Process Parameters Optimization and Numerical Simulation of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coating via Laser Cladding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Gray Correlation Theory
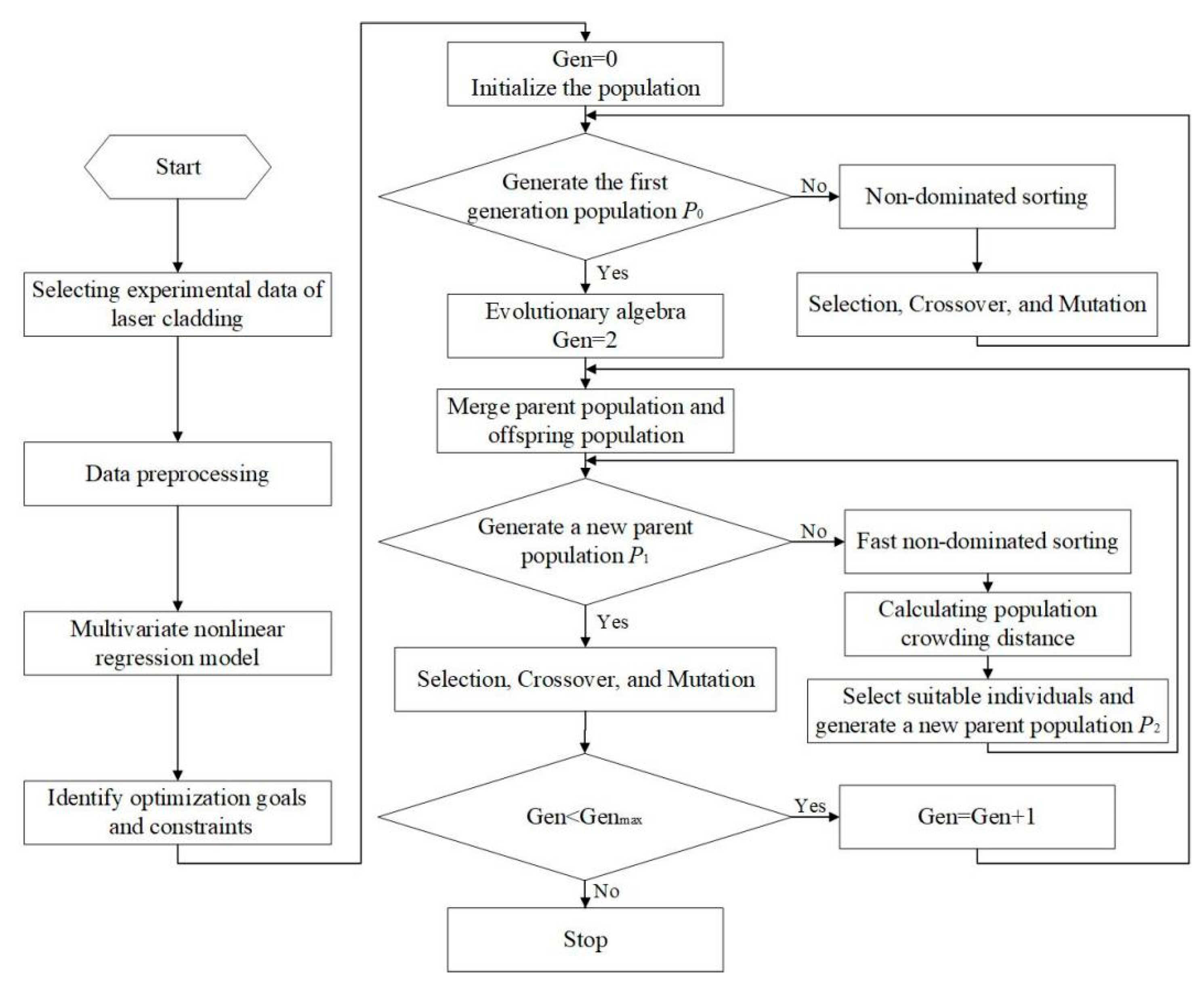
2.3. Multi-Objective Optimization Model
3. Results and Discussion
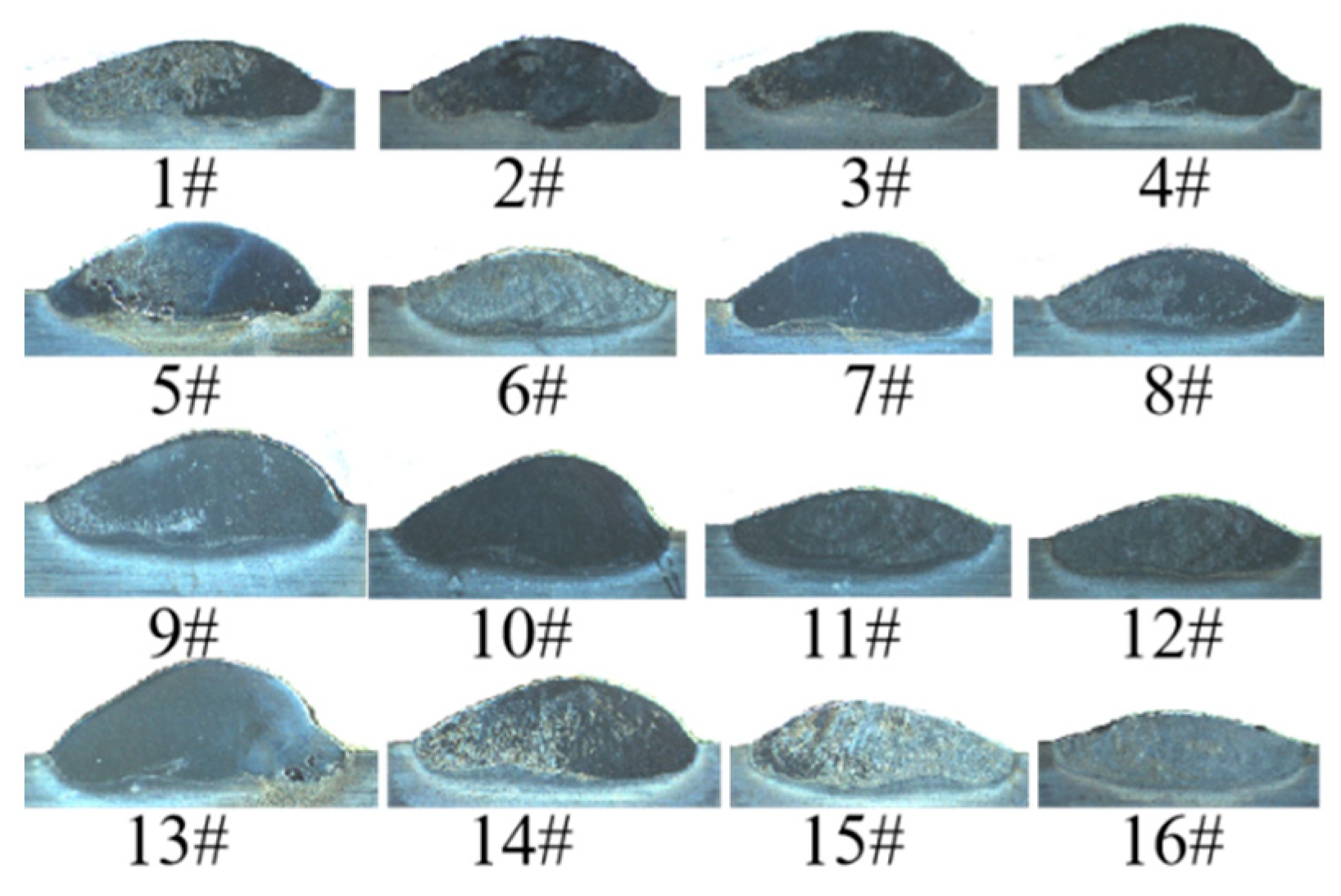
3.1. Orthogonal Experiment Results
3.2. Gray Correlation Analysis
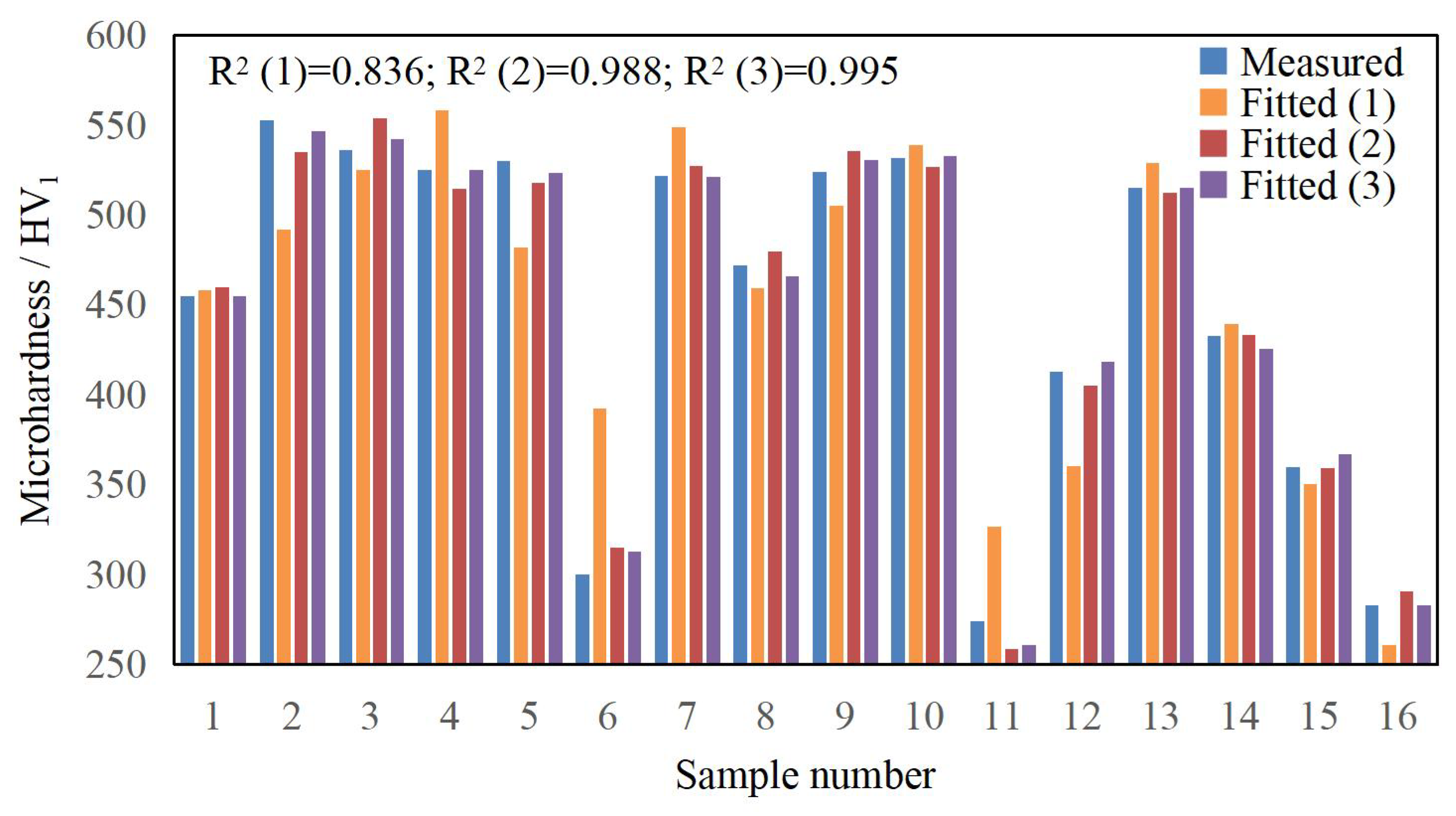
3.3. Multiple Nonlinear Regression Results
3.4. Multi-Objective Optimization Results
3.5. Numerical Simulation
3.5.1. Theoretical Basis
- (1)
- Assume that, except for density, coefficient of thermal expansion, thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity, Young’s modulus, and Poisson’s ratio, which change with temperature, the thermal physical parameters of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy powder and H13 substrate do not change with temperature;
- (2)
- Assume that the powder and the substrate are both isotropic and uniformly continuous, and ignore the influence of cracks, voids, and other defects inside the substrate and cladding layer on the material performance parameters;
- (3)
- Assume that the laser power is constant and ignore the influence of gases in the air on the laser power;
- (4)
- Ignore the influence of powder velocity, flow rate, and pressure of high-purity argon gas used as shielding gas, as well as the chemical reactions, liquid flow, and stirring effect inside the molten pool, on the temperature;
- (5)
- Neglect the heat exchange between the H13 substrate and the laser cladding experimental platform;
- (6)
- Neglect the influence of interface thermal resistance at the cladding layer–substrate interface, solid–liquid interface, and other interfaces on heat transfer.
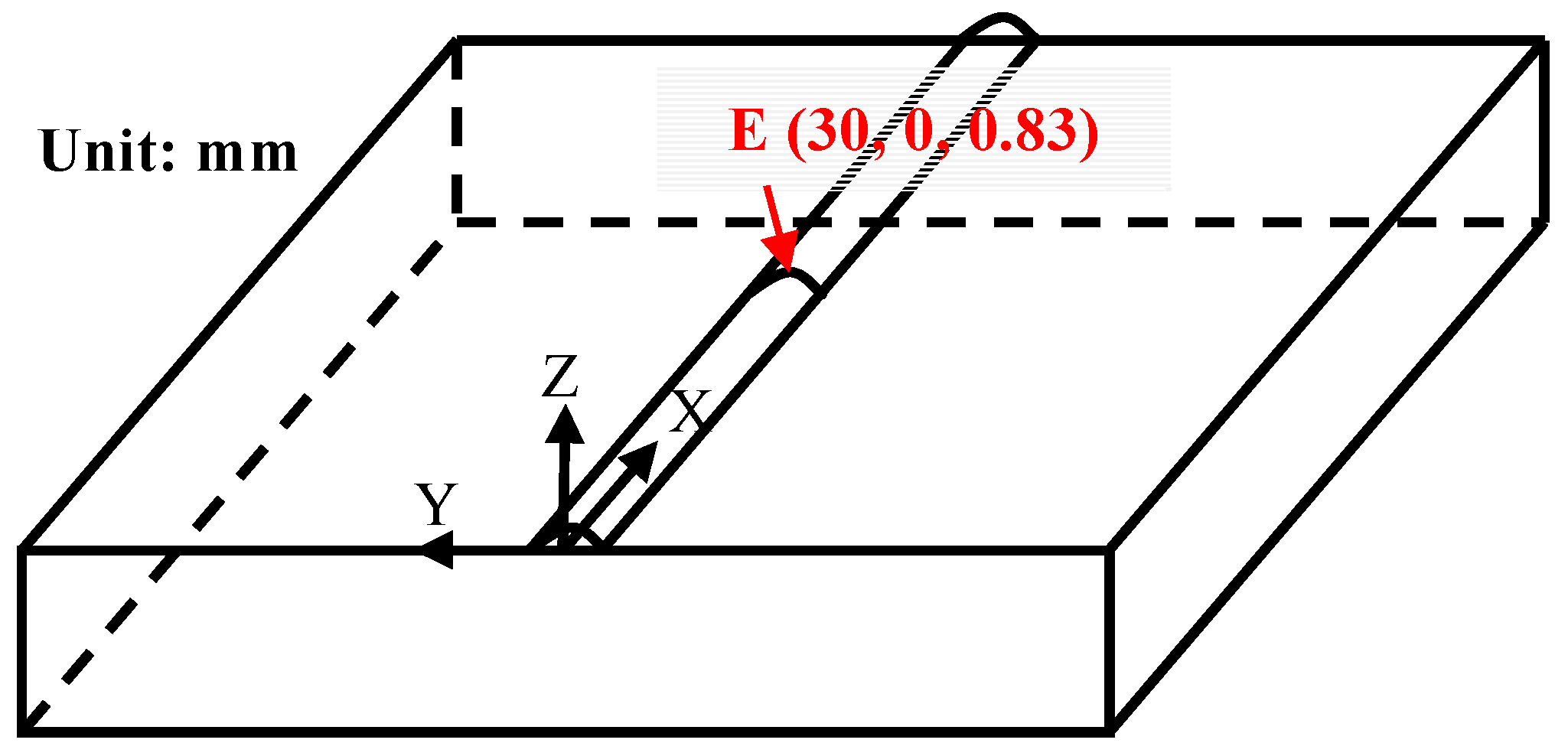
3.5.2. Construction of Finite Element Models
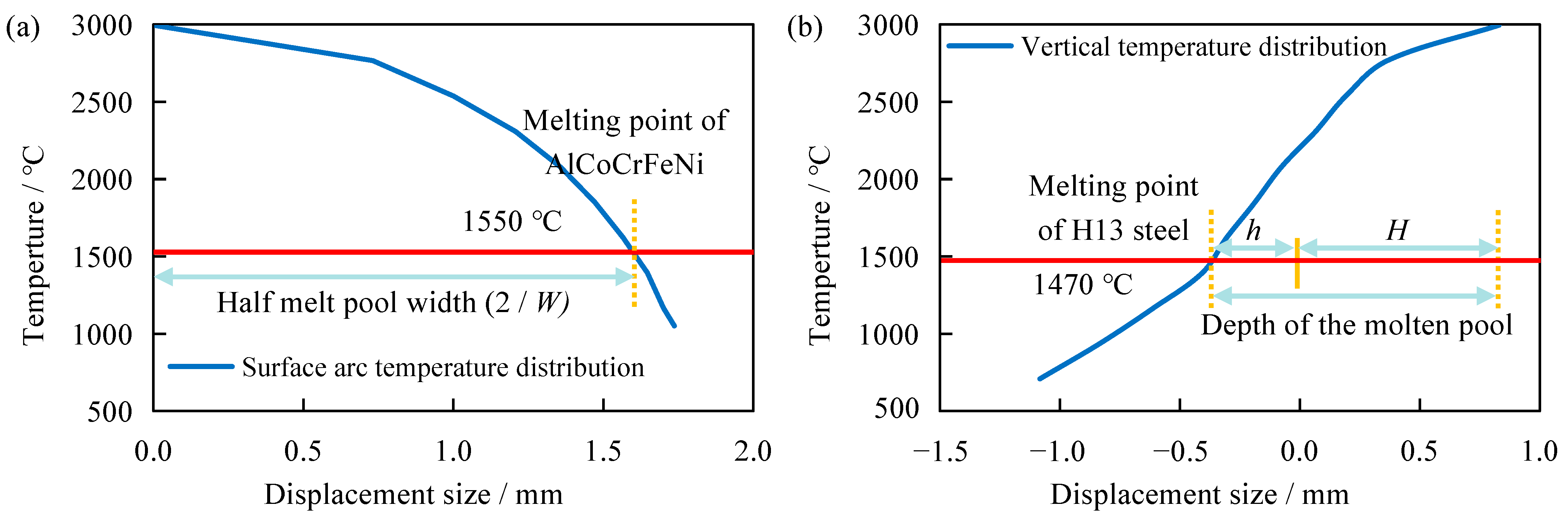
3.5.3. Temperature Field Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Jiang, W.Q.; Liu, C.T.; Zhang, Z.W.; Liaw, P.K. Nanoprecipitate-Strengthened High-Entropy Alloys. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W. High-Entropy Alloys: A Critical Review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, D.; Fieser, D.; Santiago, J.J.; Hu, A.M. Novel Frontiers in High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2023, 13, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalati, P.; Fuji, M.; Edalati, K. Superfunctional high-entropy alloys and ceramics by severe plastic deformation. Rare Metals 2023, 42, 3246–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mu, Y.K.; Wang, G.; Jia, Y.D.; Wang, R.Z. Effect of annealing on irradiation resistance of (FeCoNi)86Al7Ti7 high entropy alloys. Mater. Lett. 2022, 316, 131970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Gupta, A.K.; Mishra, R.K.; Ahmad, M.S.; Shahi, R.R. A Comprehensive Review: RecentProgress on Magnetic High Entropy Alloys and Oxides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 554, 169142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.G.; Qi, P.B.; Liang, X.B.; Chen, Y.X.; Hu, Y.L.; Hu, Z.F. Different-Shaped Ultrafine MoNbTaW HEA Powders Prepared via Mechanical Alloying. Materials 2018, 11, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, C.S.; Zheng, H.X. Computational insights into gas atomization of FeCoNiCrMoBSi high-entropy alloy: From droplet formation to rapid solidification. