Influence of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on the Corrosion Residual Strength of an AZ91D Magnesium Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
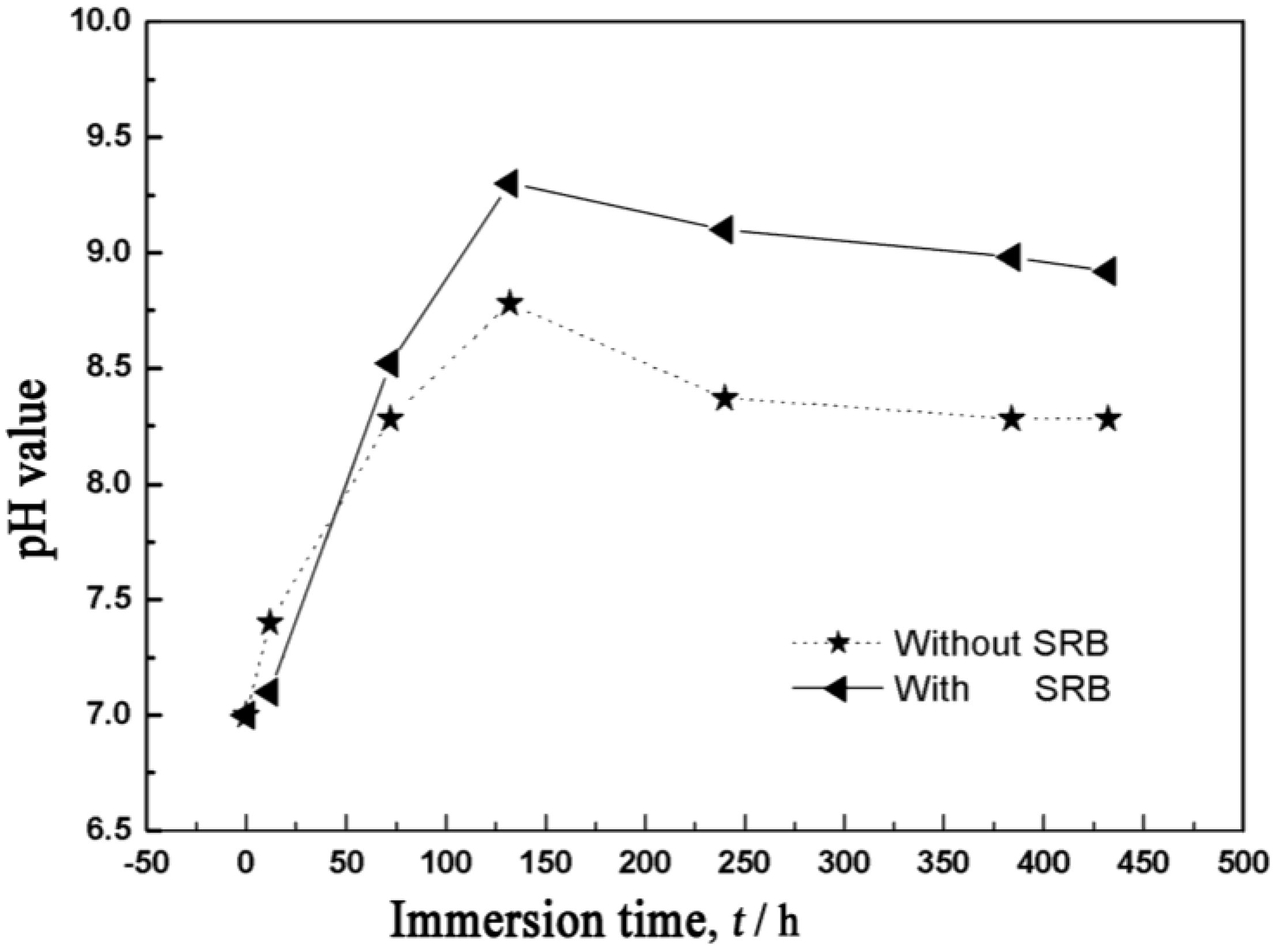
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphology of the Corrosion Product


