Numerical Study on Effect of Aggregate Moisture on Mixing Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Contact Model
2.1. Dry Particle Contact Model
2.2. Wet Particle Contact Model
2.2.1. Liquid Bridge Force
2.2.2. Linear Cohesive Contact Model
3. Experiment
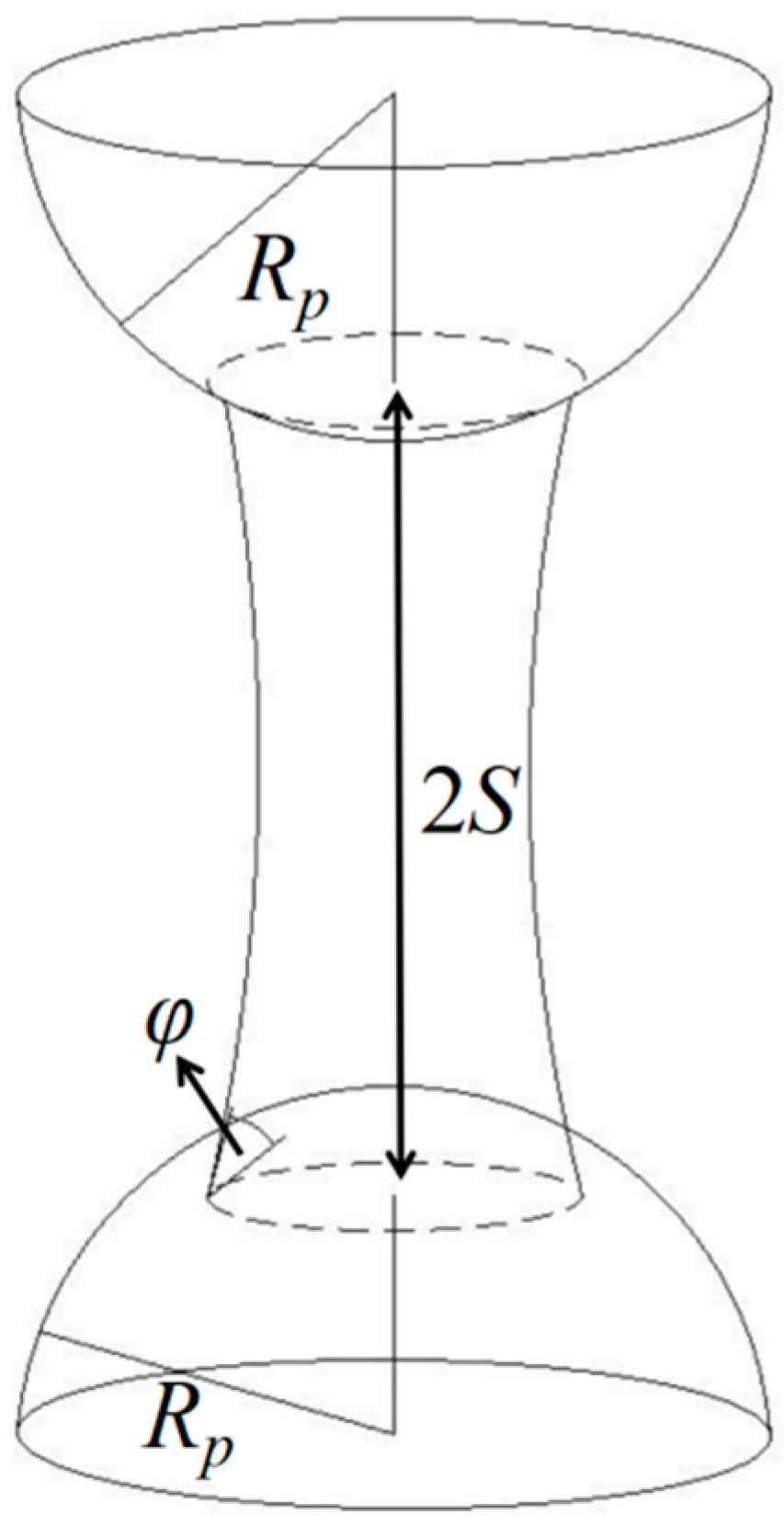
3.1. Angle of Repose Experiments
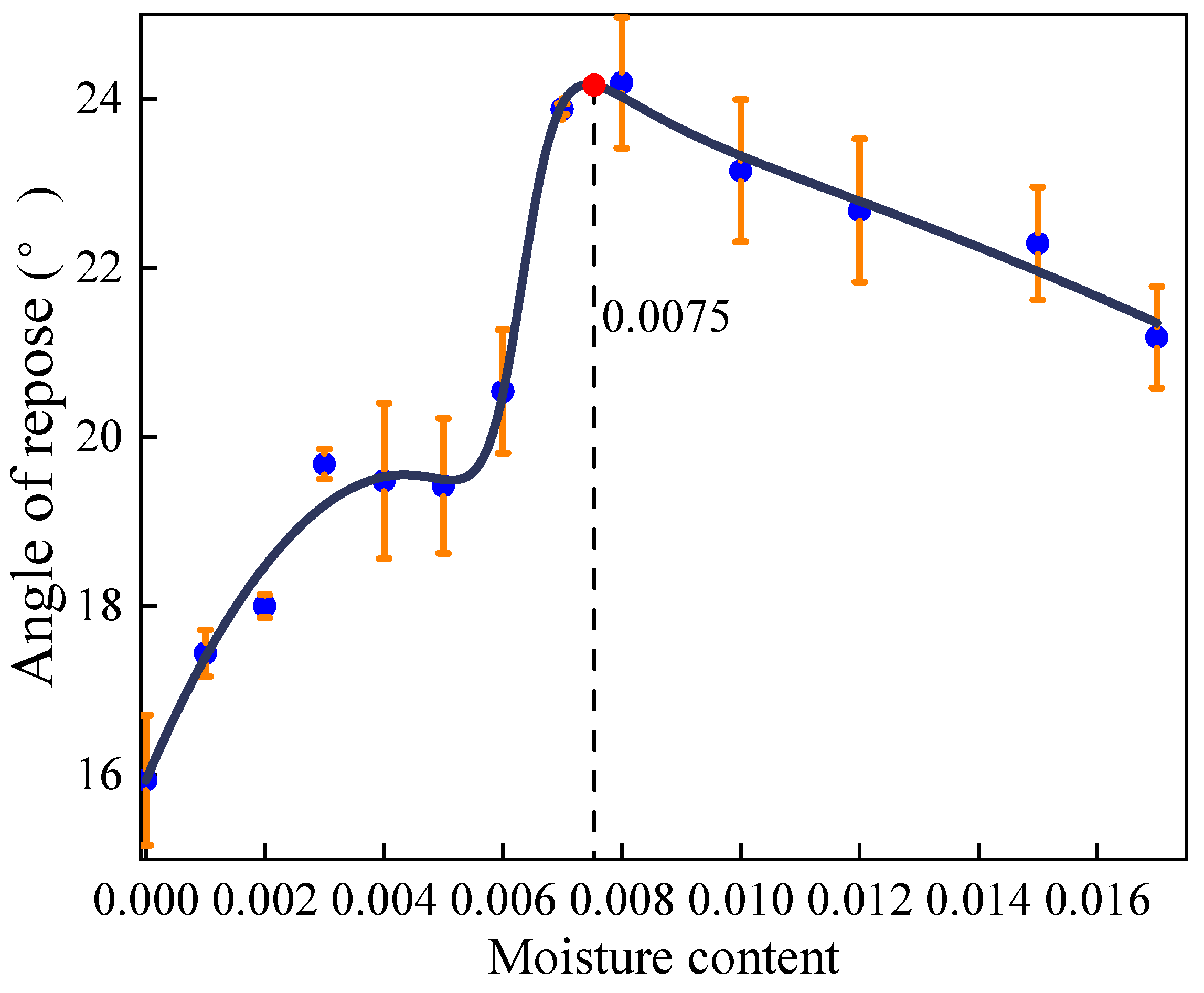
3.1.1. Relationship between Angle of Repose and Moisture of Pebbles
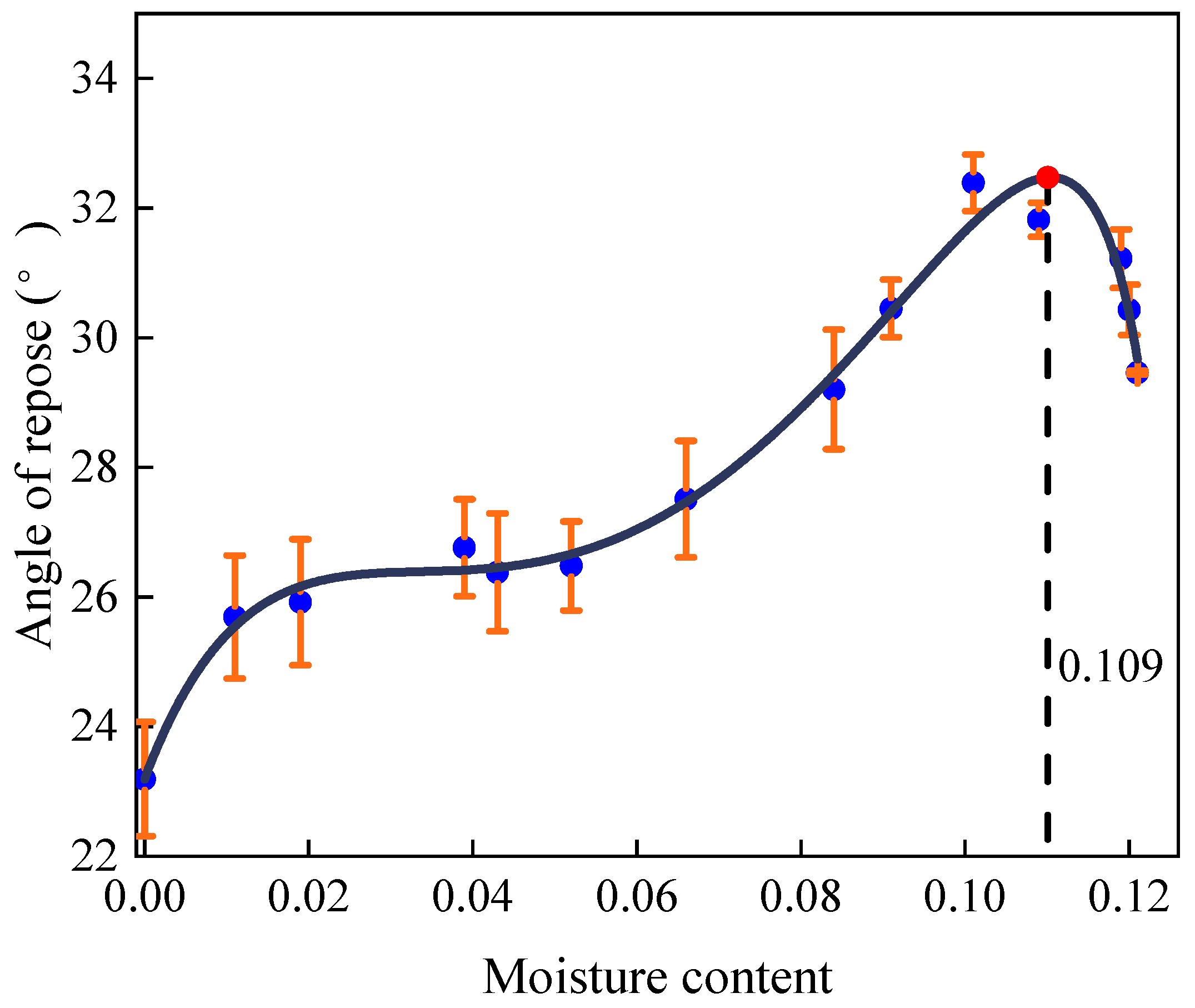
3.1.2. Relationship between Angle of Repose and Moisture of Sand
3.2. Sand and Pebble Mixing Experiment
3.2.1. Material
3.2.2. Sampling Method
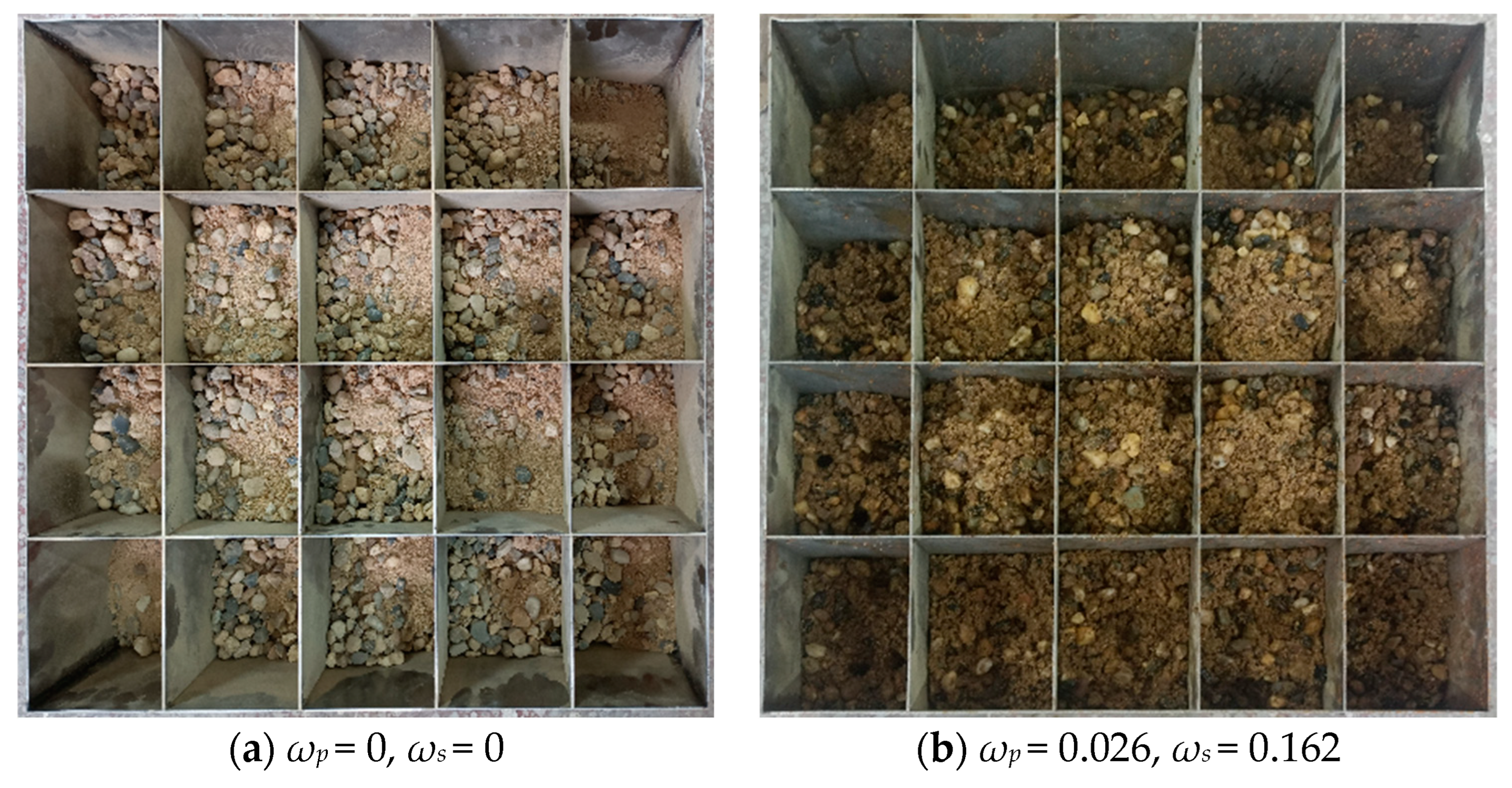
3.2.3. Result of Mixing Experiment
4. Simulation
4.1. Parameter Setting
4.2. Simulation of Angle of Repose
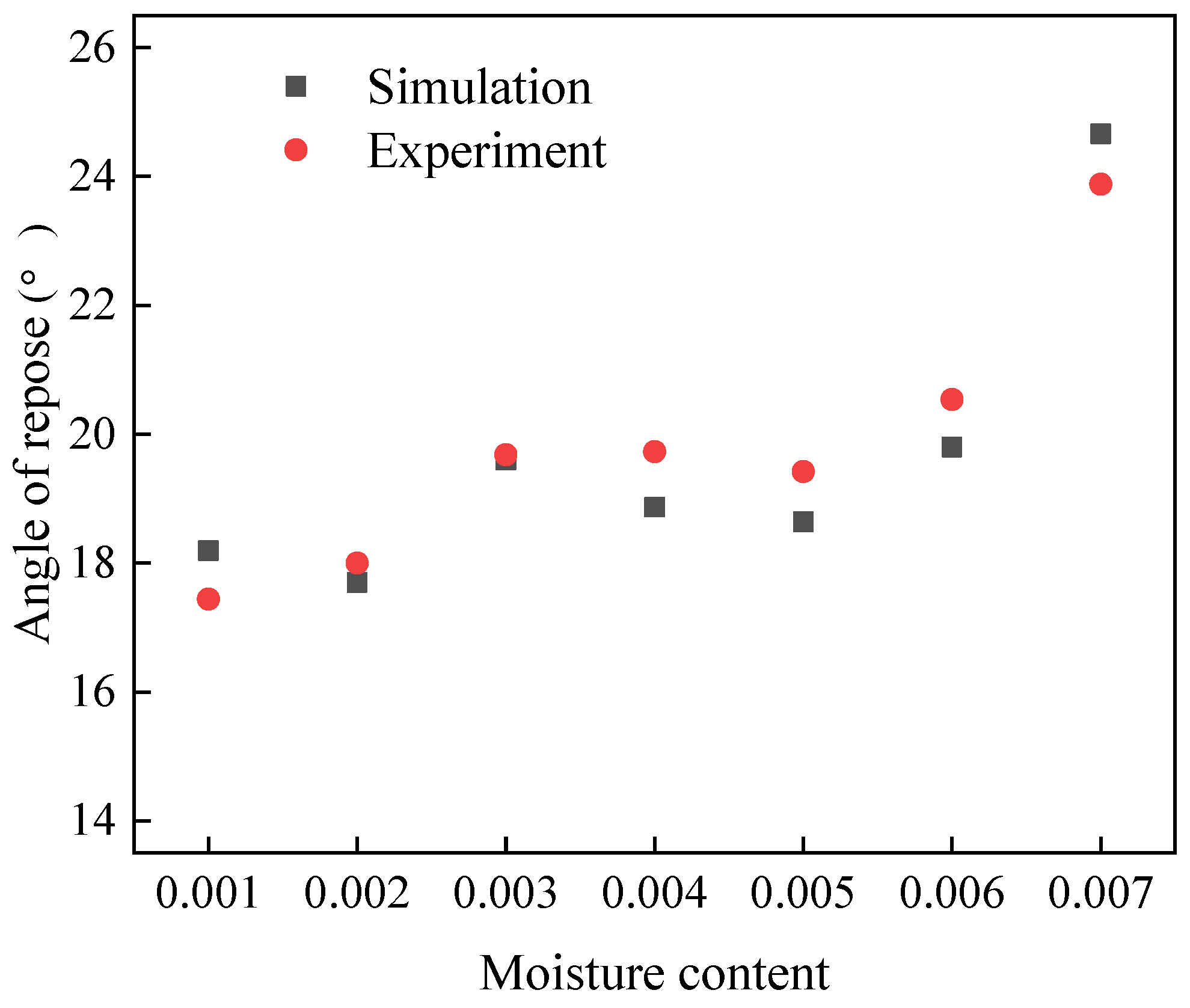
4.2.1. Simulation of Pebble Angle of Repose
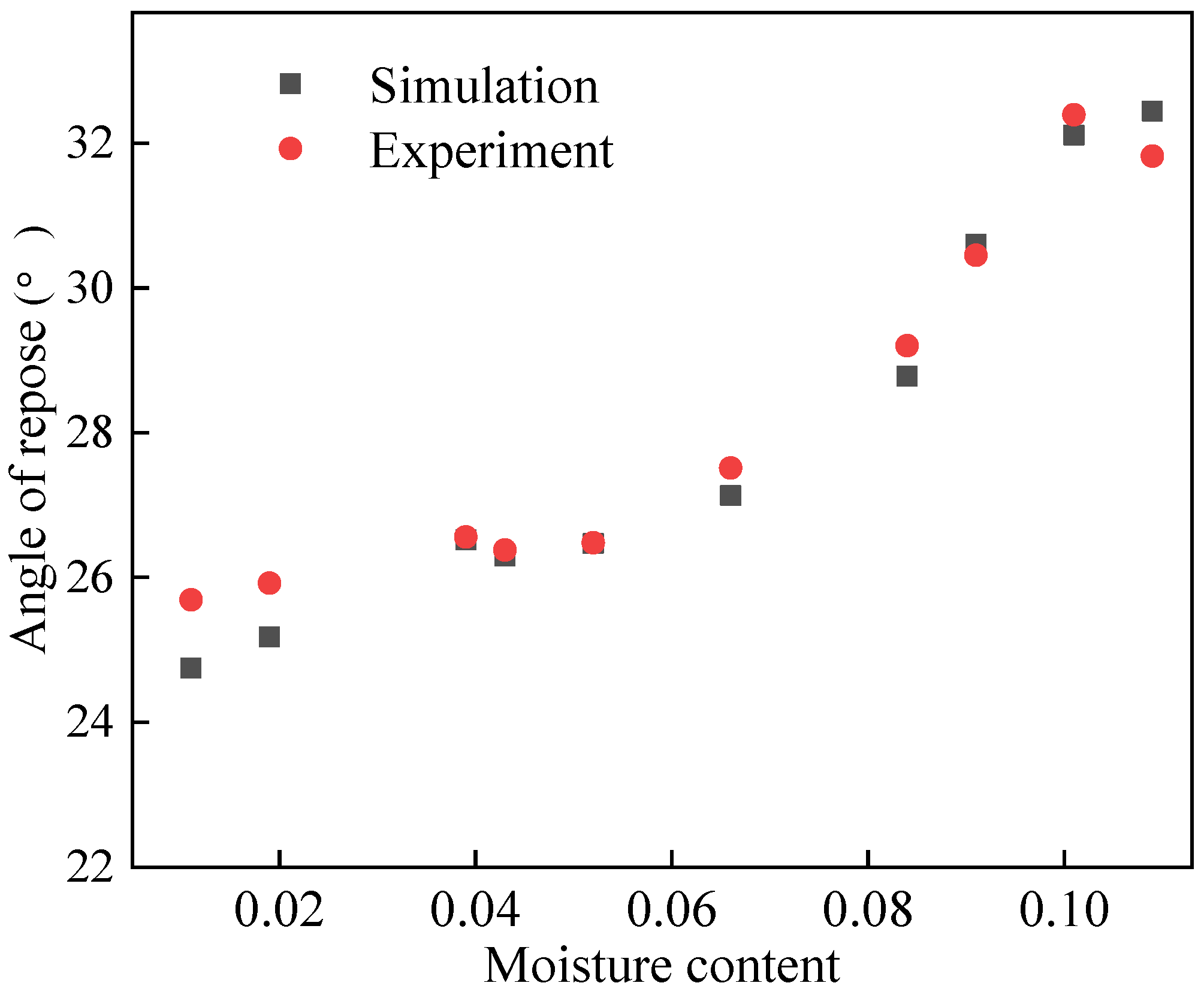
4.2.2. Simulation of Sand Angle of Repose
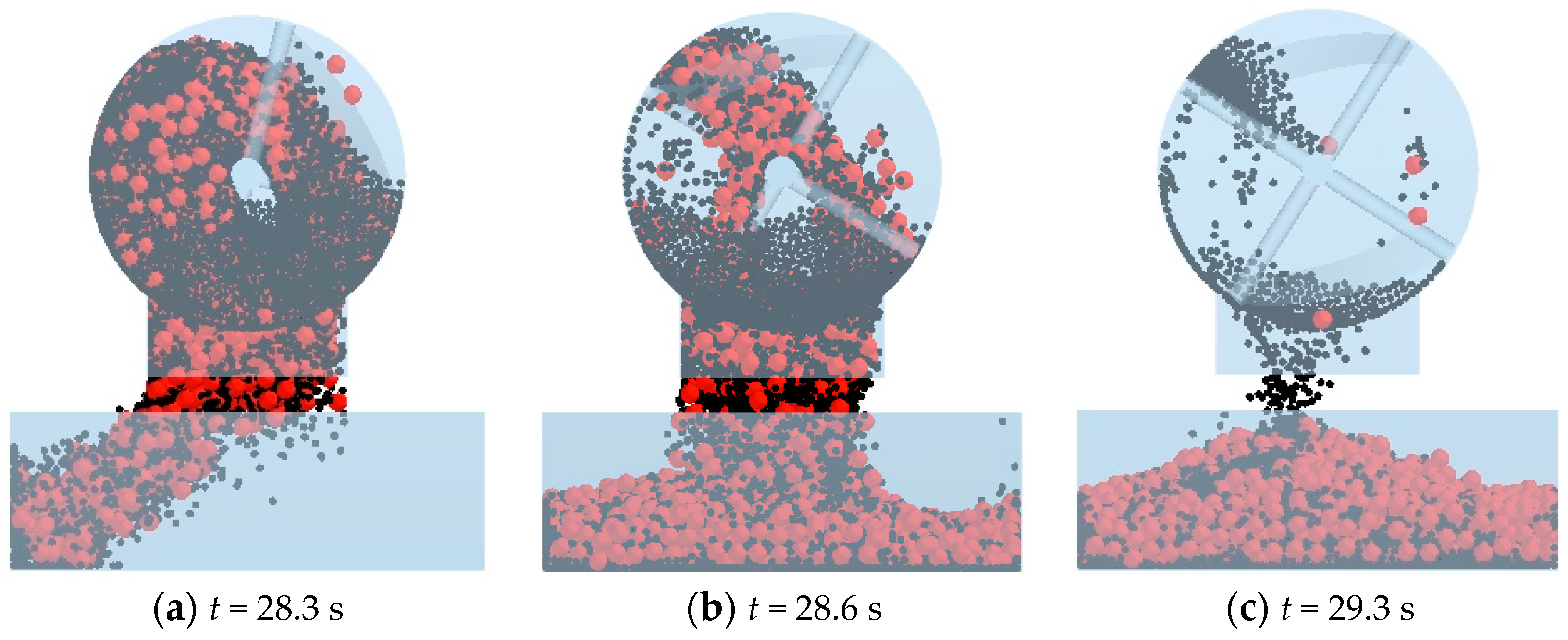
4.3. Simulation of Mixing of Sand and Pebbles
4.4. Effect of Mixing Time on Homogeneity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tahmasebi, P. A State-of-the-Art Review of Experimental and Computational Studies of Granular Materials: Properties, Advances, Challenges, and Future Directions. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 138, 101157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Yan, H. Two-Particle Method for Liquid–Solid Two-Phase Mixed Flow. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 033317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, J. Sands, Powders, and Grains: An Introduction to the Physics of Granular Materials. J. Fluid Mech. 2000, 419, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, S.Y.; Christman, L.E.; Jacobs, D.T.; Johnson, N.S.D.E.F.; Palchoudhuri, P.; Tieman, C.E.; Vajpeyi, A.; Wainwright, E.R.; Walker, J.E.; Wilson, I.S.; et al. Universal Aspects of Cohesion. Granul. Matter 2022, 24, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, L.; Vidales, A.M.; Uñac, R.; Roht, Y.L.; Gómez-Arriaran, I.; Ippolito, I. Effect of Humidity on the Static Angle in Granular Systems. Granul. Matter 2021, 23, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, J.M.; Castellanos, A.; Ramos, A.; Watson, P.K. Avalanches in Fine, Cohesive Powders. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 6851–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badetti, M.; Fall, A.; Chevoir, F.; Aimedieu, P.; Rodts, S.; Roux, N. Rheology and Microstructure of Unsaturated Granular Materials: Experiments and Simulations. J. Rheol. 2018, 62, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquet, L.; Charlaix, E.; Ciliberto, S.; Crassous, J. Moisture-Induced Ageing in Granular Media and the Kinetics of Capillary Condensation. Nature 1998, 396, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restagno, F.; Ursini, C.; Gayvallet, H.; Charlaix, E. Aging in Humid Granular Media. Phys. Review. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2002, 66, 021304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegzes, P.; Albert, R.; Paskvan, M.; Barabási, A.-L.; Vicsek, T.; Schiffer, P. Liquid-Induced Transitions in Granular Media. Phys. Rev. E 1999, 60, 5823–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadani, A.; Kudrolli, A. Angle of Repose and Segregation in Cohesive Granular Matter. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 051301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadani, A.; Kudrolli, A. Segregation Transitions in Wet Granular Matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 85, 5102–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-C.; Huang, Y.-Y. Experimental Investigate the Effect of Liquid Distribution State on Size Segregation of Wet Granular Materials in Rotating Drums. Powder Technol. 2021, 381, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geromichalos, D.; Kohonen, M.M.; Mugele, F.; Herminghaus, S. Mixing and Condensation in a Wet Granular Medium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 168702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wu, C.; Yin, H. Virtual Experiments of Particle Mixing Process with the SPH-DEM Model. Materials 2021, 14, 2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cundall, P.A.; Strack, O.D.L. A Discrete Numerical Model for Granular Assemblies. Géotechnique 1979, 29, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, C.D.; Adams, M.J.; Johnson, S.A.; Seville, J.P.K. Capillary Bridges between Two Spherical Bodies. Langmuir 2000, 16, 9396–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iveson, S.M. Granule Coalescence Modelling: Including the Effects of Bond Strengthening and Distributed Impact Separation Forces. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 2215–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, V.; Wensrich, C.M.; Moreno-Atanasio, R. Elucidation of the Role of Cohesion in the Macroscopic Behaviour of Coarse Particulate Systems Using DEM. Powder Technol. 2020, 361, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, S. DEM Simulation of Wet Granular-Fluid Flows in Spouted Beds: Numerical Studies and Experimental Verifications. Powder Technol. 