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 228, 125628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.B.; Mo, J.Y.; Shen, B.L.; Liang, X.B. Structures and properties of the (NbMoTaW)100−XCX high-entropy composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 889, 161645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, P.D.; Licavoli, J.J.; Gao, M.C.; Hawk, J.A. Manufacturing of High Entropy Alloys. Jom 2015, 67, 2278–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.J.; Park, C.; Byun, J.; Kim, Y.D. Fabrication of Molybdenum Alloy with Distributed High-Entropy Alloy Via Pressureless Sintering. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2020, 65, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, B.R.; Sun, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.R.; Wang, W.M.; Ma, P.Y.; Ji, W.; Fu, Z.Y. Powder metallurgy of high-entropy alloys and related composites: A short review. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2021, 28, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Cai, Z.B.; Pu, J.B.; Lu, Z.X.; Chen, S.Y.; Zheng, S.J.; Zeng, C. Effects of nitriding on the microstructure and properties of VAlTiCrMo high-entropy alloy coatings by sputtering technique. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 827, 153836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.K.; Kang, J.J.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Z.Q.; Zhu, L.N.; She, D.S. Effect of vacuum heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of HVOF sprayed AlCoCrFeNiCu high-entropy alloy coating. Mater. Lett. 2022, 323, 132551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soare, V.; Burada, M.; Constantin, I.; Mitrica, D.; Badilita, V.; Caragea, A.; Tarcolea, M. Electrochemical deposition and microstructural characterization of AlCrFeMnNi and AlCrCuFeMnNi high entropy alloy thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 358, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.X.; Yang, Y.; Lou, Z.; Feng, L.Z.; Guo, L.; Yu, J.X. Microstructure and wear resistance of TiC reinforced AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high entropy alloy layer fabricated by micro-plasma cladding. Mater. Lett. 2021, 284, 128859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.H.; Li, C.J.; Li, C.X. High-temperature oxidation behavior of CuAlNiCrFe high-entropy alloy bond coats deposited using high-speed laser cladding process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 398, 126093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Cai, Z.B.; Guan, Y.J.; Cui, X.F.