Novel Magnesium Nanocomposite for Wire-Arc Directed Energy Deposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Casting
2.2. Extrusion

2.3. Ignitability
2.4. Wire-Arc Directed Energy Deposition
2.5. Microstructure, Calcium Content, Hardness, and Mechanical Characterization
3. Results
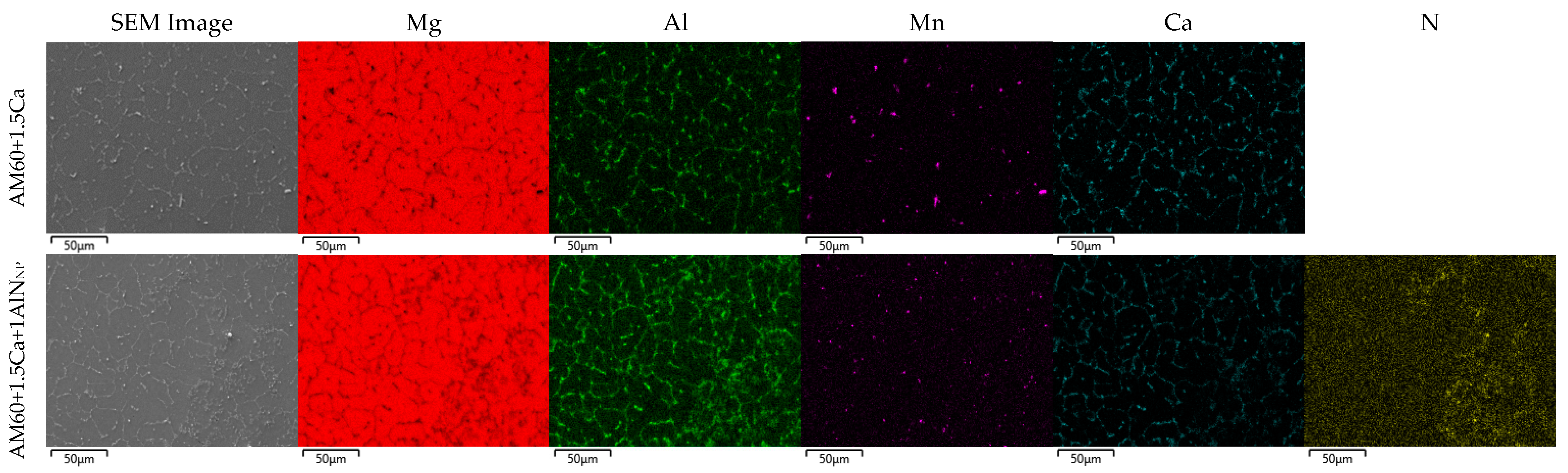
3.1. Microstructure and Hardness
3.2. Mechanical Properties in Tensile Tests
3.3. Ignitability of the Wires
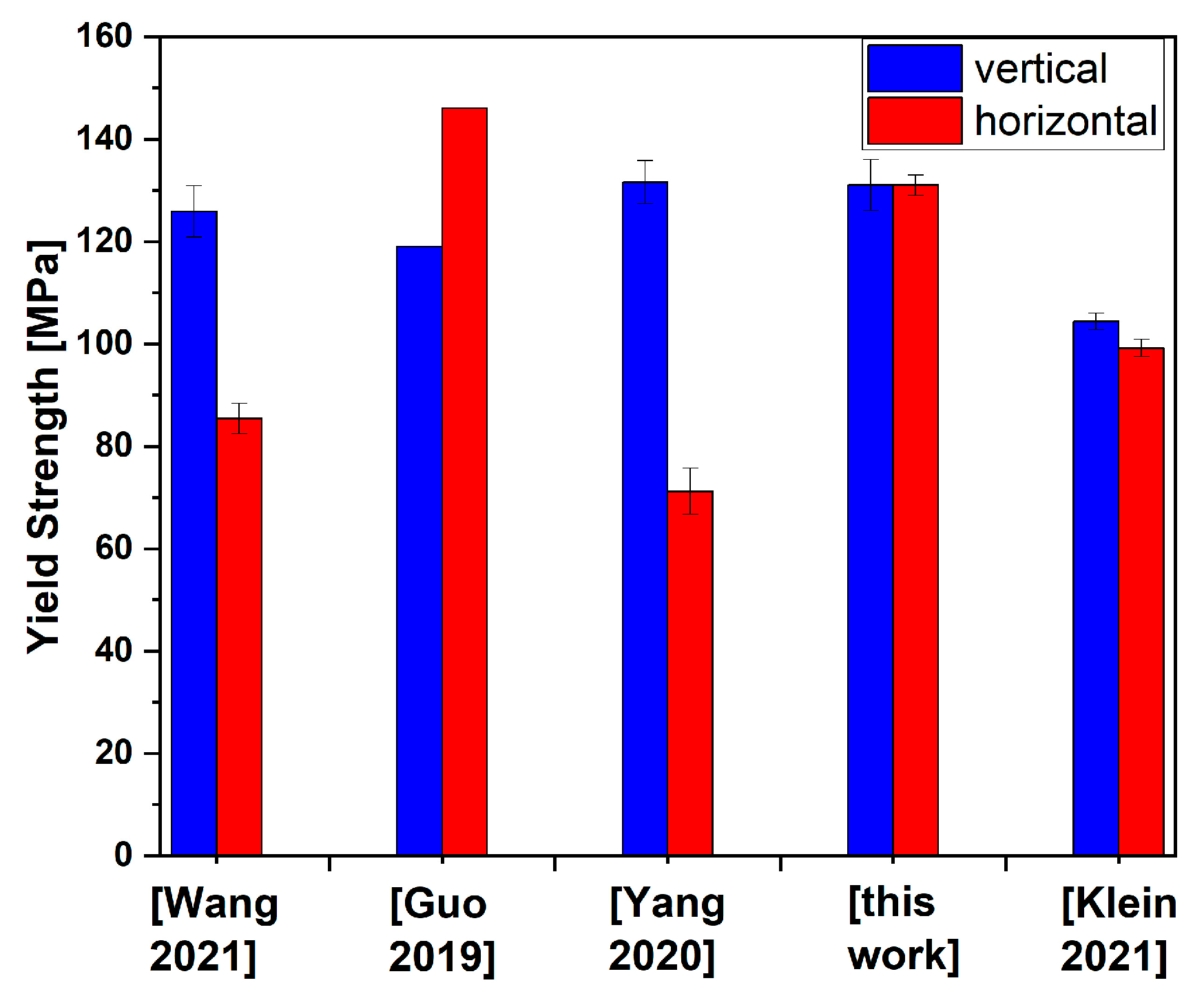
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karunakaran, R.; Ortgies, S.; Tamayol, A.; Bobaru, F.; Sealy, M.P. Additive manufacturing of magnesium alloys. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, T.; Rose, D.; Ranjbar, E.; Ghasri-Khouzani, M.; Tavakoli, M.; Henein, H.; Wolfe, T.; Jawad Qureshi, A. Large-scale metal additive manufacturing: A holistic review of the state of the art and challenges. Int. Mater. Rev. 2022, 67, 410–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Li, R.; Wu, Y.; Tu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Fu, P.; Peng, L.; Tang, H. Effect of multiple thermal cycles on the microstructure evolution of GA151K alloy fabricated by laser-directed energy deposition. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 57, 102957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, S.L.; An, J.; Yeong, W.Y.; Wiria, F.E. Laser and Electron-Beam Powder-Bed Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Implants: A Review on Processes, Materials and Designs. J. Orthop. Res. 2016, 34, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.; Arnoldt, A.; Schnall, M.; Gneiger, S. Microstructure Formation and Mechanical Properties of a Wire-Arc Additive Manufactured