Silibinin-Loaded Amphiphilic PLGA–Poloxamer Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization, Release Kinetics, and Bioactivity Evaluation in Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Nanoparticles (NPs)
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis of the NPs
2.3.1. Particle Size and Surface Charge Analyses
2.3.2. Stability Study
2.3.3. Nanoparticle Morphology
2.3.4. Yield, Drug Entrapment Efficiency, and Drug Loading of Nanoparticles
2.3.5. Thermal Characterization via Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. In Vitro Bioactivity of PP-SLB Nanoparticles
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology and Characterization of NPs
3.2. In Vitro Drug Release Kinetics
3.3. In Vitro Bioactivity of PP-SLB Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inoue, T.; Fu, B.; Nishio, M.; Tanaka, M.; Kato, H.; Tanaka, M.; Itoh, M.; Yamakage, H.; Ochi, K.; Ito, A.; et al. Novel Therapeutic Potentials of Taxifolin for Obesity-Induced Hepatic Steatosis, Fibrogenesis, and Tumorigenesis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, A.; Dallio, M.; Loguercio, C. Silymarin/Silybin and Chronic Liver Disease: A Marriage of Many Years. Molecules 2017, 22, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Anati, L.; Essid, E.; Reinehr, R.; Petzinger, E. Silibinin Protects OTA-mediated TNF-α Release from Perfused Rat Livers and Isolated Rat Kupffer Cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Singh, R.P.; Chan, D.C.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin Induces Growth Inhibition and Apoptotic Cell Death in Human Lung Carcinoma Cells. Anticancer. Res. 2003, 23, 2649–2655. [Google Scholar]
- Polachi, N.; Bai, G.; Li, T.; Chu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Gu, N.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Modulatory Effects of Silibinin in Various Cell Signaling Pathways against Liver Disorders and Cancer—A Comprehensive Review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiruthiga, P.V.; Pandian, S.K.; Devi, K.P. Silymarin Protects PBMC against B(a)P Induced Toxicity by Replenishing Redox Status and Modulating Glutathione Metabolizing Enzymes—An in Vitro Study. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 247, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takke, A.; Shende, P. Magnetic-Core-Based Silibinin Nanopolymeric Carriers for the Treatment of Renal Cell Cancer. Life Sci. 2021, 275, 119377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takke, A.; Shende, P. Nanotherapeutic Silibinin: An Insight of Phytomedicine in Healthcare Reformation. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 21, 102057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirsaadat, S.; Jafari-Gharabaghlou, D.; Alijani, S.; Mousazadeh, H.; Dadashpour, M.; Zarghami, N. Metformin and Silibinin Co-Loaded PLGA-PEG Nanoparticles for Effective Combination Therapy against Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Samaligy, M.S.; Afifi, N.N.; Mahmoud, E.A. Increasing Bioavailability of Silymarin Using a Buccal Liposomal Delivery System: Preparation and Experimental Design Investigation. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 308, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, B. Fast Degradable Polycaprolactone for Drug Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2302–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.Y. Nanotechnology Platforms and Physiological Challenges for Cancer Therapeutics. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serri, C.; Argirò, M.; Piras, L.; Mita, D.G.; Saija, A.; Mita, L.; Forte, M.; Giarra, S.; Biondi, M.; Crispi, S.; et al. Nano-Precipitated Curcumin Loaded Particles: Effect of Carrier Size and Drug Complexation with (2-Hydroxypropyl)-β-Cyclodextrin on Their Biological Performances. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 520, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girotra, P.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, G. Development of Zolmitriptan Loaded PLGA/Poloxamer Nanoparticles for Migraine Using Quality by Design Approach. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 85, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhzad, O.C. Nanotechnology for Drug Delivery: The Perfect Partnership. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2008, 5, 927–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayol, L.; Serri, C.; Menale, C.; Crispi, S.; Piccolo, M.T.; Mita, L.; Giarra, S.; Forte, M.; Saija, A.; Biondi, M.; et al. Curcumin Loaded PLGA–Poloxamer Blend Nanoparticles Induce Cell Cycle Arrest in Mesothelioma Cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, G.; Nazim, U.; Sharma, A.; Manuel, V.; Elnaggar, M.G.; Taye, A.; Nasr, N.E.H.; Hofni, A.; Abdel Hakiem, A.F. Selective Targeting of the Novel CK-10 Nanoparticles to the MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golombek, S.K.; May, J.-N.; Theek, B.; Appold, L.; Drude, N.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Tumor Targeting via EPR: Strategies to Enhance Patient Responses. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 130, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Sousa, F.; Araújo, F.; Sarmento, B. Functionalizing PLGA and PLGA Derivatives for Drug Delivery and Tissue Regeneration Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, T.; Grumetto, L.; Neri, I.; De Falco, M.; Graziano, S.F.; Damiano, S.; Giaquinto, D.; Maruccio, L.; De Girolamo, P.; Villapiano, F.; et al. Investigating the Effect of Surface Hydrophilicity on the Destiny of PLGA-Poloxamer Nanoparticles in an In Vivo Animal Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Ke, W.; Dirisala, A.; Toh, K.; Tanaka, M.; Li, J. Stealth and Pseudo-Stealth Nanocarriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 198, 114895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, D.; Athawale, R.; Bajaj, A.; Shrikhande, S.; Goel, P.N.; Gude, R.P. Studies on Stabilization Mechanism and Stealth Effect of Poloxamer 188 onto PLGA Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 109, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmaso, S.; Caliceti, P. Stealth Properties to Improve Therapeutic Efficacy of Drug Nanocarriers. J. Drug Deliv. 2013, 2013, 374252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaly, N.; Yameen, B.; Wu, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Degradable Controlled-Release Polymers and Polymeric Nanoparticles: Mechanisms of Controlling Drug Release. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2602–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarvand, R.; Sepehri, N.; Manouchehri, S.; Rouhani, H.; Atyabi, F. Polylactide-Co-Glycolide Nanoparticles for Controlled Delivery of Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 877–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csaba, N.; Caamaño, P.; Sánchez, A.; Domínguez, F.; Alonso, M.J. PLGA:Poloxamer and PLGA:Poloxamine Blend Nanoparticles: New Carriers for Gene Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmani-Javan, E.; Jafari-Gharabaghlou, D.; Bonabi, E.; Zarghami, N. Fabricating Niosomal-PEG Nanoparticles Co-Loaded with Metformin and Silibinin for Effective Treatment of Human Lung Cancer Cells. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1193708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.-C.; Zhu, J.-J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.-L.; Huang, C.