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Dong, M.L.; Zhang, D. High temperature wear performance of laser-cladded FeNiCoAlCu high-entropy alloy coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 445, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y.B.; Dong, Q.; Han, Y.F. Designing Rules of Laser-Clad High-Entropy Alloy Coatings with Simple Solid Solution Phases. Acta Metall. Sin.-Engl. Lett. 2020, 33, 1064–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzban, J.; Ghaseminejad, P.; Ahmadzadeh, M.H.; Teimouri, R. Experimental investigation and statistical optimization of laser surface cladding parameters. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.J.; Zhang, M.; Guo, S.R.; Cao, Y.L.; Zeng, W.H.; Li, X.L.; Zheng, B. Multi-objective numerical simulation of geometrical characteristics of laser cladding of cobalt-based alloy based on response surface methodology. Meas. Control 2021, 54, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.Y.; Feng, A.X.; Zhao, J.; Pan, X.M.; Zhang, G.S.; Zhu, Y.H.; Chen, C.L. Study on process optimization of WC-Ni60A cermet composite coating by laser cladding. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 37, 107400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.H.; Du, Y.B.; Liang, Q.; Zhou, Z.J.; Shu, L.S. Modeling and Optimization Method of Laser Cladding Based on GA-ACO-RFR and GNSGA-II. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2023, 10, 1207–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.R.; Bai, H.Q.; Li, C.F.; Shu, L.S.; Zhang, X.H.; Jia, Z.Q. Numerical Simulation and Multi-Objective Parameter Optimization of Inconel718 Coating Laser Cladding. Coatings 2022, 12, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Q.; Wang, X.B.; Wu, S.Y.; Yan, L.C.; Guo, T.; Gao, K.W.; Pang, X.L.; Volinsky, A.A. Design of super-hard high-entropy ceramics coatings via machine learning. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 32064–32072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashistha, S.; Mahanta, B.K.; Singh, V.K.; Singh, S.K. Machine learning assisted optimization of tribological parameters of Al-Co-Cr-Fe-Ni high-entropy alloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2023, 38, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.Y.; Xiong, W.J.; Lian, Y.; Han, D.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J. Modeling and optimization for laser cladding via multi-objective quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 381, 125129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.D.; Tieu, A.K.; Wexler, D.; Su, L.H.; Nguyen, C.; Yang, J.; Deng, G.Y. High temperature tribological performance of a cost-effective eutectic high entropy alloy Al0.8CrFeNi2.2: Comparison with AlCoCrFeNi2.1. Tribol. Int. 2023, 184, 108445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, M.; Soltanieh, M.; Alamolhoda, S.; Aghamiri, S.M.S.; Mehdizade, M. Microstructural characterization and corrosion behavior of AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 273, 