Nanomaterials for Removal and Speciation of Chromium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Removal of Chromium by Nanomaterials
2.1. Carbon Nanotubes
2.2. Graphene Derivatives
2.3. Layered Double Hydroxides
2.4. Molybdenum Disulfide
2.5. Other Nanocomposites
3. Speciation of Chromium
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tumolo, M.; Ancona, V.; De Paola, D.; Losacco, D.; Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Chromium Pollution in European Water, Sources, Health Risk, and Remediation Strategies: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 28, 5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewicki, S.; Zdanowski, R.; Krzyżowska, M.; Lewicka, A.; Dębski, B.; Niemcewicz, M.; Goniewicz, M. The role of Chromium (III) in the organism and its possible use in diabetes and obesity treatment. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2024, 21, 331–335. [Google Scholar]
- DesMarais, T.L.; Costa, M. Mechanisms of Chromium-Induced Toxicity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2019, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Jankar, J.S. A Comparative Study of Chromium: Therapeutic Uses and Toxicological Effects on Human Health. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2022, 13, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Monga, A.; Fulke, A.B.; Dasgupta, D. Recent developments in essentiality of trivalent chromium and toxicity of hexavalent chromium: Implications on human health and remediation strategies. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 7, 10011. [Google Scholar]
- Vaiopoulou, E.; Gikas, P. Regulations for chromium emissions to the aquatic environment in Europe and elsewhere. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Chromium in Drinking Water. Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO/HEP/ECH/WSH/2020.3; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Procópio, V.A.; Pereira, R.M.; Lange, C.N.; Freire, B.M.; Batista, B.L. Chromium Speciation by HPLC-DAD/ICP-MS: Simultaneous Hyphenation of Analytical Techniques for Studies of Biomolecules. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4912. [Google Scholar]
- Pechancová, R.; Gallo, J.; Milde, D.; Pluháček, T. Ion-exchange HPLC-ICP-MS: A new window to chromium speciation in biological tissues. Talanta 2020, 218, 121150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.; Chekri, R.; Leufroy, A.; Guérin, T.; Sloth, J.J.; Jitaru, P. Development and validation of a single run method based on species-specific isotope dilution and HPLC-ICP-MS for simultaneous species interconversion correction and speciation analysis of Cr(III)/Cr(VI) in meat and dairy products. Talanta 2021, 222, 121538. [Google Scholar]
- Badawy, M.E.I.; El-Nouby, M.A.M.; Kimani, P.K.; Lim, L.W.; Rabea, E.I. A review of the modern principles and applications of solid-phase extraction techniques in chromatographic analysis. Anal. Sci. 2020, 38, 1457–1487. [Google Scholar]
- Matczuk, M.; Ruzik, L.; Kepplen, B.K.; Timerbaew, A.T. Nanoscale Ion-Exchange Materials: From Analytical Chemistry to Industrial and Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2023, 28, 6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moral, A.; Borull, F.; Moarcé, R.M.; Fontanales, N. Novel materials for sorptive extraction techniques for the analysis of environmental water samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 181, 118005. [Google Scholar]
