Preparation and Properties of Attapulgite/Brucite Fiber-Based Highly Absorbent Polymer Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
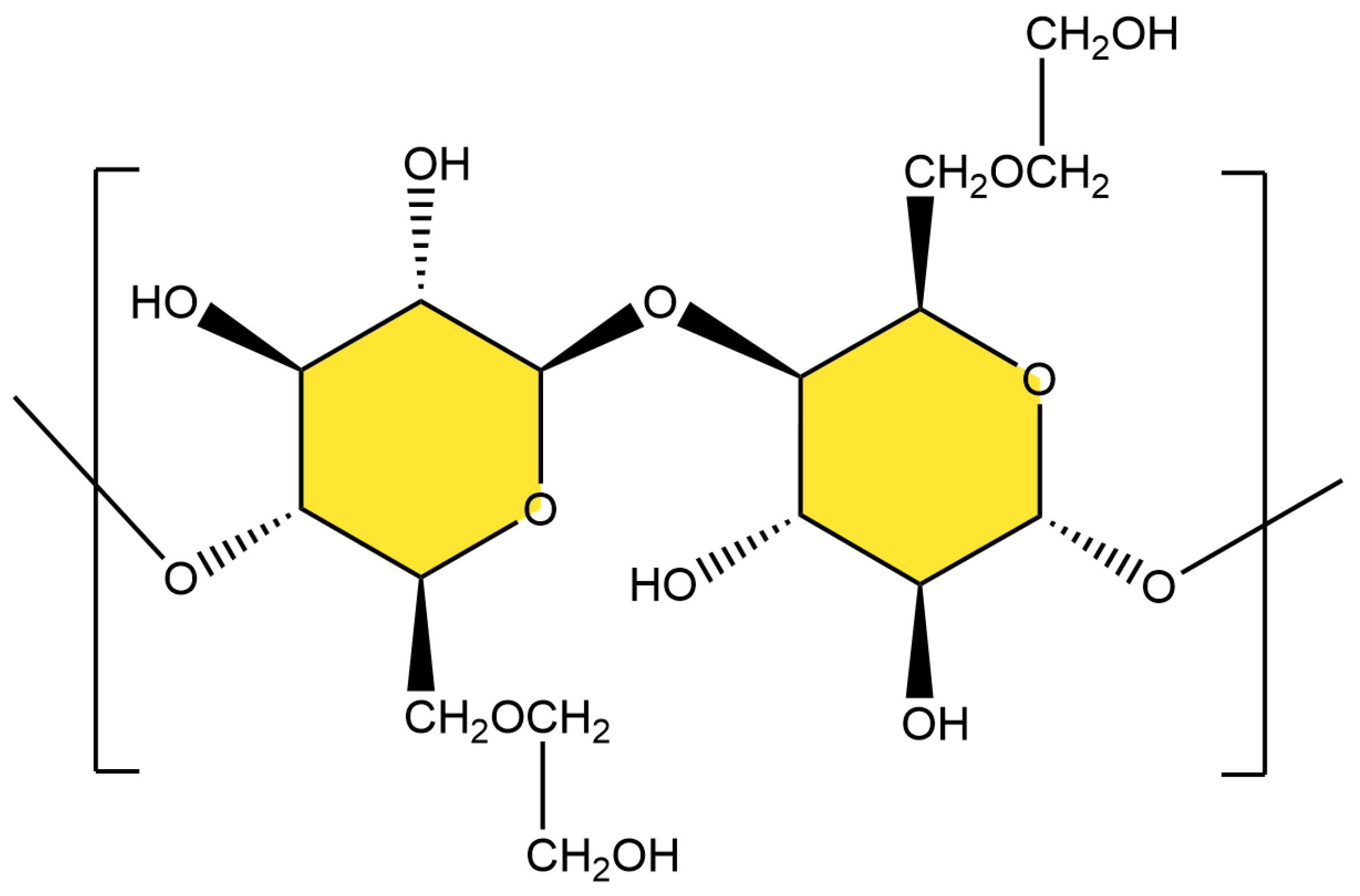
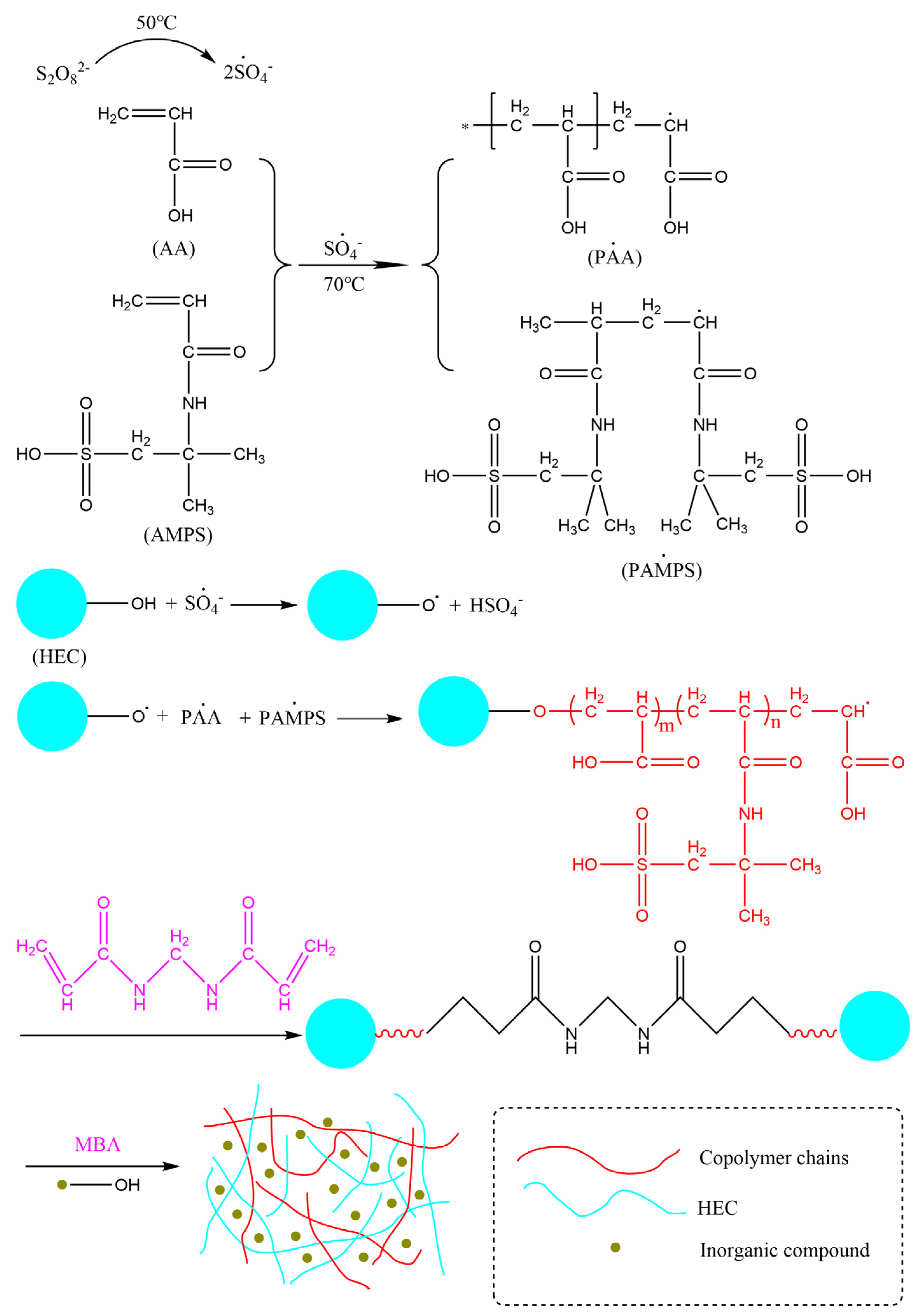
2.2. Preparation of ATP-BF-P(HEC-AA-AMPS) Highly Absorbent Polymer
2.3. Testing and Characterization
2.3.1. SEM
