New Mcconnellite Ceramic Pigment as a Selective Solar Absorber: Effects of Microwave Firing and Rare Earth Doping
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
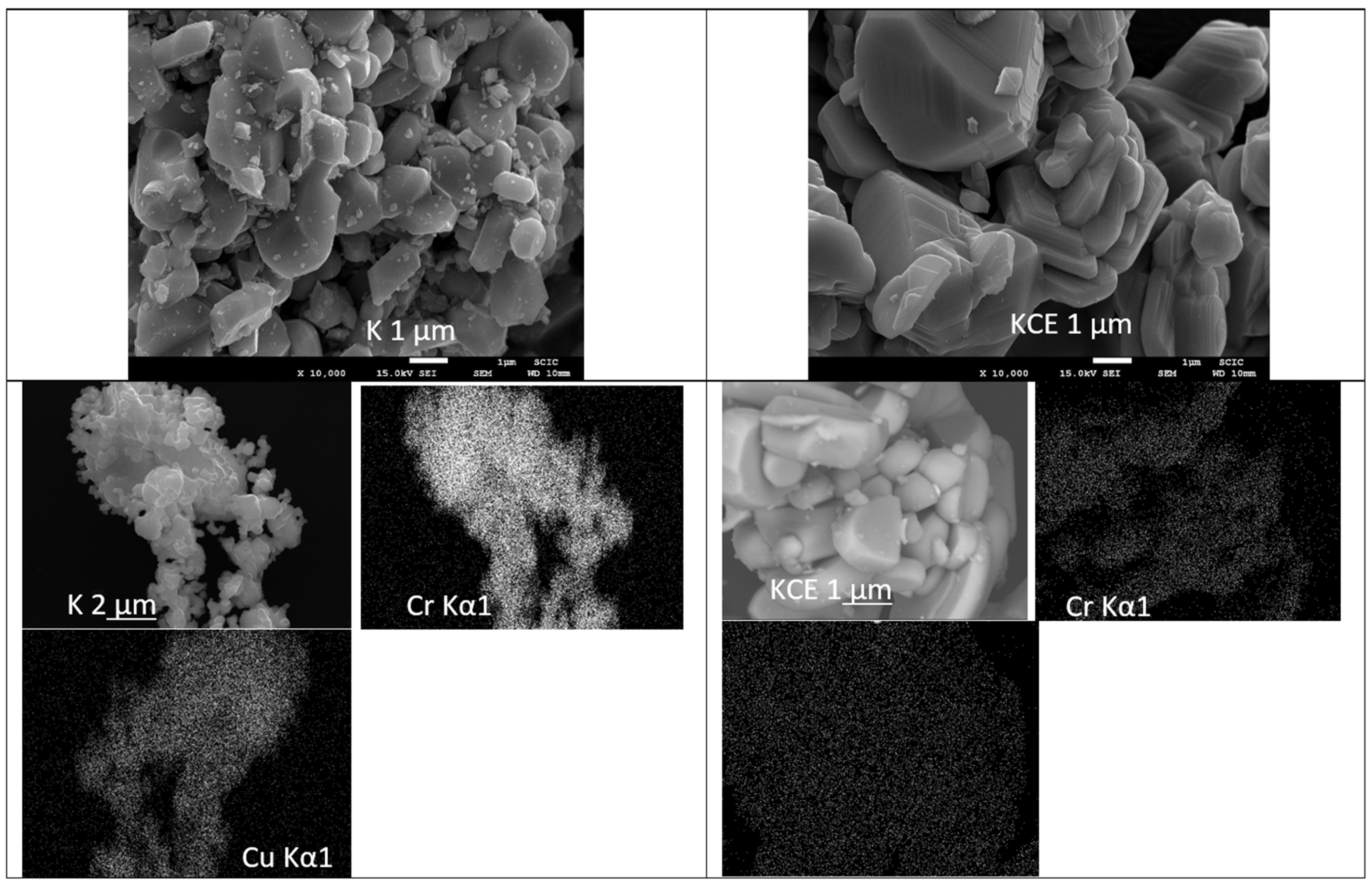
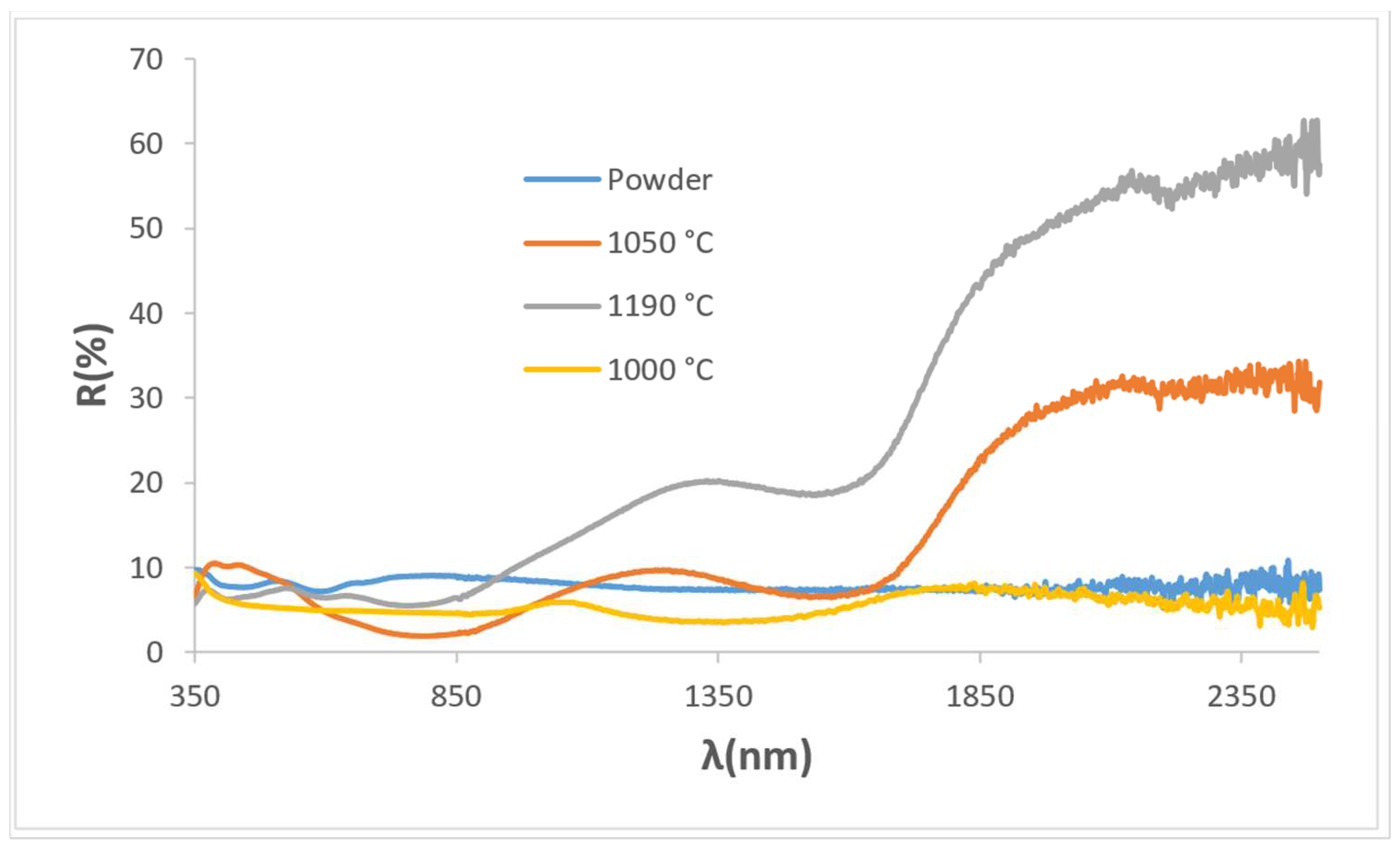
3.1. Characterization of Powders: Effect of Microwaves Firing
3.2. Characterization of Glazed Samples in Double-Firing Glaze at 1000 °C: Effect of Microwave Glazing
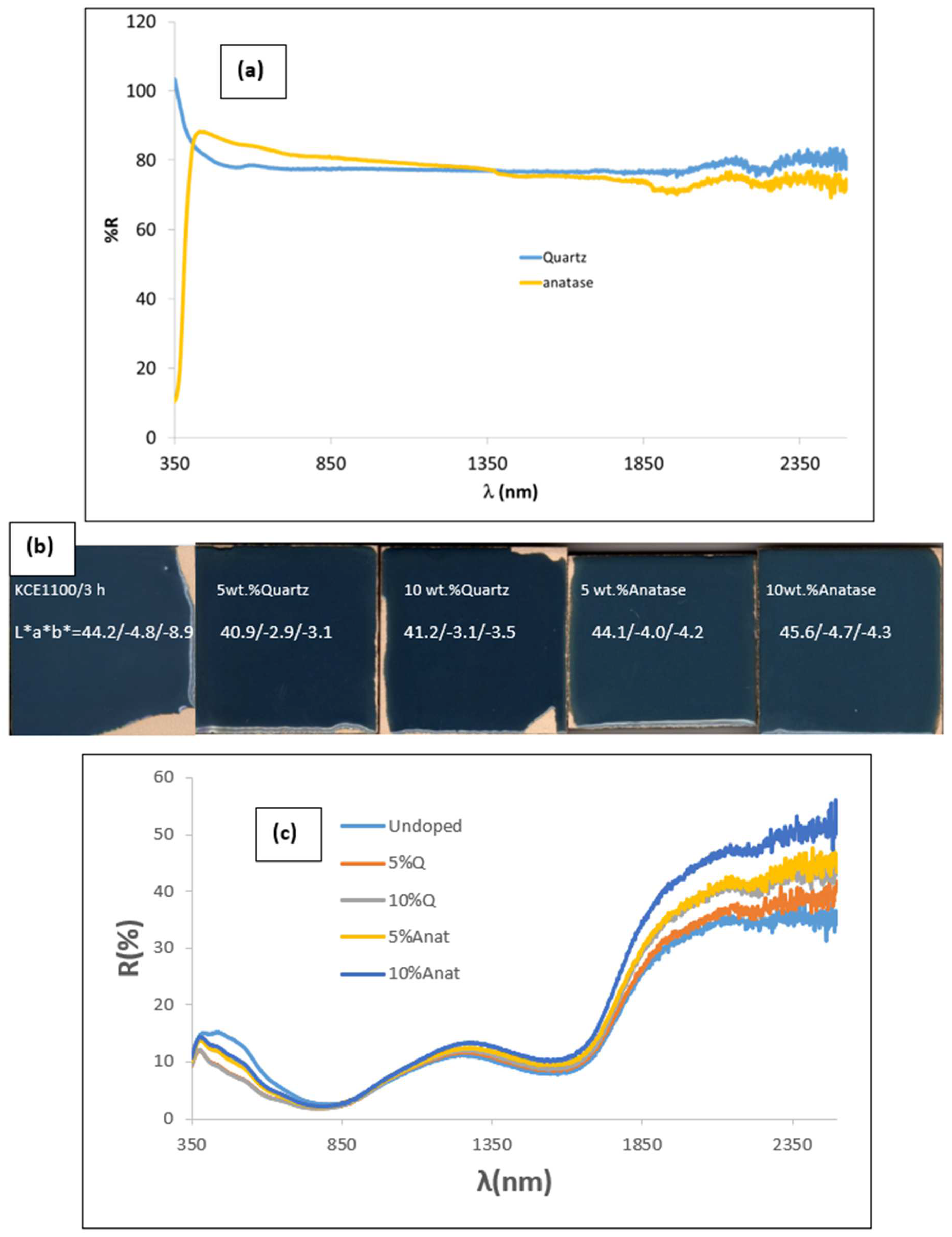
3.3. Characterization of Glazed Samples in Double-Firing Glaze at 1050 °C: Effect of Addition of Colour Modifiers (Quartz and Anatase)
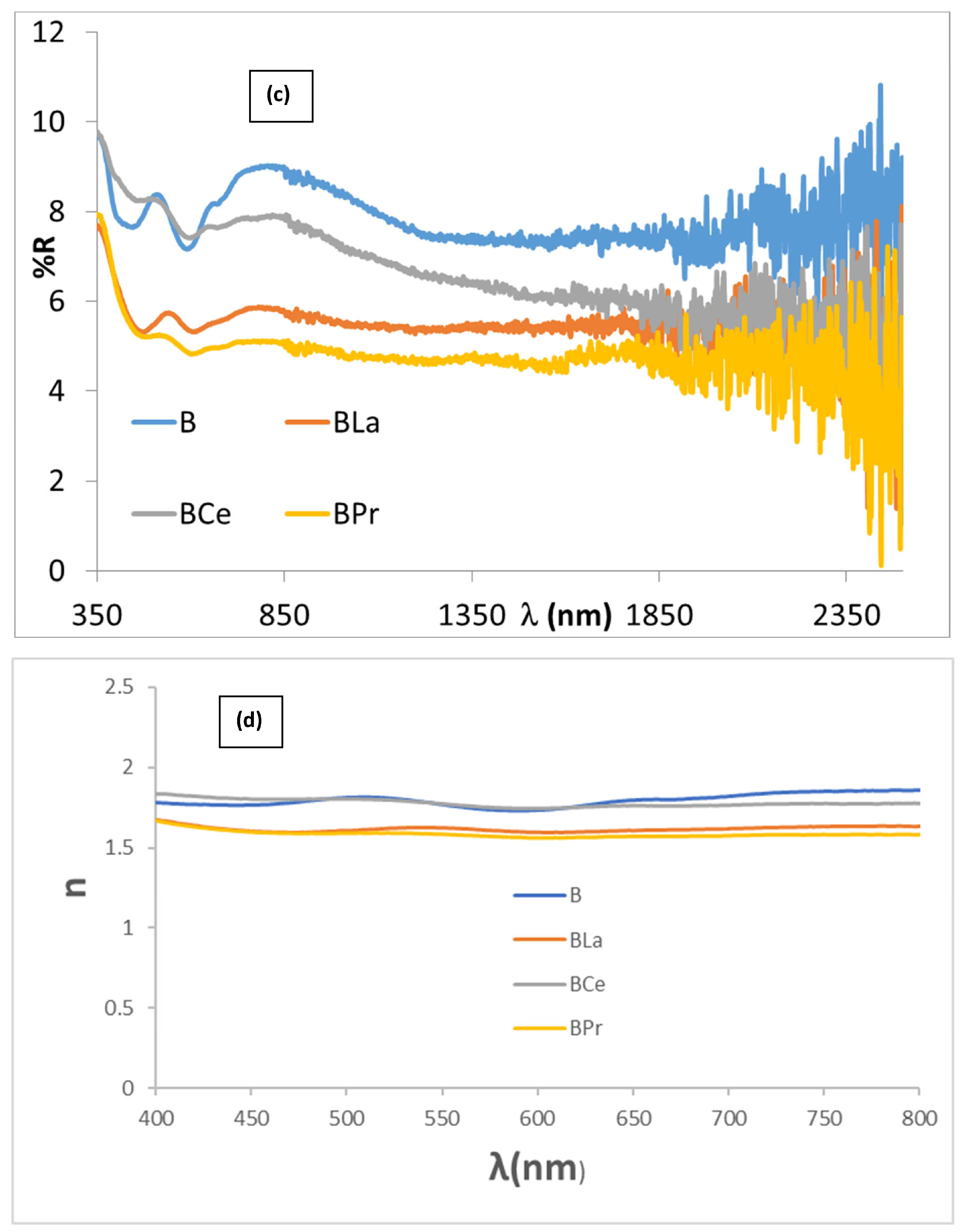
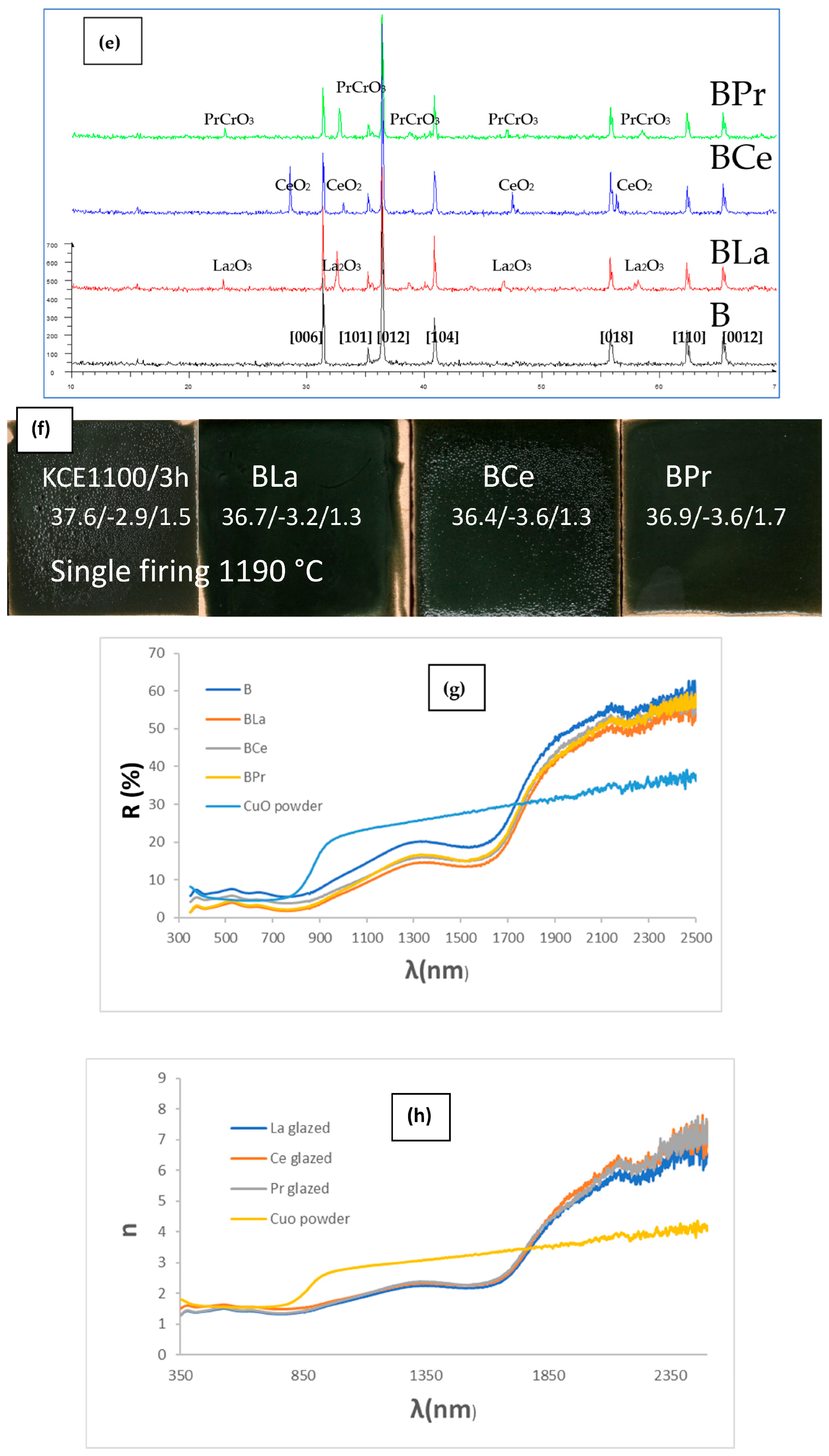
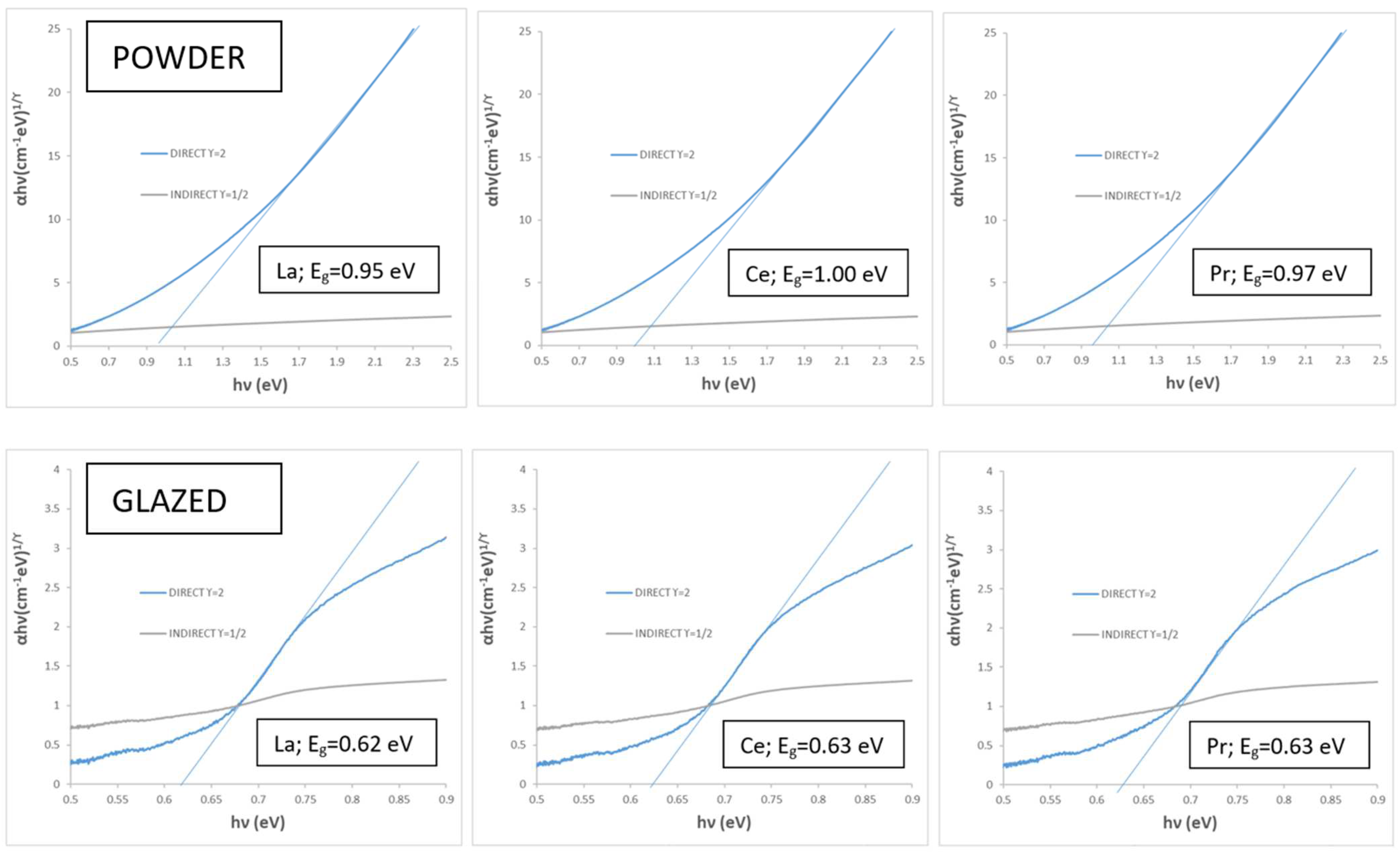
3.4. Doping Effect with Lanthanide Oxides (CuCr0.9Ln0.1O2, Ln = La, Ce, Pr)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SSA | Selective solar absorber |
| FPSC | Flat-plate solar collector |
| IR | Infrared |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SEM–EDS | Scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive spectroscopy |
| JCPDS | Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards |
| UV-Vis-NIR | Ultraviolet–visible–near-infrared |
References
- Kohler, B.U.; Jansen, M. Synthesis and crystal structure of 2H-CuAlO2. Z. Fur Krist. 1983, 165, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, M.N.; Yan, Y.; Walsh, A.; Wei, S.; Al-Jassim, M.M. Group-IIIA versus IIIB delafossites: Electronic structure study. Phys. Rev. 2009, 80, 035205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, M.C.; de Figueredo, G.P.; Rodrigues, S.F.; Cabral, A.A.; Castro, M.A.M.; Oliveira, M.M. Synthesis of delafossite CuCrO2 via solution combustion method and its acid functionalization for biodiesel production. Cerâmica 2023, 69, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, P.; Li, D.; Deng, Z.; Dong, W.; Tao, R.; Fang, X. Preparation