Fabrication of Stainless Steel/Alumina Composite Powders by Spray Granulation and Plasma Spheroidization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- -
- -
- A powder metallurgy process with the following steps: powder mixing, powder preparation, debinding and sintering. In order to form the ceramic powder into the component shapes, uniaxial compaction is generally used; metal injection moulding can also be employed [12]. Different sintering processes are possible: pressureless sintering [3,5], hot pressing [6] and spark plasma sintering (SPS) [13,14].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Initial Powders
2.2. Suspension and Spray Granulation
2.3. Plasma Spheroidization
2.4. Characterization of Spray-Granulated and Spheroidized Granules
2.5. Densification
2.6. Characterization of Sintered Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Initial Powders
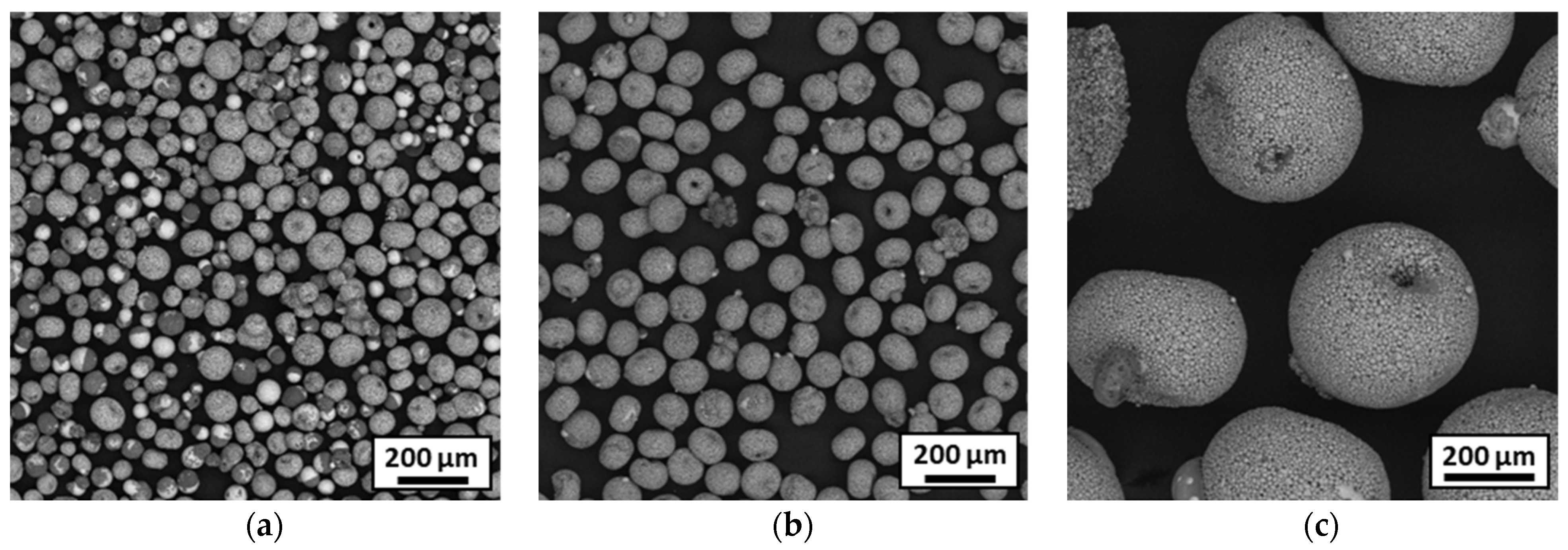
3.2. Spray Granulation Optimization
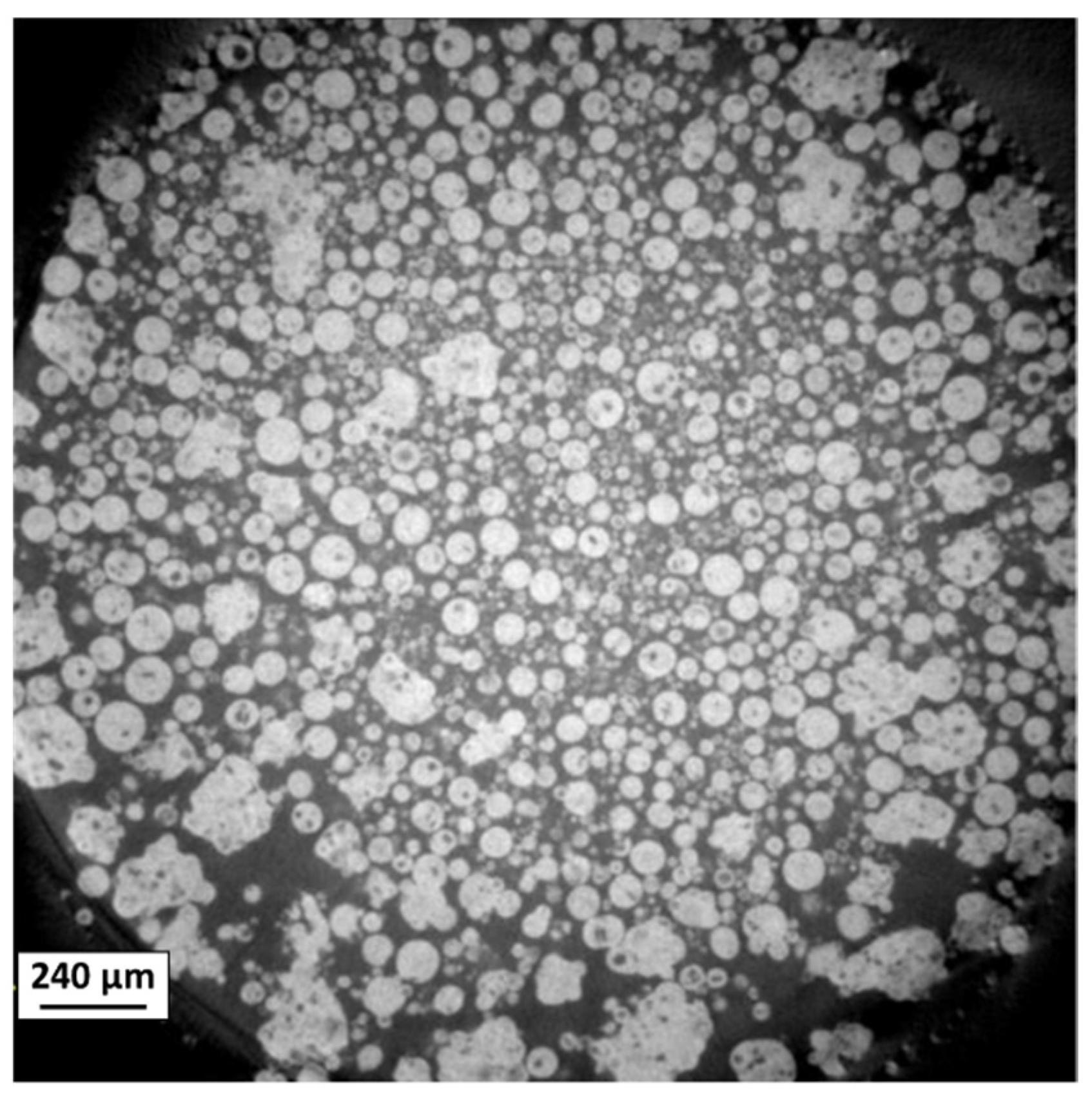
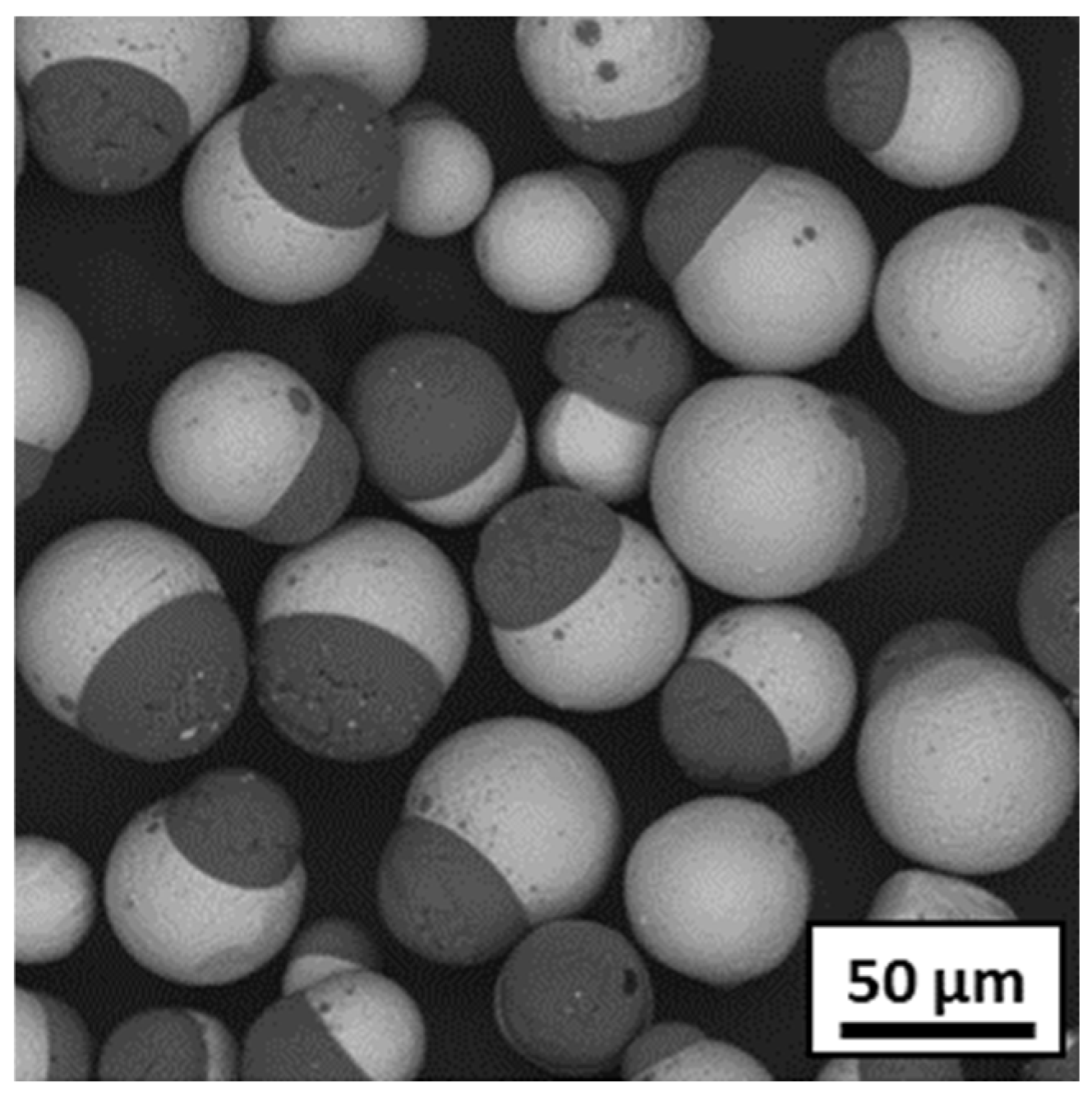
3.3. Plasma Spheroidization
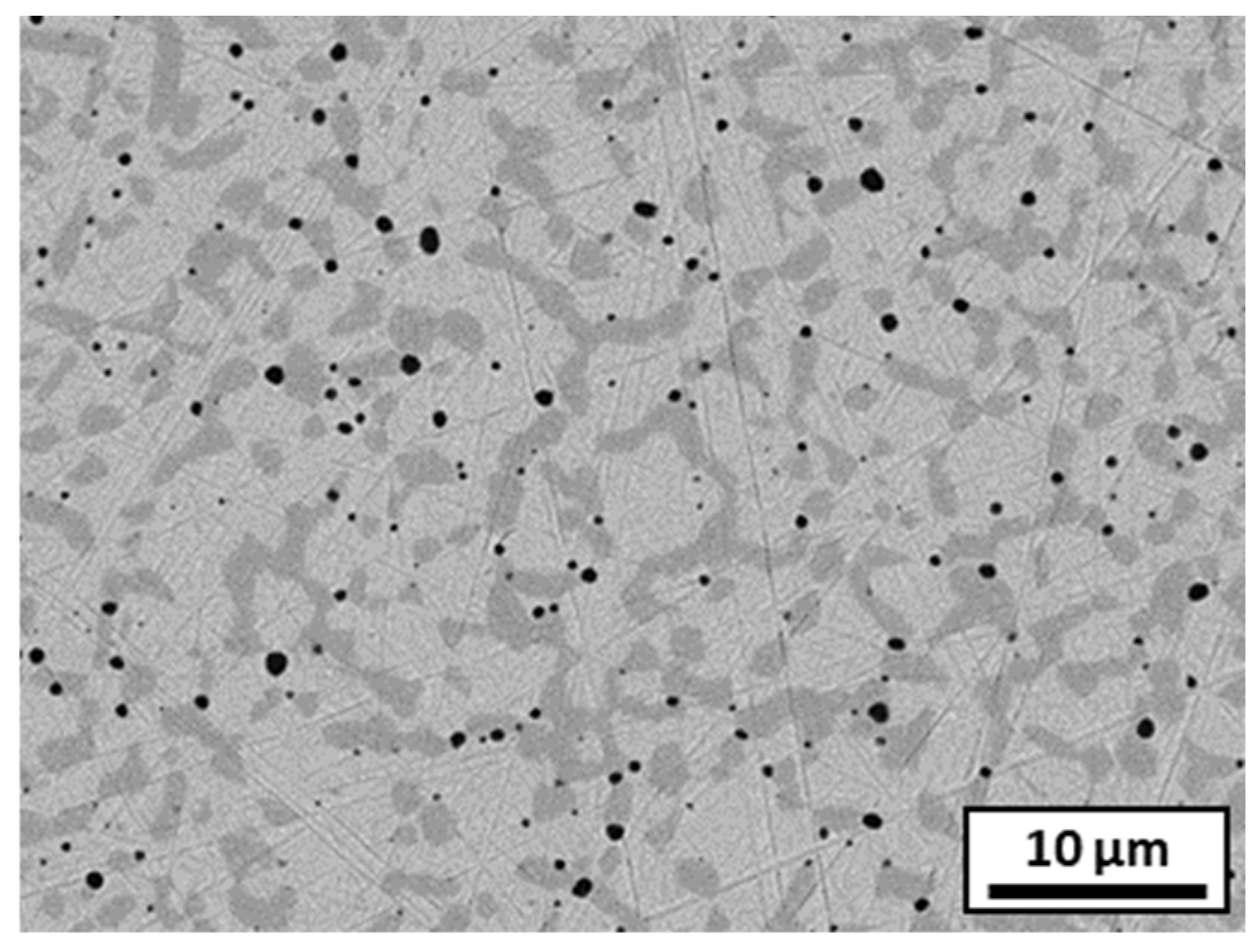
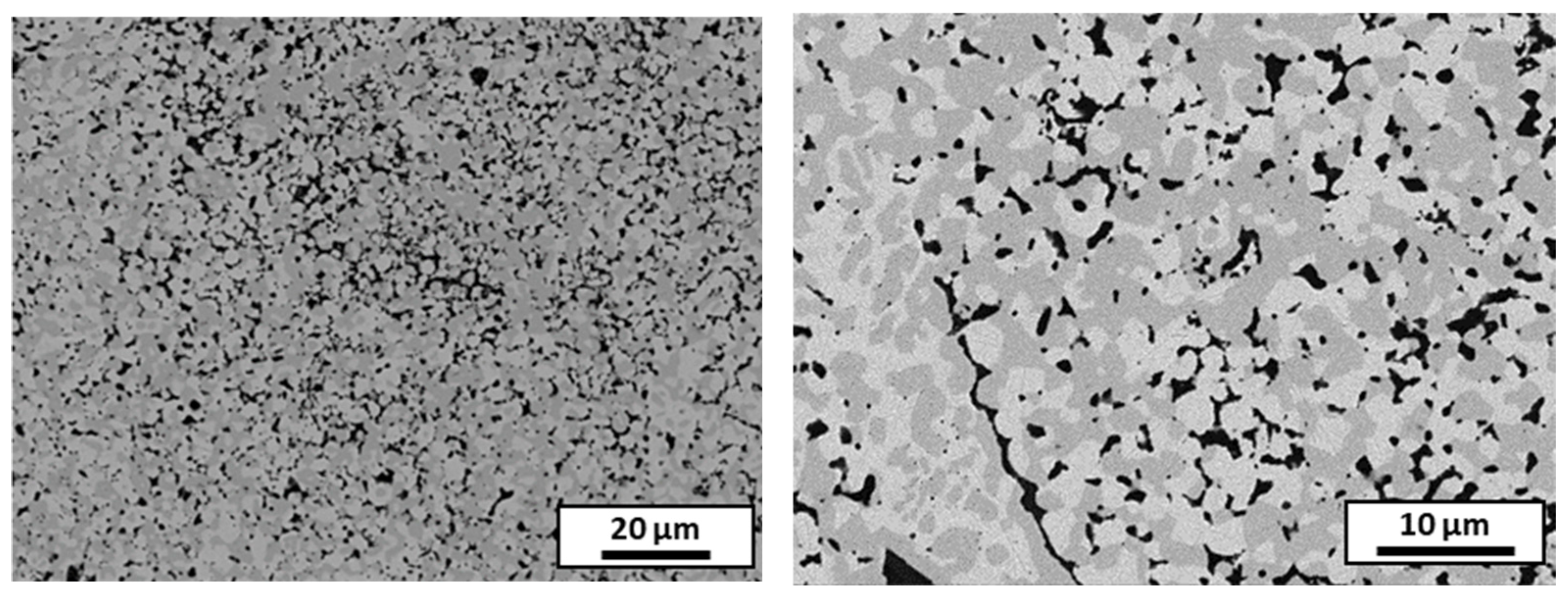
3.4. Microstructure and Hardness of Sintered Composites
3.4.1. Sintered 316L Stainless Steel
3.4.2. Composite Sintered from Ball-Milled Mixture
3.4.3. Composite Sintered from Spray-Granulated Granules
3.4.4. Composite Sintered from Granules Spheroidized with Preliminary Parameters
3.4.5. Composites Sintered from Granules Spheroidized with Optimal Parameters
