.; Dupla, J.-C.; Kedar, S.; et al. An Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Some Martian Regolith Simulants with Respect to the Surface Properties at the InSight Mission Landing Site. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 211, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, J.E.; Batiste, S.; Horányi, M.; Robertson, S.; Sture, S. Lunar Surface: Dust Dynamics and Regolith Mechanics. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, K.A.P.; Abel, P.B.; Suzuki, M.; Suzuki, M.; Miyoshi, K. Wear of Materials by Lunar Regolith Simulant. Toraibarojisuto/J. J. Jpn. Soc. Tribol. 2010, 55, 398–405. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, K.; Suzuki, M.; Nishida, S.-I.; Wakabayashi, S. Tribological Properties of Solid Lubricants in Moon Dust Environment. In Proceedings of the World Tribology Congress 2009, Kyoto, Japan, 6–11 September 2009; Society: Tokyo, Japan, 2009; p. 804. [Google Scholar]
- Barkó, G.; Kalácska, G.; Keresztes, R.; Zsidai, L.; Shegawu, H.; Kalácska, Á. Abrasion Evaluation of Moon and Mars Simulants on Rotating Shaft/Sealing Materials: Simulants and Structural Materials Review and Selection. Lubricants 2023, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Ren, S.; Lu, Z.; Wang, L. A Feasible Multilayer Structure Design for Solid Lubricant Coatings in a Lunar Environment. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 65504–65517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makówka, M. MOS2 (TI, W) Coatings as Surface Modification of Friction Pairs Operating in Space and Dusty Lunar Atmosphere. Presented at the European Space Mechanisms and Tribology Symposium, Warsaw, Poland, 20–22 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, K.; Takada, S.; Yokoyama, T.; Kasahara, H.; Ota, T.; Okado, J.; Oka, M. Development of Mechanical Seal against Dust for Lunar Exploration. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Aeronaut. SPACE Sci. Aerosp. Technol. Jpn. 2020, 18, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunneparambil Sukumaran, A.; Zhang, C.; Nisar, A.; Agarwal, A. Recent Trends in Tribological Performance of Aerospace Materials in Lunar Regolith Environment—A Critical Review. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 73, 846–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, I.R.; Handschuh, M.J. Preliminary Assessment of Seals for Dust Mitigation of Mechanical Components for Lunar Surface Systems. In Proceedings of the 40th Aerospace Mechanisms Symposium, Cocoa Beach, FL, USA,, 12–14 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Agui, J.; Nakagawa, M. Dust on the Moon and Mars. In Proceedings of the 43rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 10–13 January 2005; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Damięcka-Suchocka, M.; Katzer, J. Terrestrial Laser Scanning of Lunar Soil Simulants. Materials 2022, 15, 8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exolith Lab LHS-1 Lunar Highlands Simulant. Available online: https://spaceresourcetech.com/collections/regolith-simulants/products/lhs-1-lunar-highlands-simulant (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Exolith Lab. LMS-1 Lunar Mare Simulant. Available online: https://spaceresourcetech.com/collections/regolith-simulants/products/lms-1-lunar-mare-simulant (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Exolith Lab. MGS-1 Mars Global Simulant. Available online: https://spaceresourcetech.com/products/mgs-1-mars-global-simulant (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Exolith Lab. JEZ-1 Jerezo Delta Simulant. Available online: https://spaceresourcetech.com/products/jez-1-jezero-delta-simulant (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Eleöd, A.; Berthier, Y.; Baillet, L.; Törköly, T. Transient and Stationary Changes of the Mechanical Properties of the First Body Governed by the Hydrostatic Pressure Component of the Local Stress State during Dry Friction. In Tribology Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 43, pp. 553–561. ISBN 978-0-444-51706-7. [Google Scholar]
- Descartes, S.; Berthier, Y. Rheology and Flows of Solid Third Bodies: Background and Application to an MoS1.6 Coating. Wear 2002, 252, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthier, Y. Background on Friction and Wear. In Handbook of Materials Behavior Models; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 676–699. [Google Scholar]
- Bashandeh, K.; Lan, P.; Polycarpou, A.A. Abrasive Wear of PEEK and ATSP-Based Polymer Composite Coatings under Lunar Regolith Conditions. Wear 2022, 506–507, 204461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkirigawa, K.; Kato, K. An Experimental and Theoretical Investigation of Ploughing, Cutting and Wedge Formation during Abrasive Wear. Tribol. Int. 1988, 21, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Adachi, K. Wear Mechanisms. In Modern Tribology Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 273–300. [Google Scholar]
- Zum Gahr, K.-H. Microstructure and Wear of Materials, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Hokkirigawa, K.; Kato, K.; Li, Z.Z. The Effect of Hardness on the Transition of the Abrasive Wear Mechanism of Steels. Wear 1988, 123, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalácska, Á.; De