High-Efficiency Adsorption Removal of Congo Red Dye from Water Using Magnetic NiFe2O4 Nanofibers: An Efficient Adsorbent
Highlights
- Production of NiFe2O4 nanofibers by Solution Blow Spinning.
- Removal efficiency exceeding 96% within 30 minutes of adsorption.
- Chemisorption and homogeneous mechanism suggested as the main adsorption processes.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
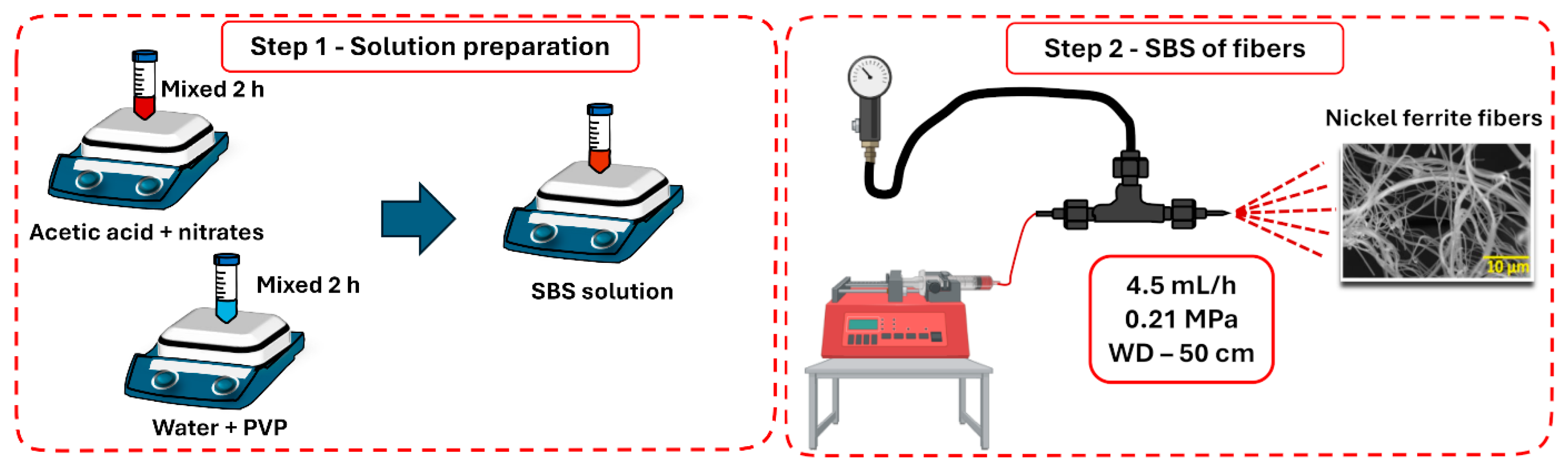
2.1. Synthesis of NiFe2O4 Fibers
2.2. Sample Characterizations
2.3. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
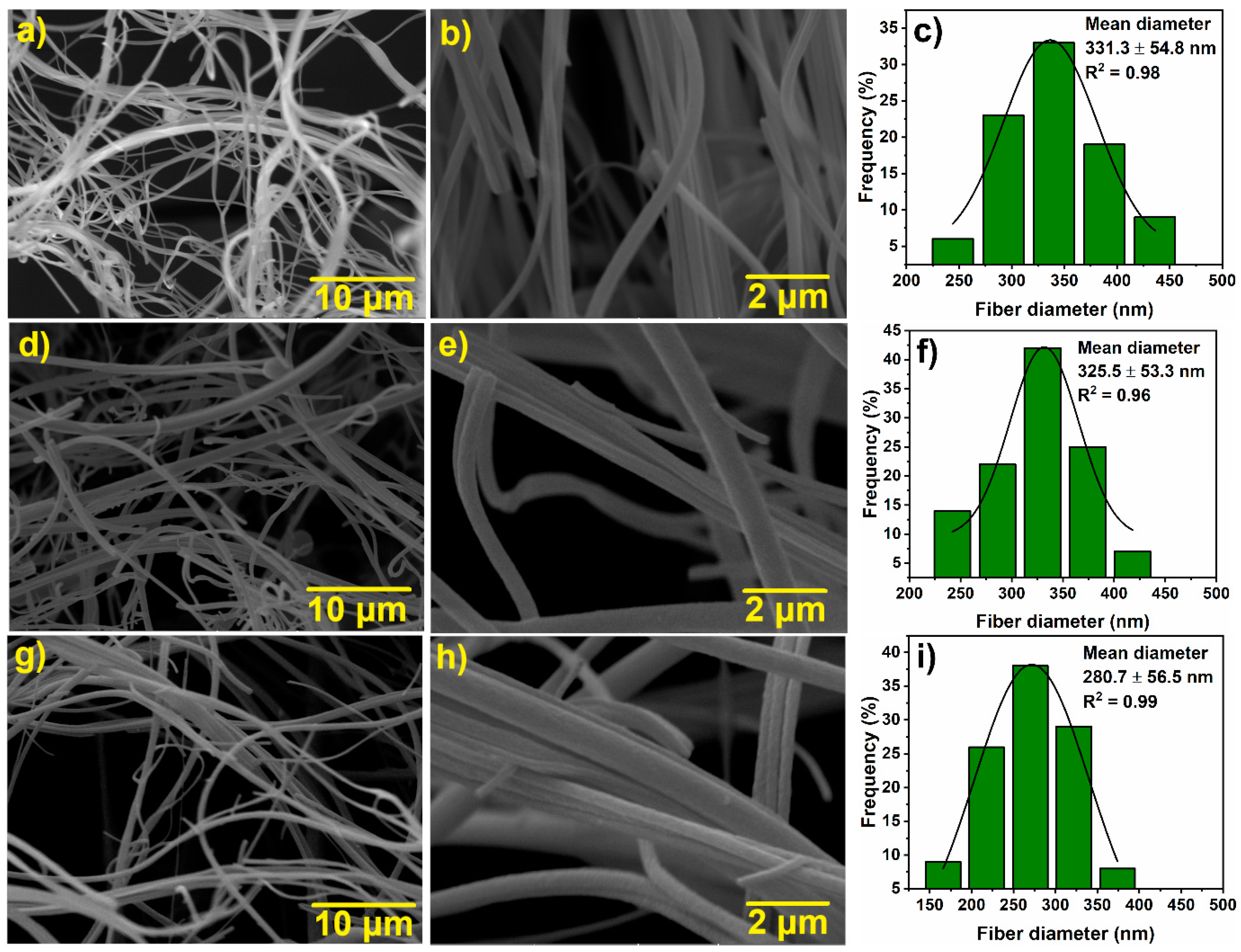
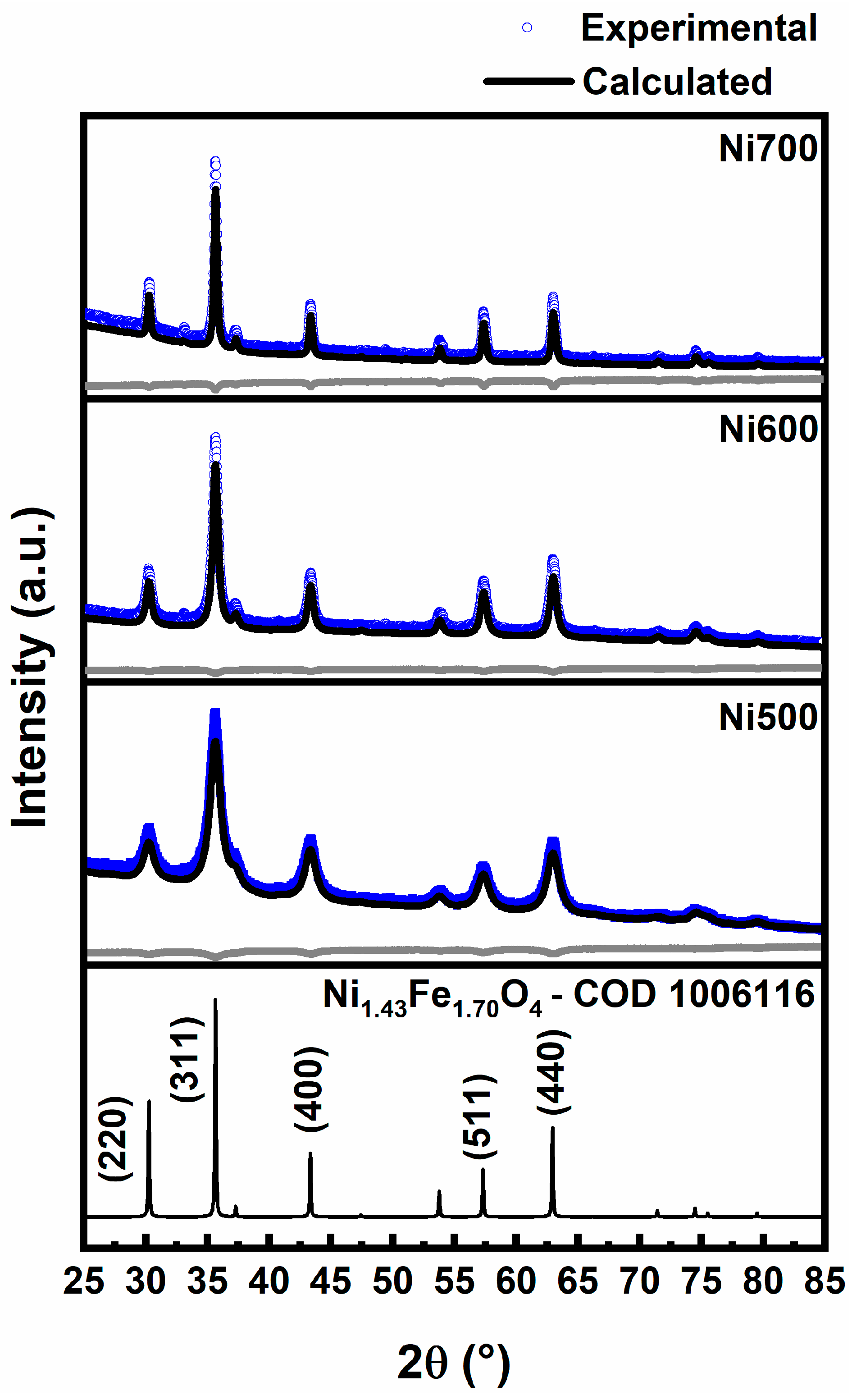
3.1. Microstructure Characterization
3.2. Adsorption Experiment
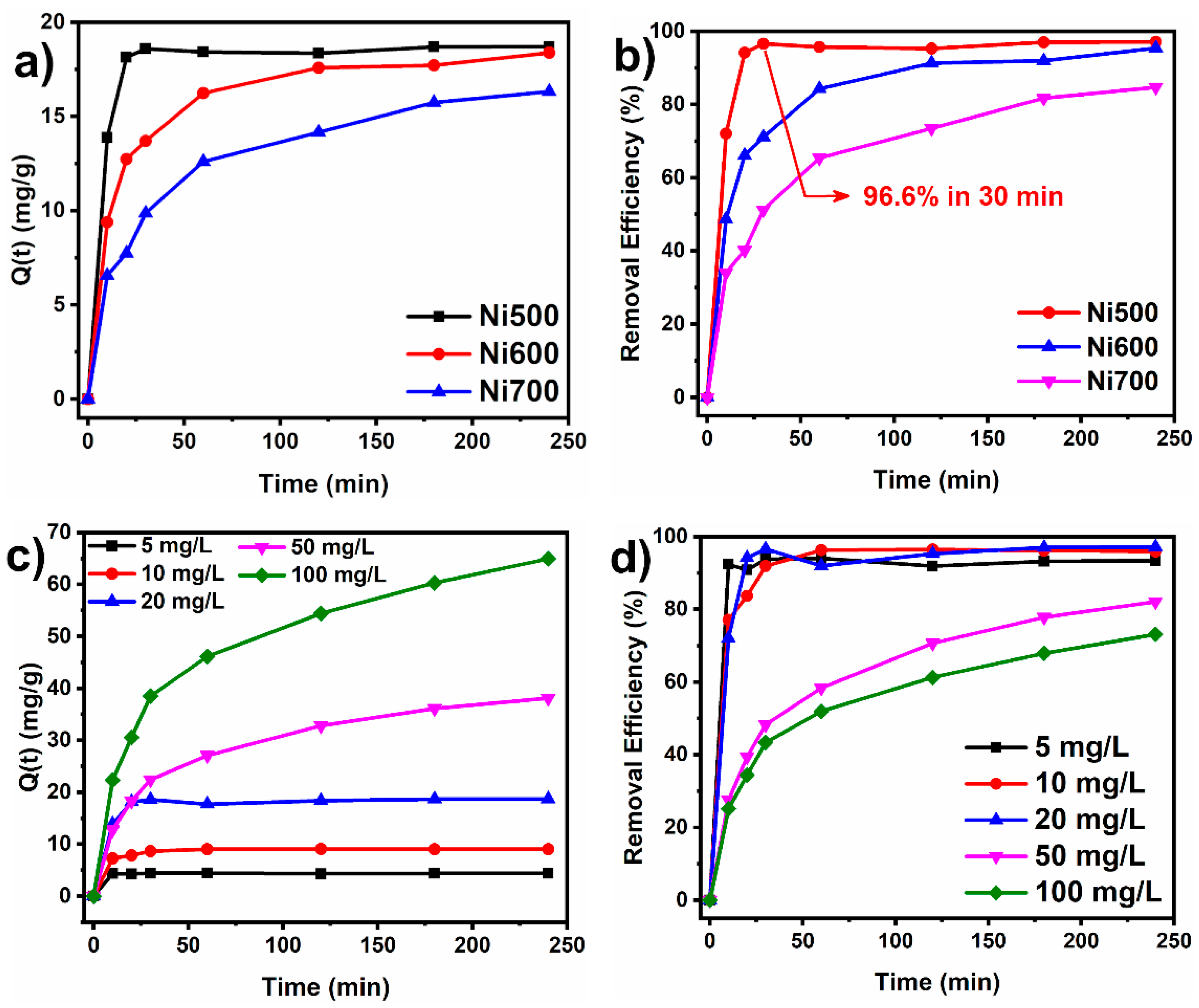
3.2.1. Effect of Contact Time and Initial Concentration
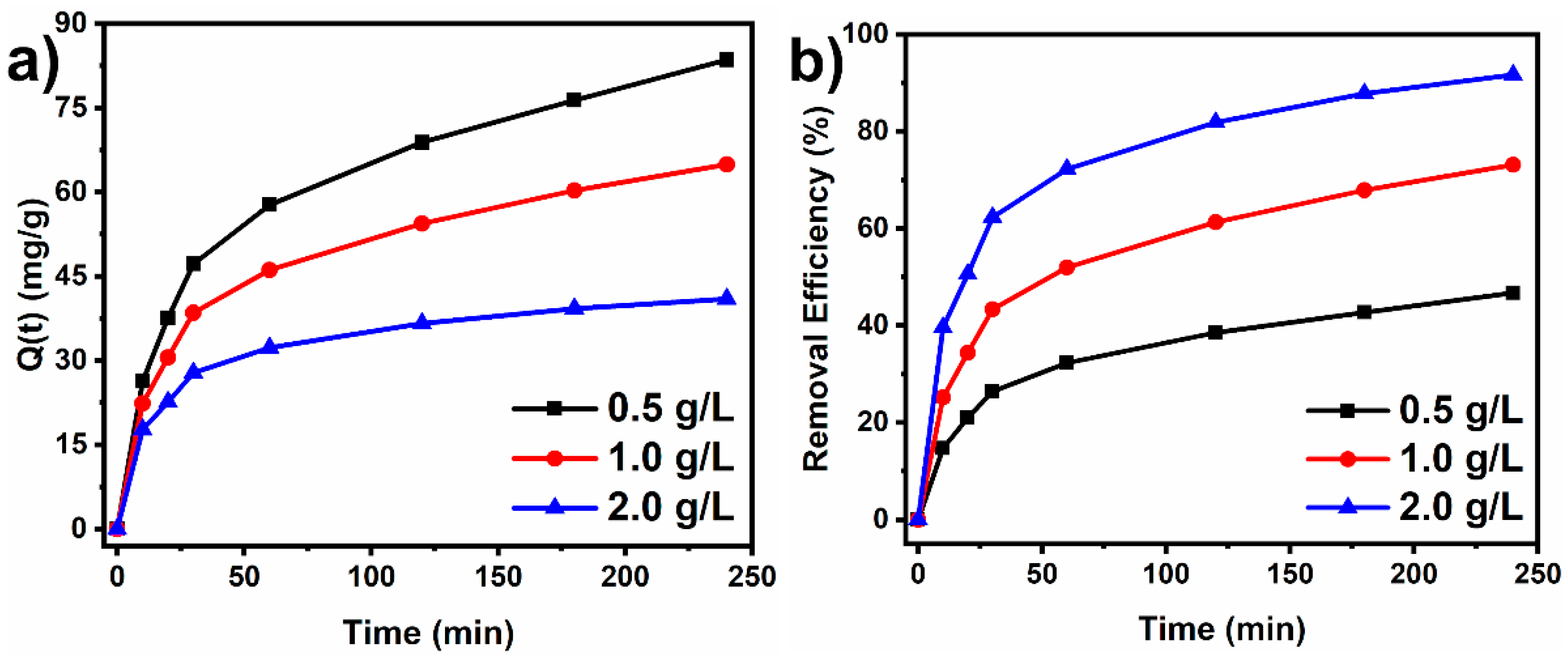
3.2.2. Effect of Adsorbent Mass
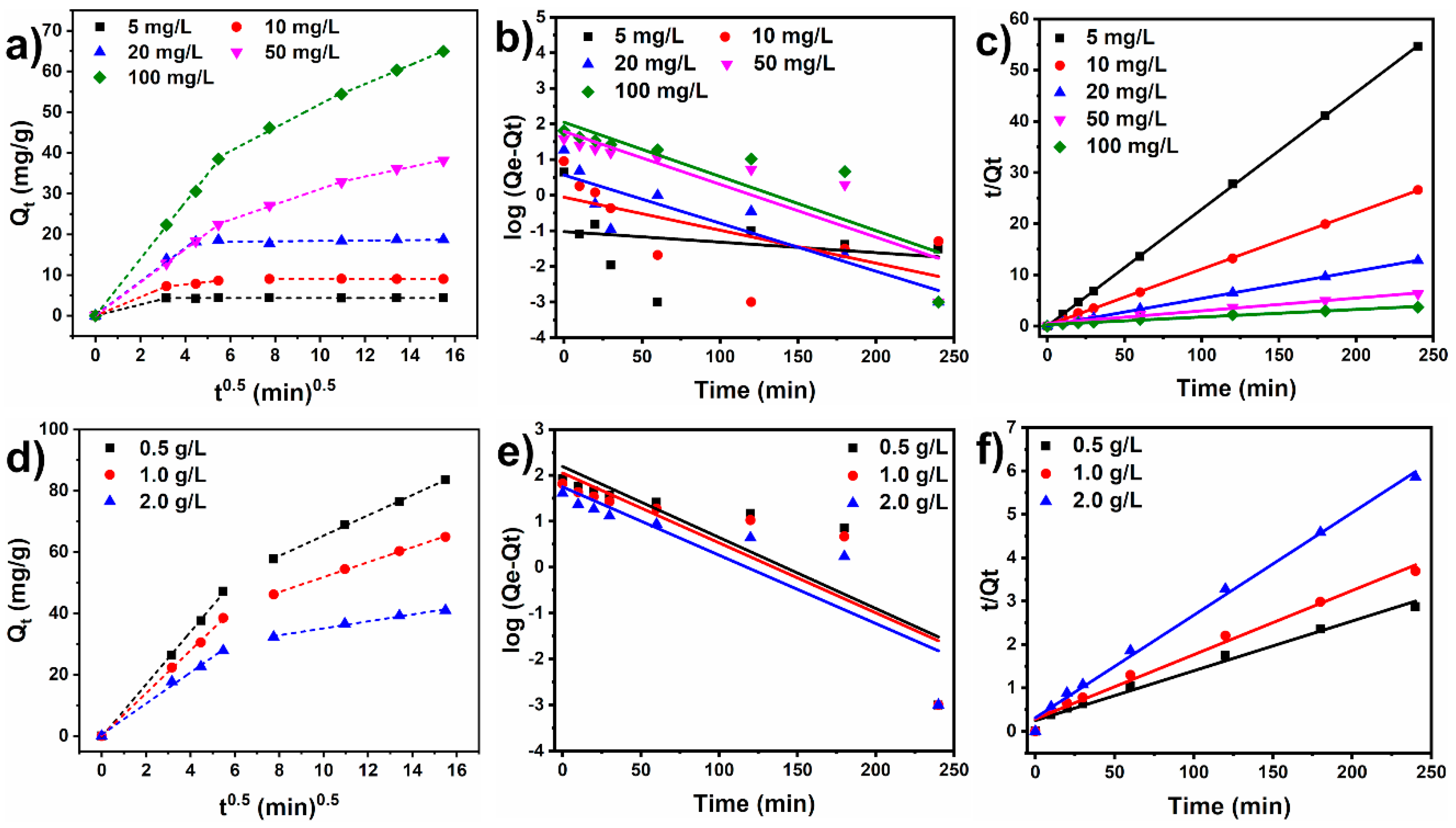
3.2.3. Kinetic Study
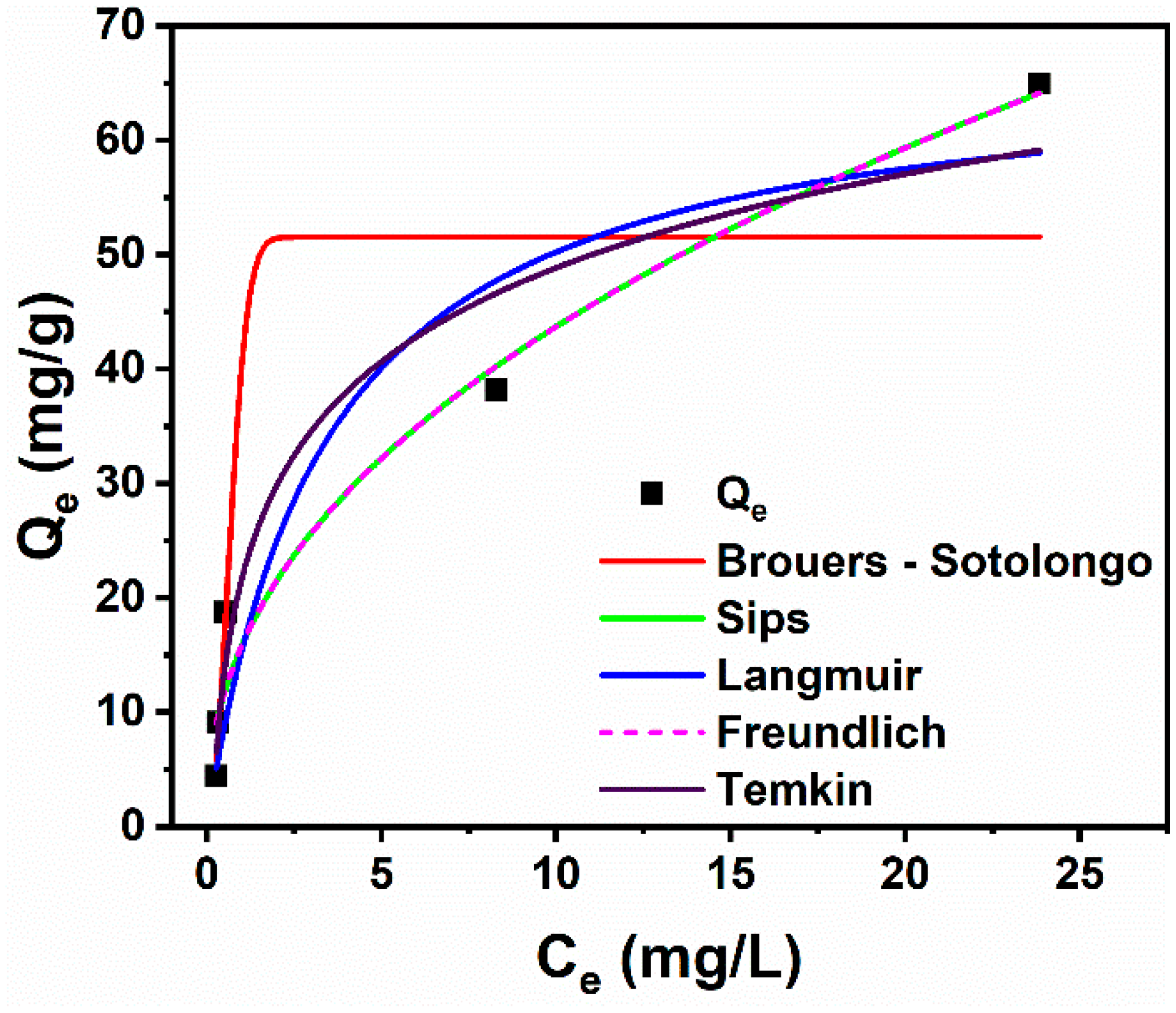
3.2.4. Adsorption Isotherm Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manzoor, K.; Batool, M.; Naz, F.; Nazar, M.F.; Hameed, B.H.; Zafar, M.N. A Comprehensive Review on Application of Plant-Based Bioadsorbents for Congo Red Removal. Biomass Convers. Biorefin 2024, 14, 4511–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Available online: https://www.statista.com/ (accessed on 26 January 2025).
- Samsami, S.; Mohamadi, M.; Sarrafzadeh, M.-H.; Rene, E.R.; Firoozbahr, M. Recent Advances in the Treatment of Dye-Containing Wastewater from Textile Industries: Overview and Perspectives. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 143, 138–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lellis, B.; Fávaro-Polonio, C.Z.; Pamphile, J.A.; Polonio, J.C. Effects of Textile Dyes on Health and the Environment and Bioremediation Potential of Living Organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.K.; Rawat, V.; Banerjee, S.; Sanroman, M.A.; Soni, S.; Singh, S.K.