Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Cementitious Composites Reinforced with Multi-Scale Carbon Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Ratio and Specimen Preparation
2.2.1. Mixing Ratios
2.2.2. Specimen Preparation
- (1)
- Specimen preparation process of CRCC with nano-scale fibrous materials
- (2)
- Specimen preparation process of CRCC with CFs
2.3. Performance Test Methods
2.3.1. Uniaxial Tensile Test
2.3.2. Conductivity Test
3. Results and Discussion
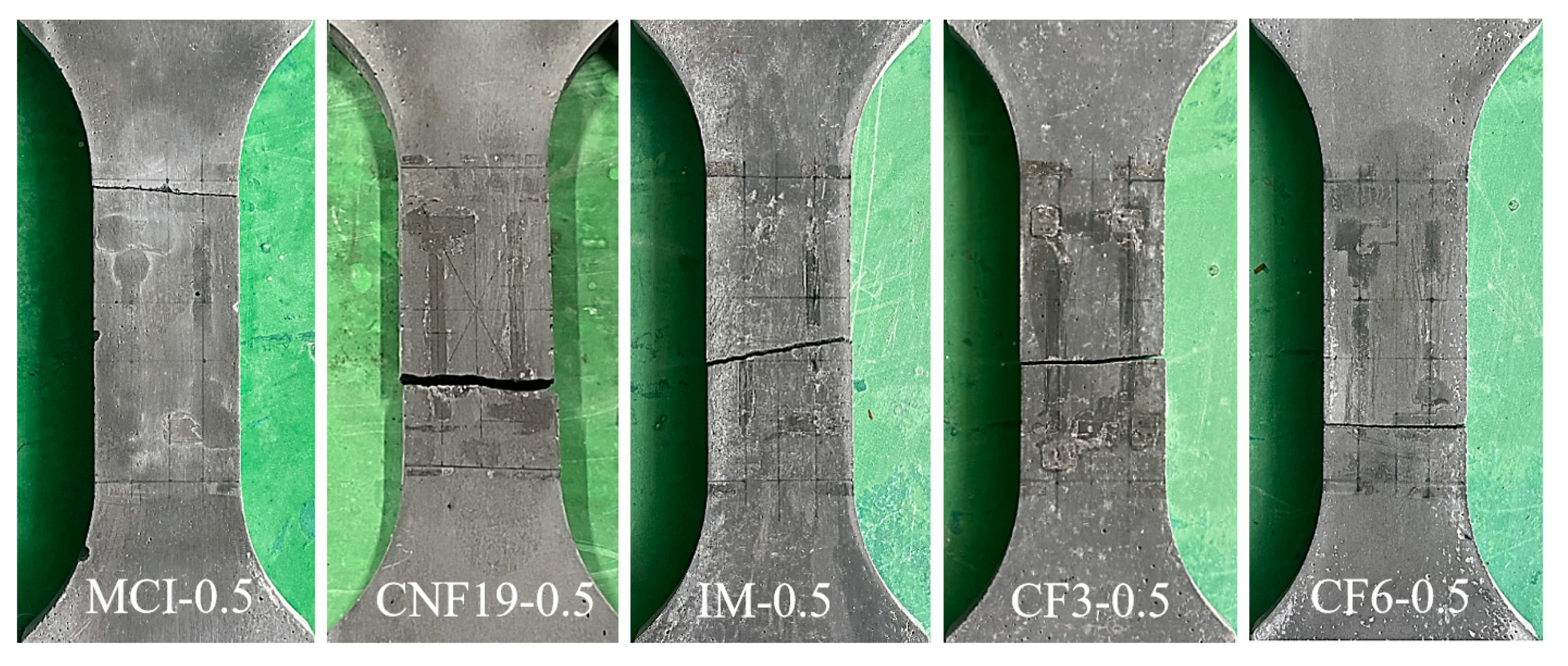
3.1. Modes of Failure
3.2. Stress–Strain Curves
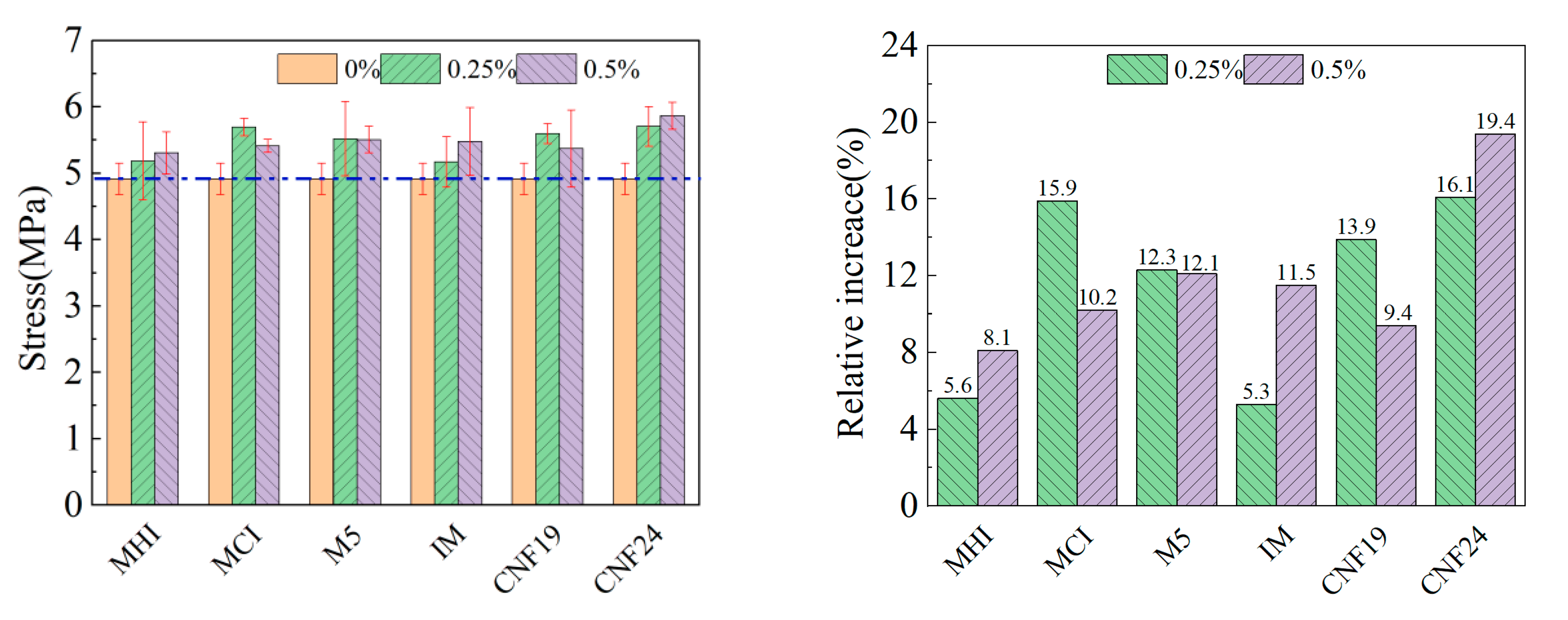
3.3. Uniaxial Tensile Strength
