Control and Modelling of Laser Shock Peening without Coating (LSPwC) Texture of AISI 9310 Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
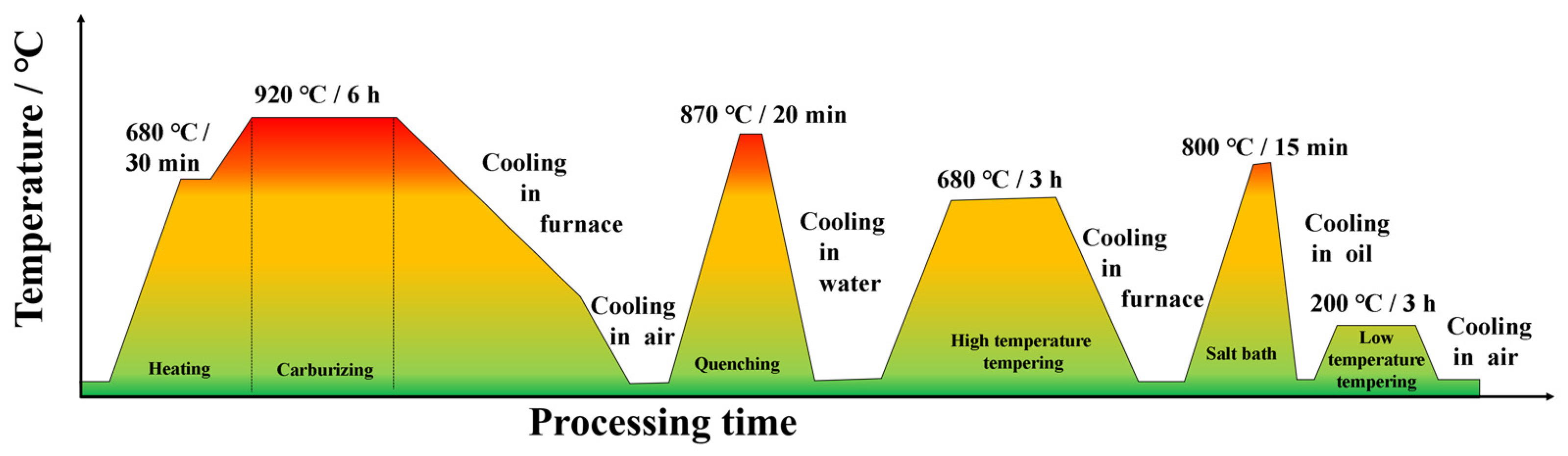
2.2. LSPwC Scheme
2.3. Surface Observation and Measurement Scheme
3. Result and Discussion
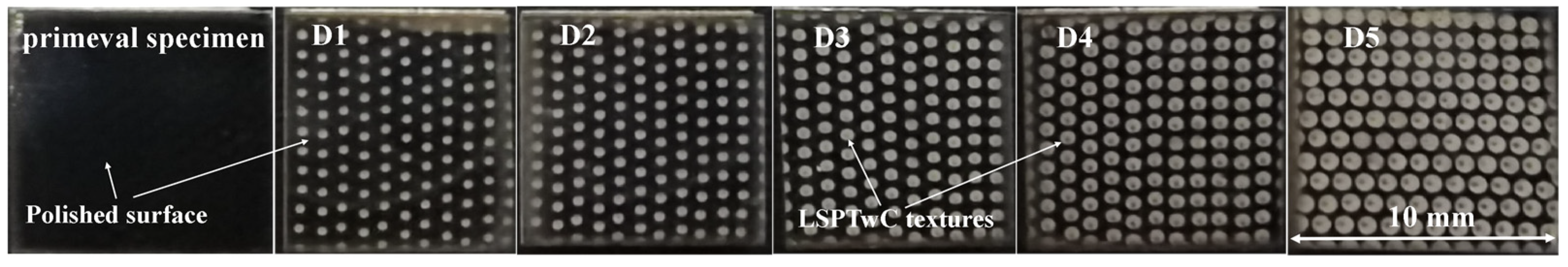