2.3.2. EDS
2.3.3. FT-IR
2.3.4. Thermodynamic Analysis
2.3.5. Measurement of Swelling Behavior
2.3.6. Determination of Water Retention at Different Temperatures
2.3.7. pH Dynamic Perception Test
2.3.8. Mechanical Test
3. Results and Discussion
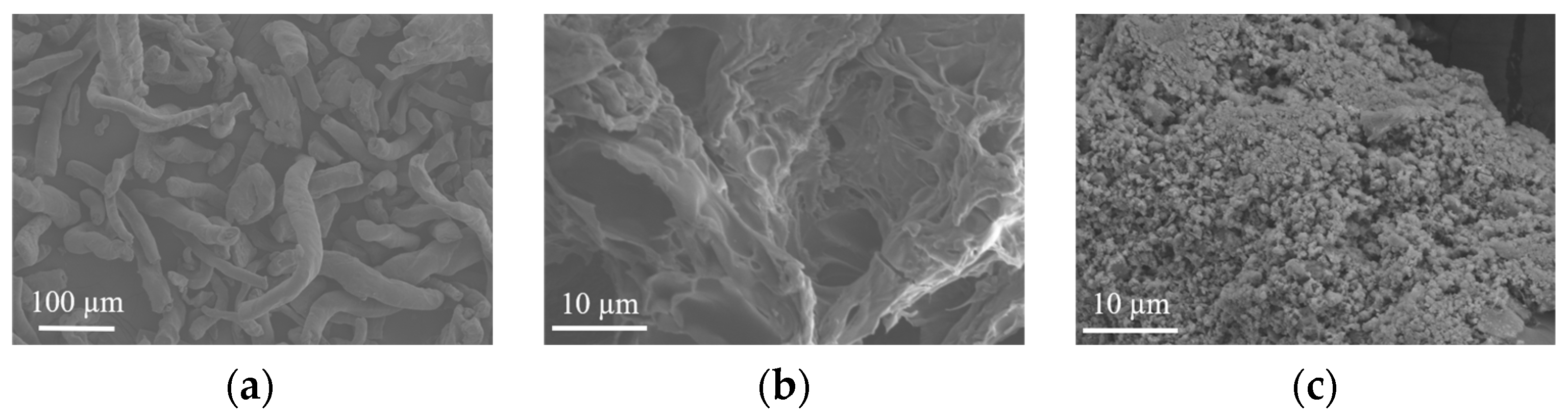
3.1. SEM
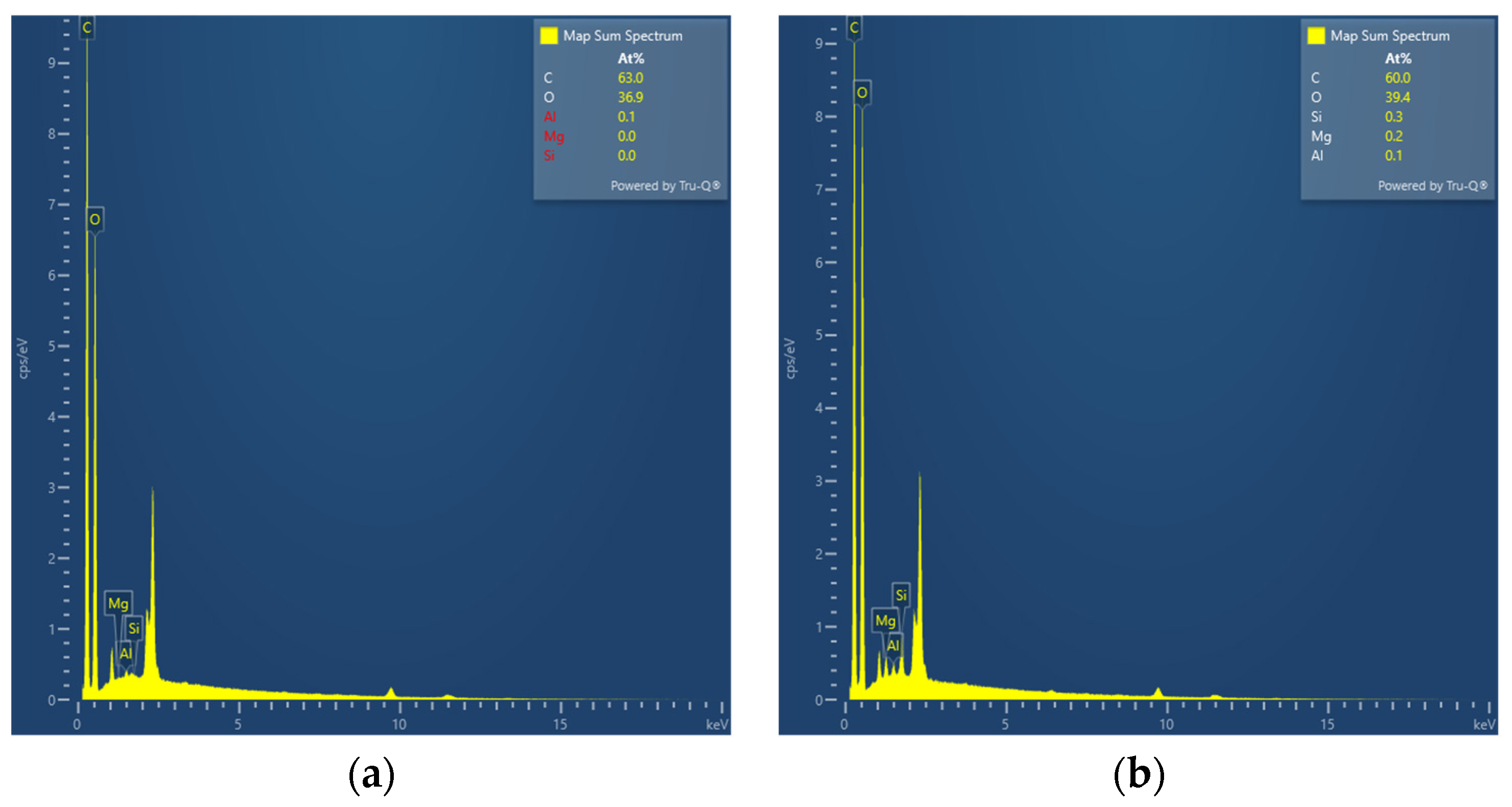
3.2. EDS