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Synthesis of Bimetallic Fe–Zn Nanoparticles and Its Application towards Adsorptive Removal of Carcinogenic Dye Malachite Green and Congo Red in Water. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 212, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Martínez, J.D.; Balagurusamy, N.; Montañez, J.; Peralta, R.A.; de Fátima Peralta Muniz Moreira, R.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M.; Morales-Oyervides, L. Synthetic Dyes Biodegradation by Fungal Ligninolytic Enzymes: Process Optimization, Metabolites Evaluation and Toxicity Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksoud, M.I.A.A.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Farrell, C.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Rooney, D.W.; Osman, A.I. Insight on Water Remediation Application using Magnetic Nanomaterials and Biosorbents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 403, 213096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuello, C.; Chambel, L.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Ferreira, L.P.; Cruz, M.M. Magnetotactic Bacteria: Magnetism Beyond Magnetosomes. IEEE Trans. NanoBioscience 2018, 17, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, P.; Fu, S.; Yang, J.; Gao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Rong, D. Interfacing MXene Flakes on a Magnetic Fiber Network as a Stretchable, Flexible, Electromagnetic Shielding Fabric. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonel, A.G.; Mansur, A.A.P.; Mansur, H.S. Advanced Functional Nanostructures based on Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanomaterials for Water Remediation: A Review. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najdanović, S.M.; Petrović, M.M.; Kostić, M.M.; Velinov, N.D.; Vucić, M.D.R.; Matović, B.Z.; Bojić, A.L. New Way of Synthesis of Basic Bismuth Nitrate by Electrodeposition from Ethanol Solution: Characterization and Application for Removal of RB19 from Water. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 9939–9950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.N.; Nascimento, E.P.; Firmino, H.C.T.; Macedo, D.A.; Neves, G.A.; Morales, M.A.; Menezes, R.R. α-Fe2O3 Fibers: An Efficient Photocatalyst for Dye Degradation under Visible Light. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 882, 160683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, K.; Petrović, M.; Najdanović, S.; Velinov, N.; Hurt, A.; Bojić, A.; Kostić, M. Highly Efficient Nano Sorbent as a Superior Material for the Purification of Wastewater Contaminated with Anthraquinone Dye RB19. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 67, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yao, H.; Chu, S.; Song, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, W. Magnetotactic Bacteria: Characteristics and Environmental Applications. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Zhang, B.; Gao, X.; Cui, S.; Guan, C.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Peng, Y. Recent Progresses, Challenges, and Opportunities of Carbon-Based Materials Applied in Heavy Metal Polluted Soil Remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 158810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, J.J.; Suthindhiran, K. Magnetotactic Bacteria and Magnetosomes–Scope and Challenges. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, B.; Fan, J.; Yu, J.; Ho, W. Review on Nickel-Based Adsorption Materials for Congo Red. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Das, R. Strong Adsorption of CV Dye by Ni Ferrite Nanoparticles for Waste Water Purification: Fits Well the Pseudo Second Order Kinetic and Freundlich Isotherm Model. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 16199–16215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.J.; Behera, S.N. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanoparticles of Cobalt and Nickel Ferrites for Elimination of Hazardous Organic Dyes from Industrial Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 53323–53338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starko, I.; Tatarchuk, T.; Naushad, M.; Danyliuk, N. Enhanced Activity of La-Substituted Nickel–Cobalt Ferrites in Congo Red Dye Removal and Hydrogen Peroxide Decomposition. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2024, 235, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, R.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y. Shan One-Pot Solvothermal Preparation of MFe2O4 (M = Ca, Mg and Ni) Ferrite- Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites for Adsorption of Acridine Orange. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 298, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Farias, R.M.; Severo, L.L.; Klamczynski, A.P.; de Medeiros, E.S.; de Lima Santana, L.N.; de Araújo Neves, G.; Glenn, G.M.; Menezes, R.R. Solution Blow Spun Silica Nanofibers: Influence of Polymeric Additives on the Physical Properties and Dye Adsorption Capacity. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangamani, K.S.; Muthulakshmi Andal, N.; Ranjith Kumar, E.; Saravanabhavan, M. Utilization of Magnetic Nano Cobalt Ferrite Doped Capra Aegagrus Hircus Dung Activated Carbon Composite for the Adsorption of Anionic Dyes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2820–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Kamali, A.R. Waste Plastic Derived Co3Fe7/CoFe2O4@carbon Magnetic Nanostructures for Efficient Dye Adsorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 886, 161201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, X.; Doshmanziari, M.; Esmaeili, H. Elimination of Methyl Violet 2B Dye from Water Using Citrus Limetta Leaves-Activated Carbon Modified by Copper-Ferrite Nanoparticles. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Gull, M.; Shaikh, A.J.; Hussain, S.; Hussain, R.; Haq, S.; Waseem, M. Grafting the Ferrites of Cobalt and Zinc on MWCNTs for Adsorption of Crystal Violet. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 12465–12480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, W.; Garba, Z.N.; Lawan, I.; Wang, L.; Yuan, Z. Adsorption of Organic Dyes from Wastewater by Metal-Doped Porous Carbon Materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah-Ntiamoah, R.; Baye, A.F.; Gadisa, B.T.; Abebe, M.W.; Kim, H. In-Situ Prepared ZnO-ZnFe2O4 with 1-D Nanofiber Network Structure: An Effective Adsorbent for Toxic Dye Effluent Treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paswan, S.K.; Kamari, S.; Kar, M.; Singh, A.; Pathak, H.; Borah, J.P.; Kumar, L. Optimization of Structure-Property Relationships in Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles Annealed at Different Temperature. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 151, 109928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacaş, Z.K.; Boncukcuoğlu, R.; Karacaş, I.H.; Ertuğrul, M. The Effects of Heat Treatment on the Synthesis of Nickel Ferrite (NiFe2O4) Nanoparticles using the Microwave Assisted Combustion Method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D.; Graham, C.D. Introduction to Magnetic Materials; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780471477419. [Google Scholar]
- Nawale, A.B.; Kanhe, N.S.; Patil, K.R.; Bhoraskar, S.V.; Mathe, V.L.; Das, A.K. Magnetic Properties of Thermal Plasma Synthesized Nanocrystalline Nickel Ferrite (NiFe2O4). J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 4404–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, A.; Kokkiripati, A.; Bhaduri, B. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Anchored on Nickel Ferrite/Oxidized-Graphite Composite for the Efficient Reduction of Aqueous P-Nitrophenol. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 143, 109806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgizadeh, M.; Azarpira, N.; Lotfi, M.; Daneshvar, F.; Salehi, F.; Sattarahmady, N. Sonodynamic Cancer Therapy by a Nickel Ferrite/Carbon Nanocomposite on Melanoma Tumor: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 27, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.-Y.; Jiang, R.; Fu, Y.-Q.; Li, R.