Fabrication of Sustainable Diatomite-Based Foams with a Micro-Macroporous Synergistic Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Foam Preparation Process
2.2. Mix Design
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Dry Density
2.3.2. Compressive Strength
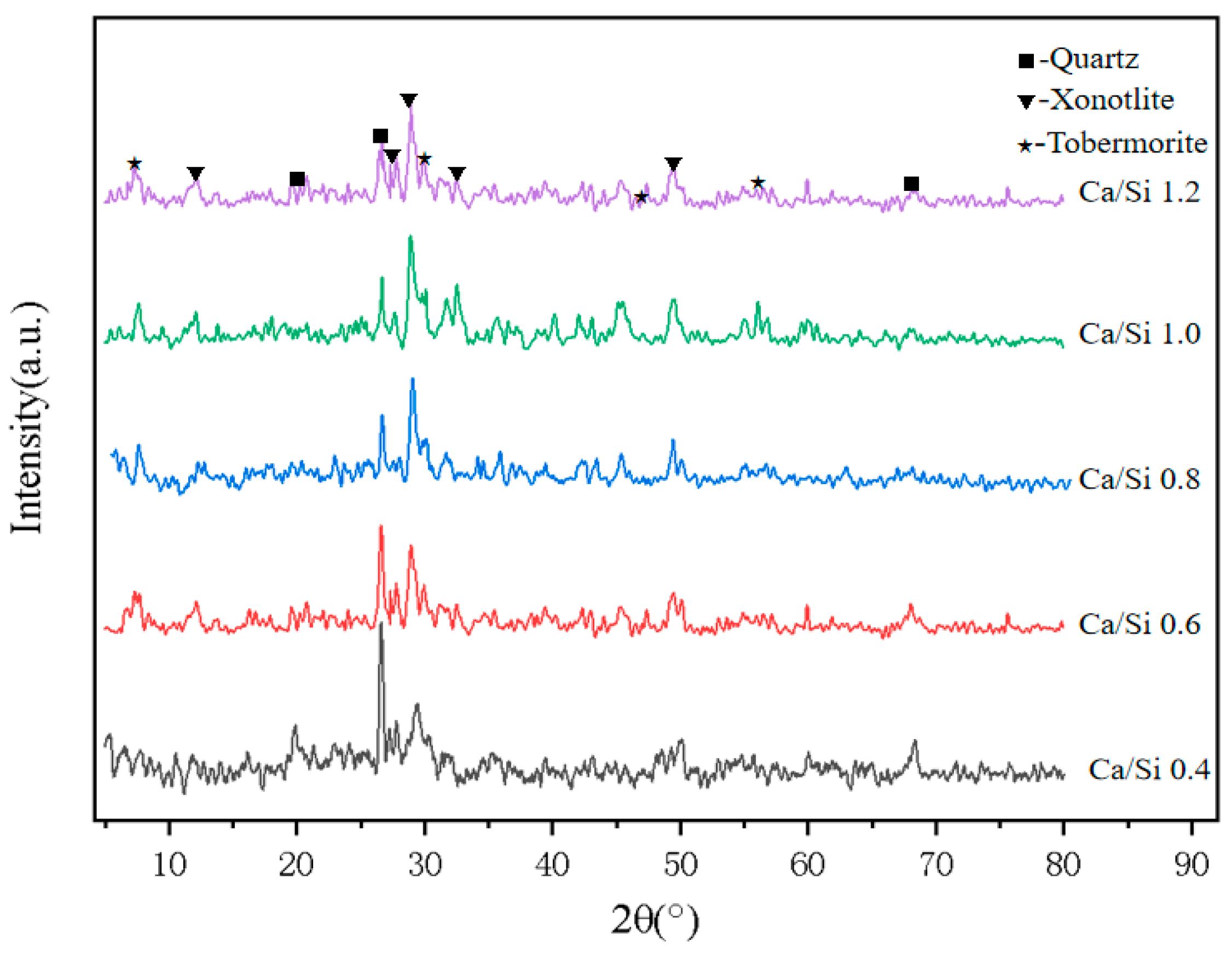
2.3.3. Phase Analysis
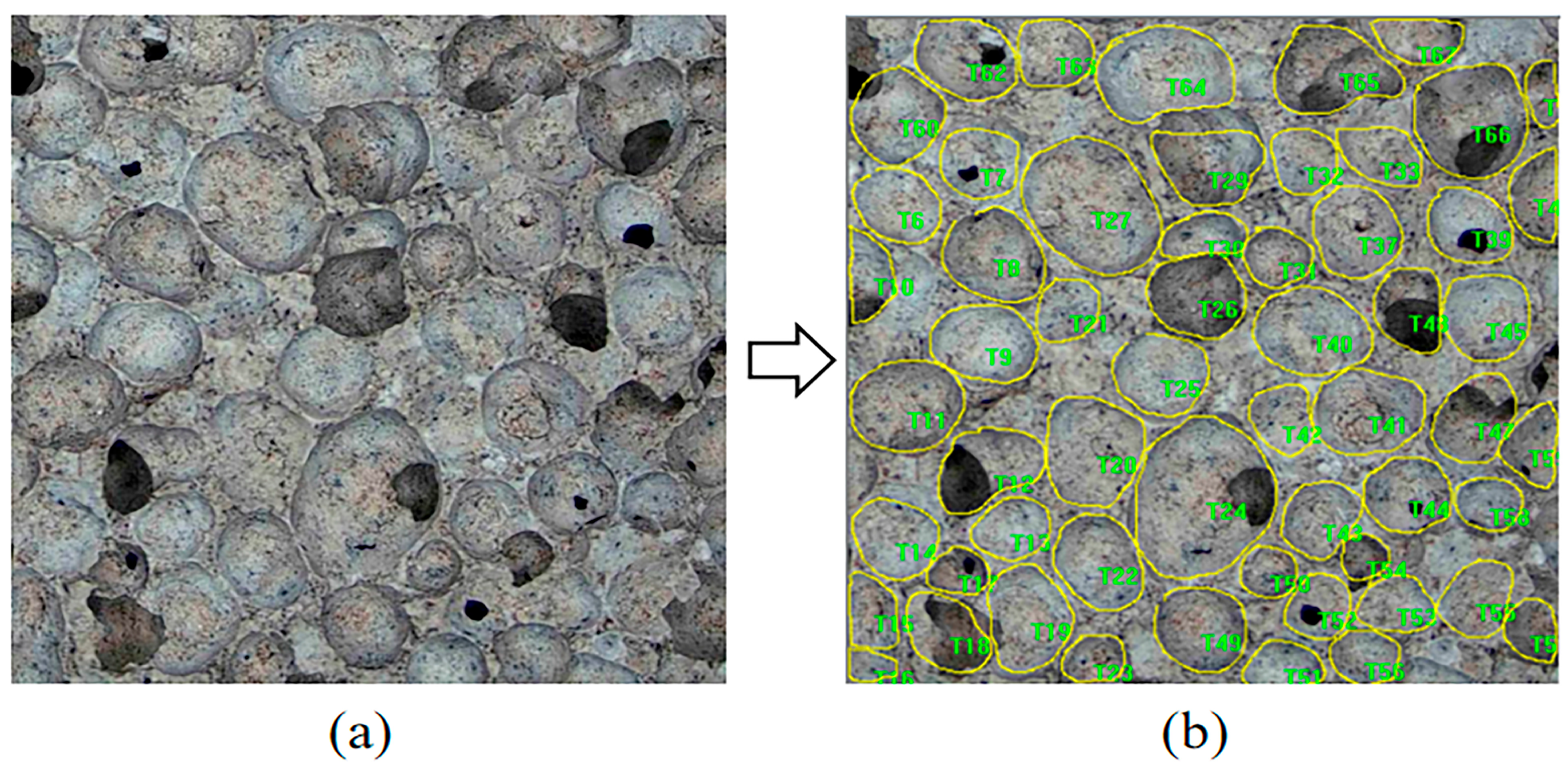
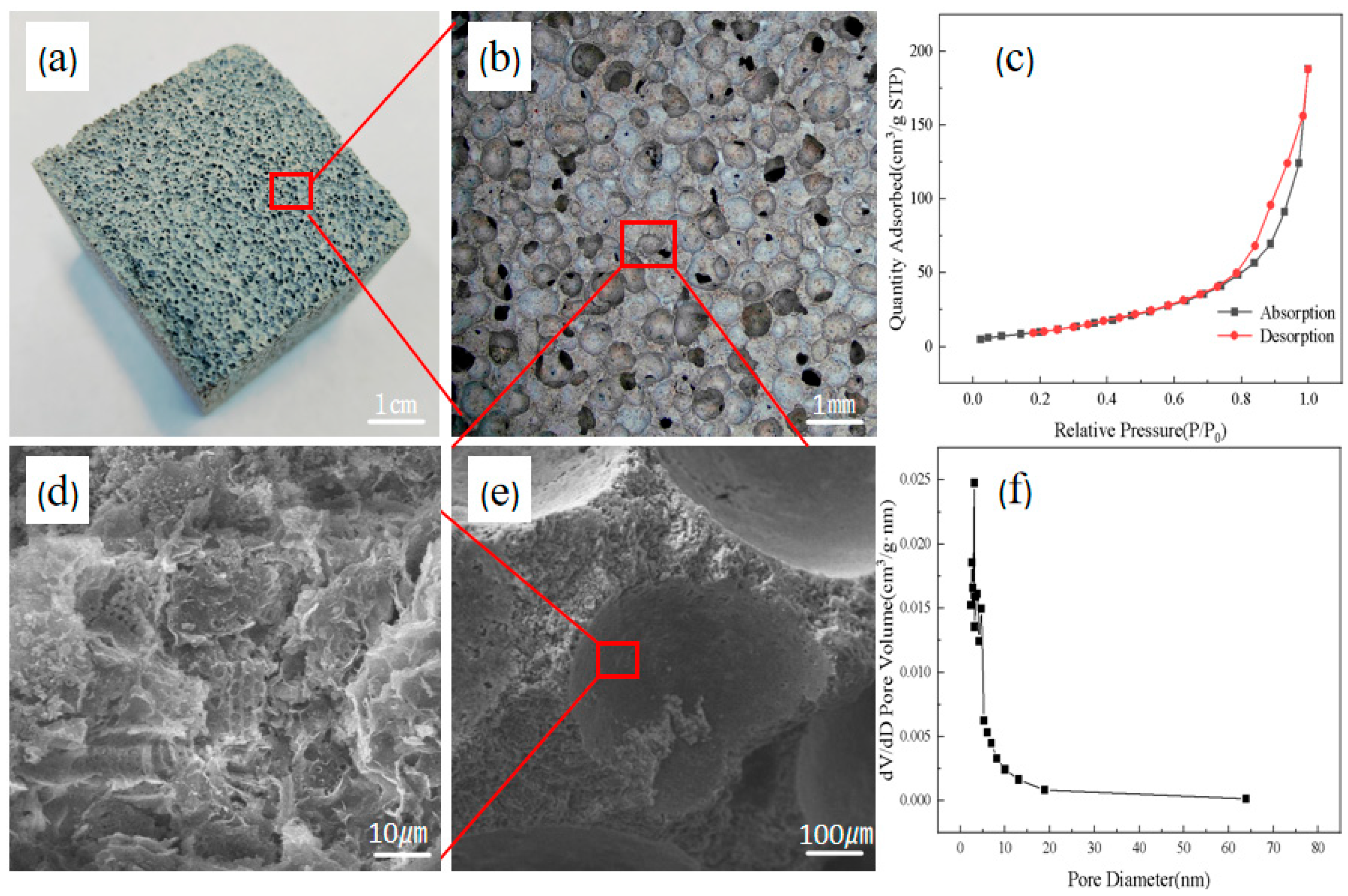
2.3.4. Pore Structure Analysis
2.3.5. Surface Area Analysis and Porosity Testing
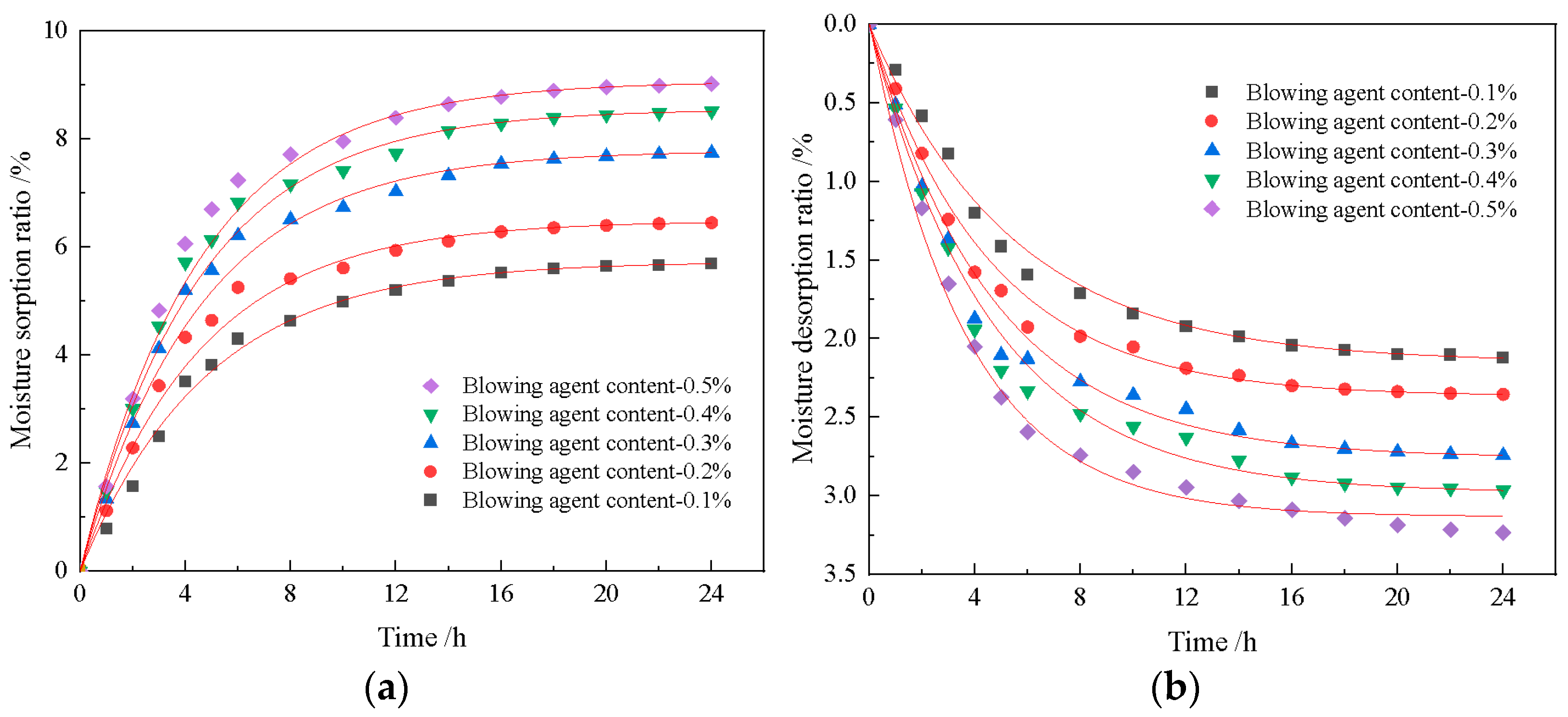
2.3.6. Moisturizing Performance Testing
3. Results and Discussion
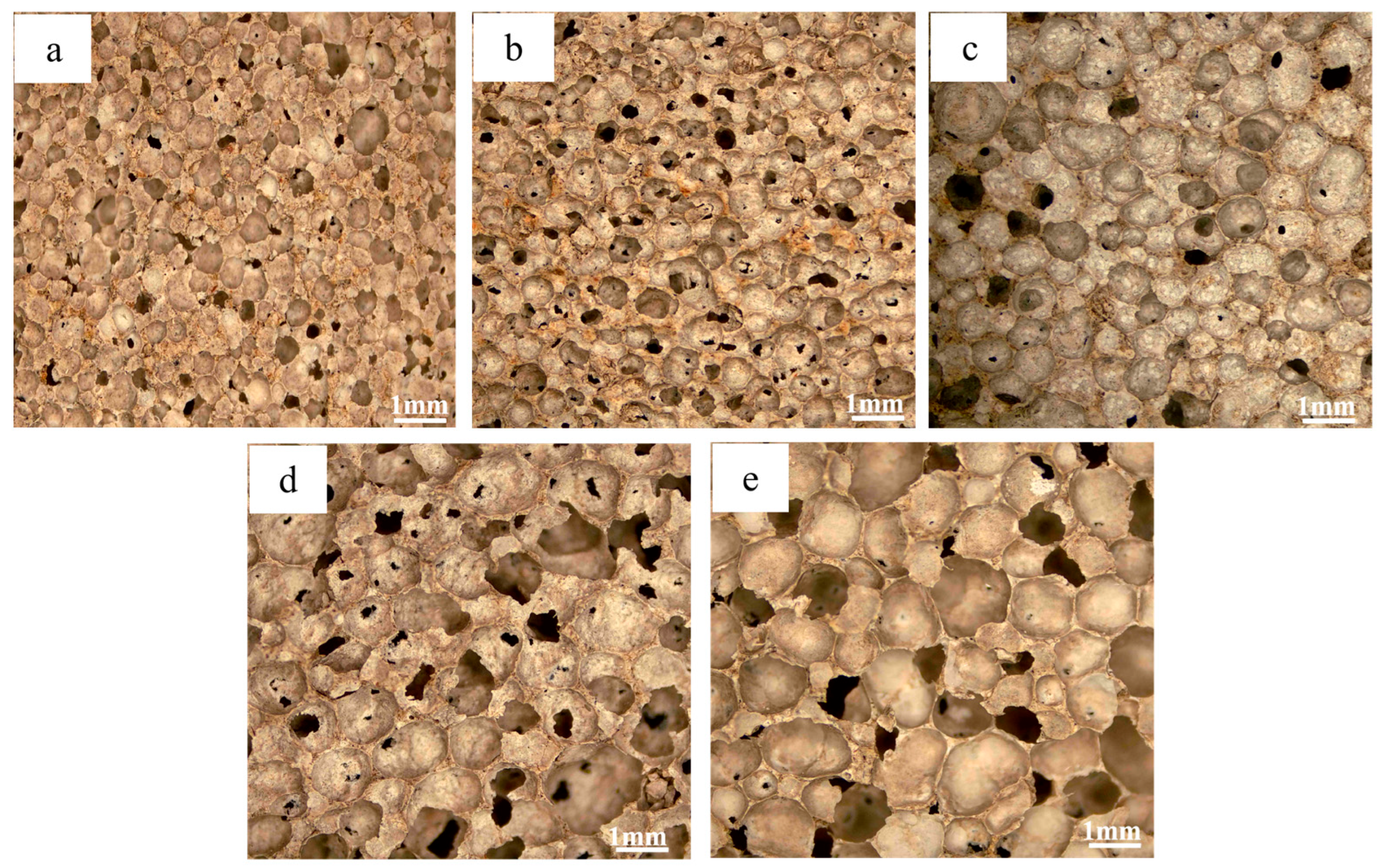
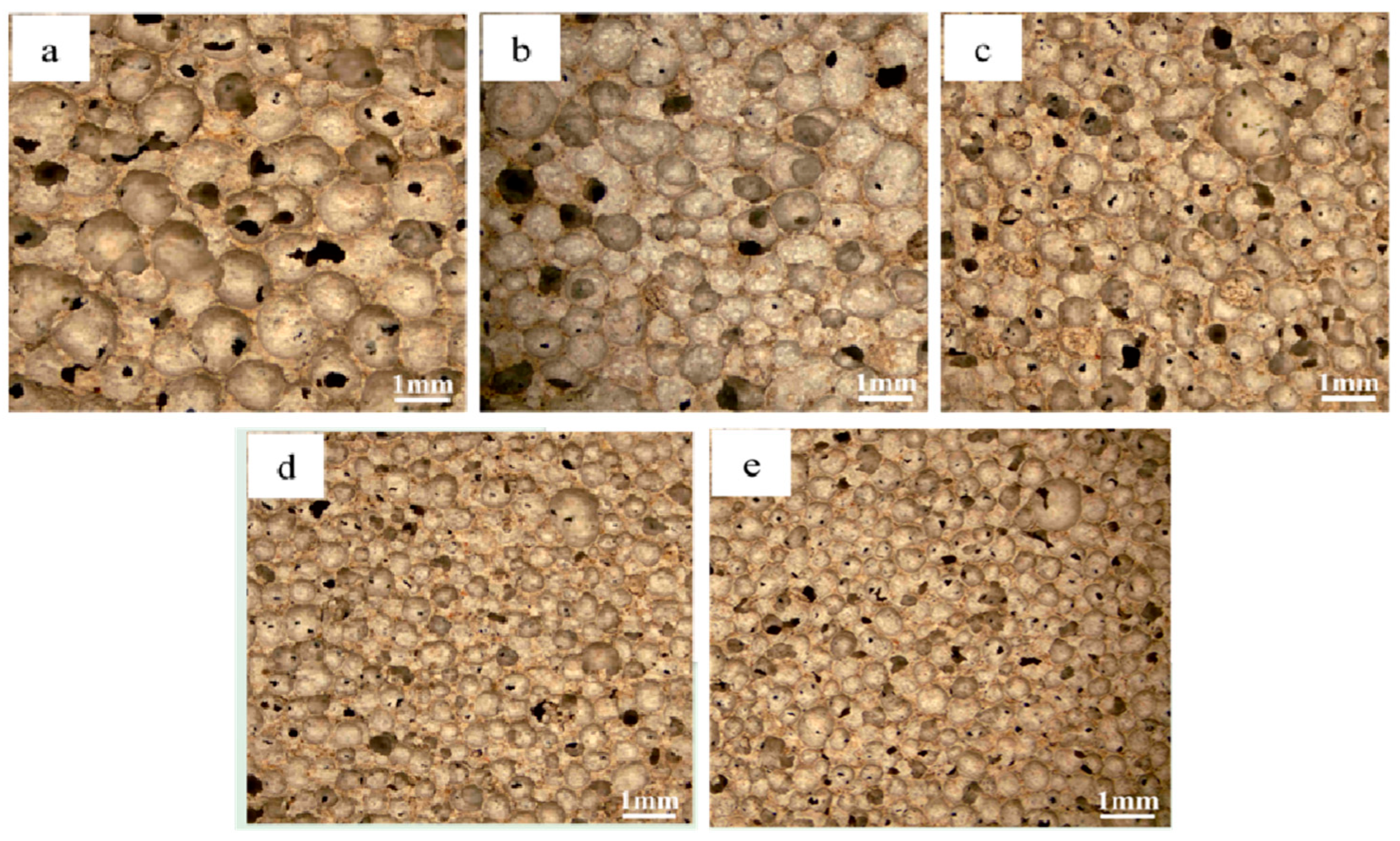
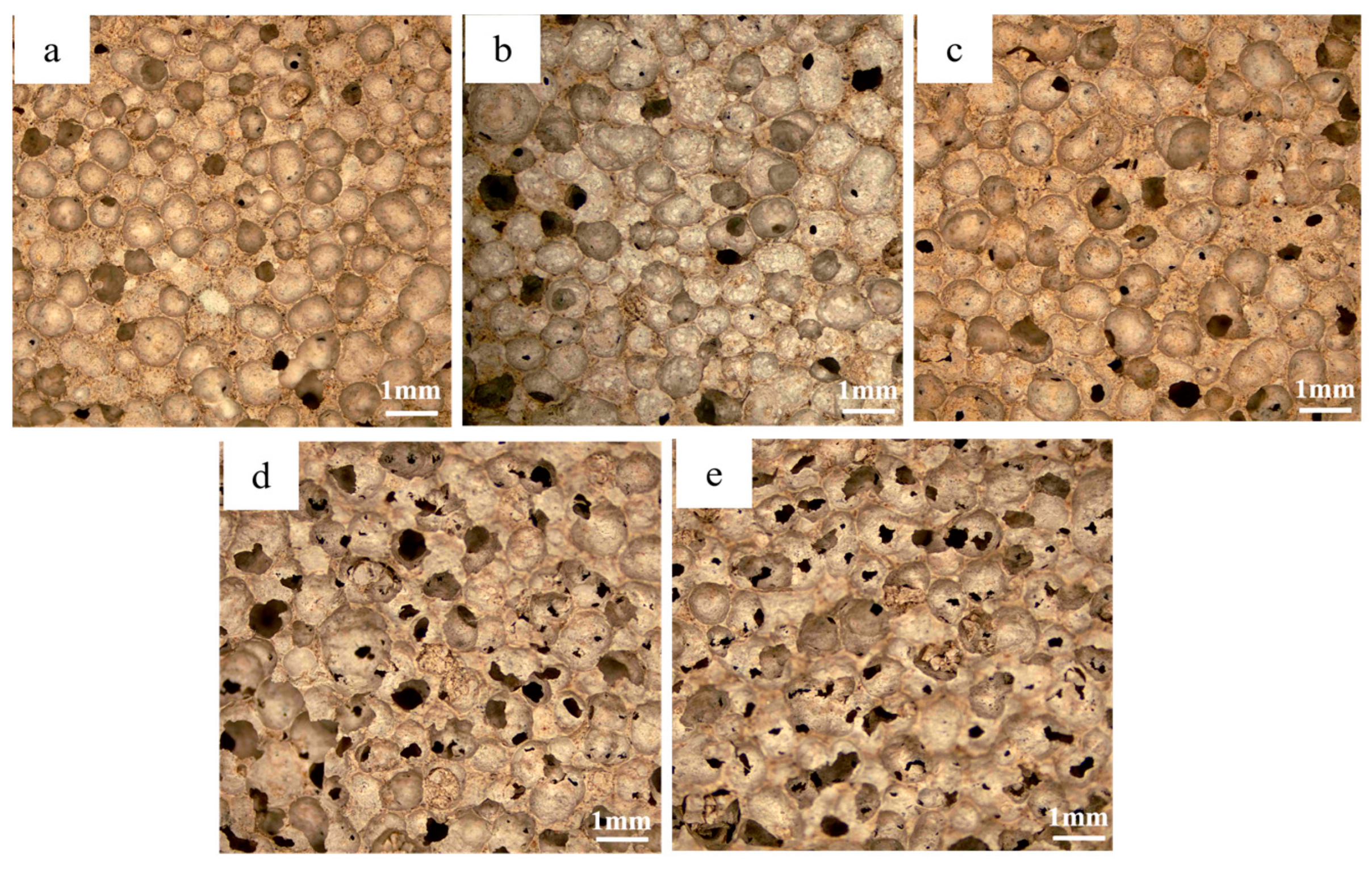
3.1. Morphological and Porosity Analysis
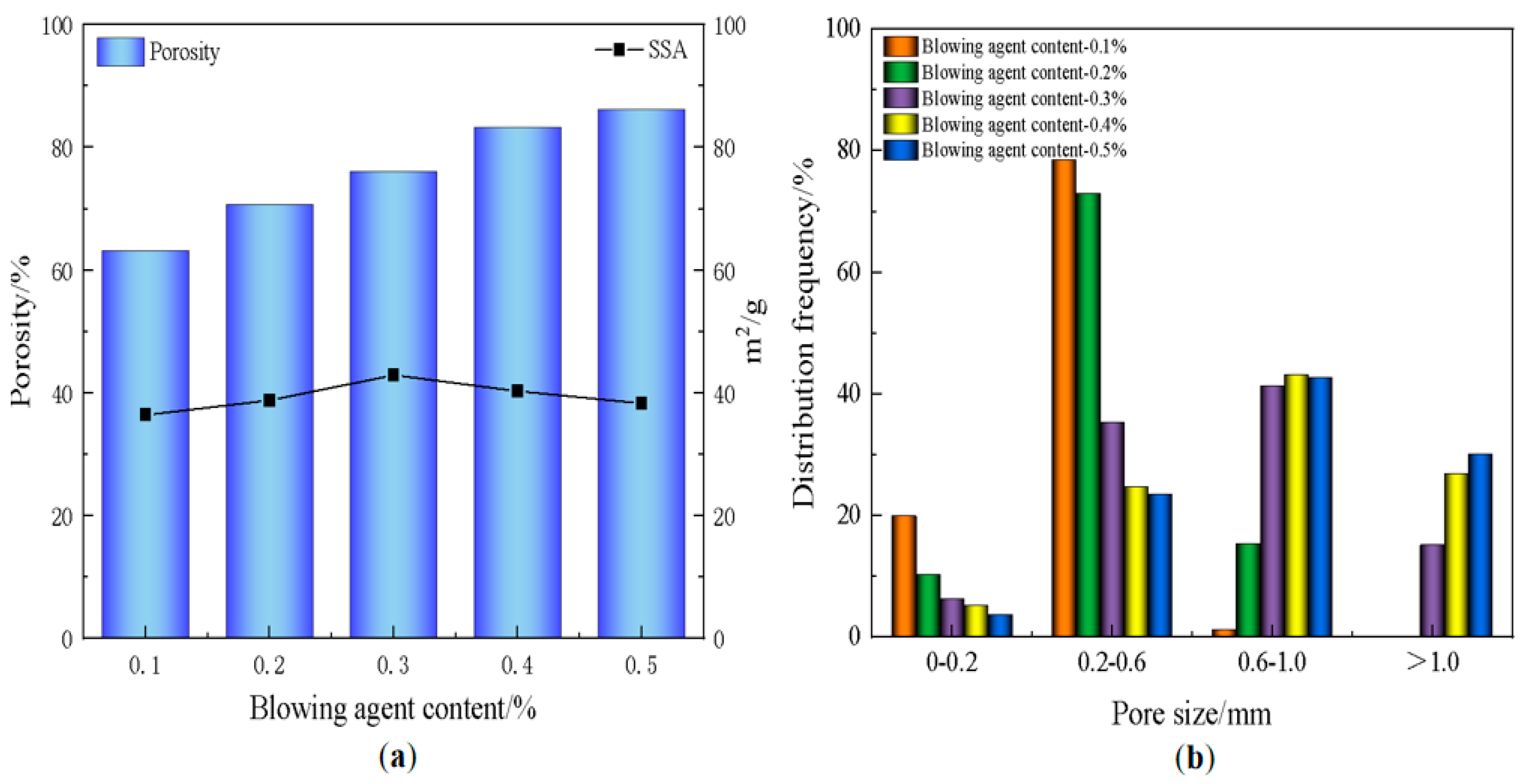
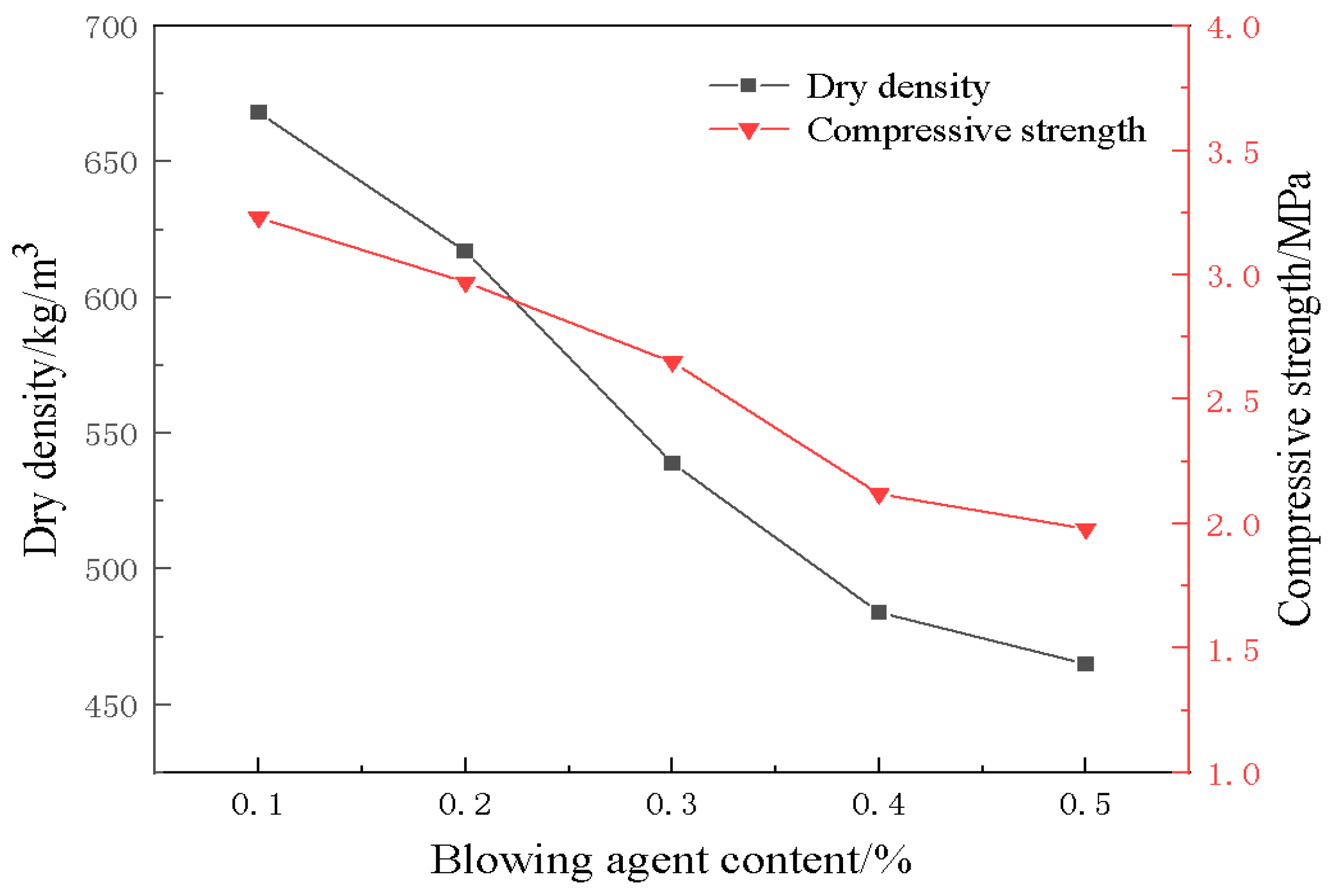
3.2. Effect of Blowing Agent on Material Properties
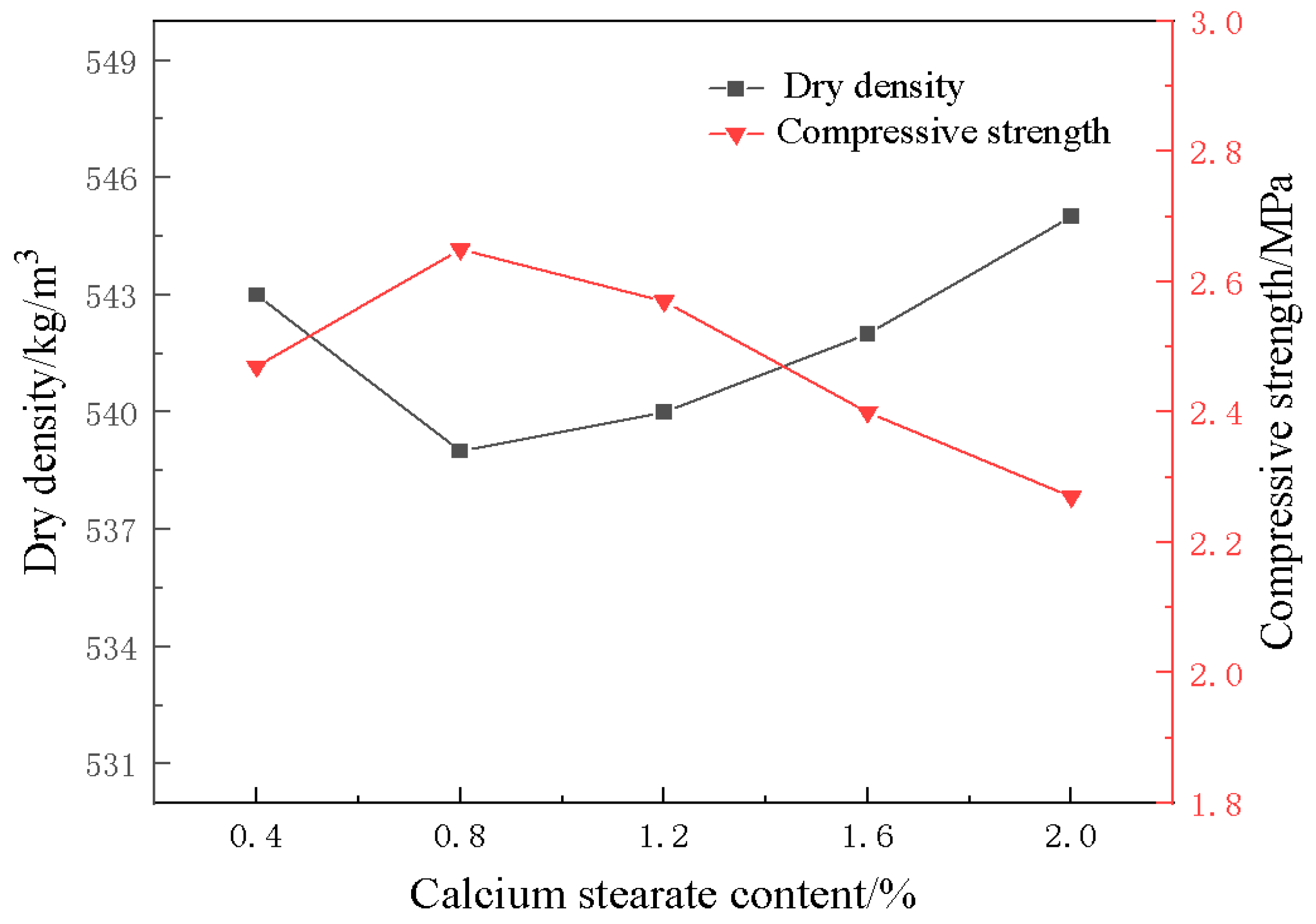
3.3. Effect of Foam Stabilizer on Material Properties
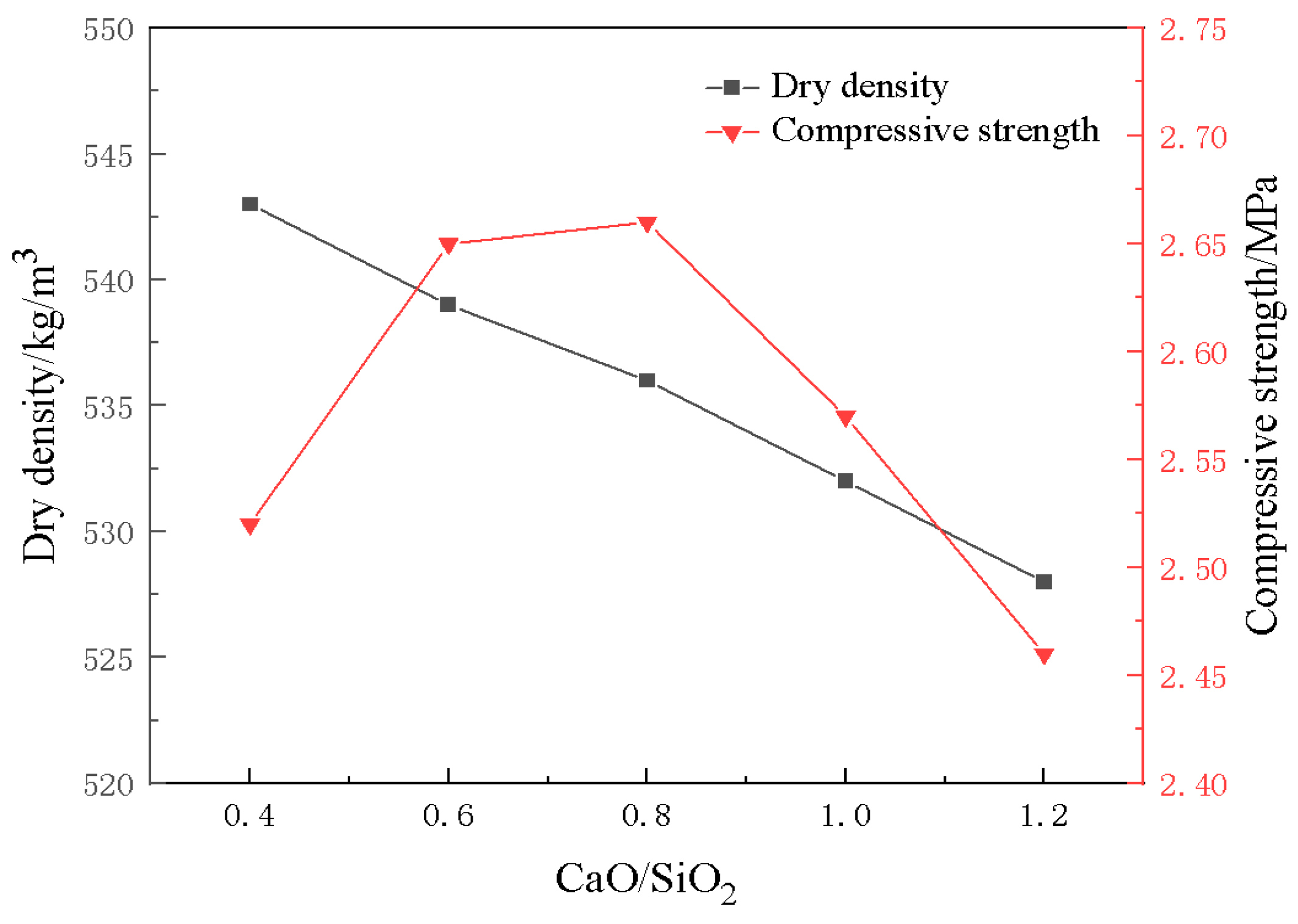
3.4. Effect of CaO/SiO2 on Material Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The blowing agent dosage has a large effect on the porosity, with the increase of blowing agent dosage, the porosity and average pore diameter of the foamed material increase, the specific surface area shows a trend of rising and then decreasing, and the dry density and compressive strength are gradually decreasing. When the dosage of the blowing agent is 0.3%, the specific surface area of the foamed material reaches a maximum of 42.9 m2/g, the dry density is 539 kg/m3, and the compressive strength is 2.65 MPa.
- (2)
- With the addition of foam stabilizer calcium stearate, the compressive strength of the foamed material decreases and then increases, and when the amount of calcium stearate added is 0.8%, it can obviously improve the pore structure and compressive strength of the foamed material.
- (3)
