Identification and Methods of Influencing the Oxidation States of Mn and Ce in Silicate Glasses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Glass Preparation
2.2. Glass Characterization
2.3. Optical-Basicity Evaluation
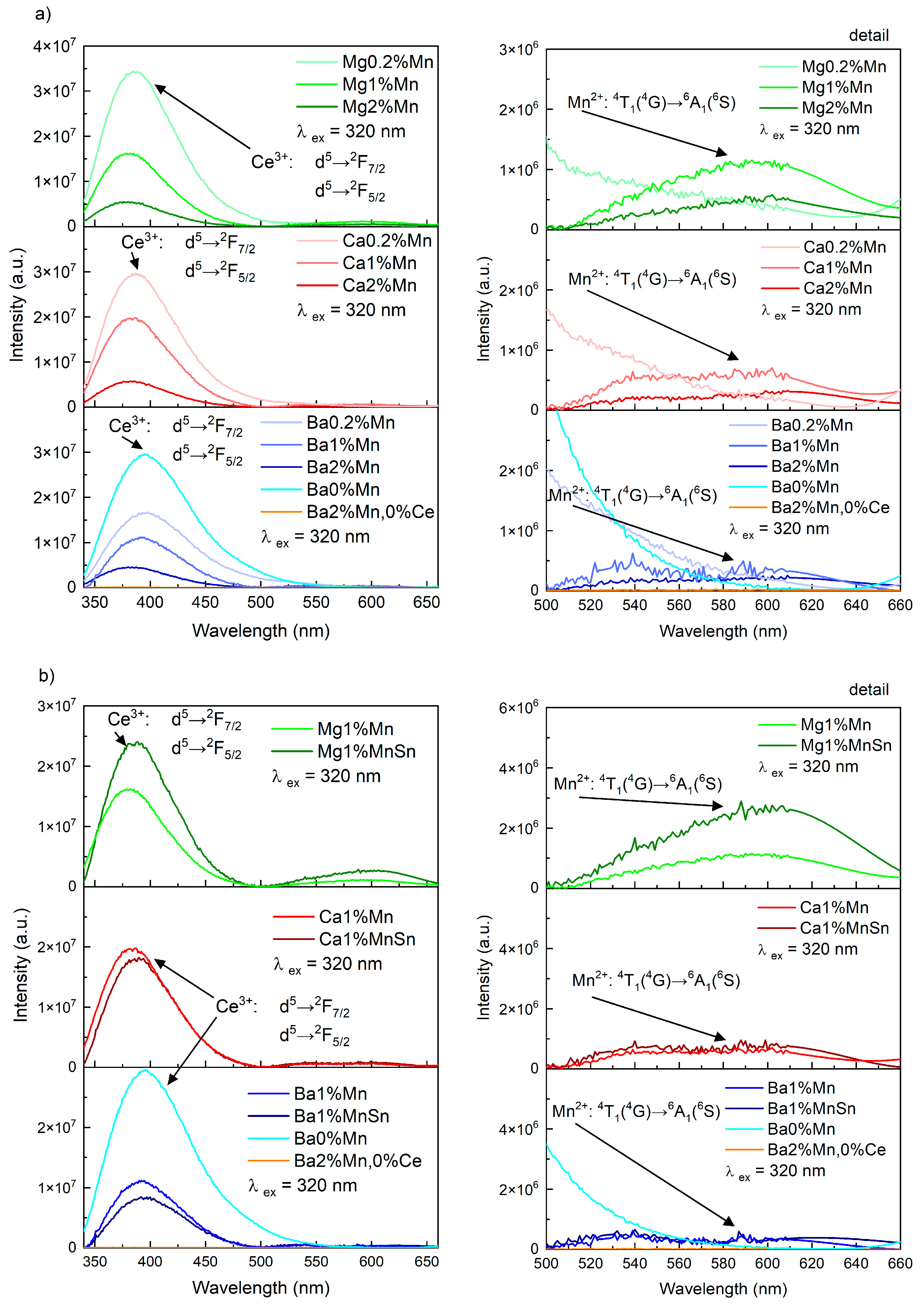
3. Results
3.1. General Properties of the Prepared Glass
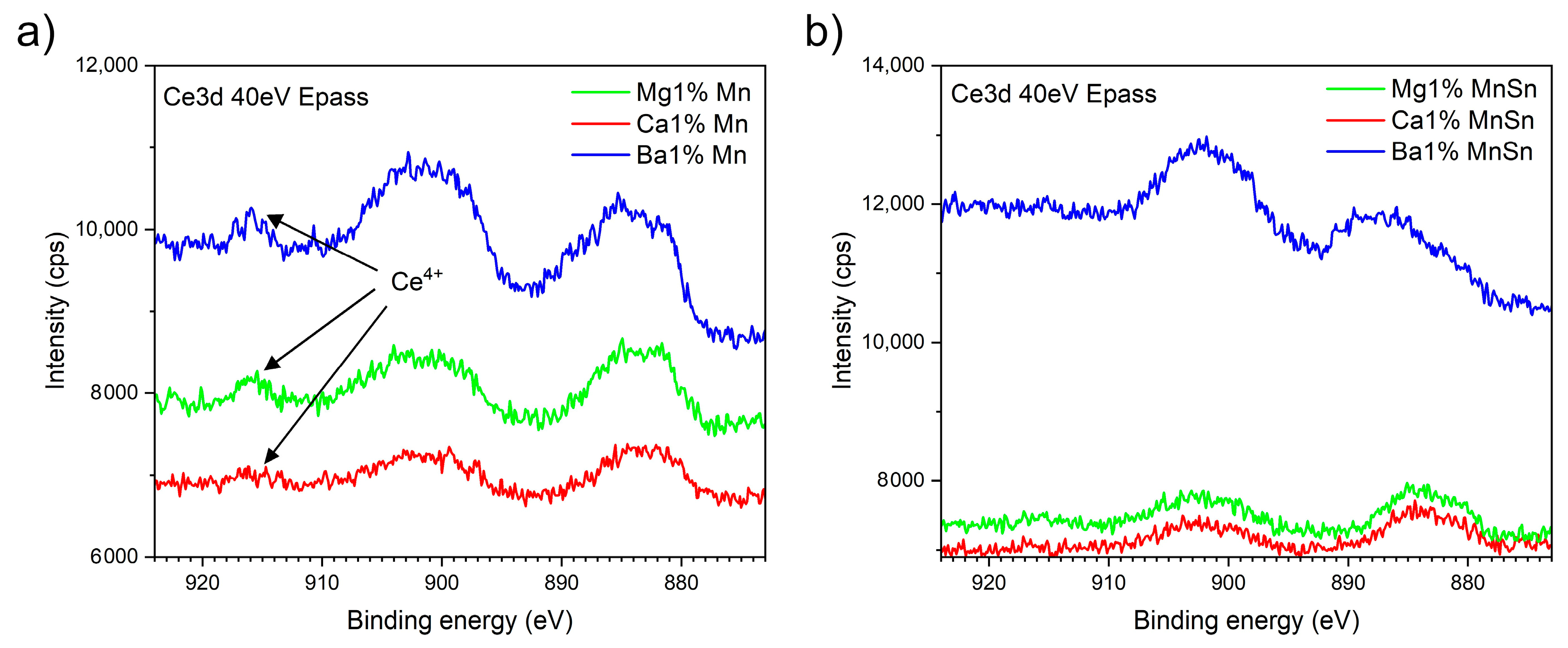
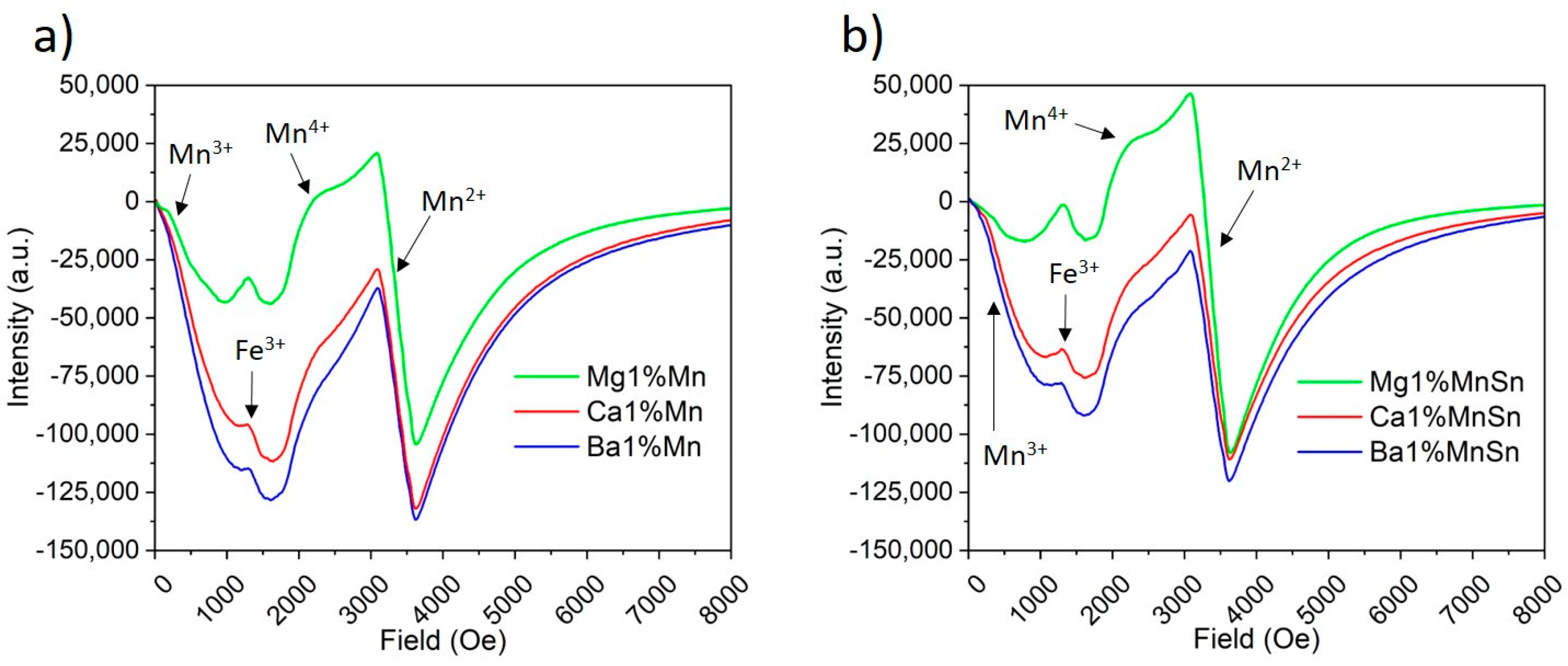
3.2. The Determination of the Oxidation States of Ce and Mn
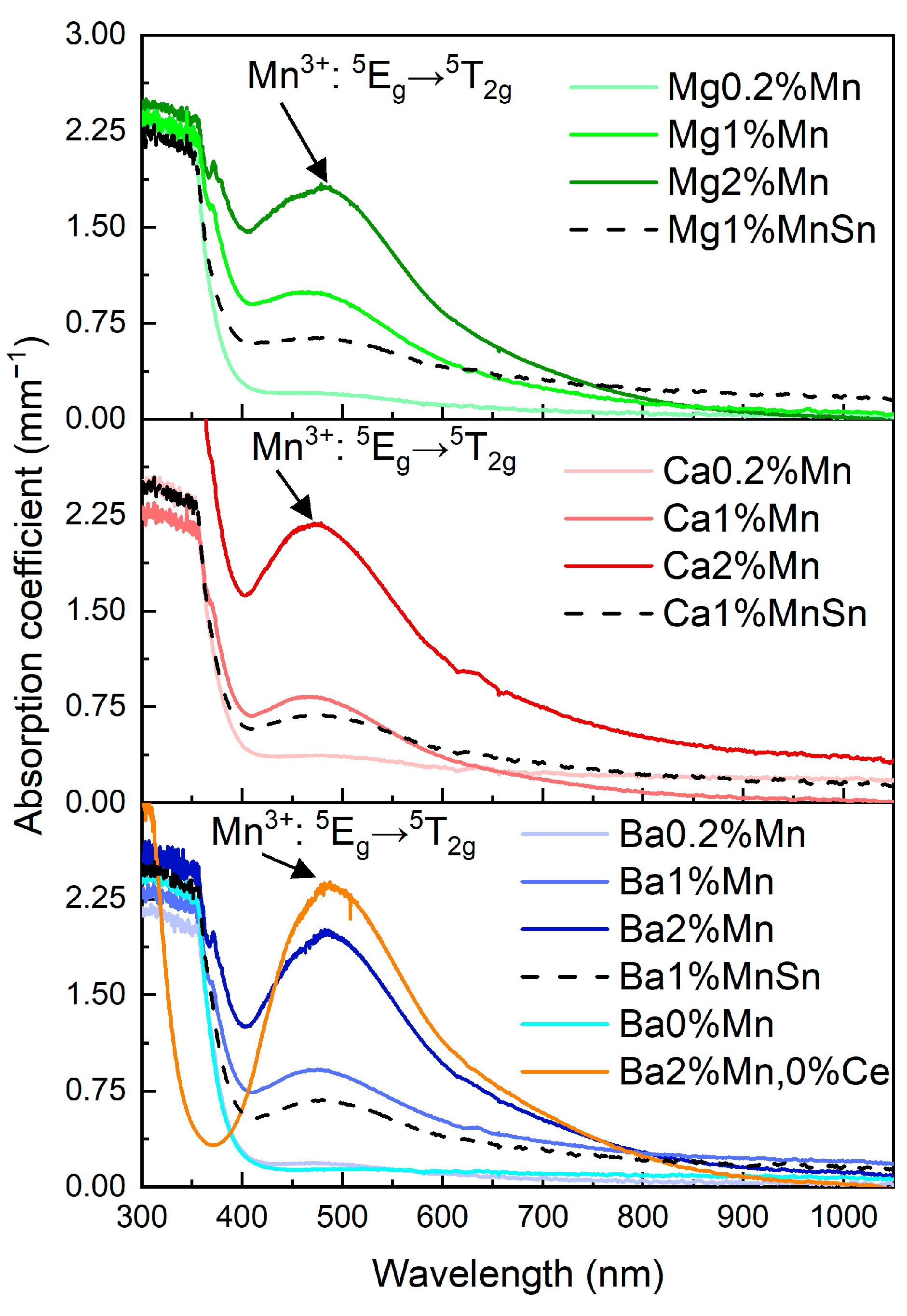
3.3. The Absorption of the Prepared Glasses
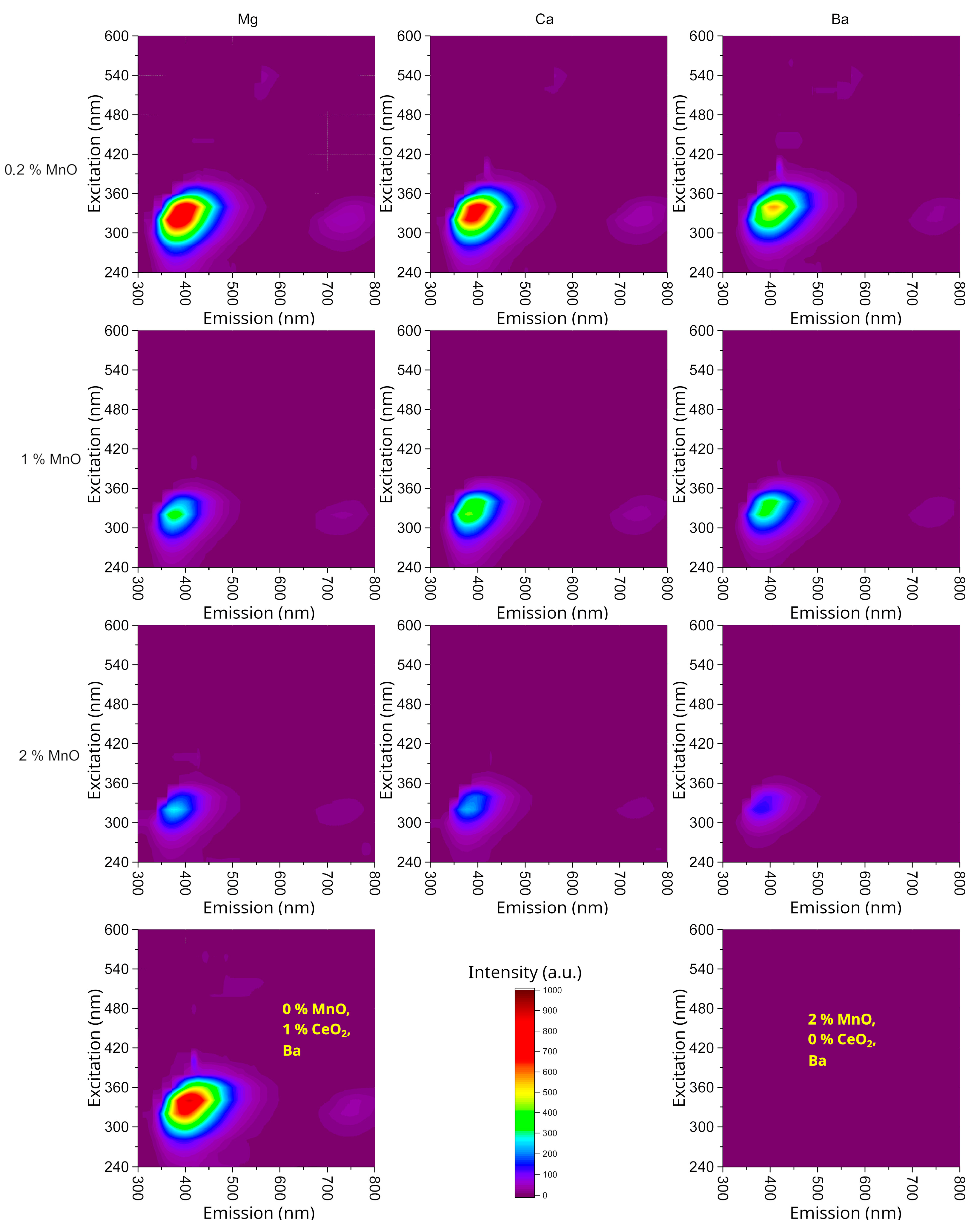
3.4. The Luminescence of the Prepared Glasses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miao, S.; Xia, Z.; Molokeev, M.S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q. Crystal Structure Refinement and Luminescence Properties of Blue-Green-Emitting CaSrAl2SiO7:Ce3+, Li+, Eu2+ Phosphors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 8322–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chewpraditkul, W.; Shen, Y.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; Prusa, P.; Nikl, M.; Beitlerova, A.; Wanarak, C. Luminescence and Scintillation of Ce3+-Doped High Silica Glass. Opt. Mater. 2012, 34, 1762–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Brahme, N.; Bisen, D.P.; Dewangan, P.; Tigga, S.; Tiwari, G.; Khare, A. Study on Photoluminescence and Thermoluminescence Properties of UV-Irradiated CaSrAl2SiO7: Ce3+ Phosphors. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffray, E.; Akchurin, N.; Benaglia, A.; Borisevich, A.; Cowden, C.; Damgov, J.; Dormenev, V.; Dragoiu, C.; Dudero, P.; Korjik, M.; et al. DSB:Ce3+ Scintillation Glass for Future. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 587, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Wen, J.; Luo, W.; Dong, Y.; Pang, F.; Chen, Z.; Peng, G.; Wang, T. Improved Scintillating Properties in Ce:YAG Derived Silica Fiber with the Reduction from Ce4+ to Ce3+ Ions. J. Lumin. 2020, 221, 117063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Z.; Shi, Z.; Song, Y.; Zou, B.; Zou, H. Ba3Lu(BO3)3:Ce3+,Tb3+/Mn2+: Dual-Functional Material for WLEDs and Optical Pressure Sensing. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 4288–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Hua, D.; Liu, B.; Guo, M.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Deng, T.; Zhou, J. RGB-Tricolor Multimodal Luminescence of Ce3+ and Mn2+ in Mg2Al4Si5O18 via Site Occupancy Engineering for Anticounterfeiting Applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 40, 102287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Fang, L.; Zhou, X.; Xia, H.; Song, H.; Chen, B. High Sensitivity Dual-Mode Ratiometric Optical Thermometry Based on Ce3+/Mn2+ Co-Doped LiYF4 Single Crystal. Opt. Mater. 