-R.; Yao, J.; Jiang, S.-T. Novel Multifunctional NiFe2O4/ZnO Hybrids for Dye Removal by Adsorption, Photocatalysis and Magnetic Separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 369, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Cui, T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Tong, G. Facile Hydrothermal Synthesis of Fe3O4/C Core–Shell Nanorings for Efficient Low-Frequency Microwave Absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7370–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Ding, S. Synthesis, Characterization and Microwave Absorption of MXene/NiFe2O4 Composites. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 24713–24720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, H.; Mohammad Azari, M.; Shokuhfar, A. A Facile Approach for Obtaining NiFe2O4@C Core-Shell Nanoparticles and Their Magnetic Properties Assessment. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 110, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, B.; Martin, A.; Lu, H.; Mahbub, R.; Ahmadi, Z.; Azadehranjbar, S.; Mishra, E.; Shield, J.E.; Jeelani, S.; Rangari, V. Changing the Polarization and Mechanical Response of Flexible PVDF-Nickel Ferrite Films with Nickel Ferrite Additives. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 283, 115815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Atri, A.K.; Qadir, I.; Sharma, S.; Manhas, U.; Singh, D. Role of Different Fuels and Sintering Temperatures in the Structural, Optical, Magnetic, and Photocatalytic Properties of Chromium-Containing Nickel Ferrite: Kinetic Study of Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B Dye. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 6302–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sing, K.S.W. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity (Provisional). Pure Appl. Chem. 1982, 54, 2201–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.; Klobes, P. NIST Recommended Practice Guide; NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2006.
