A Bioactive Degradable Composite Bone Cement Based on Calcium Sulfate and Magnesium Polyphosphate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Optimizing of CS/MPP/C3S Composite Bone Cement
2.3. Characterization of CS/MPP/C3S Composite Bone Cement
2.4. Degradation In Vitro
2.5. Cytocompatibility
2.6. Osteogenic Differentiation
2.7. Statistical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
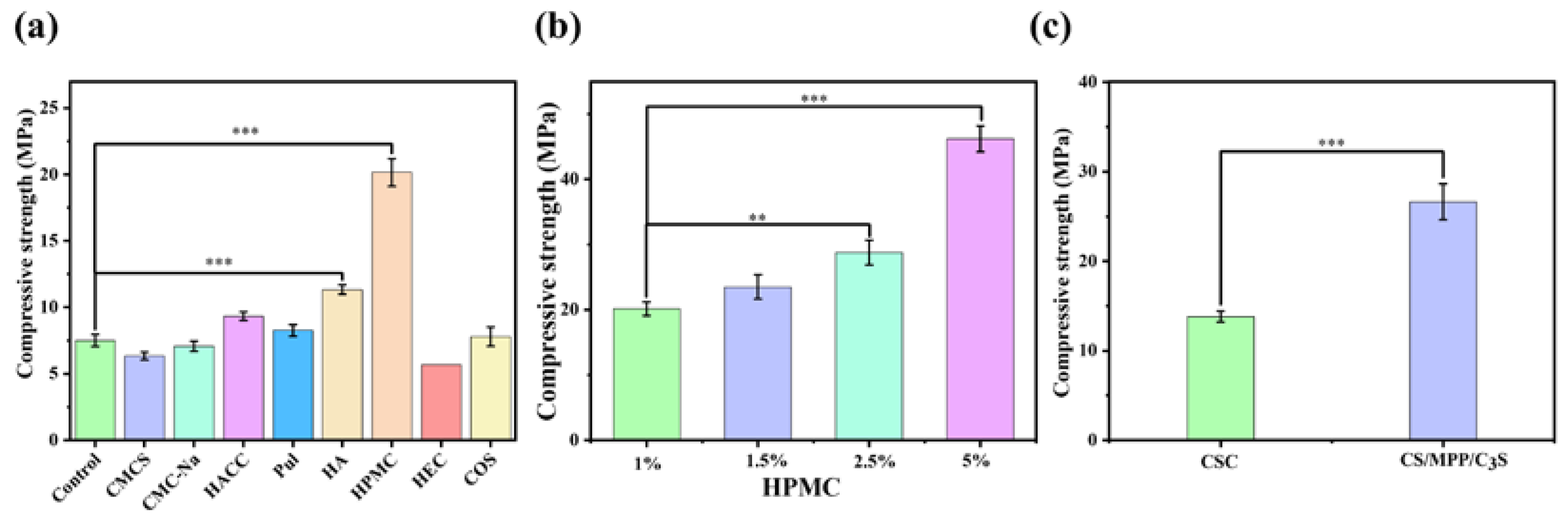
3.1. Optimization of Bone Cement Components
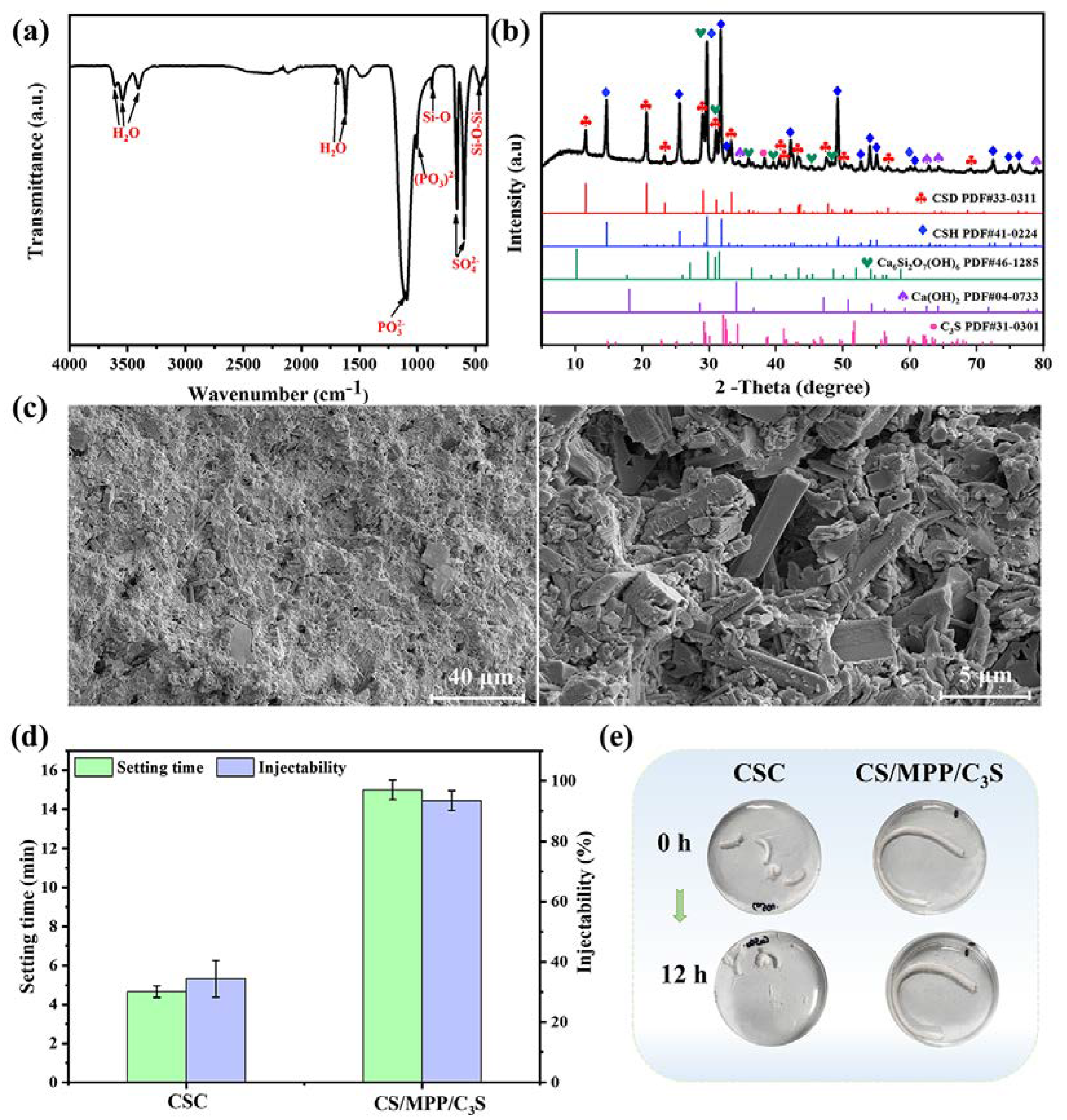
3.2. Characterization and Properties of Bone Cement
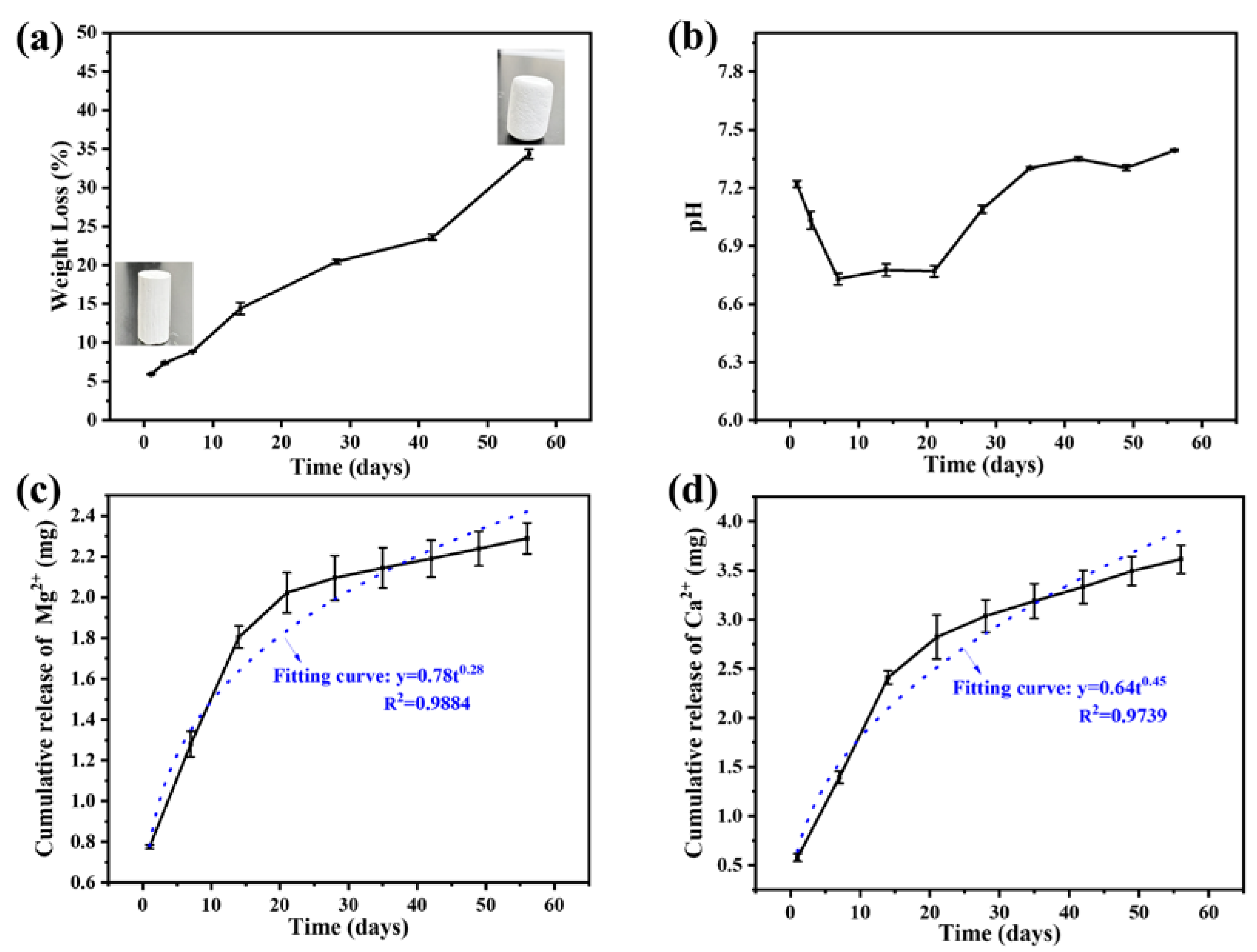
3.3. Degradation of Bone Cement In Vitro
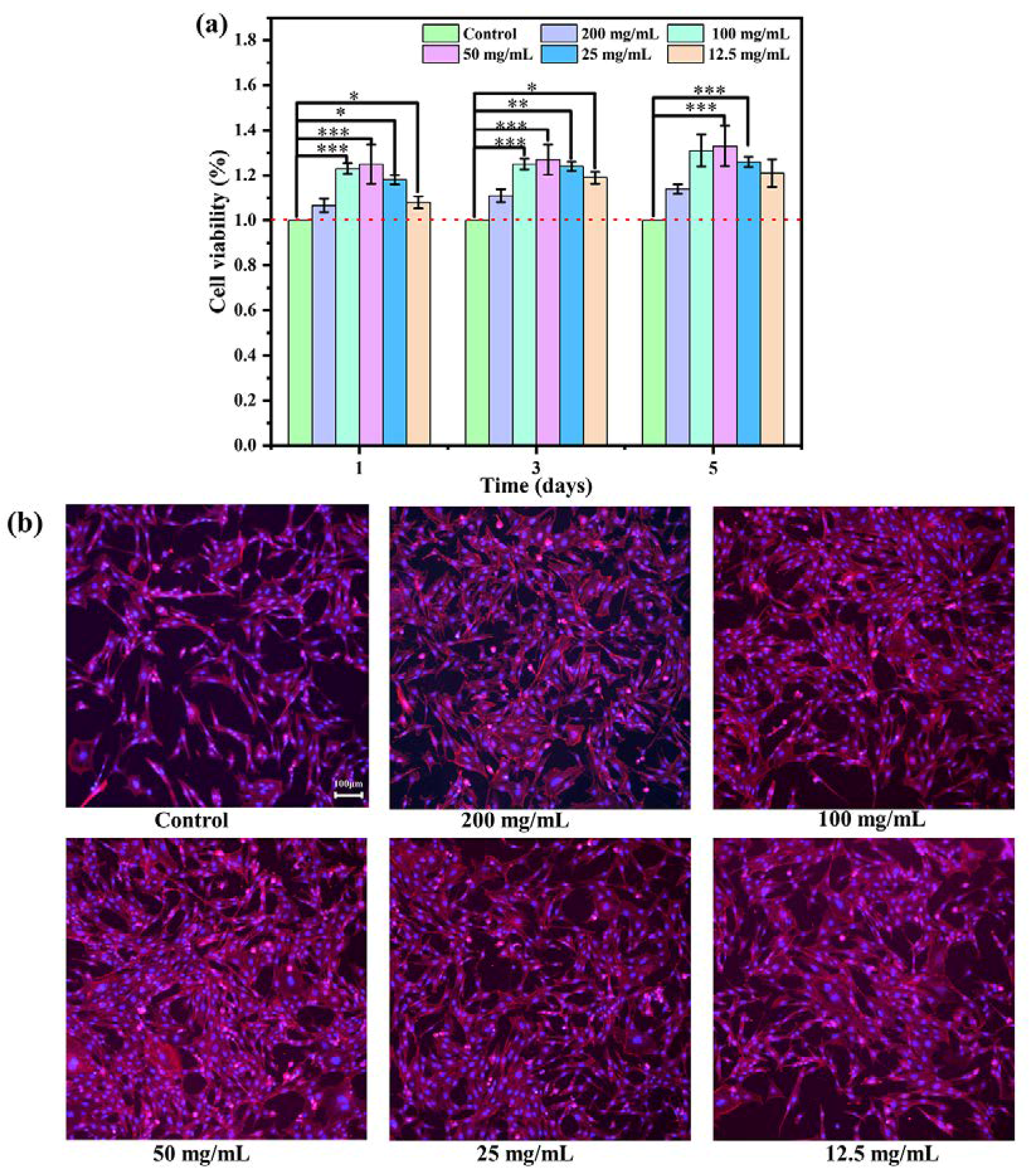
3.4. Cytotoxicity and Osteogenic Differentiation In Vitro
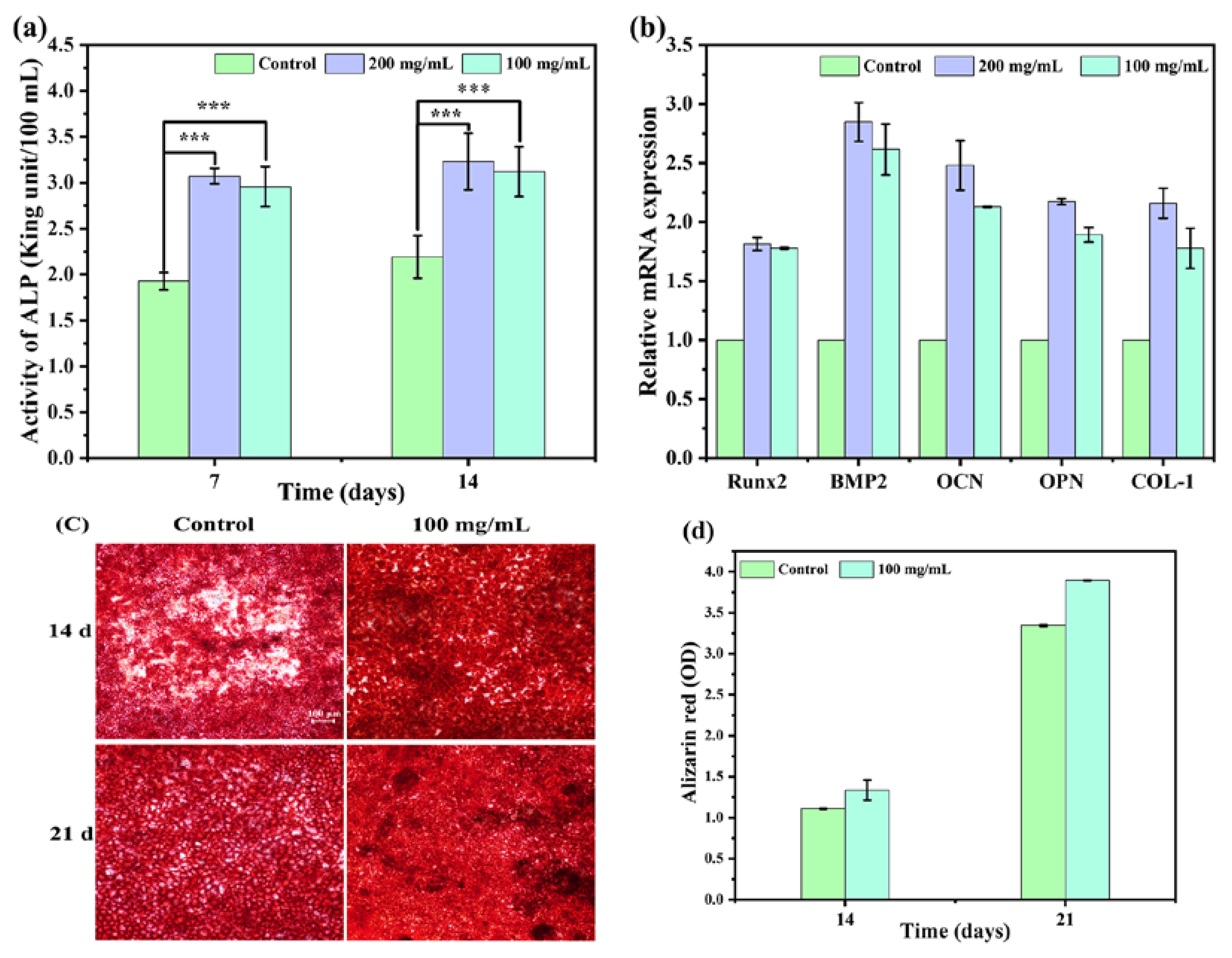
3.5. Osteogenic Differentiation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Chen, S.-K.; Li, L.; Qin, L.; Wang, X.-L.; Lai, Y.-X. Bone Defect Animal Models for Testing Efficacy of Bone Substitute Biomaterials. J. Orthop. Transl. 2015, 3, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wu, Q.; He, B.; Rao, J.; Chow, D.H.K.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Ning, C.; Dai, K. Interactive Effects of Cerium and Copper to Tune the Microstructure of Silicocarnotite Bioceramics towards Enhanced Bioactivity and Good Biosafety. Biomaterials 2022, 288, 121751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santolini, E.; West, R.; Giannoudis, P.V. Risk Factors for Long Bone Fracture Non-Union: A Stratification Approach Based on the Level of the Existing Scientific Evidence. Injury 2015, 46, S8–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schemitsch, E.H. Size Matters: Defining Critical in Bone Defect Size! J. Orthop. Trauma 2017, 31, S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriou, R.; Mataliotakis, G.I.; Angoules, A.G.; Kanakaris, N.K.; Giannoudis, P.V. Complications Following Autologous Bone Graft Harvesting from the Iliac Crest and Using the RIA: A Systematic Review. Injury 2011, 42, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, L.; Li, M.; Han, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Liu, L. Fabrication and Properties of PLA/Nano-HA Composite Scaffolds with Balanced Mechanical Properties and Biological Functions for Bone Tissue Engineering Application. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021, 10, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Fu, C. Engineered Bone Cement Trigger Bone Defect Regeneration. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 929618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Cui, C.; Chen, W.; Shi, J.; Li, B.; Chen, S. Biodegradable Cements for Bone Regeneration. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, E.; Yanni, T.; Jamshidi, P.; Grover, L.M. Inorganic Cements for Biomedical Application: Calcium Phosphate, Calcium Sulphate and Calcium Silicate. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2015, 114, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Yu, H.; Han, J.; Hou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhou, W.; Chen, J. Tunicate Cellulose Nanocrystals Reinforced Modified Calcium Sulfate Bone Cement with Enhanced Mechanical Properties for Bone Repair. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 323, 121380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ji, M.; Ding, Z.; Yan, Y. Vitamin D3-Loaded Calcium Citrate/Calcium Sulfate Composite Cement with Enhanced Physicochemical Properties, Drug Release, and Cytocompatibility. J. Biomater. Appl. 2020, 34, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.-Y.; Kuo, H.-C.; Syu, M.-L.; Tuan, W.-H.; Lai, P.-L. A Head-to-Head Comparison of the Degradation Rate of Resorbable Bioceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 106, 110175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Hu, J.; Chen, H.; Ding, Z.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y. A Novel Degradable Tricalcium Silicate/Calcium Polyphosphate/Polyvinyl Alcohol Organic-Inorganic Composite Cement for Bone Filling. J. Biomater. Appl. 2021, 36, 772–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnaloja, F.; Jacchetti, E.; Soncini, M.; Raimondi, M.T. Natural and Synthetic Polymers for Bone Scaffolds Optimization. Polymers 2020, 12, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koons, G.L.; Diba, M.; Mikos, A.G. Materials Design for Bone-Tissue Engineering. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 584–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reffitt, D.M.; Ogston, N.; Jugdaohsingh, R.; Cheung, H.F.J.; Evans, B.A.J.; Thompson, R.P.H.; Powell, J.J.; Hampson, G.N. Orthosilicic Acid Stimulates Collagen Type 1 Synthesis and Osteoblastic Differentiation in Human Osteoblast-like Cells In Vitro. Bone 2003, 32, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.C.; Wang, X.H.; Wiens, M.; Diehl-Seifert, B.; Kropf, K.; Schloßmacher, U.; Müller, W.E.G. Silicate Modulates the Cross-Talk between Osteoblasts (SaOS-2) and Osteoclasts (RAW 264.7 Cells): Inhibition of Osteoclast Growth and Differentiation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 3197–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chang, J. Bioactive Silicate Materials Stimulate Angiogenesis in Fibroblast and Endothelial Cell Co-Culture System through Paracrine Effect. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6981–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Xing, H.; Song, C. Recent Advances in Biomedical Engineering of Nano-Hydroxyapatite Including Dentistry, Cancer Treatment and Bone Repair. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 215, 108790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyhausen, G.; Lorenz, B.; Zhu, H.; Geurtsen, W.; Bohnensack, R.; Müller, W.E.G.; Schröder, H.C. Inorganic Polyphosphate in Human Osteoblast-like Cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1998, 13, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-L.; Stanford, C.M.; Keller, J.C. Calcium and Phosphate Supplementation Promotes Bone Cell Mineralization: Implications for Hydroxyapatite (HA)-Enhanced Bone Formation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, B.; Schröder, H.C. Mammalian Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase Acts as Highly Active Exopolyphosphatase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2001, 