Improving Mechanical Properties of Co-Cr-Fe-Ni High Entropy Alloy via C and Mo Microalloying
Abstract
:1. Introduction
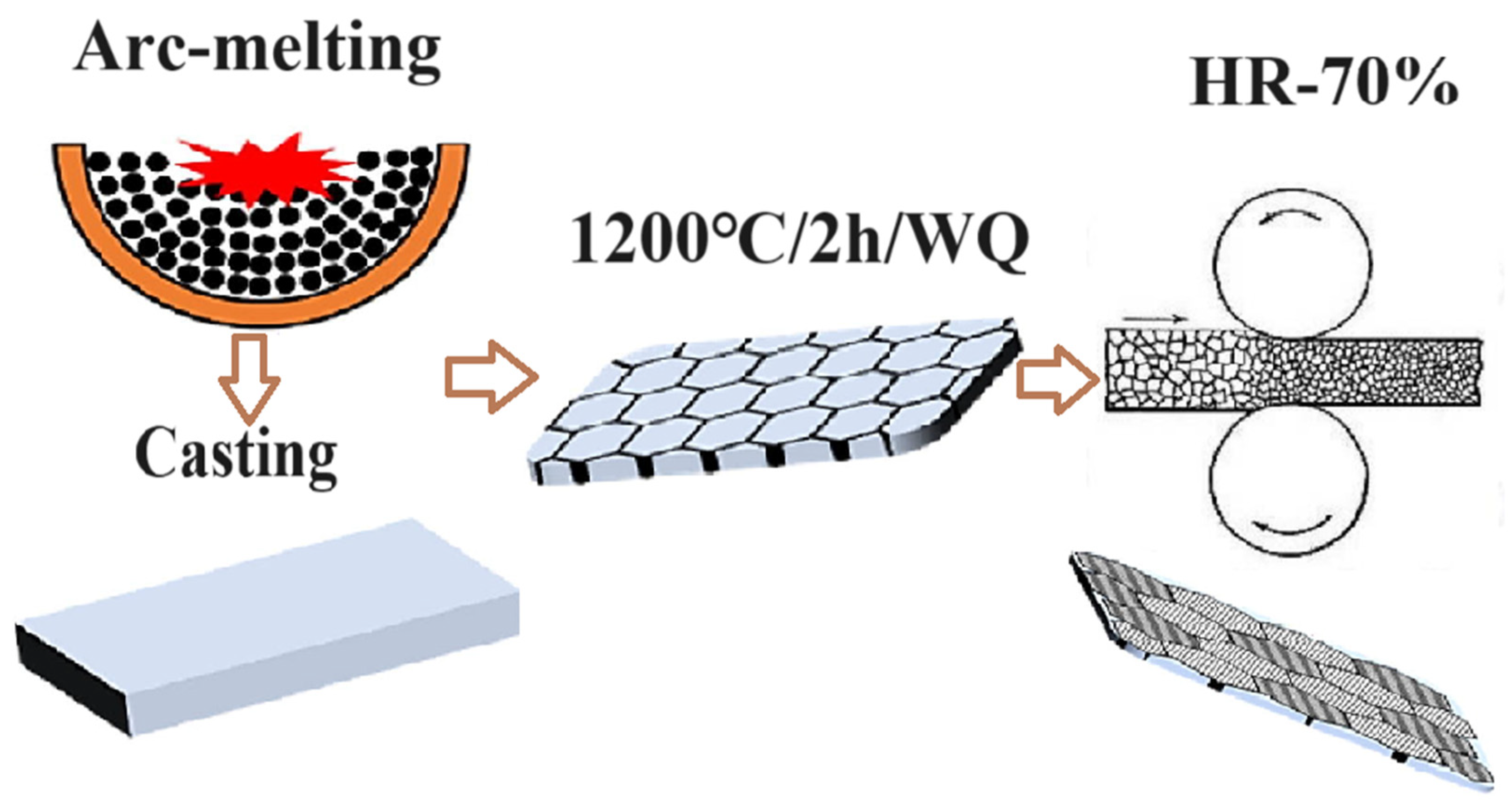
