Technology and Electrophysical Properties of PZT-Type Ceramics Doped by Samarium
Highlights
- Complex doping of PZT material was applied and the influence of samarium Sm dopant on PZT properties was investigated.
- A positive influence of samarium doping in the base composition on the functional parameters of PZT-type material was demonstrated.
- PZT-type materials exhibit high permittivity values with simultaneous low dielectric loss factor values and low DC electrical conductivity.
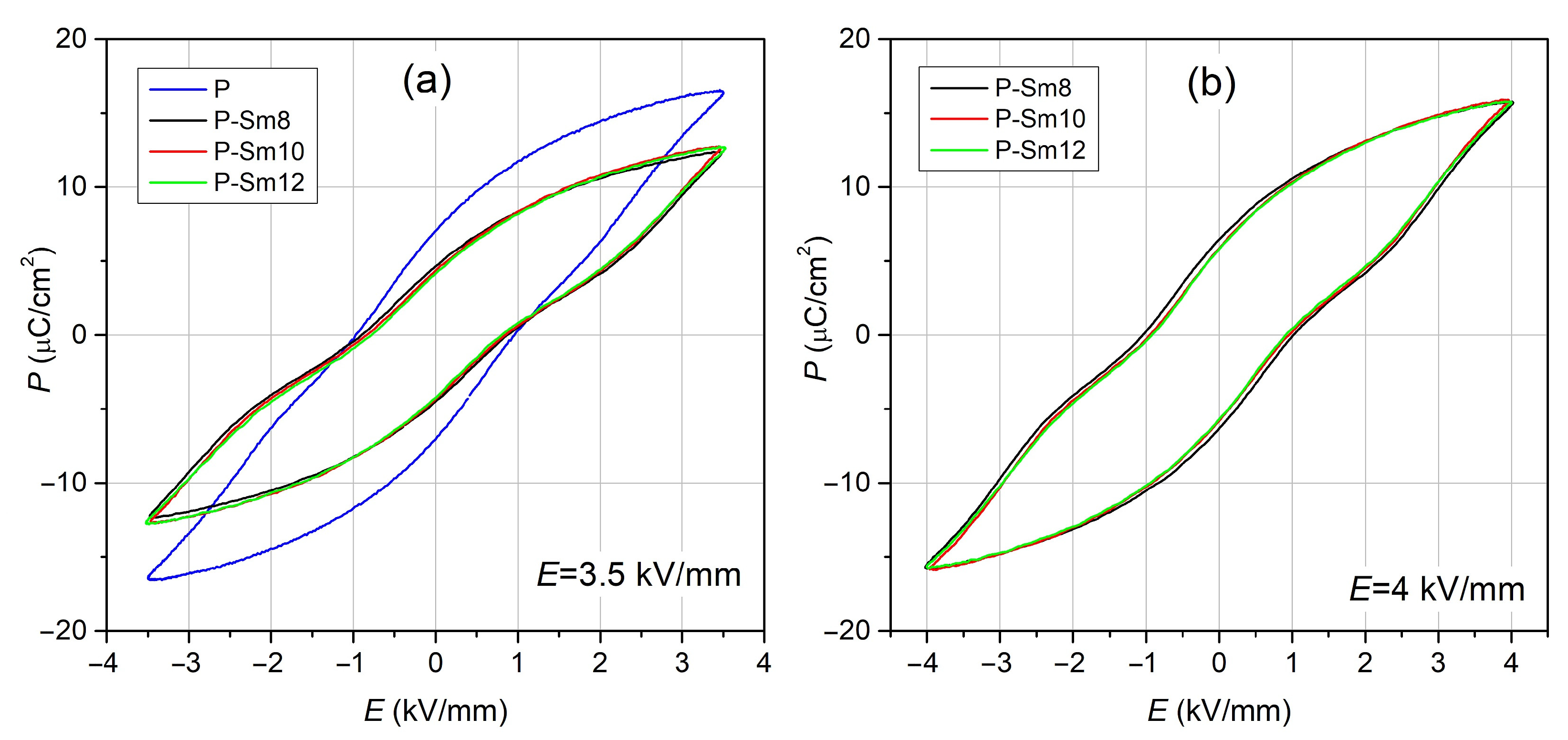
- P-E hysteresis measurement confirmed the ferroelectric nature of PZT-type materials with high maximum polarization values.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material and Technological Process
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Measurement
3.2. Microstructure Measurement
3.3. Dielectric Tests
3.4. DC Conductivity Test
3.5. Ferroelectric Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panda, P.K.; Sahoo, B. PZT to lead free piezo ceramics: A review. Ferroelectrics 2015, 47, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Murakami, K.; Sugiyama, O.; Kaneko, S. Piezoelectric properties, densification behavior and microstructural evolution of low temperature sintered PZT ceramics with sintering aids. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 21, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.J.; Kungl, H. High strain lead-based perovskite ferroelectrics. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2004, 8, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endriss, A.; Hammer, M.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Kolleck, A.; Schneider, G.A. Microscopic and macroscopic ferroelectric-ferroelastic and piezoelectric behavior of PZT ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 19, 1229–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dong, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Cao, F.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H. Dynamic hysteresis and scaling behavior for Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 124103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, K.; Ravichandran, G. Ferroelectric perovskites for electromechanical actuation. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 5941–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Zachariasz, R. Structure and physical properties of PZT-type ceramics with cadmium and tungsten dopands. Phase Transit. 2015, 88, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zuo, R. Giant electrostrains accompanying the evolution of a relaxor behavior in Bi(Mg,Ti)O3–PbZrO3–PbTiO3 ferroelectric ceramics. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 3687–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.; Kumar Singh, A.; Baik, S. Stability of ferroic phases in the highly piezoelectric Pb(ZrxTi1−x)O3 ceramics. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 2008, 64, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitko, R.; Zawisza, B.; Jurczyk, J.; Bochenek, D.; Płońska, M. Multielement XRF semimicroanalysis of Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 type ferroelectric ceramic materials doped with Pb(Nb,Mn)O3 and Bi2O3 by the thin layer method. Microchim. Acta 2004, 144, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haertling, G. Ferroelectric ceramics: History and technology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 797–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, B.; Cook, W.R., Jr.; Jaffe, H. Piezoelectric Ceramics; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Schierholz, R.; Fuess, H.; Tsuda, K.; Ogata, Y.; Terauchi, M.; Theissmann, R. Crystal symmetry in single domains of PbZr0.54Ti0.46O3. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 024118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.R.; Senos, A.M.R.; Mantas, P.Q. Phase coexistence region and dielectric properties of PZT ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 20, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Singhi, A.P.; Pandey, D. Thermodynamic nature of phase transitions in Pb(ZrxTi1−x)O3 ceramics near the morphotropic phase boundary. I. Structural studies. Philos. Mag. 1997, 76, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, L.A.; Schönau, K.A.; Theissmann, R.; Fuess, H.; Kungl, H.; Hoffmann, M.J. Composition dependence of the domain configuration and size in ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 074107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noheda, B.; Cox, D.E.; Shirane, G.; Guo, R.; Jones, B.; Cross, L.E. Stability of the monoclinic phase in the ferroelectric perovskite PbZr1−xTixO3. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 63, 014103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasatkhetragarn, A.; Yimnirun, R. Phase formation, electrical properties and morphotropic phase boundary of 0.95Pb(ZrxTi1−x)O3–0.05Pb(Mn1/3Nb2/3)O3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, S91–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theissmann, R.; Schmitt, L.A.; Kling, J.; Schierholz, R.; Schönau, K.A.; Fuess, H.; Knapp, M.; Kungl, H.; Hoffmann, M.J. Nanodomains in morphotropic lead zirconate titanate ceramics: On the origin of the strong piezoelectric effect. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 024111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Cross, L.E.; Park, S.-E.; Noheda, B.; Cox, D.E.; Shirane, G. Origin of the high piezoelectric response in PbZr1−xTixO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 5423–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, K. (Ed.) Piezoelectric Actuators and Ultrasonic Motors; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y. Ferroelectric Materials and Their Applications; Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Tzou, H.S.; Lee, H.-J.; Arnold, S.M. Smart materials, precision sensor/actuators, smart structures, and structronic systems. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struc. 2004, 11, 367–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.-Y.; Chen, T.-Y.; Tsai, I.-T.; Water, W. Doping effects of Nb additives on the piezoelectric and dielectric properties of PZT ceramics and its application on SAW device. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2004, 113, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, E.; Guiffard, B.; Lebrun, L.; Guyomar, D. Effects of Zr/Ti ratio on structural, dielectric and piezoelectric properties of Mn- and (Mn, F)-doped lead zirconate titanate ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2006, 32, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.P.; Wolf, R.A., Jr.; Wang, Y.; Deng, K.; Zou, L.; Davis, R.J.; Troiler-McKinstry, S. Design, fabrication, and measurement of high-sensitivity piezoelectric microelectromechanical systems accelerometers. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Wang, Q.M. High sensitivity piezoelectric sensors using flexible PZT thick-film for shock tube pressure testing. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 235, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcawich, R.G.; Scanlon, M.; Pulskamp, J.; Clarkson, J.; Conrad, J.; Washington, D.; Piekarz, R.; Trolier-McKinstry, S.; Dubey, M. Design and fabrication of a lead zirconate titanate (PZT) thin film acoustic sensor. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2003, 54, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, L. Design and analysis of a PZT-based micromachined acoustic sensor with increased sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2005, 52, 1840–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, C.A.; Bhalla, A.S.; Shrout, T.R.; Cross, L.E. Classification and consequences of complex lead perovskite ferroelectrics with regard to B-site cation order. J. Mater. Res. 1990, 5, 829–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariasz, R.; Bochenek, D. Modified PZT ceramics as a material that can be used in micromechatronics. Eur. Phys. J. B 2015, 88, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khacheba, M.; Abdessalem, N.; Hamdi, A.; Khemakhem, H. Effect of acceptor and donor dopants (Na, Y) on the microstructure and dielectric characteristics of high Curie point PZT-modified ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dong, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Cao, F.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H. Identical scaling behavior of saturated dynamic hysteresis in rhombohedral lead zirconate titanate bulk ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 244101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.J.; Hammer, M.; Endriss, A.; Lupascu, D.C. Correlation between microstructure, strain behavior, and acoustic emission of soft PZT ceramics. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiec, P.; Skulski, R.; Bochenek, D.; Wawrzała, P. Diffused AFE/RFE/PE phase transitions in (Pb0.88Ba0.1La0.02)(Zr0.6Sn0.4−xTix)0.995O3 ceramics obtained from oxides and carbonates. Phase Transit. 