124937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, R.K.; Xu, Z.; Wu, M.Y.; He, A.; Chen, D.L.; Li, D.Y. Microstructure, mechanical properties, corrosion and wear behavior of high-entropy alloy AlCoCrFeNix (x > 0) and medium-entropy alloy (x = 0). J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 11949–11968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.C.; Sharma, A.; Lee, H.; Ahn, B. Phase separation and mechanical behavior of AlCoCrFeNi-X (X = Cu, Mn, Ti) high entropy alloys processed via powder metallurgy. Intermetallics 2021, 139, 107369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Xue, W.T.; Fan, C.L.; Chen, R.R.; Wang, L.; Su, Y.Q.; Ding, H.S.; Guo, J.J. Effect of Co content on phase formation and mechanical properties of (AlCoCrFeNi)100-xCox high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2018, 710, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, S.; Dey, S. Probing the mechanical and deformation behaviour of CNT-reinforced AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy—A molecular dynamics approach. Mol. Simul. 2023, 49, 1726–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.G.; Yang, B.T.; Wei, J.C. Effect of TiB2 on the Phase Composition, Microstructure, and Tribological Properties of AlCoCrFeNi/TiB2 Composites. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 2021, 59, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.Y.; Sun, Y.N.; Xu, Y.F.; Zhang, R.H.; Zhao, F.; Chen, L.N. Wear and Corrosion Properties of Nano-TiC Reinforced AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy Prepared by Laser Cladding. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 2022, 51, 607–614. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.W.; Xin, B.B.; Chen, J.J.; Shi, P.Y.; Yi, G.W.; Wan, S.H.; Meng, J.H.; Wang, W.Z.; Shan, Y. Effect of the high temperature phase transition on the tribological behavior of atmospheric plasma sprayed AlCoCrFeNi-Bi2O3 coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 476, 130286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.L.; Chen, J.L.; Cheng, Q.Q. Microstructure and sliding wear behavior of (AlCoCrFeNi)1−x(WC)x. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 19399–19411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.X.; Jiang, J.C.; Zheng, F.D.; Zhao, W.; Liaw, B.Y.; Ruan, H.J.; Han, Z.G.; Zhang, W.G. Practical state of health estimation of power batteries based on Delphi method and grey relational grade analysis. J. Power Sources 2015, 282, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Pant, M.; Snasel, V. A Comprehensive Review on NSGA-II for Multi-Objective Combinatorial Optimization Problems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 57757–57791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Hao, Y.B.; Liang, X.D.; Li, W.Q.; Zhao, K. Multi-objective optimization of process parameters for laser metal deposition of NiTi shape memory alloy based on neural network and genetic algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 130, 4663–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Liang, X.D.; Wang, W.; Yang, P.; Hao, Y.B.; Zhau, Z.L. Multi-Objective Optimization of Coaxial Powder Feeding Laser Cladding Based on NSGA-II. Chin. J. Lasers 2020, 47, 0102004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, P.K.