3.4.6. Summary of Results for Sintered Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Auger, J.M. Etude de la Frittabilité de Composites Céramique-Métal (Alumine-Acier Inoxydable 316L)—Application à la Conception et à L’élaboration de Pieces Multimatériaux Multifonctionnelles Architectures. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Mines de Saint-Etienne, Saint-Étienne, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, A.; Włodarczyk, R. Composite 316L+Al2O3 for Application in Medicine. Mater. Sci. Forum 2012, 706–709, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canpolat, O.; Çanakçı, A.; Erdemir, F. SS316L-Al2O3 functionally graded material for potential biomedical applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 293, 126958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuforiji, C.; Nganbe, M. Fabrication and characterisation of SS316L-Al2O3 composites for wear applications. In proceeding of the International Conference & Exhibition on Advanced and Nanomaterials, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 10–12 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Coovattanachai, O.; Mima, S.; Yodkaew, T.; Krataitong, R.; Morkotjinda, M.; Daraphan, A.; Tosangthum, N.; Vetayanugul, B.; Panumas, A.; Poolthong, N.; et al. Effect of admixed ceramic particles on properties of sintered 316L stainless steel. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Powder Metallurgy and Particulate Materials, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Canpolat, O.; Çanakçı, A.; Erdemir, F. Evaluation of microstructure, mechanical, and corrosion properties of SS316L/Al2O3 composites produced by hot pressing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 280, 125826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Figueiredo Soares, L.; Brito