Baets, P.; Ben Hamouda, H.; Theuwissen, K.; Sukumaran, J. Tribological Investigation of Abrasion Resistant Steels with Martensitic and Retained Austenitic Microstructure in Single- and Multi–Asperity Contact. Wear 2021, 482–483, 203980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, J.J.; Sinatora, A. Effect of Abrasive Size on Wear of Metallic Materials and Its Relationship with Microchips Morphology and Wear Micromechanisms: Part 2. Wear 2011, 271, 1804–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


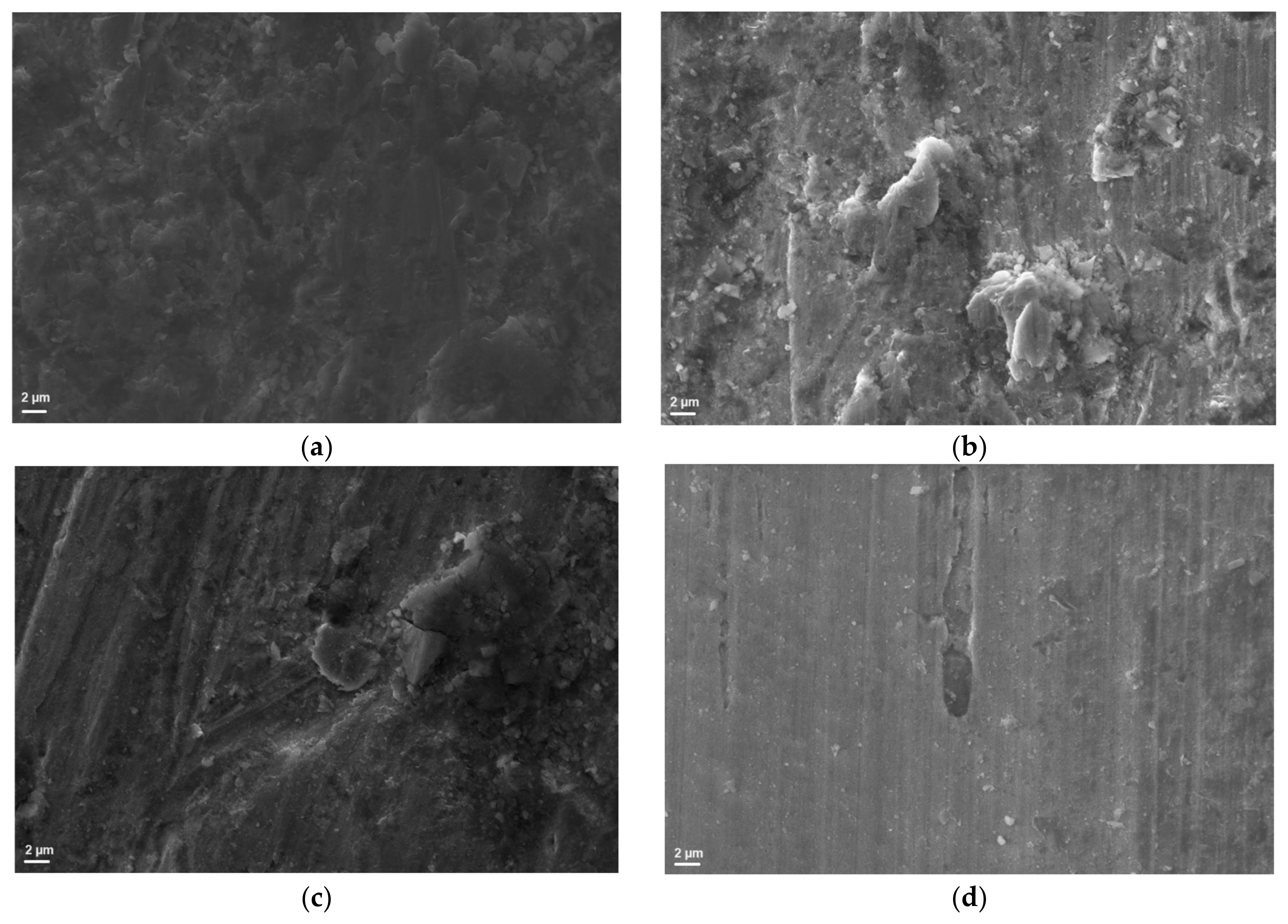


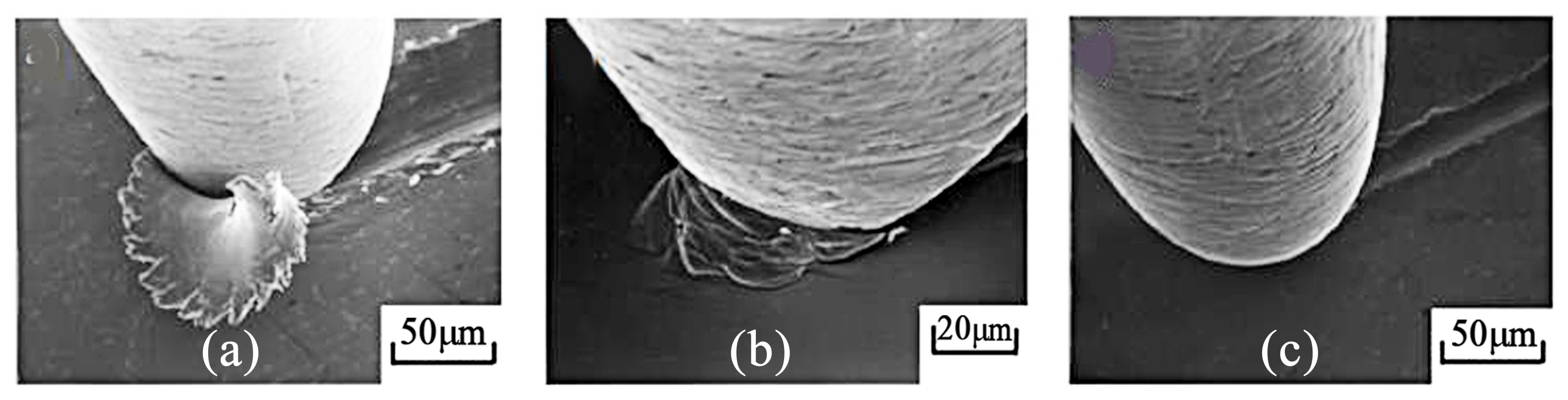
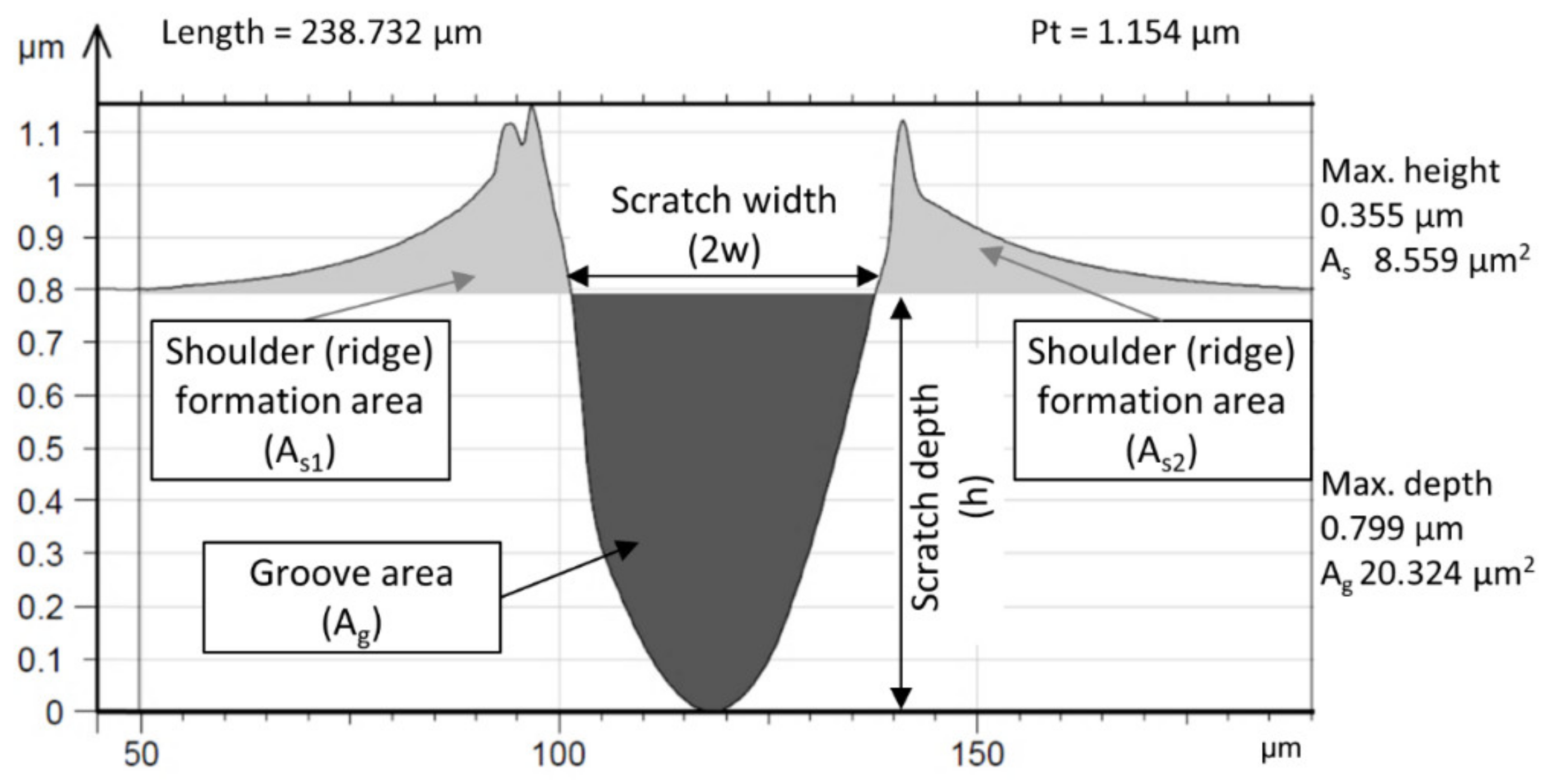

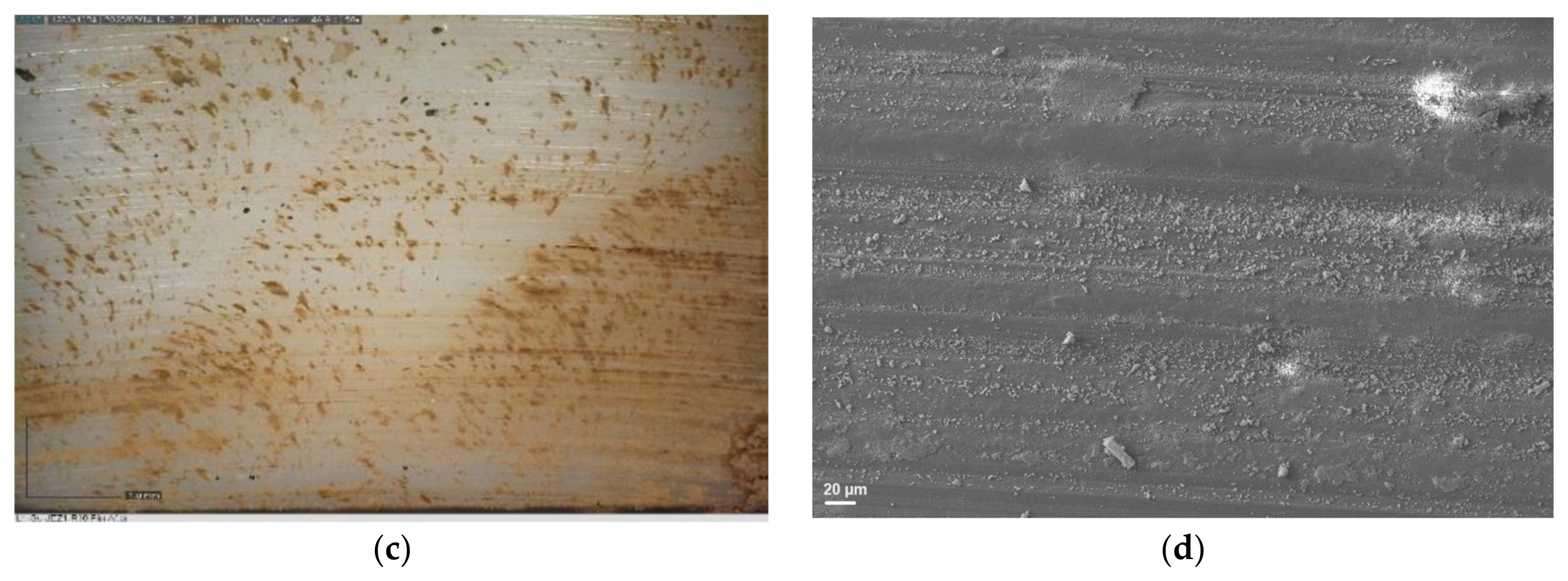
| Regolith Simulants | LMS-1 | LHS-1 | MGS-1 | JEZ-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Material | Average Lunar Mare Soil | Average Lunar Highland Soil | Average Martian Soil | Martian Soil of Jezero Crater |
| Phase Composition |
|
|
|
|
| Physical Properties |
|
|
|
|
| Reference | [18] | [17] | [19] | [20] |
| 3D Parameters, µm | Regolith Simulants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LHS-1 | LMS-1 | MGS-1 | JEZ-1 | ||
| Sa | Pristine | 1.01 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 1.02 |
| Worn | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0.70 | 0.71 | |
| Difference, % | −22 | −12 | −32 | −30 | |
| Sz | Pristine | 168.24 | 171.64 | 171.64 | 166.87 |
| Worn | 18.69 | 19.22 | 14.13 | 9.32 | |
| Difference, % | −89 | −89 | −92 | −94 | |
| Sq | Pristine | 1.72 | 1.85 | 1.85 | 1.917 |
| Worn | 1.01 | 1.16 | 0.89 | 0.88 | |
| Difference, % | −41 | −38 | −52 | −54 | |
| Ssk | Pristine | 2.34 | 3.65 | 3.65 | 3.82 |
| Worn | −0.19 | 0.05 | −0.32 | 0.09 | |
| Difference, % | −108 | −99 | −109 | −98 | |
