Temperature Uniformity Control of 12-Inch Semiconductor Wafer Chuck Using Double-Wall TPMS in Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
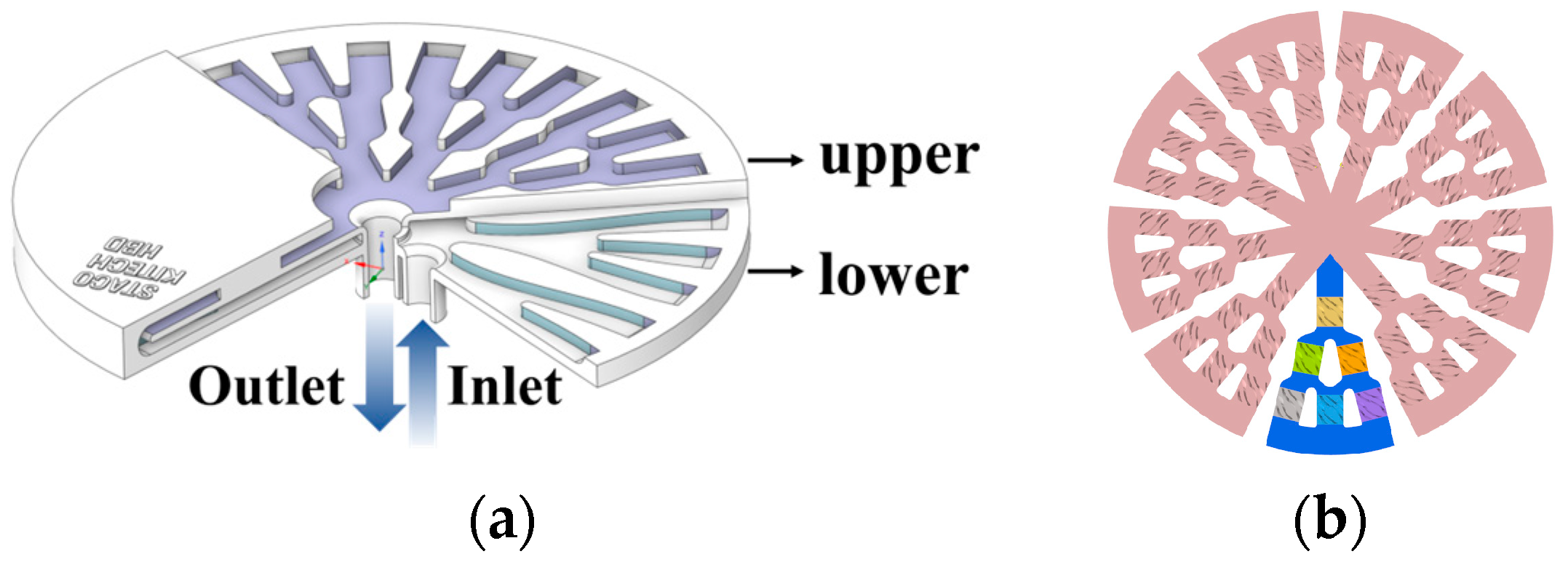
1.1. Semiconductor Wafer Chuck
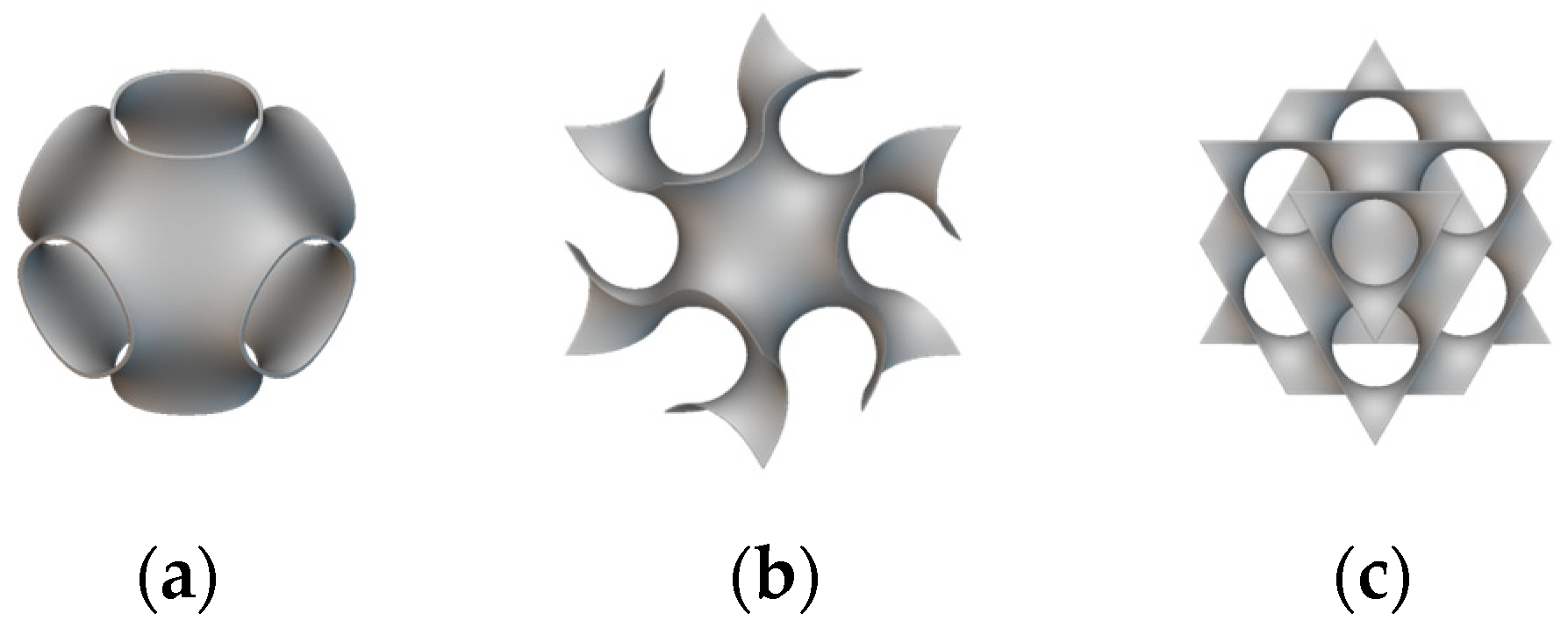
1.2. Introduction to Triply Periodic Minimal Surfaces
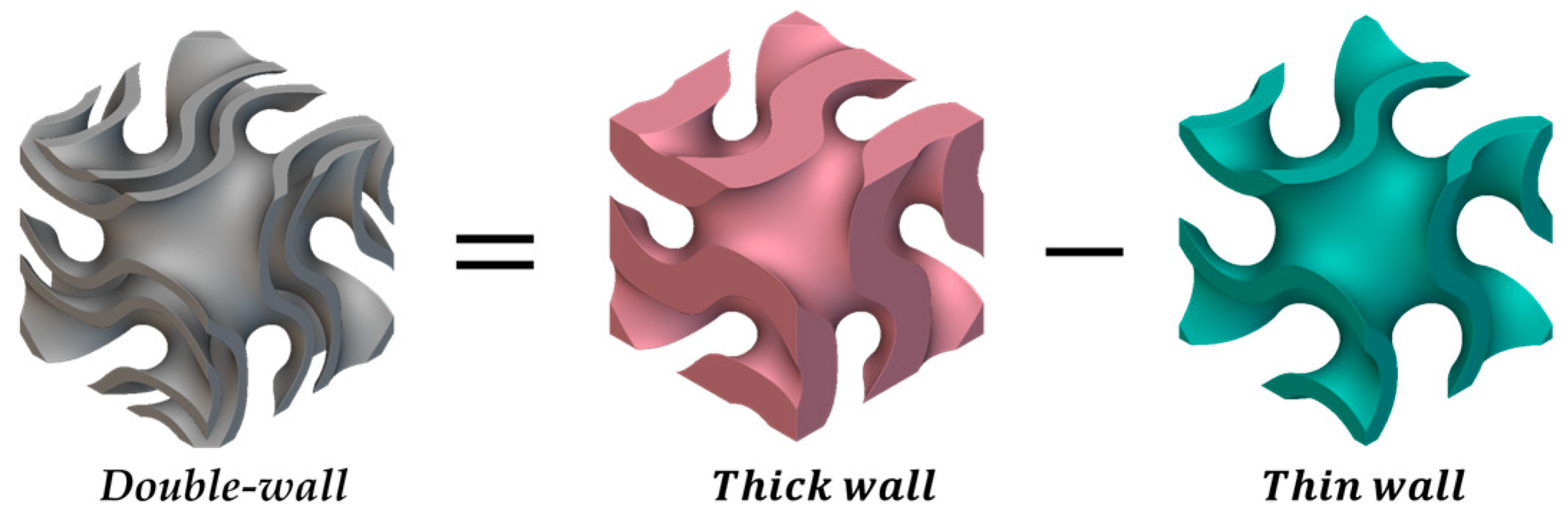
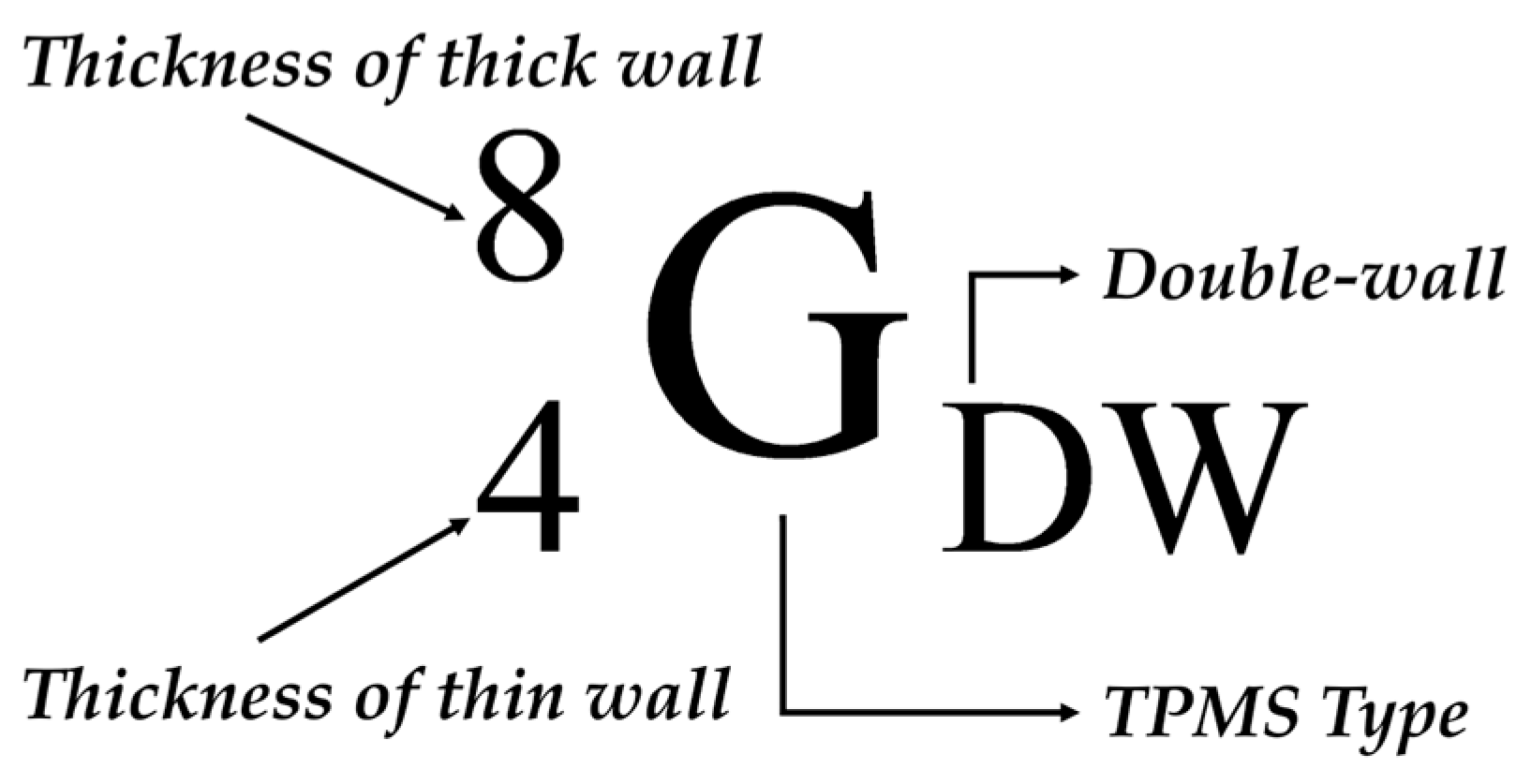
2. Double-Wall Sheet TPMS
2.1. Concept of Double-Wall Sheet TPMS
2.2. Thermo-Fluid Trends of Double-Wall Sheet TPMS
2.2.1. Thermo-Fluid CFD Analysis
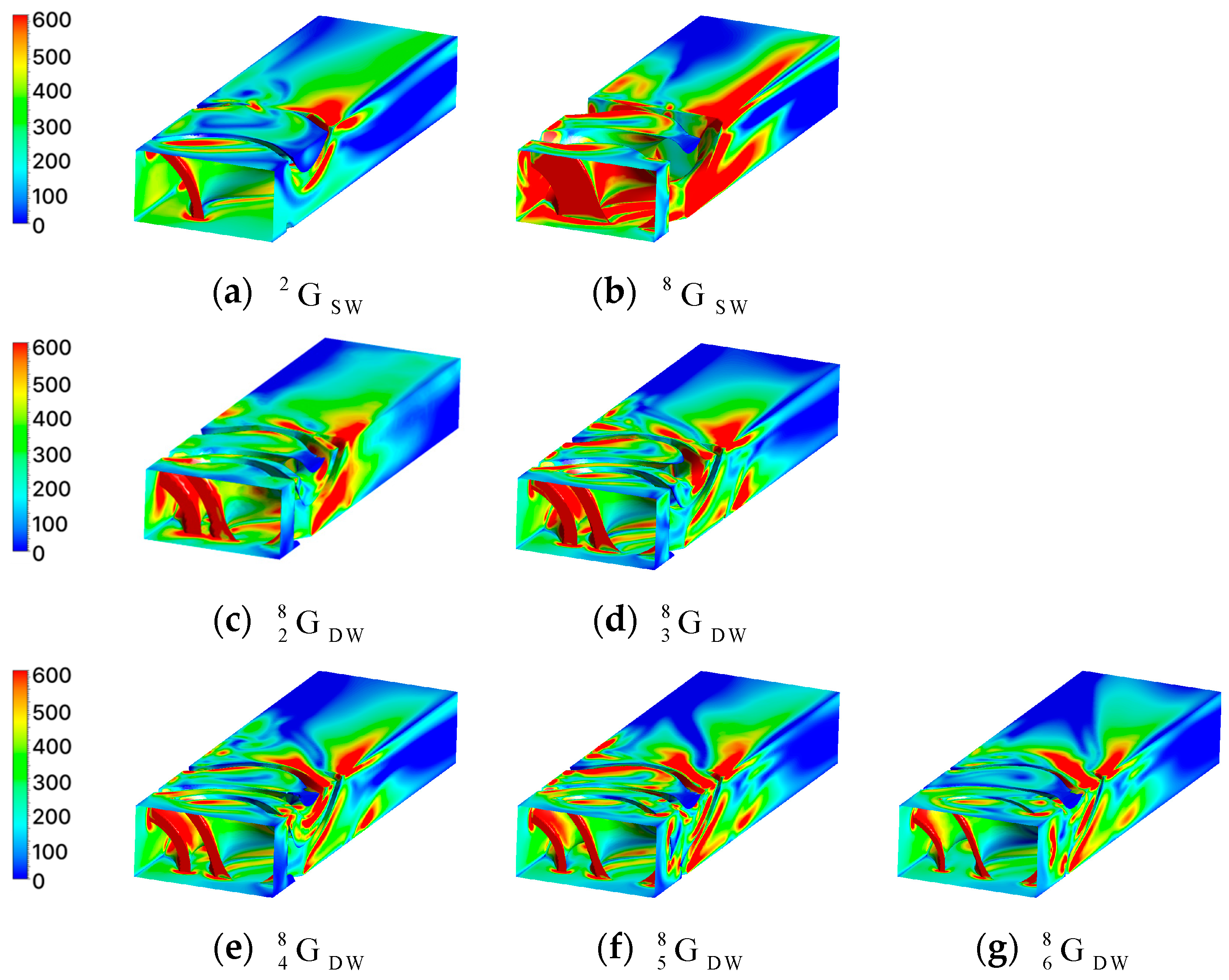
2.2.2. CFD Results of Diamond Structure
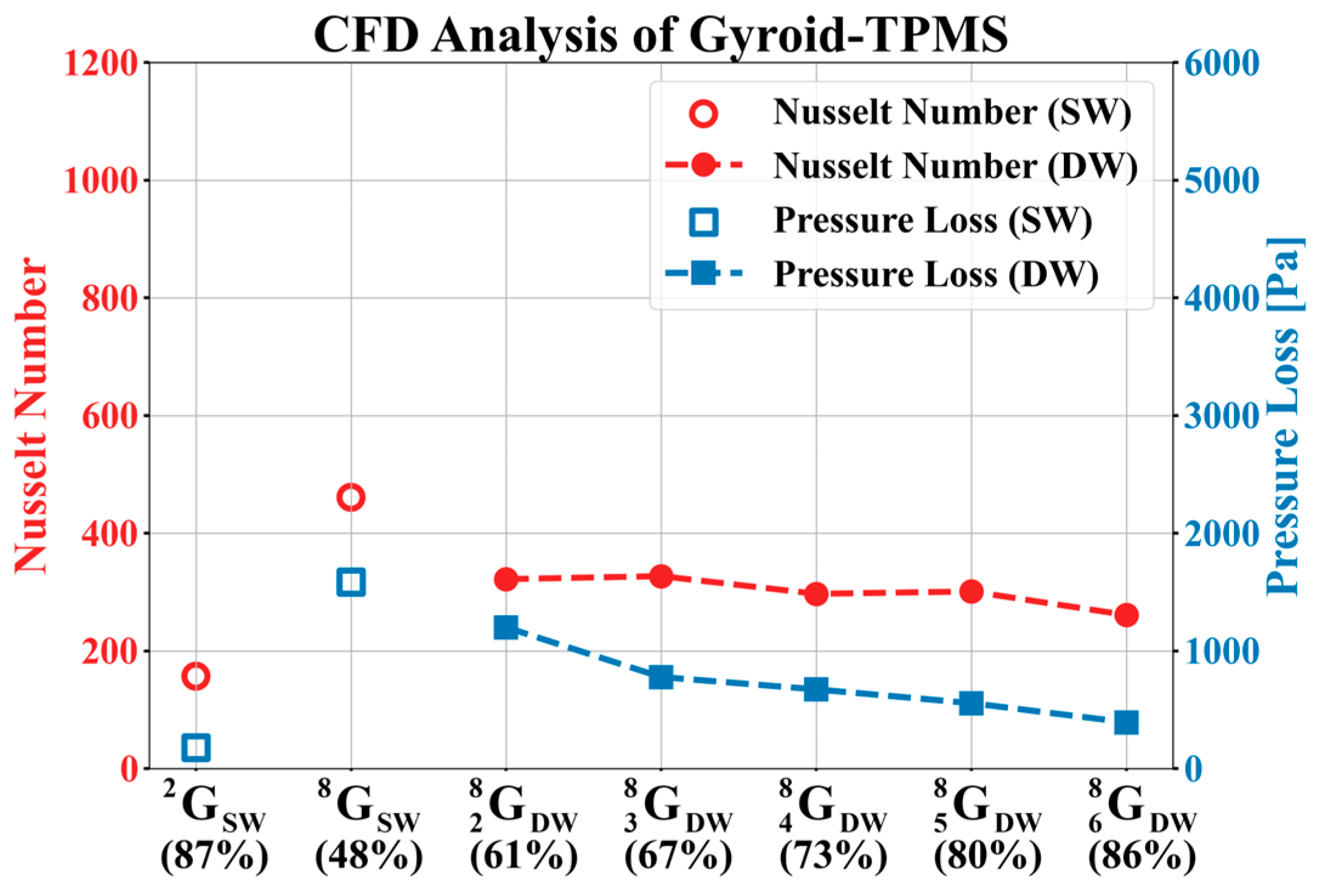
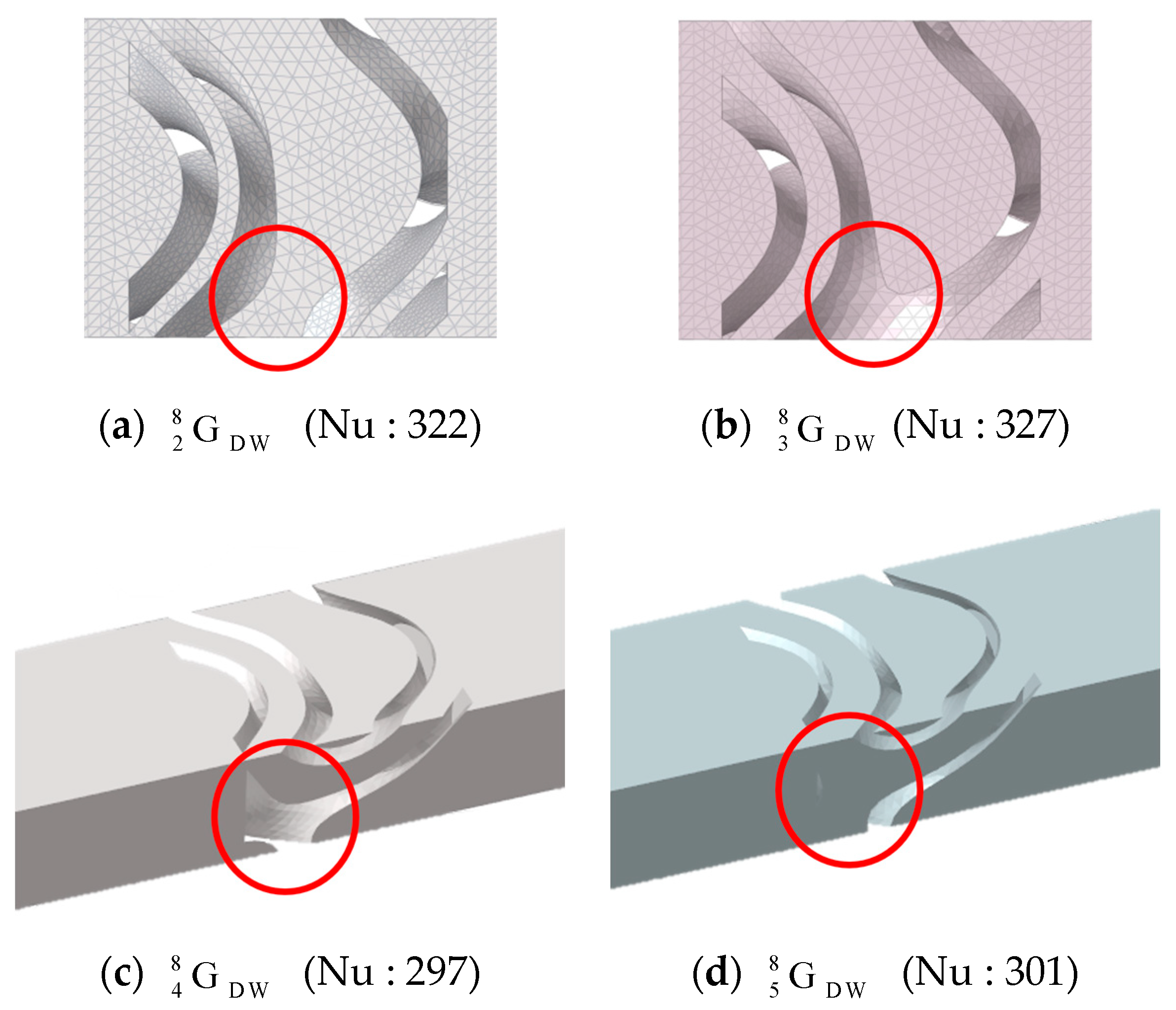
2.2.3. CFD Results of Gyroid Structure
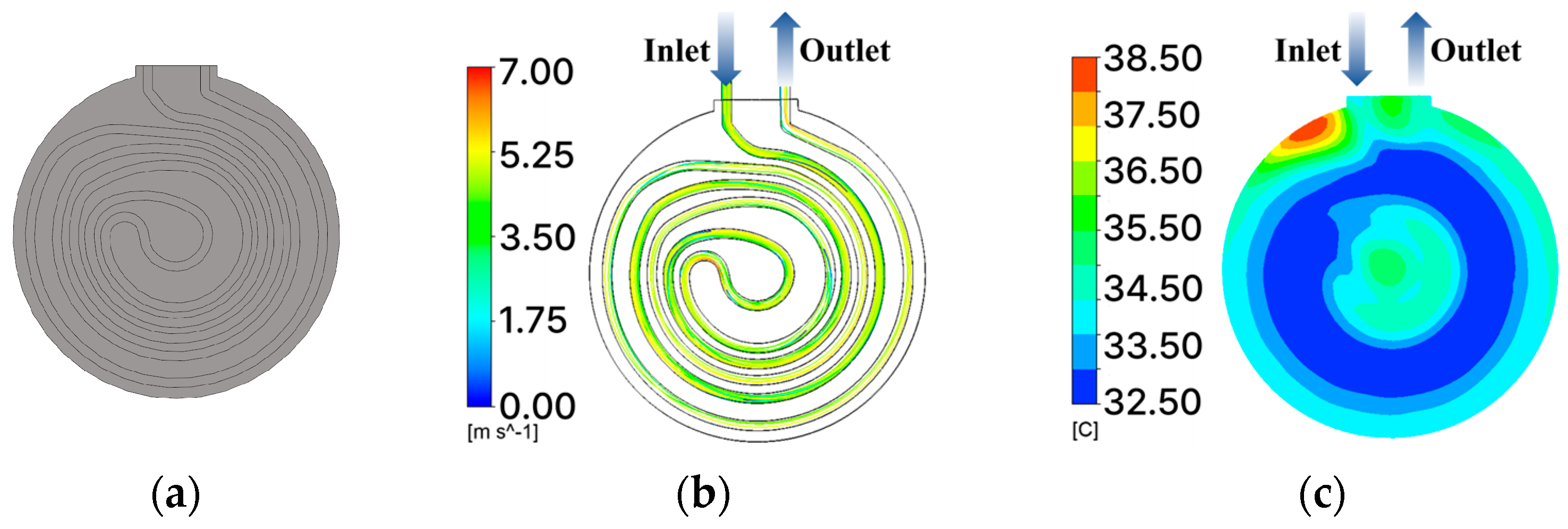
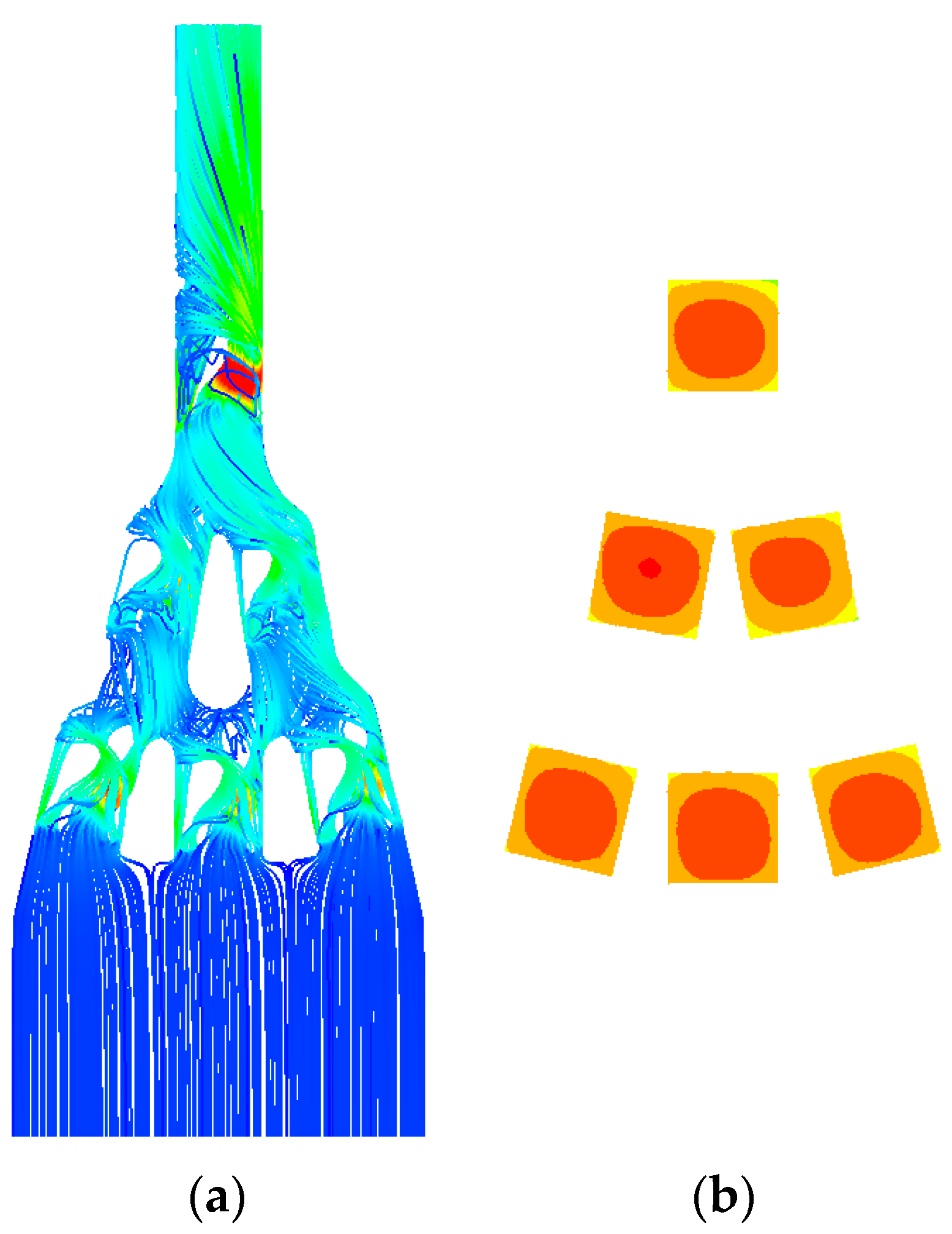
3. Optimal Design of the 12-Inch Chuck
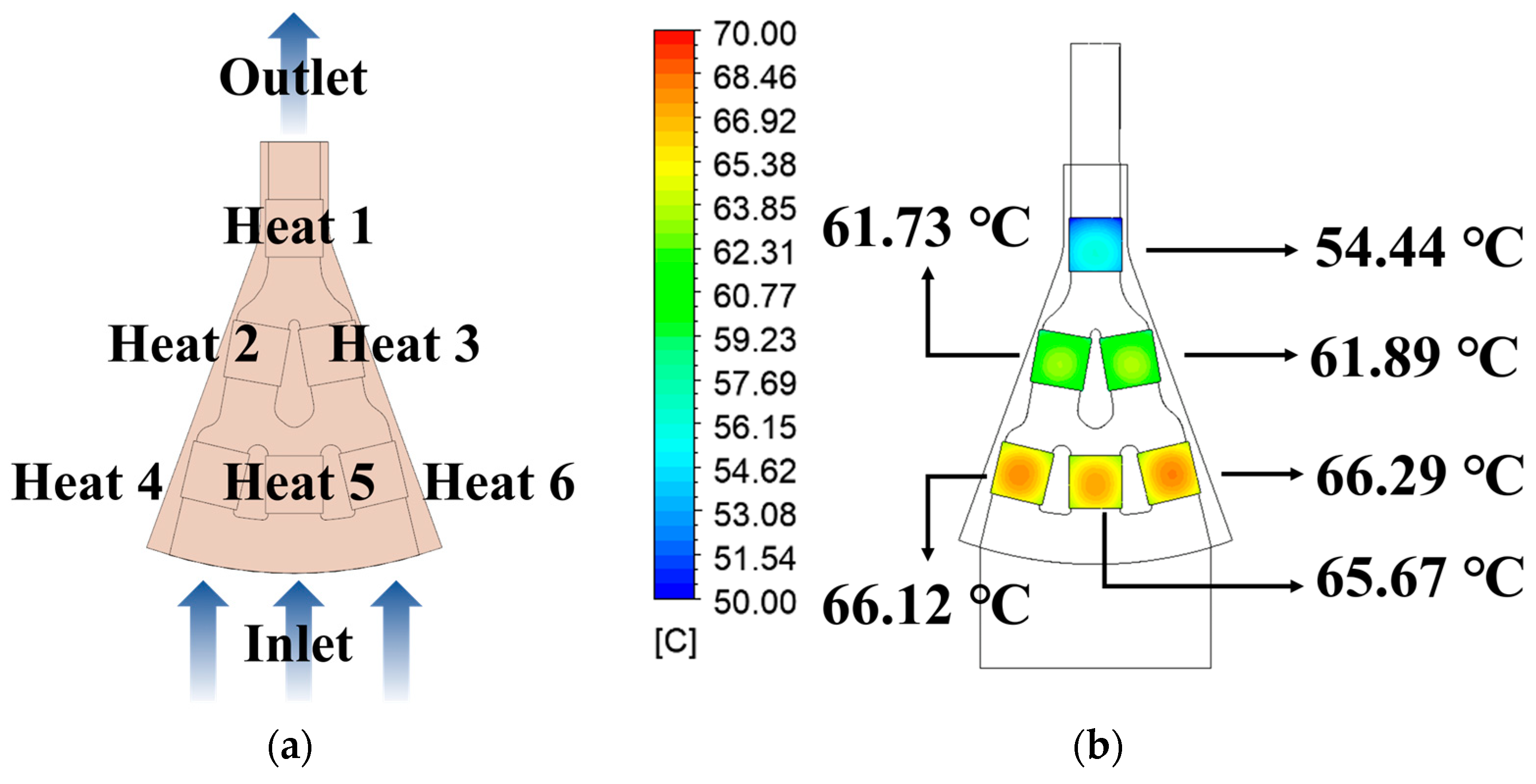
3.1. Radial Structure of the 12-Inch Chuck 1/9 Model
3.2. Optimal Design Using Double-Wall Sheet-Diamond
3.2.1. Selection of Design Variables for Heat 1
3.2.2. Discrete Latin Hypercube Design
3.2.3. Sequential Approximate Optimization
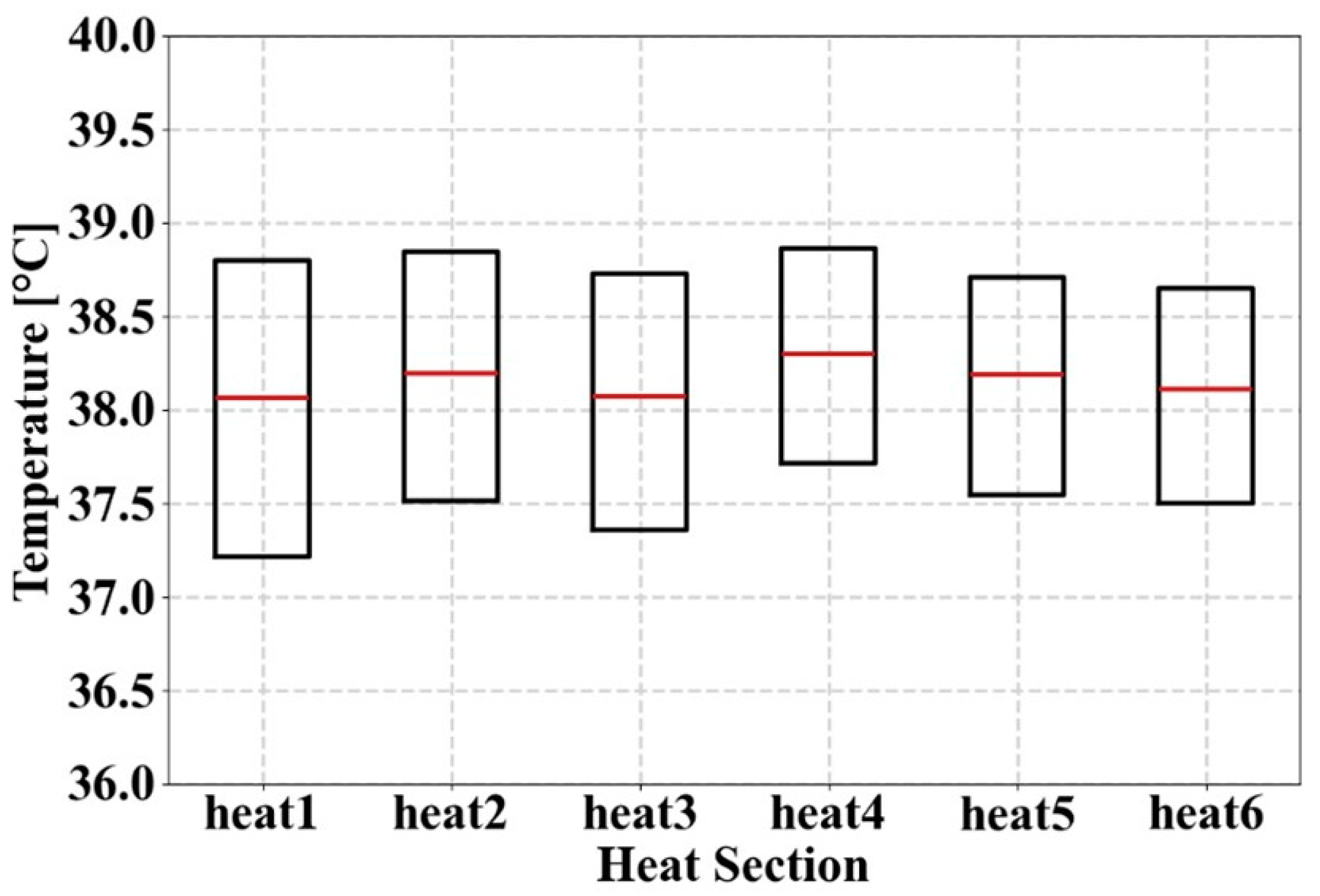
3.2.4. Verification of Temperature Distribution Using Boxplot
3.3. Optimal Design Using Double-Wall Sheet Gyroid
3.3.1. Selection of Design Variables for Heat 1
3.3.2. Discrete Latin Hypercube Design
3.3.3. Sequential Approximate Optimization
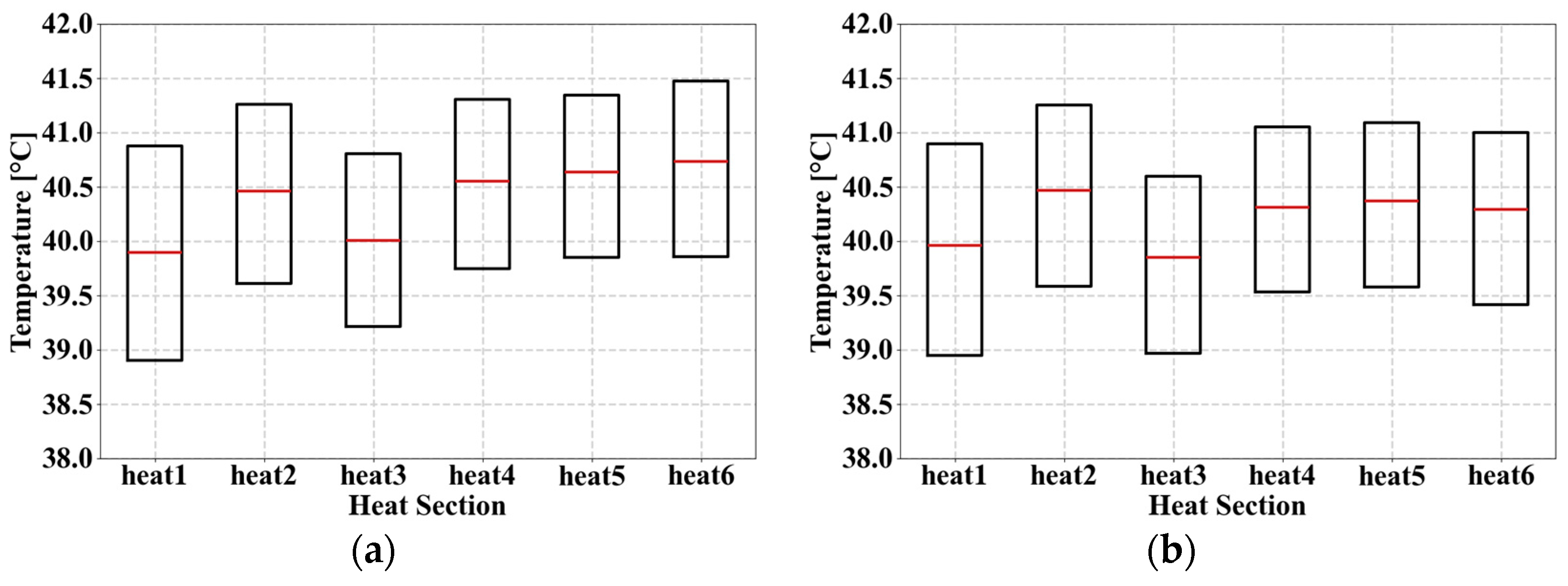
3.3.4. Verification of Temperature Distribution Using Boxplot
4. Conclusions
- Diamond:
- Gyroid:
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoon, T.W.; Choi, M.; Hong, S.J. Thermal and electrical analysis of the electrostatic chuck for the etch equipment. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2023, 36, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Koo, Y.; Song, W.; Hong, S.J. On-wafer temperature monitoring sensor for condition monitoring of repaired electrostatic chuck. Electronics 2022, 11, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Yang, H. A design method to improve temperature uniformity on wafer for rapid thermal processing. Electronics 2018, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ketan, O.; Rowshan, R.; Al-Rub, R.K.A. Topology-mechanical property relationship of 3D printed strut, skeletal, and sheet based periodic metallic cellular materials. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 19, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Riccio, A. A systematic review of design for additive manufacturing of aerospace lattice structures: Current trends and future directions. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2024, 149, 101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.S.; Ning, H.Y.; Li, N.; Tang, G.H.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Nan, X.Y.; Li, X.H. Thermal-hydraulic performance of TPMS-based regenerators in combined cycle aero-engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 250, 123510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, R.; Graziosi, S. Biomimetic scaffolds using triply periodic minimal surface-based porous structures for biomedical applications. SLAS Technol. 2023, 28, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormiston, S.; Srinivas Sundarram, S. Fiberglass-reinforced triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS) lattice structures for energy absorption applications. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gado, M.G.; Ookawara, S. 3D-printed triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) structures: Towards potential application of adsorption-based atmospheric water harvesting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 297, 117729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Gan, J.; Zhang, L.; Tan, H.; Li, E.; Li, B. Enhancing impact resistance of hybrid structures designed with triply periodic minimal surfaces. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 245, 110365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.H.; An, C.H.; Seo, B.; Kim, J.; Park, C.Y.; Park, K. Functional morphology change of TPMS structures for design and additive manufacturing of compact heat exchangers. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 76, 103778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, F.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, D.Z. Numerical study on the anisotropy in thermo-fluid behavior of triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS). Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 215, 124541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Zeng, M.; Ma, T.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, Z. Investigation on flow and heat transfer in various channels based on triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS). Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 283, 116955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Xuan, H.; Tran, K.Q.; Thai, C.H.; Lee, J. Modelling of functionally graded triply periodic minimal surface (FG-TPMS) plates. Compos. Struct. 2023, 315, 116981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ding, J.; Li, X.; Qu, S.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Lu, W.F.; Song, X.; Zhai, W. Interpenetrating phase composites with 3D printed triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) lattice structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 248, 110351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.Q.; Hoang, T.D.; Lee, J.; Nguyen-Xuan, H. Three novel computational modeling frameworks of 3D-printed graphene platelets reinforced functionally graded triply periodic minimal surface (GPLR-FG-TPMS) plates. Appl. Math. Model. 2024, 126, 667–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; Wan, Y.; Shen, Y.; Fang, J. Experimental and numerical studies on mechanical properties of TPMS structures. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 261, 108657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, S.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, H. A study of multi-stage energy absorption characteristics of hybrid sheet TPMS lattices. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 190, 110989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, S.; Xiao, H. Multi-morphology TPMS structures with multi-stage yield stress platform and multi-level energy absorption: Design, manufacturing, and mechanical properties. Eng. Struct. 2023, 294, 116733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ketan, O.; Abu Al-Rub, R.K. Multifunctional mechanical metamaterials based on triply periodic minimal surface lattices. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 1900524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Che, S. An overview of materials with triply periodic minimal surfaces and related geometry: From biological structures to self-assembled systems. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Hao, L.; Yang, L.; Hussein, A.Y.; Young, P.G.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Lattices Additively Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yeranee, K.; Rao, Y. A review of recent investigations on flow and heat transfer enhancement in cooling channels embedded with triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS). Energies 2022, 15, 8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, I.; Singh, P. Flow and thermal transport characteristics of Triply-Periodic Minimal Surface (TPMS)-based gyroid and Schwarz-P cellular materials. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2021, 79, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Fu, J.; Yao, X.; He, Y. Triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) porous structures: From multi-scale design, precise additive manufacturing to multidisciplinary applications. Int. J. Extreme Manuf. 2022, 4, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yoo, D.J. Design and fabrication method of new compact heat exchangers using triply periodic minimal surface. J. Koeran Soc. Precis. Eng. 2017, 37, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Ali, M.I.H.; Khan, K.A.; Al-Rub, R.A. Forced convection heat transfer in heat sinks with topologies based on triply periodic minimal surfaces. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 38, 102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, J.; Moore, T.; Nguyen, D.; Roy, P.; Stolaroff, J. Heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of heat exchangers based on triply periodic minimal and periodic nodal surfaces. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 209, 118192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, M.; Jiang, C.; Yang, P.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Fu, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. Analysis on the convective heat transfer process and performance evaluation of Triply Periodic Minimal Surface (TPMS) based on Diamond, Gyroid and Iwp. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 201, 123642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.; Sienz, J.; Toropov, V. Formulation of the optimal Latin hypercube design of experiments using a permutation genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 45th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics & Materials Conference, Palm Springs, CA, USA, 19 April–22 April 2004; p. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Viana, F.A. A tutorial on Latin hypercube design of experiments. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2016, 32, 1975–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschio, C.; Schiozer, D.J. Probabilistic history matching using discrete Latin Hypercube sampling and nonparametric density estimation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 147, 98–115. [Google Scholar]
- von Hohendorff Filho, J.C.; Maschio, C.; Schiozer, D.J. Production strategy optimization based on iterative discrete Latin hypercube. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2016, 38, 2473–2480. [Google Scholar]




| Single | Surface [mm2] | Volume Fraction [%] | Surface [mm2] | Volume Fraction [%] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2022 | 87 | 2174 | 86 | ||
| 2 | 1689 | 48 | 1718 | 39 | ||
| Double | Surface [mm2] | Volume Fraction [%] | Surface [mm2] | Volume Fraction [%] | ||