1547, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Schepler, H.; Neufurth, M.; Wang, S.; Ferrucci, V.; Zollo, M.; Tan, R.; Schröder, H.C.; Wang, X. The Physiological Polyphosphate as a Healing Biomaterial for Chronic Wounds: Crucial Roles of Its Antibacterial and Unique Metabolic Energy Supplying Properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 135, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Wang, S.; Tolba, E.; Neufurth, M.; Ackermann, M.; Muñoz-Espí, R.; Lieberwirth, I.; Glasser, G.; Schröder, H.C.; Wang, X. Transformation of Amorphous Polyphosphate Nanoparticles into Coacervate Complexes: An Approach for the Encapsulation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Small 2018, 14, 1801170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Teng, H.; Fan, D.; Du, W.; Guo, Z. Progress and Applications of Polyphosphate in Bone and Cartilage Regeneration. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 5141204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Wang, S.; Ackermann, M.; Gerich, T.; Neufurth, M.; Wiens, M.; Schröder, H.C.; Wang, X. Biologization of Allogeneic Bone Grafts with Polyphosphate: A Route to a Biomimetic Periosteum. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1905220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E.G. Amorphous Polyphosphate, a Smart Bioinspired Nano-/Bio-Material for Bone and Cartilage Regeneration: Towards a New Paradigm in Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 2385–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Xi, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y. Novel, Degradable, and Cytoactive Bone Cements Based on Magnesium Polyphosphate and Calcium Citrate. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 13137–13148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Song, C. Design and Characterization of Injectable Abalone Shell/Calcium Sulfate Bone Cement Scaffold for Bone Defect Repair. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Lin, K. The Development of Collagen Based Composite Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, Z.; Haugen, H.J.; Loca, D.; Rossi, F.; Perale, G.; Moghanian, A.; Ma, Q. Review on the Strategies to Improve the Mechanical Strength of Highly Porous Bone Bioceramic Scaffolds. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 44, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Gauthier, O.; Sourice, S.; Pilet, P.; Rethore, G.; Khairoun, K.; Bouler, J.-M.; Tancret, F.; Weiss, P. A Simple and Effective Approach to Prepare Injectable Macroporous Calcium Phosphate Cement for Bone Repair: Syringe-Foaming Using a Viscous Hydrophilic Polymeric Solution. Acta Biomater. 2016, 31, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, R.M.; Turner, T.M.; Hall, D.J.; Infanger, S.I.; Cheema, N.; Lim, T.-H.; Richelsoph, K. An Injectable Calcium Sulfate-Based Bone Graft Putty Using Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose as the Plasticizer. Orthopedics 2004, 27, S155–S159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feroz, S.; Dias, G. Hydroxypropylmethyl Cellulose (HPMC) Crosslinked Keratin/Hydroxyapatite (HA) Scaffold Fabrication, Characterization and in Vitro Biocompatibility Assessment as a Bone Graft for Alveolar Bone Regeneration. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comeau, P.A.; Filiaggi, M.J. Calcium Polyphosphate Precipitation—A Strategy to Tune the Chain Length of the Glass and Control the Subsequent Release of Vancomycin. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 159, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9597-2008; Cement—Test Methods—Determination of Setting Time and Soundness. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Xu, C.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, Y.; Huan, Z.; Chang, J. In Vitro Self-Setting Properties, Bioactivity, and Antibacterial Ability of a Silicate-Based Premixed Bone Cement. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2018, 15, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-12; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 12: Sample Preparation and Reference Materials. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Li, X.-D.; Yan, D.-W.; Ren, H.-H.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Yan, Y.-G. Fabricating Biodegradable Calcium Phosphate/Calcium Sulfate Cement Reinforced with Cellulose: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Chen, H.; Peng, S.