2017, 318, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R. A DEM Numerical Investigation on Dry and Wet Particles Mixing in Rectangular Spouted Bed. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Krenzer, K. Simulating Mixing Processes of Fresh Concrete Using the Discrete Element Method (DEM) under Consideration of Water Addition and Changes in Moisture Distribution. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 115, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radl, S.; Kalvoda, E.; Glasser, B.J.; Khinast, J.G. Mixing Characteristics of Wet Granular Matter in a Bladed Mixer. Powder Technol. 2010, 200, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, M.; Siraj, M.S. DEM Studies of Polydisperse Wet Granular Flows. Powder Technol. 2018, 328, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, B.; Khinast, J.G.; Glasser, B.J. Wet Granular Flows in a Bladed Mixer: Experiments and Simulations of Monodisperse Spheres. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 3354–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, G.N.; Siraj, M.S. DEM Study of Dry and Wet Granular Flows in a Vertical Bladed Mixer. Part. Sci. Technol. 2021, 39, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iveson, S.M.; Litster, J.D.; Hapgood, K.; Ennis, B.J. Nucleation, Growth and Breakage Phenomena in Agitated Wet Granulation Processes: A Review. Powder Technol. 2001, 117, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitarai, N.; Nori, F. Wet Granular Materials. Adv. Phys. 2006, 55, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EDEM User Guide (2008). Available online: http://tm.spbstu.ru/images/2/28/EDEM2.4_user_guide.