| 1 | 2655 | 61 | 2747 | 53 | ||
| 2 | 2690 | 67 | 2803 | 60 | ||
| 3 | 2723 | 73 | 2860 | 67 | ||
| 4 | 2756 | 80 | 2919 | 75 | ||
| 5 | 2789 | 86 | 2985 | 83 |
| Position [mm] | x = 0 | x = 3 | x = 6 | x = 9 | x = 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Section Area () |  |  |  |  |  |
| Area [mm2] | 477 | 407 | 426 | 426 | 407 |
| Position [mm] | x = 0 | x = 3 | x = 6 | x = 9 | x = 12 |
| Section Area () |  |  |  |  |  |
| Area [mm2] | 673 | 683 | 636 | 636 | 683 |
| Position [mm] | x = 0 | x = 3 | x = 6 | x = 9 | x = 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Section Area () |  |  |  |  |  |
| Area [mm2] | 410 | 307 | 321 | 321 | 307 |
| Position [mm] | x = 0 | x = 3 | x = 6 | x = 9 | x = 12 |
| Section Area () |  |  |  |  |  |
| Area [mm2] | 632 | 656 | 564 | 564 | 656 |
| Inlet mass flow | 3.33 LPM |
| Inlet temperature | 26.9 °C |
| Outlet Pressure | 0 bar |
| Heat flux | 126,263 W/m2 |
| Single | [m] | Re | Nu | Pressure Loss [Pa] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.03680 | 4627 | 326 | 544 | |
| 2 | 0.04657 | 5856 | 1072 | 5444 | |
| Double | [m] | Re | Nu | Pressure Loss [Pa] | |
| 1 | 0.02912 | 3662 | 487 | 2561 | |
| 2 | 0.02854 | 3589 | 440 | 1801 | |
| 3 | 0.02797 | 3517 | 372 | 1098 | |
| 4 | 0.02741 | 3446 | 357 | 914 | |
| 5 | 0.02680 | 3370 | 308 | 689 |
| Single | [m] | Re | Nu | Pressure Loss [Pa] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.03956 | 4975 | 157 | 179 | |
| 2 | 0.04737 | 5956 | 461 | 1586 | |
| Double | [m] | Re | Nu | Pressure Loss [Pa] | |
| 1 | 0.03013 | 3789 | 322 | 1200 | |
| 2 | 0.02974 | 3740 | 327 | 778 | |
| 3 | 0.02938 | 3694 | 297 | 673 | |
| 4 | 0.02903 | 3650 | 301 | 556 | |
| 5 | 0.02867 | 3607 | 261 | 393 |
| 12-Inch Chuck | |
|---|---|
| Flow Rate | 30 LPM |
| Power | 3000 W |
| Type (1) | Avg. Temp. [°C] | Type (2) | Avg. Temp. [°C] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat 1 | 37.67 | Heat 1 | 36.82 | ||
| Heat 2 | 38.36 | Heat 2 | 38.04 | ||
| Heat 3 | 38.13 | Heat 3 | 38.04 | ||