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.J. Multi-objective optimization of laser cladding process parameters for Q345B steel. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 108679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Y.; Yuan, J.F.; Wu, M.Y.; Arif, A.M.; Li, D.Y. Effect of laser cladding parameters on Inconel 718 coating performance and multi-parameter optimization. Opt. Laser. Technol. 2023, 158, 108850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Fu, S.; Lu, H.F.; Li, W.Y. Process optimization, microstructure characterization, and tribological performance of Y2O3 modified Ti6Al4V-WC gradient coating produced by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 478, 130496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.T.; Kao, J.Y.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hong, P.D. Multi-response optimization of mechanical properties for ZrWN films grown using grey Taguchi approach. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Panda, S.S. Optimization of process parameters in ECDM machining using Taguchi based grey relation analysis. Measurement 2023, 216, 112971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.X.; Shuai, M.R.; Wang, J.M.; Li, Y.J.; Ma, C.R. Multi-objective Optimization of Laser Cladding Single-pass Forming Process Parameters Based on NSGA-II Algorithm. China Surf. Eng. 2023, 36, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.G.; Li, C.G.; Tian, D.C.; Li, X.T.; Wang, J.Q.; Xu, Z.H.; Sun, X.G. Numerical Simulation Analysis of Temperature Distribution of NbC-Reinforced Ti-Based Composite Coating by Laser Cladding. Metals 2023, 13, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.S.; Tchuindjang, J.T.; Paydas, H.; Mertens, A.; Jardin, R.T.; Duchêne, L.; Carrus, R.; Lecomte-Beckers, J.; Habraken, A.M. 3D thermal finite element analysis of laser cladding processed Ti-6Al-4V part with microstructural correlations. Mater. Des. 2017, 128, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.S.; Wang, J.S.; Bai, H.Q.; He, Y.J.; Wang, B. Numerical and Experimental Investigation on Laser Cladding Treatment of Wear Shaft Surface. J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 55, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamanna, N.; Crouch, R.; Naher, S. Progress in numerical simulation of the laser cladding process. Opt. Laser. Eng. 2019, 122, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.P.; Li, J.B.; Shi, Y.M.; Ren, S.X.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, X.F. Effect of process parameters on microstructure and tribological properties of Ni60A/Cr3C2 laser cladding on 60Si2Mn steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 473, 130005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