- Corps Ricardo, A.I.; Abujaber, F.; Guzmán Bernardo, F.J.; Rodríguez Martín-Doimeadios, R.C.; Ríos, Á. Magnetic solid phase extraction as a valuable tool for elemental speciation analysis. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 27, e00097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filik, H.; Avan, A.A. Magnetic nanostructures for preconcentration, speciation and determination of chromium ions: A review. Talanta 2019, 203, 168–177. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Xin, Y.N.; Zou, J.; Khoso, F.M.; Liu, Y.P.; Jiang, X.Y.; Peng, S.; Yu, J.G. Removal of Chromium Species by Adsorption: Fundamental Principles, Newly Developed Adsorbents and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2023, 28, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbas, Z.; Ozalp, O.; Matin, A.A.; Soylak, M. Speciation of Chromium by Magnetic Solid Phase Microextraction Using an Activated Charcoal-Molybdenum (IV) Selenide-Magnetite Composite with Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric (FAAS) Detection. Anal. Lett. 2024, 57, 2727–2744. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, J.C.; Cardodo, C.E.D.; Taavares, D.S.; Freitas, R.; Trindadw, T.; Vale, C.; Pereira, E. Chromium removal from contaminated waters using nanomaterials—A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 277–291. [Google Scholar]
- Pyrzynska, K. Nanomaterials in speciation analysis of metals and metalloids. Talanta 2020, 212, 120784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, M.B.; Ali, I.; Yilmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Nanomaterial’s based chromium speciation in environmental samples: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 103, 44–55. [Google Scholar]
- Posta, J.; Nagy, D.; Kapitány, S.; Beni, Ă. A comparison study of analytical performance of chromium speciation methods. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 103958. [Google Scholar]
- López-García, I.; Marín-Hernández, J.J.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Speciation of chromium in waters using dispersive micro-solid phase extraction with magnetic ferrite and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2020, 24, 5268. [Google Scholar]
- Sodan, N.E.; Elci, Ş.G.; Kartal, A.A.; Hol, A.; Elci, L. Speciation and preconcentration of chromium in real samples by magnetic polythiophene nanoparticle solid-phase extraction (SPE) coupled with microsampling injection—Flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS). Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 585–603. [Google Scholar]
- Çiçek Özkul, S.L.; Kaba, I.; Ozdemir Olgun, F.A. Unravelling the potential of magnetic nanoparticles: A comprehensive review of design and applications in analytical chemistry. Anal. Meth. 2024, 13, 3620–3640. [Google Scholar]
- Sajid, M.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Nanoparticles: Synthesis, characteristics, and applications in analytical and other sciences. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104623. [Google Scholar]
- Sheoran, K.; Kaur, H.; Siwal, S.S.; Saini, A.K.; Dai-Viet, V.; Thakur, V.K. Recent advances of carbon-based nanomaterials (CBNMs) for wastewater treatment: Synthesis and application. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134364. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, H.; Devi, N.; Siwal, S.S.; Alsanie, W.F.; Thakur, M.K.; Thaku, V.K. Metal-Organic Framework-Based Materials for Wastewater Treatment: Superior Adsorbent Materials for the Removal of Hazardous Pollutants. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 9004–9030. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Tian, Y.; Sun, H.; Hagio, T. Progress in modification of 3D graphene-based adsorbents for environmental applications. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129420. [Google Scholar]
- Kaymaz, S.V.; Nobar, H.M.; Sarıgül, H.; Soylukan, C.; Akyüz, L.; Yüce, M. Nanomaterial surface modification toolkit: Principles, components, recipes, and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 322, 103035. [Google Scholar]
- Murali Manoj, G.; Shalini, M.; Thenmozhi, K.; Kumar Ponnusamy, V.; Hari, S. Recent advancements in the surface modification and functionalization of magnetic nanomaterials. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2024, 21, 100608. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.; Shen, D.; Wu, F.; Pleixats, R.; Pan, J. Functionalized silica nanoparticles: Classification, synthetic approaches and recent advances in adsorption applications. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 15998–16016. [Google Scholar]