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
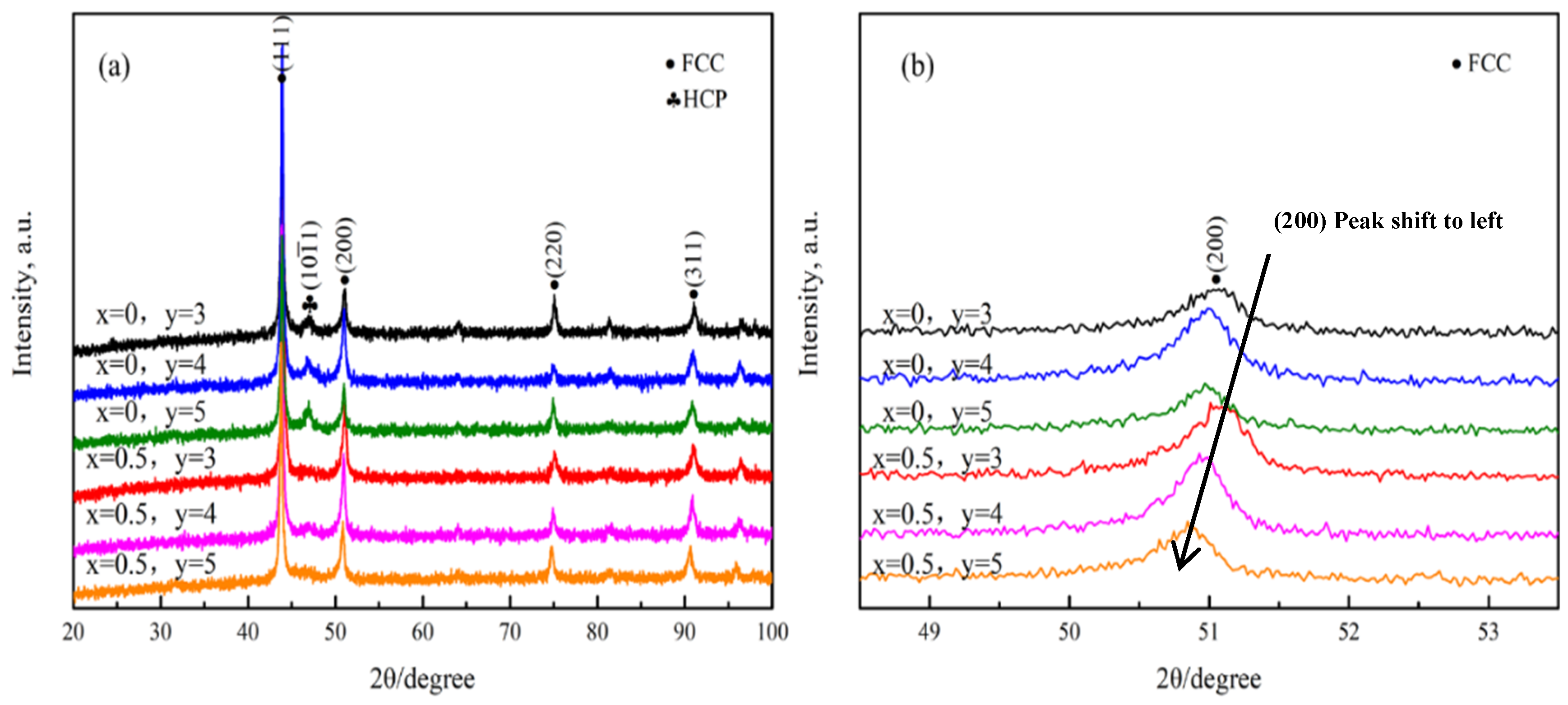
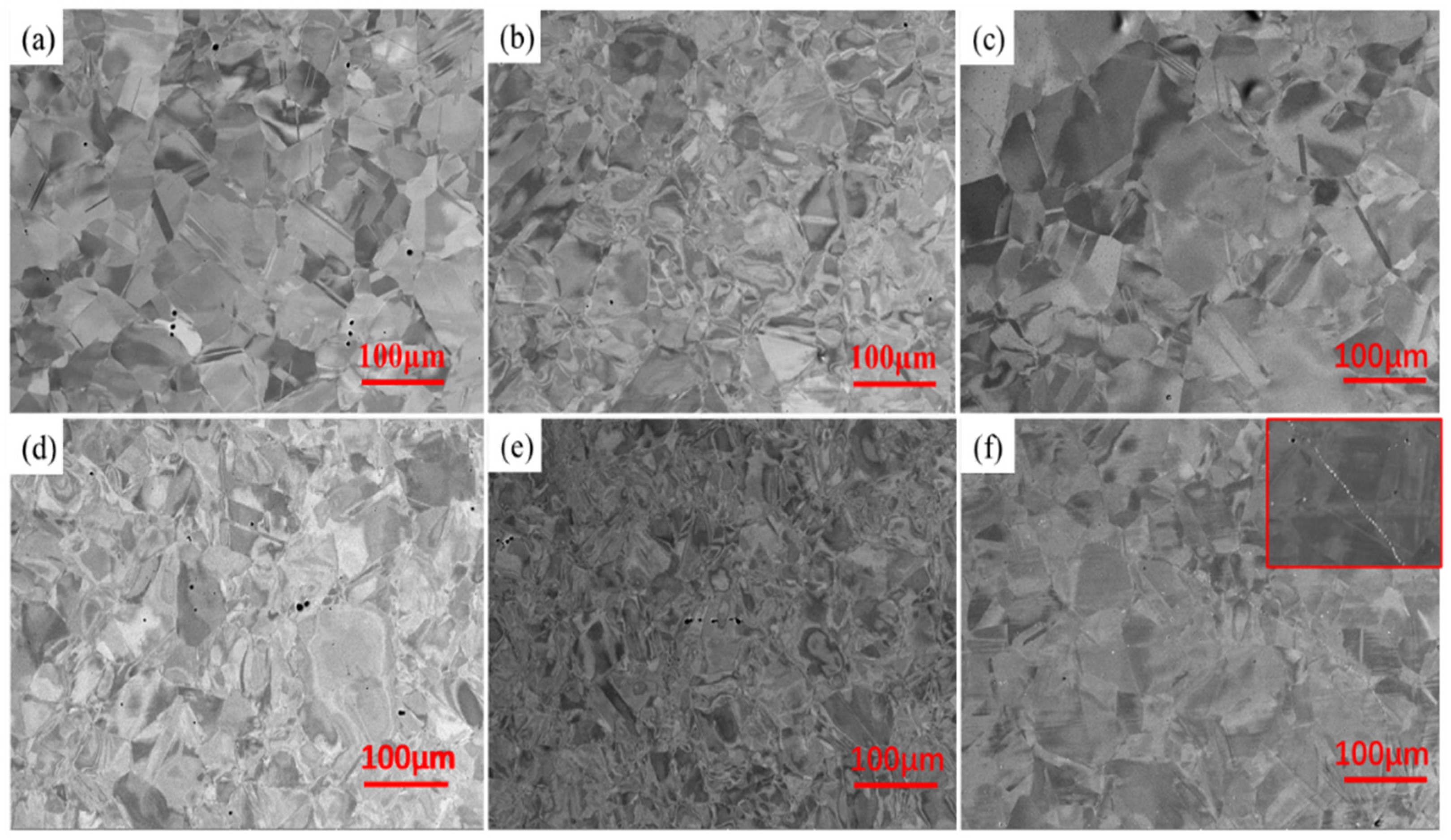
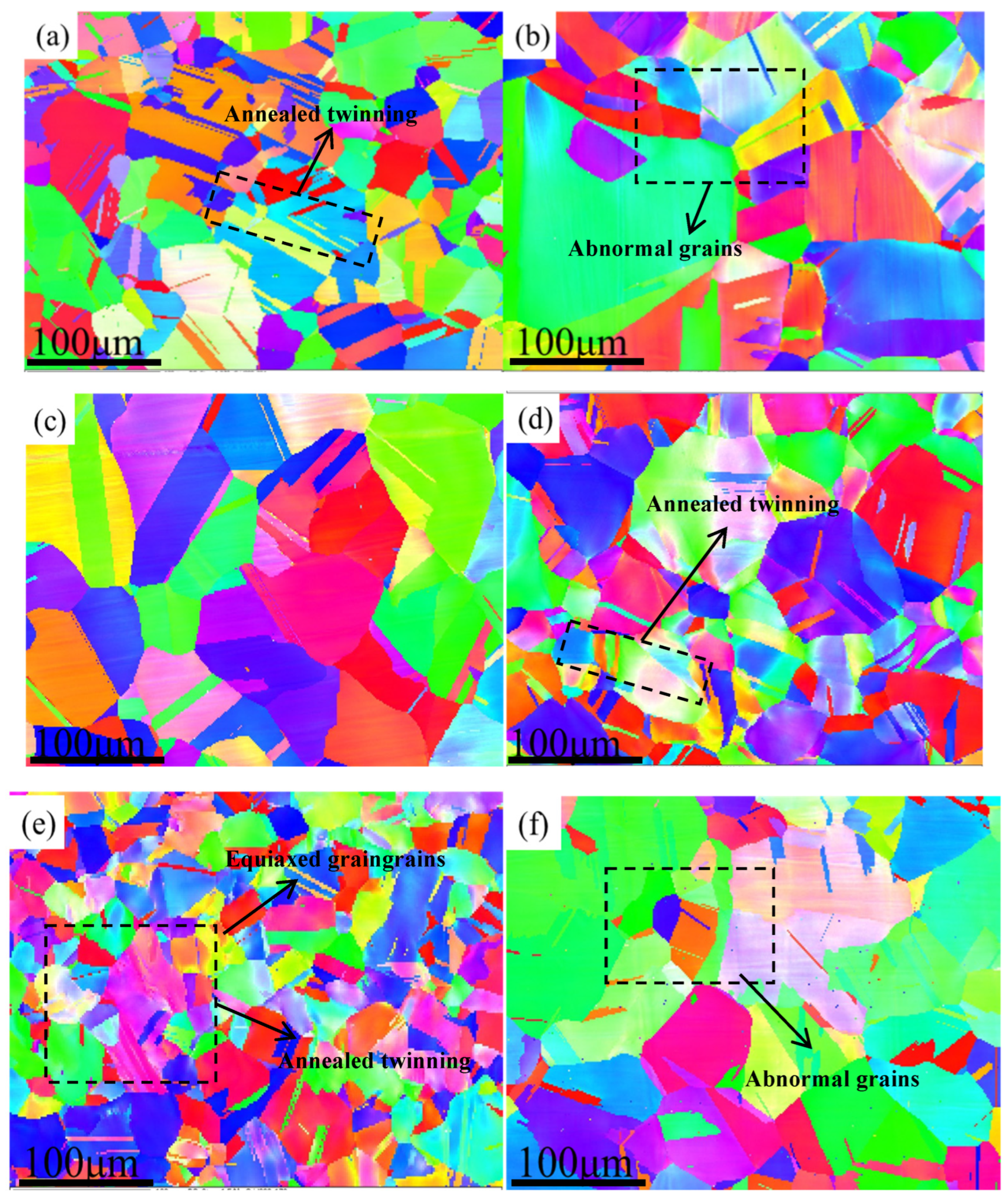