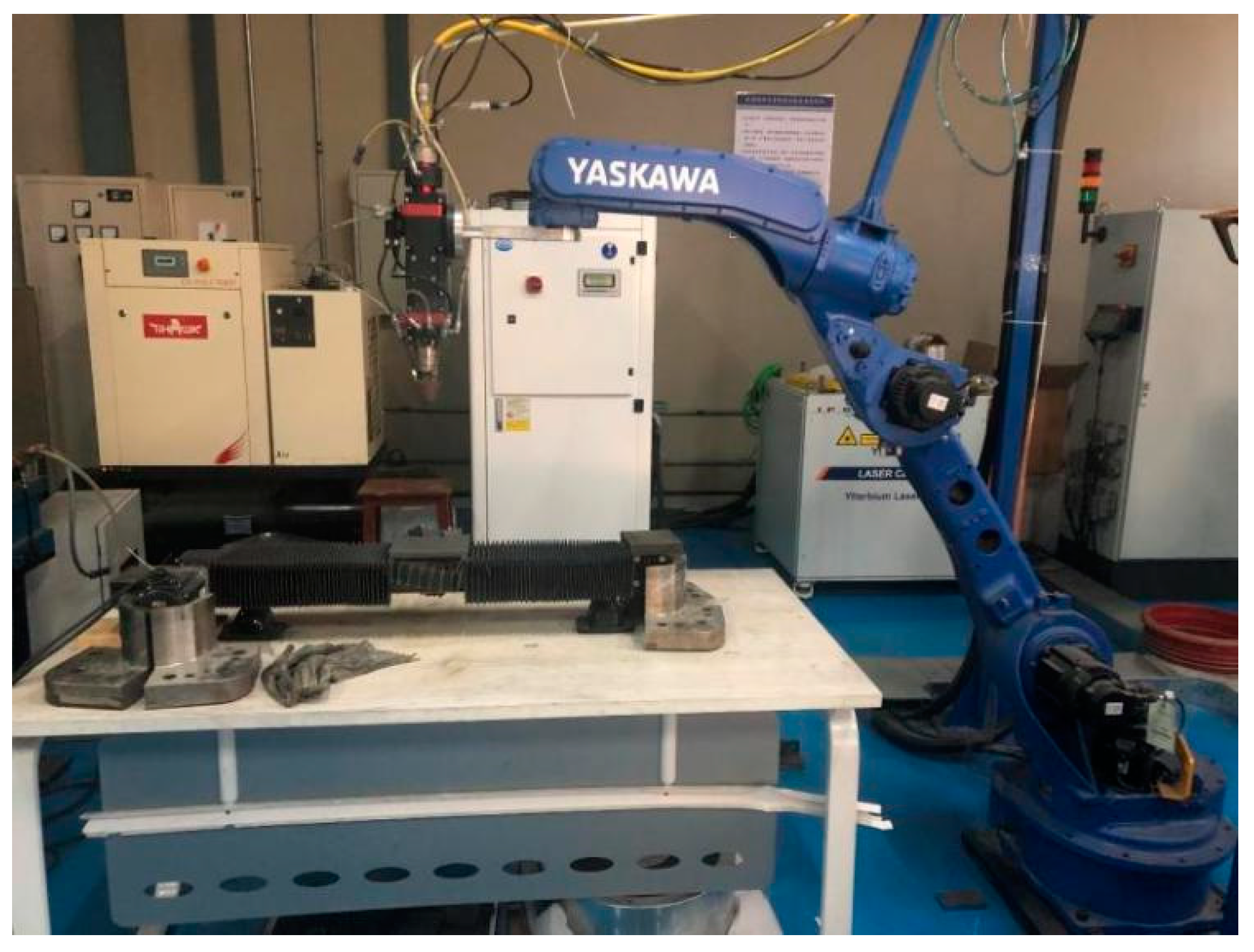

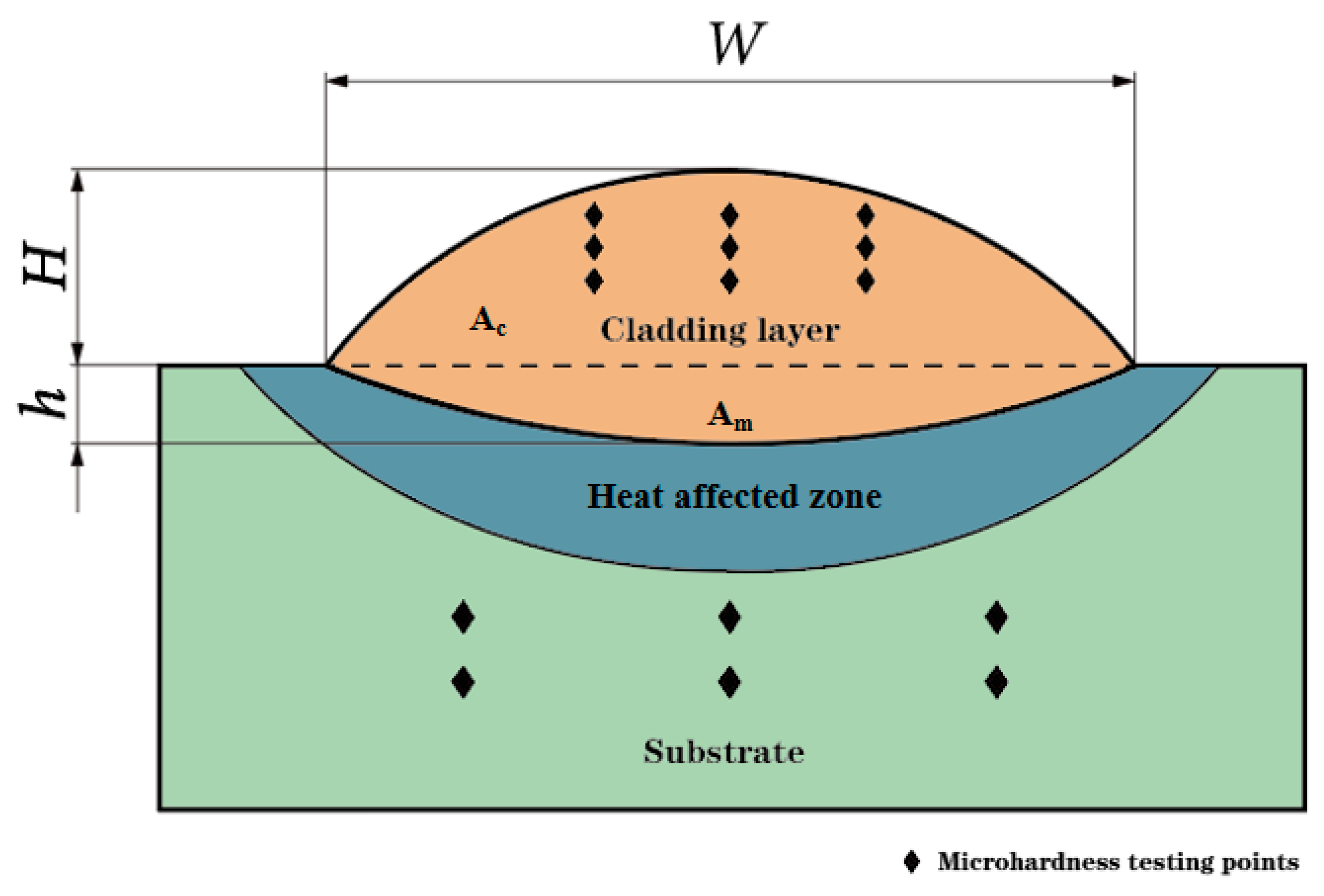

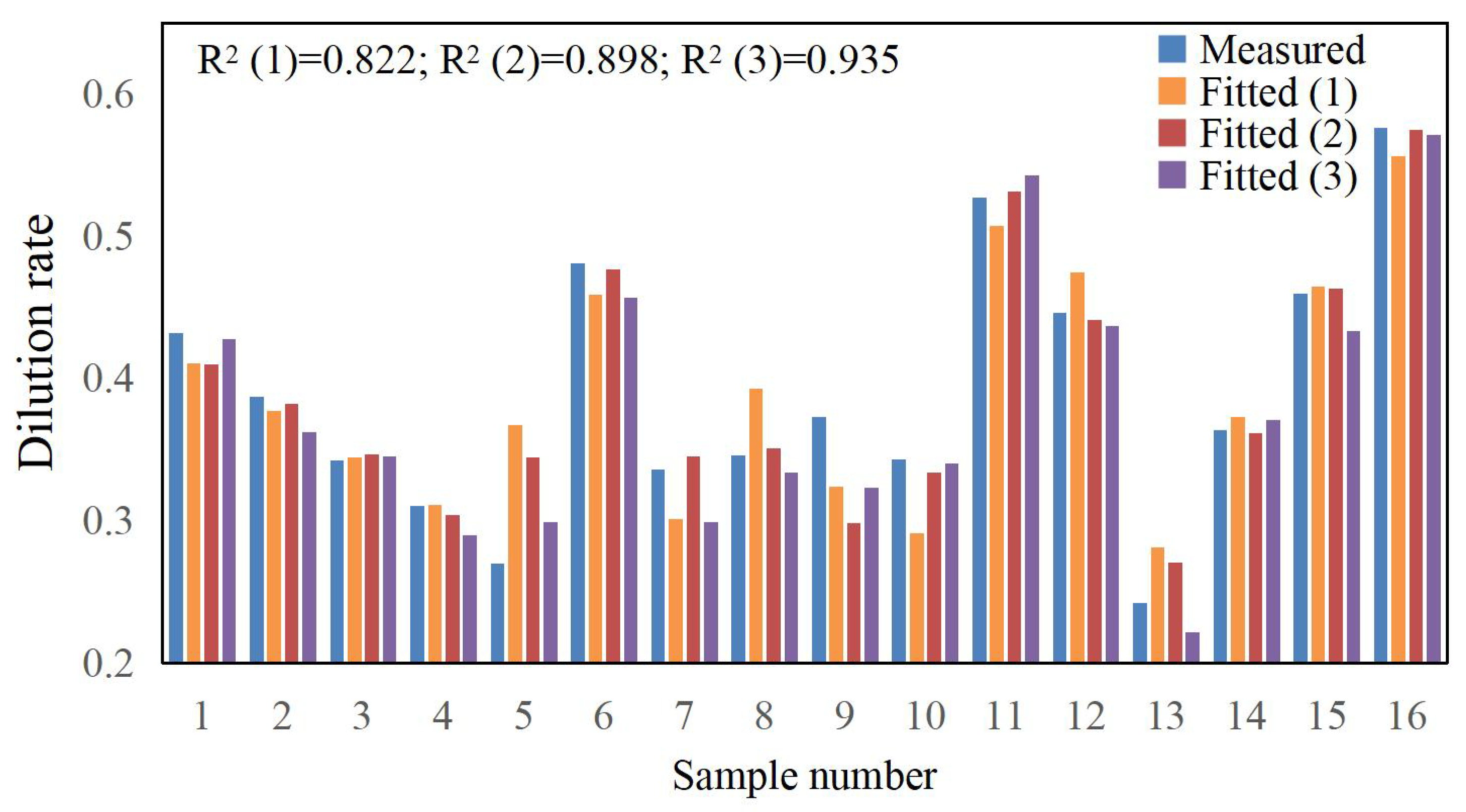
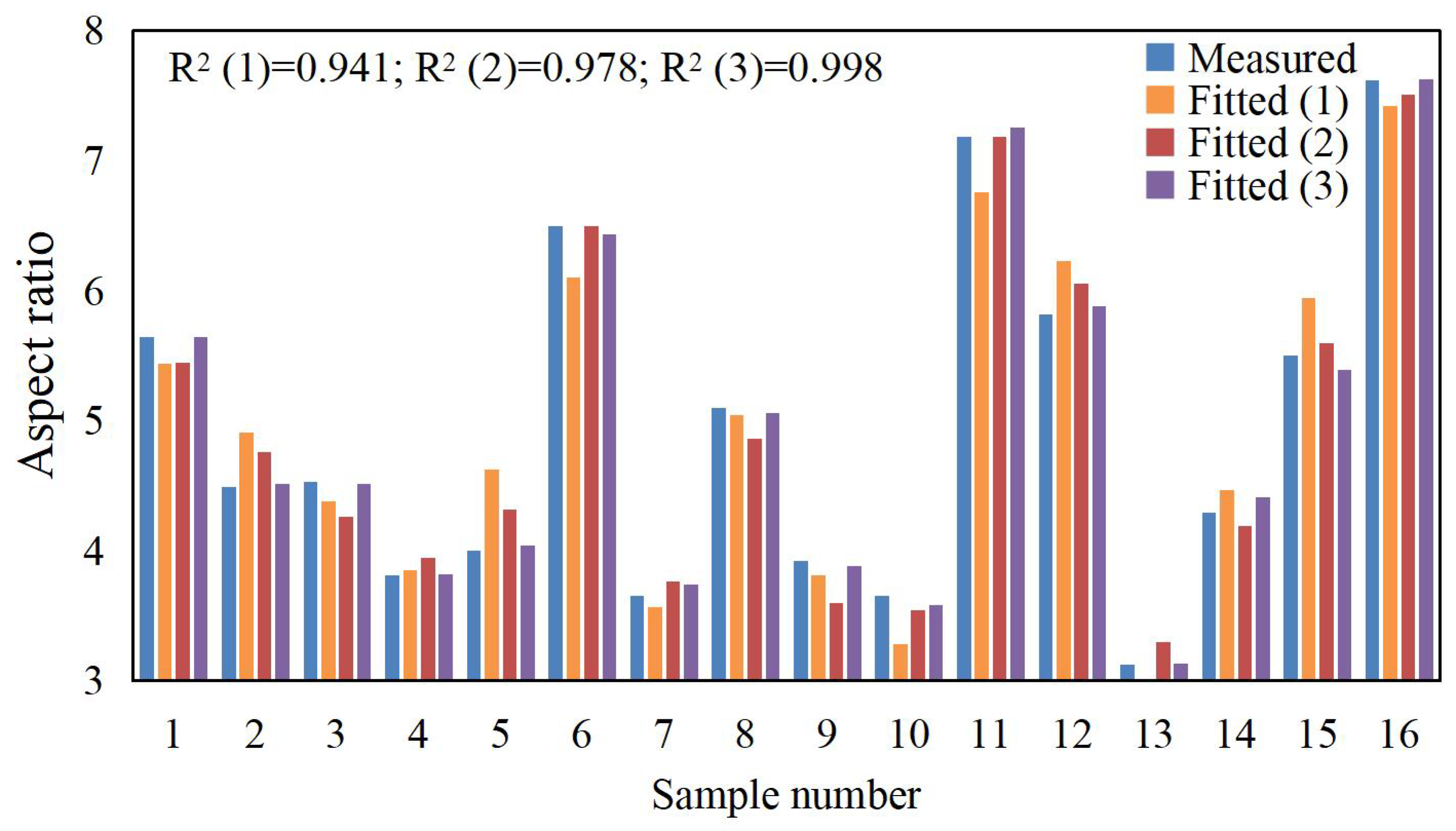
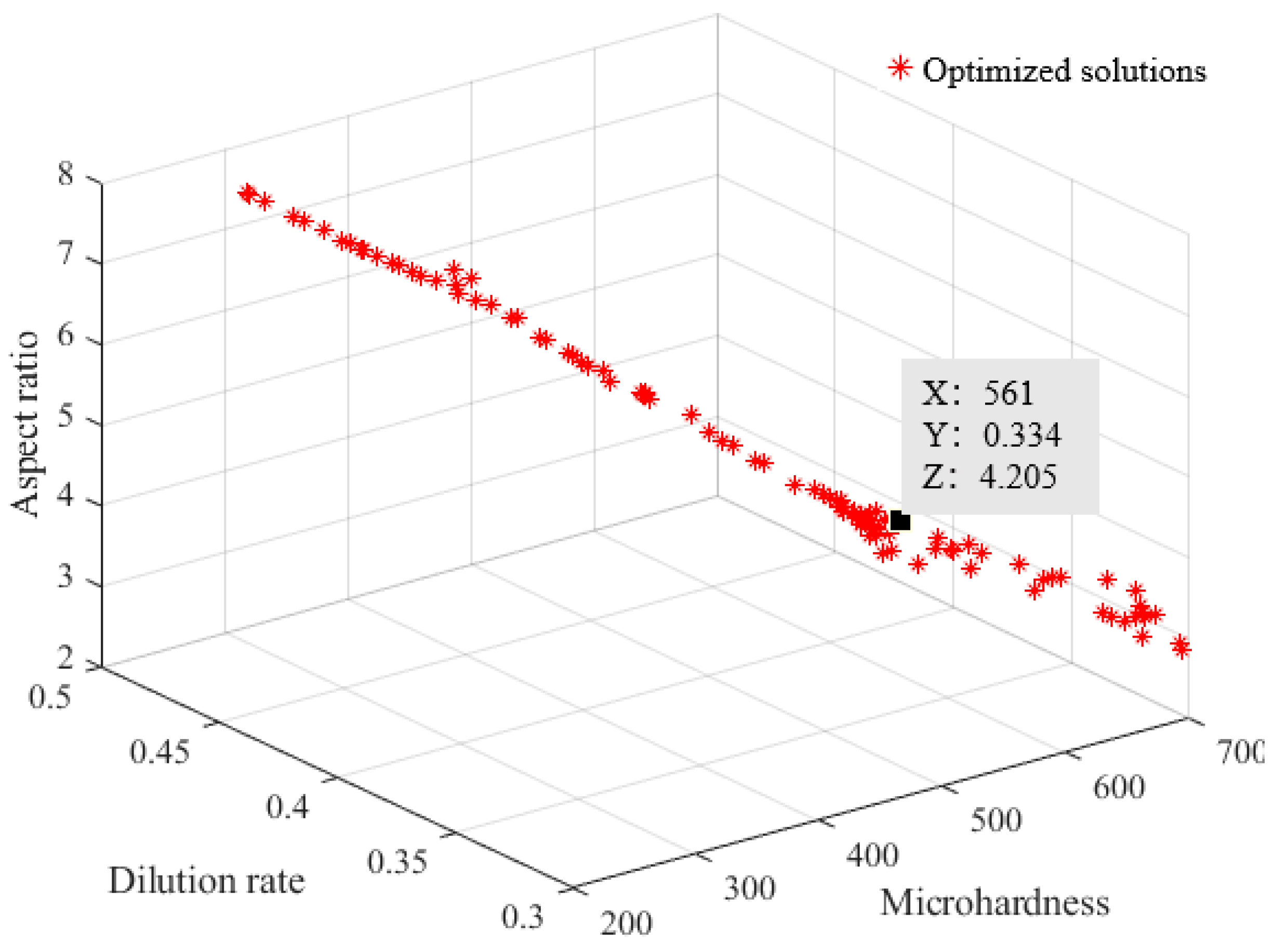
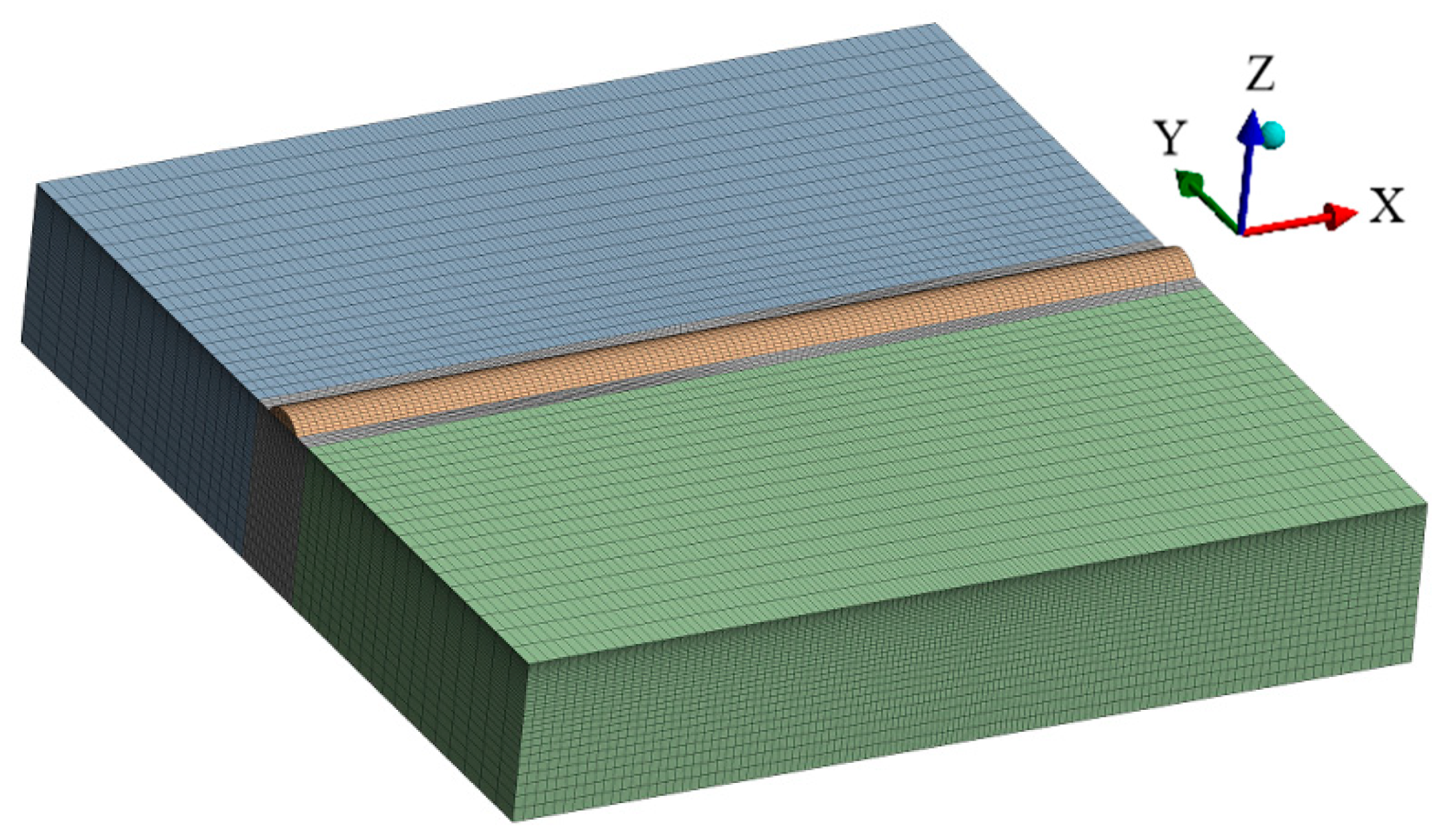



| Element | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | V | P | S | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 0.39 | 0.83 | 0.38 | 5.00 | 1.22 | 0.86 | 0.022 | 0.005 | Bal. |
| Element | Al | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 10.69 | 23.34 | 20.60 | 22.12 | 23.25 |
| Levels | Factors | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Power P/kW | Scanning Speed v/mm·s−1 | Powder Feeding Rate q/g·min−1 | |
| Level 1 | 2.1 | 8 | 9.76 |
| Level 2 | 2.2 | 10 | 11.89 |
| Level 3 | 2.3 | 12 | 14.03 |
| Level 4 | 2.4 | 14 | 16.24 |
| Number | Process Parameters | Measurement Results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Power P/kW | Scanning Speed v/mm·s−1 | Powder Feeding Rate q/g·min−1 | Microhardness HV/HV1 | Dilution Rate η | Aspect Ratio W/H | |
| 1# | 2.1 | 8 | 9.76 | 455 | 0.432 | 5.644 |
| 2# | 2.1 | 10 | 11.89 | 553 | 0.387 | 4.488 |
| 3# | 2.1 | 12 | 14.03 | 536 | 0.342 | 4.531 |
| 4# | 2.1 | 14 | 16.24 | 525 | 0.310 | 3.810 |
| 5# | 2.2 | 8 | 11.89 | 530 | 0.270 | 3.999 |
| 6# | 2.2 | 10 | 9.76 | 300 | 0.481 | 6.493 |
| 7# | 2.2 | 12 | 16.24 | 522 | 0.336 | 3.654 |
| 8# | 2.2 | 14 | 14.03 | 472 | 0.346 | 5.097 |
| 9# | 2.3 | 8 | 14.03 | 524 | 0.373 | 3.918 |
| 10# | 2.3 | 10 | 16.24 | 532 | 0.343 | 3.651 |
| 11# | 2.3 | 12 | 9.76 | 274 | 0.527 | 7.186 |
| 12# | 2.3 | 14 | 11.89 | 413 | 0.446 | 5.821 |
| 13# | 2.4 | 8 | 16.24 | 515 | 0.242 | 3.124 |
| 14# | 2.4 | 10 | 14.03 | 433 | 0.364 | 4.289 |
| 15# | 2.4 | 12 | 11.89 | 360 | 0.460 | 5.498 |
| 16# | 2.4 | 14 | 9.76 | 283 | 0.576 | 7.617 |
| 0.933 | 0.727 | 0.752 | 1.007 | 1.108 | 1.146 |
| 0.933 | 0.909 | 0.916 | 1.224 | 0.992 | 0.911 |
| 0.933 | 1.091 | 1.081 | 1.187 | 0.878 | 0.920 |
| 0.933 | 1.273 | 1.251 | 1.162 | 0.795 | 0.773 |
| 0.978 | 0.727 | 0.916 | 1.173 | 0.694 | 0.812 |
| 0.978 | 0.909 | 0.752 | 0.664 | 1.235 | 1.318 |
| 0.978 | 1.091 | 1.251 | 1.156 | 0.863 | 0.742 |
| 0.978 | 1.273 | 1.081 | 1.045 | 0.888 | 1.035 |
| 1.022 | 0.727 | 1.081 | 1.160 | 0.956 | 0.795 |
| 1.022 | 0.909 | 1.251 | 1.178 | 0.879 | 0.741 |
| 1.022 | 1.091 | 0.752 | 0.607 | 1.353 | 1.459 |
| 1.022 | 1.273 | 0.916 | 0.914 | 1.145 | 1.182 |
| 1.067 | 0.727 | 1.251 | 1.140 | 0.620 | 0.634 |
| 1.067 | 0.909 | 1.081 | 0.959 | 0.935 | 0.871 |
| 1.067 | 1.091 | 0.916 | 0.797 | 1.181 | 1.116 |
| 1.067 | 1.273 | 0.752 | 0.627 | 1.477 | 1.546 |
| Δ11(k) | Δ12(k) | Δ13(k) | Δ21(k) | Δ22(k) | Δ23(k) | Δ31(k) | Δ32(k) | Δ33(k) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.074 | 0.280 | 0.255 | 0.175 | 0.381 | 0.356 | 0.212 | 0.419 | 0.394 |
| 0.291 | 0.315 | 0.308 | 0.059 | 0.083 | 0.076 | 0.022 | 0.002 | 0.005 |
| 0.253 | 0.096 | 0.106 | 0.055 | 0.213 | 0.203 | 0.014 | 0.171 | 0.161 |
