Effect of Deposition Temperature on Zn Interstitials and Oxygen Vacancies in RF-Sputtered ZnO Thin Films and Thin Film-Transistors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Deposition of ZnO Thin Films
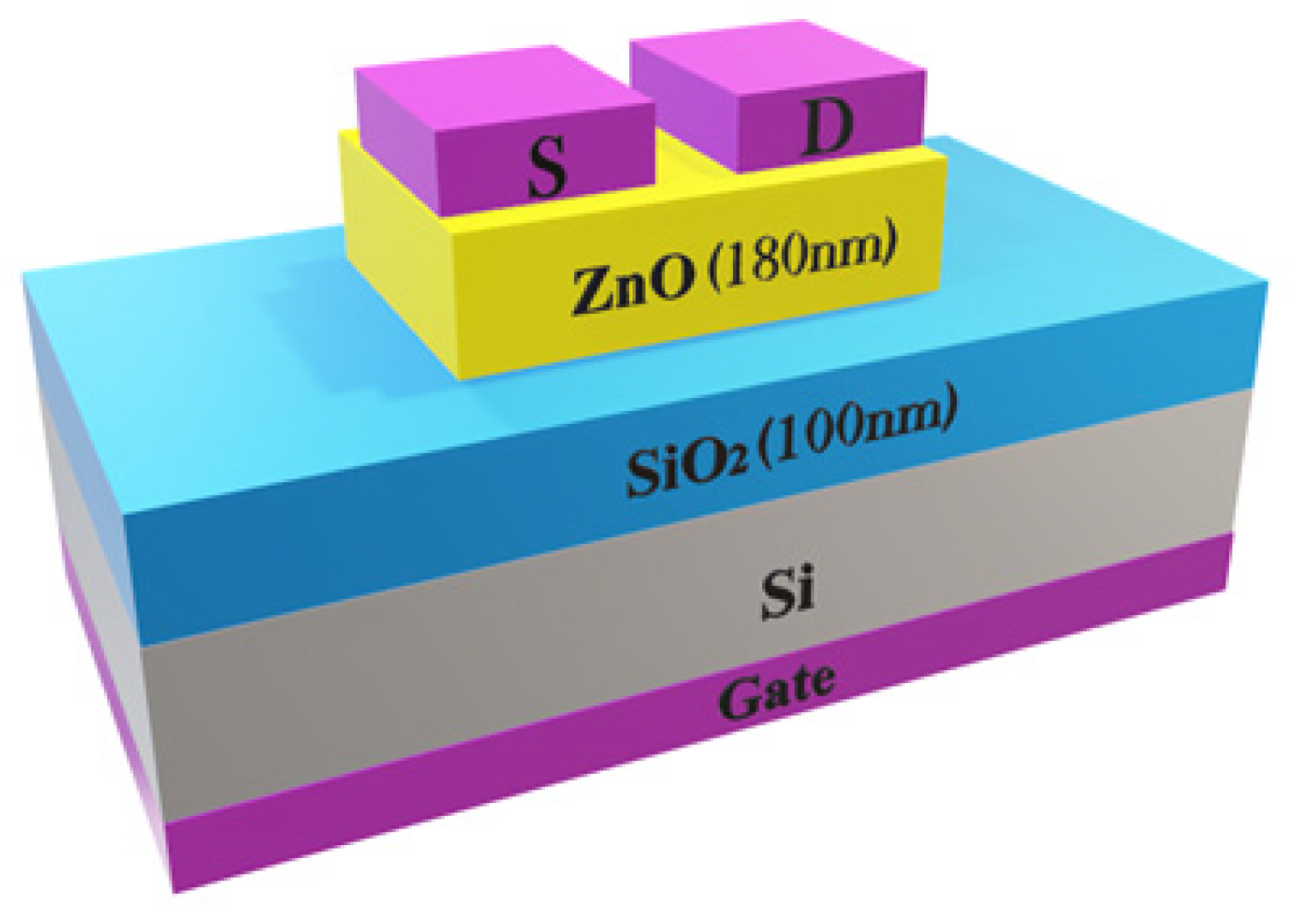
2.2. Device Fabrication and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
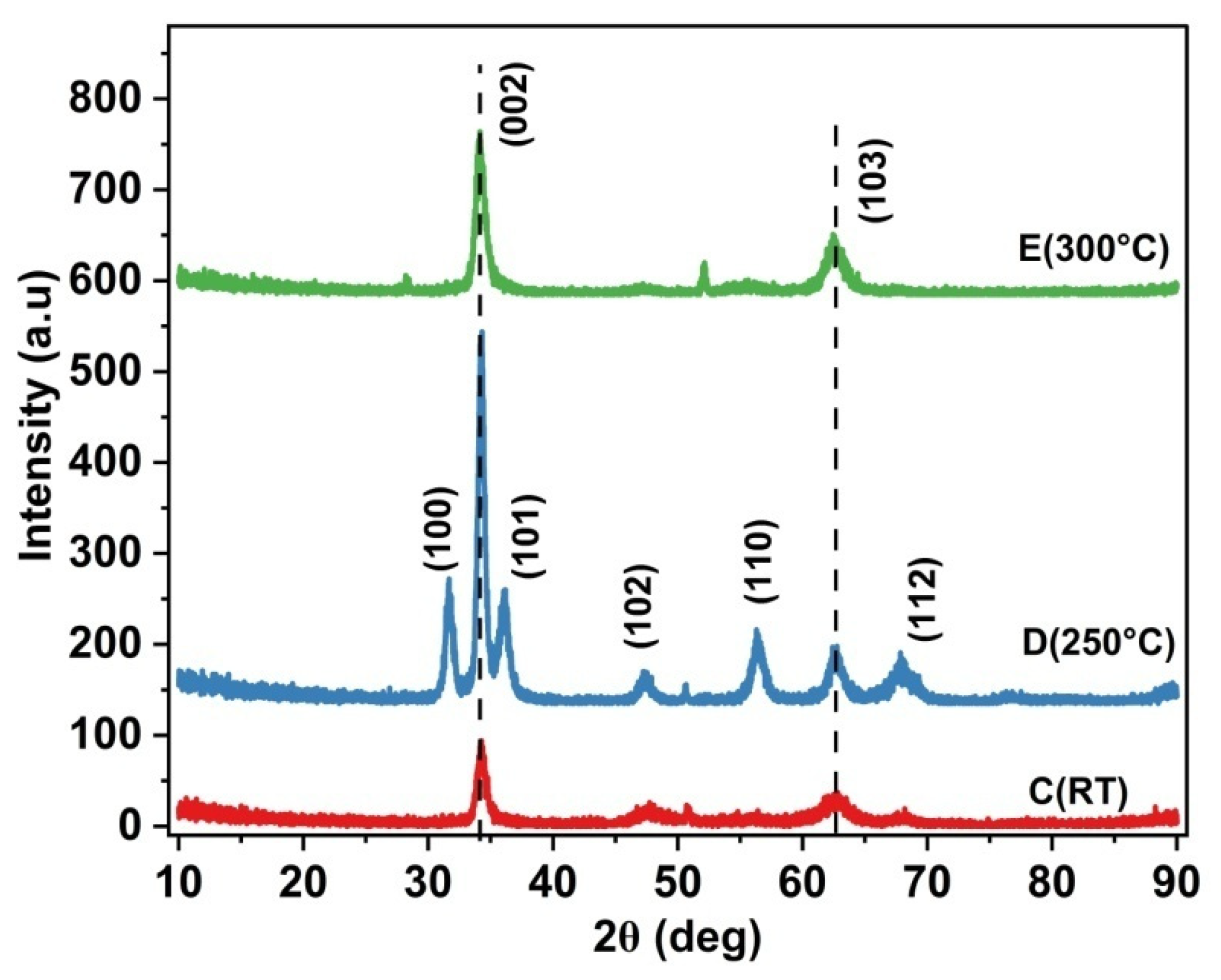
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
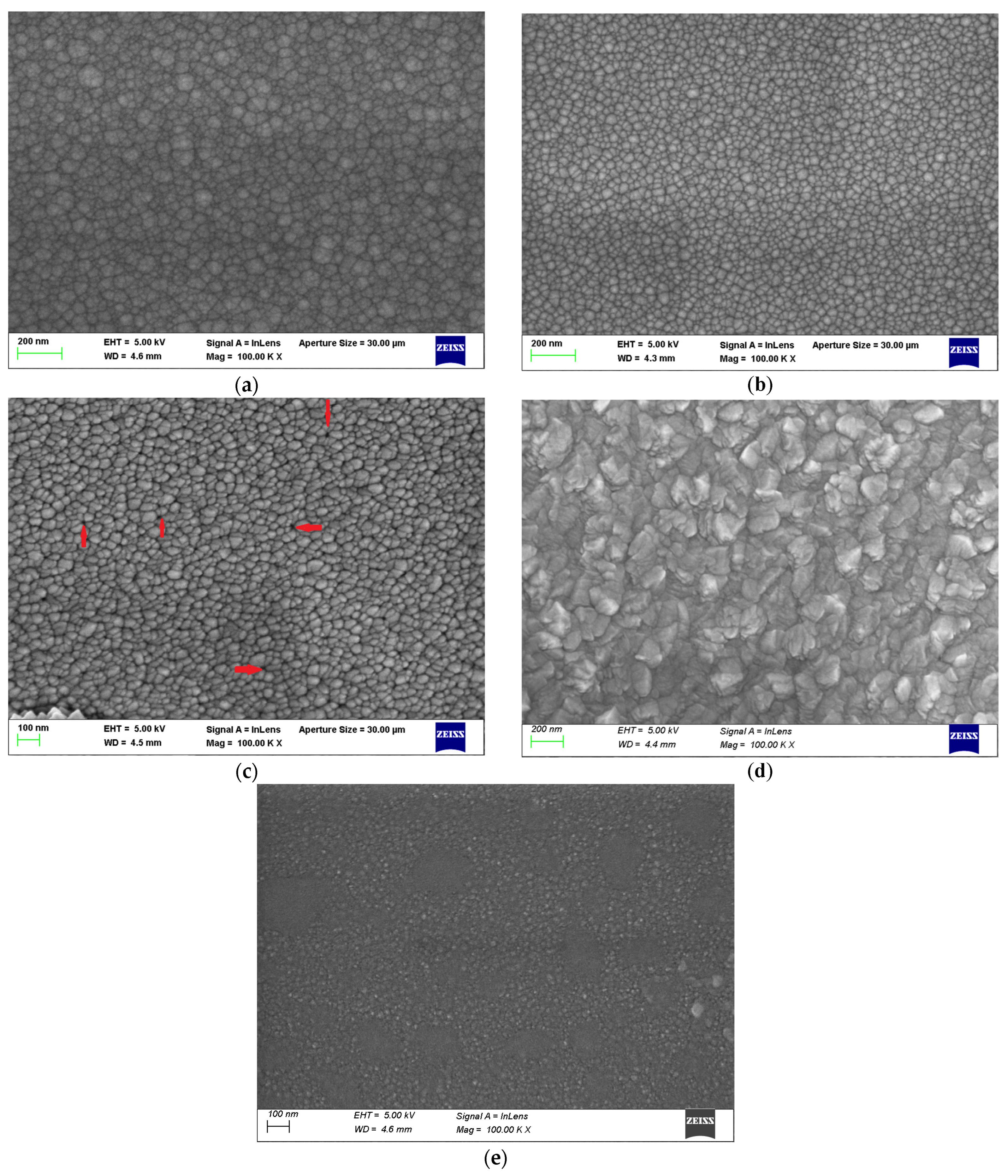
3.2. SEM
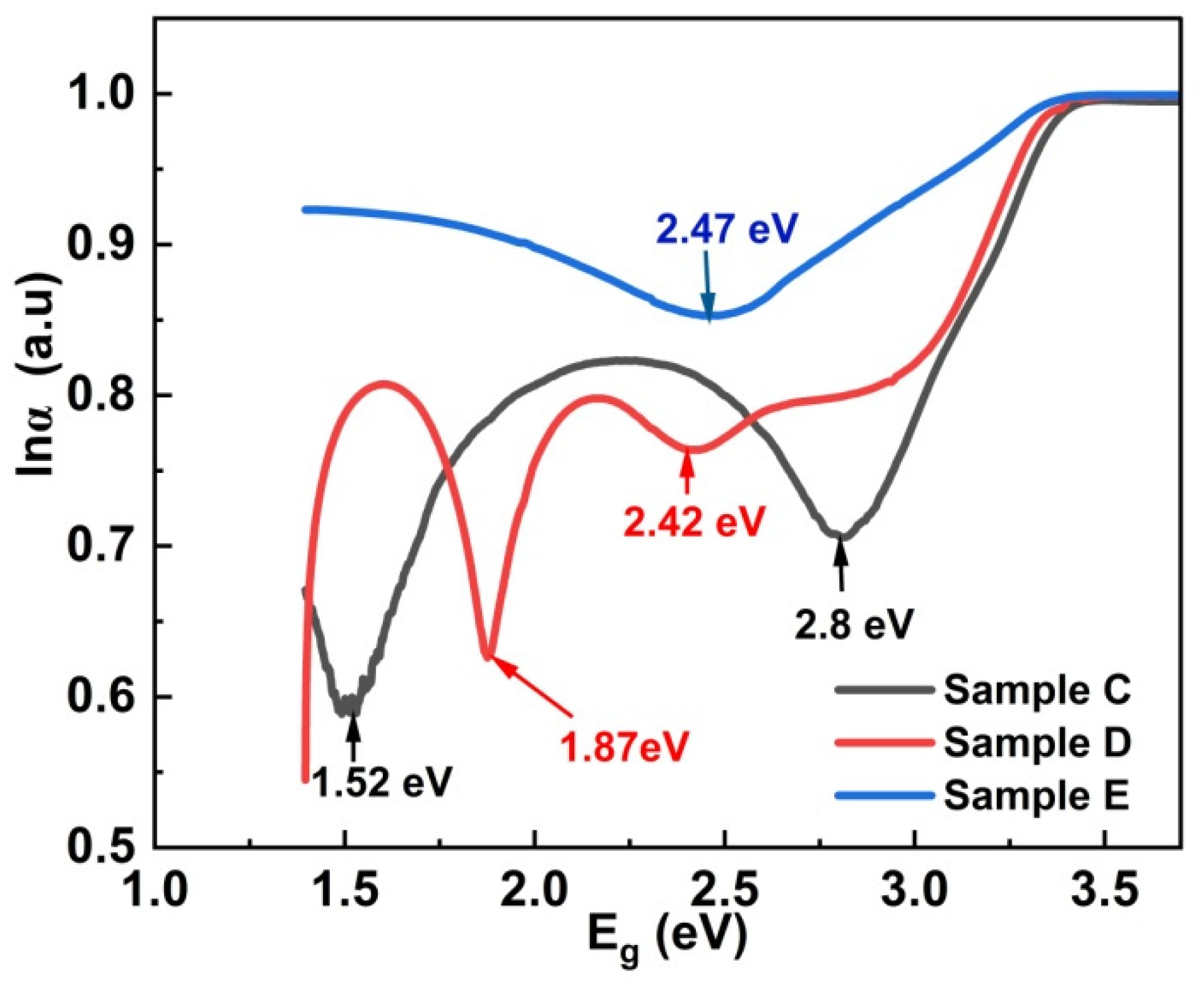
3.3. Optical Characterization
3.4. XPS
3.5. Device Characterization
3.5.1. Drain Characteristics
3.5.2. Transfer Characteristics
3.5.3. Variation in ZnO Layer Thickness
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, L.; Ma, Z.Q.; Shen, C.; Li, F.; He, B.; Xu, F. Studies on fabrication and characterization of a ZnO/p-Si-based solar cell. Superlattices Microstruct. 2010, 48, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.K.S.; Zhuk, S.; Masudy-Panah, S.; Dalapati, G.K. Current Status and Future Prospects of Copper Oxide Heterojunction Solar Cells. Materials 2016, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouras, K.; Schmerber, G.; Rinnert, H.; Aureau, D.; Park, H.; Ferblantier, G.; Colis, S.; Fix, T.; Park, C.; Kim, W.K.; et al. Structural, optical and electrical properties of Nd-doped SnO2 thin films fabricated by reactive magnetron sputtering for solar cell devices. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 145, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saim, H.B.; Campbell, D.S. Properties of indium-tin-oxide (ITO)/silicon heterojunction solar cells by thick-film techniques. Sol. Energy Mater. 1987, 15, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Zhuo, M.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Jiang, J.; Gao, F.; Wan, Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, T. Indium-tin-oxide thin film transistor biosensors for label-free detection of Avian influenza virus H5N1. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 773, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amutha Surabi, M.; Chandradass, J.; Park, S.J. ZnO-Based Thin Film Transistor Fabricated Using Radio Frequency Magnetron Sputtering at Low Temperature. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2015, 30, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presley, R.E.; Munsee, C.L.; Park, C.-H.; Hong, D.; Wager, J.F.; Keszler, D.A. Tin oxide transparent thin-film transistors. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2004, 37, 2810–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jawhari, H.A. A review of recent advances in transparent p-type Cu2O-based thin film transistors. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 40, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Fang, X.; Liao, M.; Xu, X.; Zeng, H.; Yoshio, B.; Golberg, D. A comprehensive review of one-dimensional metal-oxide nanostructure photodetectors. Sensors 2009, 9, 6504–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Sheng, H.