of delafossite-type CuCrO2 films by sol–gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 5715–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Feng, J.; Ao, X.; Hu, M.; Pei, G. Spectral optimization of solar selective absorbing coating for parabolic trough receiver. Energy 2019, 183, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Du, M.; Hao, L.; Mi, J.; Yu, Q.; Li, S. A review of high-temperature selective absorbing coatings for solar thermal applications. J. Mater. 2020, 6, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Monti, M.; di Giamberardino, F.; Palmieri, V.G. Characterization of selective solar absorber under high vacuum. Opt. Express 2018, 26, A480–A486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, C.; Huang, J.; Chi, C.; Huang, B. Spectrally Selective Absorbers/Emitters for Solar Steam Generation and Radiative Cooling-Enabled Atmospheric Water Harvesting. Glob. Chall. 2021, 5, 2000058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Liu, Y.; Ling, L.; Sheng, Z.; Yi, Z.; Song, Q.; Cheng, S.; Tang, B.; Ahmad, S.; Sun, T. Spectrally Selective Ultra-Broadband Solar Absorber Based on Pyramidal Structure. Adv. Photonics Res. 2024, 5, 2300305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cao, S.; Xu, J.; Cai, B. All-ceramic solar collectors. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 6009–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.E.; Forbes, A. An analytical expression for the instantaneous efficiency of a flat plate solar water heater and the influence of absorber plate absorptance and emittance. Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 1416–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monrós, G.; Delgado, C.; Monrós-Andreu, G.; Badenes, J.; Llusar, M. Black Coloured Glazes with Tetragonal CuCr2O4 Ceramic Pigment as Selective Solar Absorbers for Integral Ceramic Solar Collectors. J. Sol. Energy Res. Updates 2024, 11, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, V.; Kim, V.; Warren, N.; Guo, N.; Zhang, X.; Wang, V.; Willemsen, A. Hierarchically micro-and nanostructured polymer via crystallinity alteration for sustainable environmental cooling. Langmuir 2024, 40, 20195–20203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saez Puche, R.; Norton, M.; White, T.R.; Glaunsinger, W.S. Magnetic properties of the semiconducting lanthanide cuprates Ln2CuO4 and their interpretation: Evidence for a new series of planar copper antiferromagnets. J. Solid State Chem. 1983, 50, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukovozov, I.E.; Ezerets, A.M.; Vishniakov, A.V.; Mendeleev, D.I.; Forni, L.; Oliva, C. Structural effects of interaction between lanthanum cuprate and cerium dioxide. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 4991–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calbo, J.; Gargori, C.; Sorlí, S.; Badenes, J.; Tena, M.A.; Monrós, G. Síntesis de pigmentos cerámicos mediante radiación microondas. Bol. Soc. Esp. Ceram. Vidr. 2007, 46, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blosi, M.; Dondi, M.; Albonetti, S.; Baldi, G.; Barzanti, A.; Zanelli, C. Microwave-assisted synthesis of Pr–ZrSiO4, V–ZrSiO4 and Cr–YAlO3 ceramic pigments. J. Eur. Cer. Soc. 2009, 29, 2951–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Basak, T. A review on the susceptor assisted microwave processing of materials. Energy 2016, 97, 306–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission International de L’Eclairage (CIE). Recommendations on Uniform Colour Spaces, Colour-Difference Equations, Psychometrics Colour Terms; CIE: Paris, France, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical Properties and Electronic Structure of Amorphous Germanium. Phys. Status Solidi 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G173-03; Standard Tables for Reference Solar Spectral Irradiances: Direct Normal and Hemispherical on 37° Tilted Surface. