SEM Analysis and Micro-CT Evaluation of Four Dental Implants after Three Different Mechanical Requests—In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Implants
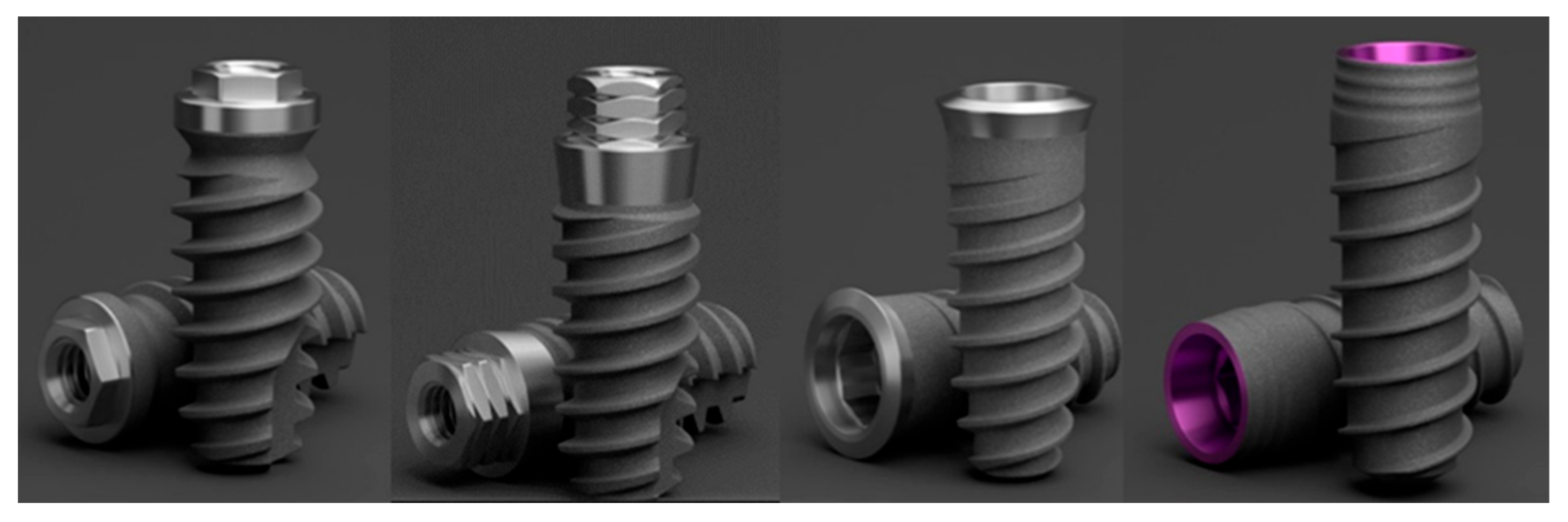

2.2. Sample Size
2.3. Mechanical Request
| Connection System | Mechanical Request | Sample Code |
|---|---|---|
| SK2® | Control | S |
| Vega® | Control | V |
| KL® | Control | K |
| Essential® | Control | E |
| SK2® | Single Tightening | SU |
| Vega® | Single Tightening | VU |
| KL® | Single Tightening | KU |
| Essential® | Single Tightening | EU |
| SK2® | Multiple Tightening | SM |
| Vega® | Multiple Tightening | VM |
| KL® | Multiple Tightening | KM |
| Essential® | Multiple Tightening | EM |
| SK2® | Multiple Tightening + Cyclic load. | SMC |
| Vega® | Multiple Tightening + Cyclic load. | VMC |
| KL® | Multiple Tightening + Cyclic load. | KMC |
| Essential® | Multiple Tightening + Cyclic load. | EMC |
2.4. SEM Evaluation
2.5. Residual Stress
2.6. Scratch Test
2.7. Micro-CT Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis: MICRO-CT
3. Results
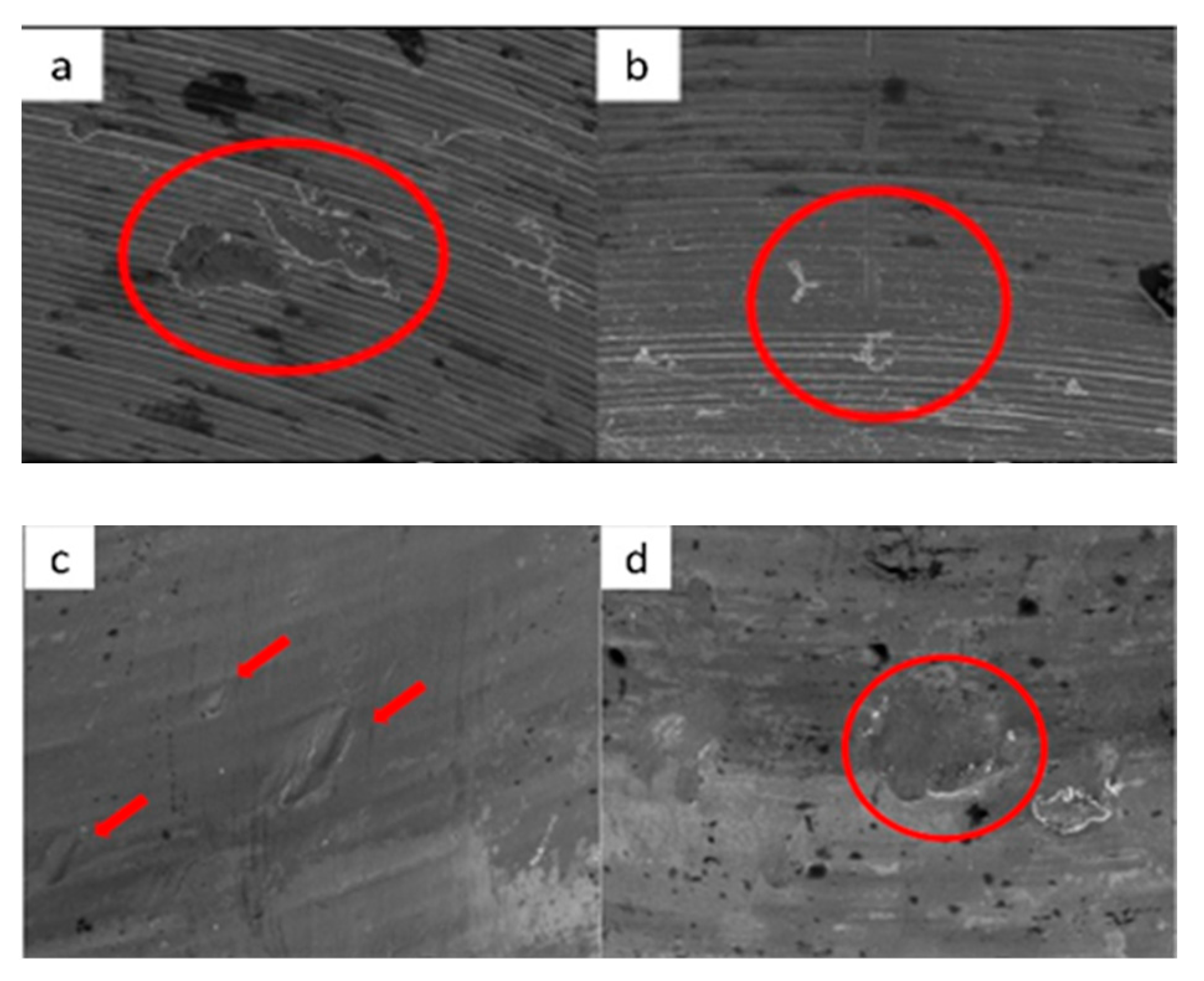
3.1. SEM
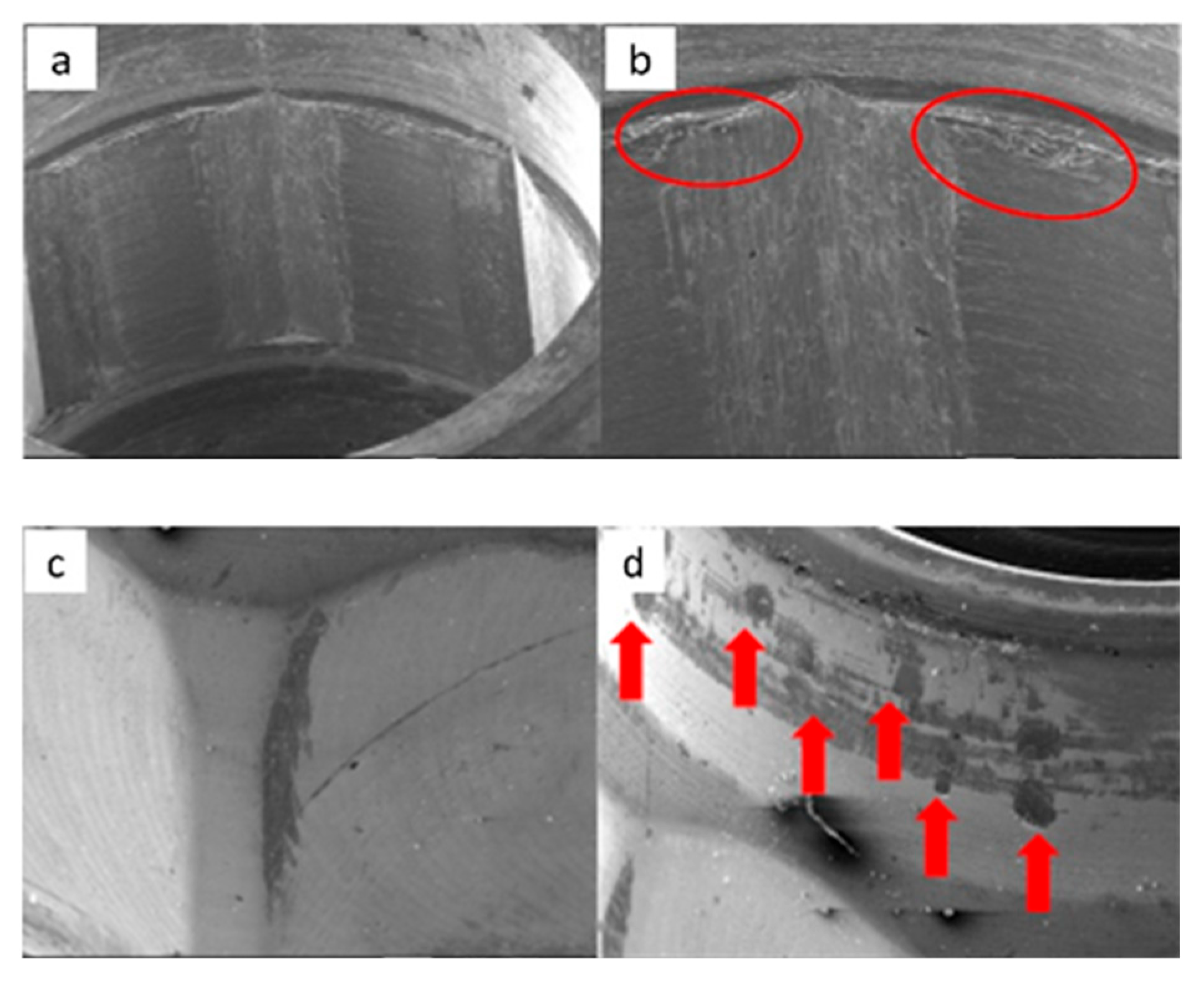
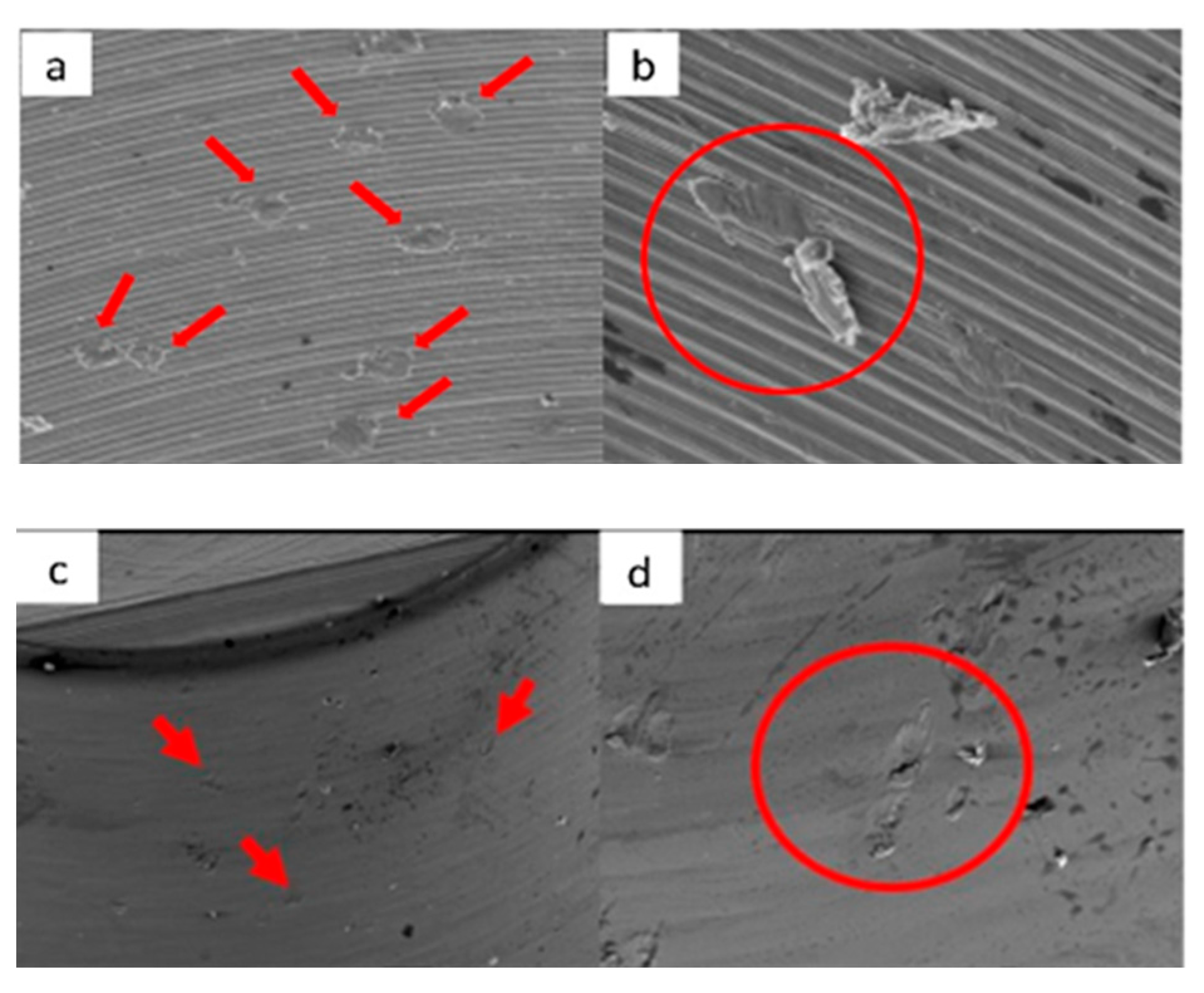
3.1.1. KL Implants
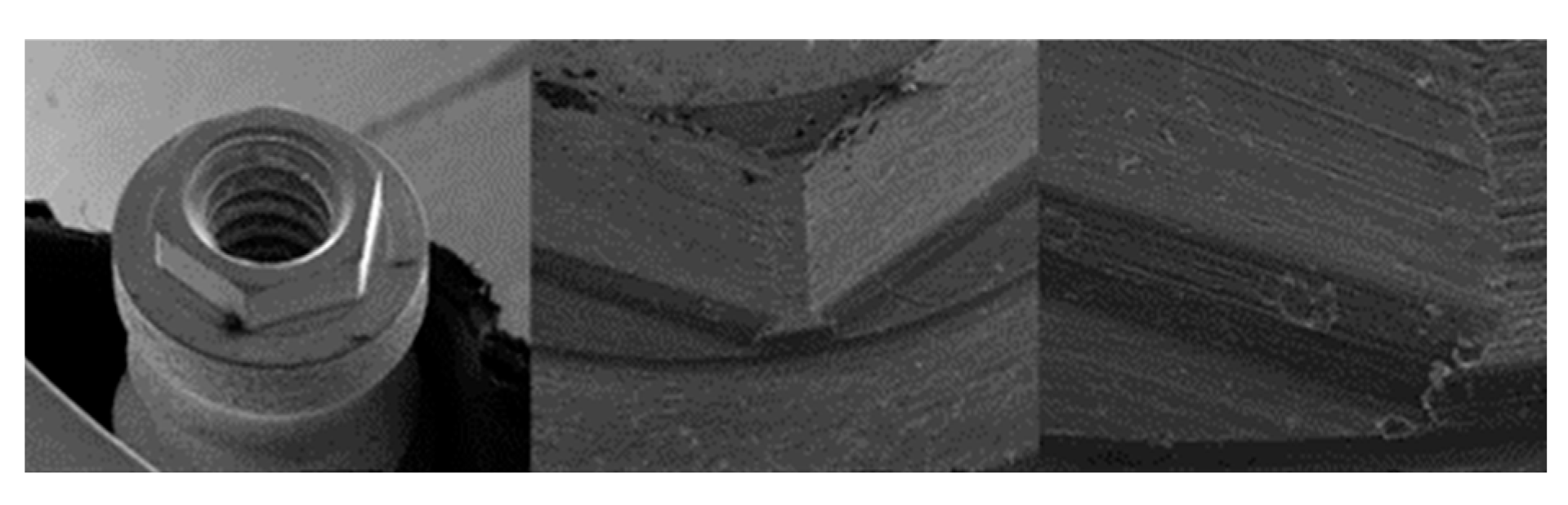
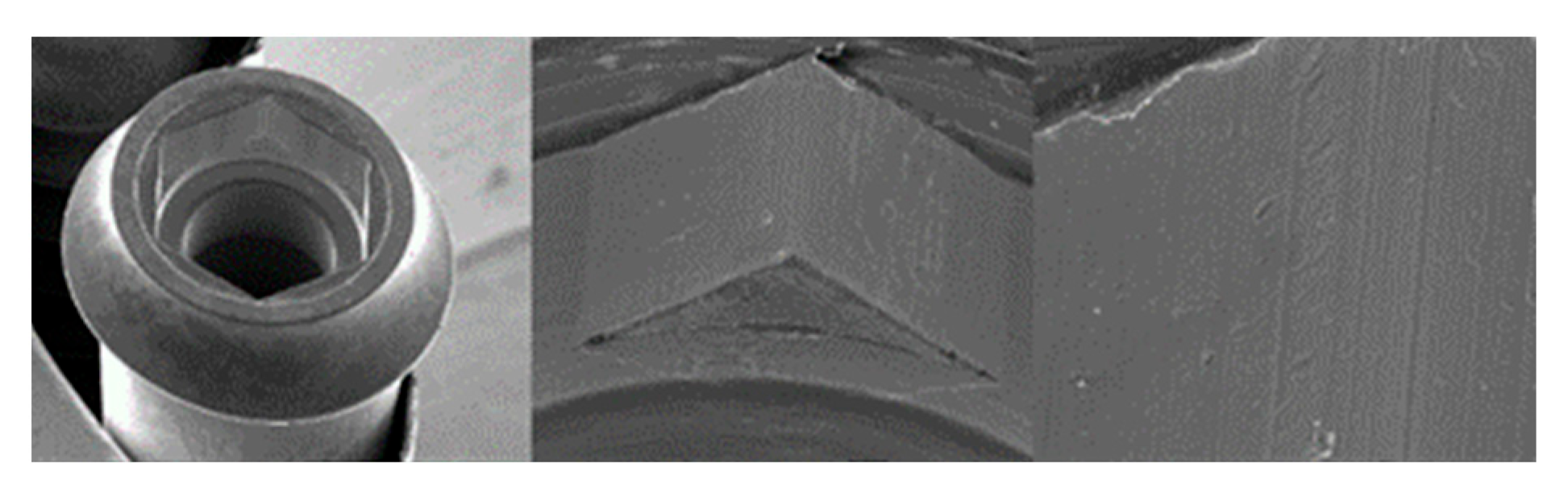


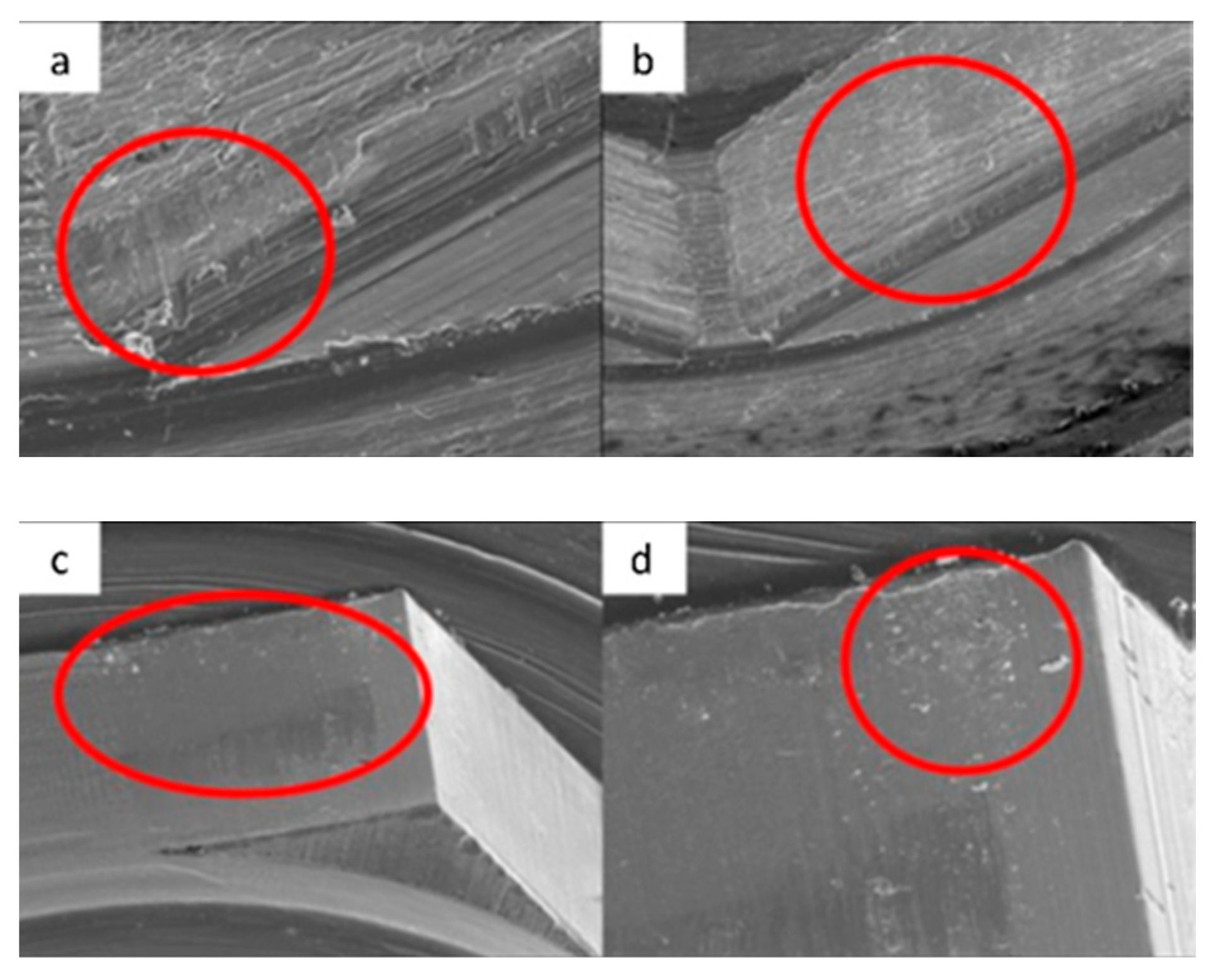

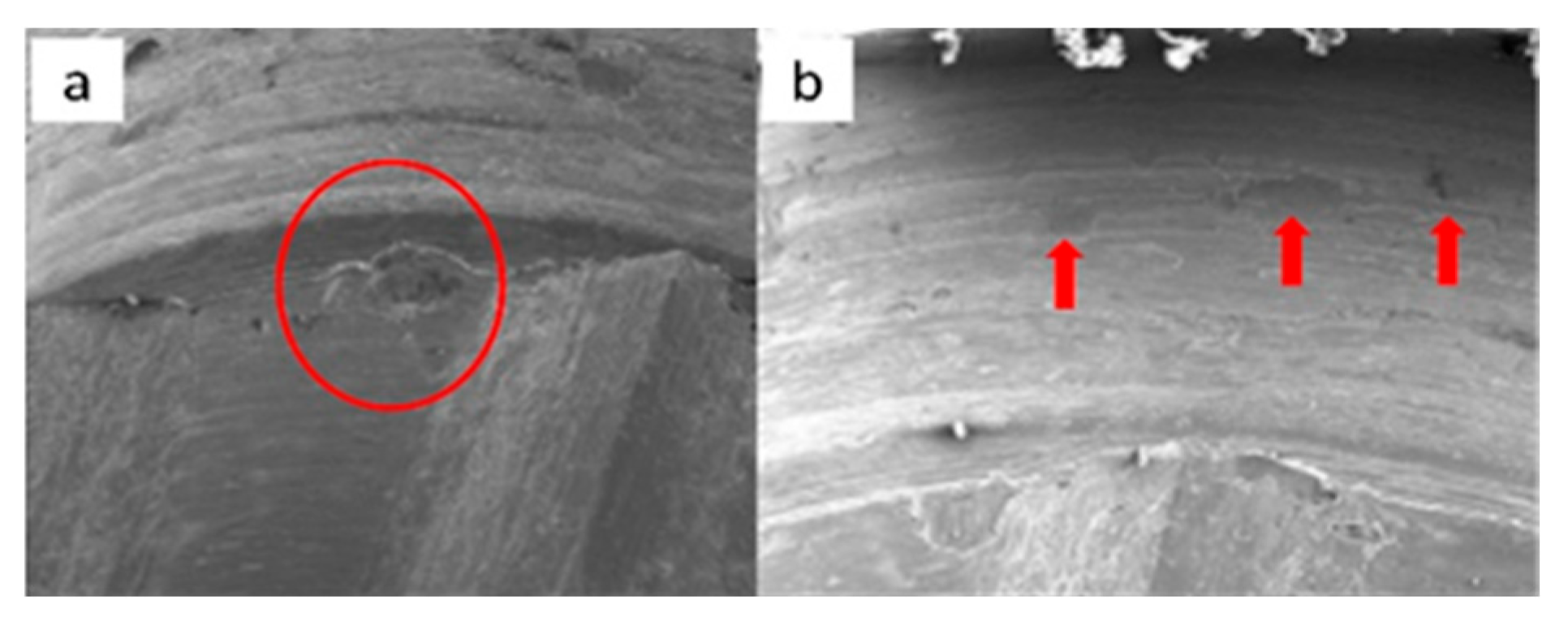
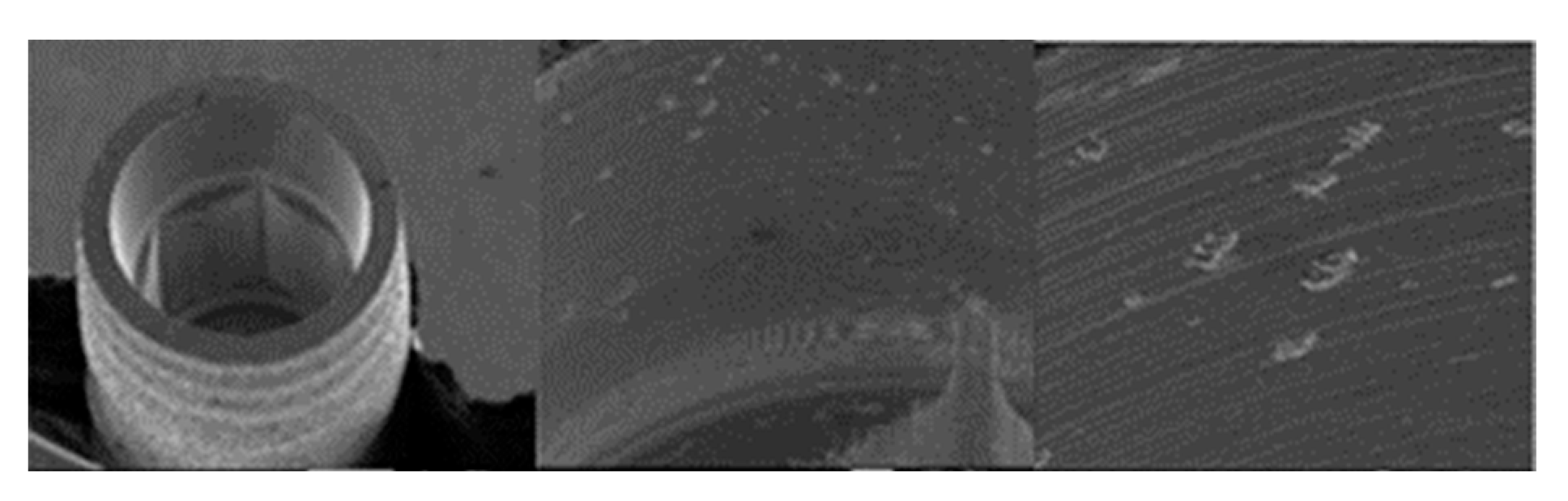
3.1.2. Essential Implants
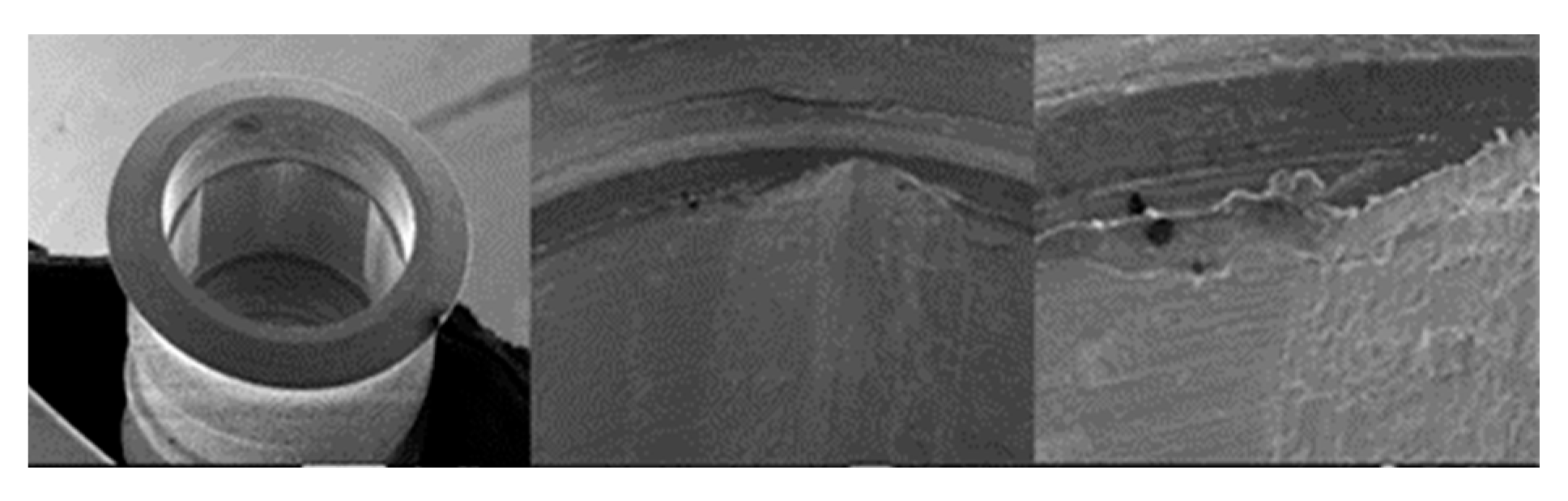
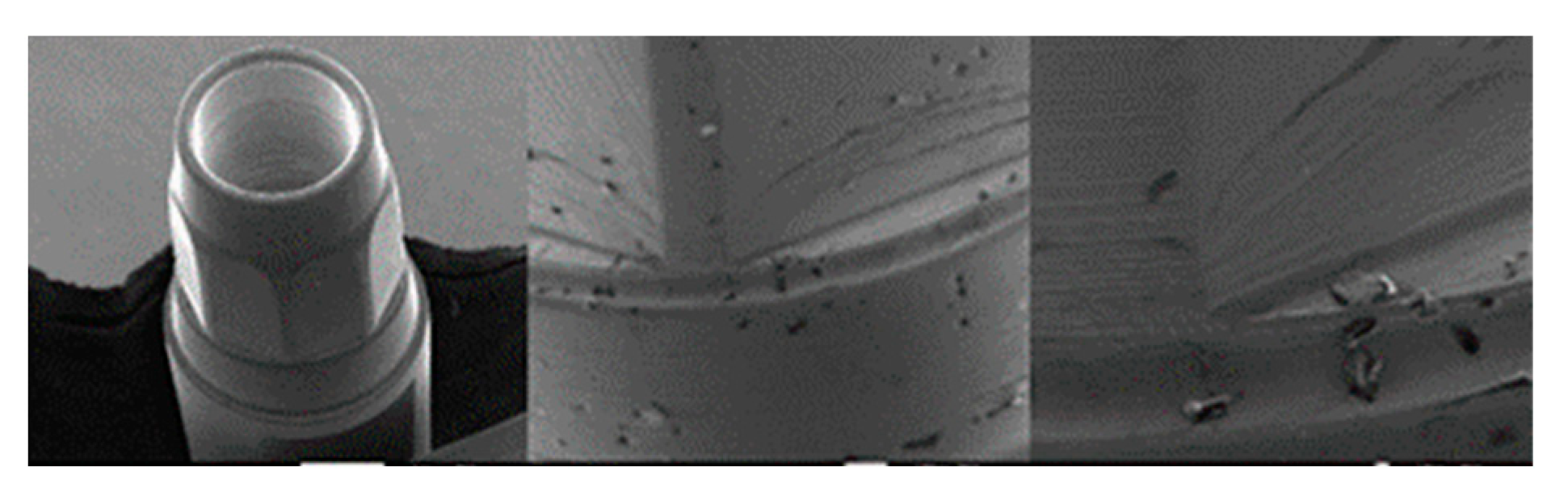


3.1.3. SK2 Implants

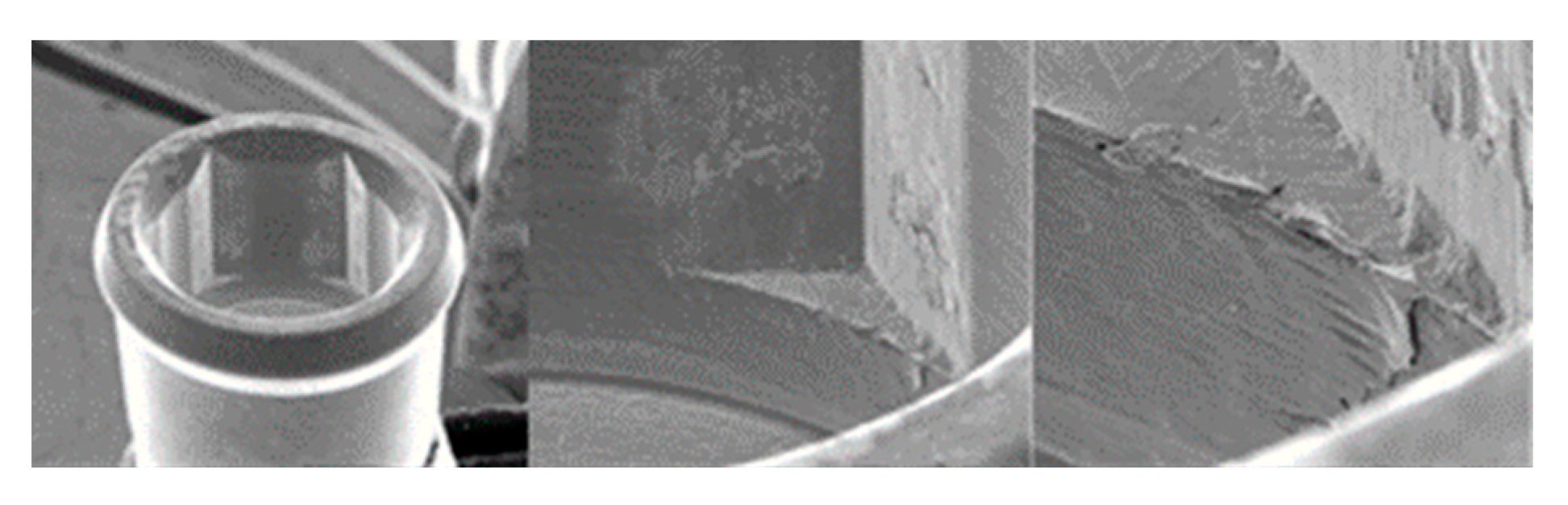



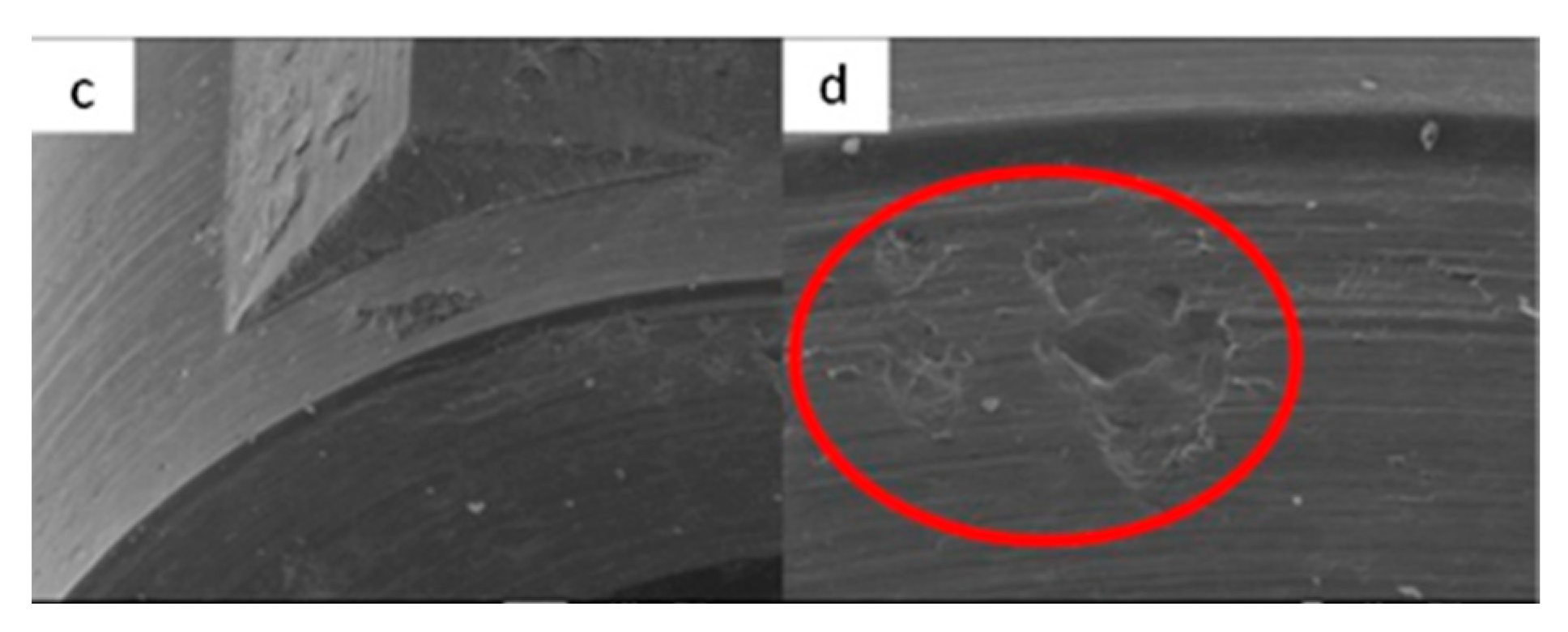
3.1.4. Vega Implants


3.2. Residual Stress
3.3. Scratch Test
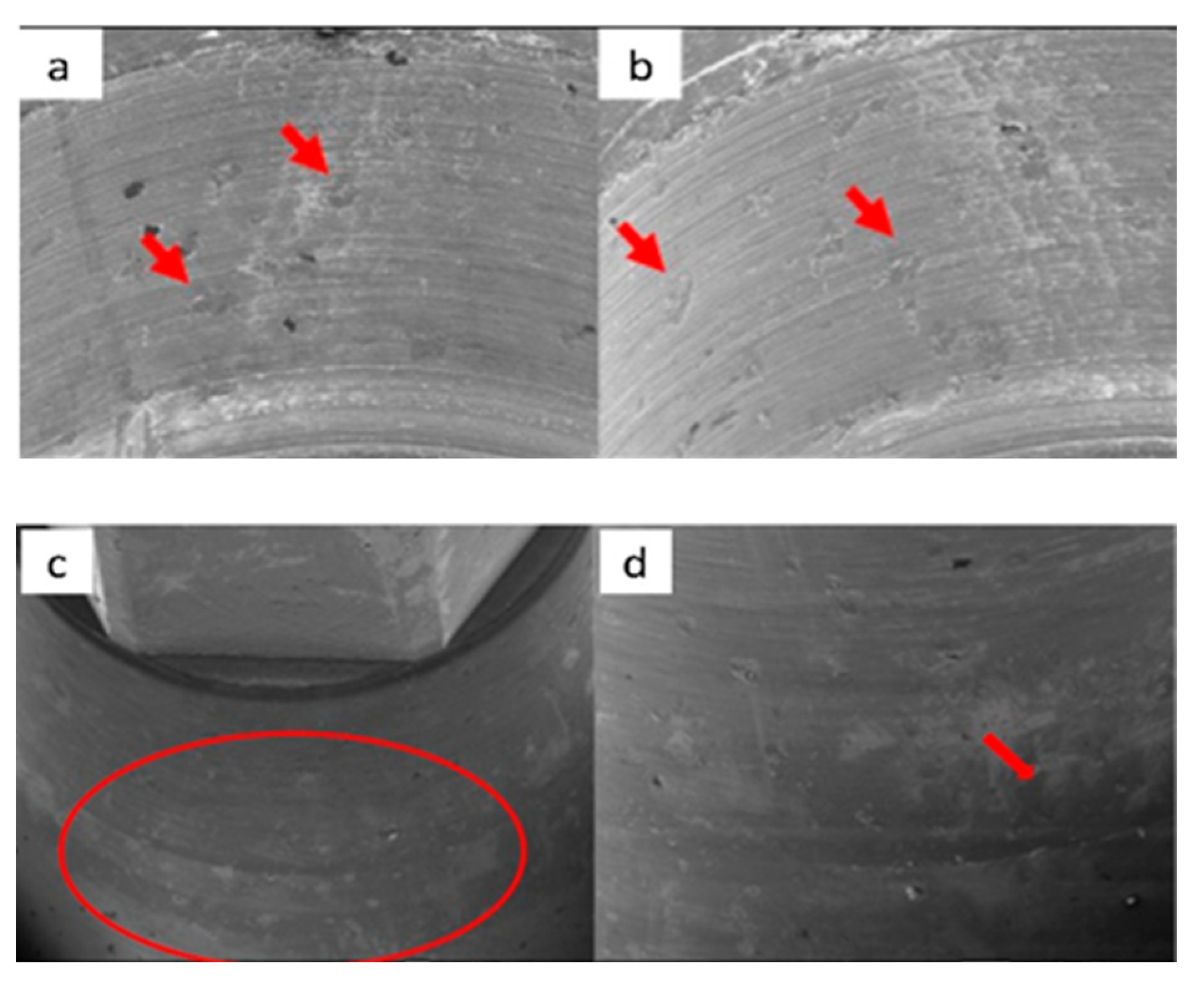
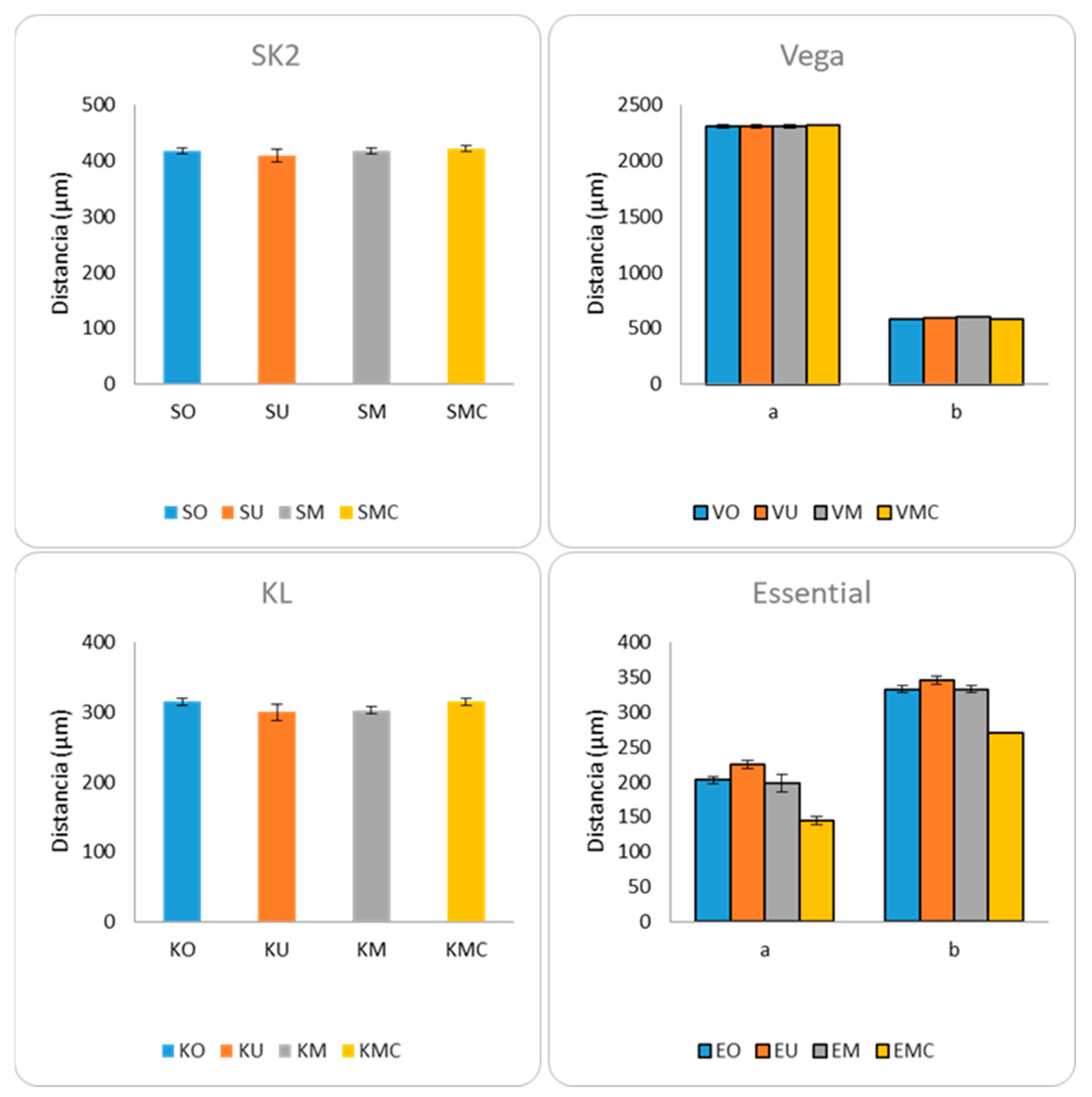
3.4. Micro-CT


| Model | Measure | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| SK2 | a | 0.403 |
| Vega | a | 0.871 |
| b | 0.020 | |
| KL | a | 0.052 |
| Essential | a | 0.005 |
