Research on the Synthesis of Zinc–Ammonium Phosphate Using Galvanic Waste Sludge as a Source of Zinc
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Studies on Zinc Waste
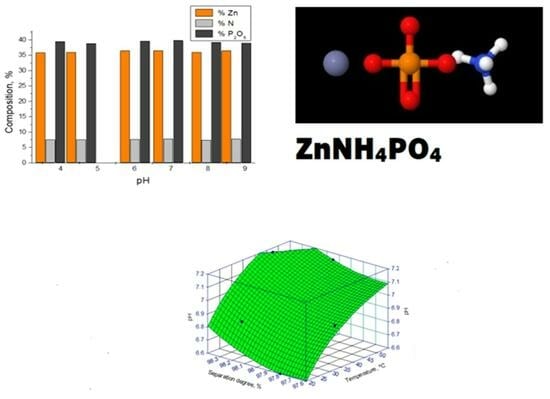
3.1.1. Composition
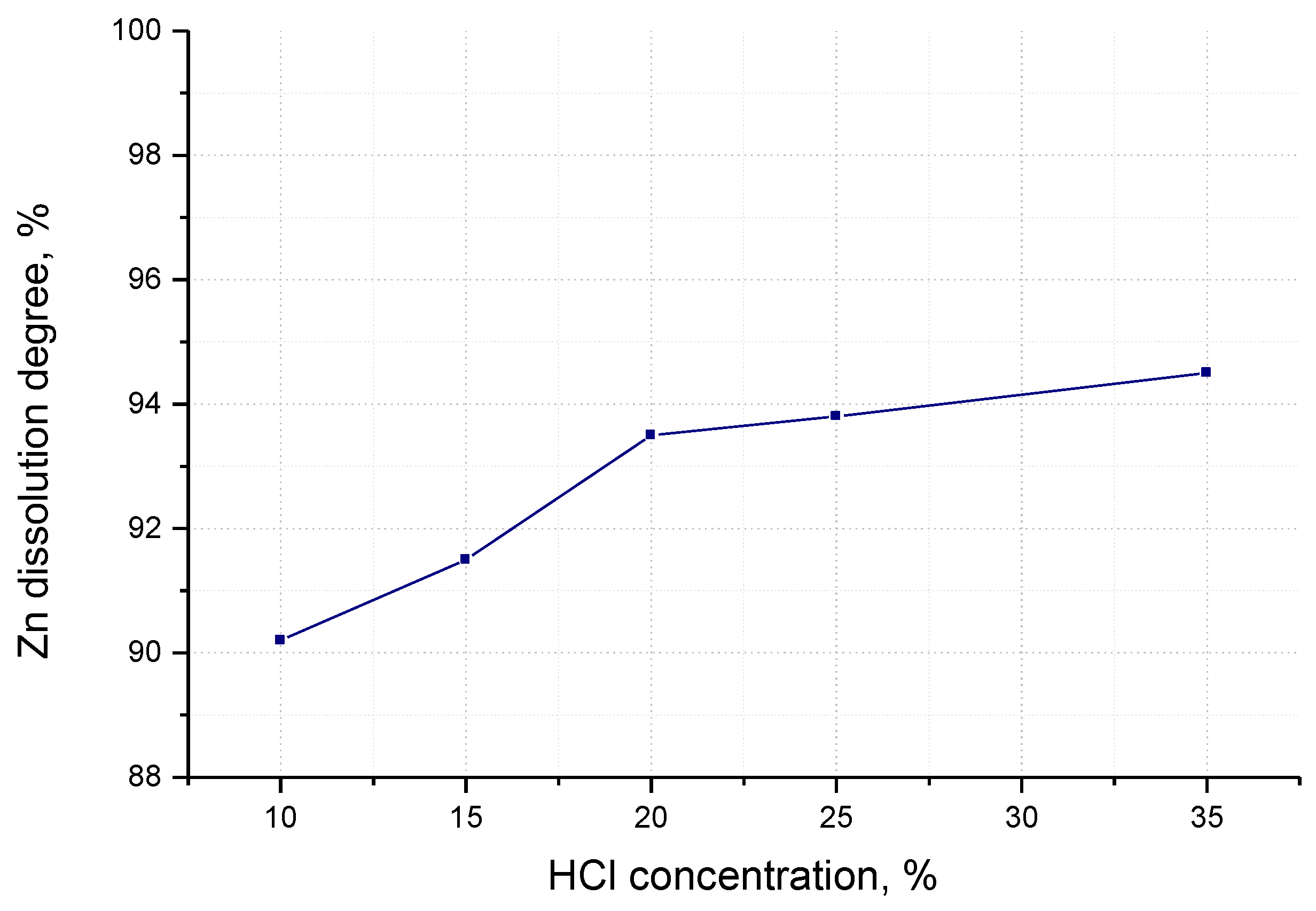
3.1.2. Dissolution
3.2. Studies Regarding the Separation Process of Zinc from Solution
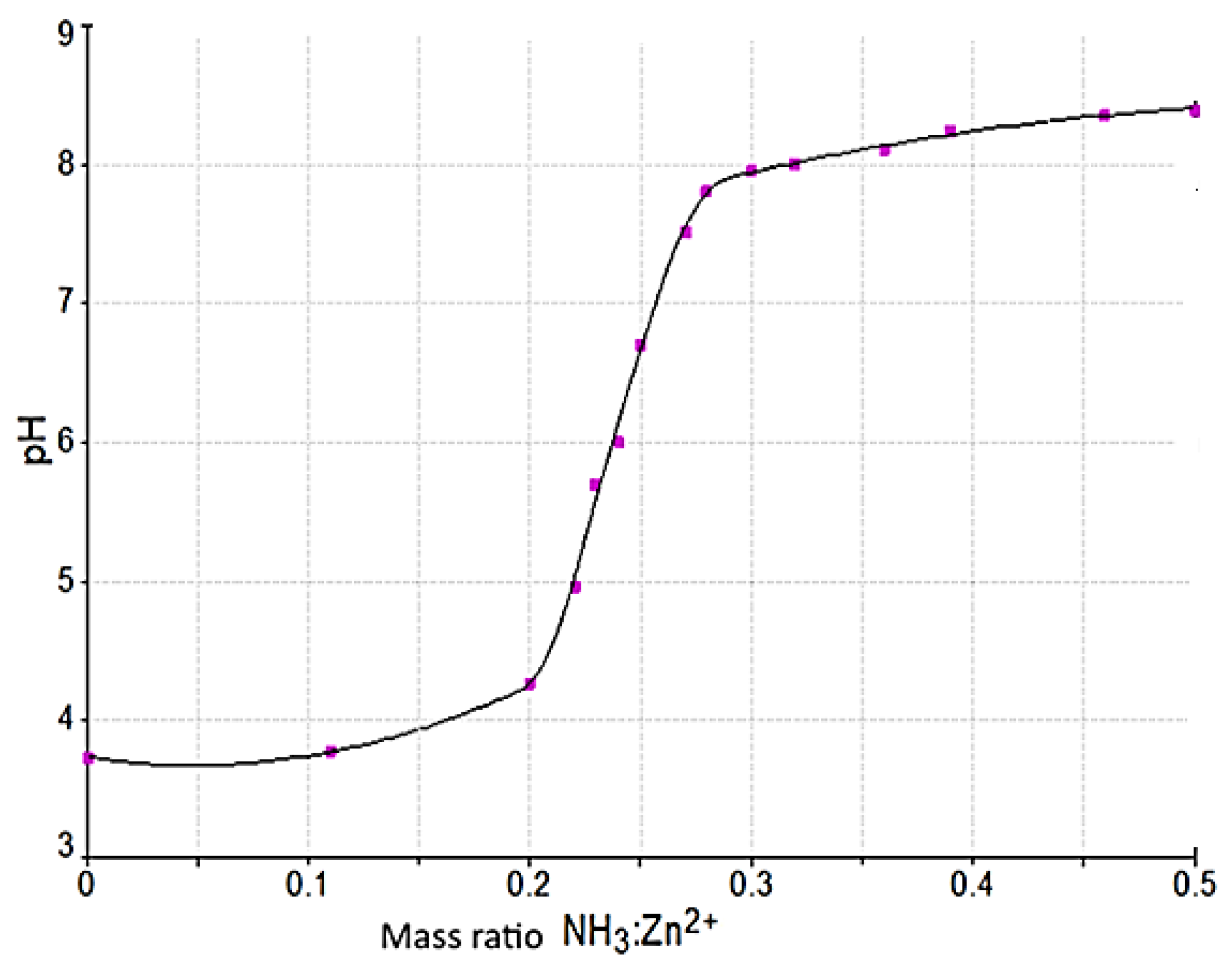
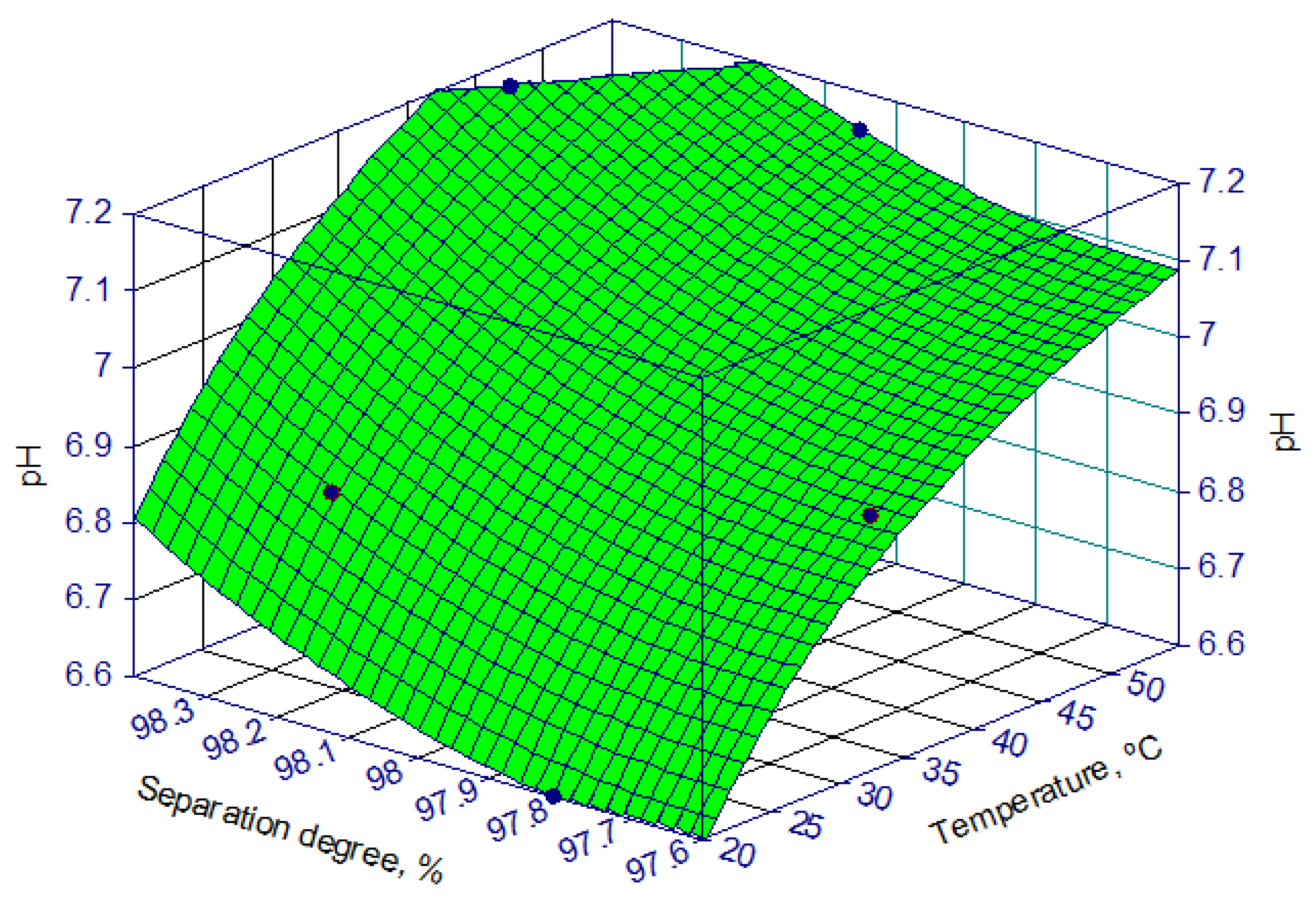
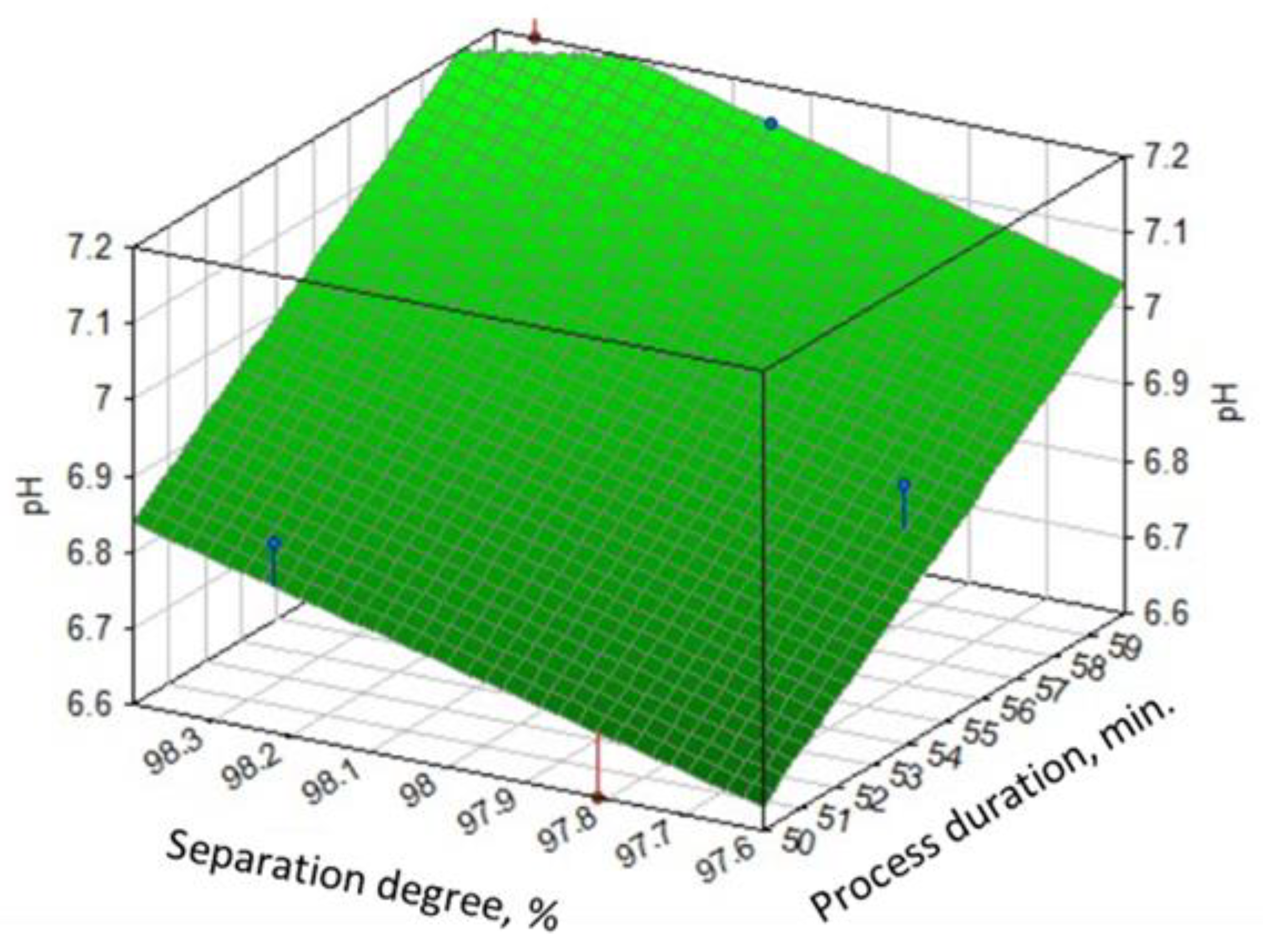
3.2.1. pH of the Reaction Mass
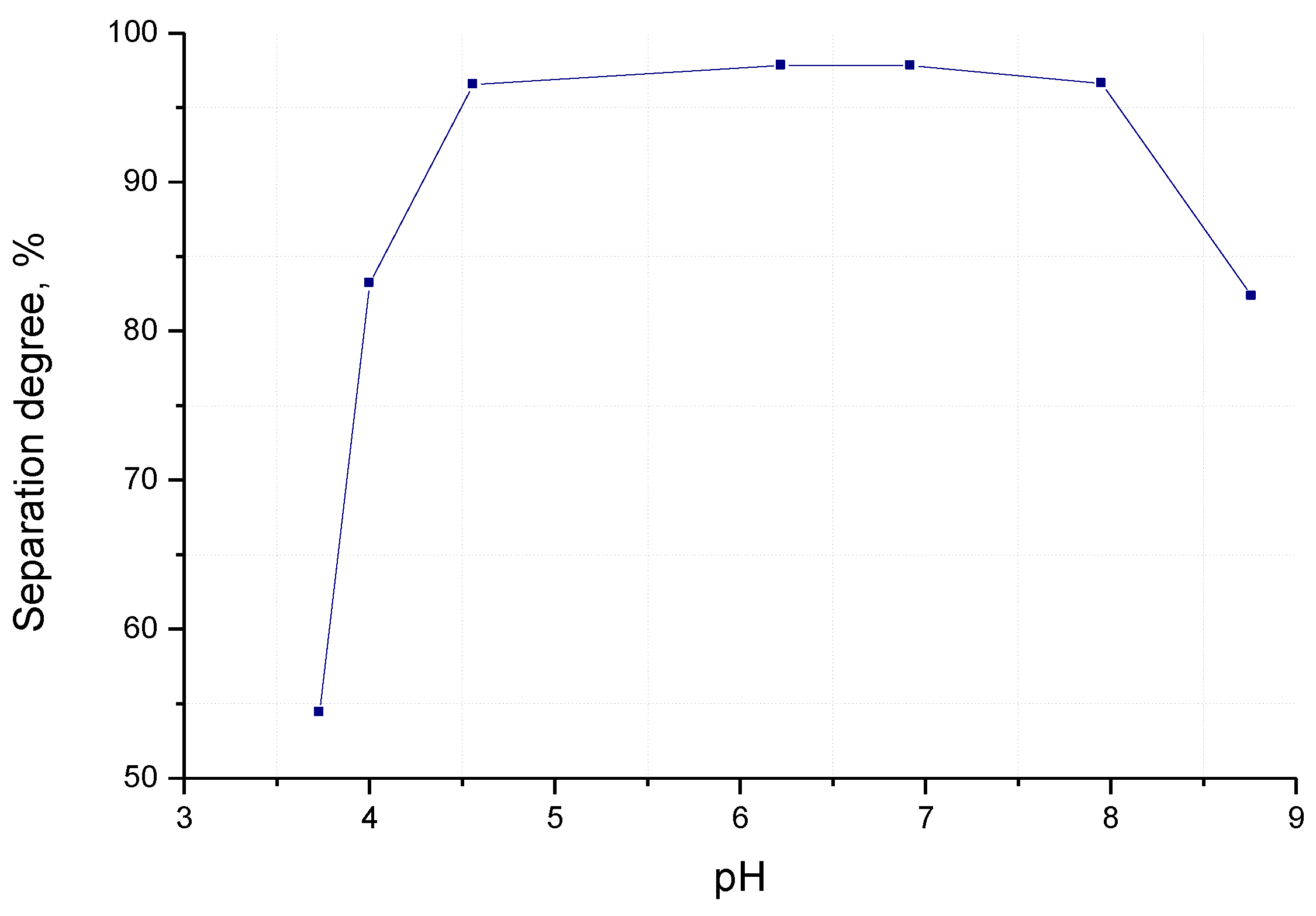
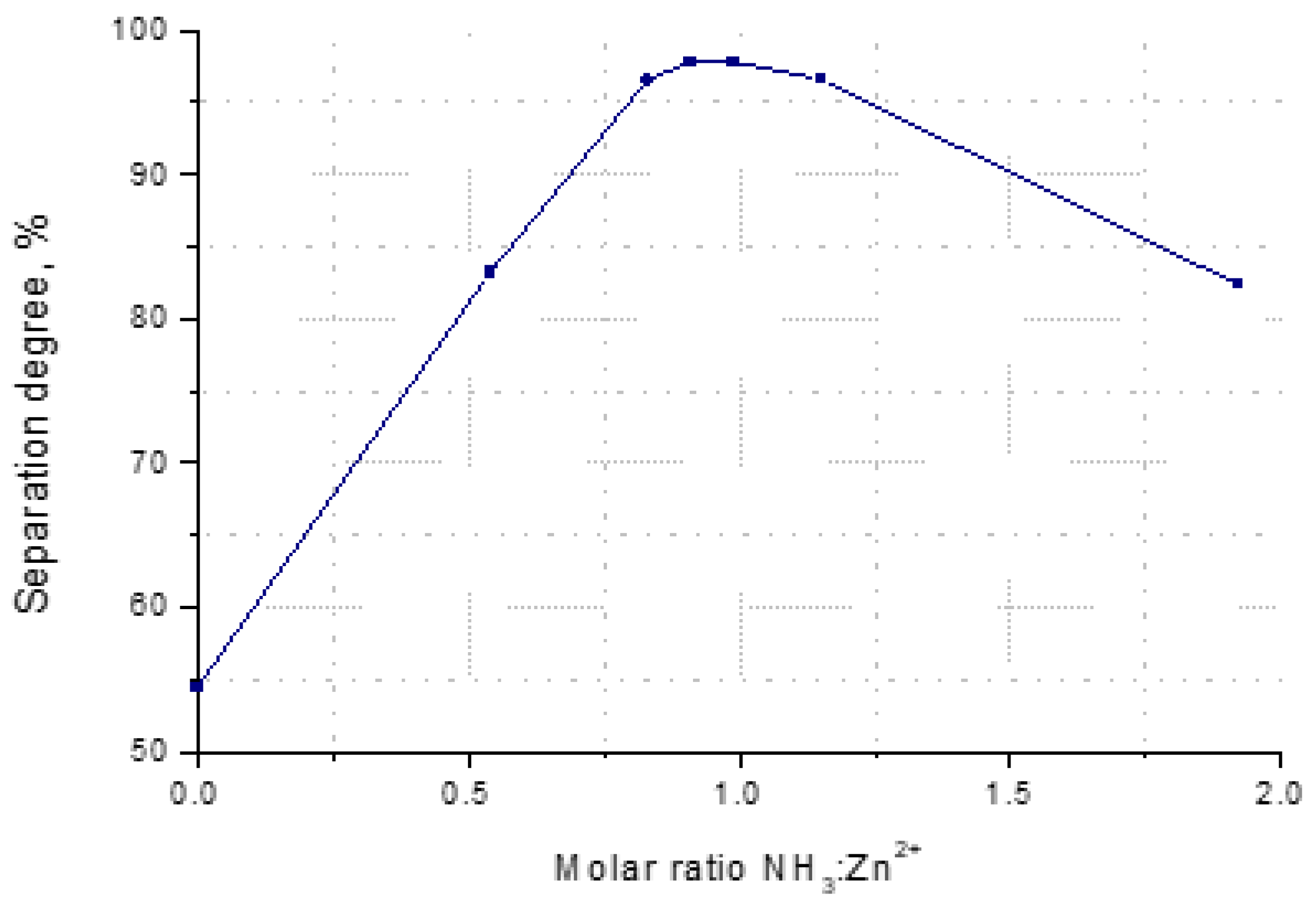
3.2.2. The Separation Degree of Zinc from Solution
- pH of the reaction mass.
- Molar ratio NH3:Zn2+.
- Zinc concentration.
- Temperature.
- Duration of the process.
3.3. Studies on the Obtained Products
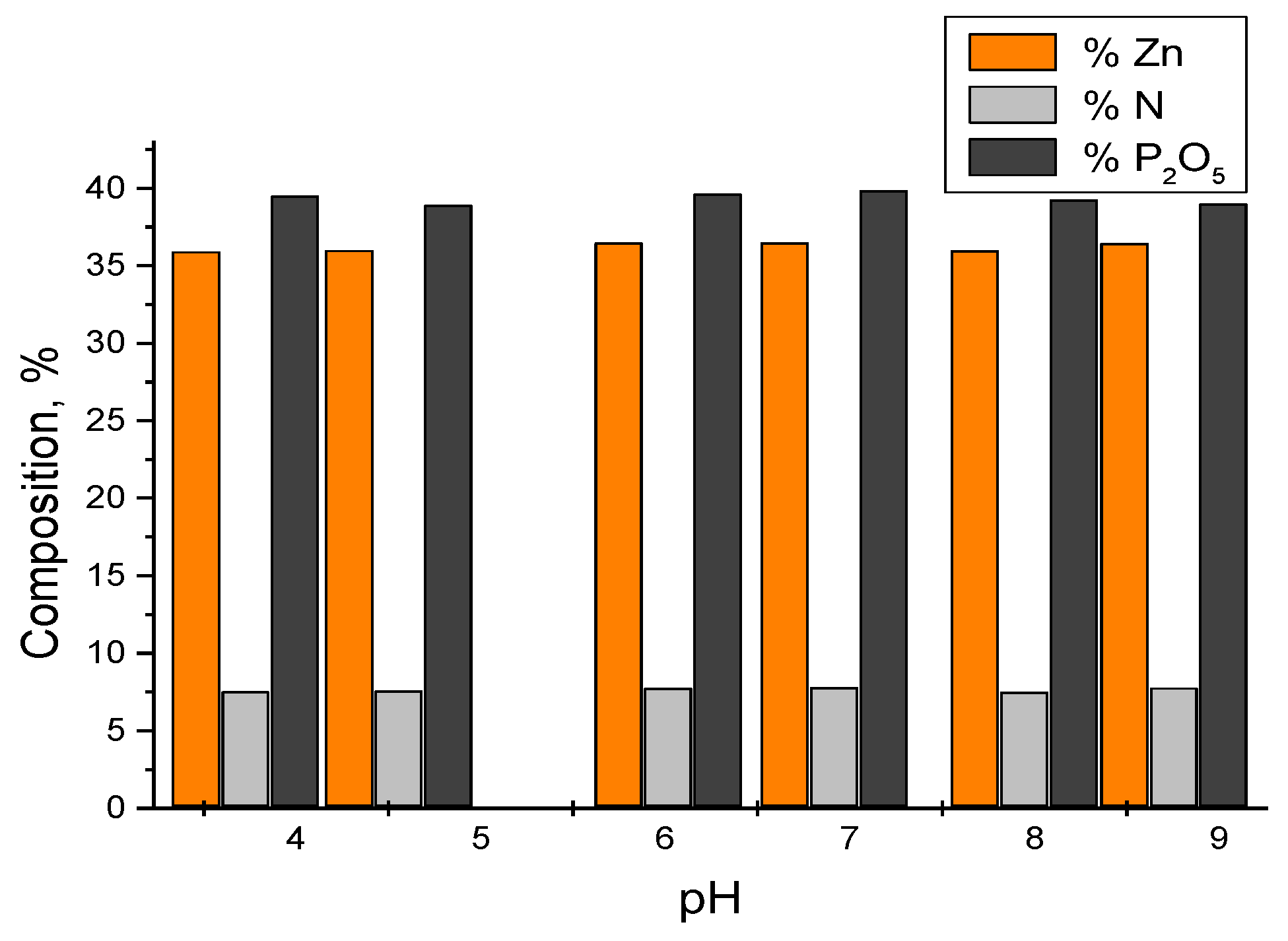
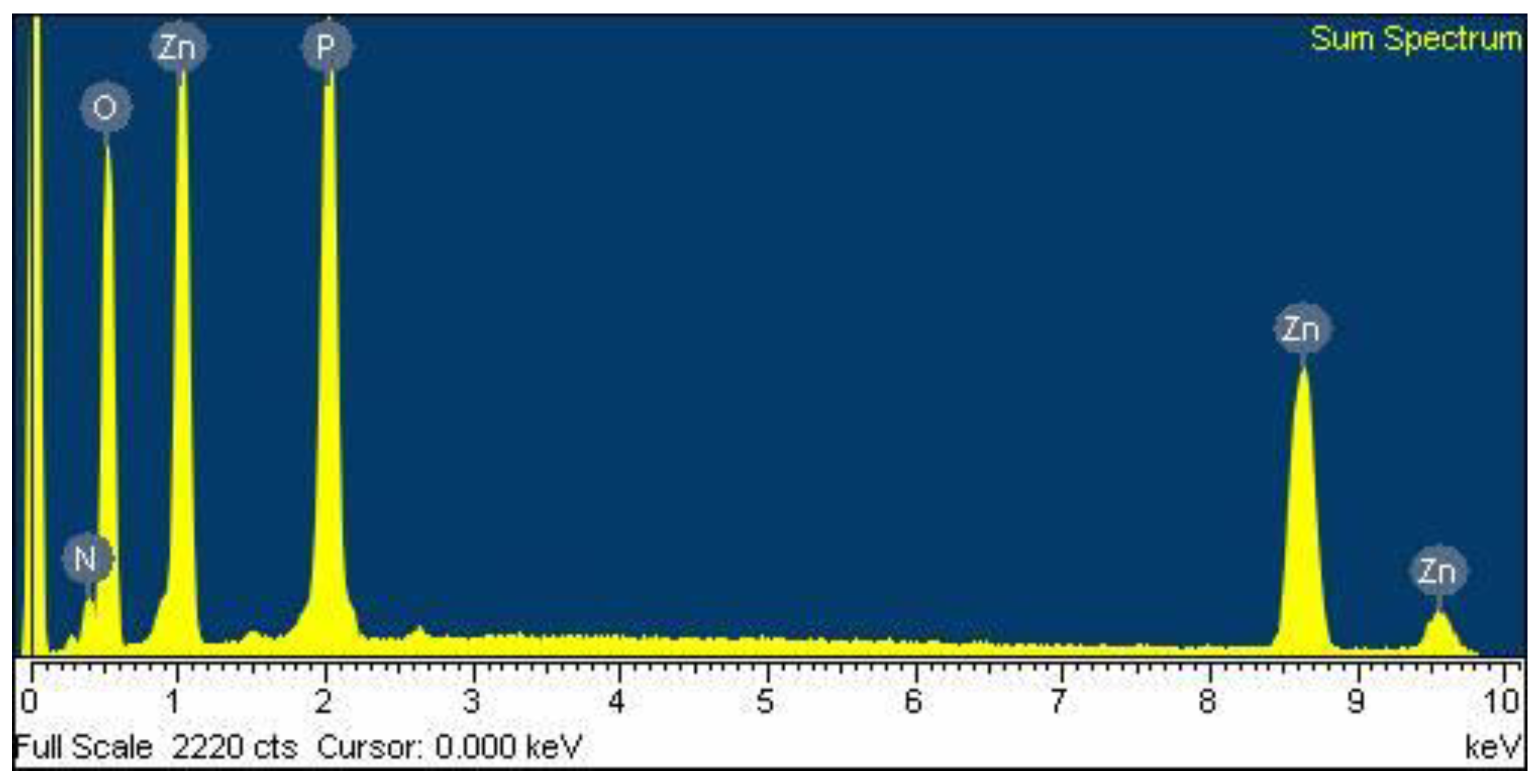
3.3.1. Chemical Composition
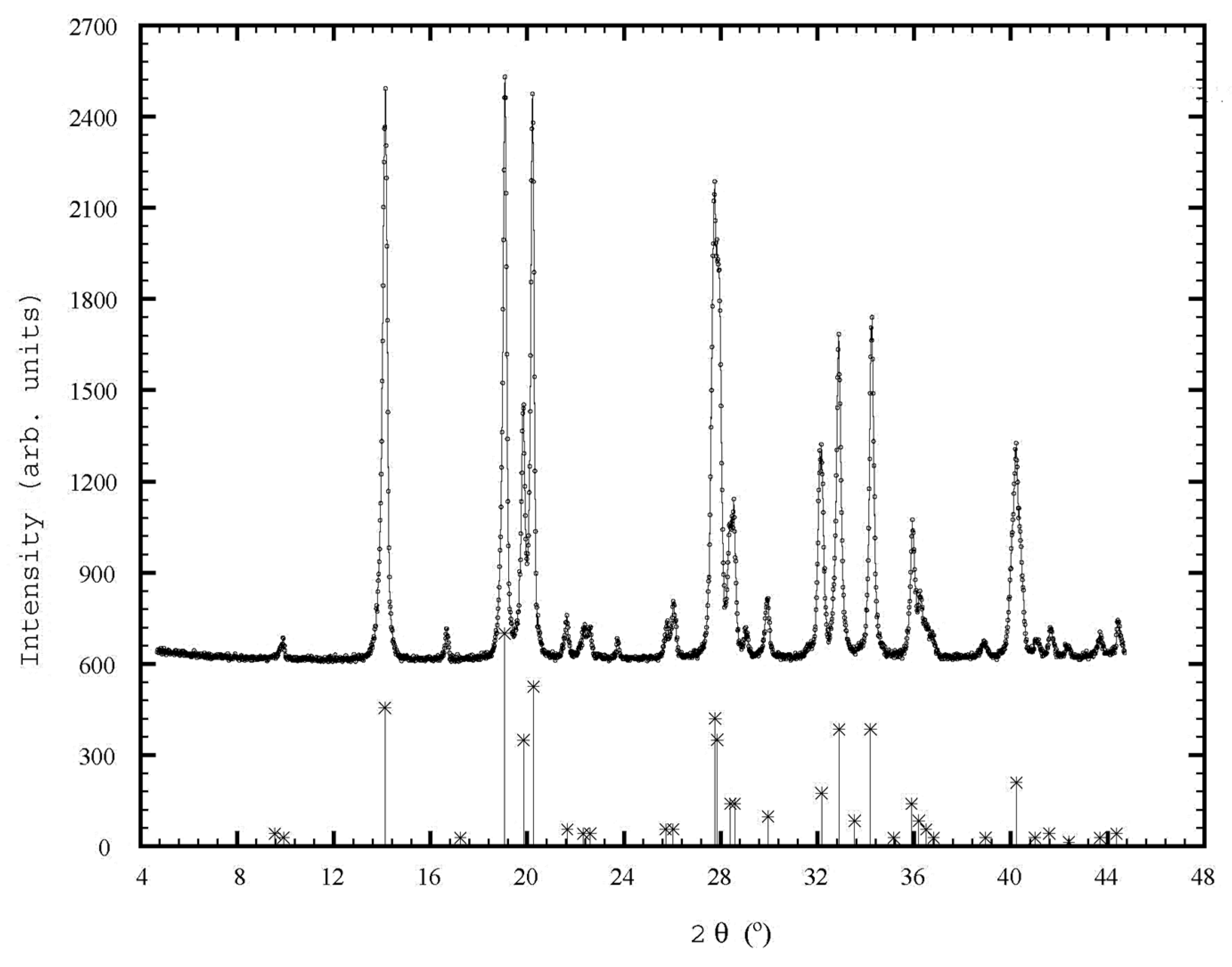
3.3.2. X-ray Diffraction Studies
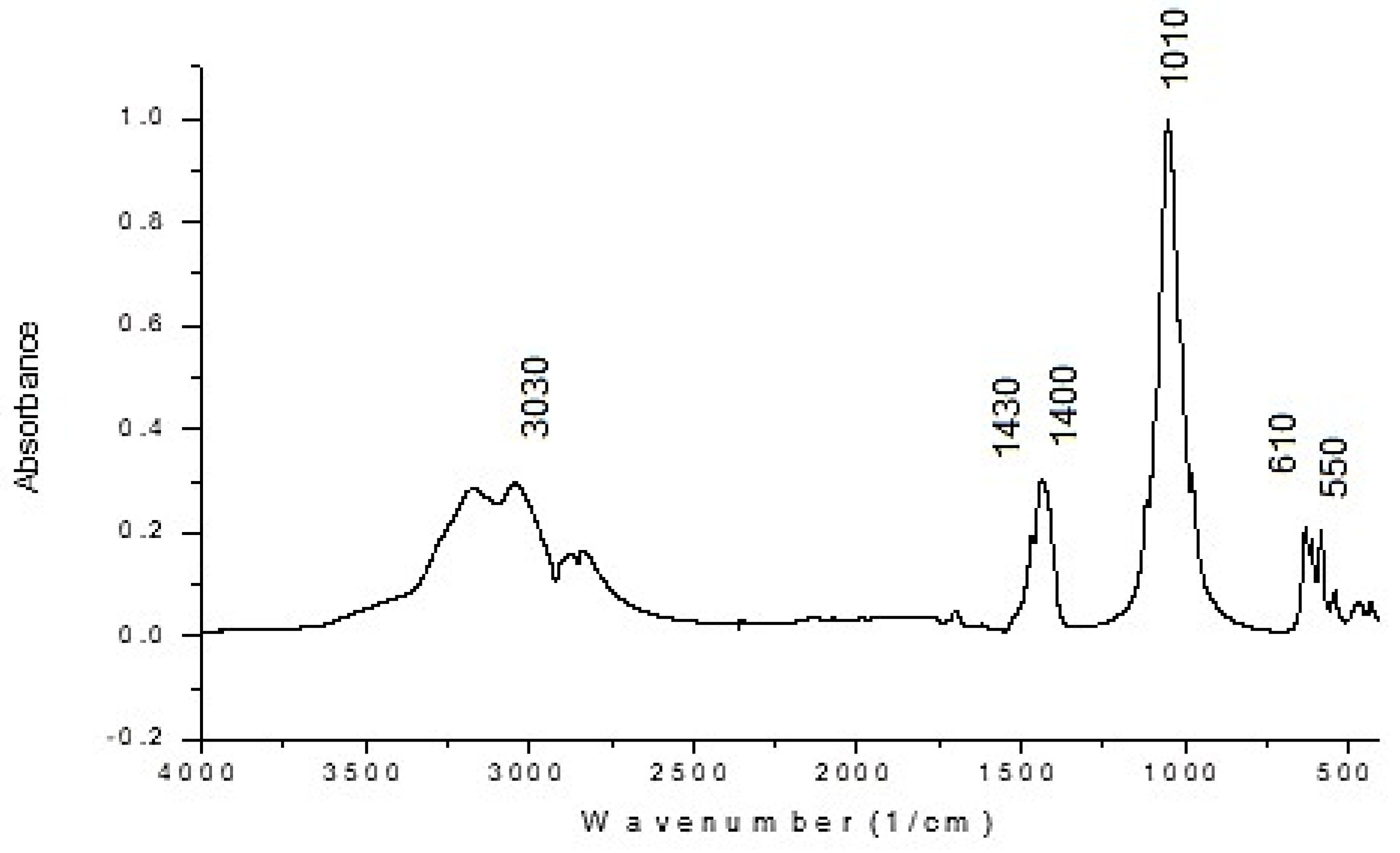
3.3.3. FT-IR Spectroscopic Studies
3.3.4. Thermogravimetric and Thermodifferential Studies
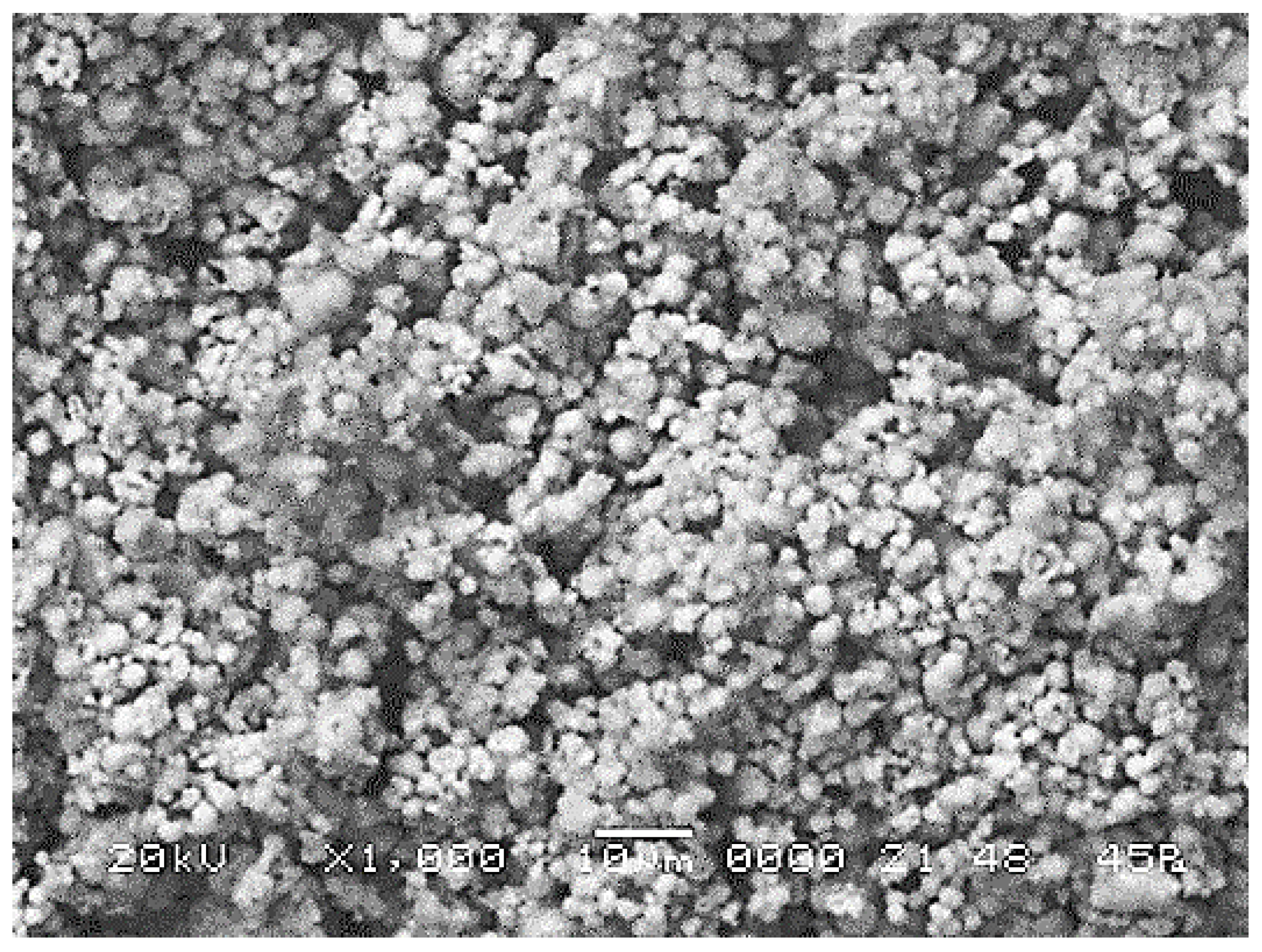
3.3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morgovan, C.M. Contributions to the Study of the Processes for the Recovery of Metallic Ions from the Waste of the Galvanic Industry in the Form of Microelement Fertilizers; Politehnica: Timisoara, Romania, 2009; pp. 98–116. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Raja, T.A.; Vickraman, P.; Justin, A.S.; Reddy, B.J. Ultrasonicated graphene quantum dots dispersoid zinc ammonium phosphate hybrid electrode for supercapacitor applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 33, 7079–7098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, K.; Przywecka, K.; Grzmil, B. Influence of novel ammonium-modified zinc-free phosphate nanofillers on anticorrosive features of primer-less polyurethane top-coating compositions. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2019, 16, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Samanta, A.K.; Kar, T.R. Eco-friendly fire-retardant finishing of cotton fabric with mixture of ammonium sulfamate and sodium Stannate with and without zinc acetate as external reagent. Cellulose 2023, 30, 11813–11828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Hei, P.; Song, Y.; Meng, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.X. Electrochemically activated nickel-cobalt double hydroxide for aqueous ammonium-zinc hybrid battery. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 2495–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, K.; Mohanty, S.; Biswal, M.; Nayak, S.K. Flame retardancy of EPDM/Kevlar fibre composites with zinc borate, magnesium hydroxide and ammonium polyphosphate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 8189–8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elokhov, A.M.; Lesnov, A.E.; Kudryashova, O.S. Salting out of potassium bis(alkylpolyoxyethylene)phosphate with ammonium salts as the base of micellar extraction processes development. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2015, 85, 2657–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wen, S.; Feng, Q.; Wang, H. Enhanced sulfidization of azurite surfaces by ammonium phosphate and its effect on flotation. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2022, 29, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheprasova, V.I.; Zalyhina, O.S. Spent zinc-plating electrolytes as secondary raw material for production of pigments. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 90, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, G.E.; Fodor, A.; Petrehele, A.I.G.; Maior, I.; Toderaș, M.; Morgovan, C.M. Evaluation of Phosphopolyoxometalates with Mixed Addenda (Mo, W, V) as Corrosion Inhibitors for Steels. Materials 2023, 16, 7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Mohapatra, T. Interaction between Macro- and Micro-Nutrients in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 665583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Khan, Q.U.; Alem, A.; Hendi, A.A.; Zaman, U.; Khan, S.U.; Rehman, K.u.; Khan, A.A.; Ullah, I.; Anwar, Y.; et al. Zinc and Potassium Fertilizer Synergizes Plant Nutrient Availability and Affects Growth, Yield, and Quality of Wheat Genotypes. Plants 2023, 12, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejwoda, P.; Świnder, H.; Thomas, M. Evaluation of the mobility of heavy metals in the sediments originating from the post-galvanic wastewater treatment processes. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 7877–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zykova, I.V.; Panov, V.P. Recovery of Heavy Metals from Excess Active Sludges with Aeration. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2005, 78, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethu, V.S.; Aziz, A.R.; Aroua, M.K. Recovery and reutilisation of copper from metal hydroxide sludges. Clean. Technol. Environ. Policy 2008, 10, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Takaoka, M.; Ichiura, H.; Oshita, K.; Fujimori, T. Evaluation of metals in the residue of paper sludge after recovery of pulp components using an ionic liquid. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2016, 18, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podol’skaya, Z.V.; Buzaeva, M.V.; Klimov, E.S. Adsorption of heavy metal ions on galvanic sludges and disposal of the sludges in soil. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2011, 84, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasowski, M.; Migas, P.; Ślęzak, M.; Gondek, Ł.; Cieniek, Ł. Utilization of High-Zn Content Ferrous Landfill Sludge with the Use of Hydrogen. Materials 2023, 16, 7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zueva, S.B.; Ferella, F.; Innocenzi, V.; De Michelis, I.; Corradini, V.; Ippolito, N.M.; Vegliò, F. Recovery of Zinc from Treatment of Spent Acid Solutions from the Pickling Stage of Galvanizing Plants. Sustainability 