Neto, F.M.; Reis, L.M.M.; Dos Santos Vacchi, G.; Monteiro, S.N.; Della Rovere, C.A.; Arantes, V.L. Corrosion behavior of 316L stainless steel reinforced by dispersed yttria stabilized zirconia fabricated by spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Liu, L.; Yang, S. NbC Particles-Reinforced 316L Stainless Steel Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting: Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Strengthening Mechanisms. Appl. Phys. A 2024, 130, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, J.; Bai, P.; Qu, H.; Liang, M.; Liao, H.; Wu, L.; Huo, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiC-Reinforced 316L Stainless Steel Composites Fabricated Using Selective Laser Melting. Metals 2019, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kracun, A.; Tehnovnik, F.; Kafexhiu, F.; Kosec, T.; Jenko, D.; Podgornik, B. Stainless steel matrix composites reinforced with ceramic particles through ingot casting process. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 188, 01023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Willy, H.J.; Chang, S.; Lu, W.; Herng, T.S.; Ding, J. Selective laser melting of stainless steel and alumina composite: Experimental and simulation studies on processing parameters, microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Des. 2018, 145, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülsoy, H.Ö.; Baykara, T.; Özbek, S. Injection moulding of 316L stainless steels reinforced with nanosize alumina particles. Powder Met. 2011, 54, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Zine, H.R.; Horváth, Z.E.; Balázsi, K.; Balázsi, C. Novel Alumina Dispersion-Strengthened 