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Z.; Lu, Y.; Shen, H. ZnO Schottky ultraviolet photodetectors. J. Cryst. Growth 2001, 225, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Du, H.; Wang, P.; Lim, T.-T.; Sun, X.W. A high-performance UV/visible photodetector of Cu2O/ZnO hybrid nanofilms on SWNT-based flexible conducting substrates. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 9536–9542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.; Mahajan, B.K.; Singh, L.R.; Shubhajit, V.; Rajib Kumar, N.; Mitra, B.S. Enhancing Detectivity of Indium-Oxide-Based Photodetectors via Vertical Nano structuring Through Glancing Angle Deposition. J. Electron. Mater. 2021, 50, 3722–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruc, F.B.; Cimen, F.; Rizk, A.; Ghaffari, M.; Nayfeh, A.; Okyay, A.K. Thin-Film ZnO Charge-Trapping Memory Cell Grown in a Single ALD Step. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2012, 33, 1714–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Aluguri, R.; Chand, U.; Tseng, T.Y. Metal oxide resistive switching memory: Materials, properties and switching mechanisms. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.; Mahajan, B.K.; Sarkar, M.B. Ag Nanoparticles Sheltered In2O3 Nanowire as a Capacitive MOS Memory Device. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2020, 19, 856–863. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Ghanshyam, C.; Ram, N.; Bajpai, R.P.; Bedi, R.K. Detection mechanism of metal oxide gas sensor under UV radiation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 97, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendi, A.A.; Alorainy, R.H. New fabrication of zinc oxide nanostructure thin film gas sensors. Superlattices Micro Struct. 2014, 66, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-W.; Chen, H.-I.; Chen, T.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Hsu, C.-S.; Liu, R.-C.; Liu, W.-C. On an indium–tin-oxide thin film based ammonia gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.C.; Hunter, G.W.; Lukco, D.; Liu, C.-C.; Ward, B.J. Novel Carbon Dioxide Micro sensor Based on Tin Oxide Nanomaterial Doped With Copper Oxide. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 235–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şerban, I.; Enesca, A. Metal Oxides-Based Semiconductors for Biosensors Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, K.; Tomar, M.; Gupta, V. CuO thin film based uric acid biosensor with enhanced response characteristics. Bio Sens. Bio Electron. 2012, 38, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batra, N.; Tomar, M.; Gupta, V. Efficient detection of cholesterol using ZnO thin film based matrix. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2012, 8, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, I.