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Ren, H.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Q. Multifunctional Magnesium-Organic Framework Doped Biodegradable Bone Cement for Antibacterial Growth, Inflammatory Regulation and Osteogenic Differentiation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 2872–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensted, J.; Prakash, S. Investigation of the Calcium Sulphate-Water System by Infrared Spectroscopy. Nature 1968, 219, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarizadeh, M.; Esfandiari, N.; Honarvar, B.; Sajadian, S.A.; Azdarpour, A. Kinetic Modeling to Explain the Release of Medicine from Drug Delivery Systems. ChemBioEng Rev. 2023, 10, 1006–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazeni, N.; Hesaraki, S.; Behnamghader, A.; Esmaeilzadeh, J.; Orive, G.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Borhan, S. Design and Manufacture of Bone Cements Based on Calcium Sulfate Hemihydrate and Mg, Sr-Doped Bioactive Glass. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauschmann, M.A.; Wichelhaus, T.A.; Stirnal, V.; Dingeldein, E.; Zichner, L.; Schnettler, R.; Alt, V. Nanocrystalline Hydroxyapatite and Calcium Sulphate as Biodegradable Composite Carrier Material for Local Delivery of Antibiotics in Bone Infections. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, S.; Mohanan, P.V.; Sabareeswaran, A.; Varma, H.K.; Komath, M. Preclinical Safety and Efficacy Evaluation of ‘BioCaS’ Bioactive Calcium Sulfate Bone Cement. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 12, 015022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Wang, C.-W.; Hsueh, N.-S.; Ding, S.-J. Improvement of in Vitro Physicochemical Properties and Osteogenic Activity of Calcium Sulfate Cement for Bone Repair by Dicalcium Silicate. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 585, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Wang, S.; Weng, W.; Chen, X.; Cao, L.; Wei, J.; Shin, J.