2013, 86, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Niemiec, P.; Adamczyk, M.; Machnik, Z.; Dercz, G. Dielectric properties of the multicomponent PZT-type solid solution. Eur. Phys. J. B 2015, 88, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahia, S.C.; Das, P.R.; Choudhary, R.N.P. Ferroelectric studies for soft Gd-modified PZT ceramics. Phase Transit. 2018, 91, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, B.; Babu, T.; Choudhary, R.N.P. Dielectric response of Mn and Ce substituted PZT ferroelectric ceramics. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.-Y.; Ahn, J.-H.; Lee, W.-J.; Kim, H.-G. Electrical properties of Sb-doped PZT films deposited by d.c. reactive sputtering using multi-targets. Mater. Lett. 1998, 37, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.M.; Simoes, A.Z.; Zaghete, M.A.; Paiva-Santos, C.O.; Varela, J.A.; Longo, E. Synthesis and electrical characterization of tungsten doped Pb(Zr0.53Ti0.47)O3 ceramics obtained from a hybrid process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 103, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Carvajal, J. Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Physical B 1995, 192, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiec, P.; Bartkowska, J.A.; Brzezińska, D.; Dercz, G.; Stokłosa, Z. Electrophysical properties of the multiferroic PFN–ferrite composites obtained by spark plasma sintering and classical technology. Appl. Phys. A-Mater. 2020, 126, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayssi, C.; El-Kossi, S.; Dhahri, J.; Khirouni, K. Frequency and temperature-dependence of dielectric permittivity and electric modulus studies of the solid solution Ca0.85Er0.1Ti1–xCo4x/3O3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.1). RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 17139–17150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Mak, C.-L. Impedance spectroscopic characterization of fine-grained magnetoelectric Pb(Zr0.53Ti0.47)O3-(Ni0.5Zn0.5)Fe2O4 ceramic composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 513, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Xie, S.; Wu, B.; Tan, Z.; Jiang, L.; Xie, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Xiao, D.; Zhu, J. Influence of different lanthanide ions on the structure and properties of potassium sodium niobate based ceramics. Scr. Mater. 