- The construction of multilevel pore size is conducive to the advantage of diatomite microporosity. With an increase in foaming agent dosage, the porosity of the material increases continuously, and the moisture regulating performance also improves. When the dosage of the blowing agent is 0.3%, the dosage of the foam stabilizer is 0.8%, and the CaO/SiO2 is 0.8, the comprehensive performance of the foamed material is the best. At this time, the porosity of the foamed material was 76.9%, the maximum moisture absorption rate was 8.51%, the maximum moisture release rate was 2.97%, and the compressive strength reached 2.67 MPa.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sousa, V.; Bogas, J.A. Comparison of energy consumption and carbon emissions from clinker and recycled cement production. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 306, 127277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chiang, P.-C.; Cai, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.-L.; Wei, S.; Huang, Q. Application of Wall and Insulation Materials on Green Building: A Review. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanshal, S.A.; Al-Qazaz, H.K. Consequences of cement dust exposure on pulmonary function in cement factory workers. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2020, 64, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, D.M.; Horvath, A.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Comparative environmental assessment of limestone calcined clay cements and typical blended cements. Environ. Res. Commun. 2023, 5, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asdrubali, F.; Grazieschi, G.; Roncone, M.; Thiebat, F.; Carbonaro, C. Sustainability of Building Materials: Embodied Energy and Embodied Carbon of Masonry. Energies 2023, 16, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones-Llorente, R.; Barbosa, R.; Almeida, M.; Montero García, E.A.; Rodríguez Saiz, Á. Ecological Design of New Efficient Energy-Performance Construction Materials with Rigid Polyurethane Foam Waste. Polymers 2020, 12, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, T.; D’Amato, M.; Sulla, R.; Cardinale, N. Mechanical and Physical Characterization of Papercrete as New Eco-Friendly Construction Material. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, M.; Abriak, N.-E. Development, Characterization, Application and Recycling of Novel Construction Materials. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roviello, G.; Ricciotti, L.; Molino, A.J.; Menna, C.; Ferone, C.; Asprone, D.; Cioffi, R.; Ferrandiz-Mas, V.; Russo, P.; Tarallo, O. Hybrid Fly Ash-Based Geopolymeric Foams: Microstructural, Thermal and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhasindrakrishna, K.; Pasupathy, K.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Sanjayan, J. Progress, current thinking and challenges in geopolymer foam concrete technology. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 116, 103886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, M.; Sheng, K.; Shao, Z.; Yao, Y.; Hong, B. Development of new material for geopolymer lightweight cellular concrete and its cementing mechanism. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Hao, Y.; Ma, G. Electromagnetic wave absorption performance of porous geopolymer: Dual effects of fly ash on alkali activation and microwave dissipation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 153, 105722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, M.; Serpieri, R. A critical review of 100 years of permeability tests for the sustainability of concrete structures. J. Sustain. Cem.-Based Mater. 2024, 13, 1725–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaburro, G.; Iannace, G.; Ricciotti, L.; Apicella, A.; Perrotta, V.; Aversa, R. Acoustic Applications of a Foamed Geopolymeric-Architected Metamaterial. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Qian, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, S. A comparative study of porous geopolymers synthesized by pre-foaming and H2O2 foaming methods: Strength and pore structure characteristics. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 17807–17817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.; Fediuk, R.; Vatin, N.; Huei Lee, Y.; Murali, G.; Ozbakkaloglu, T.; Klyuev, S.; Alabduljabber, H. Fibre-Reinforced Foamed Concretes: A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Dai, S.; Ma, B.; Jiang, Q. Investigation of silica fume as foam cell stabilizer for foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 237, 117514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Hou, W.; Sun, Z.; Lv, W. Study of In Situ Foamed Fly Ash Geopolymer. Materials 2020, 13, 4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, H.; Yan, C.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J. Investigating the Mechanical and Durability Characteristics of Fly Ash Foam Concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ding, S.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Q. Preparation and Properties of Foam Concrete Incorporating Fly Ash. Materials 2022, 15, 6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, T.P.P.; Bezerra, B.P.; Verza, J.R.; Luz, A.P.; Morelli, M.R. Physico-mechanical properties of metakaolin and diatomite-based geopolymers. Mater. Lett. 2023, 349, 134784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishna, B.; Pasla, D. Development of metakaolin based high strength recycled aggregate geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 391, 131810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykiel, M.; Korniejenko, K.; Setlak, K.; Melnychuk, M.; Polivoda, N.; Kozub, B.; Hebdowska-Krupa, M.; Łach, M. The Influence of Diatomite Addition on the Properties of Geopolymers Based on Fly Ash and Metakaolin. Materials 2024, 17, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Garcia, F.; Rubio-Cintas, M.D.; Parron-Rubio, M.E.; Garcia-Manrique, J.M. Advances in the Analysis of Properties Behaviour of Cement-Based Grouts with High Substitution of Cement with Blast Furnace Slags. Materials 2020, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, G.; Liang, K. Development of fly ash and slag based high-strength alkali-activated foam concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 128, 104447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Ren, X.; He, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Xing, P. Microstructure evolution and properties of red mud/slag-based cenosphere/geopolymer foam exposed to high temperatures. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 34362–34374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahajská, P.; Opfergelt, S.; Fritz, S.C.; Stadmark, J.; Conley, D.J. What is diatomite? Quat. Res. 2020, 96, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galzerano, B.; Cabello, C.I.; Muñoz, M.; Buonocore, G.G.; Aprea, P.; Liguori, B.; Verdolotti, L. Fabrication of Green Diatomite/Chitosan-Based Hybrid Foams with Dye Sorption Capacity. Materials 2020, 13, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-H.; Geng, J.-T.; Cai, J.-C.; Cai, Y.-F.; Cao, C.-Y. Adsorption performance of basic fuchsin on alkali-activated diatomite. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2020, 38, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; He, Y.; Zheng, R.; Guo, Z.; Gao, H.; He, X.; Wu, F.; Ji, X. The preparation and characterization of calcined diatomite with high adsorption properties by CaO hydrothermal activation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 636, 128134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Li, F.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Foam-gelcasting preparation, microstructure and thermal insulation performance of porous diatomite ceramics with hierarchical pore structures. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 2717–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, B.; Riaz Ahmad, M. Characterization of a novel bio-insulation material for multilayer wall and research on hysteresis effect. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 290, 123162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-G.; Huang, Y.; Shih, Y.-F.; Wang, W.-C.; Wang, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-X.; Chang, H.-W. Mechanical and thermal insulation performance of waste diatomite cement mortar. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 4739–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łach, M.; Gliścińska, E.; Przybek, A.; Smoroń, K. The Influence of Diatomite on the Sound Absorption Ability of Composites. Materials 2024, 17, 4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Shi, J.; Ma, Q.; Dai, X.; Chen, Z. Experimental study on humidity control performance of diatomite-based building materials. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 114, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.S.; Shi, C.; Hashem, F.S.; Israde-Alcantara, I.; Pfeiffer, H. Exploring diatomite as a novel natural resource for ecofriendly-sustainable hybrid cements. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 202, 107402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Yu, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, K.; Ma, Y.; Fu, J. Roles of diatomite in hydration, microstructure and strength development of cement paste. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 37, 107555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, B.; Chen, W.; Tao, H. Mechanical property, volume stability and microstructure of lightweight engineered cementitious composites (LECC) containing high-volume diatomite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 133884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Sathyan, D.; Mini, K.M. Physical and functional characteristics of foam concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, R.; Jaya, R.P.; Muthusamy, K.; Sulaiman, M.; Duraisamy, Y.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Przybył, A.; Sochacki, W.; Skrzypczak, T.; Vizureanu, P.; et al. Relation between Density and Compressive Strength of Foamed Concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Effect of calcium to silica ratio on the synthesis of calcium silicate hydrate in high alkaline desilication solution. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 104, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, B.; Xu, G. Preparation of autoclaved aerated concrete by using graphite tailings as an alternative silica source. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 267, 121792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C495-2022; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Lightweight Insulating Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ISO 12571-2013; Hygrothermal Performance of Building Materials and Products—Determination of Hygroscopic Sorption Properties. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Hou, L.; Li, J.; Lu, Z.; Niu, Y. Influence of foaming agent on cement and foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 280, 122399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Meng, J.; Ning, B.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, W.; Cui, T.; Shi, X. Effects of foam stabilizers on the properties and microstructure of autoclaved aerated concrete from iron tailings. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 18395–18411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Luo, Y.; Song, C.; Jin, W.; Xiang, T.; Qiao, M.; Dang, J.; Bai, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, J. Effect of calcium stearate hydrophobic agent on the performance of mortar and reinforcement corrosion in mortar with cracks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 450, 138684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Composition | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | K2O | MgO | Na2O | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass fraction | 56.02 | 12.04 | 7.76 | 1.69 | 1.50 | 1.61 | 0.60 | 16.17 |
| Code | Al (g) | CS (g) | Diatomite (g) | CaO (g) | Silica Fume (g) | PCE (g) | Water (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0.2 | 1.6 | 124 | 56 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| A2 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 124 | 56 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| A3 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 124 | 56 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| A4 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 124 | 56 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| A5 | 1.0 | 1.6 | 124 | 56 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| B1 