-W.; Su, J. Influences of Doping Mesoporous Magnesium Silicate on Water Absorption, Drug Release, Degradability, Apatite-Mineralization and Primary Cells Responses to Calcium Sulfate Based Bone Cements. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Z.; Chang, J. Self-Setting Properties and in Vitro Bioactivity of Calcium Sulfate Hemihydrate–Tricalcium Silicate Composite Bone Cements. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, D.; Deakin, M.; Chapman-Sheath, P.; Bruce, W.; Debes, J.; Gillies, R.M.; Walsh, W.R. In Vivo Evaluation of Resorbable Bone Graft Substitutes in a Rabbit Tibial Defect Model. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5037–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauschmann, M.; Vogl, T.; Verheyden, A.; Pflugmacher, R.; Werba, T.; Schmidt, S.; Hierholzer, J. Bioceramic Vertebral Augmentation with a Calcium Sulphate/Hydroxyapatite Composite (CeramentTM SpineSupport) in Vertebral Compression Fractures Due to Osteoporosis. Eur. Spine J. 2010, 19, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Pei, P.; Zhu, M.; Du, X.; Xin, C.; Zhao, S.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y. Three Dimensional Printing of Calcium Sulfate and Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Scaffolds for Improving Bone Regeneration In Vitro and In Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, F.; Qin, L.; Liu, J.; Chang, J.; Huan, Z.; Wu, L. Assessment of Calcium Sulfate Hemihydrate–Tricalcium Silicate Composite for Bone Healing in a Rabbit Femoral Condyle Model. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 88, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamidwar, S.; Weiner, M.; Alexander, H.; Ricci, J. In Vivo Bone Response to Calcium Sulfate/Poly l-Lactic Acid Composite. Implant Dent. 2008, 17, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Huo, S.; Li, X.; You, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J. Characteristics of Calcium Sulfate/Gelatin Composite Biomaterials for Bone Repair. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 799–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-R.; Oh, C.-W.; Kyung, H.-S.; Park, I.-H.; Kim, P.-T.; Baek, S.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, S.