Magnesium Alloy. JOM 2021, 73, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, G.; Montevecchi, F.; Bandini, F.; Scippa, A.; Campatelli, G. Feature based three axes computer aided manufacturing software for wire arc additive manufacturing dedicated to thin walled components. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.; Lockett, H.; Ding, J.; Martina, F.; Marinelli, G.; Williams, S. A modular path planning solution for Wire + Arc Additive Manufacturing. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2019, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, G.; Spoerk-Erdely, P.; Maawad, E.; Burtscher, M.; Kiener, D.; Clemens, H.; Klein, T. Effect of wire-arc directed energy deposition on the microstructural formation and age-hardening response of the Mg-9Al-1Zn (AZ91) alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 11, 1944–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, M.I.; Glazkova, E.A.; Lozhkomoev, A.S.; Svarovskaya, N.V.; Bakina, O.V.; Pervikov, A.V.; Psakhie, S.G. Synthesis of Al nanoparticles and Al/AlN composite nanoparticles by electrical explosion of aluminum wires in argon and nitrogen. Powder Technol. 2016, 295, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Patel, J.B.; Yang, X.; Gavras, S.; Dieringa, H. Properties of Mg-based Metal Matrix Nanocomposites Processed by High Shear Dispersion Technique (HSDT)—A Review. Curr. Nanomater. 2021, 6, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienaber, M.; Yi, S.; Kainer, K.U.; Letzig, D.; Bohlen, J. On the Direct Extrusion of Magnesium Wires from Mg-Al-Zn Series Alloys. Metals 2020, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gneiger, S.; Koutný, D.; Senck, S.; Silmbroth, M.; Klein, T. Exploring