2024, 154, 115652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Sun, B.; Wei, Y.; Liu, L.; Yu, J. Cyan to Orange Color Tunable Emitting of Ca2GdHf2Al3O12: Ce3+, Mn2+ Phosphors via Energy Transfer. Opt. Mater. 2024, 155, 115801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, D.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lian, H.; Dang, P.; Li, G.; Lin, J. High-Performance, Narrow-Band Green-Emitting Phosphors for White LEDs: Recent Advances and Perspectives. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 13, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicconi, M.R.; Veber, A.; Neuville, D.R.; Baudelet, F.; De Ligny, D. Cerium Speciation in Silicate Glasses: Structure-Property Relationships. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2021, 563, 120785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavarini, S.; Guittet, M.J.; Trocellier, P.; Gautier-Soyer, M.; Carrot, F.; Matzen, G. Cerium Oxidation during Leaching of CeYSiAlO Glass. J. Nucl. Mater. 2003, 322, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creaser, D.A.; Harrison, P.G.; Morris, M.A.; Wolfindale, B.A. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopic Study of the Oxidation and Reduction of a Cerium(III) Oxide/Cerium Foil Substrate. Catal. Lett. 1994, 23, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Xu, W.; Ollier, N.; Guzik, M.; Boulon, G.; Yu, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, C.; Wang, S.; Hu, L. Suppression Mechanism of Radiation-Induced Darkening by Ce Doping in Al/Yb/Ce-Doped Silica Glasses: Evidence from Optical Spectroscopy, EPR and XPS Analyses. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 153101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curti, E.; Grolimund, D.; Borca, C.N. A Micro-XAS/XRF and Thermodynamic Study of CeIII/IV Speciation after Long-Term Aqueous Alteration of Simulated Nuclear Waste Glass: Relevance for Predicting Pu Behavior? Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicconi, M.R.; Neuville, D.R.; Blanc, W.; Lupi, J.-F.; Vermillac, M.; de Ligny, D. Cerium/Aluminum Correlation in Aluminosilicate Glasses and Optical Silica Fiber Preforms. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2017, 475, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisittipokakun, N.; Kedkaew, C.; Kaewkhao, J.; Limsuwan, P. Coloration in Soda-Lime-Silicate Glass System Containing Manganese. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 93–94, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidhyanathan, B.; Kumar, C.P.; Rao, J.L.; Rao, K.J. Spectroscopic Investigations of Manganese Ions in Microwave-Prepared NaPO3PbO Glasses. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1998, 59, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash Singh, S.; Chakradhar, R.P.S.; Rao, J.L.; Karmakar, B. EPR, Optical Absorption and Photoluminescence Properties of MnO2 Doped 23B2O3–5ZnO–72Bi2O3 Glasses. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2010, 405, 2157–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, N.K.; Reddy, M.R.; Jayasankar, C.K.; Veeraiah, N. Spectroscopic and Dielectric Studies on MnO Doped PbO–Nb2O5–P2O5 Glass System. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 458, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Tanner, P.A.; Cheng, B.-M. Optical Properties of 3dN Transition Metal Ion-Doped Lead Borate Glasses. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 83, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tuyen, H.; Nonaka, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Chau, P.M.; Quy Hai, N.T.; Quang, V.X.; Nogami, M. Fluorescence Properties of Valence-Controlled Eu2+ and Mn2+ Ions in Aluminosilicate Glasses. J. Lumin. 2017, 184, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.S.; Hila, F.C.; Reddy, M.S.; Hussain, S. Effect of Zirconium Oxide Nanoparticles on Thermal, Optical, and Radiation Shielding Properties of Bi2O3-B2O3-MnO2 Glasses. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2024, 205, 111183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandonà, A.; Castaing, V.; Shames, A.I.; Helsch, G.; Deubener, J.; Becerro, A.I.; Allix, M.; Goldstein, A. Oxidation and Coordination States Assumed by Transition Metal Dopants in an Invert Ultrabasic Silicate Glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2023, 603, 122094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griscom, D.L. Electron Spin Resonance in Glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1980, 40, 211–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padlyak, B.V.; Gutsze, A. EPR Study of the Impurity Paramagnetic Centres in (CaO−Ga2O3−GeO2) Glasses. Appl. Magn. Reson. 1998, 14, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, I.; Jacobsohn, O.; Niazov, T.; Werckmann, J.; Iliescu, M.; Richard-Plouet, M.; Burghaus, O.; Reinen, D. Manganese in Precipitated Hydroxyapatites. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 2003, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakazey, M.; Ivanova, N.; Sokolsky, G.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J.G. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance of MnO[Sub 2] Powders. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2001, 4, J1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldiño, U.; Álvarez, E.; Speghini, A.; Bettinelli, M. Cold and Warm White Light Generation Using Zn(PO3)2 Glasses Activated by Ce3+, Dy3+ and Mn2+. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 2077–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulose, P.I.; Jose, G.; Thomas, V.; Unnikrishnan, N.V.; Warrier, M.K.R. Sensitized Fluorescence of Ce3+/Mn2+ System in Phosphate Glass. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2003, 64, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldiño, U.; Hernández-Pozos, J.L.; Flores, C.; Speghini, A.; Bettinelli, M. Photoluminescence of Ce3+ and Mn2+ in Zinc Metaphosphate Glasses. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, 7297–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Martínez, R.; Speghini, A.; Bettinelli, M.; Falcony, C.; Caldiño, U. White Light Generation through the Zinc Metaphosphate Glass Activated by Ce3+, Tb3+ and Mn2+ Ions. J. Lumin. 2009, 129, 1276–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Salces, S.; Barreda-Argüeso, J.A.; Valiente, R.; Rodríguez, F. A Study of C3+ to Mn2+ Energy Transfer in High Transmission Glasses Using Time-Resolved Spectroscopy. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 9021–9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Pan, F.; Wu, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Su, Q. Highly Thermally Stable Single-Component White-Emitting Silicate Glass for Organic-Resin-Free White-Light-Emitting Diodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C.; Parent, C.; Le Flem, G.; Hagenmuller, P. White Light Emitting Glasses. J. Solid. State Chem. 1991, 93, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Dai, N.; Sheng, Y.; Luan, H.; Peng, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Yang, L. Ce-Tb-Mn Co-Doped White Light Emitting Glasses Suitable for Long-Wavelength UV Excitation. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 19473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Huang, Z.; Gao, H.; Cheng, X.; Mao, Y. Broadband Emission from Ce3+/Mn2+/Yb3+ Tri-Doped Oxyfluoride Glasses for Glass Greenhouse. Opt. Mater. 