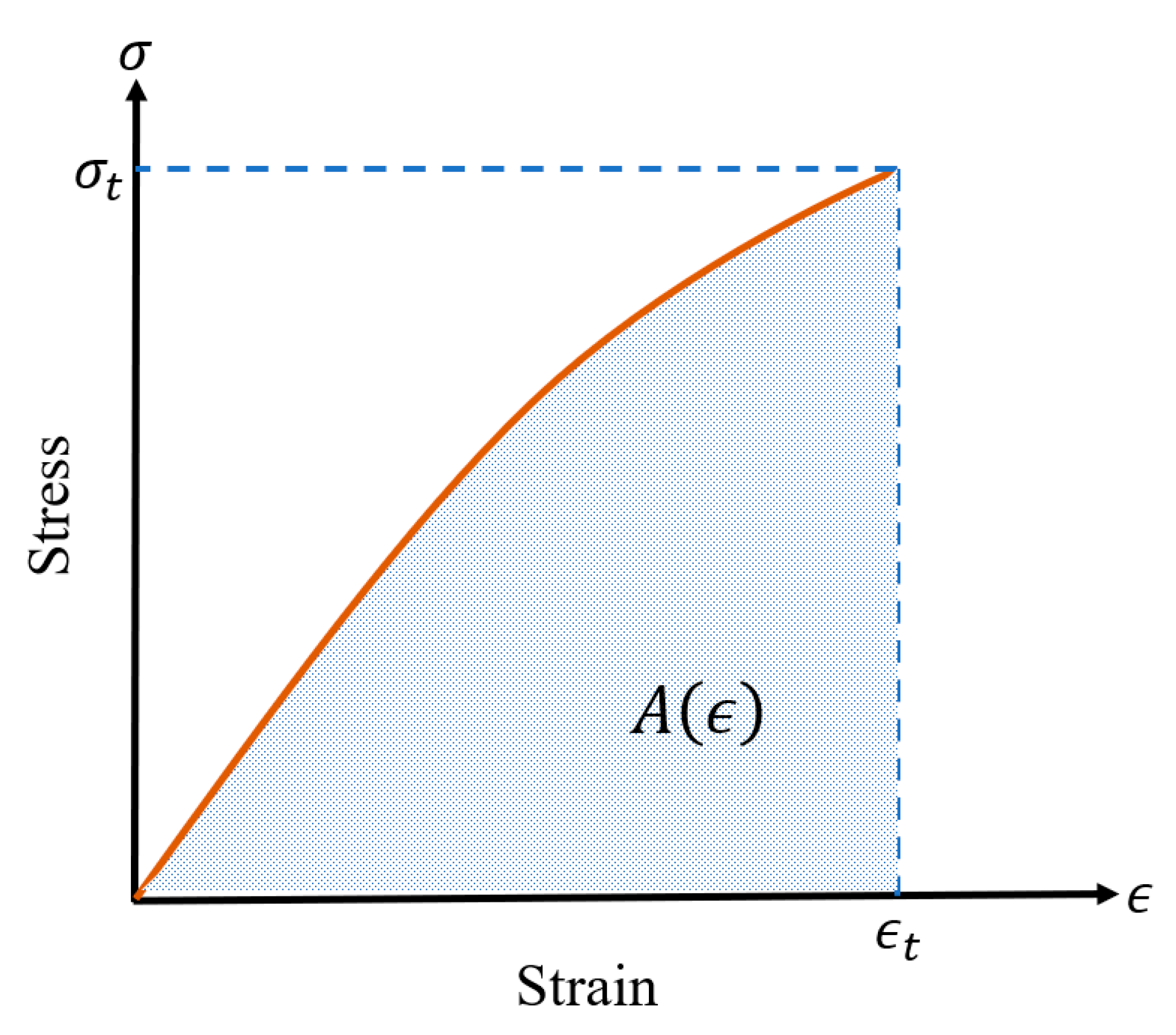
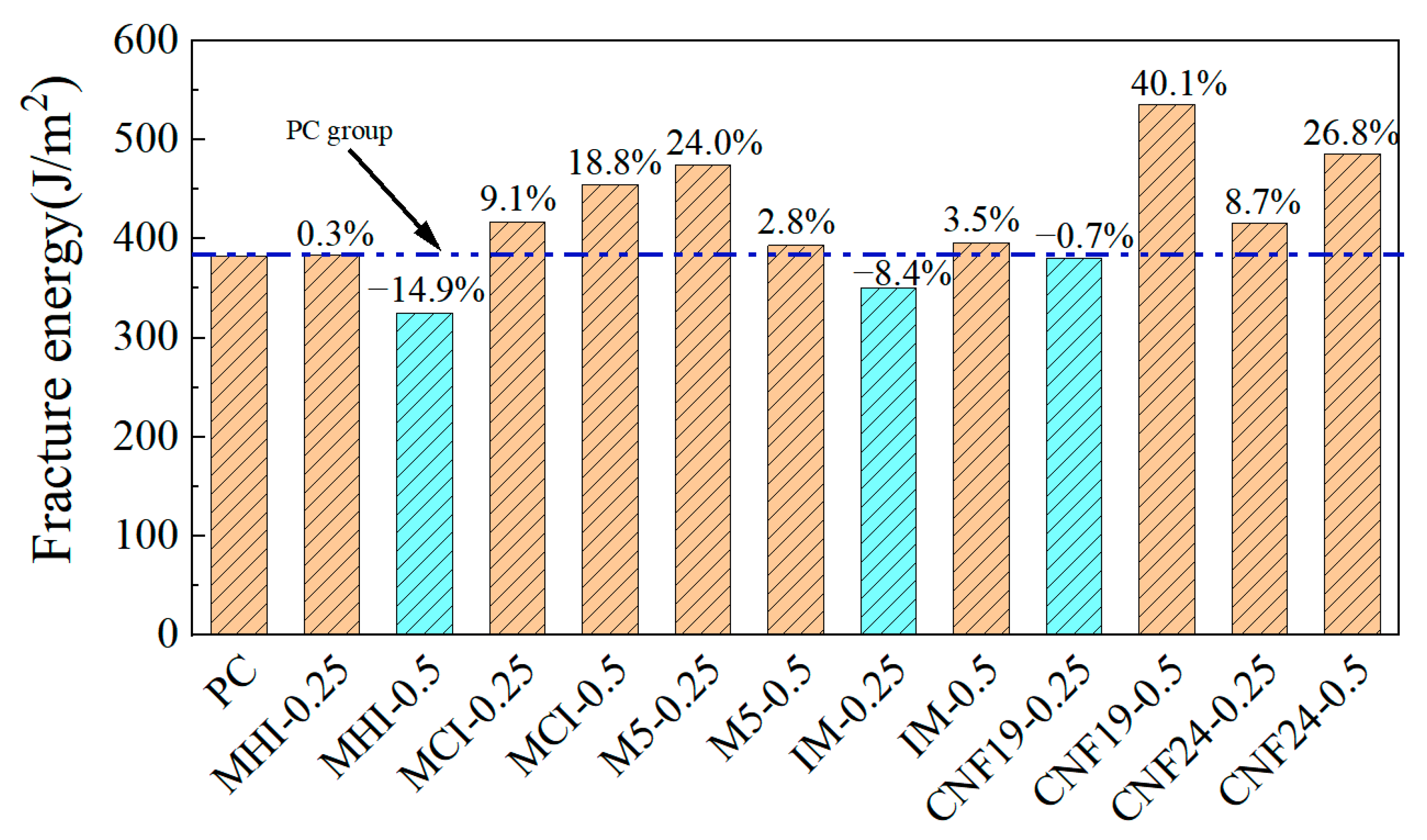
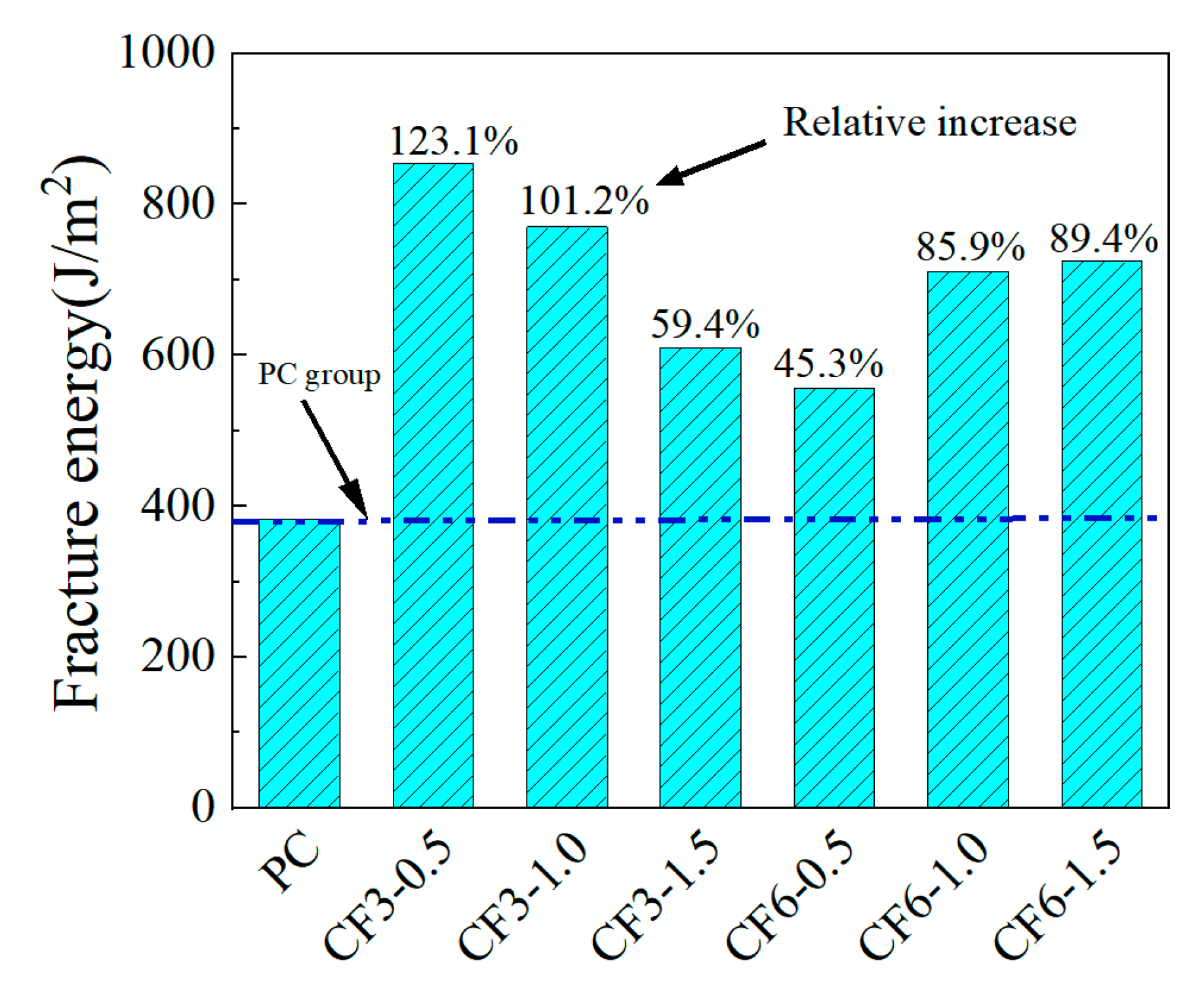
3.4. Fracture Strain Energy
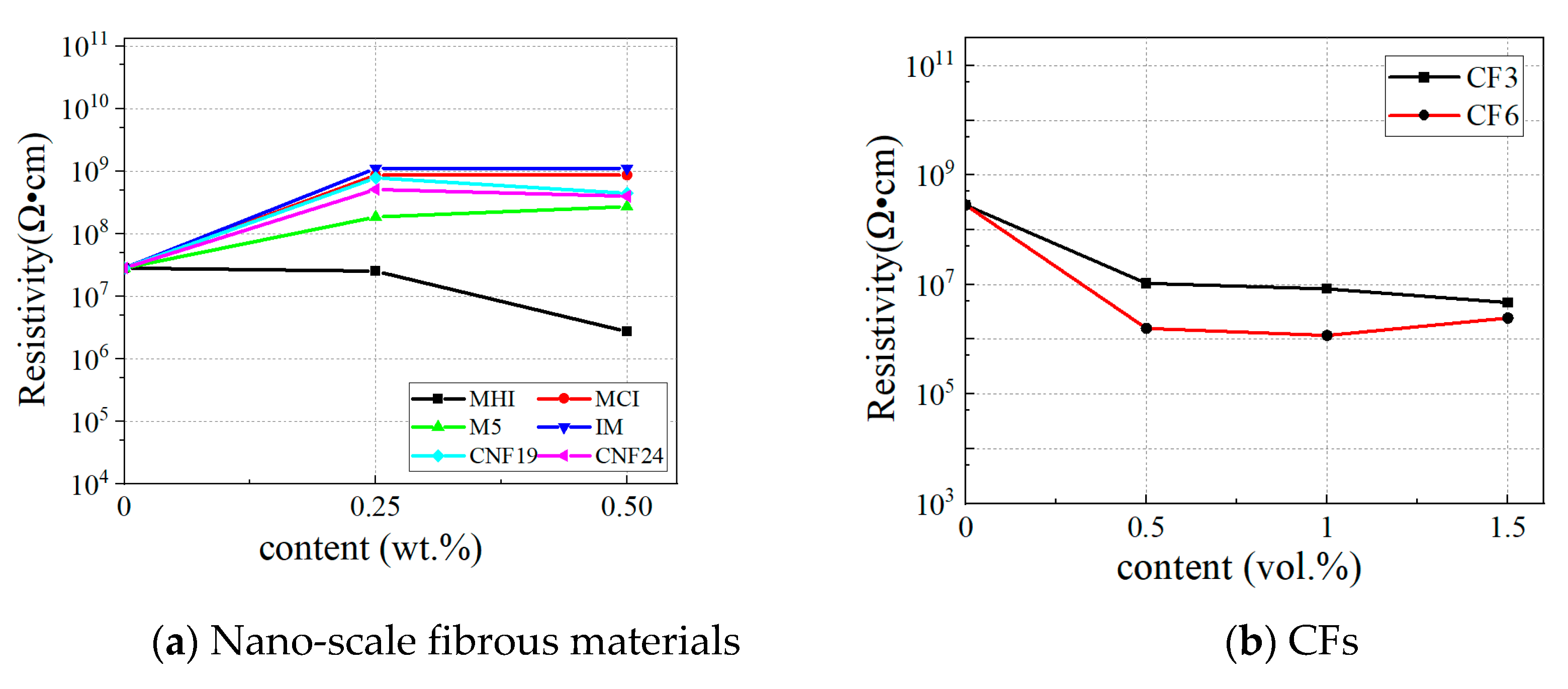
3.5. Conductivity
3.6. The Relationship Between Fracture Strain Energy and Electrical Conductivity
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- All of the MWCNTs, CNFs, and CFs can significantly enhance the uniaxial tensile strength of cementitious composites at a suitable dosage. The enhancement effect is closely related to the geometric dimensions of the nanofillers, gradually decreasing in the order of carbon nanotubes, carbon nanofibers, and short-cut carbon fibers.