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Li, H. Impact of Cohesion Forces on Particle Mixing and Segregation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, R.; Albert, I.; Hornbaker, D.; Schiffer, P.; Barabási, A.-L. Maximum Angle of Stability in Wet and Dry Spherical Granular Media. Phys. Rev. E 1997, 56, R6271–R6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megias-Alguacil, D.; Gauckler, L.J. Analysis of the Capillary Forces between Two Small Solid Spheres Binded by a Convex Liquid Bridge. Powder Technol. 2010, 198, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, X.; Rossetti, D.; Iveson, S.M.; Simons, S.J.R. Modeling the Evolution and Rupture of Pendular Liquid Bridges in the Presence of Large Wetting Hysteresis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 232, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z. Numerical Study of Particle Flow and Mixing Characteristics in a Ribbon Mixer. Master's Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z. The Numerical Simulation and Experiment Research of Wet Particles Flow in a Hopper. Nat. Sci. J. Hainan. Univ. 2003, 22, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, G. Introduction to Particle Mechanics; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Lu, Y. 3D DEM Simulation of Random Packing of Particulates under Gravity. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2006, 28, 2139–2143. [Google Scholar]
- Beccati, N.; Ferrari, C.; Bonanno, A.; Balestra, M. Calibration of a CFD Discharge Process Model of an Off-Road Self-Loading Concrete Mixer. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelzle, S.; Nirschl, H. DEM Simulations: Mixing of Dry and Wet Granular Material with Different Contact Angles. Granul. Matter 2018, 20, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z. Study on the Mixing Process of Powder Particles and the Blade Erosion in an Intensive Mixer. Ph.D. Thesis, Xiangtan University, Xiangtan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
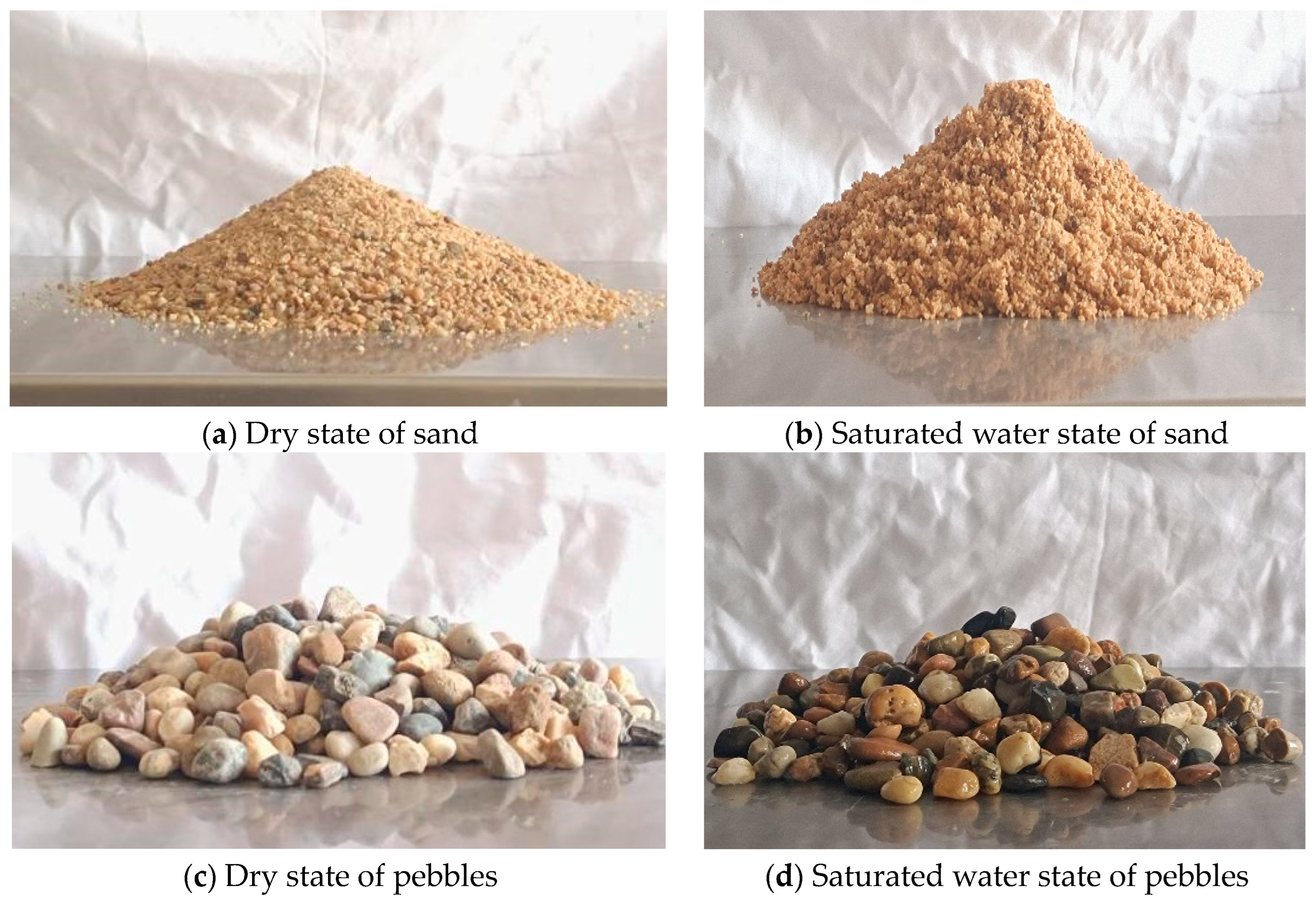




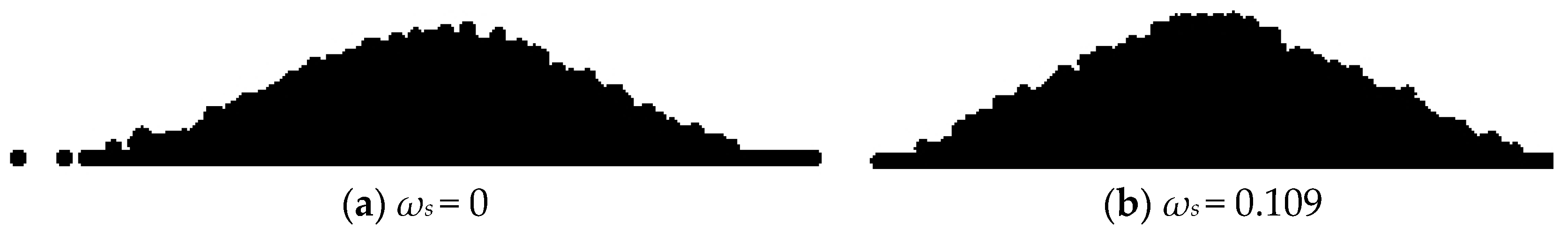

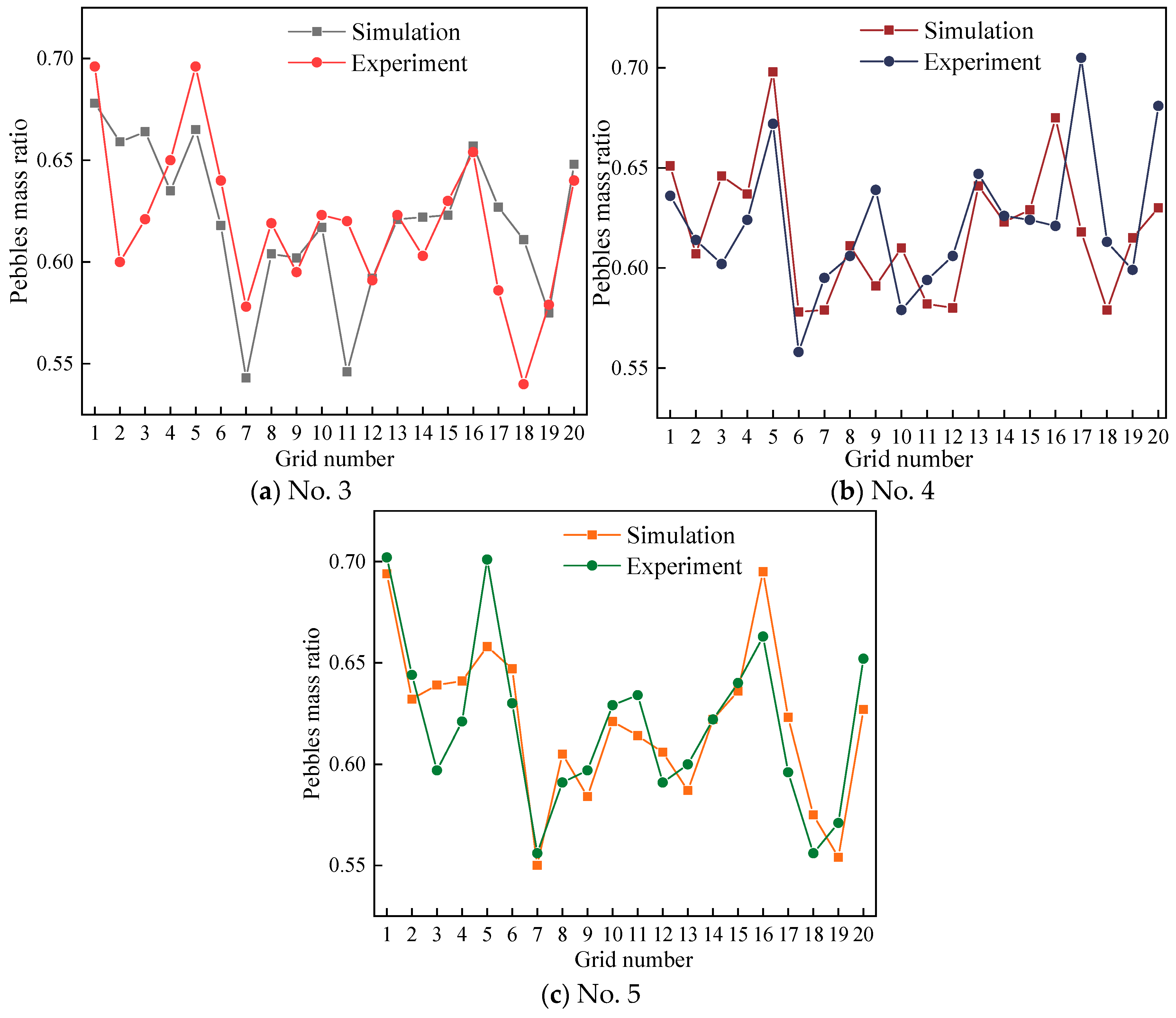
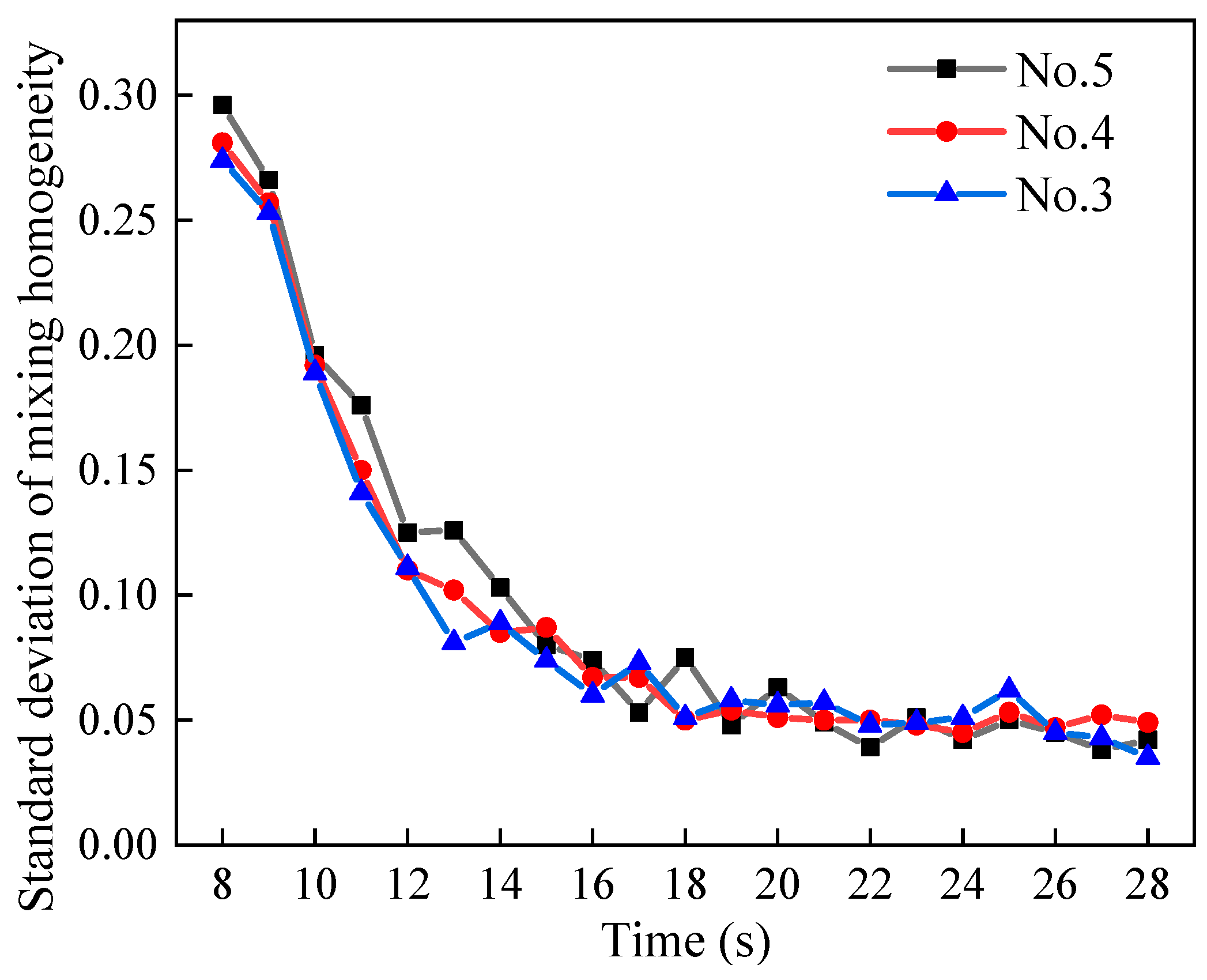
| Moisture Content | Experiment Value (°) | Average Value (°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 0 | 15.07 | 16.22 | 16.53 | 15.94 |
| 0.001 | 17.24 | 19.95 | 17.63 | 17.44 |
| 0.002 | 17.9 | 20 | 18.09 | 18.00 |
| 0.003 | 19.8 | 22.66 | 19.55 | 19.68 |
| 0.004 | 18.56 | 20.4 | 19.49 | 19.48 |
| 0.005 | 18.69 | 20.27 | 19.29 | 19.42 |
| 0.006 | 20.02 | 21.39 | 20.81 | 20.54 |
| 0.007 | 20.38 | 23.92 | 23.83 | 23.88 |
| 0.008 | 23.3 | 24.59 | 24.68 | 24.19 |
| 0.010 | 22.21 | 23.39 | 23.84 | 23.15 |
| 0.012 | 21.72 | 23.03 | 23.3 | 22.68 |
| 0.015 | 21.53 | 22.58 | 22.77 | 22.29 |
| 0.017 | 20.75 | 24.03 | 21.6 | 21.18 |
| Moisture Content | Experiment Value (°) | Average Value (°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 0 | 23.61 | 22.18 | 23.79 | 23.19 |
| 0.011 | 25.36 | 24.95 | 26.76 | 25.69 |
| 0.019 | 25.8 | 25.02 | 26.95 | 25.92 |
| 0.039 | 26.45 | 26.21 | 27.61 | 26.76 |
| 0.043 | 25.86 | 25.64 | 27.65 | 26.38 |
| 0.052 | 26.21 | 25.97 | 27.26 | 26.48 |
| 0.066 | 26.92 | 27.07 | 28.55 | 27.51 |
| 0.084 | 28.18 | 29.98 | 29.44 | 29.20 |
| 0.091 | 30.96 | 30.19 | 30.19 | 30.45 |
| 0.101 | 32.44 | 32.8 | 31.93 | 32.39 |
| 0.109 | 32.01 | 31.93 | 31.52 | 31.82 |
| 0.119 | 31.5 | 31.47 | 30.7 | 31.22 |
| 0.120 | 30.66 | 30.64 | 29.98 | 30.43 |