2016, 62, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.A. A Review of Optical Basicity and Its Applications to Oxidic Systems. Geochim. Et. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 3961–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragic, P.; Cavillon, M.; Ballato, J. Materials for Optical Fiber Lasers: A Review. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2018, 5, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, V.; Sakka, S. Electronic Oxide Polarizability and Optical Basicity of Simple Oxides. I. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 1736–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, T.; Dimitrov, V.; Tasheva, T.; Honma, T. Electronic Polarizability in Silicate Glasses by Comparison of Experimental and Theoretical Optical Basicities. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2021, 12, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, A.J.; Ingram, M.D.; Sommerville, I.D. Acid–Base Properties of Molten Oxides and Metallurgical Slags. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1978, 74, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomonik, V.G. The Effective Dipole Polarizabilities of the Ions in MX Molecules. J. Struct. Chem. 1979, 19, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DasMohapatra, G.K. A Spectroscopic Study of Cerium in Lithium–Alumino–Borate Glass. Mater. Lett. 1998, 35, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving Surface Chemical States in XPS Analysis of First Row Transition Metals, Oxides and Hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, A. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy of CeO2–Na2O–SiO2 Glasses. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2005, 142, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzan, R.S.; Donoso, J.P.; Magon, C.J.; Silva, I.; D’ANCIÃES, A.; Rüssel, C.; Nalin, M. Optical and Structural Studies of Mn2+ Doped SbPO4-ZnO-PbO Glasses. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2015, 26, 2607–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, R.; Carlier, D.; Sendova-Vassileva, M.; Yoncheva, M.; Zhecheva, E.; Nihtianova, D.; Delmas, C. Stabilization of Over-Stoichiometric Mn4+ in Layered Na2/3MnO2. J. Solid. State Chem. 2010, 183, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised Effective Ionic Radii and Systematic Studies of Interatomic Distances in Halides and Chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Salces, S.; Barreda-Argüeso, J.A.; Valiente, R.; Rodríguez, F. Solarization-Induced Redox Reactions in Doubly Ce3+/Mn2+-Doped Highly Transmission Glasses Studied by Optical Absorption and Photoluminescence. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 157, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.-S.; Xu, X.-H.; Yu, X.; Yu, H.-L.; Wang, D.-J.; Zhou, D.-C.; Qiu, J.-B. Tunable Full-Color Emitting Borosilicate Glasses via Utilization of Ce3+ Ions as Multiple Energy Transfer Contributors. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2014, 385, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, A.; Schonland, D.; Symons, M.C.R. 132. Structure and Reactivity of the Oxyanions of Transition Metals. Part IV. Some Relations between Electronic Spectra and Structure. J. Chem. Soc. 1957, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryffroy, D.; Vandenberghe, R.E.; Poelman, D. Optical Absorption of Ni2+ (D8) and Mn4+ (D3) in Some Spinel Oxides. Solid. State Commun. 1992, 82, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupesh Kumar, A.; Rao, T.G.V.M.; Veeraiah, N.; Rami Reddy, M. Fluorescence Spectroscopic Studies of Mn2+ Ions in SrO–Al2O3–B2O3–SiO2 Glass System. Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Sun, B.; Fan, J.; Hao, H.; Shen, F.; Wang, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, L.; Sun, J. Defect Assisted Self-Reduction and Post Annealing of Mn Ions Activated Garnet Transparent Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 107, 4282–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorenbos, P. The 5d Level Positions of the Trivalent Lanthanides in Inorganic Compounds. J. Lumin. 2000, 91, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volf, M.B. Chemie Skla, 1st ed.; Nakladatelství Techn. Lit: Praha, Czech Republic, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Zheng, S.; Jiang, X.; Fan, S.; Chen, D. Luminescence and Scintillation of High Silica Glass Containing SnO. Mater. Lett. 2017, 204, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatramaiah, N.; Ramakrishna, B.; Kumar, A.R.; Veeraiah, N.; Venkatesan, R. Enhanced Stokes Shift of S2→S0 Emission and Structural Investigations of Sn(IV)Porphyrins Doped Hybrid Borate Glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 513, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajanikanth, P.; Gandhi, Y.; Veeraiah, N. Enrichment of Orange Emission of Er3+ Ion with Sn4+ Ion as Sensitizer in Lithium Lead Phosphate Glass System. Opt. Mater. 