- (2)
- There is a scaling effect in determining the fracture energy of cementitious composites in terms of strain by direct tensile test, and the larger the length of carbon fibers, the higher the fracture energy. The doping of macrofibers can significantly improve the uniaxial tensile fracture strain energy of cementitious composites, with a 0.5 vol.% incorporation of 3 mm-long short-cut carbon fibers having the most significant effect.
- (3)
- Compared with other carbon nanofibers, the elongated hydroxyl-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes are more likely to form an effective conductive network, thereby contributing to the enhancement of the electrical conductivity of a CRCC. The macro-short-cut carbon fibers have the most significant effect on enhancing the electrical conductivity of cementitious composites, and the longer the fibers, the more pronounced the improvement in resistivity. Additionally, the resistivity of cementitious composites displays a percolation phenomenon when short-cut carbon fibers are added within the range of 0.5 vol.% to 1.0 vol.%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, C.J.; He, W.; Wu, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhu, D.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, J. Research progress on the effect of fiber on the mechanical properties of UHPC. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 34, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.H.; Ma, Y.; Fu, J.; Hu, J.; Ouyang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H. Utilization of fibers in ultra-high performance concrete: A review. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2022, 241, 109995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Shi, C.J.; Wu, Z.M.; Zhang, C.H. Steel fiber-matrix interfacial bond in ultra-high performance concrete: A review. Engineering 2023, 22, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, I.; Mróz, K. Role of polypropylene fibres in concrete spalling risk mitigation in fire and test methods of fibres effectiveness evaluation. Materials 2019, 12, 3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Chen, W.Z.; Zhang, B.S.; Yu, J.J.; Liu, H. The mechanical properties and damage evolution of UHPC reinforced with glass fibers and high-performance polypropylene fibers. Materials 2021, 14, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchen, A.; Young, S.; Penumadu, D. An investigation of mechanical properties of recycled carbon fiber reinforced ultra-high-performance concrete. Materials 2023, 16, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollo, R.F. Fiber-reinforced concrete: An overview after 30 years of development. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1997, 19, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Fang, Z.; Wang, K. Design and behavior of super-long span cable-stayed bridge with CFRP cables and UHPC members. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2019, 164, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesoglu, M.; Güneyisi, E.; Muhyaddin, G.F.; Asaad, D.S. Strain hardening ultra-high performance fiber reinforced cementitious composites: Effect of fiber type and concentration. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2016, 103, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.P.; Sluijsmans, M.J.C.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Yu, Q.L. Functionally graded ultra-high performance cementitious composite with enhanced impact properties. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2020, 183, 107680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Dong, H.; Yao, W.; Wang, X.; Sun, W. Influence of fiber mixture on impact response of ultra-high-performance hybrid fiber reinforced cementitious composite. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2019, 163, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, C.Q.; Wu, P.T.; Li, Z.X. Influences of nano-particles on dynamic strength of ultra-high performance concrete. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2016, 91, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.D.L. Use polymers for cement-based structural materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 2973–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, J.K.; Wen, X.Y.; Hu, X.; Deng, Z.H. Mechanical properties and constitutive model of carbon fiber reinforced coral concrete under uniaxial compression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Li, Z.X.; Guo, J.; Gong, H.; Gu, C.P. Research progress on CNTs/CNFs-modified cement-based composites—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.N.; Wang, X.Y.; Qiu, L.S.; Ye, H.L.; Maimaitituersun, N.; Han, B.G. Effect of nickel-coated carbon nanotubes on the tensile behaviors of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): Insights from experiments and molecular dynamic simulations. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 17225–17240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, B.M.; Abu Al-Rub, R.K.; Yazdanbakhsh, A.; Grasley, Z. Carbon nanotubes and carbon nanofibers for enhancing the mechanical properties of nanocomposite cementitious materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Al-Rub, R.K.; Ashour, A.I.; Tyson, B.M. On the aspect ratio effect of multi-walled carbon nanotube reinforcements on the mechanical properties of cementitious nanocomposites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Wei, H.; Du, S.; Yan, J. Surface-treated carbon nanotubes in cement composites: Dispersion, mechanical properties and microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 310, 125262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Bogas, J.A.; Guedes, M.; Pereira, M.F.C. Dispersion and reinforcement efficiency of carbon nanotubes in cementitious composites. Mag. Concr. Res. 2019, 71, 408–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuaguluchi, O.; Panesar, D.K.; Sain, M. Properties of nanofibre reinforced cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 63, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Danoglidis, P.A.; Falara, M.G.; Nitodas, S.F. Fresh and mechanical properties, and strain sensing of nanomodified cement mortars: The effects of MWCNT aspect ratio, density and functionalization. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 82, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, J.; Thomas, B.S.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Nazar, S. Hybrid graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes reinforced cement paste: An investigation on hybrid ratio. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 119815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, F.; Hu, J.; Ren, M.; Wei, J.; Yu, Q. Enhanced mechanical properties of cement paste by hybrid graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, K.; Wang, R. Effect and mechanism of carbon nanotubes on the properties of polyacrylate/cement composite cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 443, 137687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrechea, S.; Guerrero-Gutiérrez, E.M.A.; Velásquez, L.; Cardona, J.; Posadas, R.; Callejas, K.; Torres, S.; Díaz, R.; Barrientos, C.; García, E. Effect of additions of multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNT, MWCNT-COOH, and MWCNT-Thiazol) in the mechanical compression properties of a cement-based material. Materialia 2020, 11, 100739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Wang, P.M.; Zhao, X. Mechanical behavior and microstructure of cement composites incorporating surface-treated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2005, 43, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.K.; Yu, J.; Li, G.Y.; Zhang, M.; Leung, C.K.Y. Corrosion behavior of steel rebar embedded in hybrid CNTs-OH/polyvinyl alcohol modified concrete under accelerated chloride attack. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 100, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Al-Rub, R.K.; Tyson, B.M.; Yazdanbakhsh, A.; Grasley, Z. Mechanical properties of nanocomposite cement incorporating surface-treated and untreated carbon nanotubes and carbon nanofibers. J. Nanomech. Micromech. 2012, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Xu, J.Y.; Meng, B.X.; Peng, G. Experimental study on the effect of carbon nanofiber content on the durability of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, H.R.; Khattak, M.J.; Madani, M.; Khattab, A. Piezoresistive response of conductive Hot Mix Asphalt mixtures modified with carbon nanofibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Danoglidis, P.A.; Shah, S.P. High modulus concrete: Effects of low carbon nanotube and nanofiber additions. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2019, 103, 102295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Batis, G.; Danoglidis, P.A.; Zacharopoulou, A.K.; Zacharopoulou, E.K.; Falara, M.G.; Shah, S.P. Effect of CNT and CNF loading and count on the corrosion resistance, conductivity, and mechanical properties of nano modified OPC mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, B.; Hubler, M.H. Carbon nanofibers (CNFs) dispersed in ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): Mechanical property, workability and permeability investigation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 131, 104592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.J.; Wang, H.; Li, S.X.; Lu, L.; Mo, Y.L. Piezoresistive effect of carbon nanofiber concrete exposed to different environmental conditions. Rom. J. Mater. 