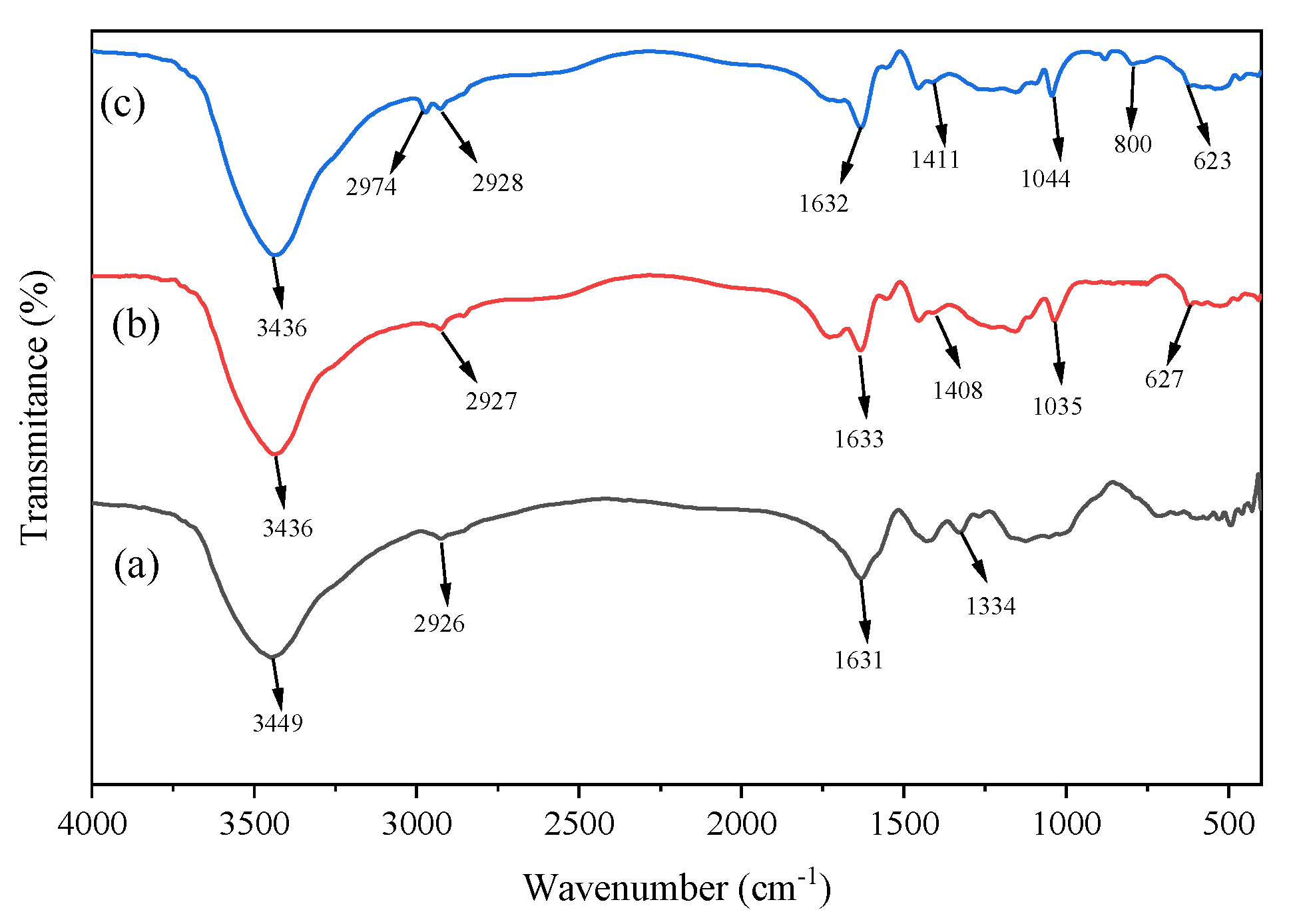
3.3. FT-IR
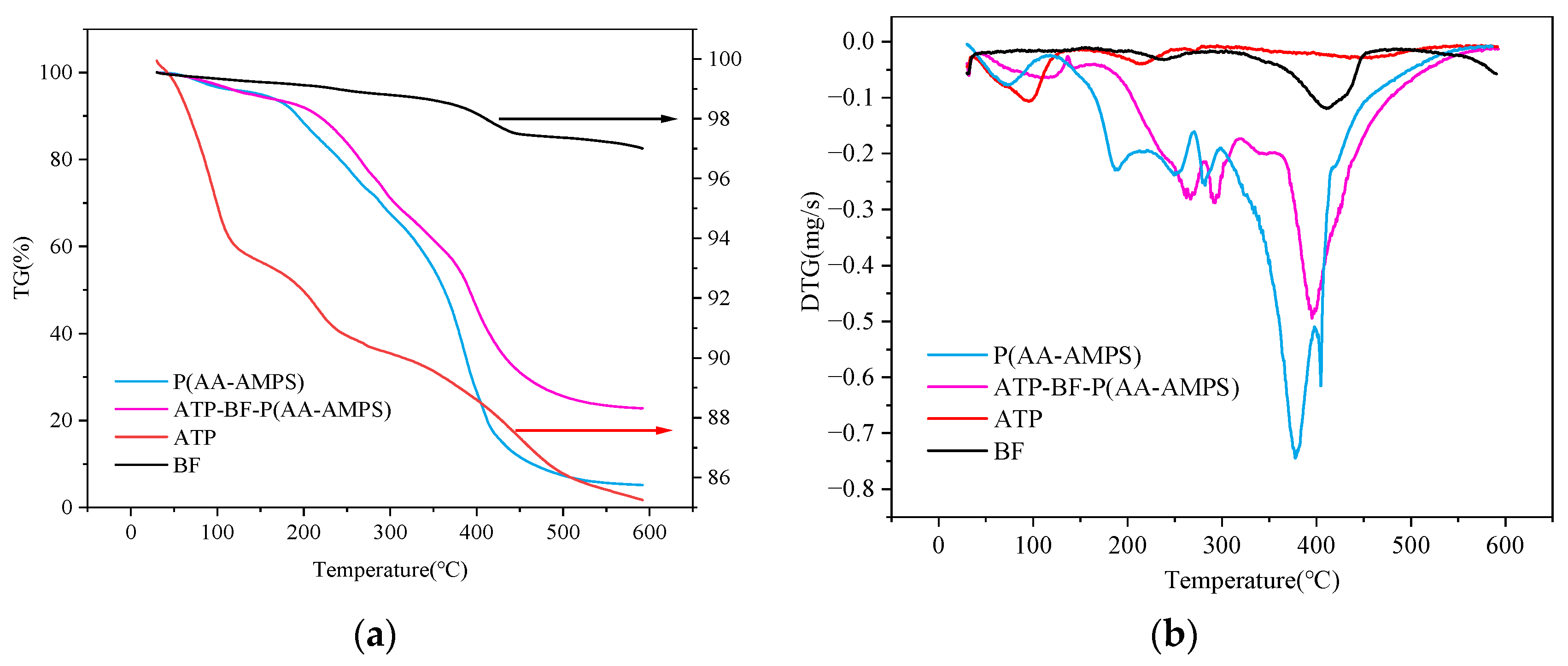
3.4. Thermal Stability Analysis
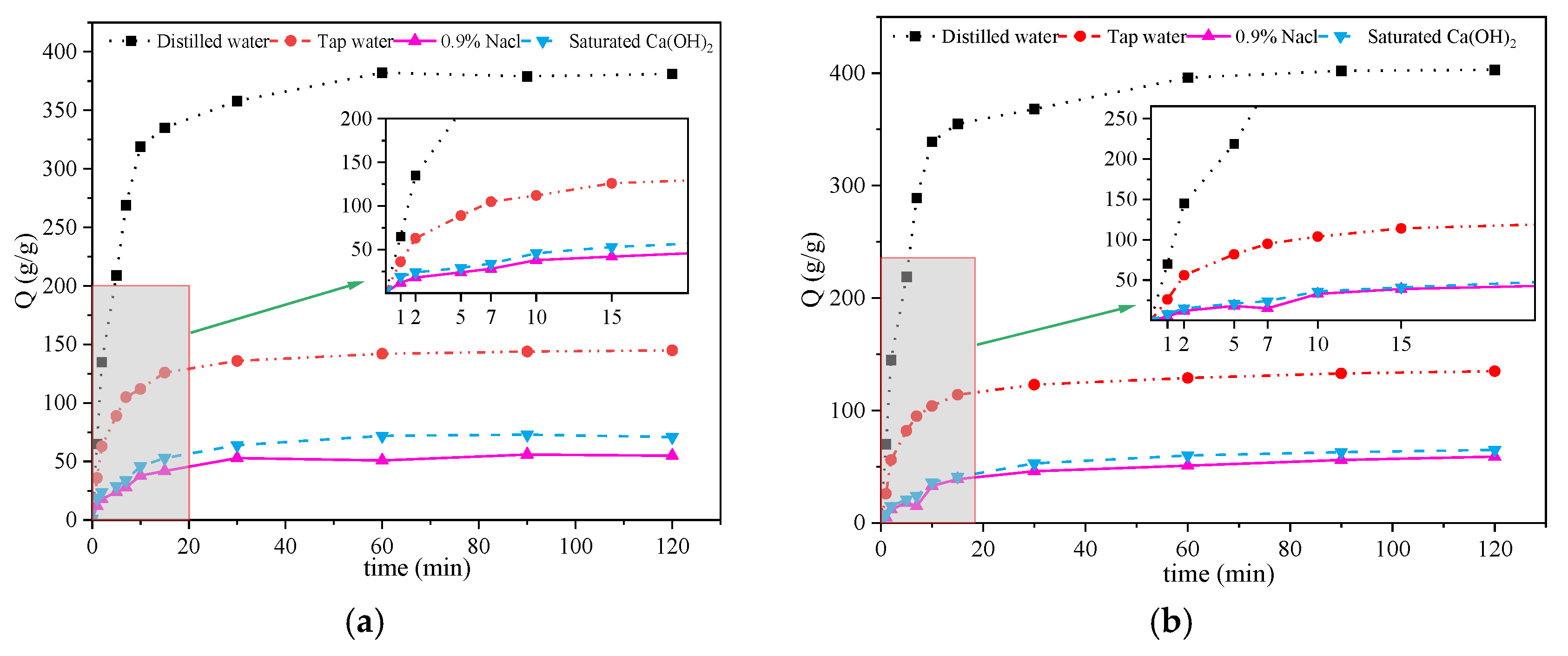
3.5. Measurement of Swelling Behavior
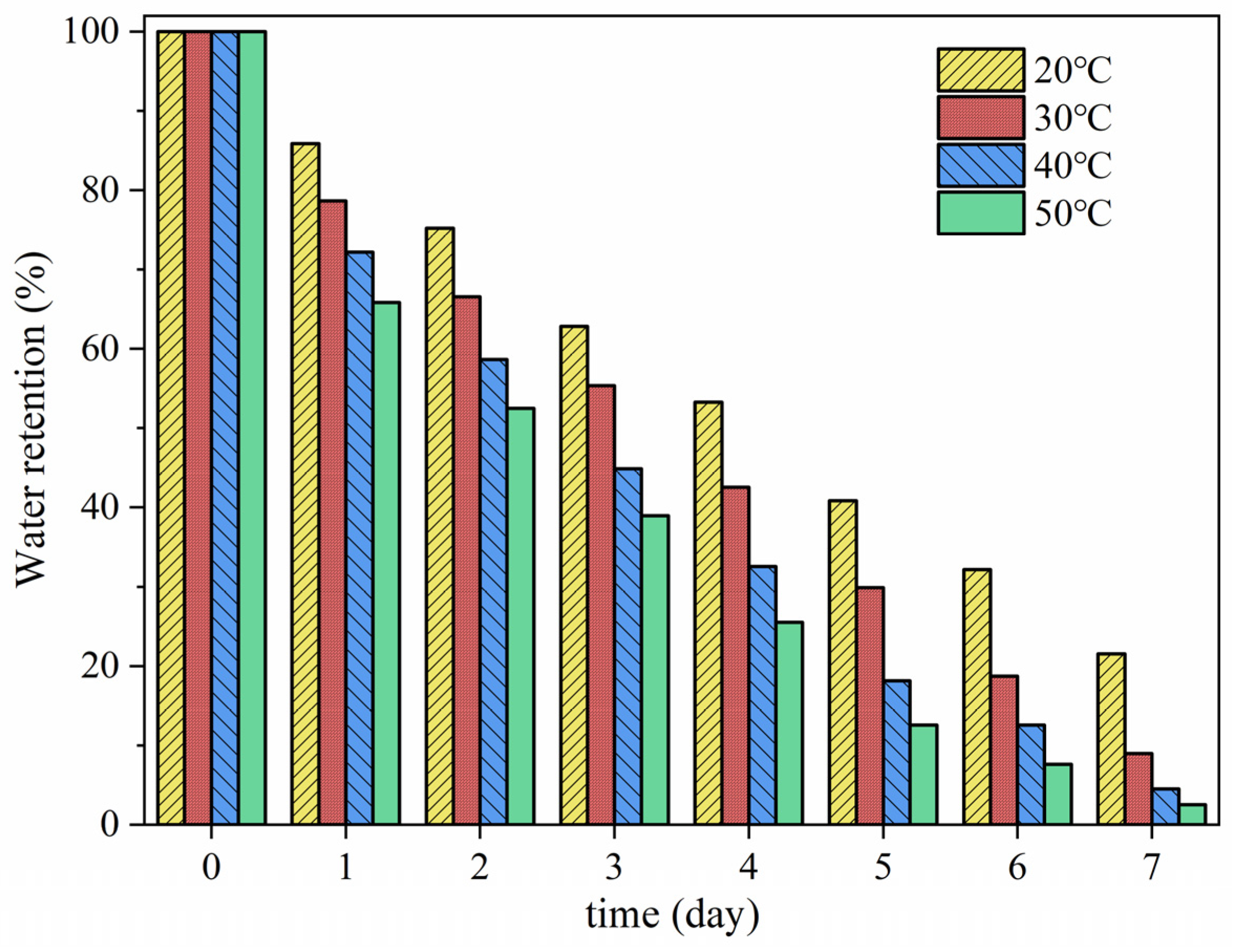
3.6. Water Retention Properties
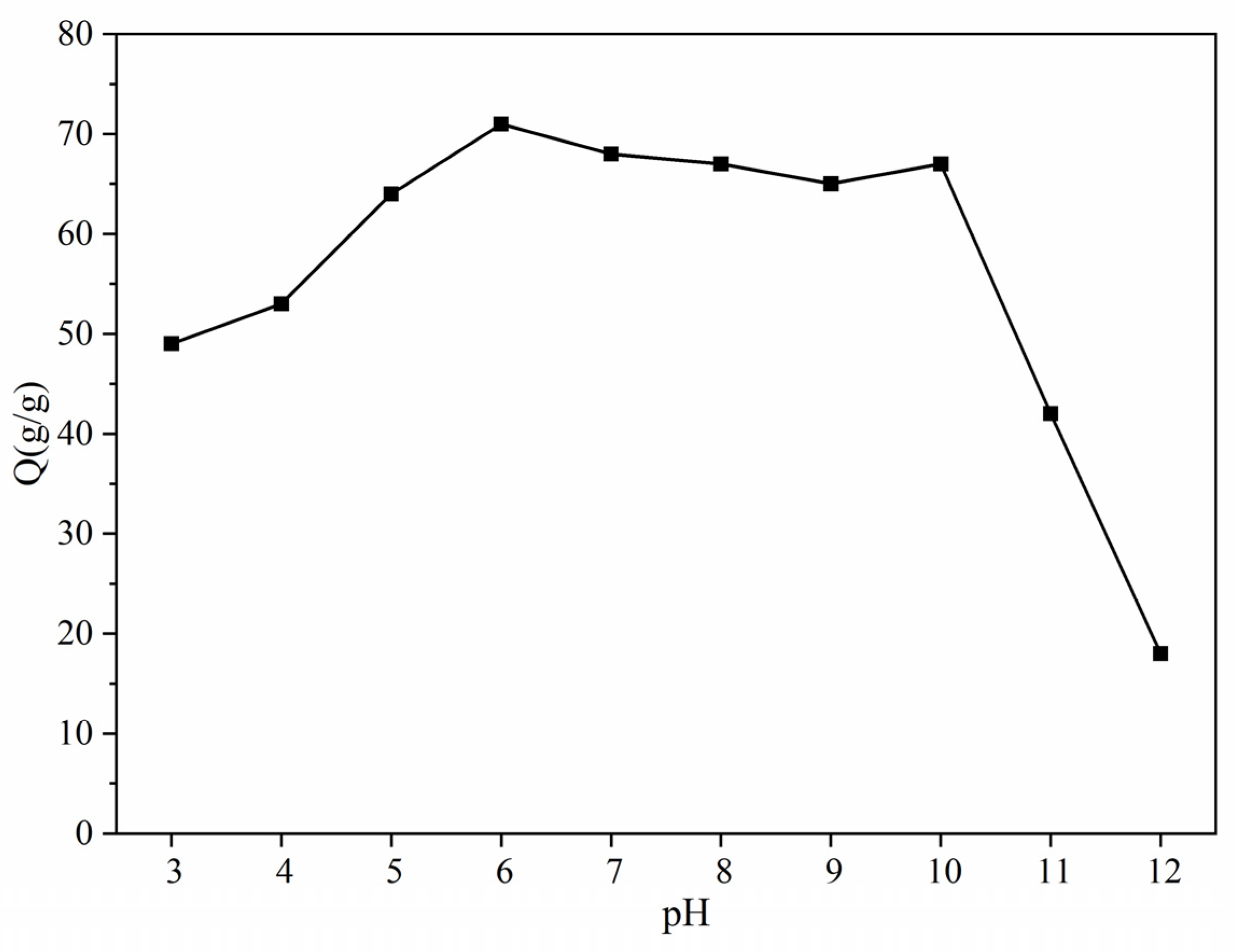
3.7. pH Dynamic Sensing