2020, 177, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.; Badapanda, T.; Singh, A.K.; Panigrahi, S. An approach for correlating the structural and electrical properties of Zr4+-modified SrBi4Ti4O15/SBT ceramic. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiec, P.; Bochenek, D.; Brzezińska, D. Effect of various sintering methods on the properties of PZT-type ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 35687–35698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhahri, R.; Tayari, F.; Haouas, A.; Alathlawi, H.J.; Albargi, H.B.; Elkenany, E.B.; Al-Syadi, A.M.; Sharma, N.; Lal, M.; Nassar, K.I. Crystal structural characteristics and optical and electrical properties of Bi-doped (Ba0.8Sr0.2)(Ti0.85Zr0.15)O3 perovskite ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2025, 36, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Dercz, G.; Chrobak, A. Electrical and magnetic properties of the BF–PFN solid solutions obtained by spark plasma sintering method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B-Adv. 2023, 295, 116625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barick, B.K.; Mishra, K.K.; Arora, A.K.; Choudhary, R.N.P.; Pradhan, D.K. Impedance and Raman spectroscopic studies of (Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 355402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.F.; Dawber, M. Oxygen-vacancy ordering as a fatigue mechanism in perovskite ferroelectrics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 3801–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.; Badole, M.; Vasavan, H.N.; Kumar, S. Influence of annealing environments on the conduction behaviour of KNN-based ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 18057–18066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagar, S.; Hooda, A.; Khasa, S.; Malik, M. Structural refinement, investigation of dielectric and magnetic properties of NBT doped BaFe12O19 novel composite system. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 826, 154214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, S. Decoding the fingerprint of ferroelectric loops: Comprehension of the material properties and structures. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbach, S.M.; Tybell, T.; Einarsrud, M.A.; Grande, T. Size-dependent properties of multiferroic BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 6478–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yao, Z.; Lai, D.; Guo, Q.; Pan, W.; Hao, H.; Cao, M.; Liu, H. Unexpectedly High Piezoelectric Response in Sm-doped PZT Ceramics Beyond the Morphotropic Phase Boundary Region. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 836, 155474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannigrahi, S.R.; Tay, F.E.H.; Yao, K.; Vhoudhary, R.N.P. Effect of rare earth (La, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Er and Yb) ion substitutions on the microstructural and electrical properties of sol-gel grown PZT ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, Y.; Shirsath, S.E.; Erdemi, H.; Meena, S.S.; Batoo, K.M.; Almessiere, M.A.; Baykal, A.; Thakur, A.; Shariq, M. Improvement in the dielectric, magnetic, ferroelectric, and magnetoelectric coupling attributes of BaTiO3/CoNb0.02Fe1.98O4 composite systems. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 22583–22598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
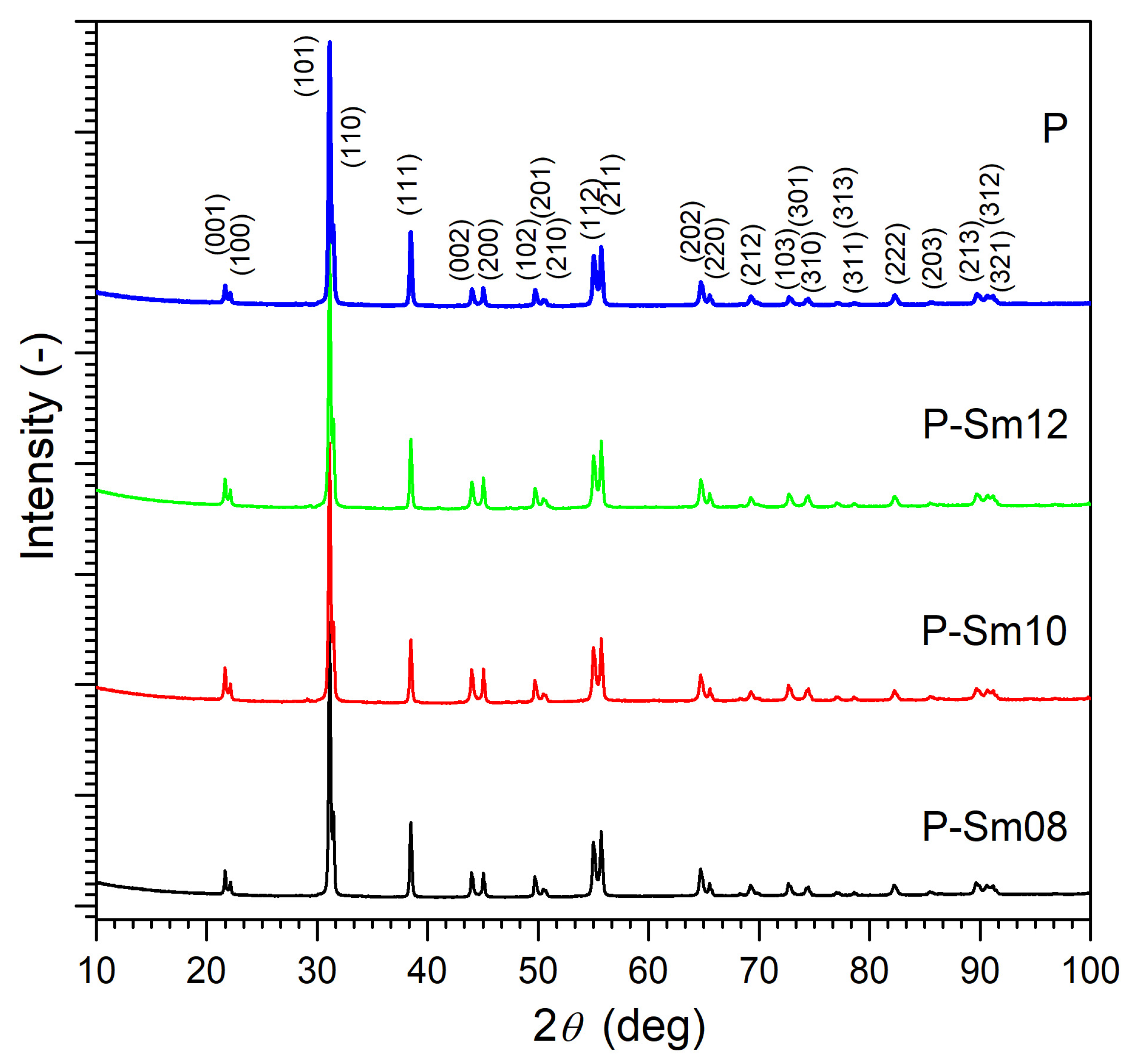
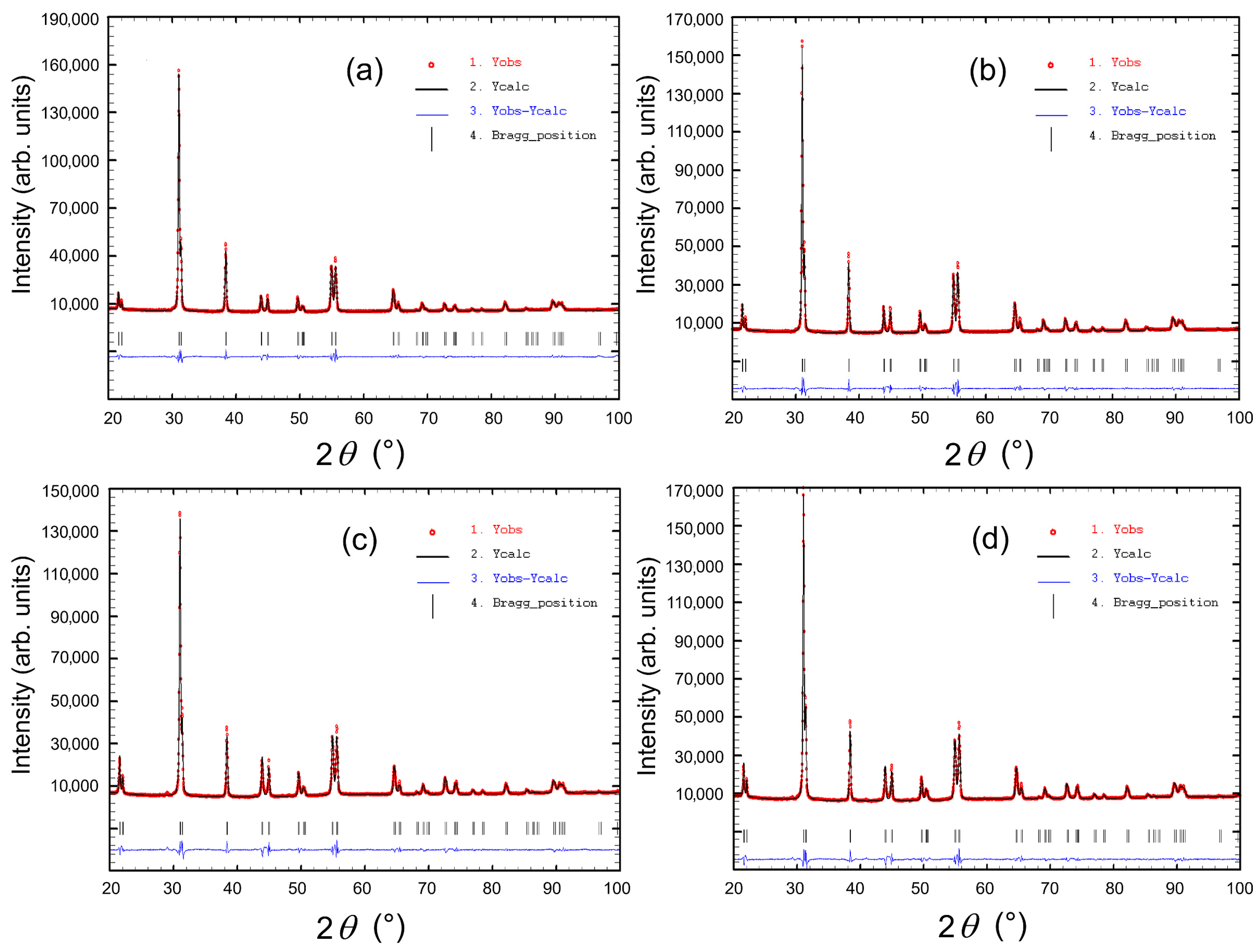
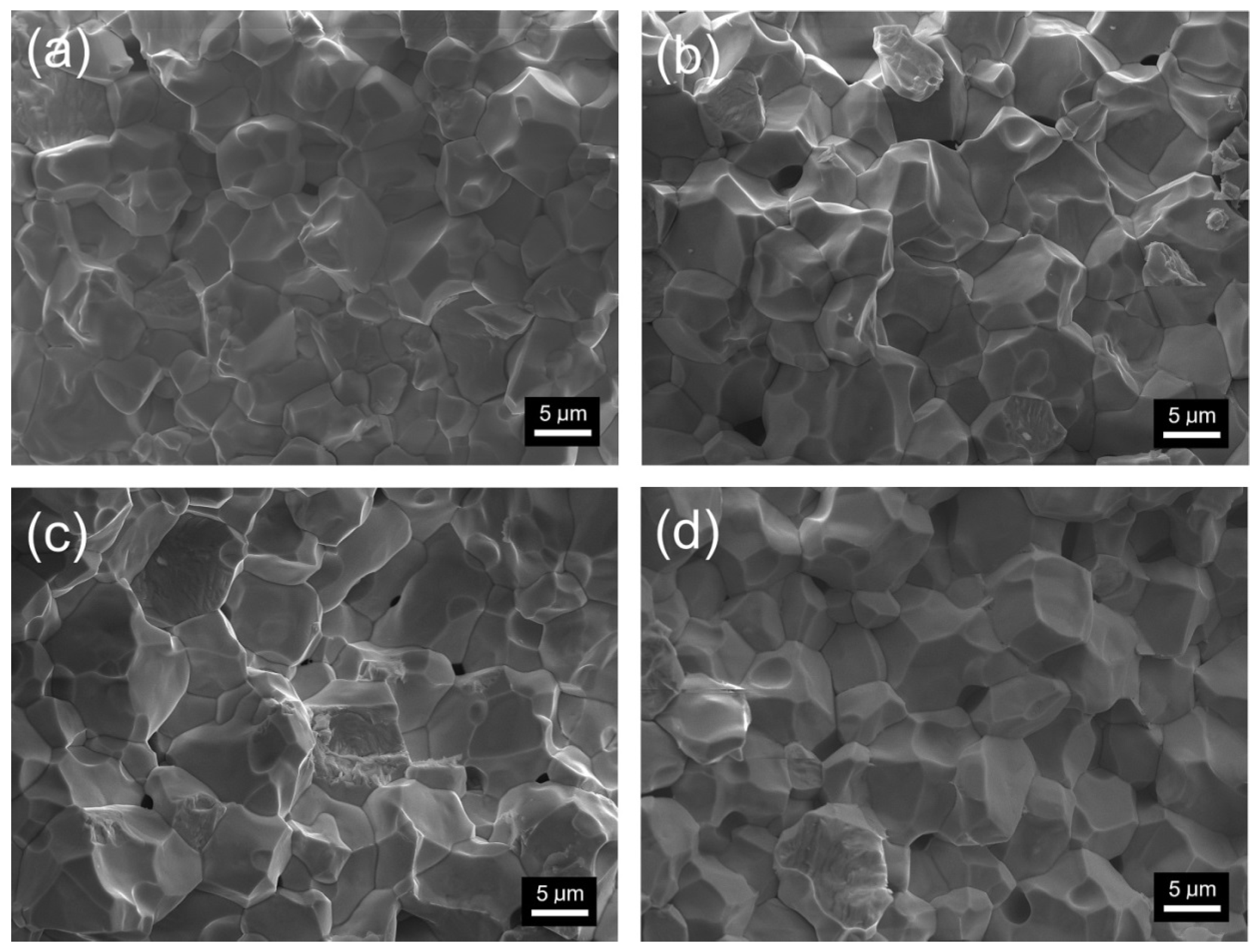
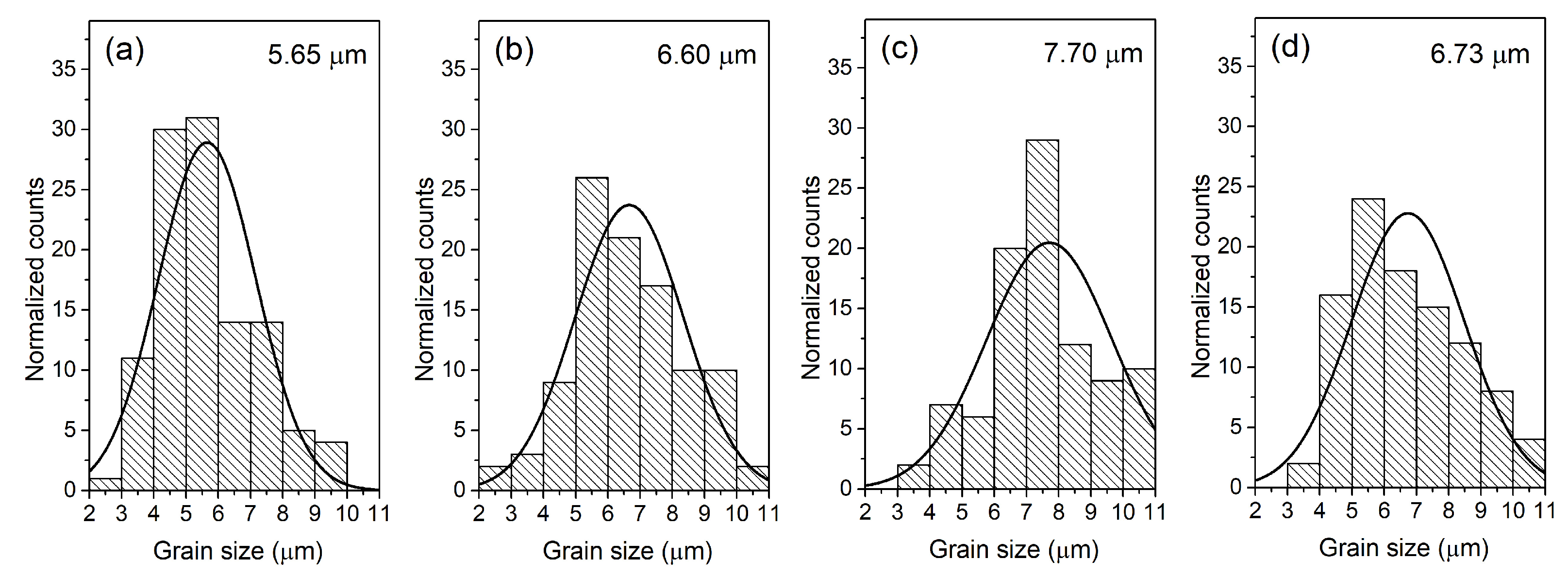
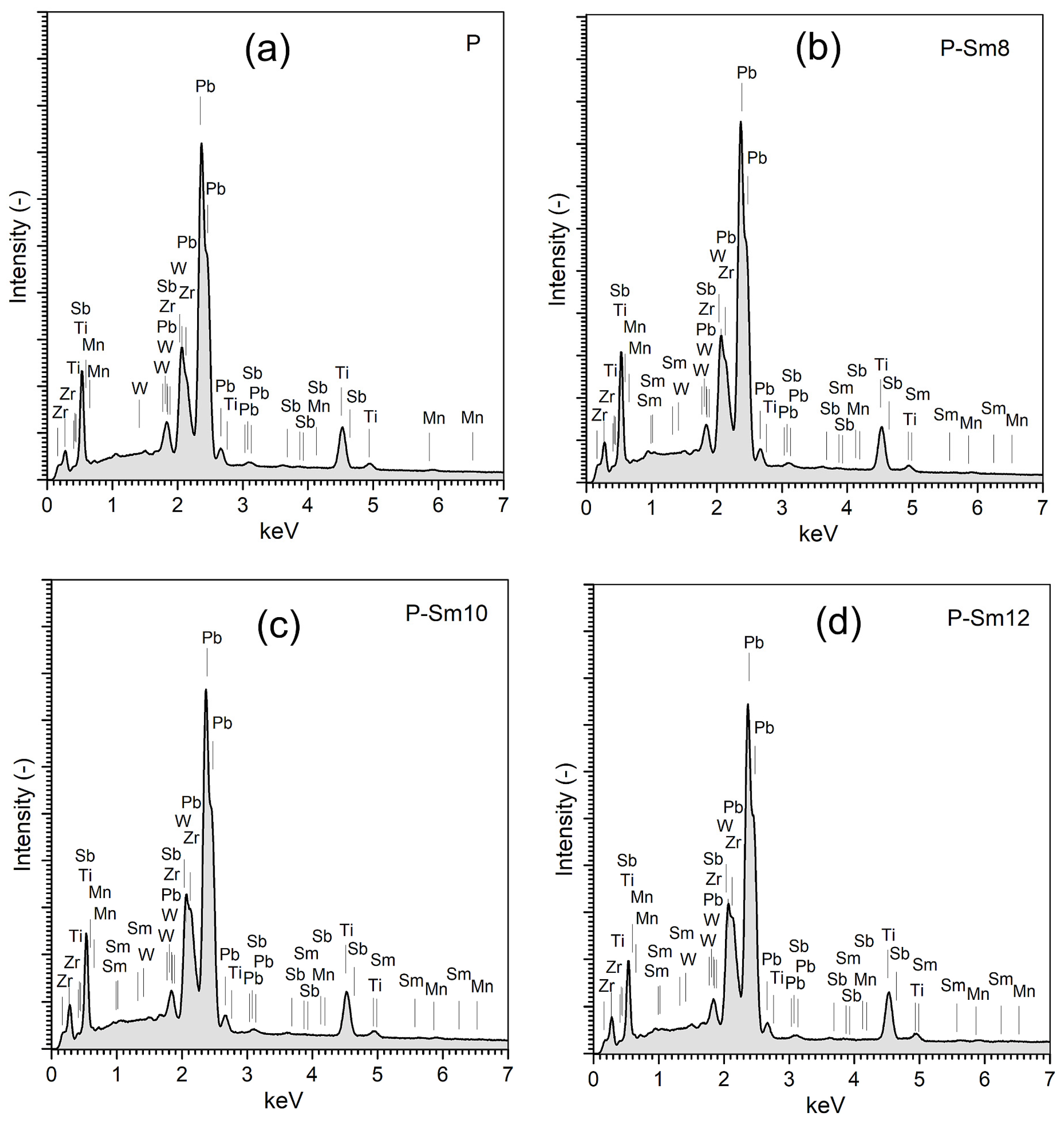
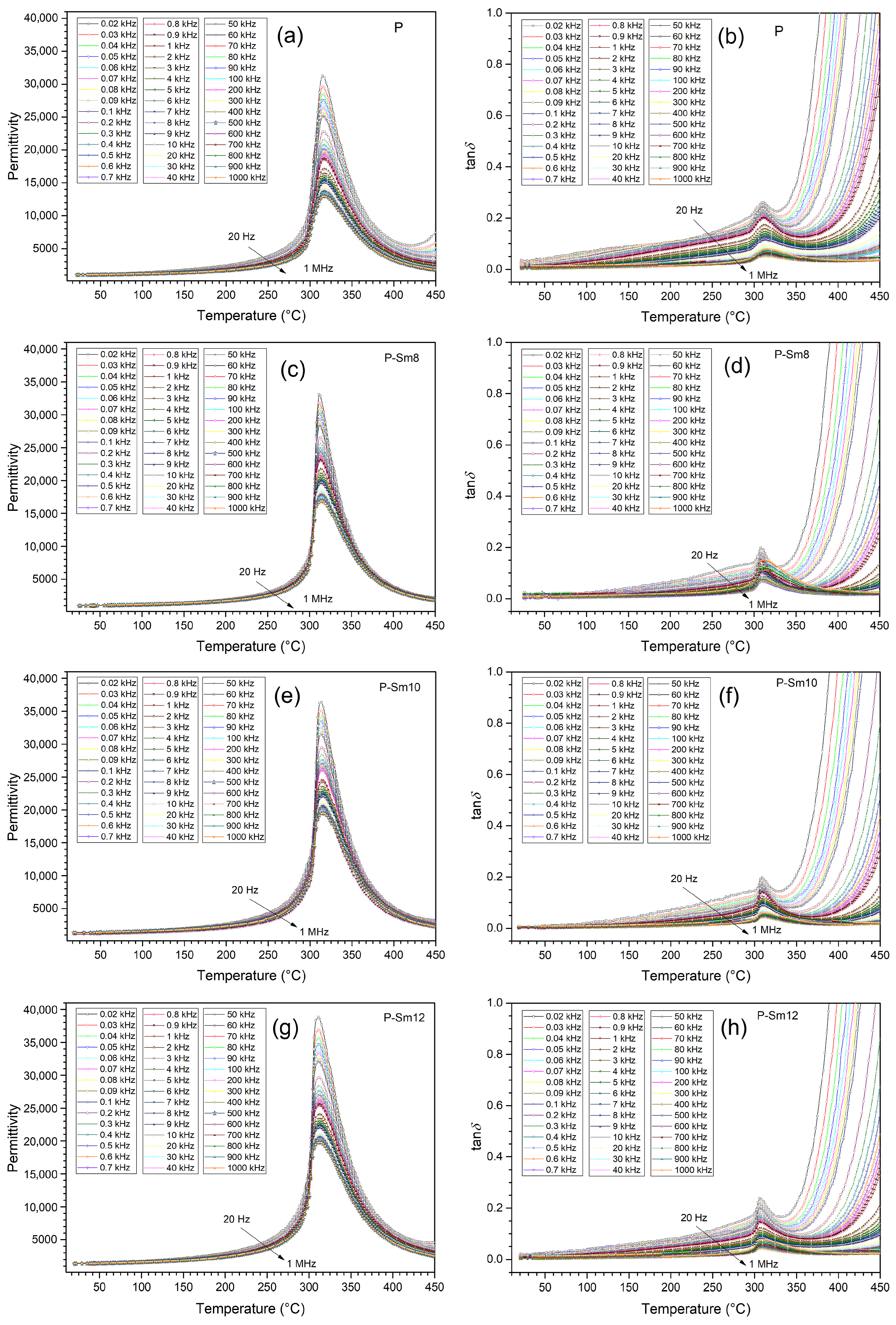
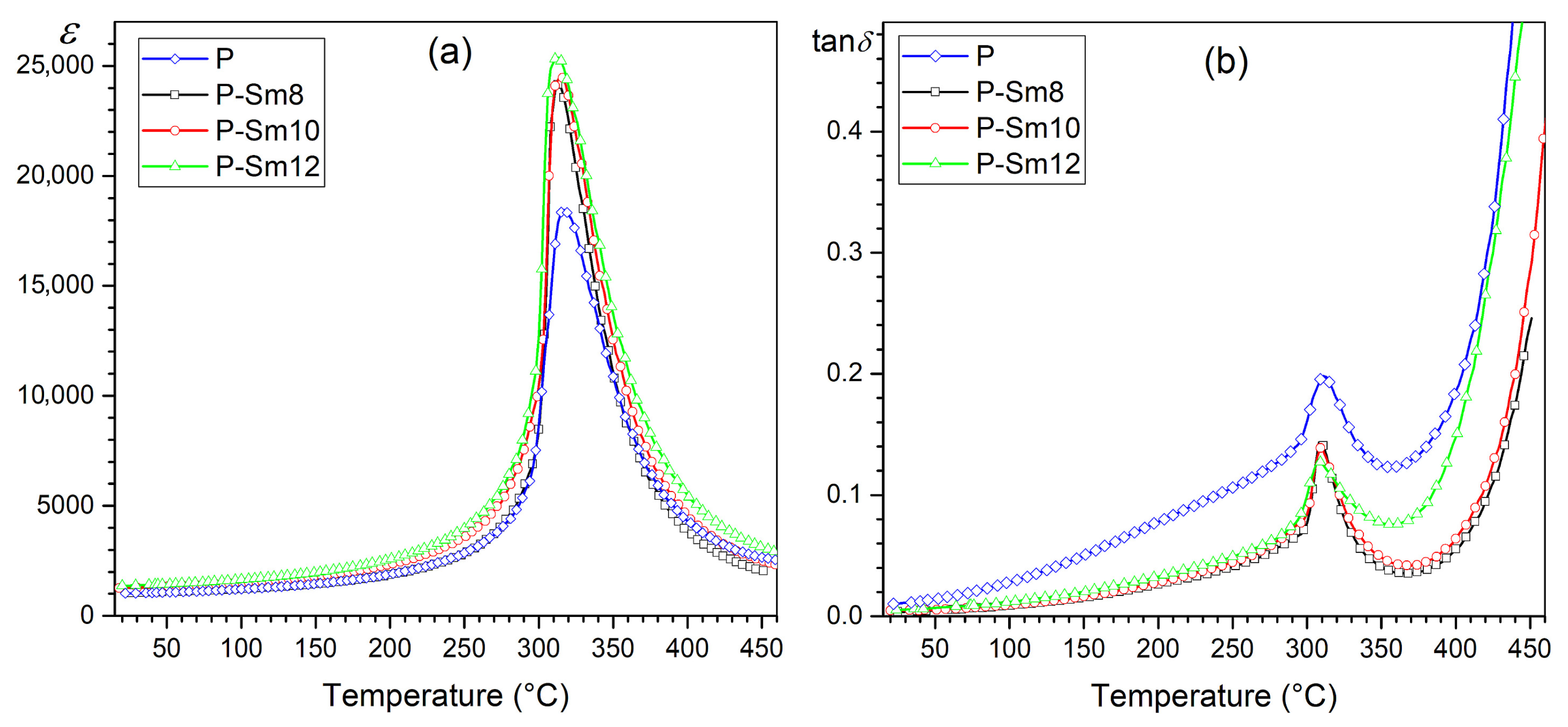
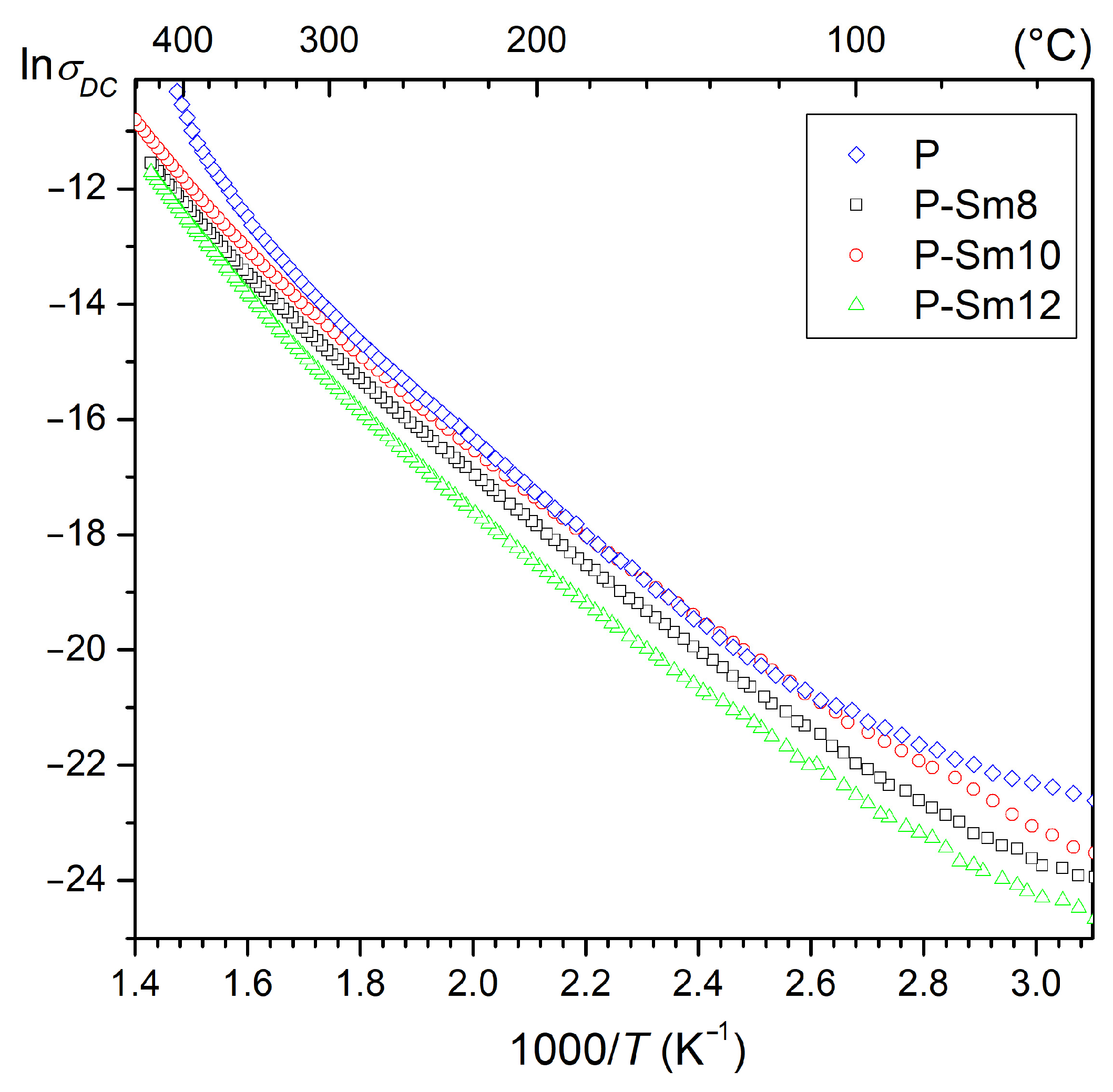
| Parameter | P | P-Sm8 | P-Sm10 | P-Sm12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lattice parameter a (Å) | 4.0336(1) | 4.0350(1) | 4.0334(1) | 4.0332(1) |
| Lattice parameter c (Å) | 4.1110(1) | 4.1244(1) | 4.1237(1) | 4.1219(1) |
| Lattice volume V (Å3) | 67.03(1) | 67.15(1) | 67.09(1) | 67.05(1) |
| Rp | 17.3 | 13.5 | 14.1 | 14.1 |
| Rwp | 12.3 | 11.6 | 12.5 | 12.0 |
| Chi2 | 12.2 | 11.2 | 12.5 | 13.8 |
| Oxide | P | P-Sm8 | P-Sm10 | P-Sm12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PbO | 74.41 | 73.59 | 73.35 | 72.47 |
| ZrO2 | 13.55 | 13.40 | 13.08 | 12.66 |