316L Steel Produced by Attrition Milling and Spark Plasma Sintering. Coatings 2023, 13, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baross, T.; Ben Zine, H.R.; Bereczki, P.; Palankai, M.; Balazsi, K.; Balazsi, C.; Veres, G. Diffusion Bonding of Al2O3 Dispersion-Strengthened 316L composite by Gleeble 3800. Materials 2024, 17, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panumas, A.; Yotkaew, T.; Krataitong, R.; Morakotjinda, S.; Daraphan, A.; Tosangthum, N.; Coovattanachai, O.; Vetayanugul, B.; Tongsri, R. Preparation of 316L-Al2O3 Composite. In proceeding of the 19th Conference of the Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand, Songkhla, Thailand, 19–21 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tongsri, R.; Asavavisithchai, S.; Mateepithukdharm, C.; Piyarattanatrai, T.; Wangyao, P. Effect of Powder Mixture Conditions on Mechanical Properties of Sintered Al2O3-SS 316L Composites under Vacuum Atmosphere. J. Met. Mater. Miner. 2007, 17, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Jina, H.; Ding, F.; Bai, L.; Yuan, F. Fabrication of homogeneous Mo-Cu composites using spherical molybdenum powders prepared by thermal plasma spheroidization process. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 73, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Shao, W.; Guo, X.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; He, D. In situ synthesis of spherical W–Mo alloy powder for additive manufacturing by spray granulation combined with thermal plasma spheroidization. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 95, 105460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samokhin, A.V.; Alekseev, N.V.; Dorofeev, A.A.; Fadeev, A.A.; Sinayskiy, M.A.; Zavertiaev, I.D.; Grigoriev, Y.V. Preparation of spheroidized W−Cu pseudo-alloy micropowder with sub-micrometer particle structure using plasma technology. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2024, 34, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Xiao, M.; Mao, X.; Khanlari, K.; Shi, Q.; Liu, X. Fabrication of spherical WC-Co powders by radio frequency inductively coupled plasma and a consequent heat treatment. Powder Technol. 2021, 385, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Hao, Z.; Ma, R.; Wang, P.; Shi, L.; Shu, Y.; He, J. Preparation of spherical WC-Co powder by spray granulation combined with radio frequency induction plasma spheroidization. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 12372–12380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Mo, Z.; Hao, Z.; Ma, R.; Wang, P.; Shu, Y.; He, J. Fabrication of spherical W–ZrC powder for additive manufacturing by spray granulation combined with plasma spheroidization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 4222–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, K.A.; Li, Y. Crystallization behaviors in the plasma-spheroidized alumina/zircon mixtures. Mater. Lett. 2001, 48, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, L.; Zhu, S. Preparation and characterization of ZrB2/SiC composite powders by induction plasma spheroidization technology. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; He, P.; Li, G.; Ye, L.; Zhang, B.; Sun, C.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Liang, X. Microstructure development of plasma sprayed dual-phase high entropy ceramic coating derived from spray dried and induction plasma spheroidized powder. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 24576–24593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massard, Q.; Si-Mohand, H.; Cabrol, E. Study on the recycling of 100Cr6 powder by plasma spheroidization for laser powder bed fusion. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 5889–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupille, J.; Lazzari, R. Improving the wetting of oxides by metals. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2006, 8, 901–908. [Google Scholar]
- Sehhat, M.H.; Chandler, J.; Yates, Z. A review on ICP powder plasma spheroidization process parameters. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 103, 105764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Preliminary Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| Power (kW) | 40 | 30 | 30 | 20 | |||
| Central gas (slpm) | Ar: 15 | ||||||
| Sheath gas (slpm) | Ar: 55/H2: 10 | Ar: 55 | |||||
| Carrier gas (slpm) | Ar: 5 | ||||||
| Injection probe position | Centre | −10 mm | Centre | ||||
| Powder feed rate (kg/h) | 8 | 4 | 2 | ||||
| Optimal Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Power (kW) | 20 |
| Central gas (slpm) | Ar: 15 |
| Sheath gas (slpm) | Ar: 55 |
| Carrier gas (slpm) | Ar: 5 |
| Injection probe position | −10 mm |
| Powder feed rate (kg/h) | 4 |
| Slurry Batch |
316L (vol%) |
Al2O3 (vol%) |
Dispersant Ratio (wt%) |
Solid Loading Ratio (wt%) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 80 | 20 | 2 PEG | 40 | 7 |
| 2 | 80 | 20 | 2 PVA | 30 | 11 |
| 3 | 80 | 20 | 0.5 PAA | 50 | 11 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|