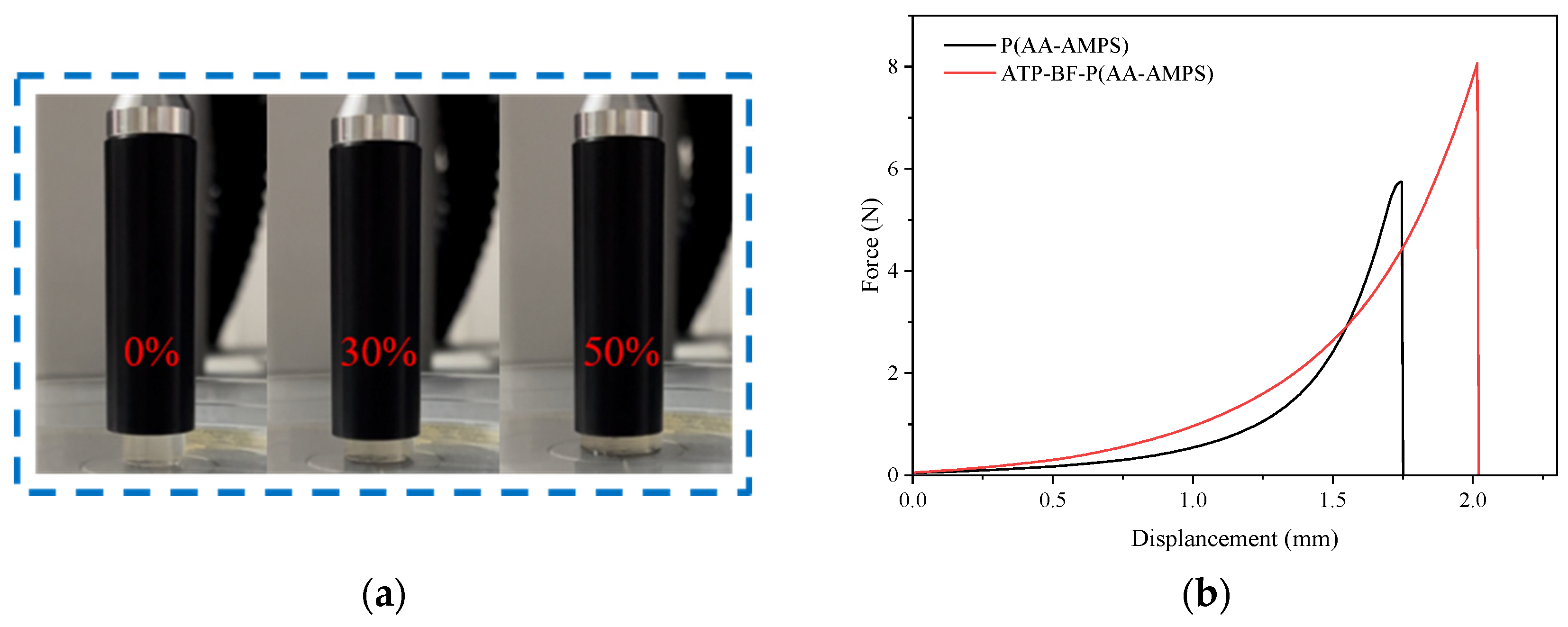
3.8. Mechanical Performance Test
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The successful polymerization of ATP-BF-P(HEC-AA-AMPS), a high-absorbency polymer, using an aqueous solution was demonstrated through SEM and FTIR. The polymer exhibited increased roughness and a higher number of micropores after the introduction of ATP and BF, significantly enhancing its liquid-absorbing capacity.
- (2)
- ATP-BF-P(HEC-AA-AMPS) exhibited superior thermodynamic stability in the temperature range of 30–600 °C compared to P(HEC-AA-AMPS), with a 17.58% reduction in mass loss at 600 °C, signifying a noteworthy improvement in thermal stability.
- (3)
- ATP-BF-P(HEC-AA-AMPS) exhibited better adaptability to the pH range, with minimal changes in dissolution multiplicity and maximum water absorption multiplicity between pH 6.0~10.0, indicating a broad range of applicability. Conversely, beyond a pH value of 10.0, the ability to absorb liquids decreased rapidly.