2021, 13, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.; Ferreira, A.G.M.; Quina, M.J. Efficient Management of Sewage Sludge from Urban Wastewaters with the Addition of Inorganic Waste: Focus on Rheological Properties. Clean. Technol. 2022, 4, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-León, G.; Baquero-Quinteros, E.; Loor, B.G.; Alvear, J.; Montesdeoca Espín, D.E.; De La Rosa, A.; Montero-Calderón, C. Waste to Catalyst: Synthesis of Catalysts from Sewage Sludge of the Mining, Steel, and Petroleum Industries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, O.; Amin, N.K.; El Ashtoukhy, E.Z. Removal of zinc ions from aqueous solution using a cation exchange resin. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgovan, C.; Marian, E.; Iovi, A.; Bratu, I.; Borodi, G. Characterisation of Copper-Ammonium Phosphate by X-ray Powder Diffraction, FT-IR and Electronic Microscopy (SEM). Rev. Chim. 2009, 60, 1282. [Google Scholar]
- Morgovan, C.; Marian, E.; Iovi, A.; Bratu, I.; Borodi, G. Studies Regarding the Obtaining Process of Iron (II)-Ammonium Phosphate from Residual Solutions. Rev. Chim. 2010, 61, 259. [Google Scholar]
- Burgot, G.; Burgot, J.L. Méthodes Instrumentales D’analyse Chimique et Applications, 2nd ed.; Lavoisier: Paris, France, 2006; pp. 283–295. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, J.; Newbury, D.E.; Joy, D.C.; Lyman, C.E.; Echlin, P.; Lifshin, E.; Sawyer, L.C.; Michael, J.R. Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-ray Microanalysis, 3rd ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 21–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phumying, S.; Sichumsaeng, T.; Kidkhunthod, P.; Chanlek, N.; Khajonrit, J.; Sonsupap, S.; Maensiri, S. Influence of polymer solution on the morphology and local structure of NH4ZnPO4 powders synthesized by a simple precipitation method at room temperature. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2022, 29, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandalakshmi, H.; Velavan, K.; Sougandi, I.; Venkatesan, R.; Rao, P.S. Single crystal EPR studies of Mn (II) doped into zinc ammonium phosphate hexahydrate (ZnNH4PO4·6H2O): A case of interstitial site for bio-mineral analogue. Pramana-J. Phys. 2004, 62, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironon, J.; Pelletier, M.; Donato, P.; Mosser, R. Characterization of smectite and illite by FTIR spectroscopy of interlayer NH4+ cations. Clay Miner. 2003, 38, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baitahe, R.; Boonchom, B. A Simple Synthesis, Characterization, Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Zinc Ammonium Phosphate, ZnNH4PO4. Int. J. Thermophys. 2020, 41, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Gu, J. Morphology controlled solvo-thermal synthesis and luminescence of NH4ZnPO4: Eu3+ submicrometer phosphor. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 479, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, R.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Chava, R.K.; Reddy, Y. X-ray powder diffraction, thermal analysis and IR studies of zinc ammonium phosphate hexahydrate. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Rapid Commun. 2010, 4, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoming, Z.; Helong, B.; He, M.; Hebin, L.; Wenxiang, Y.; Hanjie, D.; Peixin, Z.; Hong, X. Synthesis of zinc phosphate and zinc ammonium phosphate nanostructures with different morphologies through pH control. Mater. Charact. 2015, 108, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arul Raja, T.; Vickraman, P.; Simon Justin, A.; Joji Reddy, B. Microwave Synthesis of Zinc Ammonium Phosphate/Reduced Graphene Oxide Hybrid Composite for High Energy Density Supercapacitors. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Res. 2020, 217, 1900736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, W.T.A.; Sobolev, A.N.; Phillips, M.L.F. Hexagonal ammonium zinc phosphate, (NH4)ZnPO4, at 10 K. Acta Crystallogr. 2001, 57, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poonguzhali, E.; Srinivasan, R.; Ravikumar, R.V.S.S.N.; Chandrasekhar, A.V.; Reddy, B.J.; Reddy, Y.P.; Sambasiva Rao, P. Single crystal EPR and optical studies of Cu (II) doped zinc ammonium phosphate hexahydrate: A case of orhombic distortion. Phys. Scr. 2002, 66, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kripal, R.; Govind, H.; Gupta, S.K.; Arora, M. EPR and optical absorption study of Mn2+-doped zinc ammonium phosphate hexahydrate single crystals. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2007, 392, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Element | Composition, % |