the Benefits and Limitations of Wire-based Direct Energy Deposition of Magnesium Alloys. In Proceedings of the EUCASS-CEAS 2023 Conference, Ecublens, Switzerland, 9–13 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kondori, B.; Mahmudi, R. Effect of Ca additions on the microstructure, thermal stability and mechanical properties of a cast AM60 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 527, 2014–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltygin, A.V.; Bazhenov, V.E.; Belova, E.A.; Nikitina, A.A. Development of a magnesium alloy with good casting characteristics on the basis of Mg-Al-Ca-Mn system, having Mg-Al2Ca structure. J. Magn. Alloys 2013, 1, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, X. Grain Structure Evolution of Mg Alloy AM60 influenced by Ca Addition. Defect Diffus. Forum 2011, 312–315, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieringa, H.; Katsarou, L.; Buzolin, R.; Szakács, G.; Horstmann, M.; Wolff, M.; Mendis, C.; Vorozhtsov, S.; StJohn, D. Ultrasound Assisted Casting of an AM60 Based Metal Matrix Nanocomposite, Its Properties, and Recyclability. Metals 2017, 7, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulou, D.; Bohlen, J.; Ben Khalifa, N.; Dieringa, H. Influence of Extrusion Rate on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Magnesium Alloy AM60 and an AM60-Based Metal Matrix Nanocomposite. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienaber, M.; Braatz, M.; Ben Khalifa, N.; Bohlen, J. Property profile development during wire extrusion and wire drawing of magnesium alloys AZ31 and ZX10. Mater. Des. 2022, 224, 