2015, 48, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemsorn, W.; Keowkamnerd, K.; Phanichphant, S.; Suwannathada, P.; Hessenkemper, H. Influence of Glass Basicity on Redox Interactions of Iron-Manganese-Copper Ion Pairs in Soda-Lime-Silica Glass. Glass Phys. Chem. 2008, 34, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Aman; Tarafder, A. Comparative Investigation on the Effect of Alkaline Earth Oxides on the Intensity of Absorption Bands Due to Cu2+, Mn3+ and Cr3+ Ions in Ternary Silicate Glasses. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2004, 27, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Glass | Photo | Na2O | MgO | CaO | BaO | SiO2 | B2O3 | Al2O3 | MnO | CeO2 | SnO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba–Mn reference |  | 14.94 | - | - | 7.97 | 54.49 | 17.55 | 3.05 | 1.99 | - | - |
| Ba2%Mn |  | 15.23 | - | - | 8.12 | 54.97 | 15.53 | 3.11 | 2.03 | 1.01 | - |
| Ca2%Mn | 15.23 | - | 8.12 | - | 54.97 | 15.53 | 3.11 | 2.03 | 1.01 | - | |
| Mg2%Mn | 15.22 | 8.12 | - | - | 54.94 | 15.52 | 3.11 | 2.03 | 1.06 | - | |
| Ba1%Mn |  | 15.25 | - | - | 8.13 | 55.93 | 15.56 | 3.12 | 1.00 | 1.01 | - |
| Ca1%Mn | 14.89 | - | 7.94 | - | 54.61 | 17.49 | 3.05 | 0.98 | 1.04 | - | |
| Mg1%Mn | 14.89 | 7.94 | - | - | 54.61 | 17.49 | 3.05 | 0.98 | 1.04 | - | |
| Ba1%MnSn |  | 15.25 | - | - | 8.13 | 54.93 | 15.56 | 3.12 | 1.00 | 1.01 | 1.00 |
| Ca1%MnSn | 15.26 | - | 8.13 | - | 54.96 | 15.56 | 3.12 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 1.00 | |
| Mg1%MnSn | 15.25 | 8.13 | - | - | 54.93 | 15.56 | 3.12 | 1.00 | 1.01 | 1.00 | |
| Ba0.2%Mn |  | 15.18 | - | - | 8.09 | 56.94 | 15.48 | 3.10 | 0.20 | 1.01 | - |
| Ca0.2%Mn | 15.17 | - | 8.10 | - | 56.94 | 15.48 | 3.10 | 0.20 | 1.01 | - | |
| Mg0.2%Mn | 15.17 | 8.09 | - | - | 56.94 | 15.48 | 3.10 | 0.20 | 1.01 | - | |
| Ba–Ce reference |  | 15.17 | - | - | 8.09 | 57.16 | 15.47 | 3.10 | - | 1.01 | - |
| Glass | ρ (g·cm−3) | nint (589 nm) | N (632.8 nm) | A | B | C/108 | Λth | Λ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba–Mn standard | 2.89 ± 0.06 | 1.5570 | 1.5542 | 1.5355 | 9751.7722 | −7.9915 | 0.590 | 0.63 |
| Ba2%Mn | 2.87 ± 0.11 | 1.5609 | 1.5581 | 1.5391 | 9499.3330 | −6.5425 | 0.608 | 0.62 |
| Ca2%Mn | 2.48 ± 0.07 | 1.5440 | 1.5411 | 1.5231 | 9292.6726 | −7.1317 | 0.584 | 0.63 |
| Mg2%Mn | 2.54 ± 0.07 | 1.5292 | 1.5264 | 1.5088 | 9098.0695 | −7.0272 | 0.577 | 0.57 |
| Ba1%Mn | 2.89 ± 0.06 | 1.5570 | 1.5542 | 1.5355 | 9751.7722 | −7.9915 | 0.600 | 0.62 |
| Ca1%Mn | 2.56 ± 0.04 | 1.5420 | 1.5392 | 1.5214 | 9299.9315 | −7.4192 | 0.577 | 0.57 |
| Mg1%Mn | 2.49 ± 0.03 | 1.5250 | 1.5222 | 1.5043 | 9342.0628 | −7.5881 | 0.566 | 0.56 |
| Ba0.2%Mn | 2.91 ± 0.05 | 1.5555 | 1.5527 | 1.5344 | 9427.5046 | −7.2049 | 0.605 | 0.60 |