| 0.121 | 29.44 | 29.44 | 29.49 | 29.46 |
| Series No. | Drying Time (min.) | Pebbles’ Moisture Content | Sand Moisture Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0.026 | 0.162 |
| 2 | 10 | 0.009 | 0.127 |
| 3 | 20 | 0.005 | 0.084 |
| 4 | 30 | 0.001 | 0.044 |
| 5 | - | 0 | 0 |
| Drying Time | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 min. (Saturated State) | 10 min. | 20 min. | 30 min. | 24 h. (Dry State) | |
| Smh | 0.042 | 0.037 | 0.038 | 0.035 | 0.041 |
| Material | Poisson’s Ratio | Density (kg/m3) | Shear Modulus (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pebble | 0.35 | 2680 | 8 × 109 |
| Sand | 0.25 | 2500 | 1 × 108 |
| Wall | 0.30 | 7850 | 1 × 1010 |
| Type of Contact | Coefficient of Restitution | Coefficient of Static Friction | Coefficient of Rolling Friction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pebble–Pebble | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.10 |
| Sand–Sand | 0.05 | 0.32 | 0.15 |
| Pebble–Wall | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.18 |
| Sand–Wall | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.10 |
| Moisture Content | Cohesive Density (107 J/m3) | Simulation Value (°) | Experiment Value (°) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 15.51 | 16.07 | −3.48 |
| 0.001 | 1.94 | 18.19 | 17.44 | 4.30 |
| 0.002 | 2.06 | 17.70 | 18.00 | −1.67 |
| 0.003 | 2.12 | 19.60 | 19.68 | −0.41 |
| 0.004 | 2.15 | 18.87 | 19.73 | −4.36 |
| 0.005 | 2.16 | 18.64 | 19.42 | −4.02 |
| 0.006 | 2.22 | 19.80 | 20.54 | −3.60 |
| 0.007 | 2.43 | 24.66 | 23.88 | 3.27 |
| Moisture Content | Cohesive Density (105 J/m3) | Simulation Value (°) | Experiment Value (°) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.00 | 23.06 | 23.19 | −0.56 |