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 124 | 56 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| B2 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 124 | 56 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| B3 | 0.6 | 2.4 | 124 | 56 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| B4 | 0.6 | 3.2 | 124 | 56 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| B5 | 0.6 | 4.0 | 124 | 56 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| C1 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 140 | 40 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| C2 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 124 | 56 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| C3 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 108 | 72 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| C4 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 93 | 87 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
| C5 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 80 | 150 | 20 | 0.6 | 110 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, N.; Li, C.; Lu, Y.; Li, L. Fabrication of Sustainable Diatomite-Based Foams with a Micro-Macroporous Synergistic Structure. Materials 2025, 18, 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091968
Ning H, Li Z, Liu N, Li C, Lu Y, Li L. Fabrication of Sustainable Diatomite-Based Foams with a Micro-Macroporous Synergistic Structure. Materials. 2025; 18(9):1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091968
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Hailong, Zhiwu Li, Ning Liu, Chengling Li, Yao Lu, and Long Li. 2025. "Fabrication of Sustainable Diatomite-Based Foams with a Micro-Macroporous Synergistic Structure" Materials 18, no. 9: 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091968
APA StyleNing, H., Li, Z., Liu, N., Li, C., Lu, Y., & Li, L. (2025). Fabrication of Sustainable Diatomite-Based Foams with a Micro-Macroporous Synergistic Structure. Materials, 18(9), 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091968