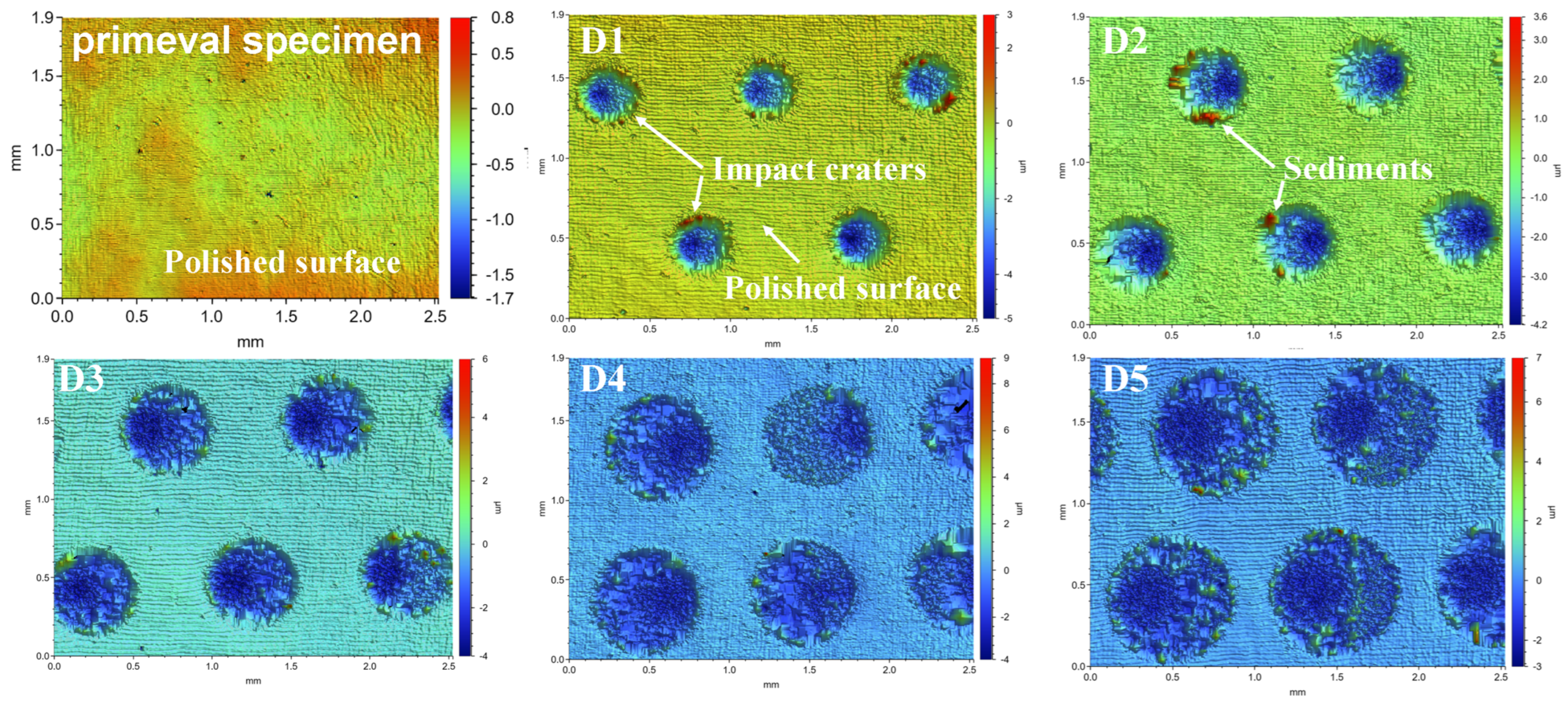
3.1. 2D Texture Observation and Analysis
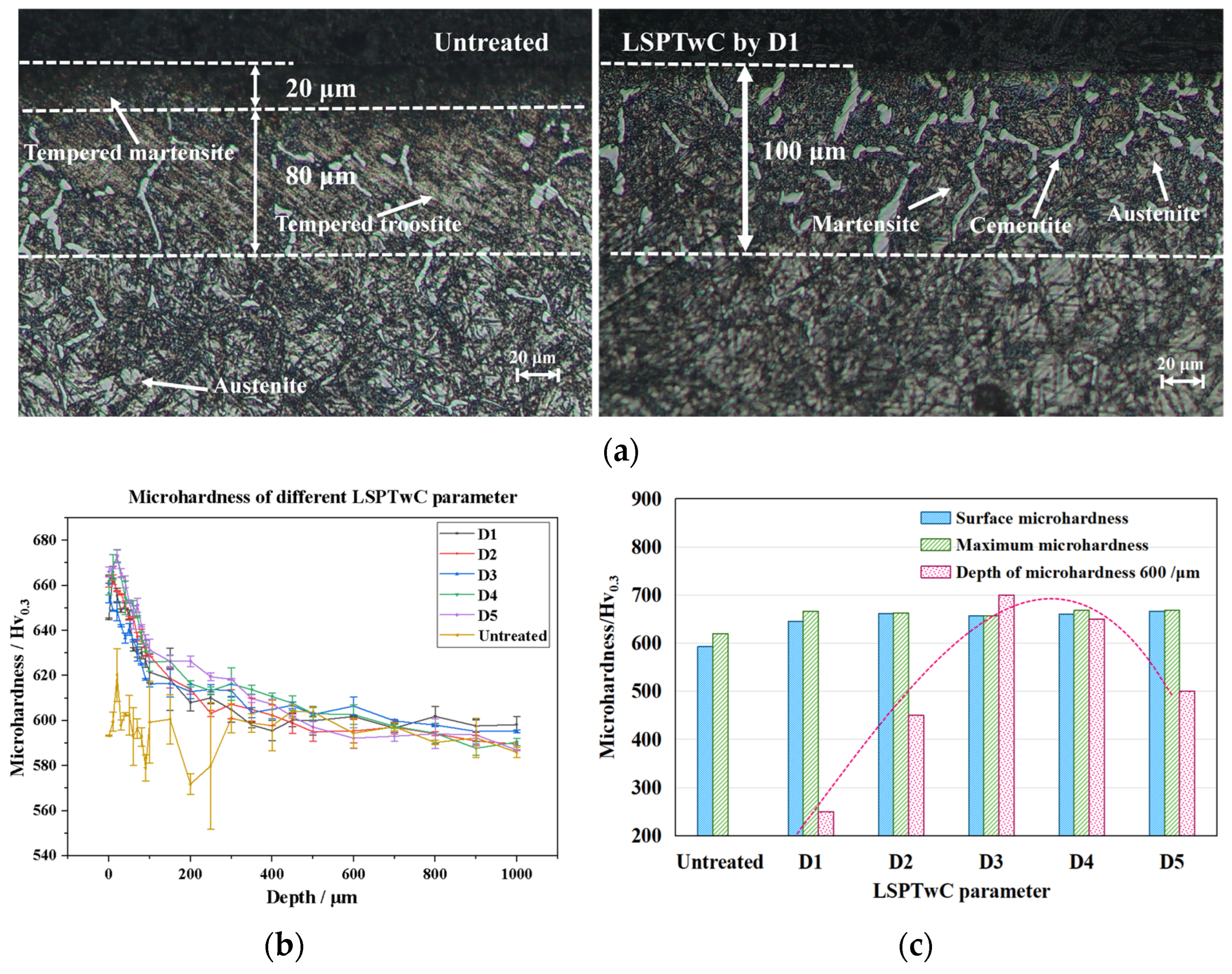
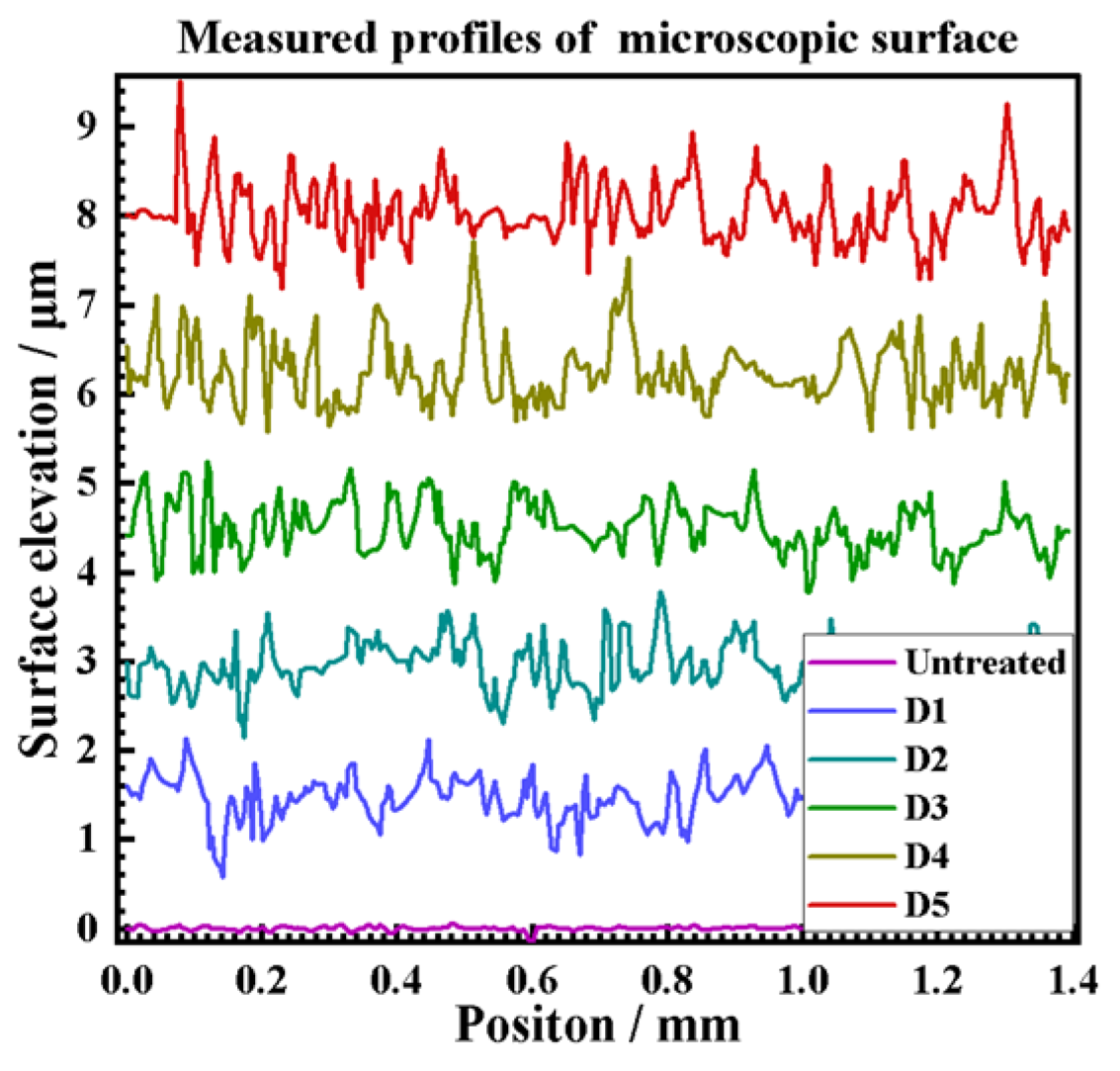
3.1.1. Optical Microscope Observations and Analysis
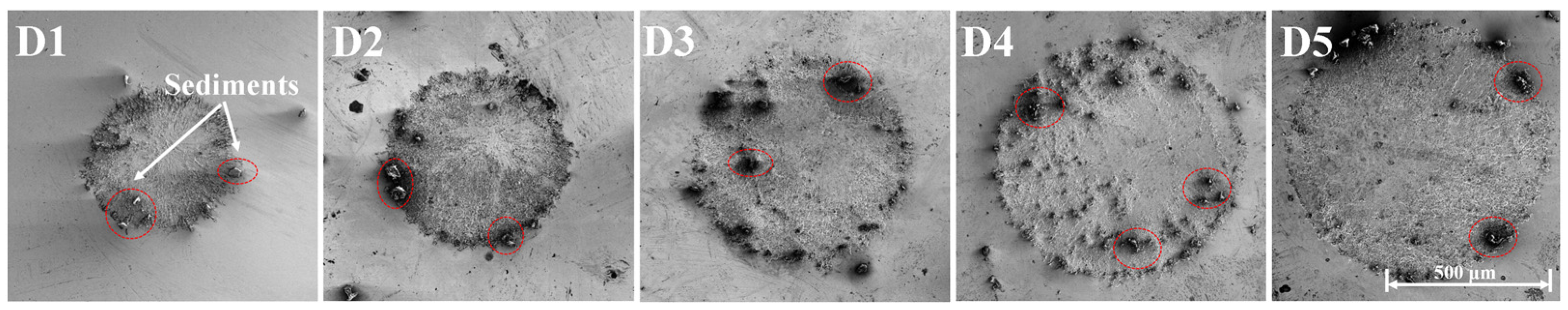
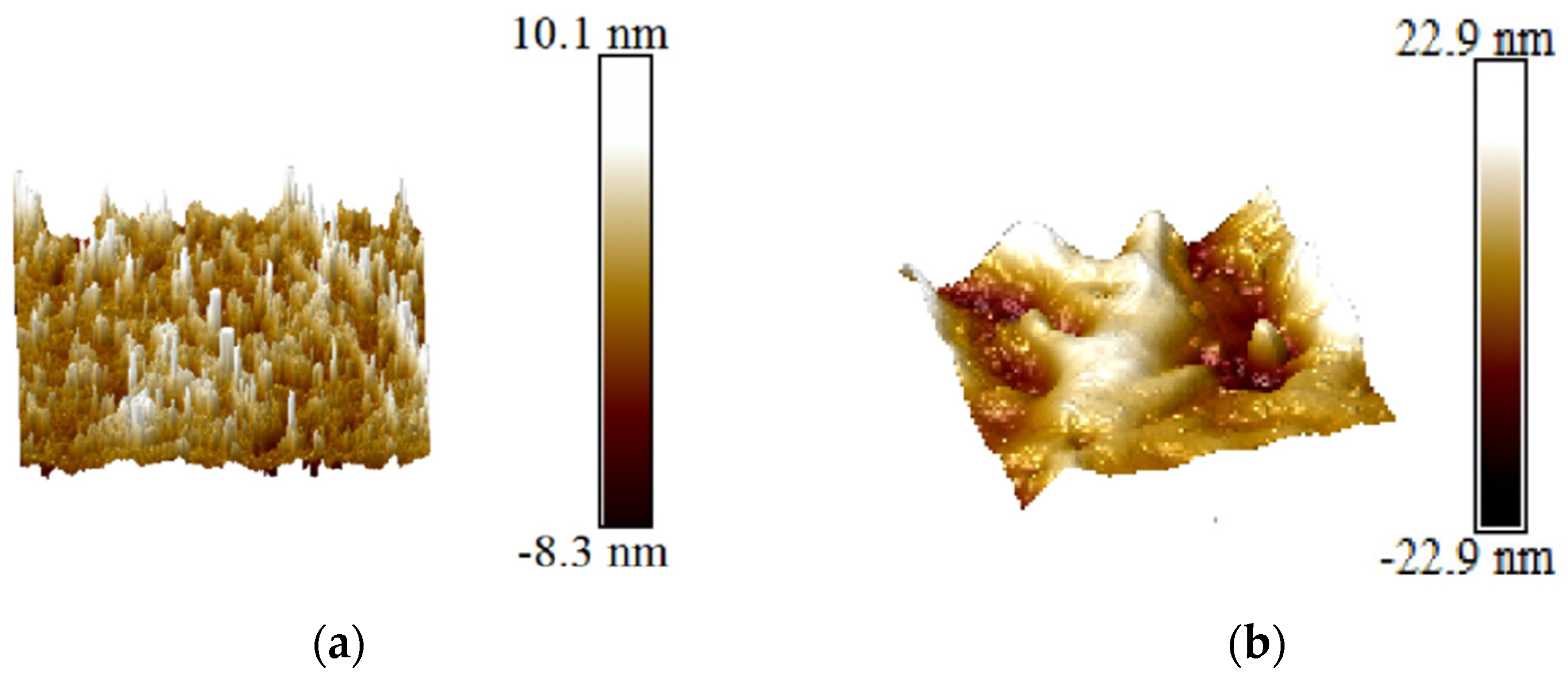
3.1.2. Electron Microscope Observations and Analysis