- Woźniak, J.; Nawała, J.; Dziedzic, D.; Popiel, S. Overview of Liquid Sample Preparation Techniques for Analysis, Using Metal-Organic Frameworks as Sorbents. Molecules 2024, 29, 4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzonkowska, L.; Leśniewska, B.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B. Recent Advances in On-Line Methods Based on Extraction for Speciation Analysis of Chromium in Environmental Matrices. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 46, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Luo, L.; Zhong, Z.; Xie, X. Advances in Sorptive Removal of Hexavalent Chromium (Cr(VI)) in Aqueous Solutions using Polymeric Materials. Polymers 2023, 15, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero-Latorre, C.; Barcielo-García, J.; García-Martín, S.; Pena-Crescente, R.M. Graphene and carbon nanotubes as solid phase extraction sorbents for the speciation of chromium: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1002, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García, A.; Rodríguez, B.; Rosales, M.; Quintero, Y.M.; GSaiz, P.; Reizabal, A.; Wuttke, S.; Celaya-Azcoaga, L.; Valverde, A.; Fernández de Luis, R. State-of-the-Art of Metal-Organic Frameworks for Chromium Photoreduction vs. Photocatalytic Water Remediation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, S.S.; Dehghan, G.; Khataee, A.; Alidokht, L.; Kudaibergenov, N. Layered double hydroxides as versatile materials for detoxification of hexavalent chromium: Mechanism, kinetics, and environmental factors. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszak, K.; Kruszelnicka, I.; Ginter-Kramarczyk, D.; Góra, W.; Baraniak, M.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Advances in the removal of Cr(III) from Spent Industrial Effluents—A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahrouei, A.E.; Rezapour, A.; Pirooz, M.; Pourebrahini, S. From classic to cutting-edge solutions: A comprehensive review of materials and methods for heavy metal removal from water environments. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Qin, C.; Li, X.; Xu, D.; Zhao, Y. Groundwater Cr(VI) contamination and remediation: A review from 1999 to 2022. Chemosphere 2024, 360, 142395. [Google Scholar]
- Maitlo, H.A.; Kim, K.H.; Kumar, V.; Kim, S.; Park, J.W. Nanomaterials-based treatment options for chromium in aqueous environments. Environ. Inter. 2019, 130, 104748. [Google Scholar]
- Assefa, H.; Singh, S.; Olu, F.E.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Mani, D.; Khan, N.A.; Singh, J.; Praveen, C.; Ramamurthy, P.C. Advances in adsorption technologies for hexavalent chromium removal: Mechanisms, materials, and optimization strategies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100576. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetics and isotherm models of heavy metals by various adsorbents: An overview. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 1837–1865. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadmoradi, P.; Taheri, S.; Bryant, S.L.; Apostolos Kantzas, A. Solvent diffusion and dispersion in partially saturated porous media: An experimental and numerical pore-level study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 191, 300–317. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghani, M.H.; Taher, M.M.; Bajpai, A.K.; Heibati, B.; Tyagi, I.; Asif, M.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Removal of noxious Cr(VI) ions using single-walled carbon nanotubes and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 344–352. [Google Scholar]