| D10: 1 µm | D10: 2 µm | D10: 2 µm |
| D50: 34 µm | D50: 26 µm | D50: 8 µm |
| D90: 266 µm | D90: 70 µm | D90: 36 µm |
| Density: 6.6 g/cm3 | Density: 6.9 g/cm3 | Density: 7.1 g/cm3 |
| Relative Density (%) | Hardness (GPa) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Unreinforced 316L | 99.5 | 3.7 | |
| Composite 80 vol% 316L/20 vol% Al2O3 | Ball-milled mixture | 91.8 | 4.3 |
| Spray-granulated granules | 97.3 | 4.6 | |
| Spheroidized granules with preliminary parameters | 98.1 | 4.1 | |
| Spheroidized granules with optimal parameters | 98.9 | 5.4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabrol, E.; Cottrino, S.; Si-Mohand, H.; Fantozzi, G. Fabrication of Stainless Steel/Alumina Composite Powders by Spray Granulation and Plasma Spheroidization. Materials 2025, 18, 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081872
Cabrol E, Cottrino S, Si-Mohand H, Fantozzi G. Fabrication of Stainless Steel/Alumina Composite Powders by Spray Granulation and Plasma Spheroidization. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081872
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabrol, Elodie, Sandrine Cottrino, Hocine Si-Mohand, and Gilbert Fantozzi. 2025. "Fabrication of Stainless Steel/Alumina Composite Powders by Spray Granulation and Plasma Spheroidization" Materials 18, no. 8: 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081872
APA StyleCabrol, E., Cottrino, S., Si-Mohand, H., & Fantozzi, G. (2025). Fabrication of Stainless Steel/Alumina Composite Powders by Spray Granulation and Plasma Spheroidization. Materials, 18(8), 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081872