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008.
- Kuhn, T.S. Black–Body Theory and the Quantum Discontinuity; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1978; ISBN 0-19-502383-8. [Google Scholar]
- Monrós, G. Scheelite and Zircon: Brightness, Color and NIR Reflectance in Ceramics; Nova Scienc Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-53619-332-9. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S. Refractive Index Measurement and its Applications. Phys. Scr. 2002, 65, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staines, M.P.; Bittar, A.; Presland, M.R. Diffuse reflectance of oriented polycrystalline YBa2Cu3O7-δ. Solid State Commun. 1989, 72, 677–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, E.; Kirk, C.J.; Dann, S.E. Structure and colour properties in the Egyptian Blue Family, M1-xM’xCuSi4O10, as a function of M, M’ where M, M’=Ca, Sr and Ba. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 73, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappe, C.O.; Pieber, B.; Dallinger, D. Microwave Effects in Organic Synthesis: Myth or Reality? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 52, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlKetbi, M.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Zedan, A.F.; Sebastián, V.; Baker, M.A.; AlKhoori, A.; Jaoude, M.A.; Alnuaimi, O.; Hinder, S.S.; Tharalekshmy, A.; et al. Tuning the activity of Cu-containing rare earth oxide catalysts for CO oxidation reaction: Cooling while heating paradigm in microwave-assisted synthesis. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 108, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verger, L.; Olivier, D.; Rousse, G.; Cotte, M.; Cormier, M.L. The Stability of Gahnite Doped with Chromium Pigments in Glazes from the French Manufacture of Sèvres. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 100, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monrós, G.; Badenes, J.A.; Llusar, M.I. Ecofriendly High NIR Reflectance Ceramic Pigments Based on Rare Earths Compared with Classical Chromophores Prepared by DPC Method. Ceramics 2022, 5, 614–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; Kareem, K.; He, L. Synthesis, characterization and resistant performance of α-Fe2O3@SiO2 composite as pigment protective coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 300, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachhap, S.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, S.K. Lanthanide-doped inorganic halide perovskites (CsPbX3): Novel properties and emerging applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 3647–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogachev, N.A.; Betina, A.A.; Bulatova, T.S.; Nosov, V.G.; Kolesnik, S.S.; Tumkin, I.I.; Ryazantsev, M.N.; Skripkin, M.Y.; Mereshchenko, A.S. Lanthanide-Ion-Doping Effect on the Morphology and the Structure of NaYF4:Ln3+ Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, V.; Sousa, E.; Costa, M.F.; Nunes, C.; Rosa, L.; Carvalho, M.J.; Collares-Pereira, M.; Roman, E.; Gago, J. Spectrally selective composite coatings of Cr–Cr2O3 and Mo–Al2O3 for solar energy applications. Thin Solid Film. 2001, 392, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monrós, G.; Delgado, C.; Llusar, M.; Badenes, J. Effect of silica addition on the photocatalytic activity of MO2@SiO2 (M=Ti, Zr, Sn, Ce) nanocomposites prepared by sol-gel. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, H.M.; Ratep, A.; Elsoud, A.M.A.; Boshta, M.; Osman, M.B.S. Influences of annealing temperature on sprayed CuFeO2 thin films. Results Phys. 2018, 9, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graef, M.; McHenry, M.E. Structure of Materials: An Introduction to Crystallography, Diffraction and Symmetry, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-1-107-00587-7. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Double Firing 1000 °C | Double Firing 1050 °C | Single Firing 1190 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxide | |||
| SiO2 | 72 | 59 | 67 |
| Na2O | 14 | 4 | - |
| K2O | 1.5 | 5 | 3 |
| CaO | 9 | 15 | 12.5 |
| MgO | - | - | 1.5 |
| ZnO | - | 9 | 6 |
| Al2O3 | 2.3 | 8 | 10 |
| PbO | - | - | - |
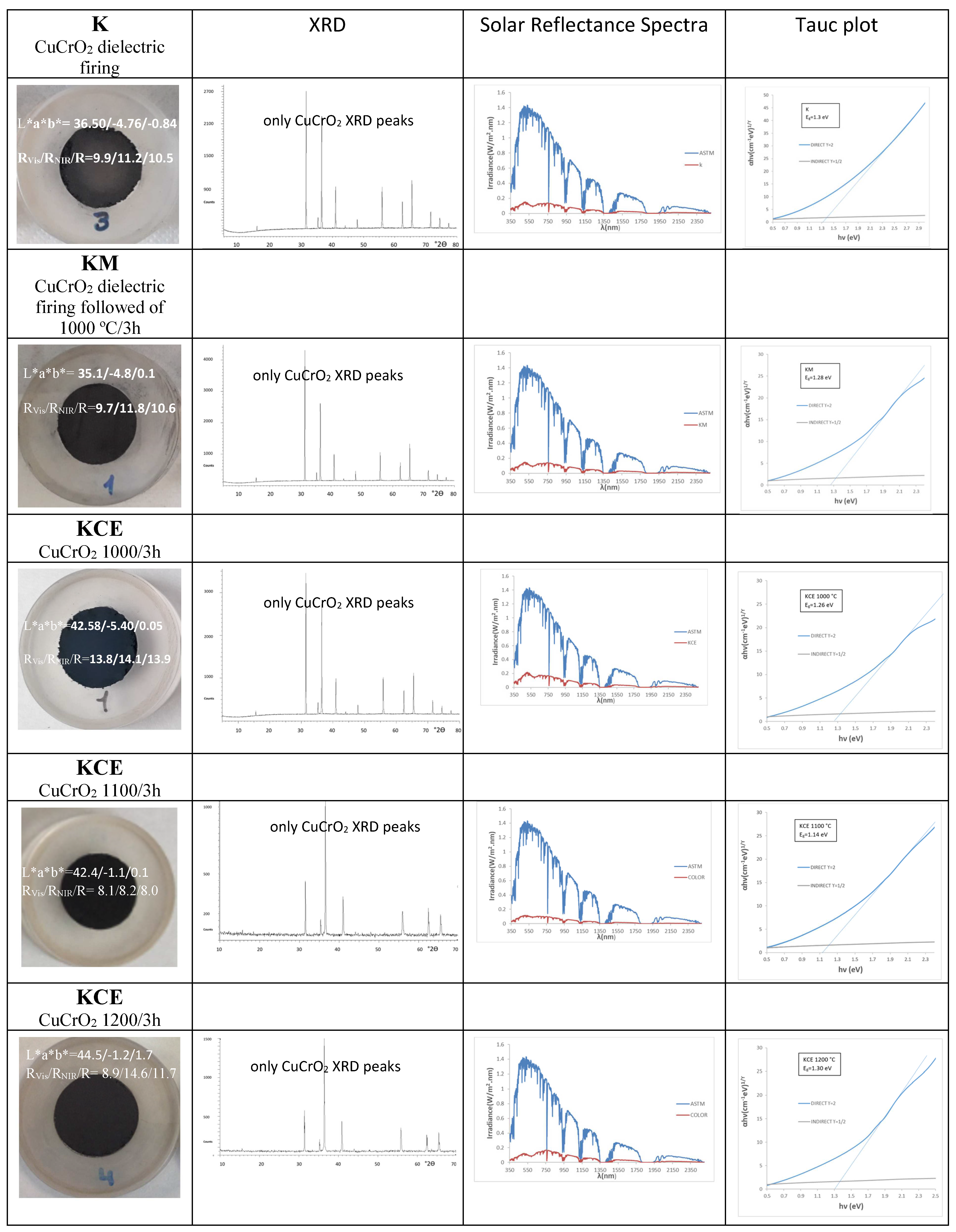
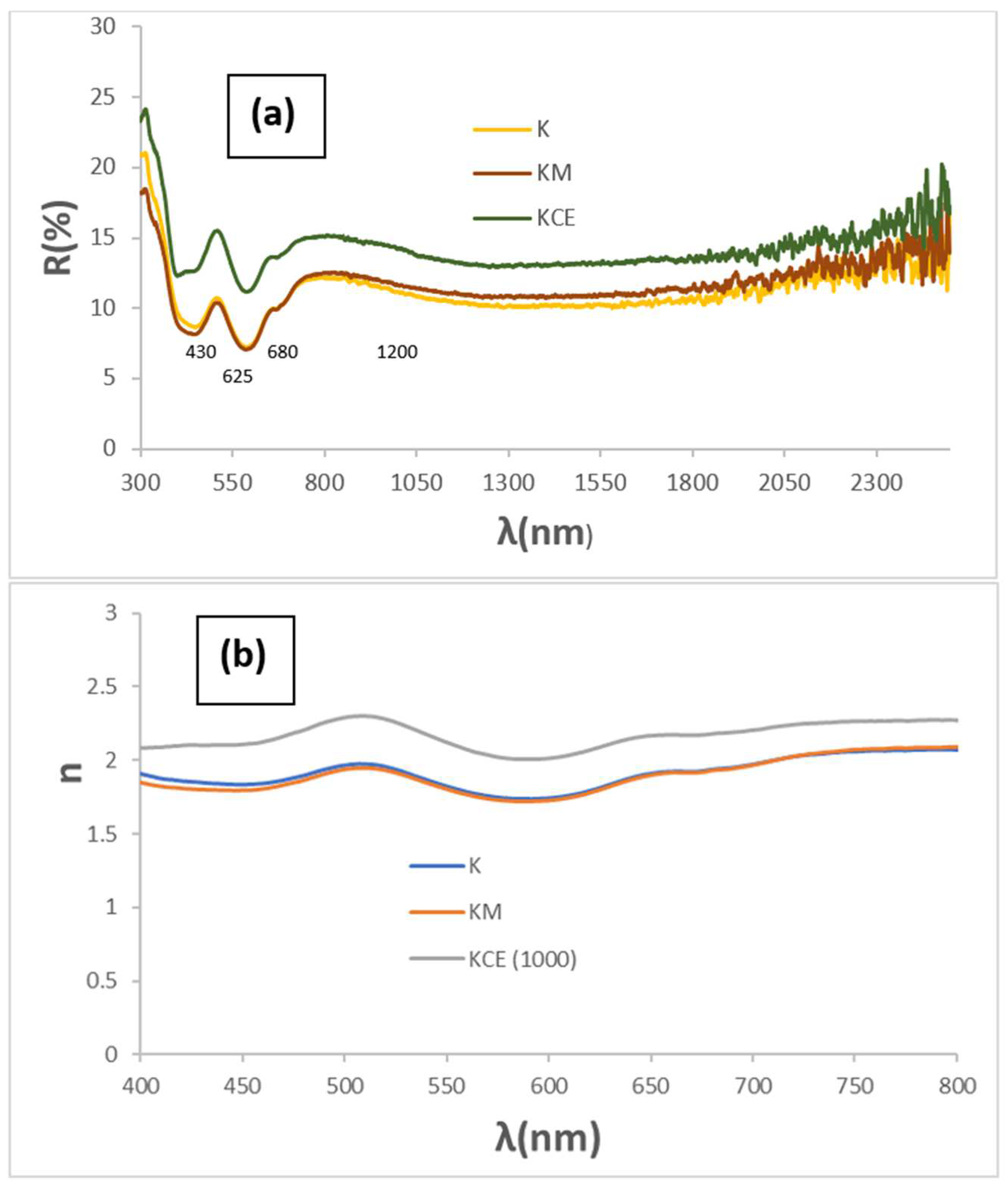
| Sample | L*a*b* | RVis/RNIR/R (%) | ΔE* | C* | h | α | ε100 | Eg (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Powders | ||||||||
| K microwaves firing | 36.5/−4.8/−0.8 | 9.9/11.2/10.5 | 17.0 | 4.9 | 189.5 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 1.30 |
| KM microwaves firing plus 1000 °C/3 h | 35.1/−4.8/0.1 | 9.7/11.8/10.6 | 15.7 | 4.8 | 178.8 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 1.28 |
| KCE electric kiln T(°C)/3 h | ||||||||
| 1000/3 h | 42.6/−5.4/0.1 | 13.8/14.1/13.9 | 23.1 | 5.4 | 178.9 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 1.26 |
| 1100/3 h | 42.4/−1.1/0.1 | 8.1/8.2/8.0 | 22.2 | 1.1 | 175.0 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 1.31 |
| 1200/3 h | 44.5/−1.2/1.7 | 8.9/14.6/11.7 | 24.4 | 2.1 | 125.2 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 1.30 |
| Glazed | ||||||||
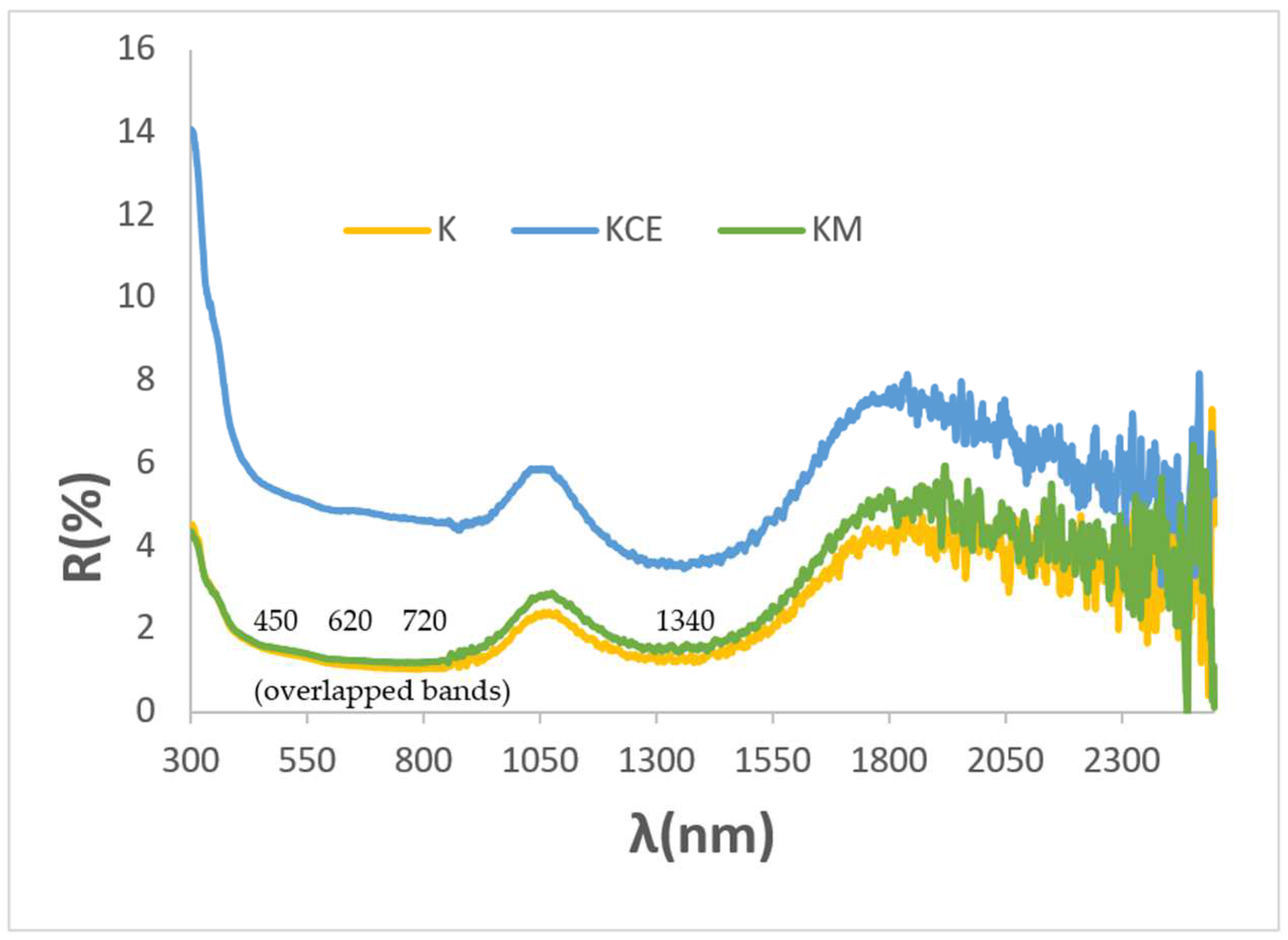
| K glazed with microwaves (Glaze 1000) | 23.5/−1.6/−0.4 | 3.9/6.2/4.9 | 3.7 | 1.7 | 166.0 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.87 |