- Araujo, R.N.; Nascimento, E.P.; Raimundo, R.A.; Macedo, D.A.; Mastelaro, V.R.; Neves, G.A.; Morales, M.A.; Menezes, R.R. Hybrid Hematite/Calcium Ferrite Fibers by Solution Blow Spinning: Microstructural, Optical and Magnetic Characterization. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 33363–33372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugutkar, A.B.; Gore, S.K.; Patange, S.M.; Mane, R.S.; Raut, S.D.; Shaikh, S.F.; Ubaidullah, M.; Pandit, B.; Jadhav, S.S. Ammonia Gas Sensing and Magnetic Permeability of Enhanced Surface Area and High Porosity Lanthanum Substituted Co–Zn Nano Ferrites. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 15043–15055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptitsyna, K.O.; Il’in, A.A.; Rumyantsev, R.N.; Sakharova, Y.N. Mechanochemical and Ceramic Synthesis of Cobalt Ferrite. Glass Ceram. 2022, 79, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutavarapu, R.; Reddy, C.V.; Syed, K.; Reddy, K.R.; Saleh, T.A.; Lee, D.-Y.; Shim, J.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Novel Z-Scheme Binary Zinc Tungsten Oxide/Nickel Ferrite Nanohybrids for Photocatalytic Reduction of Chromium (Cr (VI)), Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting and Degradation of Toxic Organic Pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Shi, Z.; Peng, X.; Zhou, S. Magnetic Calcinated Cobalt Ferrite/Magnesium Aluminum Hydrotalcite Composite for Enhanced Adsorption of Methyl Orange. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Zhou, M.; Xi, F.; Bai, C.; Wang, S.; Luo, S.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Efficient U(VI) Removal by Ti3C2Tx Nanosheets Modified with Sulfidated Nano Zero-Valent Iron: Batch Experiments, Mechanism, and Biotoxicity Assessment. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 152, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Parakhonskiy, B.V.; Lapanje, A.; Skirtach, A.G. Enhanced Cu2+ Adsorption through Double Cross-Linking of Hydrogel with in situ CaCO3. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.A.; Rehman, A.; Ali, Z.; Atif, M.; Ali, Z.; Khalid, W. Congo Red Removal by Lanthanum-Doped Bismuth Ferrite Nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 170, 110964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Pi, M.; Cheng, B.; Jiang, C.; Qin, J. Fabrication of Hierarchical Porous ZnO/NiO Hollow Microspheres for Adsorptive Removal of Congo Red. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.S.; Sanni, A.R.; Ajayi, I.A.; Rabiu, O.O. Equilibrium, Thermodynamic and Kinetic Studies for the Biosorption of Aqueous Lead(II) Ions Onto the Seed Husk of Calophyllum inophyllum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadi, R.; Saadi, Z.; Fazaeli, R.; Fard, N.E. Monolayer and Multilayer Adsorption Isotherm Models for Sorption from Aqueous Media. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuff, A.S.; Gbadamosi, A.O.; Bode-Olajide, F.B.; Igbafe, A.I. Adsorption of Methyl Ester Sulfonate Surfactant on Berea Sandstone: Parametric Optimization, Kinetics, Isotherm and Thermodynamics Studies. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 686, 133363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Chen, L.; Hu, J.; Richards, R. NiO(111) Nanosheets as Efficient and Recyclable Adsorbents for Dye Pollutant Removal from Wastewater. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 275707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, R.; Kerdari, H.; Rabbani, M.; Shafiee, M. Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorbing Properties of Hollow Zn-Fe2O4 Nanospheres on Removal of Congo Red from Aqueous Solution. Desalination 2011, 280, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizada, P.; Singh, P.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, G.; Pare, B.; Jonnalagadda, S.B.; Thakur, P. Solar Photocatalytic Activity of Nano-ZnO Supported on Activated Carbon or Brick Grain Particles: Role of Adsorption in Dye Degradation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 486, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, P.; Mondal, N.K. Effective Removal of Congo Red Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, J.P. Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorption Capability for Congo Red of CoFe2O4 Ferrite Nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 640, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.; Ren, Y.; Fan, Z.; Wei, T.; Meng, J.; Zhang, M. Synthesis of 3D Porous Ferromagnetic NiFe2O4 and Using as Novel Adsorbent to Treat Wastewater. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 362, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kang, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, H.; Cai, W. Micro/Nanostructured Porous Fe–Ni Binary Oxide and Its Enhanced Arsenic Adsorption Performances. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 458, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Ms (emu/g) | Mr/Ms | Hc (Oe) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni500 | 24.84 | 0.04 | 46 |