| TiO2 | 10.39 | 11.08 | 11.25 | 12.34 |
| MnO2 | 0.33 | 0.47 | 0.55 | 0.60 |
| Sb2O3 | 0.70 | 0.51 | 0.52 | 0.56 |
| Sm2O3 | - | 0.45 | 0.77 | 1.05 |
| WO3 | 0.62 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.33 |
| Parameters | P | P-Sm8 | P-Sm10 | P-Sm12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ (g/m3) | 7.33 | 7.02 | 7.15 | 7.22 | |
| ρDC (Ωm) at 50 °C | 4.91 × 109 | 1.75 × 1010 | 2.64 × 1010 | 5.45 × 1010 | |
| ε at RT | 1025 | 1040 | 1267 | 1365 | |
| Tm (°C) | 317 | 313 | 314 | 313 | |
| εm | 18,468 | 23,987 | 24,480 | 25,390 | |
| tanδ at RT | 0.011 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.005 | |
| tanδ at Tm | 0.188 | 0.132 | 0.138 | 0.121 | |
| Pr (μC/cm2) | for 4 kV/mm | - | 6.52 | 5.85 | 5.85 |
| for 3.5 kV/mm | 7.27 | 4.65 | 4.42 | 4.24 | |
| Pm (μC/cm2) | for 4 kV/mm | - | 15.8 | 15.9 | 15.9 |
| for 3.5 kV/mm | 16.45 | 12.38 | 12.70 | 12.72 | |
| Ec (kV/mm) | for 4 kV/mm | - | 1.03 | 0.97 | 0.92 |
| for 3.5 kV/mm | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.84 | 0.78 | |
| Ea < 300 °C (eV) | 0.71 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.65 | |
| Ea > 300 °C (eV) | 1.13 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 1.01 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bochenek, D.; Brzezińska, D.; Niemiec, P.; Zubko, M.; Osińska, K. Technology and Electrophysical Properties of PZT-Type Ceramics Doped by Samarium. Materials 2025, 18, 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081773
Bochenek D, Brzezińska D, Niemiec P, Zubko M, Osińska K. Technology and Electrophysical Properties of PZT-Type Ceramics Doped by Samarium. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081773
Chicago/Turabian StyleBochenek, Dariusz, Dagmara Brzezińska, Przemysław Niemiec, Maciej Zubko, and Katarzyna Osińska. 2025. "Technology and Electrophysical Properties of PZT-Type Ceramics Doped by Samarium" Materials 18, no. 8: 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081773
APA StyleBochenek, D., Brzezińska, D., Niemiec, P., Zubko, M., & Osińska, K. (2025). Technology and Electrophysical Properties of PZT-Type Ceramics Doped by Samarium. Materials, 18(8), 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081773