-C.; Li, Y.-S.; Tu, M.-S.; Cheng, I.-C. Complementary Oxide–Semiconductor-Based Circuits with n-Channel ZnO and p- Channel SnO Thin-Film Transistors. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2014, 35, 1263–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shijeesh, M.R.; Mohan, P.A.; Jayaraj, M.K. Complementary Inverter Circuits Based on p-Cu2O and n-ZTO Thin Film Transistors. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Mao, K.; Cai, F.; Meng, H.; Zhu, Z.; Li, T.; Yuan, S.; Xu, Z.; Feng, X.; Xu, J.; et al. Reducing non radiative recombination in perovskite solar cells with a porous insulator contact. Science 2023, 379, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Yarbrough, R.; Froeschle, M.; White, J.; Rathnayake, H. Band gap engineered zinc oxide nanostructures via a sol–gel synthesis of solvent driven shape-controlled crystal growth. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14638–14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, J.; Myers, J.; Kufel, J.; Ozer, E.; Craske, S.; Sou, A.; Ramsdale, C.; Williamson, K.; Price, R.; White, S. A natively flexible 32-bit Arm microprocessor. Nature 2021, 595, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraja, S.; Faber, H.; Kumar, M.; Na, X.; García, G.I.M.; Tang, X.; Anthopoulos, T.D.; Li, X. Three-dimensional integrated metal-oxide transistors. Nat. Electron. 2024, 7, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruddin, S.A.; Chan, K.Y.; Yow, H.K. Zinc oxide films prepared by sol–gel spin coating technique. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 104, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortel, M.; Balster, T.; Wagner, V. Chemical composition and temperature dependent performance of ZnO-thin film transistors deposited by pulsed and continuous spray pyrolysis. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 234502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, J.K.; Bukke, R.N.; Mude, N.N.; Jang, J. Significant improvement of spray pyrolyzed ZnO thin film by precursor optimization for high mobility thin film transistors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Chowdhury, F.R.; Barlage, D.; Tsui, Y.Y. Optimization of pulsed laser deposited ZnO thin-film growth parameters for thin-film transistors (TFT) application. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 110, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-A.; Zhang, J.-W.; Zhang, W.-F.; Wang, D.; Bi, Z.; Bian, X.-M.; Hou, X. Enhancement-mode thin film transistor with nitrogen-doped ZnO channel layer deposited by laser molecular beam epitaxy. Thin Solid Film. 2008, 516, 3305–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampo, H.; Shibata, H.; Maejima, K.; Yamada, A.; Matsubara, K.; Fons, P.; Kashiwaya, S.; Niki, S.; Chiba, Y.; Wakamatsu, T.; et al. Polarization-induced two-dimensional electron gases in ZnMgO/ZnO heterostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 202104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Han, D.; Yi, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. High-Performance ZnO Thin-Film Transistors Prepared by Atomic Layer Deposition. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2019, 66, 2965–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcia, P.F.; McLean, R.S.; Reilly, M.H. High-performance ZnO thin-film transistors on gate dielectrics grown by atomic layer deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 123509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navamathavan, R.; Choi, C.K.; Park, S.-J. Electrical properties of ZnO-based bottom-gate thin film transistors fabricated by using radio frequency magnetron sputtering. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 475, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Chakrabarti, P. Simulation, fabrication and characterization of ZnO based thin film transistors grown by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 1880–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, N.W.; Yun, Y. Characterization of magnesium oxide gate insulators grown using RF sputtering for ZnO thin-film transistors. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2014, 14, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Montes, M.I.; Lee, S.H.; Pérez, M.; Baldenegro-Pérez, L.A.; Quevedo-López, M.A.; Gnade, B.; Ramírez-Bon, R. Effect of Sputtered ZnO Layers on Behavior of Thin-Film Transistors Deposited at Room Temperature in a Nonreactive Atmosphere. J. Electron. Mater. 2011, 40, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandpal, K.; Gupta, N. Perspective of zinc oxide based thin film transistors: A comprehensive review. Microelectron. Int. 2018, 35, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Rim, Y.S.; Li, C.; Kim, H.-S.; Goorsky, M.; Streit, D. Deep-level defect distribution as a function of oxygen partial pressure in sputtered ZnO thin-film transistors. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2016, 16, 1369–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, T.; Nomura, K.; Hosono, H. Present status of amorphous In–Ga–Zn–O thin-film transistors. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2010, 11, 044305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.; Pradhan, A.K.; Xiao, B. Low temperature fabrication of high performance ZnO thin film transistors with high-k dielectrics. Solid State Electron. 2015, 111, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-S.; Li, Y.-S.; Cheng, I.-C. Mobility Enhancement in RF-Sputtered MgZnO/ZnO Heterostructure Thin-Film Transistors. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2016, 63, 1545–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.; Dwivedi, A.D.D.; Dwivedi, R.D. Effect of gate dielectric on the performance of ZnO based thin film transistor. Superlattices Microstruct. 