| Heat 4 | 38.53 | Heat 4 | 38.38 | ||
| Heat 5 | 38.30 | Heat 5 | 38.27 | ||
| Heat 6 | 37.99 | Heat 6 | 37.95 | ||
| Temp. Difference | 0.86 | Temp. Difference | 1.56 | ||
| Design Variables | |
|---|---|
| Heat 1 | |
| Heat 2 | |
| Heat 3 | |
| Heat 4 | |
| Heat 5 | |
| Heat 6 |
| Find | Sampling Point (x) |
| Minimize |
| Heat 1 | Heat 2 | Heat 3 | Heat 4 | Heat 5 | Heat 6 | Response | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable Section | Single 1 mm | Double 8-5, 8-6 | Double 8-5, 8-6 | Double 8-2, 8-3 | Double 8-2, 8-3 | Double 8-2, 8-3 | - |
| Point 1 | 0.86 | ||||||
| Point 2 | 0.71 | ||||||
| Point 3 | 0.40 | ||||||
| Point 4 | 0.53 | ||||||
| Point 5 | 0.62 | ||||||
| Point 6 | 0.32 | ||||||
| Point 7 | 0.39 |
| Heat 1 | Heat 2 | Heat 3 | Heat 4 | Heat 5 | Heat 6 | Response | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAO 1 | 0.44 | ||||||
| SAO 2 | 0.23 |
| Type | Ave. Temp | Median Temp | Difference (Ave. − Med) | IQR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat 1 | 38.16 | 38.07 | 0.09 | 1.58 | |
| Heat 2 | 38.36 | 38.19 | 0.17 | 1.33 | |
| Heat 3 | 38.20 | 38.07 | 0.13 | 1.36 | |
| Heat 4 | 38.38 | 38.30 | 0.08 | 1.15 | |
| Heat 5 | 38.26 | 38.19 | 0.07 | 1.16 | |
| Heat 6 | 38.20 | 38.11 | 0.08 | 1.15 |
| Type (1) | Avg. Temp [°C] | Type (2) | Avg. Temp [°C] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat 1 | 40.23 | Heat 1 | 39.78 | ||
| Heat 2 | 40.73 | Heat 2 | 40.81 | ||
| Heat 3 | 40.04 | Heat 3 | 40.13 | ||
| Heat 4 | 40.82 | Heat 4 | 41.09 | ||
| Heat 5 | 40.79 | Heat 5 | 41.05 | ||
| Heat 6 | 40.49 | Heat 6 | 41.76 | ||
| Temp. Difference | 0.78 | Temp. Difference | 1.98 | ||
| Heat 1 | Heat 2 | Heat 3 | Heat 4 | Heat 5 | Heat 6 | Response | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable Section | Single 1 mm | Double 8-5, 8-6 | Double 8-5, 8-6 | Double 8-2, 8-3 | Double 8-2, 8-3 | Double 8-2, 8-3 | - |
| Point 1 | 0.78 | ||||||
| Point 2 | 1.31 | ||||||
| Point 3 | 1.15 | ||||||
| Point 4 | 1.04 | ||||||
| Point 5 | 1.43 | ||||||
| Point 6 | 0.66 | ||||||
| Point 7 | 0.96 |