- Mpouras, T.; Polydera, A.; Dermatas, D.; Verdone, N.; Vilardi, G. Multiwall carbon nanotubes application for treatment of Cr(VI)-contaminated groundwater; Modeling of batch & column experiments. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128749. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Song, K.; Luo, W.; Yang, J. Adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) by hydroxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes: Effect of humic acid and surfactants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12746–12754. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Fu, D.; Koh, K.Y.; Chen, J.P. A new carbon nanotube modified by nano CaO2 for removal of chromate and phosphate from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liu, D.; Deng, S.; Vakili, M. Efficient chromium (VI) removal with zirconium oxide-carbon nanotubes via filtration-steam hydrolysis. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 204, 664–672. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Wu, Y.; Liu, N.; Yan, C. Adsorption behavior of Cr(VI) and As(III) on multiwall carbon nanotubes modified by iron-manganese binary oxide (FeMnOx/MWCNTs) from aqueous solution. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 192–208. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Zeng, X.; Liu, P. One-step synthesis of magnetic N-doped carbon nanotubes derived from waste plastics for effective Cr(VI) removal. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105956. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Cao, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhong, G.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Peng, F. Highly efficient and acid-corrosion resistant nitrogen doped magnetic carbon nanotubes for the hexavalent chromium removal with subsequent reutilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhao, D.; Hu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; He, C.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, R. The adsorption and reduction of anionic Cr(VI) in groundwater by novel iron carbide loaded on N-doped carbon nanotubes: Effects of Fe-confinement. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 13935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenta, E.W.; Mebratie, B.A. Advancements in carbon nanotube-polymer composites: Enhancing properties and applications through advanced manufacturing techniques. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahpishanian, S.; Ahmadian-Alam, L.; Foudazi, R. Porous polymer nanocomposites containing single-walled carbon nanotubes for chromium (VI) removal from water. React. Funct. Polym. 2023, 182, 105719. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, D.; Jing, Z.; Duan, Y.; Li, J. Ultrafast removal of Cr(VI) ions using polyamine modified carbon nanotubes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 133, 104265. [Google Scholar]
- Amaku, J.F.; Taziwa, R. Aqueous removal of Cr(VI) by Citrus sinensis juice-coated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Pap. 2024, 78, 5415–5431. [Google Scholar]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Romero, F.; de la Calle, I.; Lavilla, I.; Bendicho, C. Graphene-based nanocomposites in analytical extraction processes. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 142, 116303. [Google Scholar]
- Nanjundappa, V.S.; Ramakrishnappa, T.; Prakash, H.R.; Praveen, B.M. Efficient strategies to produce Graphene and functionalized graphene materials: A review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2023, 14, 100386. [Google Scholar]
- Tarcan, R.; Todor-Boer, O.; Petrovai, I.; Leorean, C.; Astilean, S.; Botiz, I. Reduced graphene oxide today. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 1198–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Khdoor, Z.; Makharza, S.; Qurie, M.; Fohely, F.; Taha, S.A. Hampe, Removal of toxic hexavalent chromium via graphene oxide nanoparticles: Study of kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 24345. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, N.K.; Chakraborty, S. Adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution on graphene oxide (GO) prepared from graphite: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Bulin, C. Adsorption-reduction behavior of hexavalent chromium on Fe3O4-graphene oxide surface with special implication on environmental remediation. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 33417–33429. [Google Scholar]