2018, 120, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitabha, N.; Bikram, K.M.; Aniruddha, M.; Laishram, R.S.; Mitra, B.S. Synthesis and detailed characterizations of Ag nanoparticles coated In2O3 nanostructured devices: An analytical and experimental approach. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2021, 39, 052209. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, G.; Liu, W.; Zhu, C. Origin of (103) plane of ZnO films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2013, 24, 3764–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.E.; Kamath, P.V. Electrochemical synthesis of ZnO coatings from water–isopropanol mixed baths: Control over oriented crystallization. J. Solid State Electro Chem. 2010, 14, 2083–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chou, K.Y. Solution derived Al-doped zinc oxide films: Doping effect, microstructure and electrical property. J. Sol.-Gel Sci. Technol. 2009, 49, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Singha, R.K.; Dhar, A.; Ray, S.K. Optical and structural characteristics of ZnO thin films grown by RF magnetron sputtering. Mater. Res. Bull. 2008, 43, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavindra, K.; Gupta, N.; Singh, J.; Shekhar, C. On the Threshold Voltage and Performance of ZnO- Based Thin-Film Transistors with a ZrO2 Gate Dielectric. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 3156–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Urbach, F. The Long-Wavelength Edge of Photographic Sensitivity and of the Electronic Absorption of Solids. Phys. Rev. 1953, 92, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, F.A. The Chemistry of Imperfect Crystals, 2nd ed.; North-Holland Publishing Company Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Egelhaaf, H.-J.; Oelkrug, D. Luminescence and nonradiative deactivation of excited states involving oxygen defect centers in polycrystalline ZnO. J. Cryst. Growth 1996, 161, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinthamani, S.; Ranjithkumar, M.; Sudhakar, K.B.; Anitha, S.; Sudharsanam, S.; Sasikala, M. Optical characterization of RF sputtered copper oxide for thin film solar cell applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 59, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandopadhyay, K.; Mitra, J. Zn interstitials and O vacancies responsible for n-type ZnO: What do the emission spectra reveal? RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 23540–23547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.K.; Pandey, S.K.; Mukherjee, C.; Mishra, P.; Gupta, M.; Barman, S.R.; D’Souza, S.W.; Mukherjee, S. Effect of growth temperature on structural, electrical and optical properties of dual ion beam sputtered ZnO thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2013, 24, 2541–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakonas, C.; Kuznetsov, V.L.; Cranton, W.M.; Kalfagiannis, N.; Abusabee, K.M.; Koutsogeorgis, D.C.N.; Abeywickrama, N.; Edwards, P.P. Low temperature sputter-deposited ZnO films with enhanced Hall mobility using excimer laser post-processing. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 485306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Koo, S.-M. Epitaxial ZnO thin film transistors on 4H-SiC substrates. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 14641–14644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem-ur-Rehman Khan, H.; Mehmood, M.; Ling, F.C.C.; Faheem Khan, A.; Ali, S.M. Comparative Study on Structural, Optical, and Electrical Properties of ZnO Thin Films Prepared by PLD and Sputtering Techniques. Semiconductors 2020, 54, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cao, F.; Ji, X. Optical and electrical properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films by atomic layer deposition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 17365–17374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, B.; Manuraj, M.; Surendran, K.P.; Narayanan Unni, K.N. Opto-electronic properties of solution-processed zinc oxide thin films: Role of solvents and doping. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 13570–13577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremenok, V.F.; Ivanov, V.A.; Petlitskii, A.N.; Petlitskaya, T.V.; Suleymanov, S.K.; Dyskin, V.G.; Djanklich, M.U.; Kulagina, N.A. ZnO Films Obtained by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering: Microstructure, Electrical, and Optical Characteristics. Appl. Sol. Energy 2020, 56, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Zang, H.; Ren, L.Y. Influence of annealing temperature on structural, electrical and optical properties of undoped zinc oxide thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2014, 25, 5422–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lei, S.; Han, R.; Matsumoto, S.; Ino, Y. Influence of sputtering power on properties of ZnO thin films fabricated by RF sputtering in room temperature. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2011, 55, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasada Rao, T.; Santhosh Kumar, M.C.; Ganesan, V. Effect of annealing on the structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO thin films by spray pyrolysis. Indian J. Phys. 2011, 85, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, T.; Periasamy, C.; Boolchandani, D. Performance evaluation of bottom gate ZnO based thin film transistors with different W/L ratios for UV sensing. Superlattices Microstruct. 2018, 114, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.H.; Ghazali, N.A.B.; Chong, H.M.H.; Cobley, R.J.; Li, L.; Kalna, K. Channel mobility and contact resistance in scaled ZnO thin-film transistors. Solid State Electron. 2020, 172, 107867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M. Subthreshold Conduction of Disordered ZnO-Based Thin-Film Transistors. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, A.G.; Shafi, N. Design, fabrication and characterization of circular ZnO TFT for UV detection applications. Microelectron. J. 2023, 131, 105648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, J.; Yang, G.W.; Kim, C.W.; Choi, S.-J.; Kim, D.M.; Bae, J.-H.; Kim, D.H. Analysis of a-InGaZnO TFT Threshold Voltage Instability and Mobility Boosting by Current Stress at a Cryogenic Temperature. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2023, 44, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Montes, M.I.; Baldenegro-Perez, L.A.; Sanchez-Zeferino, R.; Rojas-Blanco, L.; Becerril-Silva, M.; Quevedo-Lopez, M.A.; Ramirez-Bon, R. Effect of depth of traps in ZnO polycrystalline thin films on ZnO-TFTs performance. Solid-State Electron. 2016, 123, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


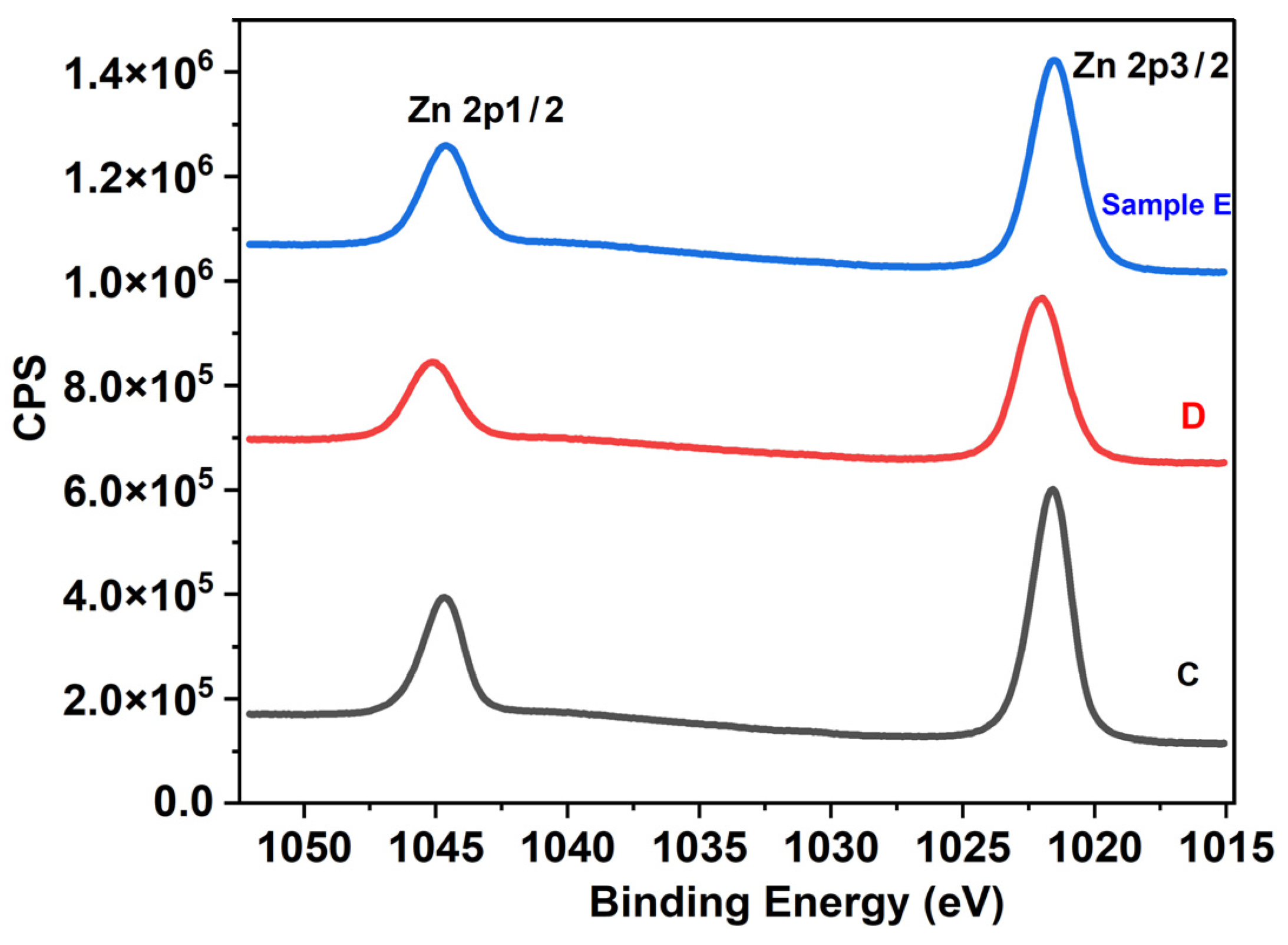
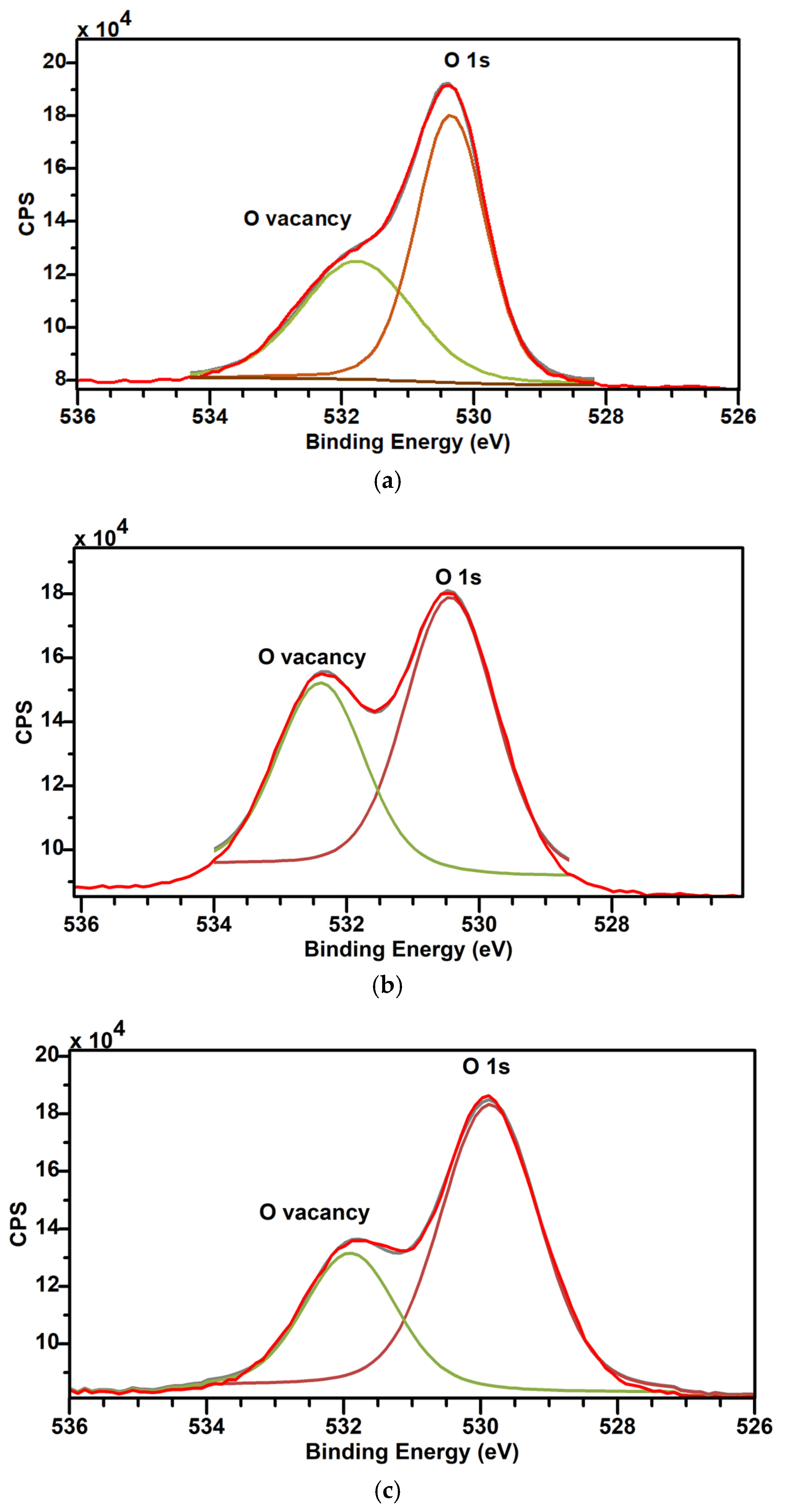
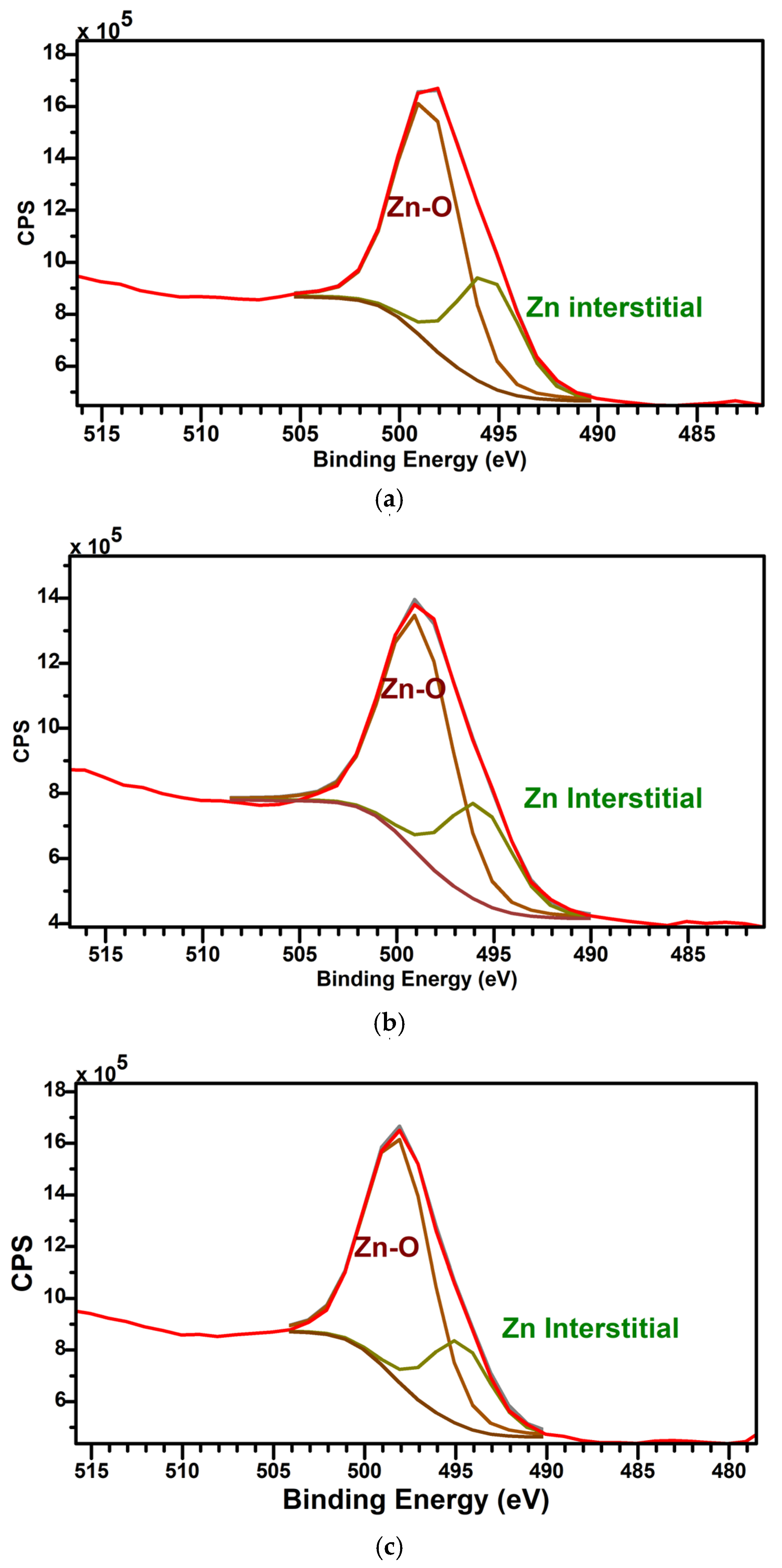
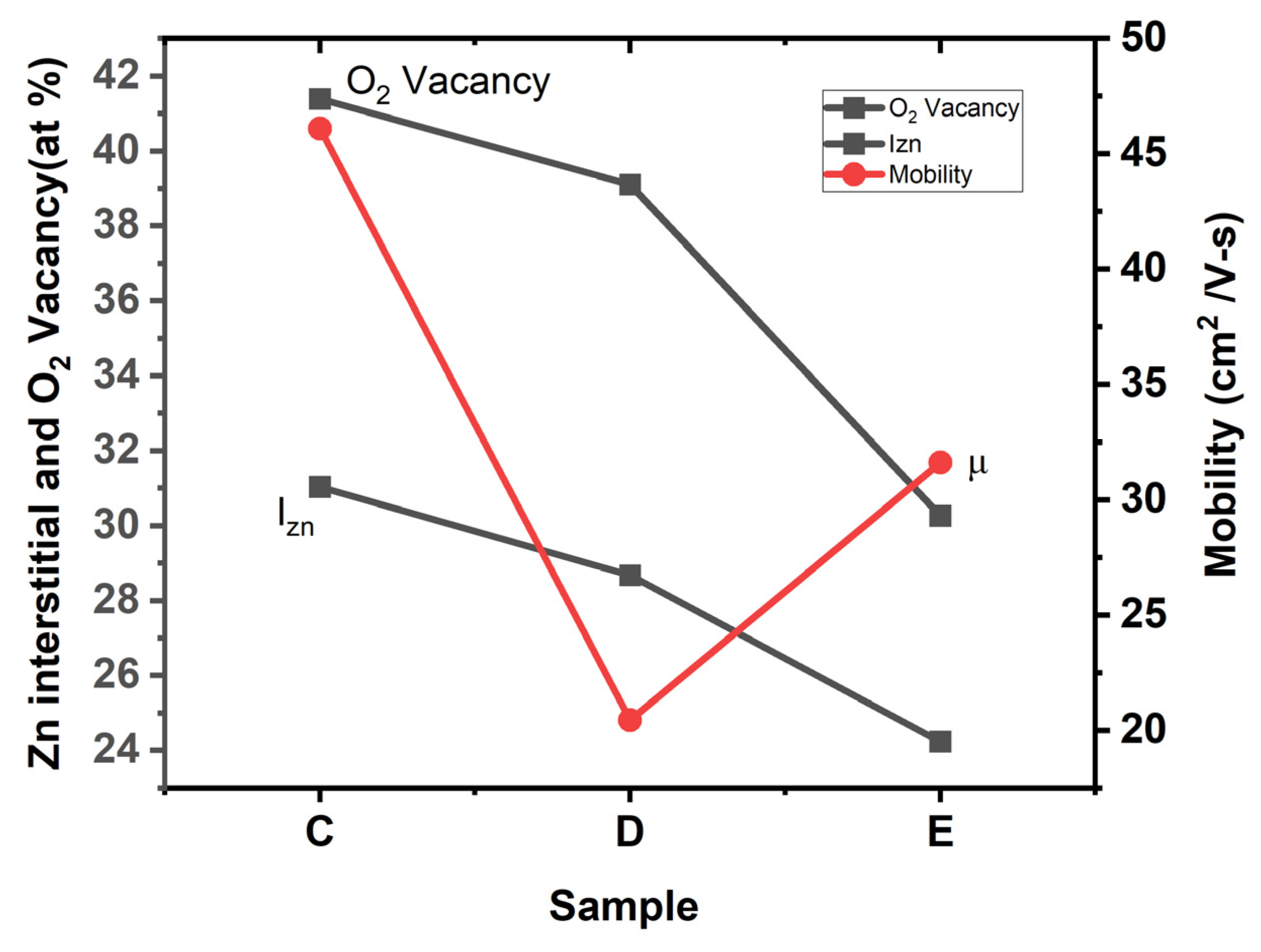
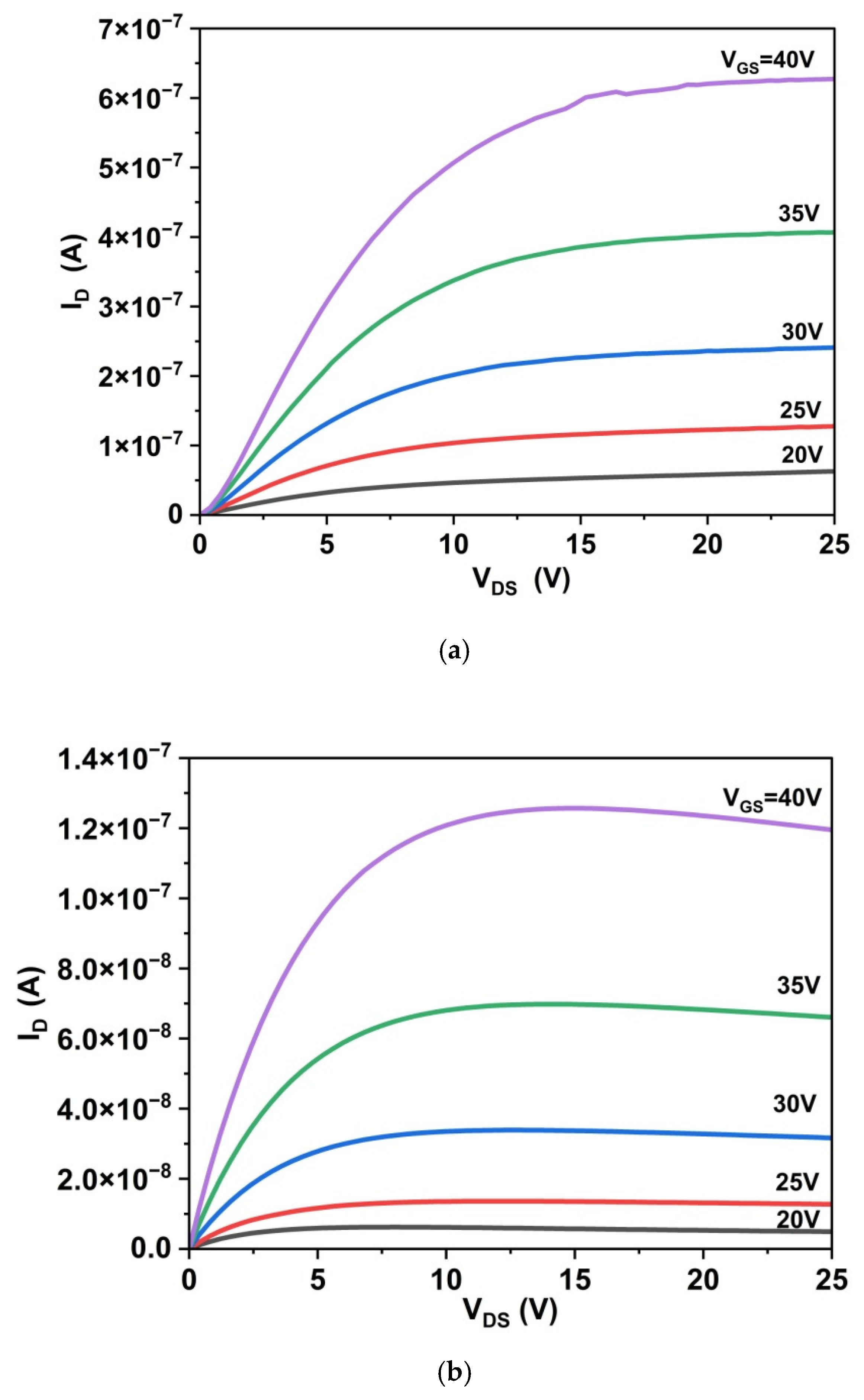
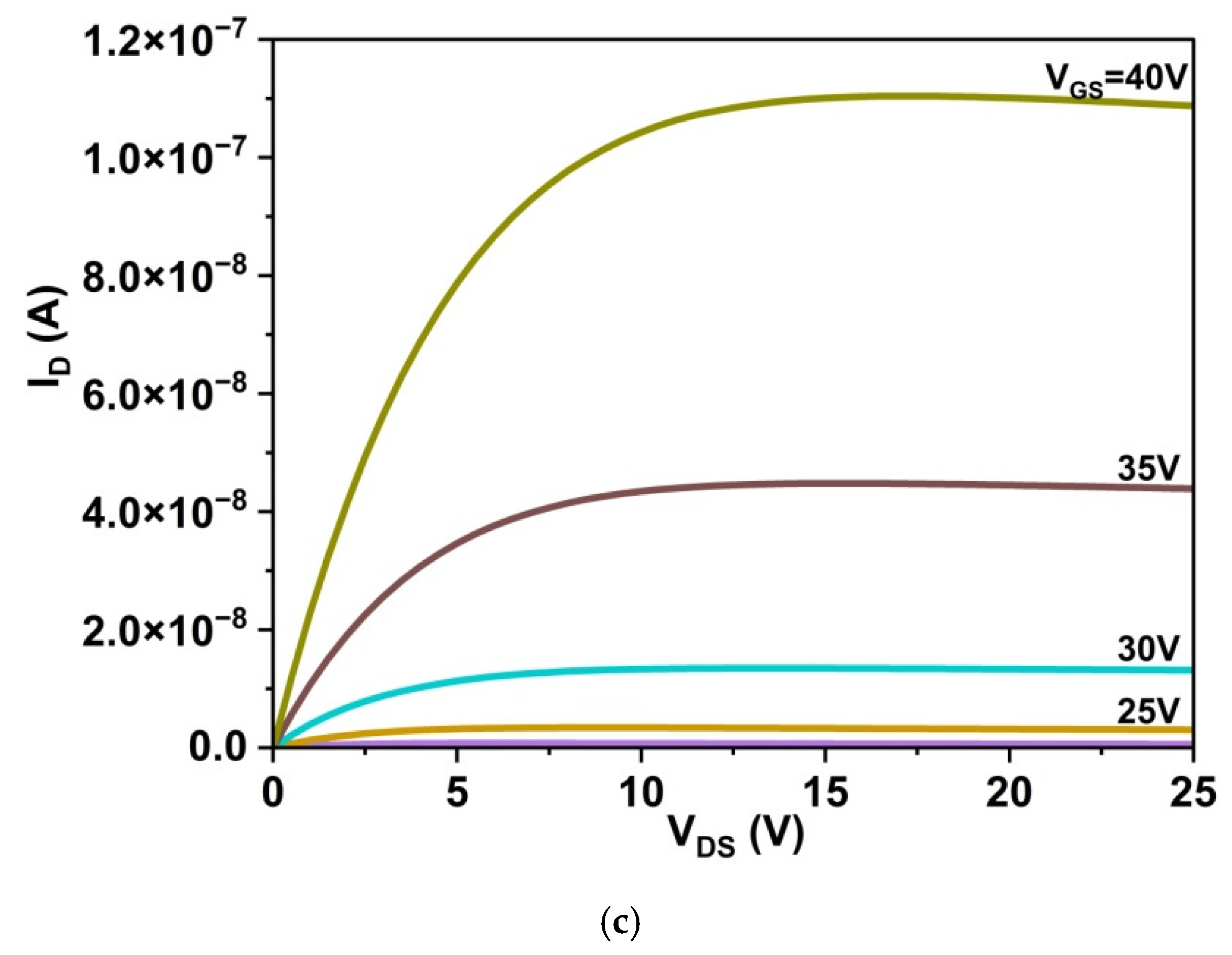
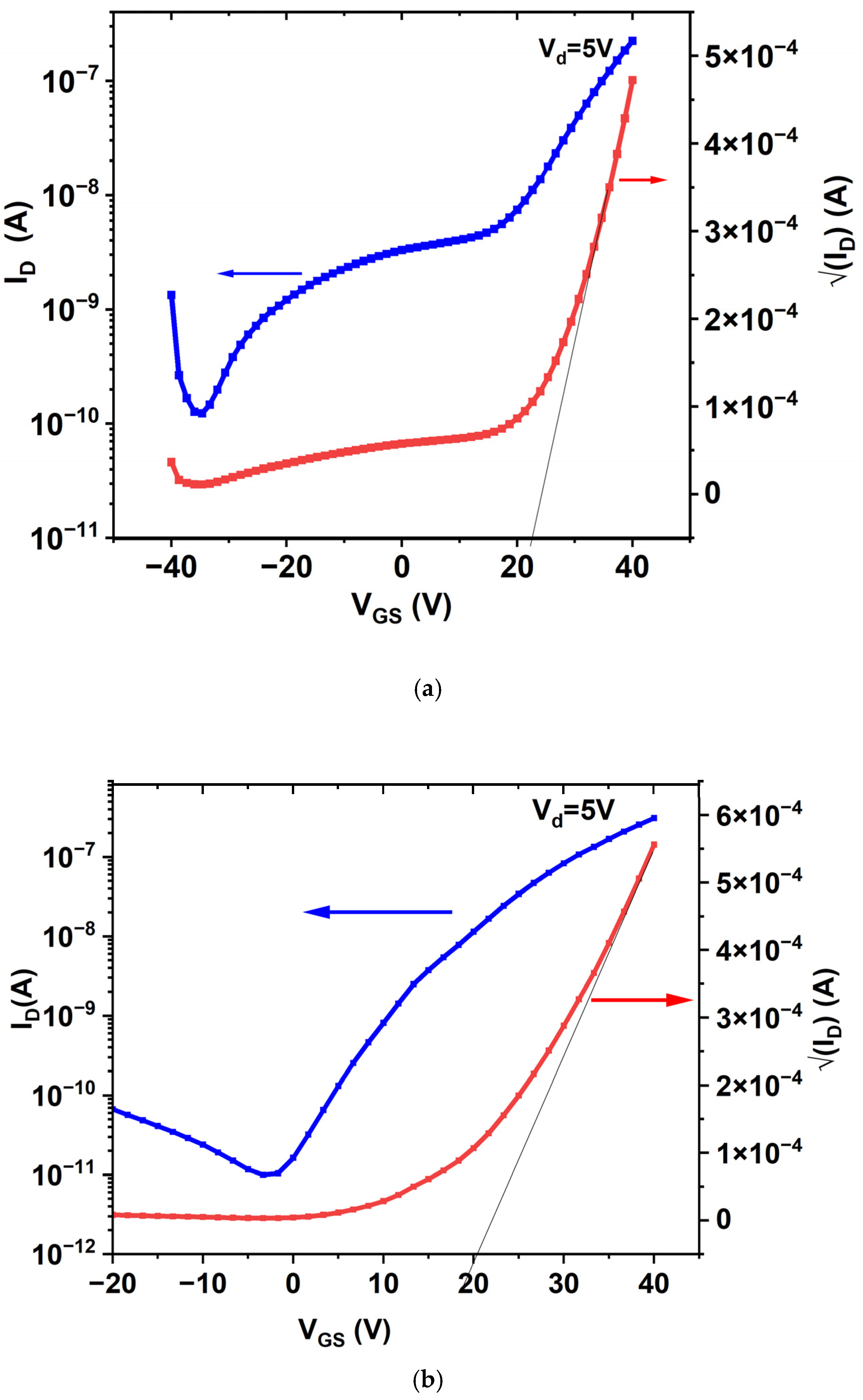
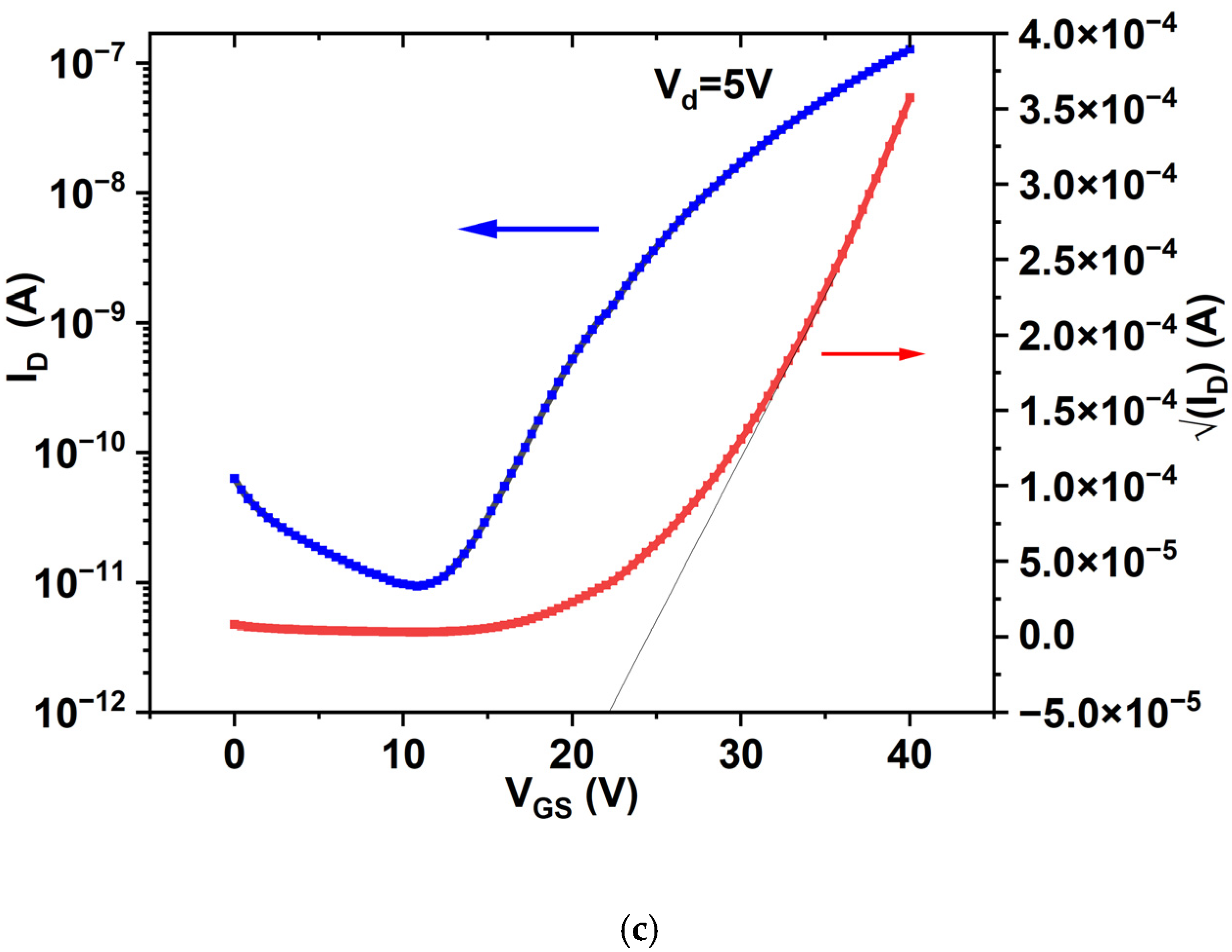
| Sample | Deposition Temperature | Ar:O2 Flow Rate | Annealing Temperature and Duration | RF Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | RT | 20:0 | N2 ambient 300 °C, 30 min | 60 W |
| B | RT | 18:2 | ||
| C | RT | 16:4 | ||
| D | 250 °C | 16:4 | ------- | 60 W |
| E | 300 °C | 16:4 |
| Sample | Deposition Temperature | Annealing Temperature and Ambient | Ar:O2 Flow Rate | Post-Contact Annealing | Carrier Concentration (cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | RT | 300 °C in N2 ambient | 16:4 | 220 °C | 2.6 1017 |
| D1 | 250 °C | - | 1 1016 | ||
| E1 | 300 °C | - | 1.6 1017 |
| Sample | FWHM (β) (Radians) | 2θ (Deg) | Crystallite Size D (nm) | Dislocation Density δ (Lines/m2) | Lattice Parameter Spacing (nm) | Micro-Strain ε |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.57 | 34.53 | 14.596 | 0.0047 | 0.260 | 0.0008 |
| B | 0.7 | 34.25 | 11.876 | 0.0071 | 0.262 | 0.0009 |
| C | 0.76 | 34.3 | 10.940 | 0.0084 | 0.261 | 0.0010 |
| D | 0.6 | 34.31 | 13.858 | 0.0052 | 0.261 | 0.0008 |
| E | 0.73 | 34.15 | 11.385 | 0.0077 | 0.262 | 0.0010 |
| Element | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|
| O 1s | 19.07 | 32.53 | 44.84 |
| Zn 2p | 73.56 | 56.76 | 47.66 |
| C | 7.36 | 10.71 | 7.5 |
| Sample | O2 Vacancy | O 1s Peak | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binding Energy (eV) | % Conc | FWHM | Binding Energy (eV) | FWHM | % Conc | |
| C | 531.77 | 41.38 | 1.99 | 530.354 | 1.25 | 58.62 |
| D | 532.38 | 39.1 | 1.54 | 530.43 | 1.6 | 60.9 |
| E | 531.88 | 30.26 | 1.57 | 529.88 | 1.7 | 69.74 |
| C | D | E | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn-O | 68.97 | 71.33 | 75.77 |