| Ca0.2%Mn | 2.51 ± 0.06 | 1.5401 | 1.5373 | 1.5197 | 9115.0583 | −6.9926 | 0.588 | 0.61 |
| Mg0.2%Mn | 2.48 ± 0.02 | 1.5226 | 1.5202 | 1.5024 | 9316.2869 | −7.7113 | 0.573 | 0.57 |
| Ba1%MnSn | 2.91 ± 0.06 | 1.5609 | 1.5581 | 1.5403 | 9041.5247 | −6.5746 | 0.605 | 0.61 |
| Ca1%MnSn | 2.66 ± 0.04 | 1.5450 | 1.5421 | 1.5242 | 9301.7890 | −7.1641 | 0.596 | 0.58 |
| Mg1%MnSn | 2.55 ± 0.03 | 1.5280 | 1.5252 | 1.5080 | 8882.9632 | −6.7283 | 0.580 | 0.58 |
| Ba–Ce standard | 2.84 ± 0.03 | 1.5545 | 1.5517 | 1.5335 | 9394.3291 | −7.2784 | 0.599 | 0.63 |
| Glass | Mn4+ Band 469 nm | Mn3+ Band 500 nm |
|---|---|---|
| Ba0.2%Mn | 0.054 | 3.294 |
| Ba1%Mn | 3.597 | 28.371 |
| Ba2%Mn | 4.301 | 119.155 |
| Ba-Mn standard | 9.123 | 348.300 |
| Mg1%Mn | 3.718 | 26.859 |
| Ca1%Mn | 5.977 | 24.553 |
| Ba1%Mn | 3.597 | 28.371 |
| Mg1%MnSn | 0.075 | 17.592 |
| Ca1%MnSn | 1.001 | 20.905 |
| Ba1%MnSn | 1.079 | 22.958 |
| Glass | Mn2+ Band Tetrahedral | Mn2+ Band Octahedral | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position nm | Area/106 | Position nm | Area/106 | |
| Ba0.2%Mn | - | - | - | - |
| Ba1%Mn | 540 | 22.702 | 601 | 10.247 |
| Ba2%Mn | 540 | 6.628 | 597 | 8.156 |
| Ba-Mn standard | - | - | - | - |
| Mg1%Mn | 551 | 28.003 | 598 | 54.165 |
| Ca1%Mn | 538 | 12.362 | 590 | 42.464 |
| Ba1%Mn | 540 | 22.702 | 601 | 10.247 |
| Mg1%MnSn | 539 | 9.478 | 583 | 63.439 |
| Ca1%MnSn | 539 | 26.365 | 593 | 7.256 |
| Ba1%MnSn | 531 | 19.762 | 602 | 11.118 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volf, J.; Vařák, P.; Buryi, M.; Kormunda, M.; Nekvindová, P. Identification and Methods of Influencing the Oxidation States of Mn and Ce in Silicate Glasses. Materials 2025, 18, 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091948
Volf J, Vařák P, Buryi M, Kormunda M, Nekvindová P. Identification and Methods of Influencing the Oxidation States of Mn and Ce in Silicate Glasses. Materials. 2025; 18(9):1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091948
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolf, Jakub, Petr Vařák, Maksym Buryi, Martin Kormunda, and Pavla Nekvindová. 2025. "Identification and Methods of Influencing the Oxidation States of Mn and Ce in Silicate Glasses" Materials 18, no. 9: 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091948
APA StyleVolf, J., Vařák, P., Buryi, M., Kormunda, M., & Nekvindová, P. (2025). Identification and Methods of Influencing the Oxidation States of Mn and Ce in Silicate Glasses. Materials, 18(9), 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091948