-G. Solubility of Silybin in Aqueous Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Fluid. Phase Equilibria 2007, 254, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, M.; Grassi, G. Application of Mathematical Modeling in Sustained Release Delivery Systems. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 1299–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, D.Y.; Lee, L.Y.; Wang, C.-H. Mathematical Modeling and Simulation of Drug Release from Microspheres: Implications to Drug Delivery Systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1274–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Modeling and Comparison of Dissolution Profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, T. Mechanism of Sustained-action Medication. Theoretical Analysis of Rate of Release of Solid Drugs Dispersed in Solid Matrices. J. Pharm. Sci. 1963, 52, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodosiou, E.; Purchartová, K.; Stamatis, H.; Kolisis, F.; Křen, V. Bioavailability of Silymarin Flavonolignans: Drug Formulations and Biotransformation. Phytochem. Rev. 2014, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Yang, Z.; Shi, H.; Turki Jalil, A.; Mahmood Saleh, M.; Mi, W. Potentiation of Curcumin-Loaded Zeolite Y Nanoparticles/PCL-Gelatin Electrospun Nanofibers for Postsurgical Glioblastoma Treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 80, 104105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Raval, M.; Manvar, A.; Airao, V.; Bhatt, V.; Shah, P. Lung Cancer Targeting Efficiency of Silibinin Loaded Poly Caprolactone/Pluronic F68 Inhalable Nanoparticles: In Vitro and In Vivo Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourtalebi Jahromi, L.; Ghazali, M.; Ashrafi, H.; Azadi, A. A Comparison of Models for the Analysis of the Kinetics of Drug Release from PLGA-Based Nanoparticles. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J. Mathematical Modeling of Bioerodible, Polymeric Drug Delivery Systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, M.; Guarnieri, D.; Yu, H.; Belli, V.; Netti, P.A. Sub-100 Nm Biodegradable Nanoparticles: In Vitro Release Features and Toxicity Testing in 2D and 3D Cell Cultures. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 045101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körber, M. PLGA Erosion: Solubility- or Diffusion-Controlled? Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2414–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, D.N.; Bhatia, A.; Kaur, R.; Sharma, R.; Kaur, G.; Dhawan, S. PLGA: A Unique Polymer for Drug Delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2015, 6, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollica, F.; Biondi, M.; Muzzi, S.; Ungaro, F.; Quaglia, F.; La Rotonda, M.I.; Netti, P.A. Mathematical Modelling of the Evolution of Protein Distribution within Single PLGA Microspheres: Prediction of Local Concentration Profiles and Release Kinetics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, M.; Indolfi, L.; Ungaro, F.; Quaglia, F.; La Rotonda, M.I.; Netti, P.A. Bioactivated Collagen-Based Scaffolds Embedding Protein-Releasing Biodegradable Microspheres: Tuning of Protein Release Kinetics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netti, P.A.; Biondi, M.; Frigione, M. Experimental Studies and Modeling of the Degradation Process of Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Microspheres for Sustained Protein Release. Polymers 2020, 12, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestri, T.; Immirzi, B.; Dal Poggetto, G.; Di Donato, P.; Mollo, V.; Mayol, L.; Biondi, M. How Poloxamer Addition in Hyaluronic-Acid-Decorated Biodegradable Microparticles Affects Polymer Degradation and Protein Release Kinetics. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, V.; Guarnieri, D.; Biondi, M.; Della Sala, F.; Netti, P.A. Dynamics of Nanoparticle Diffusion and Uptake in Three-Dimensional Cell Cultures. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 149, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateen, S.; Tyagi, A.; Agarwal, C.; Singh, R.P.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin Inhibits Human Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Cell Growth through Cell-cycle Arrest by Modulating Expression and Function of Key Cell-cycle Regulators. Mol. Carcinog. 2010, 49, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.H.; Zou, Y.; Perez-Soler, R. Induction of Senescence-like Phenotype and Loss of Paclitaxel Sensitivity after Wild-Type P53 Gene Transfection of P53-Null Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer H358 Cells. Anticancer. Res. 2000, 20, 693–702. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, H.; Lee, H.; Choi, C.-M.; Sung, Y.H.; Lee, J.C.; Rho, J.K. Contribution of P53 in Sensitivity to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davatgaran-Taghipour, Y.; Masoomzadeh, S.; Farzaei, M.H.; Bahramsoltani, R.; Karimi-Soureh, Z.; Rahimi, R.; Abdollahi, M. Polyphenol Nanoformulations for Cancer Therapy: Experimental Evidence and Clinical Perspective. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2689–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Ahmadi, Z.