| 0.229 | 0.110 | 0.089 | 0.138 | 0.478 | 0.456 | 0.160 | 0.499 | 0.478 |
| 0.196 | 0.446 | 0.257 | 0.284 | 0.033 | 0.222 | 0.166 | 0.084 | 0.104 |
| 0.314 | 0.245 | 0.088 | 0.257 | 0.325 | 0.483 | 0.340 | 0.409 | 0.566 |
| 0.178 | 0.065 | 0.095 | 0.114 | 0.227 | 0.388 | 0.236 | 0.349 | 0.509 |
| 0.067 | 0.228 | 0.036 | 0.090 | 0.385 | 0.193 | 0.057 | 0.238 | 0.046 |
| 0.138 | 0.433 | 0.079 | 0.066 | 0.229 | 0.125 | 0.227 | 0.068 | 0.286 |
| 0.156 | 0.269 | 0.073 | 0.143 | 0.030 | 0.372 | 0.281 | 0.168 | 0.510 |
| 0.416 | 0.484 | 0.145 | 0.331 | 0.262 | 0.601 | 0.437 | 0.368 | 0.707 |
| 0.108 | 0.358 | 0.002 | 0.122 | 0.128 | 0.229 | 0.159 | 0.091 | 0.266 |
| 0.074 | 0.413 | 0.111 | 0.447 | 0.107 | 0.631 | 0.432 | 0.093 | 0.617 |
| 0.108 | 0.050 | 0.122 | 0.132 | 0.026 | 0.146 | 0.196 | 0.038 | 0.210 |
| 0.270 | 0.294 | 0.119 | 0.115 | 0.090 | 0.265 | 0.050 | 0.025 | 0.200 |
| 0.440 | 0.646 | 0.125 | 0.410 | 0.204 | 0.725 | 0.480 | 0.274 | 0.794 |
| γ11(k) | γ12(k) | γ13(k) | γ21(k) | γ22(k) | γ23(k) | γ31(k) | γ32(k) | γ33(k) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.818 | 0.538 | 0.561 | 0.723 | 0.522 | 0.540 | 0.655 | 0.489 | 0.504 |
| 0.529 | 0.509 | 0.514 | 0.922 | 0.872 | 0.886 | 0.951 | 1.000 | 0.992 |
| 0.563 | 0.775 | 0.757 | 0.929 | 0.675 | 0.687 | 0.971 | 0.702 | 0.715 |
| 0.588 | 0.749 | 0.788 | 0.776 | 0.462 | 0.474 | 0.716 | 0.445 | 0.456 |
| 0.626 | 0.422 | 0.560 | 0.601 | 0.981 | 0.664 | 0.709 | 0.828 | 0.796 |
| 0.510 | 0.572 | 0.790 | 0.627 | 0.564 | 0.460 | 0.541 | 0.495 | 0.414 |
| 0.648 | 0.837 | 0.776 | 0.814 | 0.658 | 0.518 | 0.630 | 0.535 | 0.440 |
| 0.832 | 0.590 | 0.905 | 0.858 | 0.520 | 0.699 | 0.879 | 0.628 | 0.900 |
| 0.705 | 0.430 | 0.807 | 0.907 | 0.656 | 0.797 | 0.639 | 0.858 | 0.584 |
| 0.678 | 0.549 | 0.819 | 0.768 | 0.990 | 0.529 | 0.588 | 0.706 | 0.440 |
| 0.440 | 0.402 | 0.693 | 0.560 | 0.621 | 0.403 | 0.479 | 0.522 | 0.361 |
| 0.754 | 0.477 | 1.000 | 0.801 | 0.792 | 0.657 | 0.717 | 0.817 | 0.602 |
| 0.819 | 0.441 | 0.748 | 0.480 | 0.827 | 0.391 | 0.481 | 0.814 | 0.394 |
| 0.753 | 0.872 | 0.729 | 0.786 | 1.000 | 0.764 | 0.673 | 0.916 | 0.657 |
| 0.548 | 0.526 | 0.735 | 0.814 | 0.858 | 0.619 | 0.893 | 0.945 | 0.668 |
| 0.426 | 0.335 | 0.724 | 0.502 | 0.685 | 0.357 | 0.455 | 0.595 | 0.335 |
| ϕji | Laser Power P | Scanning Speed v | Powder Feeding Rate q |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microhardness HV | 0.640 | 0.564 | 0.744 |
| Dilution rate η | 0.742 | 0.730 | 0.590 |
| Aspect ratio W/H | 0.686 | 0.706 | 0.579 |
| Coefficient | Fit Function | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| f1 | f2 | f3 | |
| a0 | 60,753.53995 | 293.88582 | 726.92022 |
| a1 | −81,476.78321 | −387.21358 | −882.57317 |
| a2 | −190.68071 | 0.18548 | −0.18753 |
| a3 | 811.55869 | −1.06937 | −15.93261 |
| a4 | 34,936.43423 | 172.31339 | 397.49202 |
| a5 | −6.29712 | −0.02943 | 0.07772 |
| a6 | −51.06455 | 0.08443 | 1.14057 |
| a7 | 111.25000 | 0.07909 | −0.02923 |
| a8 | −4.93924 | −0.03661 | 0.19536 |
| a9 | −3.29580 | 5.77689 × 10−4 | −0.01491 |