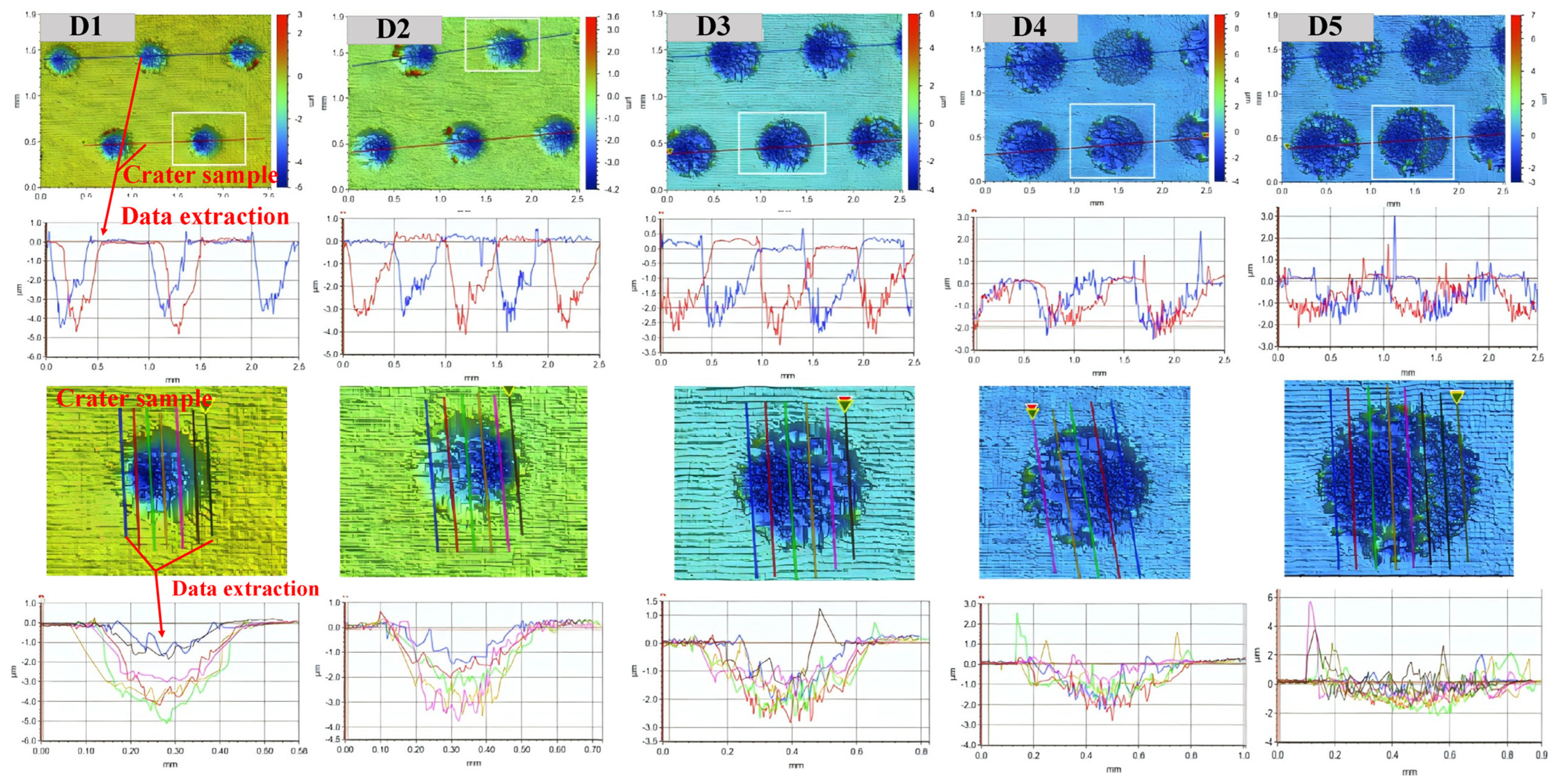
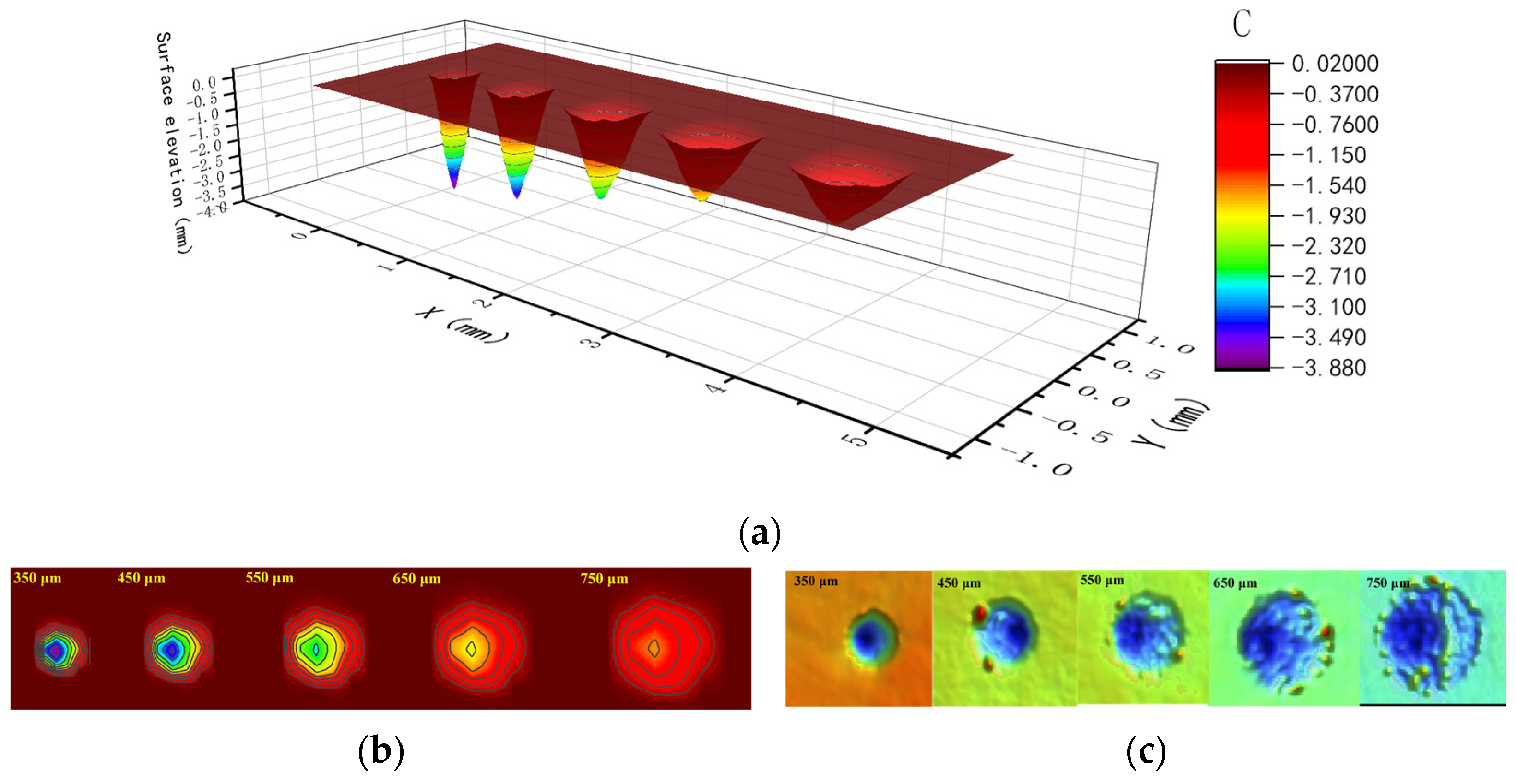
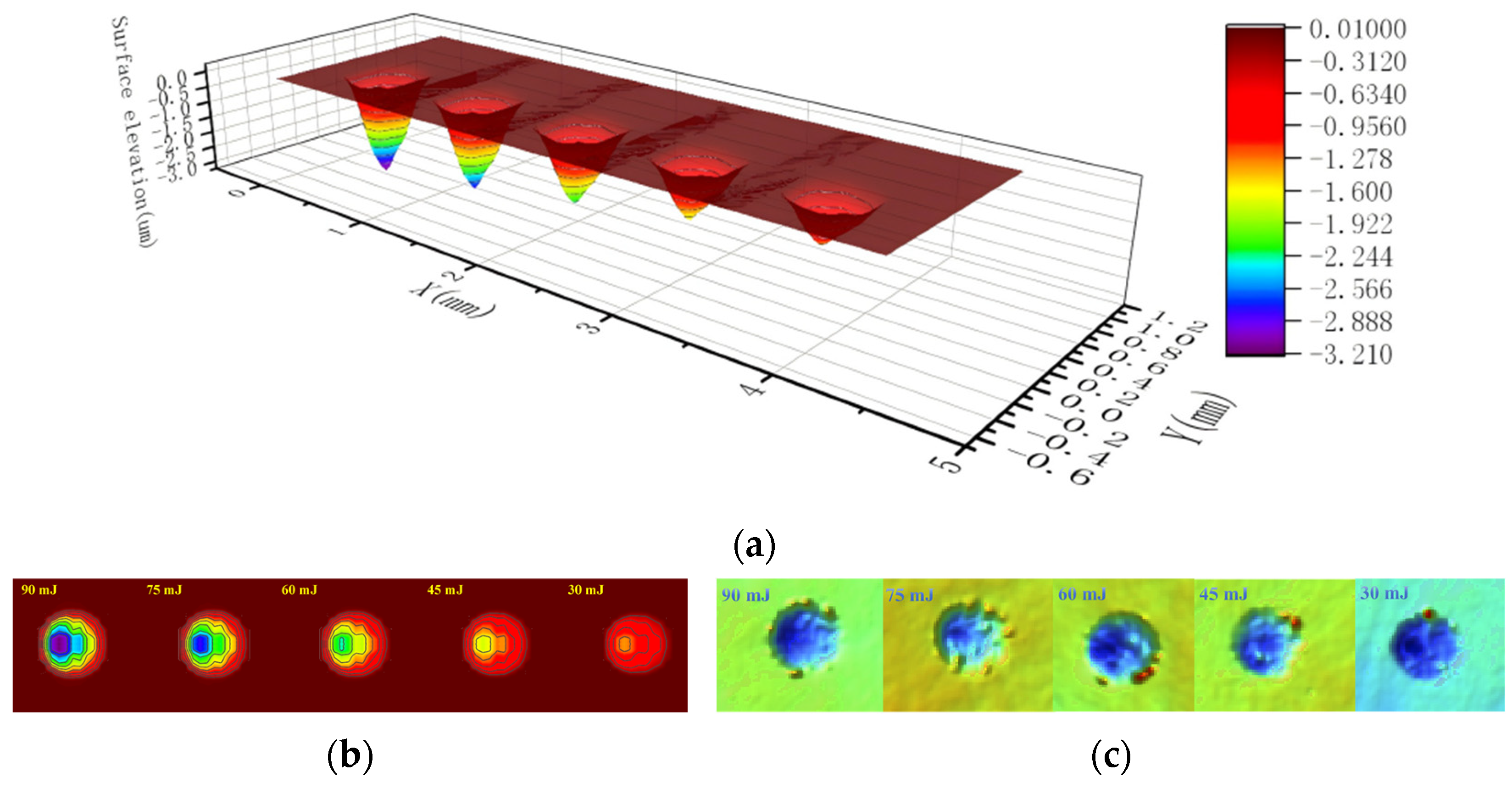
3.2. 3D Texture Observation Analysis and Modeling
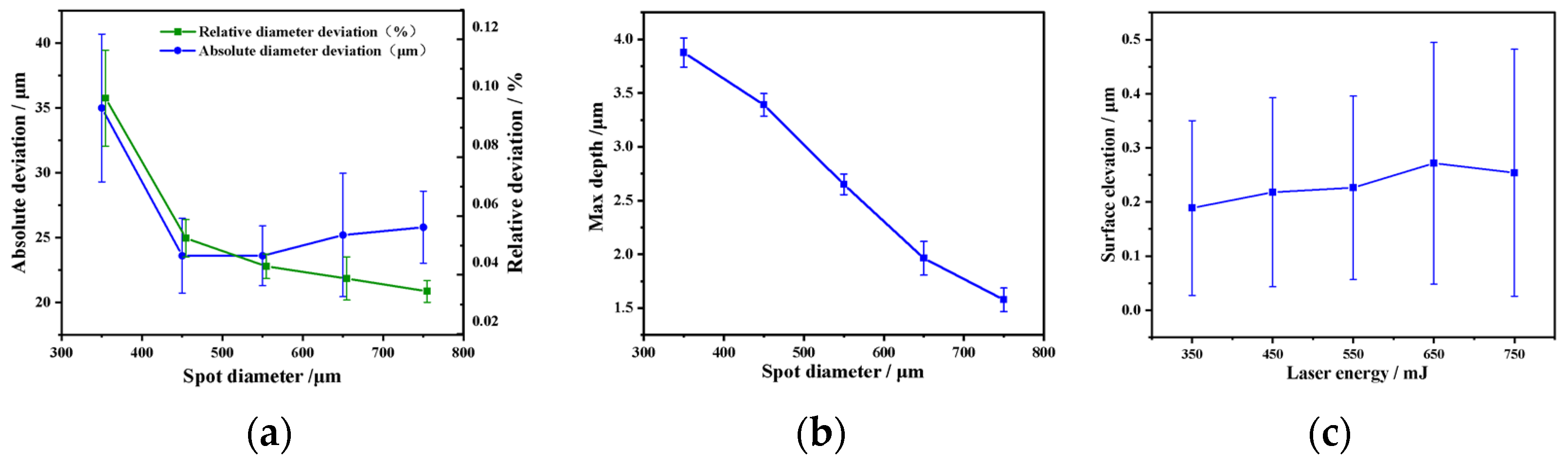
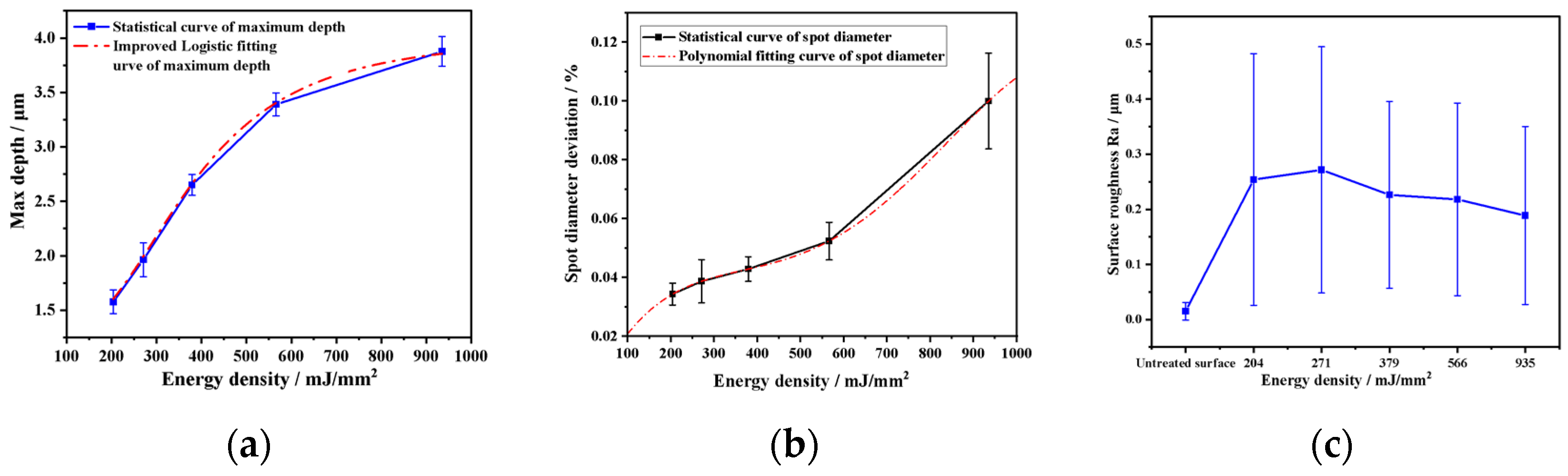
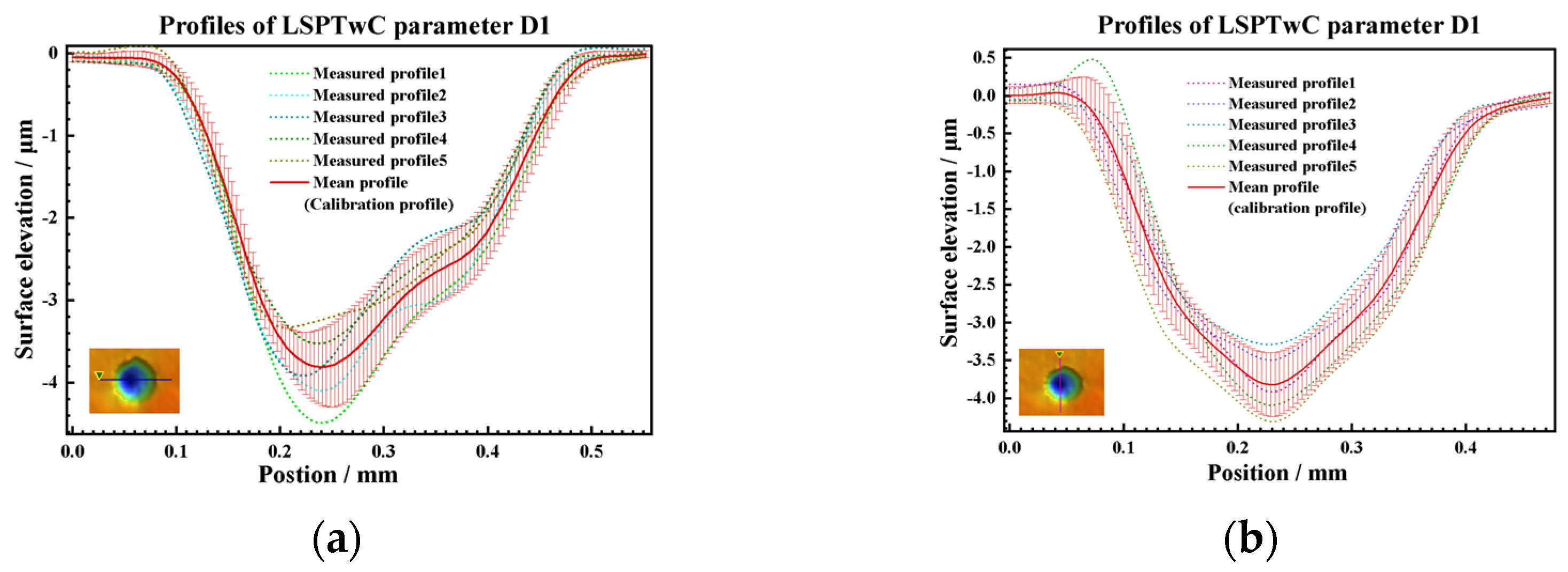
3.2.1. 3D Texture Observation and Analysis