| Zn Interstitials | 31.03 | 28.67 | 24.23 |
| Year | Deposition Method | Mobility (cm2/V-s) | Carrier Concentration (cm−3) | Resistivity (Ω-cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 [59] | Sputtering | 17.3 | 2.3 × 1018 | - |
| 2015 [60] | Sputtering | 24.17 | 6.21 × 1015 | - |
| 2020 [61] | Pulsed Laser Deposition | 34.6 | 2.28 × 1018 | 0.0792 |
| 2020 [62] | Atomic Layer Deposition | 17.36 | 4.32 × 1020 | 8.33 × 10–4 |
| 2020 [63] | Sol–gel | 0.05 | 1.2 × 1015 | - |
| 2020 [64] | Sputtering | 18 | - | 3 × 10–4 |
| 2014 [65] | Sputtering | 0.064 | 1.4 × 1019 | 6.8 |
| 2011 [66] | Sputtering | 34 | 9.29 × 1011 | 1.98 × 105 |
| 2011 [67] | Spray pyrolysis | 0.26 | 7.27 × 1015 | 3.20 × 103 |
| 2011 [40] | Sputtering | 8.9 | 4.2 × 1016 | 31.8 |
| This work | Sputtering | 46.09 | 2.6 × 1017 | 1.96 |
| TFT | ||||
| 2018 [46] | Sputtering | 0.7 * | - | - |
| 2018 [68] | Sputtering | 0.62 * | - | - |
| 2020 [69] | Plasma ALD | 0.782 * | - | - |
| 2023 [70] | ALD | 3.1 * | - | - |
| 2023 [71] | Sputtering | 0.08 * | - | - |
| This work | Sputtering | 1.1 * | - | - |
| Sample | Bulk Mobility (cm2/V-s) | ION (μA) | VON (V) | VTh (V) | SS (V/dec) | ION/IOFF Ratio | μFE (cm2/V-s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 46.09 | 0.223 | −34.6 | 23.1 | 30 | 103 | 0.062 |
| D1 | 20.43 | 1.58 | −3.33 | 20.3 | 6.61 | 104 | 0.64 |
| E1 | 31.6 | 0.127 | 10.8 | 21.7 | 4.43 | 104 | 0.10 |
| Device | VON (V) | VTh (V) | SS (V/dec) | ION/IOFF Ratio | μFE (cm2/V-s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
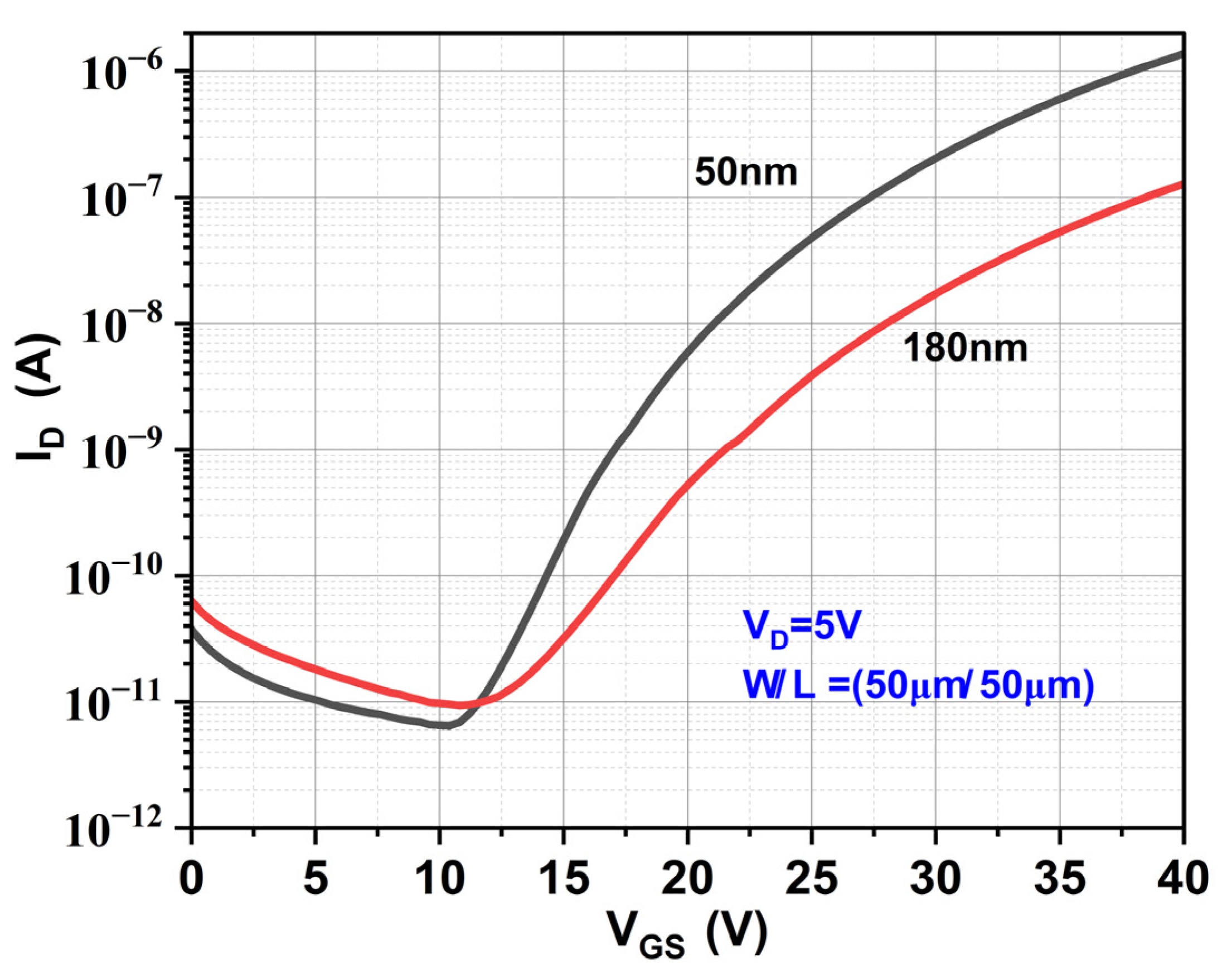
| E1 (180 nm) | 11.2 | 21.7 | 4.43 | 104 | 0.10 |
| E2 (50 nm) | 10.4 | 23.29 | 2.8 | 105 | 1.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muthusamy, S.; Bharatan, S.; Sivaprakasam, S.; Mohanam, R. Effect of Deposition Temperature on Zn Interstitials and Oxygen Vacancies in RF-Sputtered ZnO Thin Films and Thin Film-Transistors. Materials 2024, 17, 5153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215153
Muthusamy S, Bharatan S, Sivaprakasam S, Mohanam R. Effect of Deposition Temperature on Zn Interstitials and Oxygen Vacancies in RF-Sputtered ZnO Thin Films and Thin Film-Transistors. Materials. 2024; 17(21):5153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215153
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuthusamy, Sasikala, Sudhakar Bharatan, Sinthamani Sivaprakasam, and Ranjithkumar Mohanam. 2024. "Effect of Deposition Temperature on Zn Interstitials and Oxygen Vacancies in RF-Sputtered ZnO Thin Films and Thin Film-Transistors" Materials 17, no. 21: 5153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215153
APA StyleMuthusamy, S., Bharatan, S., Sivaprakasam, S., & Mohanam, R. (2024). Effect of Deposition Temperature on Zn Interstitials and Oxygen Vacancies in RF-Sputtered ZnO Thin Films and Thin Film-Transistors. Materials, 17(21), 5153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215153