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samarghandian, S. Nano-Soldiers Ameliorate Silibinin Delivery: A Review Study. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, M.M.; Amoabediny, G.; Rezayat, S.M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Ebrahimi, B. In Vitro Co-Delivery Evaluation of Novel Pegylated Nano-Liposomal Herbal Drugs of Silibinin and Glycyrrhizic Acid Nano-Phytosome) to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cell J. 2016, 18, 4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuen, C.; Fakurazi, S.; Othman, S.; Masarudin, M. Increased Loading, Efficacy and Sustained Release of Silibinin, a Poorly Soluble Drug Using Hydrophobically-Modified Chitosan Nanoparticles for Enhanced Delivery of Anticancer Drug Delivery Systems. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
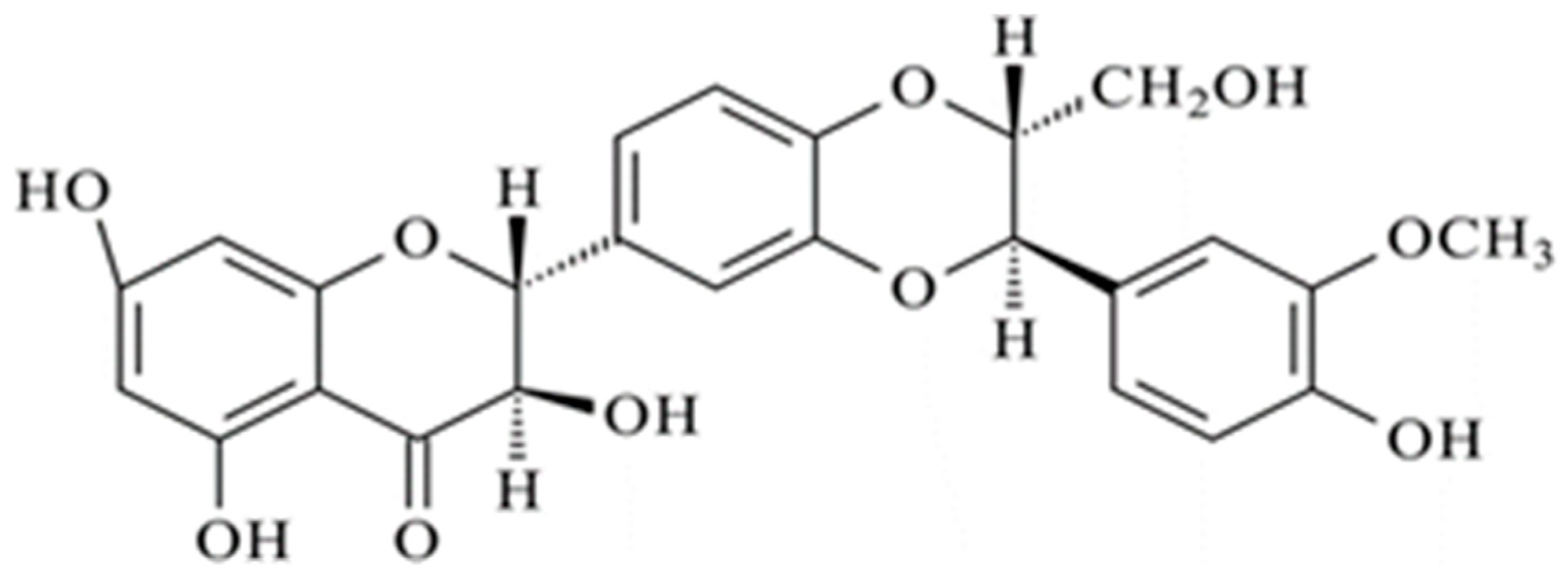

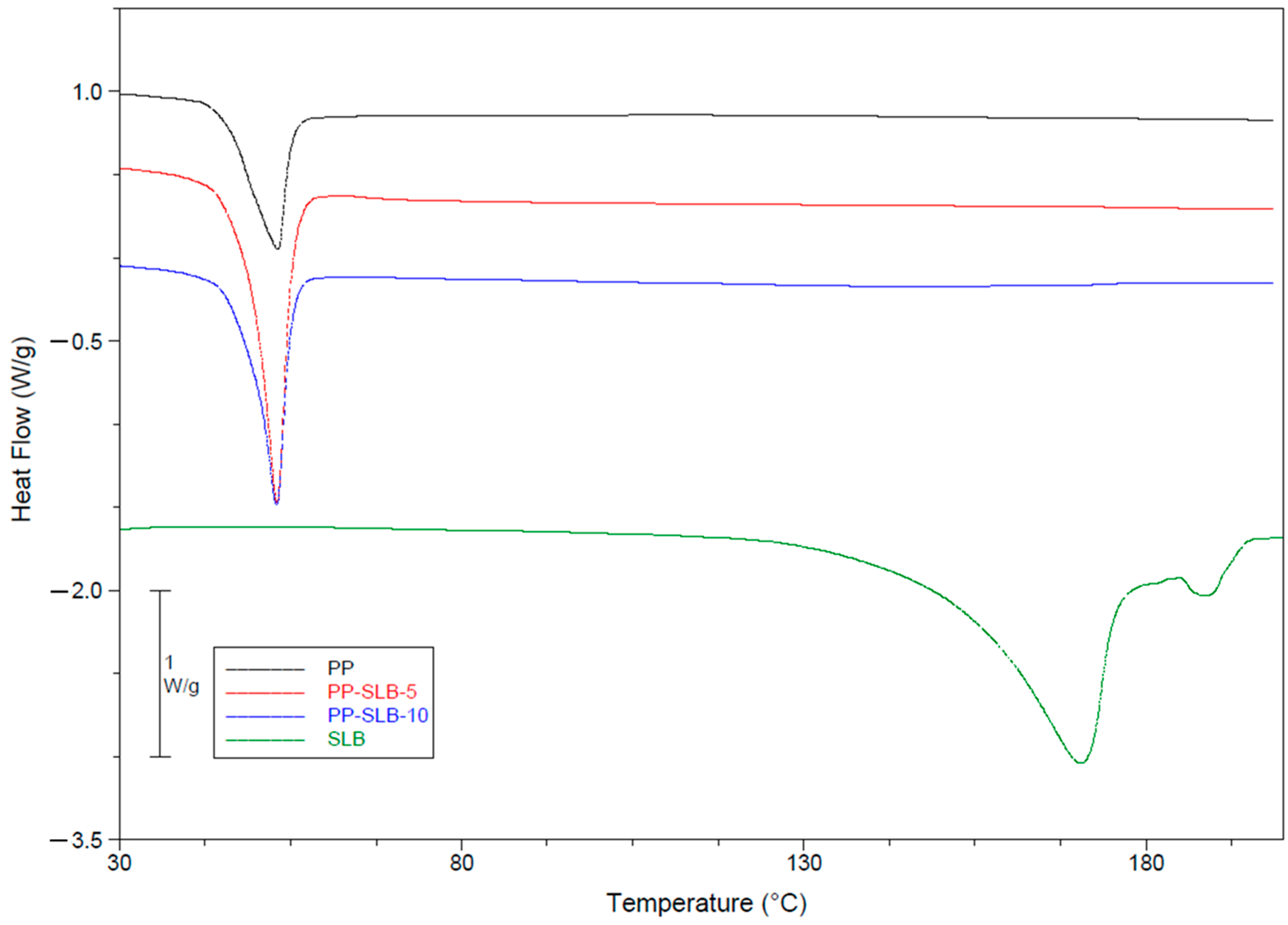

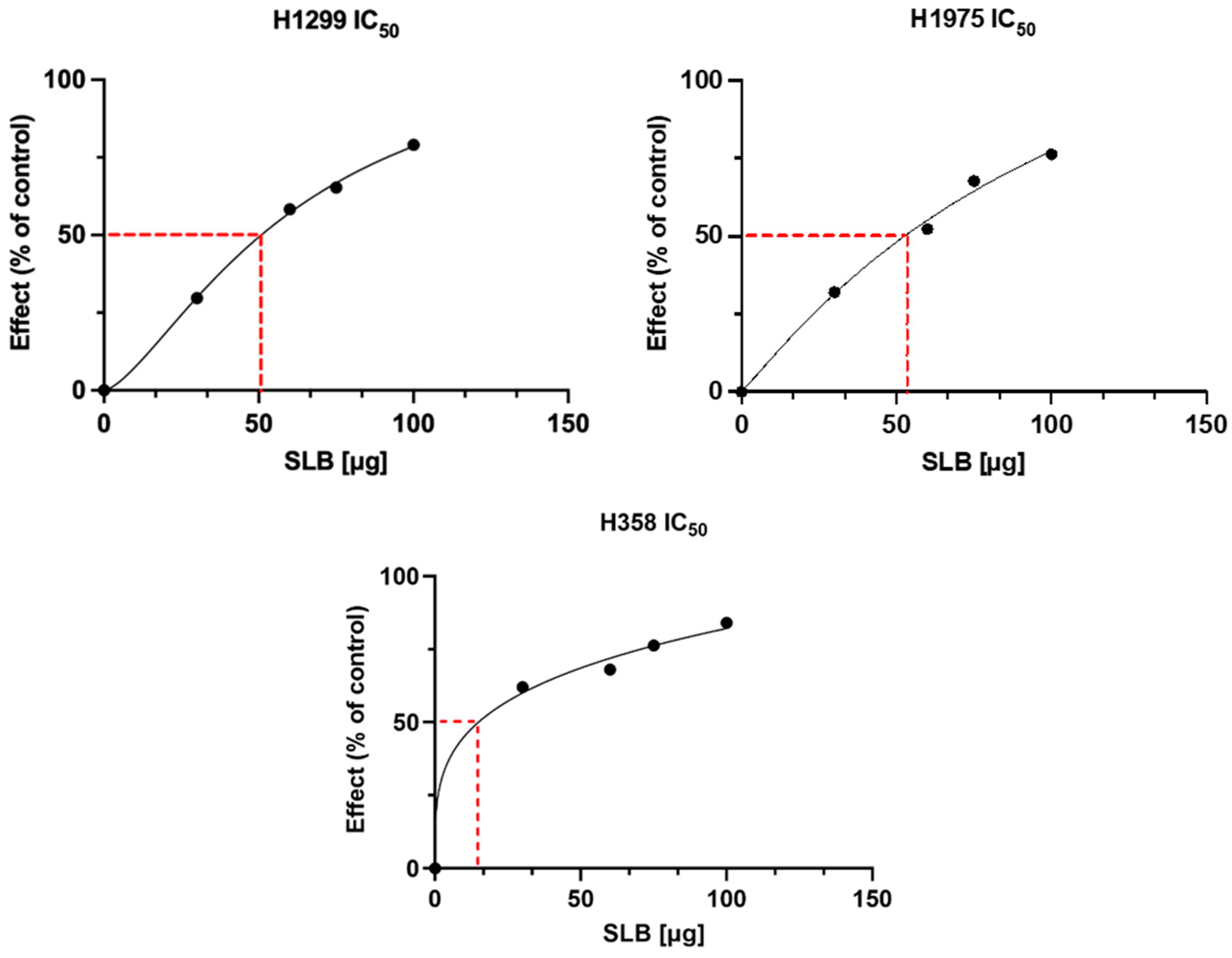

| Sample Acronym | Polymer Concentration in the Organic Phase Oil % w/v | Polox in the Aqueous Phase % w/v | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLGA% | F68% | F127% | F68% | F127% | |
| (w/v) | (w/v) | (w/v) | (w/v) | (w/v) | |
| P | 2 | 0.0175 | 0.0175 | ||
| PP | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.0175 | 0.0175 |
| PP-SLB5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.0175 | 0.0175 |
| PP-SLB10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.0175 | 0.0175 |
| Formulation | Particle Mean Diameter (nm) | Polydispersity Index (PDI) | Zeta Potential (mV) | Entrapment Efficiency (%) | Drug Loading (%) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | 153 ± 1.6 * | 0.140 ± 0.01 | −31.4 ± 2.0 * | |||
| PP | 89 ± 0.6 *#$ | 0.132 ± 0.01 $ | −19.2 ± 2.0 * | - | 57.02 ± 0.4 #$ | |
| PP-SLB5 | 98 ± 2.2 #& | 0.212 ± 0.03 & | −20.9 ± 0.4 | 84.8 ± 3.0 | 1.61 ± 1.8 | 74.3 ± 2.5 # |
| PP-SLB10 | 124 ± 2.0 $& | 0.302 ± 0.06 $& | −21 ± 2.0 | 93.9 ± 2.1 | 1.20 ± 0.1 | 72.8 ± 1.8 $ |
| Formulation | NP Diameters in Water 4 °C [nm] | NP Diameters in RPMI 37 °C [nm] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | Day 10 | Day 20 | Day 30 | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | |
| P | 153 ± 1.6 | 154 ± 0.2 | 160 ± 1.1 | 182 ± 5.4 | 166 ± 9.4 | 168 ± 2.5 | 191 ± 1.5 |
| PP | 89 ± 0.6 | 92 ± 0.4 | 89 ± 0.6 | 90 ± 1.0 | 85 ± 0.5 | 84 ± 0.8 | 84 ± 0.3 |
| PP-SLB5 | 98 ± 2.2 | 156 ± 3.3 | 153 ± 2.3 | 156 ± 1.9 | 153 ± 4.0 | 160 ± 2.0 | 164 ± 1.2 |