- (4)
- The mechanical properties of ATP-BF-P(HEC-AA-AMPS) improved by 40.59% at a 50% deformation level with the addition of ATP and BF. The overall strength of the polymer was significantly enhanced, rendering it more suitable for use in complex scenarios.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.T.; Sun, M.X.; Song, B.M. Public perceptions of and willingness to pay for sponge city initiatives in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 122, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Roberts, E.P.L.; Martin, A.D.; Holmes, S.M.; Brown, N.W.; Campen, A.K.; de las Heras, N. Electrochemical regeneration of a graphite adsorbent loaded with Acid Violet 17 in a spouted bed reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiewicz, J.; Datta, S.S.; Lejcus, K.; Marczak, D. The Characteristics of Time-Dependent Changes of Coefficient of Permeability for Superabsorbent Polymer-Soil Mixtures. Materials 2022, 15, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.T.; Zhang, A.P. Water- and Fertilizer-Integrated Hydrogel Derived from the Polymerization of Acrylic Acid and Urea as a Slow-Release N Fertilizer and Water Retention in Agriculture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5762–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, A.; Kaesaman, A.; Klinpituksa, P. Superabsorbent materials derived from hydroxyethyl cellulose and bentonite: Preparation, characterization and swelling capacities. Polym. Test. 2017, 64, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Luan, Q.; Huang, Q.D.; Tang, H.; Huang, F.H.; Li, W.L.; Wan, C.Y.; Liu, C.S.; Xu, J.Q.; Guo, P.M.; et al. A facile and efficient strategy for the fabrication of porous linseed gum/cellulose superabsorbent hydrogels for water conservation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1830–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.H.; Hong, S.G.; Moon, J. Absorption kinetics of superabsorbent polymers (SAP) in various cement-based solutions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 97, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.G.; Liu, H.Y.; Shao, L.; Zhang, X.M.; Yao, J.M. Biodegradation process and yellowing mechanism of an ecofriendly superabsorbent based on cellulose from flax yarn wastes. Cellulose 2015, 22, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.X.; Song, W.M.; Wu, H.; Zhan, Y.Q.; Wu, Z.Z.; Yin, J. Investigation on Performances and Functions of Asphalt Mixtures Modified with Super Absorbent Polymer (SAP). Materials 2023, 16, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeter, M.; Virgolici, M.; Vancea, C.; Scarisoreanu, A.; Kaya, M.G.A.; Meltzer, V. Network structure studies on γ-irradiated collagen-PVP superabsorbent hydrogels. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2017, 131, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyst, L.; Mannekens, E.; Araújo, M.; Snoeck, D.; Van Tittelboom, K.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; De Belie, N. Parameter Study of Superabsorbent Polymers (SAPs) for Use in Durable Concrete Structures. Materials 2019, 12, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.Y.; Bai, B.J.; Hou, J.R. Polymer Gel Systems for Water Management in High-Temperature Petroleum Reservoirs: A Chemical Review. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 13063–13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.Y.; Yang, X.G.; Liu, H.Y.; Yao, J.M. An Eco-Friendly Slow-Release Urea Fertilizer Based on Waste Mulberry Branches for Potential Agriculture and Horticulture Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, F.J.; Yin, X.Z.; Hu, R.C.; Ma, H.L.; Liu, W. Research into the super-absorbent polymers on agricultural water. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanta, G.F.; Burr, R.C.; Russell, C.R.; Rist, C.E. Graft copolymers of starch with mineral acid salts of dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate. Preparation and testing as flocculating agents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 15, 1889–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Liu, X.M.; Zhen, J.H.; Lei, Z.Q. Preparation of superabsorbent resin with fast water absorption rate based on hydroxymethyl cellulose sodium and its application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 225, 115214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, H.R.; Lima, I.S.; Neris, L.M.L.; Silva, A.S.; Nascimento, A.; Araújo, F.P.; Ratke, R.F.; Silva, D.A.; Osajima, J.A.; Bezerra, L.R.; et al. Superabsorbent Hydrogels Based to Polyacrylamide/Cashew Tree Gum for the Controlled Release of Water and Plant Nutrients. Molecules 2021, 26, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olad, A.; Gharekhani, H.; Mirmohseni, A.; Bybordi, A. Synthesis, characterization, and fertilizer release study of the salt and pH-sensitive NaAlg-g-poly(AA-co-AAm)/RHA superabsorbent nanocomposite. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 3353–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitalniak, M.; Bogacz, A.; Zieba, Z. The Assessment of Water Retention Efficiency of Different Soil Amendments in Comparison to Water Absorbing Geocomposite. Materials 2021, 14, 6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Ning, A.M.; Xie, P.H.; Gao, G.Q.; Xie, L.X.; Li, X.; Song, A.D. Synthesis and swelling behaviors of carboxymethyl cellulose-based superabsorbent resin hybridized with graphene oxide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaeilimoghadam, S.; Jonoobi, M.; Ashori, A.; Shahraki, A.; Azimi, B.; Danti, S. Interpenetrating and semi-interpenetrating network superabsorbent hydrogels based on sodium alginate and cellulose nanocrystals: A biodegradable and high-performance solution for adult incontinence pads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Wang, C.J.; Guo, P.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.T.; Sun, H.H.; Wen, H.Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.R.; Wang, Y.; et al. Photo-crosslinked enhanced double-network hydrogels based on modified gelatin and oxidized sodium alginate for diabetic wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 245, 125528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.S.; Hu, X.L.; Li, W.; Zhu, M.L.; Tian, J.H.; Li, L.H.; Luo, B.H.; Zhou, C.R.; Lu, L. A highly-stretchable and adhesive hydrogel for noninvasive joint wound closure driven by hydrogen bonds. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zeng, W.; Liu, X.M.; Zhao, J.J.; Qiu, X.Y.; Lei, Z.Q. Anti-evaporation Performance of Water in Soil of Superabsorbent Resin with Fast Water Absorption Rate. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Ke, W.; Chen, X.; Kong, Y.; Zheng, H.; Yin, Y.; Cai, W. Preparation and properties of quaternary ammonium chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) superabsorbent hydrogels. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 111, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Lu, H.X.; Xiao, H.Y.; Gao, K.S.; Diao, M.M. Adsorption capacity of superabsorbent resin composite enhanced by non-thermal plasma and its adsorption kinetics and isotherms to lead ion in water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Fei, Q.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of the starch grafting of superabsorbent and high oil-absorbing resin. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, S97–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.J.; Zhang, Y.G.; Wang, P.L.; Yang, Z.Y.; Yasin, A.; Zhang, L.T. Preparation and Applications of Salt-Resistant Superabsorbent Poly (Acrylic Acid-Acrylamide/Fly Ash) Composite. Materials 2019, 12, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Qi, X. Synthesis and Swelling Behavior of Poly(sodium acrylate-co-2-acryloylamino-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid)/Attapulgite Superabsorbent Composite. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 35, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Khanlari, S.; Dubé, M.A. Effect of pH on Poly(acrylic acid) Solution Polymerization. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A-Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 52, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apoorva, A.; Rameshbabu, A.P.; Dasgupta, S.; Dhara, S.; Padmavati, M. Novel pH-sensitive alginate hydrogel delivery system reinforced with gum tragacanth for intestinal targeting of nutraceuticals. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Li, C.; Guo, C.; Mou, Y.; Jiang, J.; Lv, L. Preparation and Properties of gamma-Polyglutamic Acid/Attapulgite Superabsorbent Composite. Fine Chem. 2019, 36, 414–421. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Amatjan, S.; Ismayil, N. Ultraviolet Preparation and Properties of Ester Crosslinking Acrylic Acid Sodium Superabsorbent Polymer. J. Funct. Polym. 2012, 25, 320–326. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Peng, C.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z. Synthesis and Characterization of CMC-g-PAMPS/APT Superabsorbent Resin by Microwave Irradiation. Fine Chem. 2014, 31, 427–431. [Google Scholar]


| Reagents | Abbreviation | Reagent Purity | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acrylic acid | AA | Analytical purity | Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Factory (Tianjin, China) |
| 2-Arylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid | AMPS | Analytical purity | Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| Brucite fiber | BF | / | Provinsi Shaanxi (Yulin, China) |
| Attapulgite | ATP | / | Provinsi Shaanxi |
| Methylene-bis-acrylamide | MBA | Analytical purity | Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. |
| Carboxyethyl cellulose | HEC | Analytical purity | Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. |
| Calcium hydroxide | Ca(OH)2 | Analytical purity | Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Factory (Tianjin, China) |
| Sodium chloride | NaCl | Analytical purity | Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Factory |
| Ethanol absolute | C2H6O | Analytical purity | Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Factory |
| Ammonium persulphate | APS | Analytical purity | Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Science and Technology Co. (Shanghai, China) |
| Potassium bromide | KBr | Analytical purity | Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. |
| Equipment | Model | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer | TENSOR II | Bruker (Beijing) Technology Co. (Beijing, China) |
| Synchronous Thermal Analyzer | STD650 | Waters China Ltd. (Kowloon, Hong Kong) |
| Scanning Electron Microscope | S-4800 | Hitachi Production Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan) |
| Mass Structural Analyzer | TA.TOUCH | Shanghai Baosheng Industrial Development Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| Magnetic Water Bath Stirrer | DF-101S | Henan Iuka Instrument Co. (Zhengzhou, China) |
| Henan Iuka Instrument | WGL-45B | Tianjin Tester Instrument Co. (Tianjin, China) |
| Element | C (At%) | O (At%) | Al (At%) | Mg (At%) | Si (At%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(HEC-AA-AMPS) | 63.0 | 36.9 | 0.1 | - | - |
| ATP-BF-P(HEC-AA-AMPS) | 60.0 | 39.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Temperature | Solution | Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | Deionized water | Q = 373.93816 − 366.51695 ∗ 0.83853t | 0.99228 |
| Tap water | Q = 139.67793 − 129.44161 ∗ 0.827623t | 0.97808 | |
| 0.9% NaCl solution | Q = 54.12796 − 49.18642 ∗ 0.90225t | 0.97906 | |
| Ca(OH)2 solution | Q = 71.51842 − 62.77467 ∗ 0.91987t | 0.97126 | |
| 30 °C | Deionized water | Q = 391.48654 − 384.12705 ∗ 0.83314t | 0.98907 |
| Tap water | Q = 128.06336 − 122.2181 ∗ 0.82654t | 0.97903 | |
| 0.9% NaCl solution | Q = 55.48576 − 53.88255 ∗ 0.93325t | 0.96452 | |
| Ca(OH)2 solution | Q = 62.66125 − 59.10752 ∗ 0.93333t | 0.98705 | |
| 40 °C | Deionized water | Q = 380.6345 − 372.91741 ∗ 0.86263t | 0.99273 |
| Tap water | Q = 139.67793 − 129.44161 ∗ 0.82762t | 0.97808 | |
| 0.9% NaCl solution | Q = 70.0173 − 61.89942 ∗ 0.91964t | 0.97509 | |
| Ca(OH)2 solution | Q = 71.51842 − 62.77467 ∗ 0.91987t | 0.97126 | |
| 50 °C | Deionized water | Q = 373.96533 − 363.99687 ∗ 0.8393t | 0.99229 |
| Tap water | Q = 139.67793 − 129.54161 ∗ 0.82762t | 0.97808 | |
| 0.9% NaCl solution | Q = 54.71655 − 49.6725 ∗ 0.90467t | 0.97741 | |
| Ca(OH)2 solution | Q = 56.77377 − 49.76065 ∗ 0.89635t | 0.95434 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, C.; Zhai, X.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Xiong, R.; Lu, F. Preparation and Properties of Attapulgite/Brucite Fiber-Based Highly Absorbent Polymer Composite. Materials 2024, 17, 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17081913
Deng C, Zhai X, Li W, Li Q, Xiong R, Lu F. Preparation and Properties of Attapulgite/Brucite Fiber-Based Highly Absorbent Polymer Composite. Materials. 2024; 17(8):1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17081913
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Caihong, Xinming Zhai, Wenrong Li, Qian Li, Rui Xiong, and Fuyang Lu. 2024. "Preparation and Properties of Attapulgite/Brucite Fiber-Based Highly Absorbent Polymer Composite" Materials 17, no. 8: 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17081913
APA StyleDeng, C., Zhai, X., Li, W., Li, Q., Xiong, R., & Lu, F. (2024). Preparation and Properties of Attapulgite/Brucite Fiber-Based Highly Absorbent Polymer Composite. Materials, 17(8), 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17081913