| b | 0.008 |
4. Discussion
4.1. SEM Evaluation
4.2. Micro-CT Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oh, T.J.; Yoon, J.; Misch, C.E.; Wang, H.L. The causes of early implant bone loss: Myth or science? J. Periodontol. 2002, 73, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, S.; Cehreli, M.C. The significance of passive framework fit in implant prosthodontics: Current status. Implant. Dent. 2001, 10, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goiato, M.C.; Pellizzer, E.P.; da Silva, E.V.; Bonatto Lda, R.; dos Santos, D.M. Is the internal connection more efficient than external connection in mechanical, biological, and esthetical point of views? A systematic review. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 19, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas-Junior, A.C.; Almeida, E.O.; Bonfante, E.A.; Silva, N.R.; Coelho, P.G. Reliability and failure modes of internal conical dental implant connections. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, C.M.; Nogueira-Filho, G.; Tenenbaum, H.C.; Lai, J.Y.; Brito, C.; Doering, H.; Nonhoff, J. Performance of conical abutment (Morse Taper) connection implants: A systematic review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2014, 102, 552–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkaya, D.; Muftu, S. Mechanics of the tapered interference fit in dental implants. J. Biomech. 2003, 36, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailey, B.; Jordan, L.; Blind, O.; Tavernier, B. Axial displacement of abutments into implants and implant replicas, with the tapered cone-screw internal connection, as a function of tightening torque. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, C.Y.; Lim, Y.J.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, J.H. The influence of abutment angulation on screw loosening of implants in the anterior maxilla. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2011, 26, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.G.; Park, C.J.; Cho, L.R. Axial displacements in external and internal implant-abutment connection. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2014, 25, e83–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, H.W.; Heo, S.J.; Koak, J.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.K. Axial Displacement of External and Internal Implant-Abutment Connection Evaluated by Linear Mixed Model Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2015, 30, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Nicholls, J.; Rubenstein, J. Tolerance Measurements of Various Implant Components. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1997, 12, 371–375. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, S.; Ring, K.; Ring, J.D.; Boberick, K.G. Implant screw mechanics and the settling effect: Overview. J. Oral Implantol. 2003, 29, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.H.; Huh, Y.H.; Park, C.J.; Cho, L.R. Axial Displacement in Cement-Retained Prostheses with Different Implant-Abutment Connections. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019, 34, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merz, B.R.; Hunenbart, S.; Belser, U.C. Mechanics of the implant-abutment connection: An 8-degree taper compared to a butt joint connection. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2000, 15, 519–526. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, M.S. Mechanical complications of dental implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2000, 11 (Suppl. 1), 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi Coppedê, A.; De Mattos, M.D.G.C.; Rodrigues, R.C.S.; Ribeiro, R.F. Effect of repeated torque/mechanical loading cycles on two different abutment types in implants with internal tapered connections: An in vitro study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piermatti, J.; Yousef, H.; Luke, A.; Mahevich, R.; Weiner, S. An in vitro