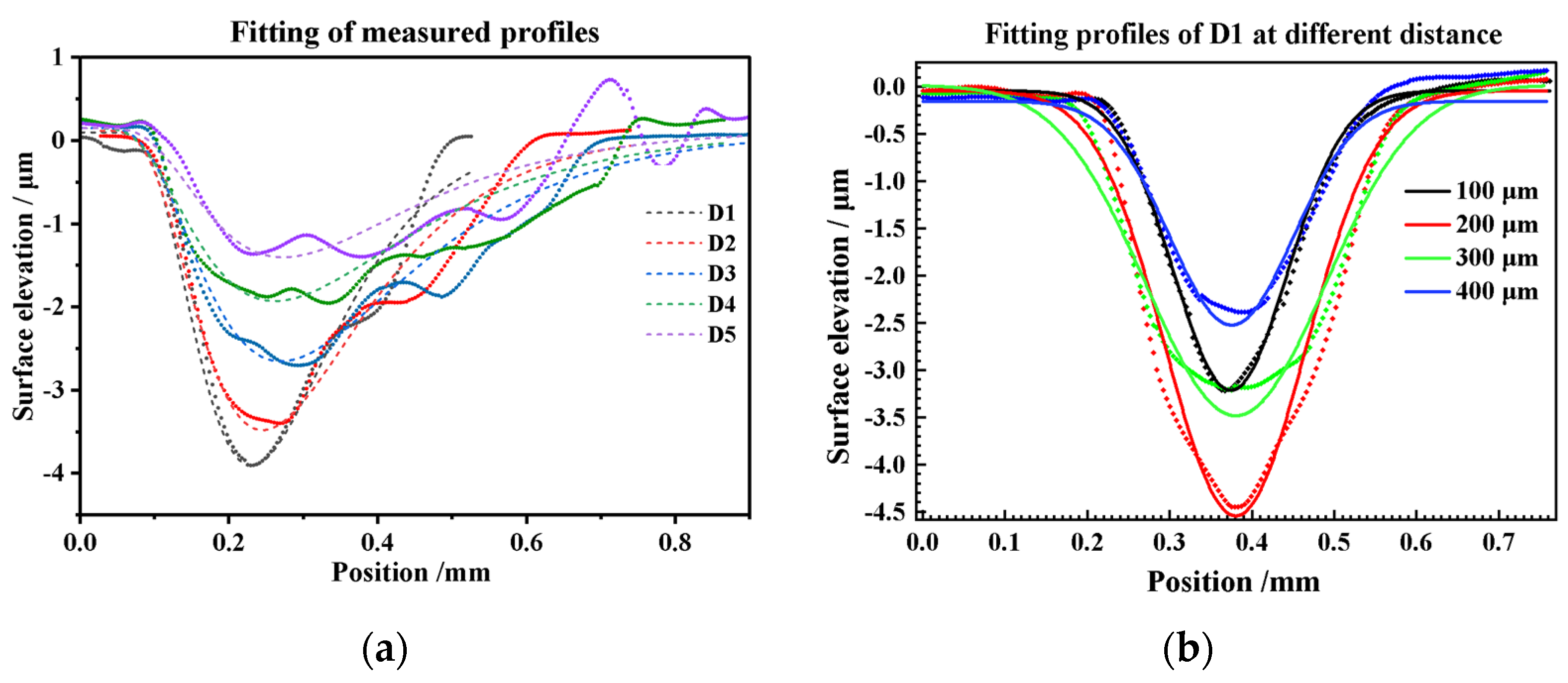
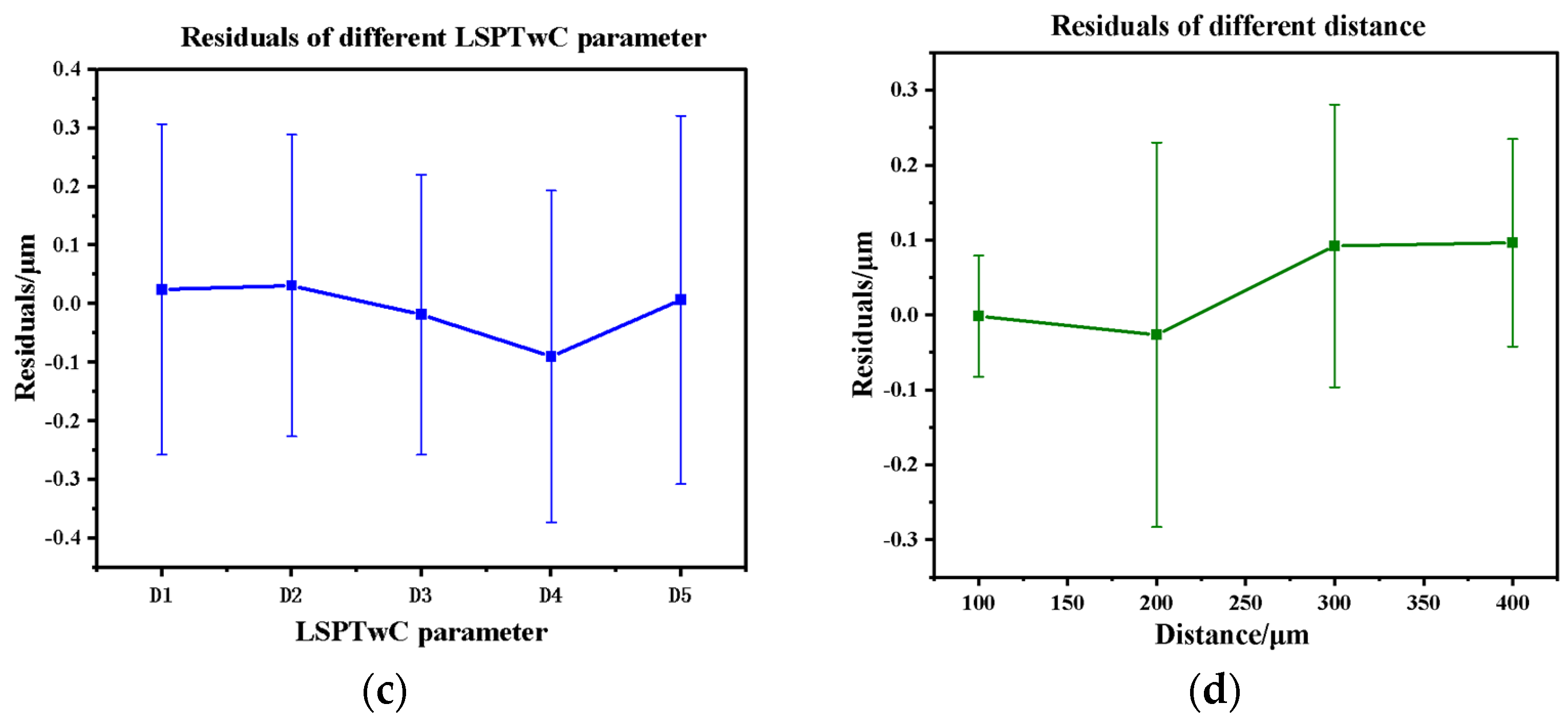
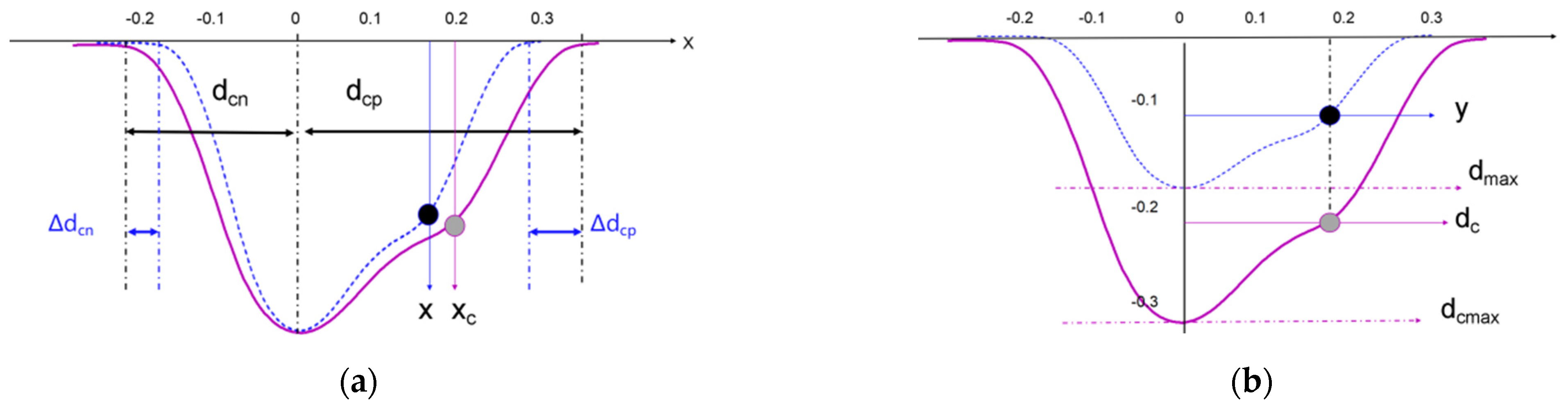
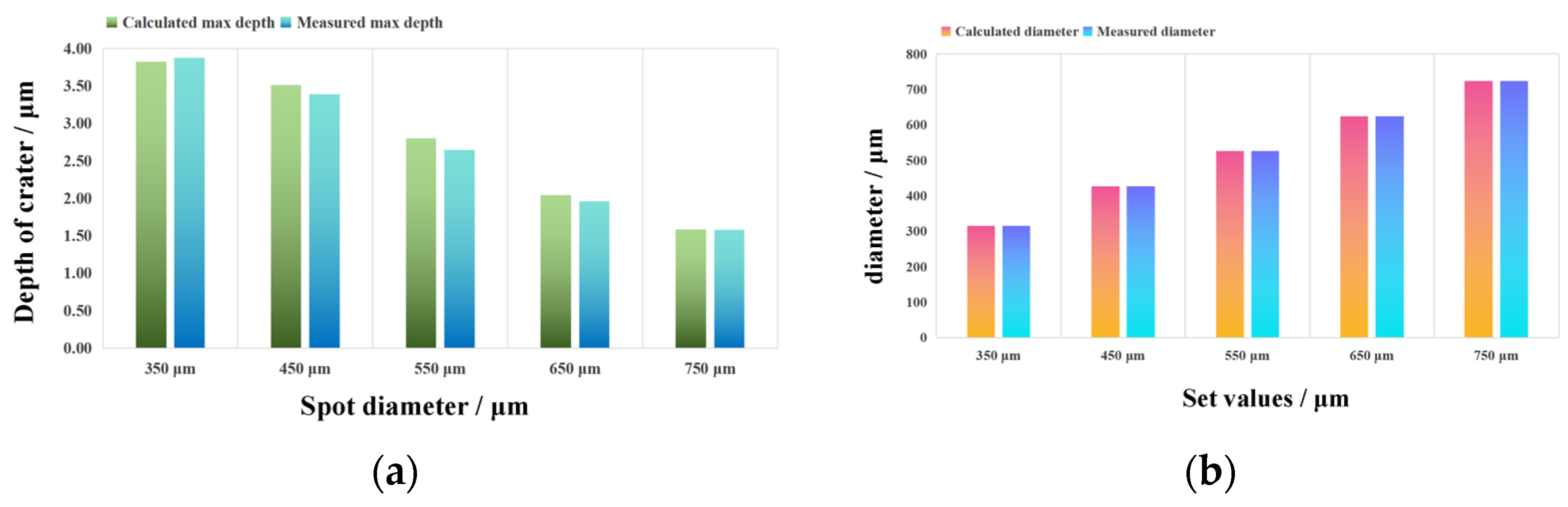
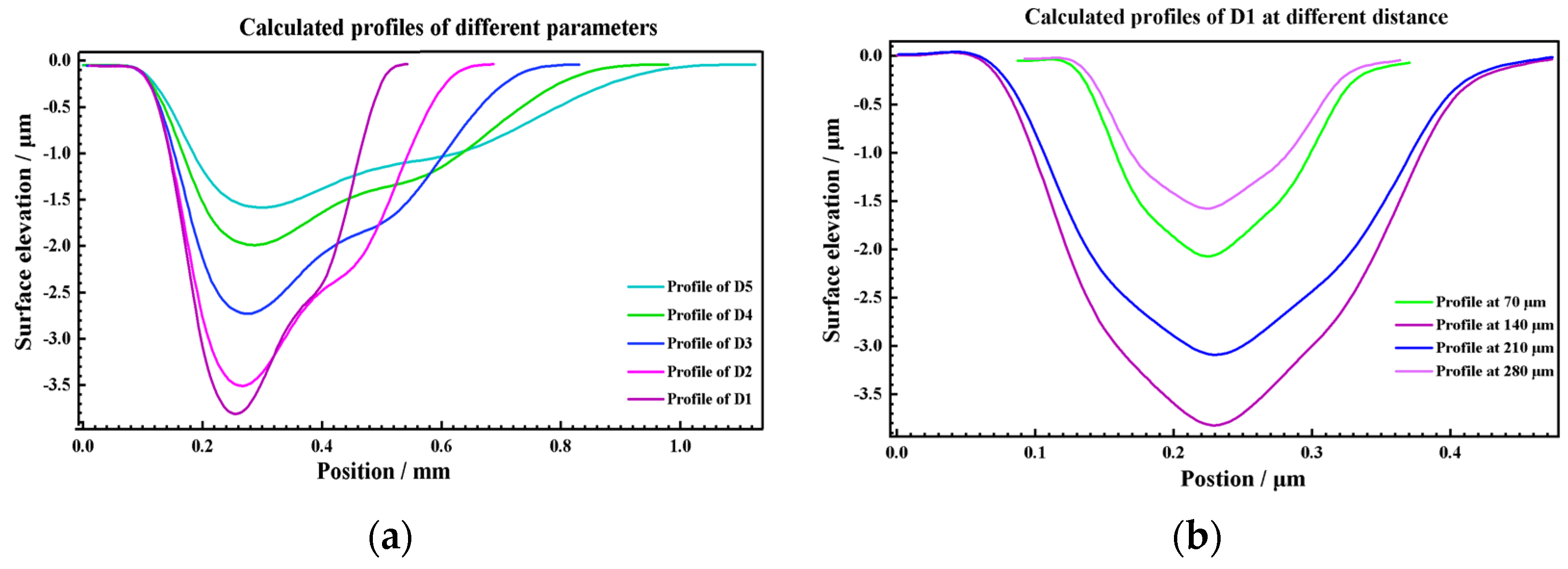
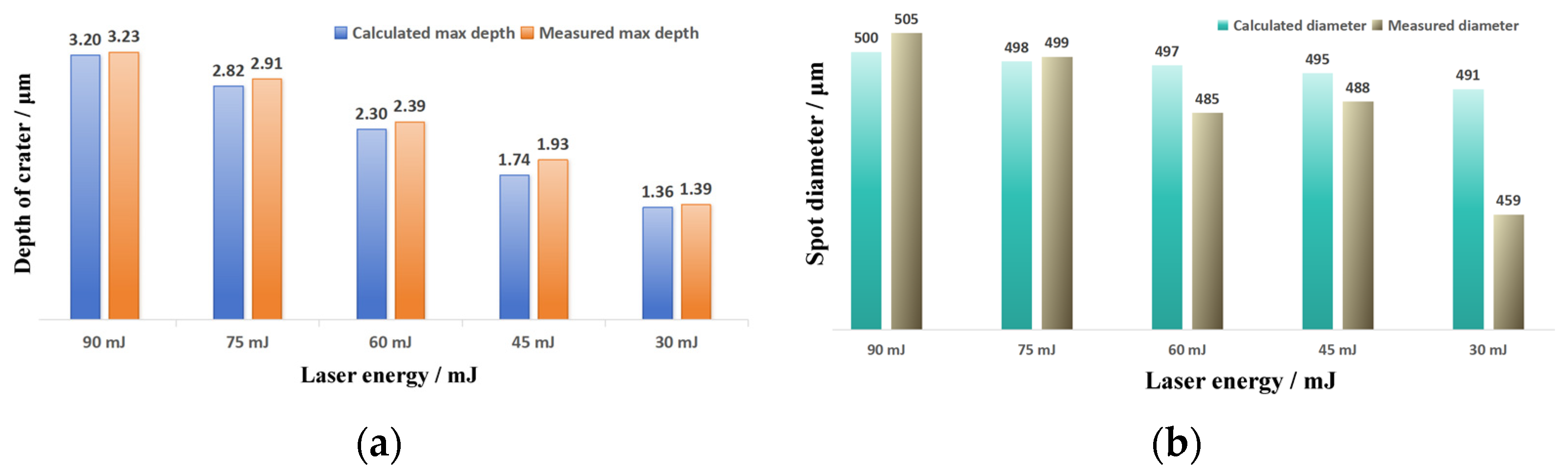
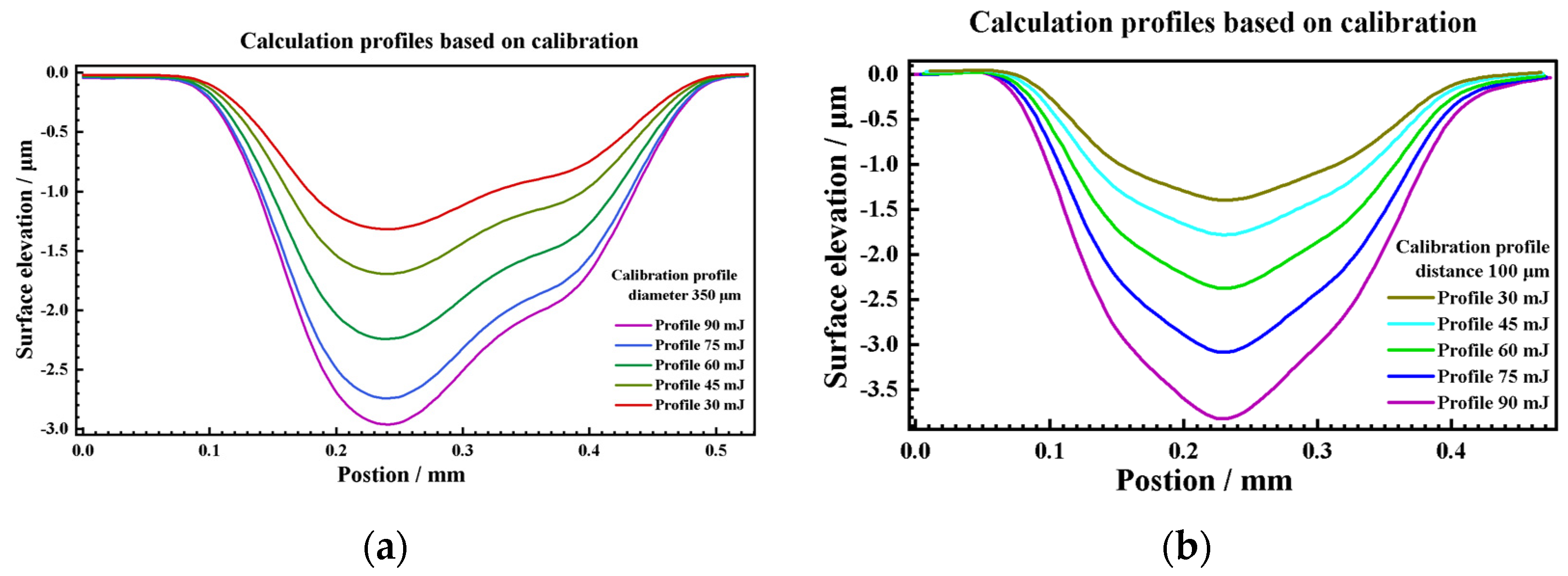
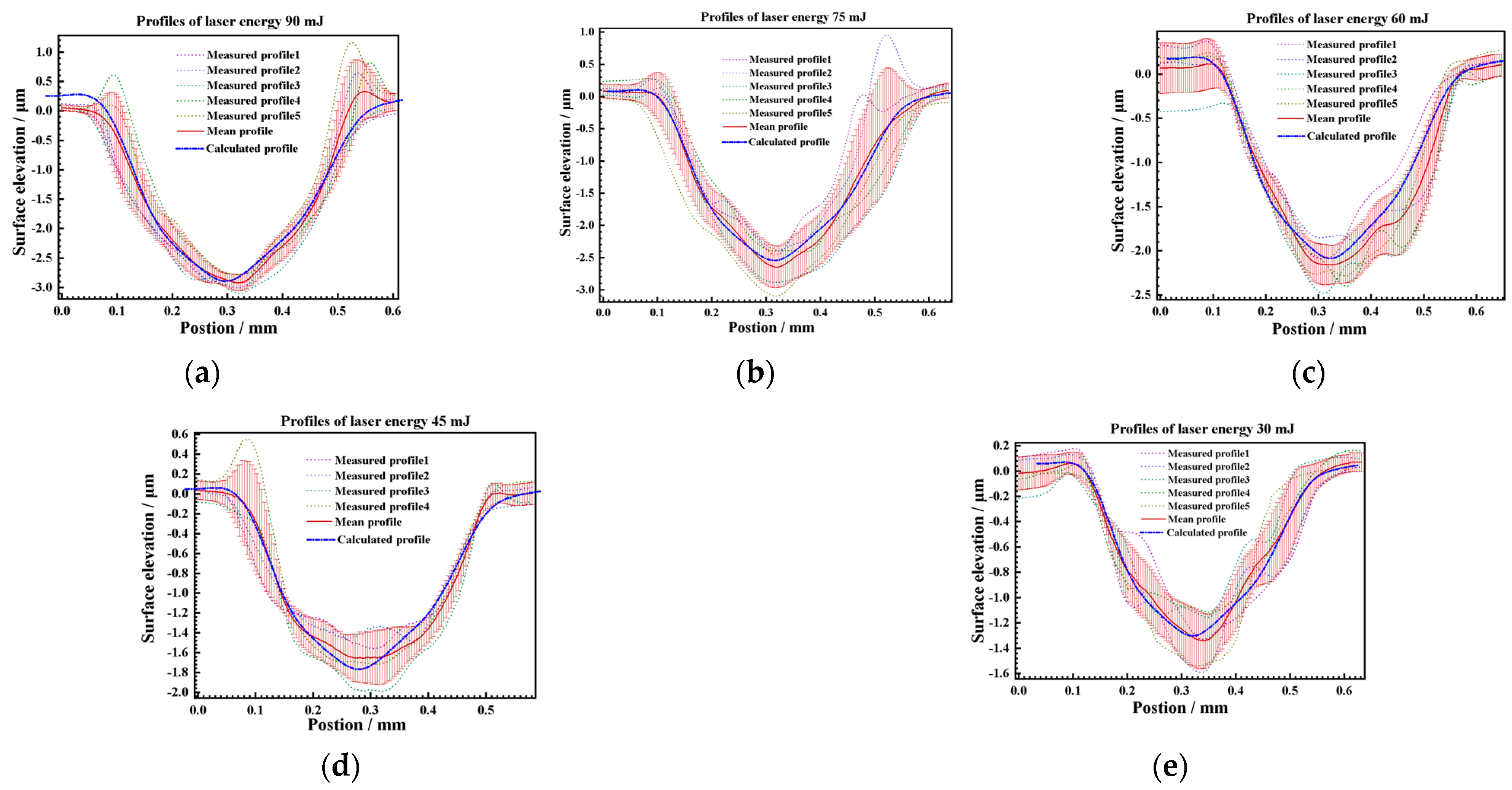
3.2.2. 3D Texture Modeling and Verification
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The spot diameter, energy density, and distribution can precisely control the macro-structural parameters of the LSPTwC crater texture and the micro-texture structure inside the crater. Therefore, LSPwC can be fully applied to controllable and designable laser surface texturing, i.e., the innovative LSPTwC technology proposed in this paper is feasible.
- (2)
- LSPTwC also has both physical and chemical effects, such as ablation, impact, remelting, and heat treatment, which can change the chemical composition, microstructure, metallographic structure, etc., of the surface material, thus forming a strengthening effect. For AISI 9310 steel, LSPTwC increases the microhardness by more than 10% with only 9.6% coverage and produces a gradient structure and a reticulated carburic organization that extends to the surface, demonstrating the technological advantages of texturizing and strengthening.