| K glazed with electric kiln (Glaze 1000) | 11.3/−0.6/−3.0 | 1.4/1.9/1.6 | 9.5 | 3.1 | 78.7 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.93 |
| KM (Glaze 1000) | 11.8/−0.6/−2.5 | 1.5/2.2/1.8 | 8.8 | 2.6 | 76.5 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.95 |
| KCE | ||||||||
| Glaze 1000 | 26.9/−0.1/−2.3 | 5.3/5.0/5.2 | 7.2 | 2.3 | 87.5 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 1.00 |
| Glaze 1050 | 44.2/−4.8/−8.91 | 6.3/7.5/6.9 | 26.0 | 10.1 | 118 | 0.91 | 0.69 | 0.59 |
| Glaze 1190 | 37.6/−2.9/1.5 | 6.7/15.9/11.2 | 17.7 | 3.3 | 27.4 | 0.89 | 0.49 | 0.63 |
| CuO | 25.8/0.3/−2.4 | 5.1/21.2/12.2 | 6.3 | 2.41 | 83.1 | 0.89 | 0.69 | 1.40 |
| Carbon Black (powder) | 20.2/0.1/0.1 | 3/3/3 | 0.14 | 45 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.40 |
| Sample | L*a*b* | RVis/RNIR/R (%) | ΔE* | C* | h | α | ε100 | Eg (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glazed 1050 | 44.2/−4.8/−8.91 | 6.3/7.5/6.9 | 26.0 | 10.1 | 118 | 0.91 | 0.69 | 0.59 |
| 5 wt.% Q | 40.9/−2.9/−3.1 | 5.7/9.0/7.3 | 21.2 | 4.2 | 46.0 | 0.92 | 0.66 | 0.59 |
| 10 wt.% Q | 41.2/−3.1/−3.5 | 5.6/9.4/7.5 | 21.6 | 4.7 | 48.5 | 0.92 | 0.63 | 0.60 |
| 5 wt.% Anat | 44.1/−4.0/−4.2 | 7.1/9.8/8.4 | 24.5 | 5.8 | 46.4 | 0.92 | 0.62 | 0.61 |
| 10 wt.% Anat | 45.6/−4.7/−4.3 | 7.6/10.6/9.1 | 26.2 | 6.4 | 42.5 | 0.91 | 0.56 | 0.62 |
| Sample | L*a*b* | RVis/RNIR/R (%) | ΔE* | C* | h | α | ε100 | Eg (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undoped powder | 42.4/−1.1/0.1 | 8.1/8.2/8.0 | 22.2 | 1.1 | 175.0 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 1.31 |
| La | 42.8/−0.2/0.9 | 5.6/5.5/5.6 | 22.6 | 0.9 | 102.5 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.95 |
| Ce | 44.0/−0.4/0.0 | 8.0/7.0/7.5 | 23.8 | 0.4 | 180.0 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 1.00 |