- Mahvi, A.H.; Balarak, D.; Bazrafshan, E. Remarkable reusability of magnetic Fe3O4-graphene oxide composite: A highly effective adsorbent for Cr(VI) ions. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 103, 3501–3521. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Song, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. Efficient removal of hexavalent chromium and Congo red by graphene oxide/silica nanosheets with multistage pores. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 4368. [Google Scholar]
- Jibin, K.P.; Augustine, S.; Velayudhan, P.; George, S.K.; Poulose, S.V.; Thomas, S. Unleashing the Power of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials for Chromium(VI) Ion Elimination from Water. Crystals 2023, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Yang, W.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y. Amino-assisted AHMT anchored on graphene oxide as high performance adsorbent for efficient removal of Cr(VI) and Hg(II) from aqueous solutions under wide pH range. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125825. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Anil, A.G.; Khasnabis, S.; Kumar, V.; Nath, B.; Adiga, V.; Kumar Naik, T.S.; Subramanian, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, J.; et al. Sustainable removal of Cr(VI) using graphene oxide-zinc oxide nanohybrid: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merija, K.S.; Rahulan, K.M.; Sujatha, R.A.; Little Flower, N.A. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from water using graphene oxide/zinc molybdate nanocomposite: Study of kinetics and adsorption isotherms. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1139604. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y. Highly efficient and ultrafast removal of Cr(VI) in aqueous solution to ppb level by poly(allylamine hydrochloride) covalently cross-linked amino-modified graphene oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124470. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Hong, M.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. New Schiff base covalently bonded graphene oxide for removing chromium(VI) from surface runoff. Environ. Res. 2025, 264, 120360. [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowska, M.A.; Bożejewicz, D. The Application of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for the Removal of Hazardous Pollutants from Aqueous Solutions—A Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, E.; Predescu, A.M.; Râpă, M.; Tarcea, C.; Pantilimon, C.M.; Favier, L.; Berbecaru, A.C.; Sohaciu, M.; Predescu, C. Removal of Chromium(VI) from Aqueous Solution Using a Novel Green Magnetic Nanoparticle–Chitosan Adsorbent. Anal. Lett. 2019, 52, 2416. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, M.S.; Bhattacharya, J.; Raj, S.; Santhanam, N.; Singh, H.; Singh, N.D.P. Efficient removal of Chromium(VI) from aqueous solution using chitosan grafted graphene oxide (CS-GO) nanocomposite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 285. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.; He, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Song, Z. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide/chitosan composite aerogel with high adsorption performance for Cr(VI) by a new crosslinking route. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126832. [Google Scholar]