| Ni600 | 36.07 | 0.15 | 141 |
| Ni700 | 41.68 | 0.22 | 179 |
| Sample | Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni500 | 48.62 | 0.21 | 127.00 |
| Ni600 | 22.78 | 0.15 | 160.99 |
| Ni700 | 13.87 | 0.13 | 80.50 |
| Parameters | Initial Concentration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 (mg/L) | 10 (mg/L) | 20 (mg/L) | 50 (mg/L) | 100 (mg/L) | |
| Qe, exp (mg/g) | 4.42 | 9.07 | 18.71 | 38.11 | 64.95 |
| Intraparticle diffusion model | |||||
| C1 | 3.140 × 10−16 | 6.28037 × 10−16 | 0.19450 | −0.03843 | 0.01006 |
| Kid1 | 1.37243 | 2.29265 | 4.11773 | 4.09207 | 6.96631 |
| R2 | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | 0.99611 | 0.99994 | 0.99931 |
| C2 | - | 5.32316 | - | 12.17902 | 23.09579 |
| Kid2 | - | 0.59417 | - | 1.89278 | 2.88666 |
| R2 | - | 0.98105 | - | 0.99826 | 0.99425 |
| Pseudo-first order | |||||
| Qe,cal (mg/g) | 0.095 | 0.883 | 3.698 | 62.011 | 112.466 |
| K1 (min) | 0.001 | 0.021 | 0.031 | 0.034 | 0.031 |
| R2 | 0.092 | 0.31 | 0.755 | 0.733 | 0.688 |
| Pseudo-second order | |||||
| Qe, cal (mg/g) | 4.383 | 9.101 | 18.804 | 40.112 | 67.659 |
| K2 (g/mg.min) | 1.233 | 0.180 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.987 | 0.986 |
| Parameters | Initial Concentration | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 (g/L) | 1.0 (g/L) | 2.0 (g/L) | |
| Qe, exp (mg/g) | 83.56 | 64.95 | 40.97 |
| Intraparticle diffusion model | |||
| C1 | −0.27225 | 0.0101 | 0.4410 |
| Kid1 | 8.55797 | 6.9663 | 5.0666 |
| R2 | 0.99935 | 0.9993 | 0.9953 |
| C2 | 32.2577 | 27.52446 | 23.87254 |
| Kid2 | 3.3088 | 2.43111 | 1.12636 |
| R2 | 0.9994 | 0.99898 | 0.98979 |
| Pseudo-first order | |||
| Qe, cal (mg/g) | 155.478 | 112.466 | 55.900 |
| K1 (min) | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.034 |
| R2 | 0.668 | 0.688 | 0.748 |
| Pseudo-second order | |||
| Qe, cal (mg/g) | 87.260 | 67.659 | 42.224 |
| K2 (g/mg.min) | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.002 |
| R2 | 0.983 | 0.986 | 0.994 |
| Adsorption isotherm | Parameters | Values | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qe, exp (mg/g) | 64.95 | ||
| Langmuir | Qm | 67.29 | 0.936 |
| KL | 0.294 | ||
| Freundlich | KF | 15.82 | 0.972 |
| N | 2.26 | ||
| Brouers–Sotolongo | Qm | 51.53 | 0.852 |
| KW | 1.512 | ||
| A | 2.006 | ||
| Sips | Qm | 5.785 | 0.972 |
| KS | 10.425 | ||
| N | 2.266 | ||
| Temkin | KT | 6.202 | 0.948 |
| b | 209.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Firmino, H.C.T.; Nascimento, E.P.; Costa, K.C.; Arzuza, L.C.C.; Araujo, R.N.; Sousa, B.V.; Neves, G.A.; Morales, M.A.; Menezes, R.R. High-Efficiency Adsorption Removal of Congo Red Dye from Water Using Magnetic NiFe2O4 Nanofibers: An Efficient Adsorbent. Materials 2025, 18, 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040754
Firmino HCT, Nascimento EP, Costa KC, Arzuza LCC, Araujo RN, Sousa BV, Neves GA, Morales MA, Menezes RR. High-Efficiency Adsorption Removal of Congo Red Dye from Water Using Magnetic NiFe2O4 Nanofibers: An Efficient Adsorbent. Materials. 2025; 18(4):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040754
Chicago/Turabian StyleFirmino, Hellen C. T., Emanuel P. Nascimento, Keila C. Costa, Luis C. C. Arzuza, Rondinele N. Araujo, Bianca V. Sousa, Gelmires A. Neves, Marco A. Morales, and Romualdo R. Menezes. 2025. "High-Efficiency Adsorption Removal of Congo Red Dye from Water Using Magnetic NiFe2O4 Nanofibers: An Efficient Adsorbent" Materials 18, no. 4: 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040754
APA StyleFirmino, H. C. T., Nascimento, E. P., Costa, K. C., Arzuza, L. C. C., Araujo, R. N., Sousa, B. V., Neves, G. A., Morales, M. A., & Menezes, R. R. (2025). High-Efficiency Adsorption Removal of Congo Red Dye from Water Using Magnetic NiFe2O4 Nanofibers: An Efficient Adsorbent. Materials, 18(4), 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040754