-T. Injected Calcium Sulfate for Consolidation of Distraction Osteogenesis in Rabbit Tibia. J. Pediatr. Orthop. Part B 2004, 13, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.N.; Thomas, M.V.; Puleo, D.A. Mechanical and Degradation Behavior of Polymer-Calcium Sulfate Composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Genes | ID | Direction | Sequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-Actin | 11461 | FORWARD | GTGCTATGTTGCTCTAGACTTCG |
| REVERSE | ATGCCACAGGATTCCATACC | ||
| runx2 | 12393 | FORWARD | ATGGCGTCAAACAGCCTCTTC |
| REVERSE | TGGTGCTCGGATCCCAAAAG | ||
| BMP2 | 12156 | FORWARD | TCTTCCGGGAACAGATACAGG |
| REVERSE | TGGTGTCCAATAGTCTGGTCA | ||
| OCN | 12096 | FORWARD | AAGACCGCCTACAAACGCATCTAT |
| REVERSE | GCACTTCCTCATCTGAACTTTATTTTG | ||
| OPN | 20750 | FORWARD | TTGGTGACTTGGTGGTGATCTAGT |
| REVERSE | TCTCCTCTGAGCTGCCAGAATC | ||
| COL1 | 12842 | FORWARD | TAAGGGTCCCCAATGGTGAGA |
| REVERSE | GGGTCCCTCGACTCCTACAT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, S.; Yang, X.; Zou, W.; Chen, X.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y. A Bioactive Degradable Composite Bone Cement Based on Calcium Sulfate and Magnesium Polyphosphate. Materials 2024, 17, 1861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17081861
Peng S, Yang X, Zou W, Chen X, Deng H, Zhang Q, Yan Y. A Bioactive Degradable Composite Bone Cement Based on Calcium Sulfate and Magnesium Polyphosphate. Materials. 2024; 17(8):1861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17081861
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Suping, Xinyue Yang, Wangcai Zou, Xiaolu Chen, Hao Deng, Qiyi Zhang, and Yonggang Yan. 2024. "A Bioactive Degradable Composite Bone Cement Based on Calcium Sulfate and Magnesium Polyphosphate" Materials 17, no. 8: 1861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17081861
APA StylePeng, S., Yang, X., Zou, W., Chen, X., Deng, H., Zhang, Q., & Yan, Y. (2024). A Bioactive Degradable Composite Bone Cement Based on Calcium Sulfate and Magnesium Polyphosphate. Materials, 17(8), 1861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17081861