111355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froend, M.; Ventzke, V.; Dorn, F.; Kashaev, N.; Klusemann, B.; Enz, J. Microstructure by design: An approach of grain refinement and isotropy improvement in multi-layer wire-based laser metal deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Bohlen, J.; Dieringa, H. Effect of AlN nanoparticles added by intensive melt shearing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of an extruded AM60 magnesium alloy nanocomposite. In Proceedings of the Processing and Fabrication of Advanced Materials XXVII (PFAMXXVII), Jonkoping, Sweden, 27–29 May 2019; Paper 62. pp. 324–336. [Google Scholar]
- Czerwinski, F. The reactive element effect on high-temperature oxidation of magnesium. Int. Mater. Rev. 2015, 60, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinski, F. Controlling the ignition and flammability of magnesium for aerospace applications. Corros. Sci. 2014, 86, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, B.-S.; Park, W.-W.; Chung, I.-S. The effect of calcium additions on the oxidation behavior in magnesium alloys. Scr. Mater. 2000, 42, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Li, Q.; Feng, M. Wire-arc additive manufacturing of AZ31 magnesium alloy fabricated by cold metal transfer heat source: Processing, microstructure, and mechanical behavior. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 288, 116895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Pan, H.; Ren, L.; Quan, G. Microstructure and mechanical properties of wire arc additively manufactured AZ80M magnesium alloy. Mater. Lett. 2019, 247, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Lin, X.; Liu, F.; Huang, W.; Liang, E. Microstructure and mechanical properties of wire and arc additive