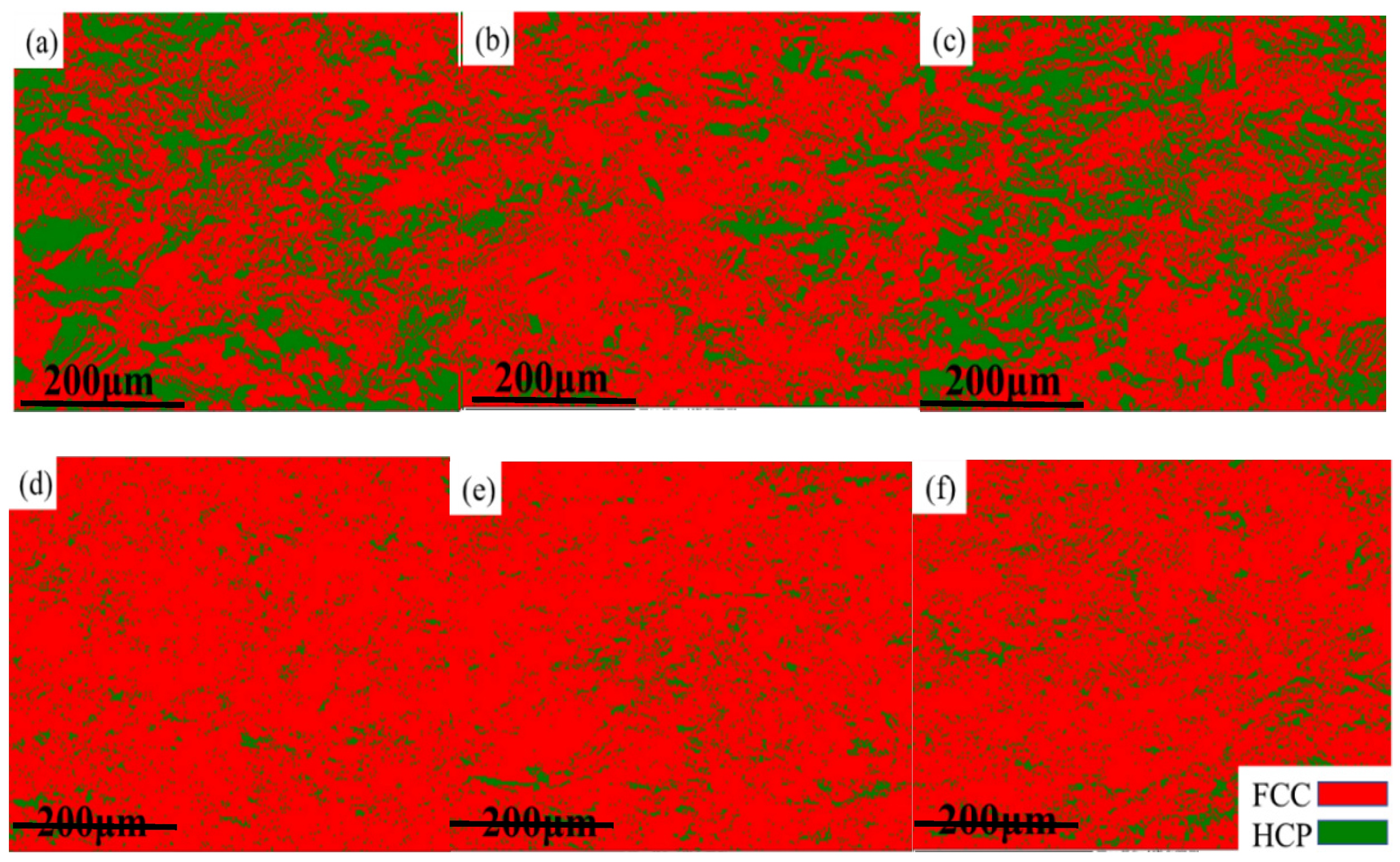
- There were FCC + HCP dual phases in Mo3, Mo4, and Mo5 HEAs when no C atoms were added. As the Mo content increased, the grain size of the alloy increased from 17 μm to 47 μm. However, only the FCC phase appeared after adding 0.5 at.% carbon, and the grain size of the Mo4C0.5 HEA decreased significantly.