analysis of implant screw torque loss with external hex and internal connection implant systems. Implant. Dent. 2006, 15, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siamos, G.; Winkler, S.; Boberick, K.G. Relationship between implant preload and screw loosening on implant-supported prostheses. J. Oral Implantol. 2002, 28, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, P.M.; Schneider, R.L.; Schneider, G.B.; Stanford, C.M.; Clancy, J.M.; Qian, F. In vitro analysis of post-fatigue reverse-torque values at the dental abutment/implant interface for a unitarian abutment design. J. Prosthodont. 2011, 20, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinhas, A.S.; Aroso, C.; Salazar, F.; Relvas, M.; Braga, A.C.; Ríos-Carrasco, B.; Gil, J.; Rios-Santos, J.V.; Fernández-Palacín, A.; Herrero-Climent, M. In Vitro Study of Preload Loss in Different Implant Abutment Connection Designs. Materials 2022, 15, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14801:2016; Dentistry-Implants Dynamic Loading Test for Endosseous Dental Imlants. International Standard, 3rd ed. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; Jiménez-Guerra, A.; Ortiz, I.; Moreno-Muñoz, J.; Nuñez-Marquez, E.; Pequeroles, M.; Perez, R.A.; Gil, F.J. Importance of the roughness and residual stresses of dental implants on fatigue and osseointegration be-havior. In vivo study in rabbits. J. Oral Implantol. 2016, 42, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegueroles, M.; Aparicio, C.; Bosio, M.; Engel, E.; Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A.; Altankov, G. Spatial Organization of Osteoblast Fi-bronectin-Matrix on Titanium Surface—Effects of Roughness, Chemical Heterogeneity, and Surface Free Energy. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, F.J.; Herrero, M.; Lázaro, P.; Rios, J.V. Implant-abutment connections: Influence of the design on the microgap and their fatigue and fracture behavior of dental implants. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzenakis, G.K.; Nagy, W.W.; Fournelle, R.A.; Dhuru, V.B. The effect of repeated torque and salivary contamination on the preload of slotted gold implant prosthetic screws. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2002, 88, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzaitis, K.L.; Knoernschild, K.L.; Viana, M.A. Effect of repeated screw joint closing and opening cycles on implant prosthetic screw reverse torque and implant and screw thread morphology. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2011, 106, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, M.; Rohanian, A.; Monzavi, A.; Nazari, M.S. Evaluation of the accuracy and related factors of the mechanical torque-limiting device for dental implants. J. Dent. 2013, 10, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Khraisat, A.; Hashimoto, A.; Nomura, S.; Miyakawa, O. Effect of lateral cyclic loading on abutment screw loosening of an external hexagon implant system. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 91, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuge, T.; Hagiwara, Y. Influence of lateral-oblique cyclic loading on abutment screw loosening of internal and external hexagon implants. Dent. Mater. J. 2009, 28, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colling, E.W. The Physical Metallurgy of Titanium Alloys; American Society for Metals: Metals Park, OH, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio, C.; Gil, F.J.; Fonseca, C.; Barbosa, M.; Planell, J.A. Corrosion behaviour of commercially pure titanium shot blasted with different materials and sizes of shot blasted with different materials and sizes of shot particles for dental implant applications. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, R.; Welsh, G.; Collings, E.W. (Eds.) Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, F.J. The effect of shot blasting and heat treatment on the fatigue behavior of titanium for dental implant applications. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 486–491. [Google Scholar]
- Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Padrós, E.; Planell, J.A. Applications of environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM) in biomaterials field. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 61, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagno, A.; di Bello, C. Surface Treatment and Roughness Properties of Ti-based Biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2004, 15, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, F.J.; Aparicio, C.; Manero, J.M.; Padrós, A. Influence of the height of the external hexagon and surface treatment on fatigue life of commercially pure titanium dental implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 583–590. [Google Scholar]
- Rack, T.; Zabler, S.; Rack, A.; Riesemeier, H.; Nelson, K. An In Vitro Pilot Study of Abutment Stability During Loading in New and Fatigue-Loaded Conical Dental Implants Using Synchrotron-Based Radiography. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.; Pereira, F. Changes in the Abutment-Implant Interface in Morse Taper Implant Connections After Mechanical Cycling: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Wiest, W.; Fella, C.; Balles, A.; Dittmann, J.; Rack, A.; Maier, D.; Thomann, R.; Spies, B.C.; Kohal, R.J.; et al. Fatigue induced changes in conical implant-abutment connections. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, M.W.; Taylor, T.D.; Goldberg, A.J. Wear at the Titanium-Zirconia Implant-Abutment Interface: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2011, 26, 970–975. [Google Scholar]
- Prisco, R.; Santagata, M.; Vigolo, P. Effect of Aging and Porcelain Sintering on Rotational Freedom of Internal-Hex One-Piece Zirconia Abutments. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gracis, S.; Michalakis, K.; Vigolo, P.; Vult von Steyern, P.; Zwahlen, M.; Sailer, I. Internal vs. external connections for abutments/reconstructions: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23 (Suppl. 6), 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh Saber, F.; Abolfazli, N.; Jannatii Ataei, S.; Taghizade Motlagh, M.; Gharekhani, V. The effect of repeated torque tightening on total lengths of implant abutments in different internal implant-abutment connections. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2017, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.R.; Huh, Y.H.; Park, C.J.; Cho, L.R. Effect of cyclic loading and retightening on reverse torque value in external and internal implants. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2015, 7, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosola, S.; Toti, P.; Babetto, E.; Covani, U.; Penarrocha-Diago, M.; Penarrocha-Oltra, D. In-vitro fatigue and fracture performance of three different ferrulized implant connections used in fixed prosthesis. J. Dent. Sci. 2021, 16, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosola, S.; Toti, P.; Babetto, E.; Covani, U.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D. In-vitro investigation of fatigue and fracture behavior of transmucosal versus submerged bone level implants used in fixed prosthesis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Residual Stress (MPa) | Scratch Force (mN) |
|---|---|---|
| S | −6.2 ± 1.3 | 159 ± 23 |
| V | −201.4 ± 14.3 * | 299 ± 18 * |
| K | −5.8 ± 0.9 | 150 ± 20 |
| E | −25.2 ± 6.2 ** | 198 ± 29 ** |
| SU | −6.0 ± 1.2 | 157 ± 20 |
| VU | −200.3 ± 10.0 * | 307 ± 19 * |
| KU | −5.5 ± 1.9 | 151 ± 32 |
| EU | −33.1 ± 7.2 ** | 190 ± 25 ** |
| SM | −5.9 ± 1.0 | 179 ± 24 |
| VM | −221.2 ± 32.0 * | 312 ± 28 * |
| KM | −6.3 ± 0.8 | 170 ± 20 |
| EM | −37.2 ± 6.2 ** | 201 ± 11 ** |
| SMC | −8.2 ± 1.9 | 189 ± 30 |
| VMC | −241.1 ± 14.3 * | 350 ± 38 * |
| KMC | −10.8 ± 2.1 | 185 ± 32 |
| EMC | −45.2 ± 7.8 ** | 218 ± 19 ** |