| PP-SLB10 | 124 ± 2.9 | 185 ± 1.5 | 163 ± 1.0 | 186 ± 4.7 | 130 ± 2.5 | 197 ± 1.8 | 198 ± 15 |
| Sample | ΔH° (J/g) | Tonset (°C) | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 28.6 ± 2.5 | 47.0 ± 1.9 | 53.3 ± 0.2 |
| PP-SLB5 | 52.8 ± 3.7 | 46.9 ± 2.6 | 52.3 ± 1.1 |
| PP-SLB10 | 40.7 ± 1.2 | 49.4 ± 1.0 | 53.3 ± 0.5 |
| SLB | 172.3 ± 10.4 | 152.6 ± 2.2 | 171.3 ± 1.0 |
| SLB 5 | SLB 10 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Parameter | R2 | R2 | ||
| Zero order | k0 [h−1] | 0.133 | 0.997 | 0.082 | 0.949 |
| First order | k1 [h−1] | 0.227 | 0.937 | 0.084 | 0.971 |
| Higuchi | kH [h−0.5] | 0.300 | 0.942 | 0.158 | 0.977 |
| Korsemeyer–Peppas | kKP [h−n] | 0.151 | 0.935 | 0.259 | 0.982 |
| n | 0.927 | 0307 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villapiano, F.; Piccioni, M.; D’Aria, F.; Crispi, S.; Rassu, G.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E.; Giancola, C.; Serri, C.; Biondi, M.; et al. Silibinin-Loaded Amphiphilic PLGA–Poloxamer Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization, Release Kinetics, and Bioactivity Evaluation in Lung Cancer Cells. Materials 2024, 17, 5480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17225480
Villapiano F, Piccioni M, D’Aria F, Crispi S, Rassu G, Giunchedi P, Gavini E, Giancola C, Serri C, Biondi M, et al. Silibinin-Loaded Amphiphilic PLGA–Poloxamer Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization, Release Kinetics, and Bioactivity Evaluation in Lung Cancer Cells. Materials. 2024; 17(22):5480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17225480
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillapiano, Fabrizio, Miriam Piccioni, Federica D’Aria, Stefania Crispi, Giovanna Rassu, Paolo Giunchedi, Elisabetta Gavini, Concetta Giancola, Carla Serri, Marco Biondi, and et al. 2024. "Silibinin-Loaded Amphiphilic PLGA–Poloxamer Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization, Release Kinetics, and Bioactivity Evaluation in Lung Cancer Cells" Materials 17, no. 22: 5480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17225480
APA StyleVillapiano, F., Piccioni, M., D’Aria, F., Crispi, S., Rassu, G., Giunchedi, P., Gavini, E., Giancola, C., Serri, C., Biondi, M., & Mayol, L. (2024). Silibinin-Loaded Amphiphilic PLGA–Poloxamer Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization, Release Kinetics, and Bioactivity Evaluation in Lung Cancer Cells. Materials, 17(22), 5480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17225480