- (2)
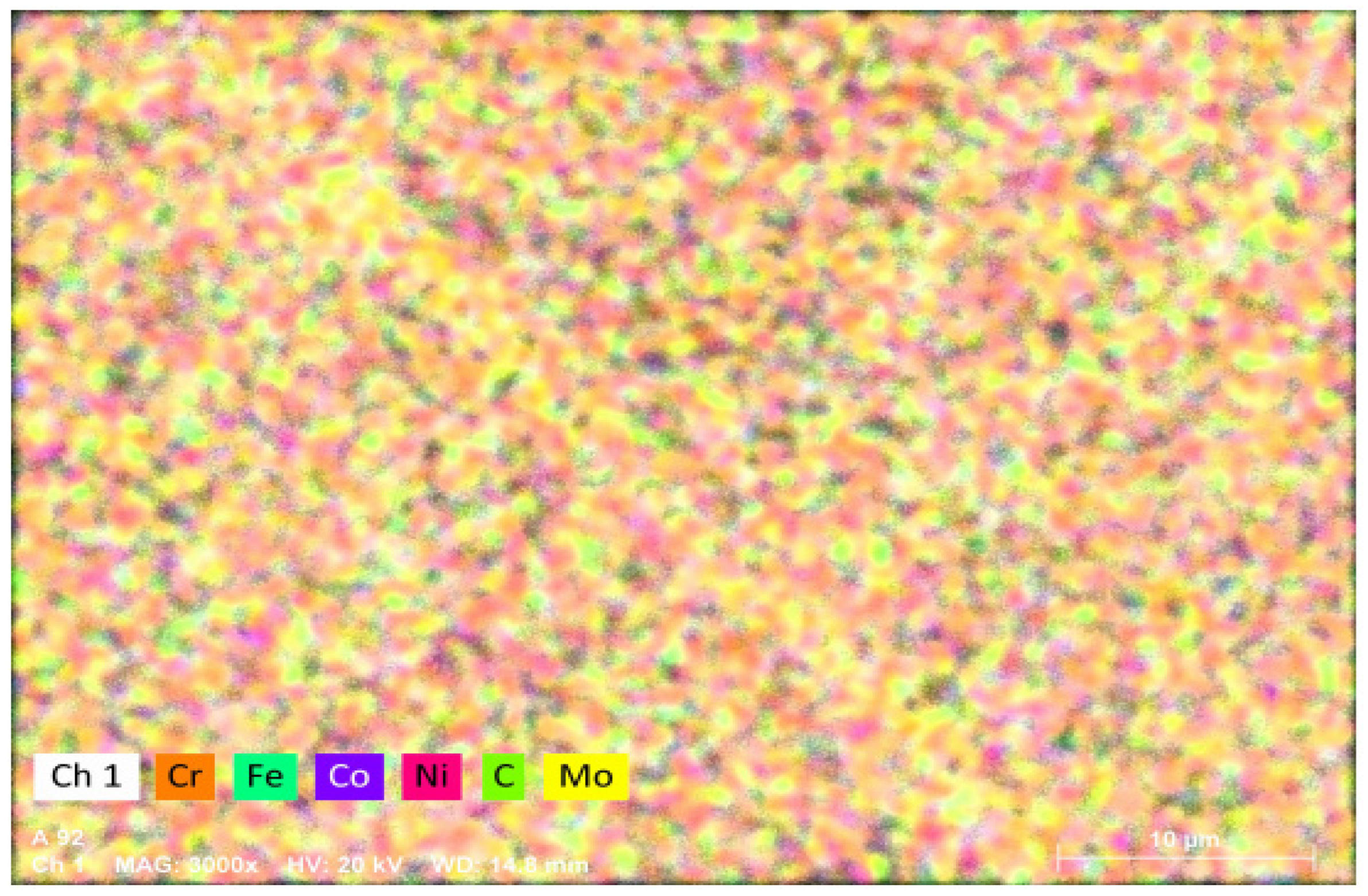
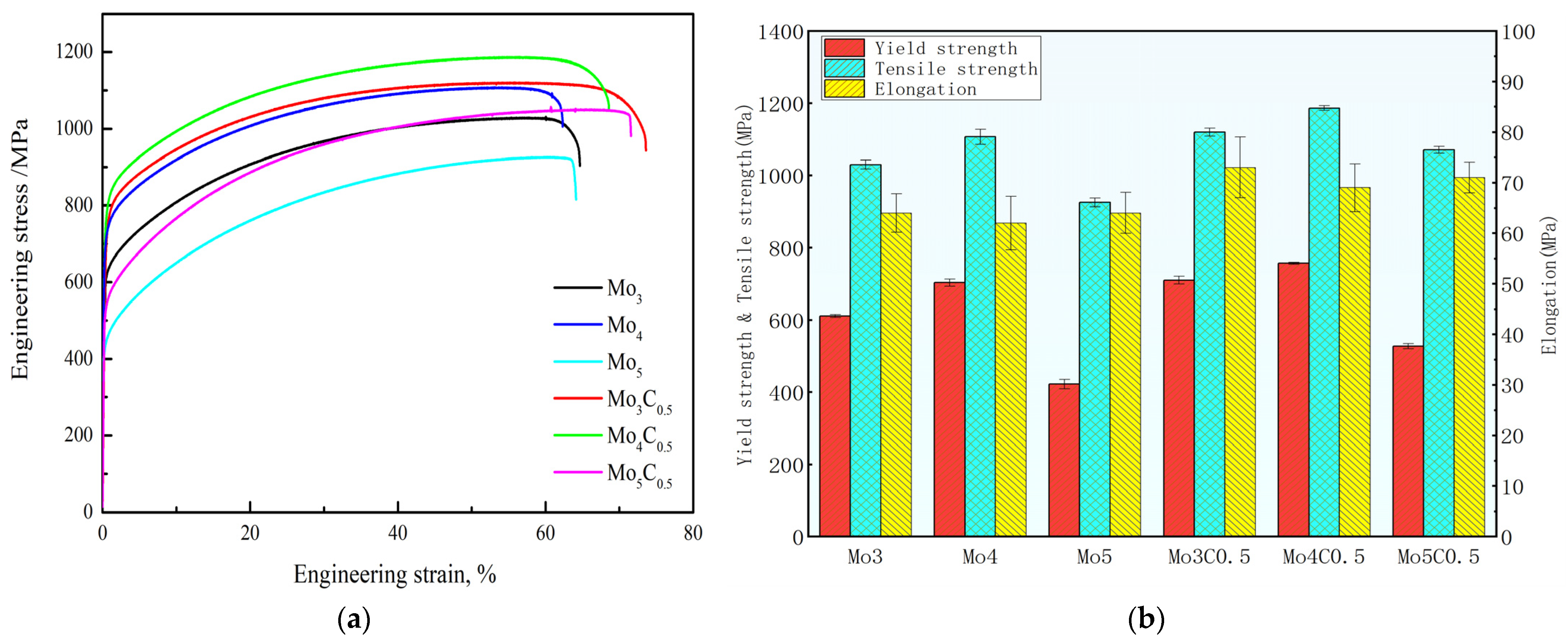
- Due to the Mo atom content exceeding the solid solution limit, the carbides of Mo combined with C element appeared in the Mo5C0.5 HEA. The strength of C and Mo microalloyed HEAs had a significant increase compared to HEAs with no C added, which was the result of interstitial solid solution strengthening caused by carbon atoms.
- (3)
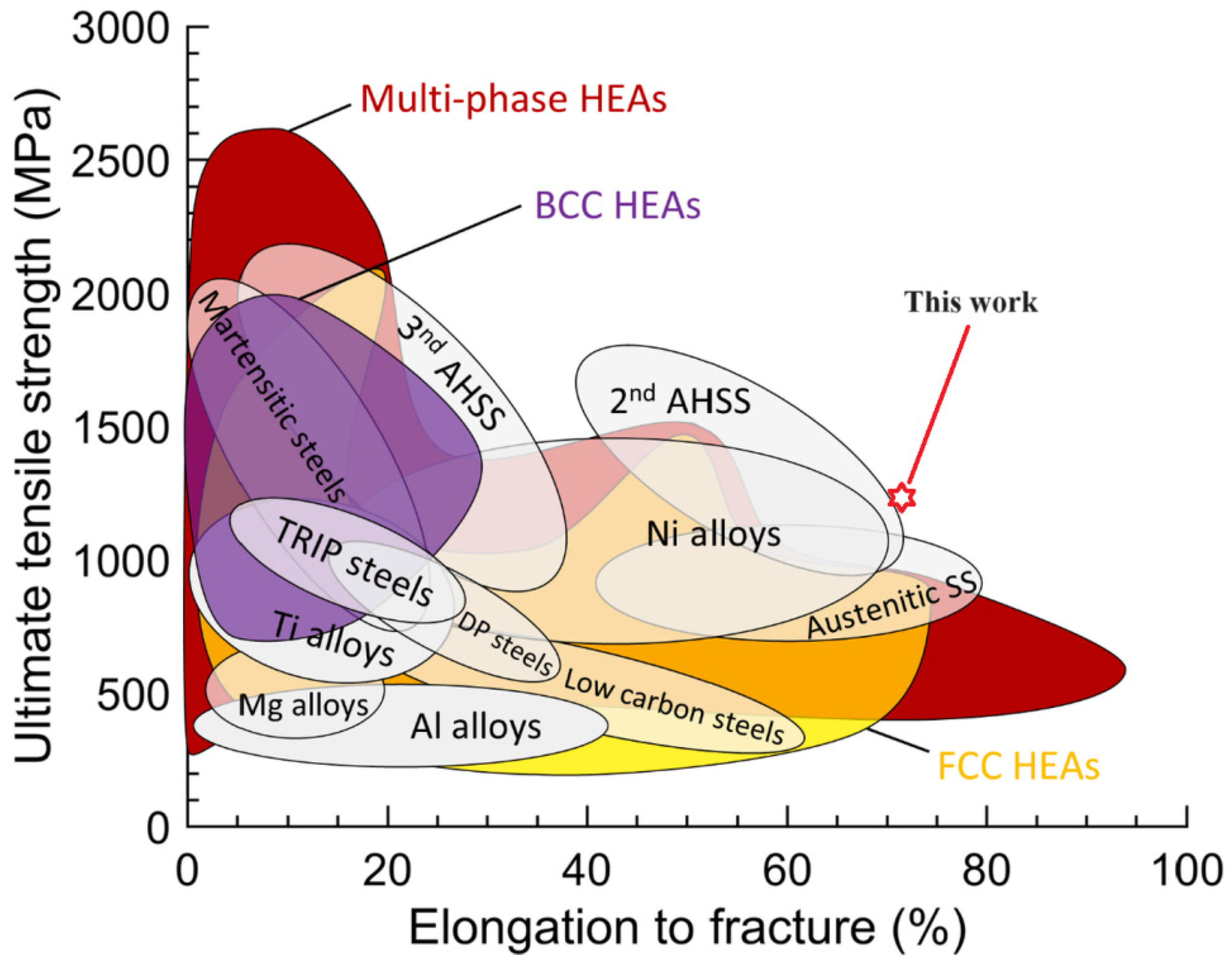
- The Mo4C0.5 HEA exhibited excellent comprehensive mechanical properties, making it superior to a majority of reported HEAs and conventional metal alloys. Its yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation were 757 MPa, 1186 MPa, and 69%, respectively. The strengthening mechanism was the combination of fine grain strengthening, the TWIP effect, and solid solution strengthening.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, T.K.; Yeh, A.C.; Kuo, C.M.; Kakehi, K.; Murakami, H.; Yeh, J.W.; Jian, S.R. The high temperature tensile and creep behaviors of high entropy superalloy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgiel, J.; Świątek, Z.; Czerwiński, F. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the new Nb25Sc25Ti25Zr25 eutectic high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 651, 590–597. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shi, T.; Bai, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Excellent room temperature ductility of as-cast TRIP high-entropy alloy via Mo and C alloying. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 2239–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Trang, T.; Lee, O.; Park, G.; Zargaran, A.; Kim, N.J. Improvement of strength—Ductility balance of B2-strengthened lightweight steel. Acta Mater. 2020, 191, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozinko, A.; Gholizadeh, R.; Zhang, Y.; Klement, U.; Tsuji, N.; Mishin, O.V.; Guo, S. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties during annealing of heavily rolled AlCoCrFeNi2. 1 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 833, 142558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Choi, C. Driving force for g/ε martensitic transformation and stacking fault energy of g in Fe-Mn binary system. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2000, 31, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Mayweg, D.; Ponge, D.; Li, Z. Microstructure and deformation behavior of two TWIP/TRIP high entropy alloys upon grain refinement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 802, 140661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Thurston, K.V.S.; Bei, H.; Wu, Z.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. Exceptional damage-tolerance of a medium-entropy alloy CrCoNi at cryogenic temperatures. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmir, H.; Asghari-Rad, P.; Mehranpour, M.S.; Forghani, F.; Kim, H.S.; Nili-Ahmadabadi, M. Evidence of FCC to HCP and BCC-martensitic transformations in a CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 807, 140875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pradeep, K.G.; Deng, Y.; Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C. Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength–ductility trade-off. Nature 2016, 534, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Tasan, C.C.; Springer, H.; Gault, B.; Raabe, D. Interstitial atoms enable joint twinning and transformation induced plasticity in strong and ductile high-entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveen, S.; Bae, J.W.; Asghari-Rad, P.; Park, J.M.; Kim, H.S. Annealing-induced hardening in high-pressure torsion processed CoCrNi medium entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 734, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, A.; Moghanni, H.; Dehghani, K. Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Al0.5CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy after Cold Rolling and Annealing Treatments. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 7817–7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimova, M.V.; Semenyuk, A.O.; Shaysultanov, D.G.; Salishchev, G.A.; Zherebtsov, S.V.; Stepanov, N.D. Effect of carbon on cryogenic tensile behavior of CoCrFeMnNi-type high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 811, 152000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Stanford, N.; Hodgson, P.; Fabijanic, D.M. Understanding the mechanical behaviour and the large strength/ductility differences between FCC and BCC AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 726, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Interstitial equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys: Carbon content, microstructure, and compositional homogeneity effects on deformation behavior. Acta Mater. 2019, 164, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZWang, Z.; Baker, I.; Cai, Z.; Chen, S.; Poplawsky, J.D.; Guo, W. The effect of interstitial carbon on the mechanical properties and dislocation substructure evolution in Fe40.4Ni11.3Mn34.8Al7.5Cr6 high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2016, 120, 228–239. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Tang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Dai, P. Effect of Ti and C additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the FeCoCrNiMn high-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 719, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ou, X.; Ni, S.; Liu, Y.; Song, M. Effects of carbon on the microstructures and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNiMn high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 746, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sairam, K.; Phaniraj, M.; Rajesh, K. Effect of molybdenum on recrystallization behavior of Fe30Mn5Al1C- x Mo lightweight austenitic steels. Scr. Mater. 2023, 230, 115399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, T.J.; Na Lee, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Körmann, F.; Baek, J.-H.; Do, H.-S.; Choi, Y.T.; Gwon, H.; Suh, J.-Y.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Compositive role of refractory element Mo in improving strength and ductility of face-centered-cubic complex concentrated alloys. Acta Mater. 2023, 255, 119030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Park, S.-J.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, T.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Hong, H.-U.; Suh, D.-W.; Kim, S.H.; Han, H.N.; Lee, B.H. Atomistic investigations of κ-carbide precipitation in austenitic Fe-Mn-Al-C lightweight steels and the effect of Mo addition. Scripta Mater. 2017, 127, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.W.; Park, J.M.; Moon, J.; Choi, W.M.; Lee, B.-J.; Kim, H.S. Effect of μ-precipitates on the microstructure and mechanical properties of non-equiatomic CoCrFeNiMo medium-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Iijima, Y.; Matsugaki, A.; Ameyama, K.; Nakano, T. Design and fabrication of Ti–Zr-Hf-Cr-Mo and Ti–Zr-Hf-Co-Cr-Mo high-entropy alloys as metallic biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 107, 110322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Gu, G.H.; Kim, E.S. Effect of Mo addition on the microstructure and high-specific tensile strength of Fe–Mn–Al–Ni–C ferrous medium-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 889, 145870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Li, X.; Schönecker, S.; Jiang, J.; Choi, W.M.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, H.S.; Chiba, A.; Kato, H. Development of strong and ductile metastable face-centered cubic single-phase high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2019, 181, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaxiang, L.; Kenta, Y.; Akihiko, C. Calculation-driven design of off-equiatomic high-entropy alloys with enhanced solid-solution strengthening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 817, 141359. [Google Scholar]