| Pr | 44.1/−0.2/−0.2 | 5.2/4.8/5.0 | 23.9 | 0.3 | 135.0 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| Glazed 1050 | 44.2/−4.8/−8.91 | 6.3/7.5/6.9 | 26.0 | 10.1 | 118.0 | 0.91 | 0.69 | 0.59 |
| La | 36.7/−3.2/1.3 | 2.9/11.2/7.0 | 13.9 | 3.5 | 158.0 | 0.93 | 0.54 | 0.62 |
| Ce | 36.4/−3.6/1.3 | 4.9/12.9/8.8 | 16.7 | 3.8 | 160.1 | 0.91 | 0.51 | 0.63 |
| Pr | 36.9/−3.6/1.7 | 3.3/12.4/7.7 | 17.2 | 4.0 | 154.7 | 0.92 | 0.52 | 0.63 |
| Sample | a (Å) | α (°) | V (Å3) | ΔV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undoped powder | 8.172 | 20.09 | 56.327 | reference |
| La | 8.281 | 19.81 | 57.032 | 1.2 |
| Ce | 8.207 | 19.97 | 56.432 | 0.2 |
| Pr | 8.195 | 19.99 | 56.271 | −0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monrós, G.; Badenes, J.A.; Delgado, C.; Monrós-Andreu, G.; Llusar, M. New Mcconnellite Ceramic Pigment as a Selective Solar Absorber: Effects of Microwave Firing and Rare Earth Doping. Materials 2025, 18, 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071520
Monrós G, Badenes JA, Delgado C, Monrós-Andreu G, Llusar M. New Mcconnellite Ceramic Pigment as a Selective Solar Absorber: Effects of Microwave Firing and Rare Earth Doping. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071520
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonrós, Guillermo, José Antonio Badenes, Carolina Delgado, Guillem Monrós-Andreu, and Mario Llusar. 2025. "New Mcconnellite Ceramic Pigment as a Selective Solar Absorber: Effects of Microwave Firing and Rare Earth Doping" Materials 18, no. 7: 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071520
APA StyleMonrós, G., Badenes, J. A., Delgado, C., Monrós-Andreu, G., & Llusar, M. (2025). New Mcconnellite Ceramic Pigment as a Selective Solar Absorber: Effects of Microwave Firing and Rare Earth Doping. Materials, 18(7), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071520