- (3)
- Based on the fitting of the experimental data, the characteristic parameters of the LSPTwC crater texture can be identified more accurately, and a higher-accuracy computational model can be constructed. Based on the calibrated profile curves with higher energy density, the textured surface models with different LSPTwC parameters can be constructed more accurately with a diameter deviation of <3% and a depth deviation of <4%. The above results can provide a design method and calculation model for single-point LSPwC crater texturing and its process parameter design of AISI 9310 steel parts for helicopters, which has engineering value.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| coefficient of maximum width | |
| coefficient of maximum depth | |
| , | maximum depth regulation interval |
| calculated elevation of profile (μm) | |
| original elevation of surface (μm) | |
| x | calculated position (μm) |
| polar transverse coordinates (μm) | |
| surface roughness (μm) | |
| calculated length (mm) | |
| Z | elevation of rough peaks and valleys (μm) |
| laser energy density (mJ.mm−2) | |
| E | laser energy (mJ) |
| d | spot diameter (μm) |
| , | width relative to the vertex of the calibrated profile (μm) |
| , | width increment relative to the vertex of the calibrated profile (μm) |
| , | maximum depth of calculated and calibrated profile (μm) |
| depth of calibrated profile (μm) | |
| D1~D5 | LSPTwC parameter of different spot diameters |
Abbreviations
| LST | laser surface texturing |
| LSP | laser shock peening |
| LSPwC | laser shock peening without coating |
| LSPTwC | laser surface texturing by laser shock peening without coating |
| LOL | loss of lubrication |
| OM | optical microscope |
| SEM | scanning electron microscope |
| AFM | atomic force microscope |
References
- Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Parker, R.G. Effects of Lubrication on Gear Performance: A Review. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 145, 103701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, S. Nonlinear Tribo-Dynamic Model and Experimental Verification of a Spur Gear Drive under Loss-of-Lubrication Condition. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 153, 107509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Mao, S.; Cao, X.; Bao, H.; Zhu, R. Multi-Time Scale Thermal Tribological Dynamics Coupling Model of the Helicopter Intermediate Reducer under Severe Loss of Lubrication. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2024, 132, 102884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, H.S.J.; Place, C.S.; Mba, D.; Keong, R.L.C.; Healey, A.; Kleine-Beek, W.; Romano, M. Reliability Model for Helicopter Main Gearbox Lubrication System Using Influence Diagrams. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 139, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, H.S.J.; Place, C.S.; Mba, D.; Lim, R.; Healey, A.; Kleine-Beek, W.; Romano, M. Helicopter MGB Oil System Failure Analysis Using Influence Diagrams and Random Failure Probabilities. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2015, 50, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yang, S.; Zheng, M. Analysis of Synergistic Friction Reduction Effect on Micro-Textured Cemented Carbide Surface by Laser Processing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 155, 108343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgornik, B.; Vilhena, L.M.; Sedlaček, M.; Rek, Z.; Žun, I. Effectiveness and Design of Surface Texturing for Different Lubrication Regimes. Meccanica 2012, 47, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morhard, B.; Lohner, T.; Stahl, K. Influence of Surface and Material Technologies on the Loss of Lubrication Performance of Gears. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng. 2024, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.M.; Jing, Y.; Zhao, F. Self-Adaptive Surface Texture Design for Friction Reduction across the Lubrication Regimes. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2015, 4, 014004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zeng, X.; Igartua, A.; Rodriguez-Vidal, E.; Van Der Heide, E. Texture Design for Reducing Tactile Friction Independent of Sliding Orientation on Stainless Steel Sheet. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, J.; An, B.; Li, R. The Design Method for Surface Texture of Sliding Friction Pairs Based on Machine Learning under Mixed Lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2024, 194, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, M.; Kumar, P.; Murtaza, Q. Surface Texturing Techniques to Enhance Tribological Performance: A Review. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 27, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, Y. Laser Peening without Coating as a Surface Enhancement Technology. JLMN 2006, 1, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trdan, U.; Porro, J.A.; Ocaña, J.L.; Grum, J. Laser Shock Peening without Absorbent Coating (LSPwC) Effect on 3D Surface Topography and Mechanical Properties of 6082-T651 Al Alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 208, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Keller, S.; Chang, Y.; Kashaev, N.; Yan, K.; Gurevich, E.L.; Ostendorf, A. Effect of Laser Shock Peening without Protective Coating on the Surface Mechanical Properties of NiTi Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 896, 163011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, T.; Pan, X.; Liu, P. Research on Wear Resistance of AISI 9310 Steel with Micro-Laser Shock Peening. Metals 2022, 12, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhao, T.; He, P.; Zhou, L.; Pan, X.; Liang, X.; Jia, W.; An, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, H. Effect of Pulsed Femtosecond Laser Shock Peening Surface Modification on Anti-Wear Failure Properties of AISI 9310 Gear Steel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 159, 108146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Luo, S.; Liang, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhao, W.; Pu, C.; He, W. Rolling Contact Fatigue and Damage Characteristic of AISI 9310 Steel with Pre-Laser Shock Peening Treatment. Int. J. Fatigue 2022, 155, 106588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wei, P.; Su, L.; Liu, H.; Wei, D.; Zhang, X.; Deng, G. Rolling-Sliding Contact Fatigue Failure and Associated Evolutions of Microstructure, Crystallographic Orientation and Residual Stress of AISI 9310 Gear Steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 170, 107511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hereñú, S.; Strubbia, R.; Rubio-González, C.; Spadaro, L.; Bolmaro, R.; Gomez-Rosas, G. High Cycle Fatigue Life Improvement of Superferritic Stainless Steel by Laser Shock Peening without Coating. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 152, 108083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, T.R.; Shivananda Nayaka, H.; Swaroop, S.; Gopi, K.R. Strength Enhancement of Magnesium Alloy through Equal Channel Angular Pressing and Laser Shock Peening. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 512, 145755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; He, W.; Zhu, D.; Liang, X.; Pang, Z.; Song, J.; Luo, S. Comparative Investigation on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of GH4169 Superalloy after Laser Shock Peening with and without Coating. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ma, T.; Gong, J.; Chen, T.; Zhou, L.; Cai, Z. Effect of Laser Shock Peening without Coating on Fretting Wear Behavior of GH4169 Superalloy at High-Temperature. Wear 2024, 546, 205349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Jiao, J.; Zhou, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Ren, X. Improvement in Cavitation Erosion Resistance of AA5083 Aluminium Alloy by Laser Shock Processing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 377, 124799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Xin, Z.; Zhou, W.; Ye, Y.; Ren, X. Dual Protection against Electrochemical Corrosion for AA5083 Al Alloys: Synergistic Action of Superhydrophobicity and Strain-Strengthening. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 472, 129945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radil, K.; Berkebile, S. Failure Progression of Spur Gears during a Simulated Loss-of-Lubrication Event in a Rotorcraft Drive System. Tribol. Trans. 2020, 63, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.G.H. Advances in Steels for Aerospace Applications. Key Eng. Mater. 1992, 77, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, J.; Grabowski, J.; Snyder, D. New High Performance Gear Steels for Rotorcraft Transmission Applications (Ferrium® C61TM and Ferrium C64TM). In Proceedings of the Volume 5: 25th International Conference on Design Theory and Methodology; ASME 2013 Power Transmission and Gearing Conference; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: Portland, OR, USA, 2013; p. V005T11A009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Yu, Z.; Pan, X.; Wang, R.; Xie, C. Improving Tension Fatigue Performance of Gray Cast Iron by LSPwC-Induced Gradient Structure and Carbon Diffusion. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 31, 3580–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhao, W.; Sun, T.; Xie, L. Enhancing the Wear Resistance of PCD Tools in Cutting Cf/SiC Materials through Low-Energy Laser Shock Peening. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 486, 130951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Liang, X.; Luo, S.; Li, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Tian, Z.; He, W. Surface Strengthening and Fatigue Life Improvement of Single Crystal Ni-Based Superalloys via Laser Shock Peening without Coating. Mater. Des. 2023, 232, 112097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, B.; Zhang, A.; Han, J.; Meng, J. The Tribological Properties of Carbon Doped Al0.2Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5 High Entropy Alloys. Wear 2021, 484–485, 204045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, A. Mechanical and tribological properties of amorphous carbon films. Tribol. Lett. 1998, 5, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Meng, X.; Wang, Z.; Lv, J.; Luo, K.; Lu, J. Progressive Developments, Challenges and Future Trends in Laser Shock Peening of Metallic Materials and Alloys: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2023, 191, 104061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, R.; Hu, C.; Zhong, M.; Wan, X.; Wu, K. Grain Refinement Strengthening Mechanism of an Austenitic Stainless Steel: Critically Analyze the Impacts of Grain Interior and Grain Boundary. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 2999–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, P.; Li, W.; Ma, F.; Guo, Z.; Rong, Y. Enhancement of the Strength and Ductility of Martensitic Steels by Carbon. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 716, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kučerová, L.; Jirková, H.; Mašek, B. The Effect of Alloying on Mechanical Properties of Advanced High Strength Steels. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2014, 59, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, G.; Liu, D.; Wang, P. Progress in Applications of Shockwave Induced by Short Pulsed Laser on Surface Processing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 157, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ren, X.; Yang, Y.; Tong, Z.; Asuako Larson, E. Finite Element Analysis of Laser Shock Peening Induced Near-Surface Deformation in Engineering Metals. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 119, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| C | Mn | Si | Cr | Ni | Mo | Al | O | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 1.3 | 2.7 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0 | 94.88 |
| C | Mn | Si | Cr | Ni | Mo | Al | O | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.2 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 3.1 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0 | 89.7 |
| Parameter ID | Spot Diameter (μm) | Cols Spacing (μm) | Line Spacing (μm) | Laser Energy (mJ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 350 | 1000 | 1000 | 90 |
| D2 | 450 | 1000 | 1000 | 90 |
| D3 | 550 | 1000 | 1000 | 90 |
| D4 | 650 | 1000 | 1000 | 90 |
| D5 | 750 | 1000 | 1000 | 90 |
| Spot Diameter (μm) | 350 | 450 | 550 | 650 | 750 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density (mJ/mm2) | 936 | 566 | 379 | 271 | 204 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Yang, Z.; Xie, C.; Yang, F.; Zhou, L. Control and Modelling of Laser Shock Peening without Coating (LSPwC) Texture of AISI 9310 Steel. Materials 2024, 17, 4776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17194776
Liu P, Yang Z, Xie C, Yang F, Zhou L. Control and Modelling of Laser Shock Peening without Coating (LSPwC) Texture of AISI 9310 Steel. Materials. 2024; 17(19):4776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17194776
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ping, Zhandiao Yang, Cenchao Xie, Fei Yang, and Liucheng Zhou. 2024. "Control and Modelling of Laser Shock Peening without Coating (LSPwC) Texture of AISI 9310 Steel" Materials 17, no. 19: 4776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17194776
APA StyleLiu, P., Yang, Z., Xie, C., Yang, F., & Zhou, L. (2024). Control and Modelling of Laser Shock Peening without Coating (LSPwC) Texture of AISI 9310 Steel. Materials, 17(19), 4776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17194776