| a10 | −5089.65692 | −25.53765 | −59.64352 |
| a11 | 0.28883 | 7.74861 × 10−4 | −0.00271 |
| a12 | 1.16376 | −0.00208 | −0.02800 |
| Microhardness HV/HV1 | Dilution Rate η | Aspect Ratio W/H | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prediction results | 561 | 0.334 | 4.205 |
| Experimental results | 575 | 0.324 | 4.142 |
| Error/% | 2.50 | 2.99 | 1.50 |
| Temperature (°C) | Density (g/(cm)3) | Specific Heat (J/(g K)) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m K) | Thermal Expansion Coefficient (10−6/K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | 7.74232 | 0.44793 | 34.22998 | 12.20303 |
| 200 | 7.69096 | 0.53212 | 33.8028 | 12.35203 |
| 400 | 7.62551 | 0.64751 | 32.08765 | 13.44289 |
| 600 | 7.55277 | 0.84721 | 29.19734 | 14.43505 |
| 800 | 7.47502 | 0.84593 | 27.48423 | 15.29497 |
| 1000 | 7.45094 | 0.71905 | 28.05636 | 13.30179 |
| 1400 | 7.20363 | 1.96216 | 32.34514 | 18.07875 |
| 1800 | 6.69282 | 0.83024 | 37.11 | 29.40634 |
| 2200 | 6.34178 | 0.83247 | 43.76672 | 31.59778 |
| 2600 | 5.9743 | 0.83321 | 50.42344 | 38.27681 |
| 3000 | 5.60184 | 0.83343 | 57.08016 | 42.78304 |
| Temperature (°C) | Density (g/(cm)3) | Specific Heat (J/(g K)) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m K) | Thermal Expansion Coefficient (10−6/K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | 7.05515 | 0.50448 | 42.66598 | 13.80349 |
| 200 | 6.97521 | 0.60063 | 42.35551 | 21.0365 |
| 400 | 6.90243 | 0.64244 | 31.54551 | 19.29267 |
| 600 | 6.81968 | 0.71864 | 32.81245 | 19.7689 |
| 800 | 6.71872 | 0.84129 | 35.08276 | 21.35085 |
| 1000 | 6.58944 | 0.86145 | 38.85223 | 24.01175 |
| 1400 | 6.02251 | 0.78449 | 28.49336 | 41.44993 |
| 1800 | 5.70202 | 0.83381 | 33.83801 | 44.46904 |
| 2200 | 5.36094 | 0.83714 | 39.18266 | 48.35054 |
| 2600 | 5.01208 | 0.83714 | 44.52732 | 52.69254 |
| 3000 | 4.66577 | 0.83714 | 49.87197 | 57.3093 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhao, J. Process Parameters Optimization and Numerical Simulation of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coating via Laser Cladding. Materials 2024, 17, 4243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174243
Chen B, Zhao Y, Yang H, Zhao J. Process Parameters Optimization and Numerical Simulation of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coating via Laser Cladding. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174243
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Bin, Yang Zhao, Hui Yang, and Jingjing Zhao. 2024. "Process Parameters Optimization and Numerical Simulation of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coating via Laser Cladding" Materials 17, no. 17: 4243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174243
APA StyleChen, B., Zhao, Y., Yang, H., & Zhao, J. (2024). Process Parameters Optimization and Numerical Simulation of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coating via Laser Cladding. Materials, 17(17), 4243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174243