|---|---|
| K | 0.75 ± 0.01 |
| Na | 0.37 ± 0.01 |
| Cu | 0.06 ± 0.005 |
| Fe | 5.7 ± 0.01 |
| Zn | 65.5 ± 0.05 |
| Cr | bdl |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morgovan, C.M.; Petrehele, A.I.G.; Badea, G.E.; Fodor, A.; Toderaș, M.; Marian, E. Research on the Synthesis of Zinc–Ammonium Phosphate Using Galvanic Waste Sludge as a Source of Zinc. Materials 2024, 17, 1690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071690
Morgovan CM, Petrehele AIG, Badea GE, Fodor A, Toderaș M, Marian E. Research on the Synthesis of Zinc–Ammonium Phosphate Using Galvanic Waste Sludge as a Source of Zinc. Materials. 2024; 17(7):1690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071690
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorgovan, Claudia Mona, Anda Ioana Gratiela Petrehele, Gabriela Elena Badea, Alexandrina Fodor, Monica Toderaș, and Eleonora Marian. 2024. "Research on the Synthesis of Zinc–Ammonium Phosphate Using Galvanic Waste Sludge as a Source of Zinc" Materials 17, no. 7: 1690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071690
APA StyleMorgovan, C. M., Petrehele, A. I. G., Badea, G. E., Fodor, A., Toderaș, M., & Marian, E. (2024). Research on the Synthesis of Zinc–Ammonium Phosphate Using Galvanic Waste Sludge as a Source of Zinc. Materials, 17(7), 1690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071690