| Sku | Pristine | 159.73 | 179.34 | 179.34 | 185.56 |
| Worn | 4.31 | 4.61 | 4.31 | 2.80 | |
| Difference, % | −97 | −97 | −98 | −98 | |
| Dp, (Rz/0.5 Rsm) | Regolith Simulants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LHS-1 | LMS-1 | MGS-1 | JEZ-1 | |
| Steel Disc | 0.043 | 0.024 | 0.041 | 0.048 |
| PTFE Pin | 0.197 | 0.239 | 0.259 | 0.158 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalácska, G.; Barkó, G.; Shegawu, H.; Kalácska, Á.; Zsidai, L.; Keresztes, R.; Károly, Z. The Abrasive Effect of Moon and Mars Regolith Simulants on Stainless Steel Rotating Shaft and Polytetrafluoroethylene Sealing Material Pairs. Materials 2024, 17, 4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174240
Kalácska G, Barkó G, Shegawu H, Kalácska Á, Zsidai L, Keresztes R, Károly Z. The Abrasive Effect of Moon and Mars Regolith Simulants on Stainless Steel Rotating Shaft and Polytetrafluoroethylene Sealing Material Pairs. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174240
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalácska, Gábor, György Barkó, Hailemariam Shegawu, Ádám Kalácska, László Zsidai, Róbert Keresztes, and Zoltán Károly. 2024. "The Abrasive Effect of Moon and Mars Regolith Simulants on Stainless Steel Rotating Shaft and Polytetrafluoroethylene Sealing Material Pairs" Materials 17, no. 17: 4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174240
APA StyleKalácska, G., Barkó, G., Shegawu, H., Kalácska, Á., Zsidai, L., Keresztes, R., & Károly, Z. (2024). The Abrasive Effect of Moon and Mars Regolith Simulants on Stainless Steel Rotating Shaft and Polytetrafluoroethylene Sealing Material Pairs. Materials, 17(17), 4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174240