| Heat 1 | Heat 2 | Heat 3 | Heat 4 | Heat 5 | Heat 6 | Response | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAO 1 | 0.71 | ||||||
| SAO 2 | 0.66 |
| Type | Ave. Temp | Median Temp | Difference (Ave. − Med) | IQR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat 1 | 40.23 | 39.90 | 0.33 | 1.97 | |
| Heat 2 | 40.63 | 40.46 | 0.17 | 1.65 | |
| Heat 3 | 40.17 | 40.00 | 0.17 | 1.59 | |
| Heat 4 | 40.72 | 40.55 | 0.17 | 1.56 | |
| Heat 5 | 40.82 | 40.64 | 0.18 | 1.49 | |
| Heat 6 | 40.83 | 40.73 | 0.10 | 1.62 |
| Type | Ave. Temp | Median Temp | Difference (Ave. − Med) | IQR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat 1 | 40.23 | 39.96 | 0.27 | 1.95 | |
| Heat 2 | 40.61 | 40.46 | 0.15 | 1.67 | |
| Heat 3 | 39.95 | 39.85 | 0.10 | 1.63 | |
| Heat 4 | 40.48 | 40.31 | 0.17 | 1.52 | |
| Heat 5 | 40.48 | 40.37 | 0.11 | 1.51 | |
| Heat 6 | 40.54 | 40.29 | 0.25 | 1.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Sung, J.; Jung, H.; Lee, H.; Kim, K. Temperature Uniformity Control of 12-Inch Semiconductor Wafer Chuck Using Double-Wall TPMS in Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2025, 18, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010211
Park S, Lee J, Lee S, Sung J, Jung H, Lee H, Kim K. Temperature Uniformity Control of 12-Inch Semiconductor Wafer Chuck Using Double-Wall TPMS in Additive Manufacturing. Materials. 2025; 18(1):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010211
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sohyun, Jaewook Lee, Seungyeop Lee, Jihyun Sung, Hyungug Jung, Ho Lee, and Kunwoo Kim. 2025. "Temperature Uniformity Control of 12-Inch Semiconductor Wafer Chuck Using Double-Wall TPMS in Additive Manufacturing" Materials 18, no. 1: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010211
APA StylePark, S., Lee, J., Lee, S., Sung, J., Jung, H., Lee, H., & Kim, K. (2025). Temperature Uniformity Control of 12-Inch Semiconductor Wafer Chuck Using Double-Wall TPMS in Additive Manufacturing. Materials, 18(1), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010211