- An, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Guo, W.; Fang, Q.; Nie, Y. Effects of C and Mo on microstructures and mechanical properties of dual-phase high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2019, 110, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.P.; Curtin, W.A.; Tasan, C.C. High entropy alloys: A focused review of mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms. Acta Mater. 2020, 188, 435–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Yang, C.; Kuijer, M.; Baker, I. Enhanced mechanical properties of carbon-doped FeNiMnAlCr high entropy alloy via hot-rolling. Mater. Charact. 2019, 158, 109983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagui, S.; Sahu, B.P.; Laha, K.; Tarafder, S.; Mitra, R. Creep deformation behavior of Inconel 617 Alloy in the temperature range of 650 °C to 800 °C. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2021, 52, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xie, D.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liaw, P.K. Mechanical behavior of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 118, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HEAs | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Mo | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mo3 | 40.000 | 25.000 | 16.000 | 16.000 | 3.000 | 0.000 |
| Mo4 | 40.000 | 25.000 | 15.500 | 15.500 | 4.000 | 0.000 |
| Mo5 | 40.000 | 25.000 | 15.000 | 15.000 | 5.000 | 0.000 |
| Mo3C0.5 | 39.800 | 24.875 | 15.920 | 15.920 | 2.9850 | 0.500 |
| Mo4C0.5 | 39.800 | 24.875 | 15.4225 | 15.4225 | 3.9800 | 0.500 |
| Mo5C0.5 | 39.800 | 24.875 | 14.9250 | 14.9250 | 4.9750 | 0.500 |
| HEAs | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mo3 | 611 | 1030 | 64 |
| Mo4 | 703 | 1107 | 62 |
| Mo5 | 422 | 925 | 64 |
| Mo3C0.5 | 710 | 1120 | 73 |
| Mo4C0.5 | 757 | 1186 | 69 |
| Mo5C0.5 | 527 | 1071 | 71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lei, Y.; Song, P.; Chen, J. Improving Mechanical Properties of Co-Cr-Fe-Ni High Entropy Alloy via C and Mo Microalloying. Materials 2024, 17, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020529
Lv Y, Guo Y, Zhang J, Lei Y, Song P, Chen J. Improving Mechanical Properties of Co-Cr-Fe-Ni High Entropy Alloy via C and Mo Microalloying. Materials. 2024; 17(2):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020529
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Yukun, Yangyang Guo, Jie Zhang, Yutian Lei, Pingtao Song, and Jian Chen. 2024. "Improving Mechanical Properties of Co-Cr-Fe-Ni High Entropy Alloy via C and Mo Microalloying" Materials 17, no. 2: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020529
APA StyleLv, Y., Guo, Y., Zhang, J., Lei, Y., Song, P., & Chen, J. (2024). Improving Mechanical Properties of Co-Cr-Fe-Ni High Entropy Alloy via C and Mo Microalloying. Materials, 17(2), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020529