| 0.011 | 0.29 | 24.75 | 25.69 | −3.66 |
| 0.019 | 0.38 | 25.18 | 25.92 | −2.85 |
| 0.039 | 0.42 | 26.52 | 26.56 | −0.15 |
| 0.043 | 0.43 | 26.30 | 26.38 | −0.30 |
| 0.052 | 0.46 | 26.47 | 26.48 | −0.04 |
| 0.066 | 0.60 | 27.13 | 27.51 | −1.38 |
| 0.084 | 0.91 | 28.78 | 29.2 | −1.44 |
| 0.091 | 1.06 | 30.60 | 30.45 | 0.49 |
| 0.101 | 1.27 | 32.11 | 32.39 | −0.86 |
| 0.109 | 1.38 | 32.44 | 31.82 | 1.95 |
| Series No. | kp (107 J/m3) | ks (104 J/m3) | kp − ks (106 J/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 2.16 | 9.12 | 2.60 |
| 4 | 1.95 | 4.32 | 2.30 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Series No. | Simulating Smh | Experimental Smh | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0.0372 | 0.0382 | −2.61 |
| 4 | 0.0333 | 0.0349 | −4.58 |
| 5 | 0.0388 | 0.0408 | −4.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, G.; Xie, S.; Deng, D.; Jiang, S. Numerical Study on Effect of Aggregate Moisture on Mixing Process. Materials 2024, 17, 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17040898
Cao G, Xie S, Deng D, Jiang S. Numerical Study on Effect of Aggregate Moisture on Mixing Process. Materials. 2024; 17(4):898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17040898
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Guodong, Sheng Xie, Daiqiang Deng, and Shengqiang Jiang. 2024. "Numerical Study on Effect of Aggregate Moisture on Mixing Process" Materials 17, no. 4: 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17040898
APA StyleCao, G., Xie, S., Deng, D., & Jiang, S. (2024). Numerical Study on Effect of Aggregate Moisture on Mixing Process. Materials, 17(4), 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17040898