- Subedi, N.; Lähde, A.; Abu-Danso, E.; Iqbal, J.; Bhatnagar, A. A comparative study of magnetic chitosan (Chi@Fe3O4) and graphene oxide modified magnetic chitosan (Chi@Fe3O4GO) nanocomposites for efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 948–959. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shan, H.; Zeng, C.; Zhan, H.; Pang, Y. Removal of Cr(VI) from Wastewater Using Graphene Oxide Chitosan Microspheres Modified with α-FeO(OH). Materials 2022, 14, 4909. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.; Gao, H.; Hu, Z.; Jia, X.; Wen, D. Ni-Fe/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites for Hexavalent Chromium Reduction in an Aqueous Environment. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 4041–4051. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, R.S.; Aparna, N.; Meril, M. Hexavalent chromium removal using reduced graphene oxide-zinc oxide composite fabricated via simple pyrolysis method. App. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2024, 19, 10053. [Google Scholar]
- da Gama, B.M.V.; Selvasembian, R.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; McKay, G.; Meili, L. Layered double hydroxides as rising-star adsorbents for water purification: A brief discussion. Molecules 2022, 27, 4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.A.; Khan, A.M.; Yahiya, G.; Manea, K.; Shahadat, M.; Ahammad, S.Z.; Ali, S.W. Graphene-supported organic-inorganic layered double hydroxides and their environmental applications: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122980. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, B.; You, W.; Yu, J.; Ho, W. 3D hierarchical graphene oxide-NiFeLDH composite with enhanced adsorption affinity to Congo red, methyl orange and Cr(VI) ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Qin, X.; Wang, K.; Peng, Y.; Wang, P.; Jiang, G. Nanoscale zero valent iron supported on MgAl-LDH-decorated reduced graphene oxide: Enhanced performance in Cr(VI) removal, mechanism and regeneration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Xiao, M.; Zhu, H.Y.; Zang, X.; Zhao, D.X.; Zhu, J.Q.; Long, Y.K.; Wang, Q. Intriguing and boosting molybdenum sulfide (MoS2)-based materials for decontamination and purification of wastewater/seawater: An upgraded review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 351, 128063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, S.; Ali, M.S.; Karmakar, S.; Chattopadhyay, D. Molybdenum disulfide: A nanomaterial that is paving the way toward a sustainable future. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 25, 100659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Yu, J.; Poon, S.; Sun, L.; Teli, M.; Liu, B.; Chen, H.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Mi, B. Highly efficient removal and sequestration of Cr(VI) in confined MoS2 interlayer Nanochannels: Performance and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 293, 121104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Fan, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y. Highly efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water based on graphene oxide incorporated flower-like MoS2 nanocomposite prepared in situ hydrothermal synthesis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 13882–13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, N.S.; Sadeq, Z.E.; Mahmoud, Z.H.; Najem Abd, A.; Al-Mahdawi, A.S.; Ali, F.K. Synthesis of Chitosan-TiO2 Nanocomposite for Efficient Cr(VI) Removal from Contaminated Wastewater Sorption Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Mechanism. J. Oleo Sci. 2023, 72, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kaim Billah, R.; Shekhawat, A.; Mansouri, S.; Majdoubi, H.; Agunaou, M.; Soufiane, A.; Jugade, R. Adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) by Chitosan-SiO2-TiO2 nanocomposite. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 18, 100695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Ge, X.; Wang, X. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal by hierarchical CoFe2O4@SiO2-NH2 via reduction and adsorption processes. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Fatema Tuj, Z.; Mahdi, M.M.; Mahmudunnabi, D.M.; Choudhury, T.R.; Alam, M.Z.; Nurnabi, M. Synthesis and characterization of graphene oxide for removal of Cr(III) from tannery effluent. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 244, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Quiñonez, J.L.; Cancino-Gordillo, F.E.; Pal, U. Removal of Cr(III) Ions from Water Using Magnetically Separable Graphene-Oxide-Decorated Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 18491–18507. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Yang, S.; Tao, E.; Xiao, X.; Liu, L.; Li, Y. Mild-method synthesized GO-TiO2 retains oxygen-containing functional groups as an effective adsorbent. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 301, 122290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Z. Adsorption of Cr(III) and Pb(II) by graphene oxide/alginate hydrogel membrane: Characterization, adsorption kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics studies. Inter. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 17, 898–910. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, N.; Cabral-Pinto, N.M.S.; Rezania, S.; Radwan, N.; Alam, J. Chromium contamination and effect on environmental health and its remediation: A sustainable approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112174. [Google Scholar]
- Pechancová, R.; Pluháček, T.; Milde, D. Recent advances in chromium speciation in biological samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2019, 152, 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Haider, F.U.; Ahmad, M.; Hussain, S.; Maqsood, M.F.; Ishfaq, M.; Shahzad, B.; Waqas, M.M.; Ali, B.; Nayyab, T.M.; et al. Chromium toxicity, speciation, and remediation strategies in soil-plant interface: A critical review. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1081624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Tiwari, S.; Saxena, R. Comparative Insight into the Performance of Two Different Amine-Functionalized CNTs for the Chemical Speciation of Chromium. Chem. Sel. 2020, 5, 6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çaylak, O. Chromium speciation in water using magnetic polyaniline nanoparticles coupled with microsampling injection-flame atomic absorption spectroscopy. Turk. J. Chem. 2024, 48, 21–35. [Google Scholar]
- Elçi, Ş.G. Speciation of chromium in beverages and seasoning samples by magnetic solid-phase extraction and microsample injection system flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Cumhur. Sci. J. 2020, 41, 550–558. [Google Scholar]
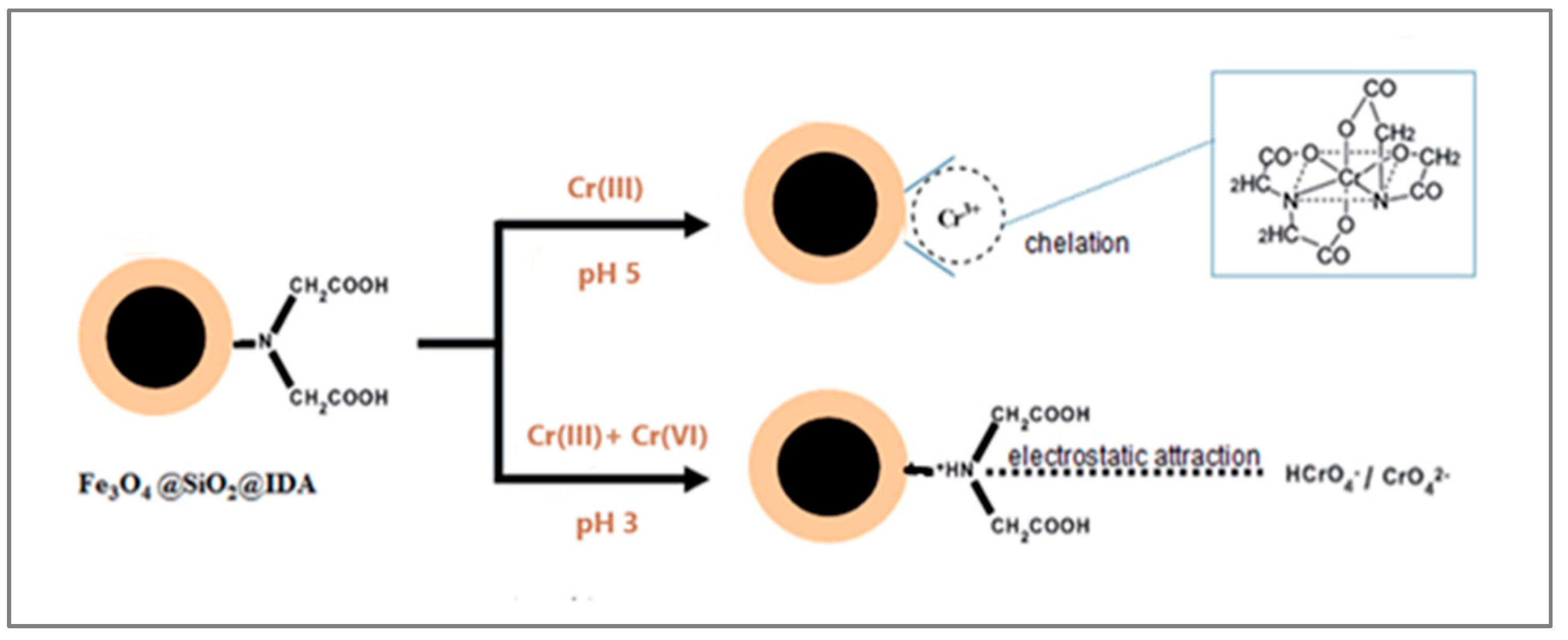
- Wei, W.; Zhao, B.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Hu, B. Iminodiacetic acid functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for speciation of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) followed by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry detection. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 8504. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan Ahmed, H.E.; Soylak, M. A MWCNTs@CuAl2O4@SiO2 Nanocomposite for the Speciation of Cr(III), Cr(VI), and Total Chromium Prior to High-Resolution Continuum Source Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Determination. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 217. [Google Scholar]
- Saboori, A. A nanoparticle sorbent composed of MIL-101(Fe) and dithiocarbamate-modified magnetite nanoparticles for speciation of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) prior to their determination by electrothermal AAS. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, A.; Malekpour, A. Octyl coated cobalt-ferrite/silica core-shell nanoparticles for ultrasonic assisted-magnetic solid-phase extraction and speciation of trace amount of chromium in water samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104530. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolmohammad-Zadeh, H.; Ayazi, Z.; Veladi, M. Nickel oxide/nickel ferrite/layered double hydroxide nanocomposite as a novel magnetic adsorbent for chromium speciation. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 105153. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.; Chen, H.; Huang, X. Magnetism-assisted in-tube solid-phase microextraction for the on-line chromium speciation in environmental water and soil samples. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 105965. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q.; Peng, X.; Xue, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Sulfite-Induced Release and Oxidation of Cr(III) in Reduced Chromite Ore Processing Residue under Visible Light: The Critical Role of Fe(IV) Intermediates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 5756–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhou, W.; Liang, J.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Tong, M. The effect of phosphate on the stability of Cr(OH)3 and CrxFe1−x(OH)3 in the presence of MnO2: Competition between dissolution, adsorption and oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137502. [Google Scholar]
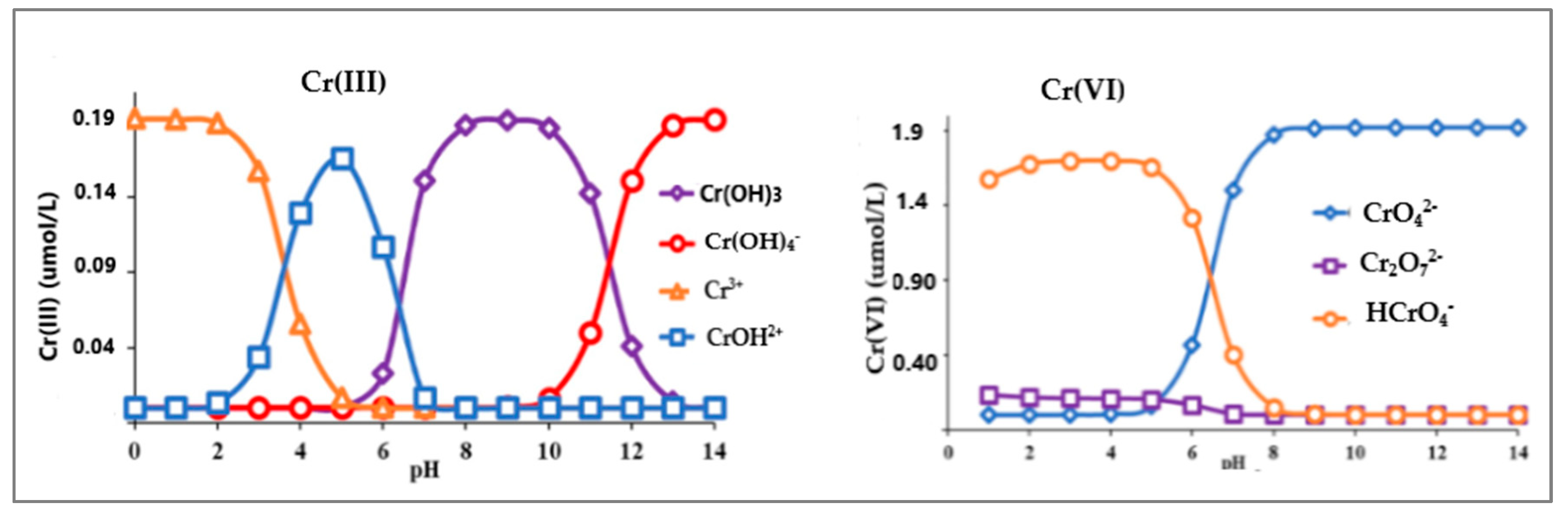
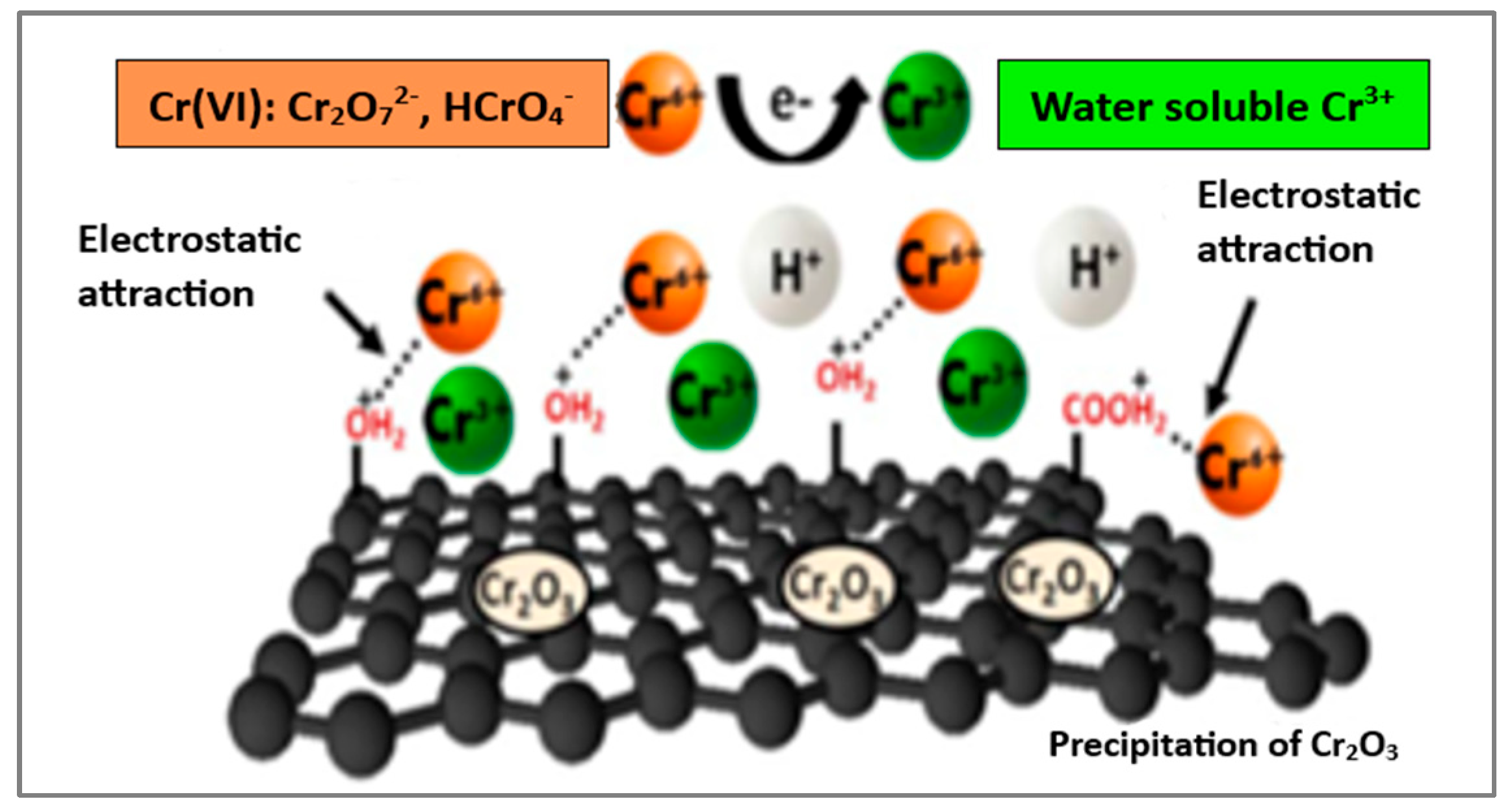

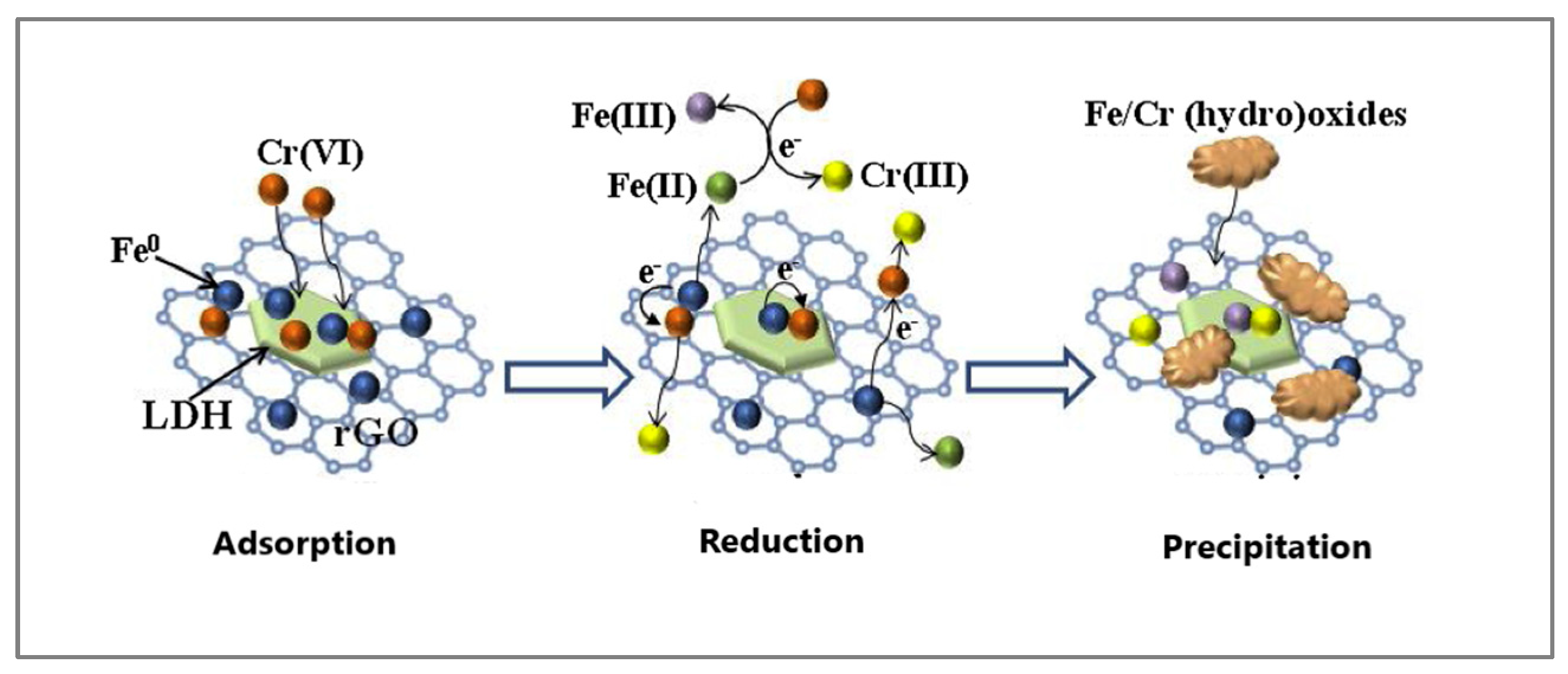
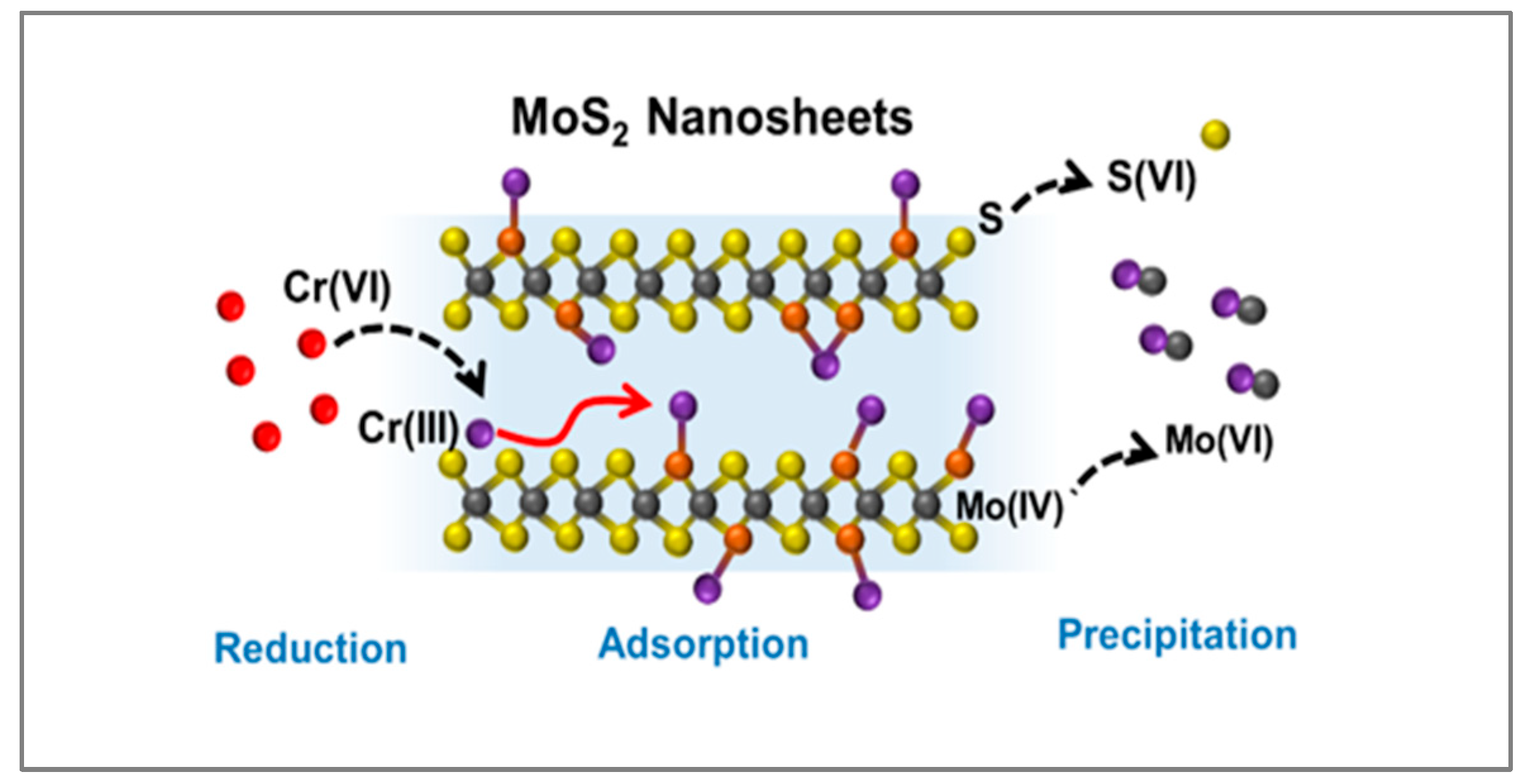
| Nanomaterial | SBET (m2/g) | Sample pH | Contact Time | qmax (mg/g) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNTs | – | 2.5 | 60 min | SWCNTs | 2.35 | [45] |
| MWCNTs | 1.26 | |||||
| CNTs@CaO2 | – | 3 | 2 h | 81% of removal | [48] | |
| MWCNTs@FeMnO4 | 360 | 2 | 24 h | 47.25 | [49] | |
| CNT@Fe@N | 158.71 | 2 | 6 h | 27.47 | [51] | |
| CNTs@Fe3N | 116.4 | 1 | 10 min | 970.87 | [52] | |
| MWNTs modified with orange juice | 21.66 | 2 | 3 h | 60.91 | [57] | |
| GO | – | 3 | 2 h | 41.27 | [61] | |
| GO | – | 4 | 40 min | 1.222 | [62] | |
| GO@Fe3O4 | 194.6 | 2 | 60 min | 140.8 | [64] | |
| GO@SiO2 | _ | 3 | 24 h | 92.3% removal | [66] | |
| PAH@AS@GO | 261.6 | 2 | 20 min | 373.1 | [67] | |
| PAH@AS@GO@Fe3O4 | 2 | 20 min | 219 | |||
| GO@ZnO | 32.95 | 8.02 | 720 min | 3.69 | [68] | |
| GO@zinc molybdate | 121.18 | 2 | 120 min | 20.40 | [69] | |
| GO@AHMT | 3 | 100 min | 734.2 | [72] | ||
| GO@CS | – | 2 | 420 min | 104.16 | [74] | |
| GO@Fe3O4@CS | 5.4 | 2 | 40 min | 100.51 | [75] | |
| GO@FeO(OH)@CS | – | 3 | 64 h | 63.19 | [77] | |
| rGO@Fe-Ni | 119.08 | 5 | 20 min | 197.43 | [78] | |
| rGO@ZnO | 29.418 | 1.5 | 24 h | 13.52 | [79] | |
| GO@NiFe@LDH | 145 | 6–7 | – | 53.6 | [82] | |
| GO@MoS2 | 4.58 | 2 | 200 min | 43.95 | [86] | |
| rGO@MoS2 | 79.39 | 2 | 150 min | 62.10 | [87] | |
| CS@TiO2 | 26 | 2 | 30 min | 488 | [88] | |
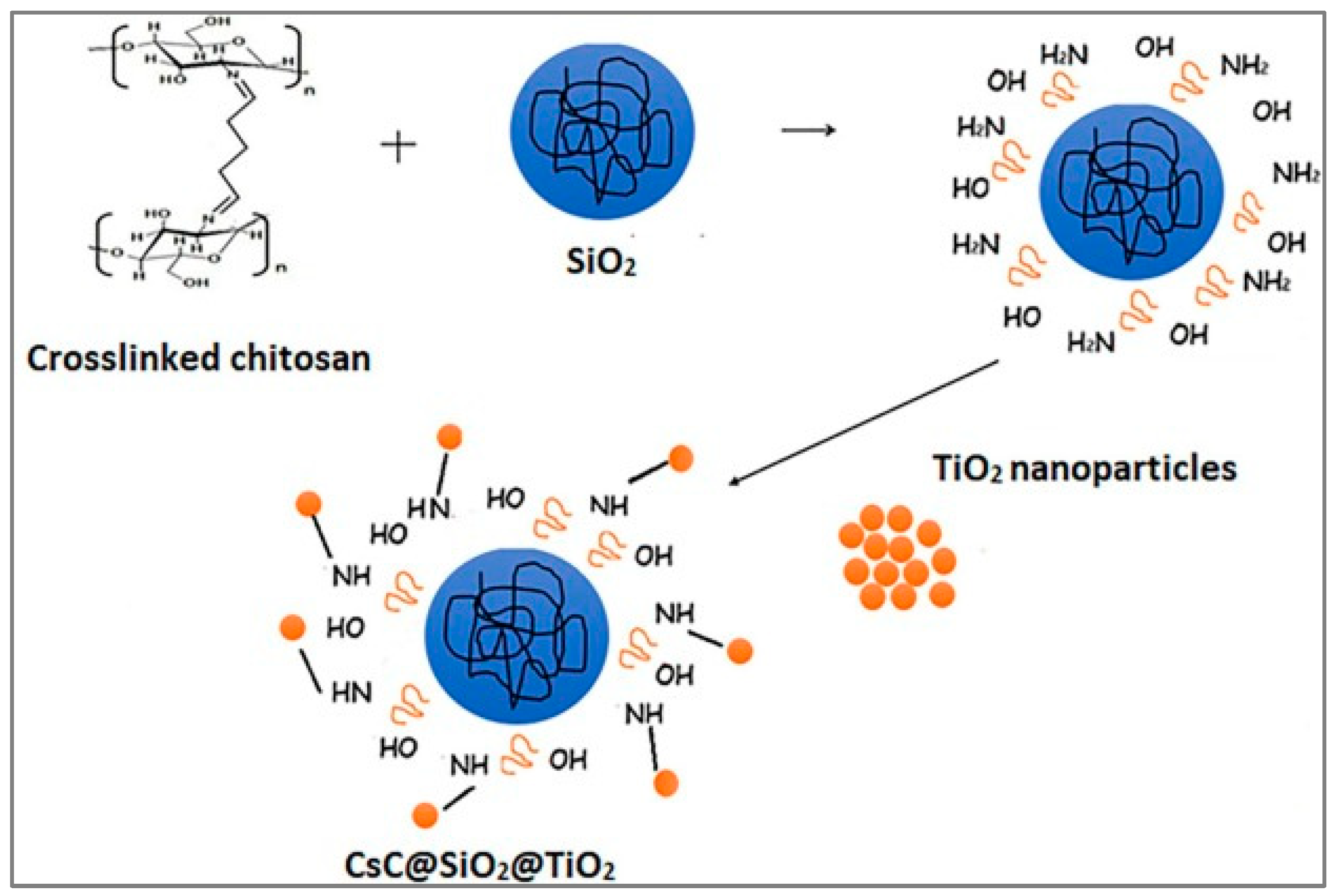
| CS@SiO2@TiO2 | – | 2 | 120 min | 182.43 | [89] | |
| CoFe2O4@SiO2-NH2 | 128.48 | 2 | 126.8 | [90] | ||
| Nanomaterial | Conditions | Eluent | EF | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Time (min) | ||||
| Selective sorption of Cr(III) | |||||
| MWCNTs-TYR | 4 | 120 | 0.2 M HNO3 | 93 | [98] |
| MWCNTs-ASA | 6 | 100 | 0.3 M HNO3 | 97 | |
| Fe3O4@PTh | 7 | 1 | 3 M HCl | 27 | [23] |
| Fe3O4@PANI | 8 | 5 | 0.2% TU + 2 M HCl | 80 | [99] |
| Fe3O4@PANI-PTh | 10 | 5 | 0.2% TU + 1 M HNO3 | 38.5 | [100] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2@IDA | 3.6 | 10 | 1.5 M HNO3 | 100 | [101] |
| Selective sorption of Cr(VI) | |||||
| MWCNTs@CuAl2O4@SiO2 | 5 | 3 M HNO3 in 10% acetone | 17 | [102] | |
| MOF-Fe@PAEDTC | 2 | 6.5 | 0.6 M EDTA + 0.3 M HNO3 | 17.6 | [103] |
| CoFe2O4@SiO2-C8 + APDC | 6 | 10 | Ethanol | 200 | [104] |
| NiO/NiFe2O4/LDH | 6 | 15 | 10% [NH4OH]Cl | 250 | [105] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pyrzynska, K. Nanomaterials for Removal and Speciation of Chromium. Materials 2025, 18, 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071485
Pyrzynska K. Nanomaterials for Removal and Speciation of Chromium. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071485
Chicago/Turabian StylePyrzynska, Krystyna. 2025. "Nanomaterials for Removal and Speciation of Chromium" Materials 18, no. 7: 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071485
APA StylePyrzynska, K. (2025). Nanomaterials for Removal and Speciation of Chromium. Materials, 18(7), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071485