manufactured AZ31 magnesium alloy using cold metal transfer process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 774, 138942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-S.; Sohn, I.; Nezafati, M.; Ferguson, J.B.; Schultz, B.F.; Bajestani-Gohari, Z.; Rohatgi, P.K.; Cho, K. Prediction models for the yield strength of particle-reinforced unimodal pure magnesium (Mg) metal matrix nanocomposites (MMNCs). J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 4191–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, D.L. Consideration of Orowan strengthening effect in particulate-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites: A model for predicting their yield strength. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.O. The deformation and Ageing of mild steel: III Discussion of Results. Phys. Soc. Sect. B 1951, 64, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petch, N.J. The Cleavage Strength of Polycrystals. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1953, 174, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
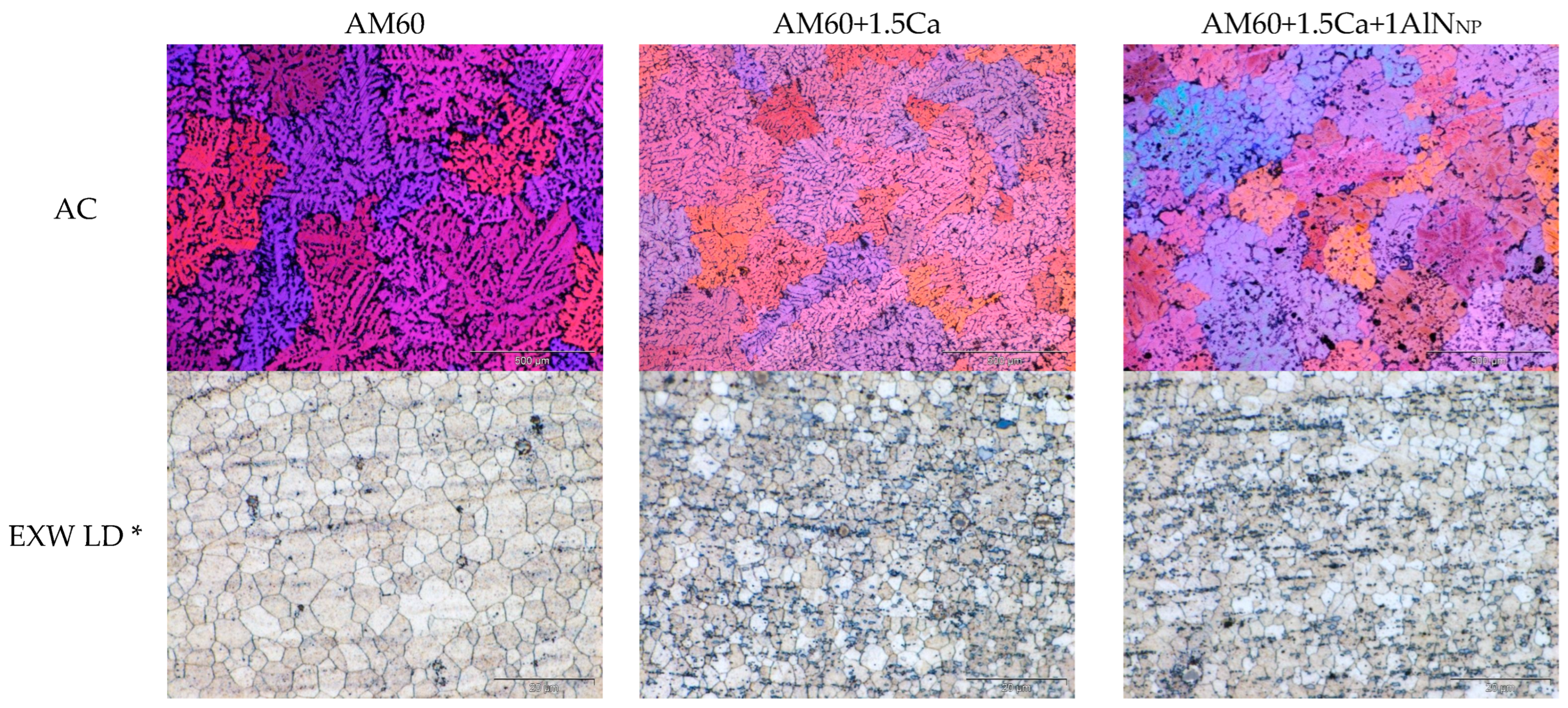
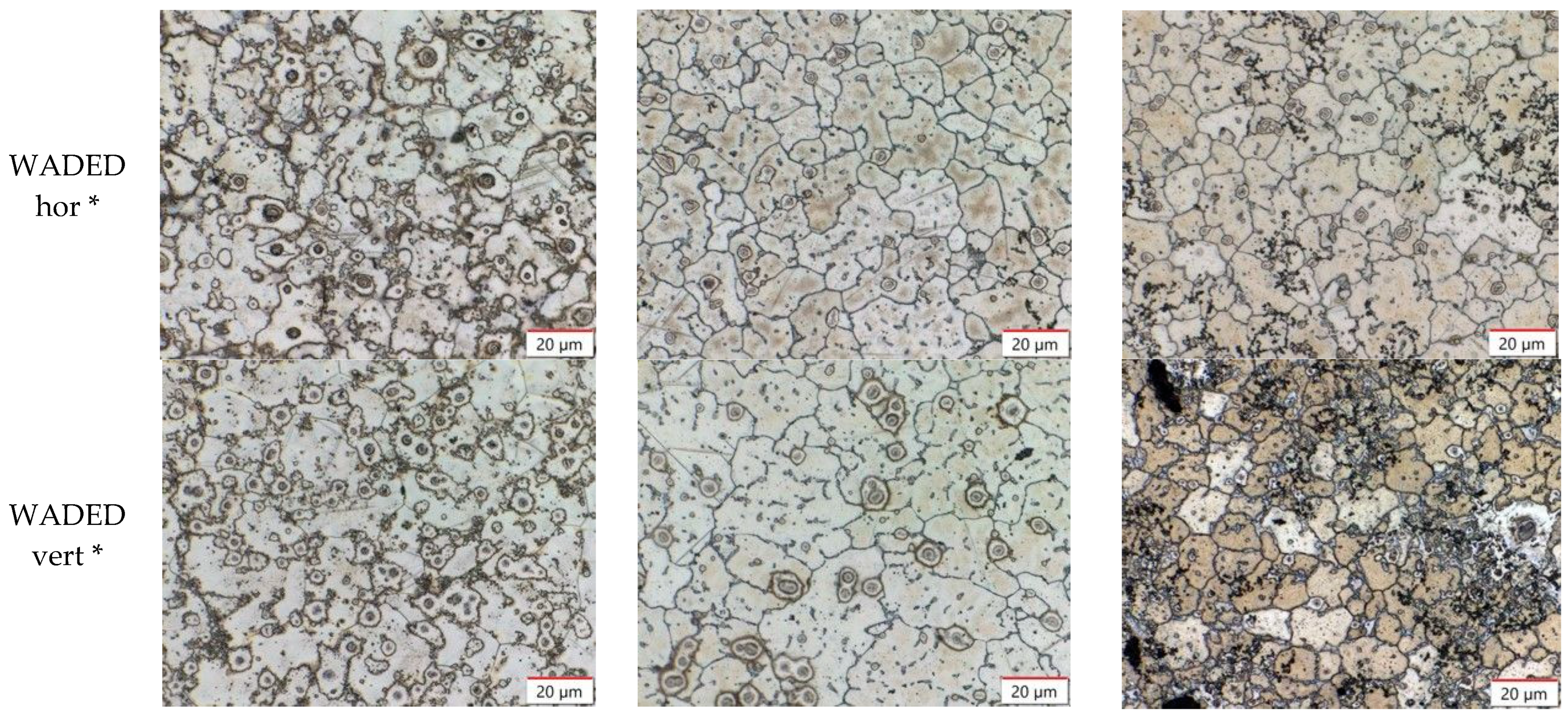

| AM60 | AM60+1.5Ca | AM60+1.5Ca+1AlNNP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC | GS: 457 ± 24 µm | GS: 363 ± 18 µm | GS: 372 ± 16 µm |
| HV5: 46.3 ± 2.2 | HV5: 54.1 ± 2.8 | HV5: 51.9 ± 8.9 | |
| EXW LD * | GS: 5.5 ± 0.3 µm | GS: 3.4 ± 0.1 µm | GS: 4.0 ± 0.1 µm |
| HV0.5: 70.4 ± 3.5 | HV0.5: 75.2 ± 2.2 | HV0.5: 74.8 ± 1.7 | |
| WADED hor * | GS: 18.4 ± 1.0 µm | GS: 18.1 ± 2.0 µm | GS: 18.3 ± 2.0 µm |
| HV0.5: 50.0 ± 1.0 | HV0.5: 60.8 ± 2.3 | HV0.5: 62.3 ± 2.2 | |
| WADED vert * | GS: 23.7 ± 2.0 µm | GS: 22.7 ± 3.0 µm | GS: 16.1 ± 1.0 µm |