| Distance b | p-Value | Distance a | p-Value | Distance b | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VO vs. VU | 0.312 | EO vs. EU | 0.025 | EO vs. EU | 0.047 |
| VO vs. VM | 0.043 | EO vs. EM | 0.739 | EO vs. EM | 1 |
| VO vs. VMC | 0.386 | EO vs. EMC | 0.025 | EO vs. EMC | 0.023 |
| VU vs. VM | 0.058 | EU vs. EM | 0.027 | EU vs. EM | 0.047 |
| VU vs. VMC | 0.083 | EU vs. EMC | 0.027 | EU vs. EMC | 0.025 |
| VM vs. VMC | 0.03 | EM vs. EMC | 0.027 | EM vs. EMC | 0.023 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vinhas, A.S.; Salazar, F.; Mendes, J.M.; Silva, A.S.; Ríos-Carrasco, B.; Ríos-Santos, J.V.; Gil, J.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Aroso, C. SEM Analysis and Micro-CT Evaluation of Four Dental Implants after Three Different Mechanical Requests—In Vitro Study. Materials 2024, 17, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020434
Vinhas AS, Salazar F, Mendes JM, Silva AS, Ríos-Carrasco B, Ríos-Santos JV, Gil J, Herrero-Climent M, Aroso C. SEM Analysis and Micro-CT Evaluation of Four Dental Implants after Three Different Mechanical Requests—In Vitro Study. Materials. 2024; 17(2):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020434
Chicago/Turabian StyleVinhas, Ana Sofia, Filomena Salazar, José Manuel Mendes, António Sérgio Silva, Blanca Ríos-Carrasco, José Vicente Ríos-Santos, Javier Gil, Mariano Herrero-Climent, and Carlos Aroso. 2024. "SEM Analysis and Micro-CT Evaluation of Four Dental Implants after Three Different Mechanical Requests—In Vitro Study" Materials 17, no. 2: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020434
APA StyleVinhas, A. S., Salazar, F., Mendes, J. M., Silva, A. S., Ríos-Carrasco, B., Ríos-Santos, J. V., Gil, J., Herrero-Climent, M., & Aroso, C. (2024). SEM Analysis and Micro-CT Evaluation of Four Dental Implants after Three Different Mechanical Requests—In Vitro Study. Materials, 17(2), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020434