2015, 45, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Bai, E.; Luo, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, G.; Chang, S. Study on the effects of carbon fibers and carbon nanofibers on electrical conductivity of concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 267, 32011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.L.; Shi, C.; Bi, Z.; Lai, Z.; She, A.; Yao, W. Recent advances in properties and applications of carbon fiber-reinforced smart cement-based composites. Materials 2023, 16, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.D.L. Self-monitoring structural materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 1998, 22, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, H.R.; Latifi, M.; Jamshidi, M. Hybrid short fiber reinforcement system in concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 142, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastali, M.; Dalvand, A.; Sattarifard, A. The impact resistance and mechanical properties of the reinforced self-compacting concrete incorporating recycled CFRP fiber with different lengths and dosages. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2017, 112, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellán-García, J. Tensile behavior of recycled-glass-UHPC under direct tensile loading. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, J.; Romouzi, V.; Kasaei, J.; Andalibi, K. An investigation of durability and the mechanical properties of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) modified with economical graphene oxide nano-sheets. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 80, 107908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, X.; Maimaitituersun, N.; Dong, S.; Li, L.; Han, B. Synergistic effects of steel fibers and steel wires on uniaxial tensile mechanical and self-sensing properties of UHPC. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 416, 134991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Jing, H.W.; Li, L.; Yin, Q.; Sh, X.S.; Zhao, Z.L. Humic acid assisted stabilization of dispersed single-walled carbon nanotubes in cementitious composites. Nano Rev. 2019, 8, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Khayat, K.H. Mechanical properties of ultra-high-performance concrete enhanced with graphite nanoplatelets and carbon nanofibers. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2016, 107, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; He, X.; Deng, X.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, J.; Hui, D. Application of nanomaterials in ultra-high performance concrete: A review. Nano Rev. 2020, 9, 1427–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.G.; Zhang, K.; Yu, X.; Kwon, E.; Ou, J.P. Fabrication of piezoresistive cnt/cnf cementitious composites with superplasticizer as dispersant. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 24, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50081-2019; Standard for Test Methods of Concrete Physical and Mechanical Properties. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- CECS 13-2009; Standard Test Methods for Fiber Reinforced Concrete. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Khalilpour, S.; BaniAsad, E.; Dehestani, M. A review on concrete fracture energy and effective parameters. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 120, 294–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, H.; Zheng, J.; Yu, R.C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z. Fracture energy of concrete after sustained loading. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2024, 308, 110350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.D.; Wu, Z.M.; Yu, R.C.; Zhang, X.X. Residual fracture energy of concrete suffering from fatigue loading. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2021, 255, 107956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 3048.1-2007; Test for Resistivity of Metallic Materials. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Chen, Z.; Lim, J.L.G.; Yang, E. Ultra high performance cement-based composites incorporating low dosage of plasma synthesized carbon nanotubes. Mater. Des. 2016, 108, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruschau, G.R.; Yoshikawa, S.; Newnham, R.E. Resistivities of conductive composites. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 72, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Suliman, M.; Xia, W. Reversed Cyclic Behavior of Carbon Nanofiber-Reinforced Concrete Shear Walls. Materials 2024, 23, 5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; He, Z.J.; Zhou, Y.C.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Jin, T. Effect of Dimethyl Sulfoxide in Hydrophobic Modification of Cotton Filter Cloth by ARGET-ATRP Mechanism. Mater. Sci. For. 2020, 993, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, Z.S.; Volz, J.S. Comparative impact behavior of four long carbon fiber reinforced concretes. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Yang, J. Experimental Study on Dynamic Splitting Characteristics of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, X.; Maimaitituersun, N.; Shao, S.; Yang, W.; Han, B. Sensing performances of hybrid steel wires and fibers reinforced ultra-high performance concrete for in-situ monitoring of infrastructures. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 58, 105022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

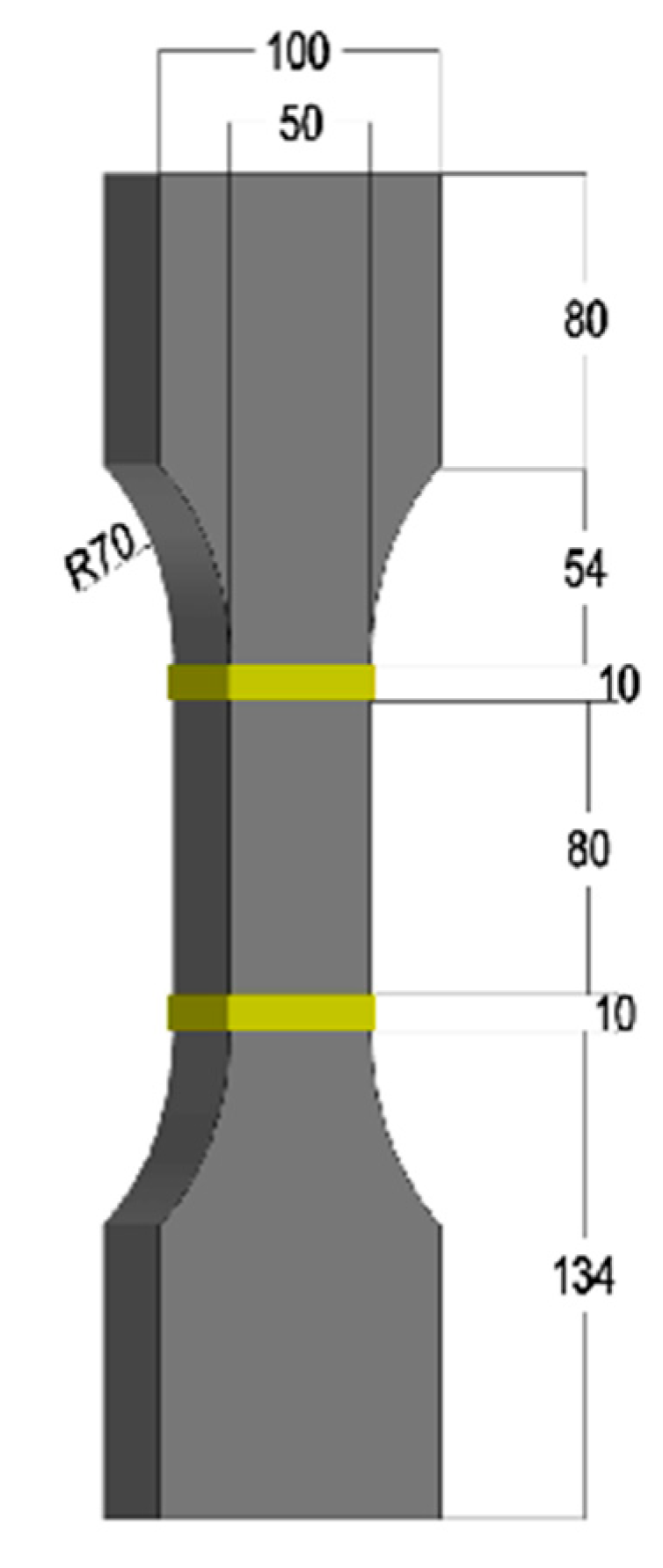

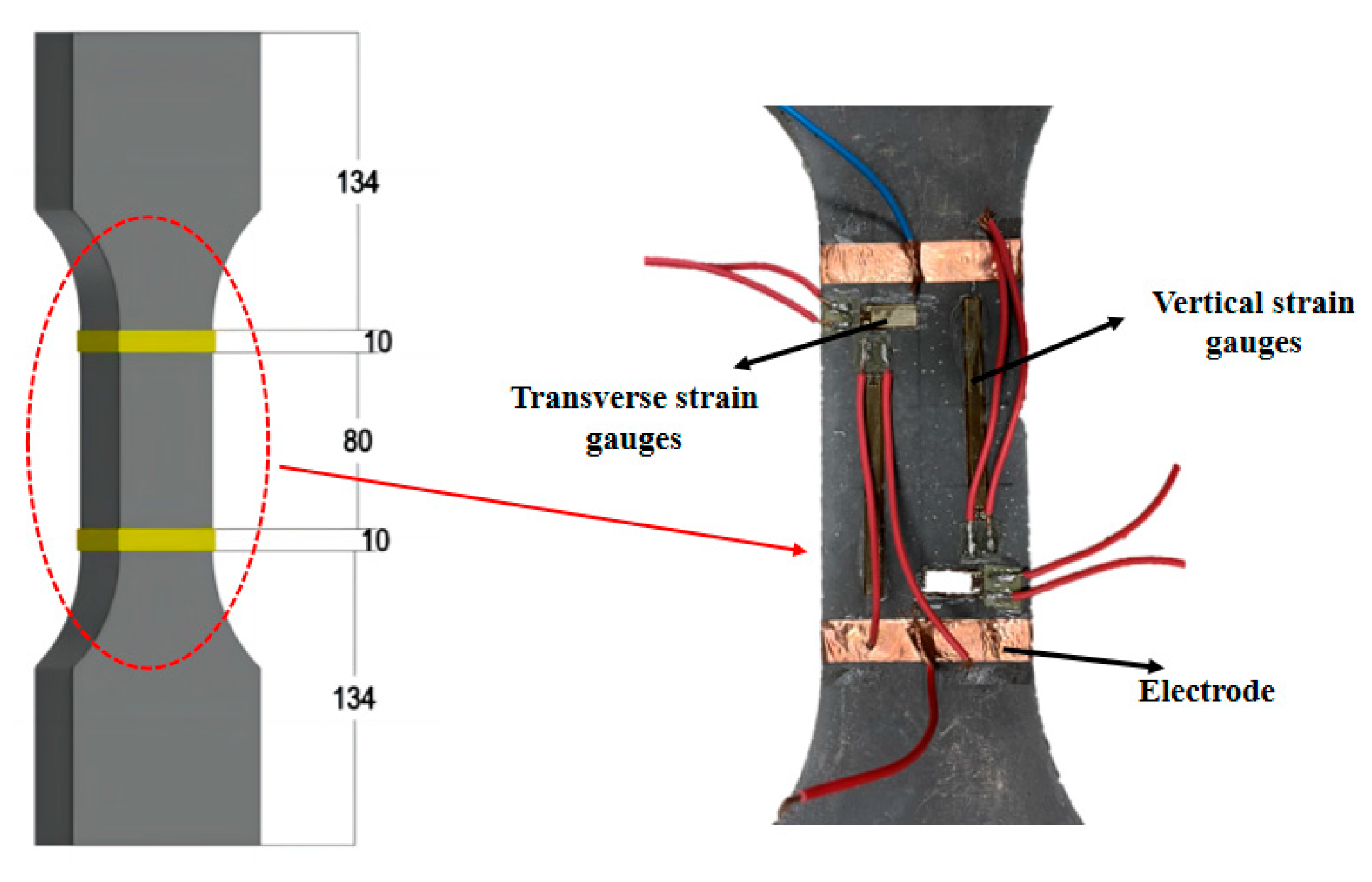


| Chemical Composition | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | MgO | SO3 | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality score (%) | 21.45 | 5.24 | 61.13 | 2.89 | 2.08 | 2.05 | 0.77 |
| Chemical Composition | C3S | C2S | C3A | C4AF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality score (%) | 46.62 | 26.32 | 8.99 | 8.78 |
| Chemical Composition | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | MgO | K2O | SO3 | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality score (%) | 49.05 | 22.48 | 9.36 | 5.95 | 5.41 | 1.48 | 0.54 | 0.98 |
| Type | Length (μm) | Outside Diameter (nm) | Inner Diameter (nm) | -COOH content (wt.%) | -OH Content (wt.%) | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MHI | 10–30 | <8 | 2–5 | – | 5.58 | >400 | 2.1 |
| MCI | 10–30 | <8 | 2–5 | 3.86 | – | >400 | 2.1 |
| M5 | 10–30 | 20–30 | 5–10 | – | – | >110 | 2.1 |
| IM | 10–20 | >50 | – | – | – | >60 | 1.9 |
| CNF19 | 50–200 | 150 | – | – | – | 15~24 | 1.9 |
| CNF24 | 50–200 | 100 | – | – | – | 41 | 1.9 |
| CF3 | 3000 | 7000 | – | – | – | – | 1.8 |
| CF6 | 6000 | 7000 | – | – | – | – | 1.8 |
| Type | Filler Dosage (wt.%) | C | FA | SF | QS | W | NSF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | – | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 0.011 |
| CRCC | 0.25% | 0.798 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 0.011 |
| 0.5% | 0.796 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 0.011 |
| Types | Length | Strain | Stress (MPa) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 wt.% | 0.5 wt.% | 0.25 wt.% | 0.5 wt.% | |||||||
| Nanoscale | MHI | 10–30 | 121.36 | 115.84 | 5.58 | 5.73 | ||||
| MCI | 10–30 | 125.93 | 145.74 | 5.53 | 5.40 | |||||
| M5 | 10–30 | 164.72 | 146.00 | 6.03 | 5.64 | |||||
| IM | 10–20 | 111.28 | 112.43 | 5.67 | 6.09 | |||||
| CNF19 | 50–200 | 124.86 | 149.80 | 5.74 | 6.25 | |||||
| CNF24 | 50–200 | 134.56 | 176.38 | 6.03 | 5.86 | |||||
| Types | Length | 0.5 vol.% | 1.0 vol.% | 1.5 vol.% | 0.5 vol.% | 1.0 vol.% | 1.5 vol.% | |||
| Macro scale | CF3 | 3000 | 315.23 | 212.83 | 202.99 | 6.98 | 7.88 | 7.38 | ||
| CF6 | 6000 | 221.49 | 255.86 | 218.30 | 6.72 | 7.11 | 7.30 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maimaitituersun, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Ning, Z. Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Cementitious Composites Reinforced with Multi-Scale Carbon Fibers. Materials 2025, 18, 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081830
Maimaitituersun N, Wang J, Wang D, Ning Z. Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Cementitious Composites Reinforced with Multi-Scale Carbon Fibers. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081830
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaimaitituersun, Nueraili, Jing Wang, Danna Wang, and Zuojun Ning. 2025. "Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Cementitious Composites Reinforced with Multi-Scale Carbon Fibers" Materials 18, no. 8: 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081830
APA StyleMaimaitituersun, N., Wang, J., Wang, D., & Ning, Z. (2025). Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Cementitious Composites Reinforced with Multi-Scale Carbon Fibers. Materials, 18(8), 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081830