| HV0.5: 50.0 ± 1.3 | HV0.5: 54.2 ± 1.1 | HV0.5: 60.4 ± 2.0 |
| Material | YS [MPa] | UTS [MPa] | εf [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM60—vertical | 121 ± 2 | 266 ± 5 | 10.9 ± 0.8 |
| AM60—horizontal | 126 ± 13 | 262 ± 4 | 9.9 ± 1.0 |
| AM60+1.5Ca—vertical | 116 ± 6 | 236 ± 4 | 6.5 ± 0.6 |
| AM60+1.5Ca—horizontal | 113 ± 5 | 221 ± 12 | 4.1 ± 1.3 |
| AM60+1.5Ca+1AlNNP—vertical | 131 ± 5 | 226 ± 4 | 4.3 ± 0.8 |
| AM60+1.5Ca+1AlNNP—horizontal | 131 ± 2 | 219 ± 8 | 3.1 ± 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dieringa, H.; Nienaber, M.; Giannopoulou, D.; Isakovic, J.; Bohlen, J.; Kujur, M.S.; Ben Khalifa, N.; Klein, T.; Gneiger, S. Novel Magnesium Nanocomposite for Wire-Arc Directed Energy Deposition. Materials 2024, 17, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020500
Dieringa H, Nienaber M, Giannopoulou D, Isakovic J, Bohlen J, Kujur MS, Ben Khalifa N, Klein T, Gneiger S. Novel Magnesium Nanocomposite for Wire-Arc Directed Energy Deposition. Materials. 2024; 17(2):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020500
Chicago/Turabian StyleDieringa, Hajo, Maria Nienaber, Danai Giannopoulou, Jonas Isakovic, Jan Bohlen, Milli Suchita Kujur, Noomane Ben Khalifa, Thomas Klein, and Stefan Gneiger. 2024. "Novel Magnesium Nanocomposite for Wire-Arc Directed Energy Deposition" Materials 17, no. 2: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020500
APA StyleDieringa, H., Nienaber, M., Giannopoulou, D., Isakovic, J., Bohlen, J., Kujur, M. S., Ben Khalifa, N., Klein, T., & Gneiger, S. (2024). Novel Magnesium Nanocomposite for Wire-Arc Directed Energy Deposition. Materials, 17(2), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020500