2.2. Corrosion Residual Strength



2.3. Fractography Analysis

2.4. Composition of the Corrosion Film
2.5. Mechanism Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Sample Preparation
| AZ91D alloy element | Al | Zn | Mn | Si | Fe | Cu | Ni | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element composition, wt% | 7.98 | 0.60 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | – |
3.2. Cultivation of SRB
| Medicine | Purity | Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium sulfate | Analytical reagent grade (≥99.5%) | 0.5 g/L |
| Ammonium chloride | 1.0 g/L | |
| Calcium chloride | 0.1 g/L | |
| Ammonium chloride | 1.0 g/L | |
| Di-potassium hydrogen orthophosphate | 0.5 g/L | |
| Magnesium sulfate | 2.0 g/L | |
| Sodium lactate | 3.5 g/L | |
| Yeast extract | 1.0 g/L |
3.3. Corrosion Experiments
3.4. Morphology of the Corrosion Product and Fractography
3.5. Tensile Experiments
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The phosphate element in the corrosion film of the AZ91D magnesium alloy decreased in the presence of SRB;
- (2)
- The metabolism of SRB changes the local corrosion environment and leads to an accelerated pitting corrosion;
- (3)
- The corrosion residual strength of the AZ91D magnesium alloy drops quickly in the SRB corrosion media due to the rapid pitting corrosion induced by SRB.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amira, S.; Huot, J. Effect of cold rolling on hydrogen sorption properties of die-cast and as-cast magnesium alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 520, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivapragash, M.; Lakshminarayanan, P.R.; Karthikeyan, R.; Hanumantha, M.; Bhatt, R.R. Hotdeformation behavior of ZE41A magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, H.; Sen, S. The effect of PVD coatings on the corrosion behaviour of AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 2006, 27, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, H.; Sinici, H. Corrosion behaviour of magnesium alloys coated with TiN by cathodic arc deposition in NaCl and Na2SO4 solutions. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, R.; Bobby, M. Influence of surface roughness on the corrosion behaviour of magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2350–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Lia, Q.; Yang, X.K.; Zhong, X.K.; Dai, Y. Corrosion resistance of AZ91D magnesium alloy with electroless plating pretreatment and Ni-TiO2 composite coating. Mater. Charact. 2010, 61, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghayani, M.K.; Niroumand, B. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on microstructure and tensile strength of AZ91 magnesium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrena, M.I.; Gómez de Salazar, J.M.; Matesanz, L.; Soria, A. Effect of heat treatments on oxidation kinetics in AZ91 and AM60 magnesium alloys. Mater. Charact. 2011, 62, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, B.P.; Shinohara, T. Corrosion behavior of AZ91 magnesium alloy in dilute NaCl solutions. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, M.; Persson, D.; Leygraf, C. Atmospheric corrosion of field-exposed magnesium alloy AZ91D. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Shen, T.; Aung, N.N. Effect of heat treatment on corrosion behaviour of magnesium alloy AZ91D in simulated body fluid. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.H. Roles of β phase in the corrosion procss of AZ91D magnesium alloy. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Ma, A.B.; Jiang, J.H.; Lin, P.H.; Yang, D.H. Corrosion behavior of bulk ultra-fine-grained AZ91D magnesium alloy fabricated by equal-channel-angular-pressed. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.G.; Zhang, S.; Bu, J.F.; Lin, C.J.; Song, G.L. Recent progress in corrosion of magnesium alloys by organic coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 73, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Wang, Q.; Song, Y.L.; Zhang, D.W.; Yu, S.R.; Zhu, X.Y. A study on the corrosion behavior of Ce-modified cast AZ91 magnesium alloy in the presence of sulfate-reducing bacteria. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 473, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.N.; Zhang, D.W. Study on the corrosion residual strength of the 1.0 wt% Ce modified AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater. Charact. 2010, 61, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhu, X.Y.; Yu, S.R.; Zhang, L.N. Study on the effect of corrosion on the tensile properties of the 1.0 wt% Yttrium modified AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 517, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, C.; Peng, J.; Park, K. Electrochemical mechanisms of anaerobic corrosion influenced by sulfate-reducing bacteria. Water Res. 1994, 28, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.Z.; Hou, B.R.; Yu, Z.G. Characteristics of sulfide corrosion products on 316L stainless steel surfaces in the presence of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2006, 26, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, W. Influence of SRB on corrosion behaviour of AZ91 magnesium alloy in two kinds of culture media. J. Mater. Eng. 2011, 9, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Forno, A.D.; Bestetti, M. Effect of the electrolytic solution composition on the performance of micro-arc anodic oxidation films formed on AM60B magnesium alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.H.; Bandopadhyay, S.; Chen, C.F.; Guo, Y.J.; Ning, C.Y. Effect of oxidation time on the corrosion behavior of micro-arc oxidation produced AZ31 magnesium alloys in simulated body fluid. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 543, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Z.; Wang, Q.D.; Ding, W.J.; Zeng, X.Q.; Zhu, Y.P. Fracture behavior of AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater. Lett. 2000, 44, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing Wrought and Cast Aluminum-and Magnesium-Alloy Products; ASTM B557-14; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J. Influence of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on the Corrosion Residual Strength of an AZ91D Magnesium Alloy. Materials 2014, 7, 7118-7129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7107118
Zhu X, Liu Y, Wang Q, Liu J. Influence of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on the Corrosion Residual Strength of an AZ91D Magnesium Alloy. Materials. 2014; 7(10):7118-7129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7107118
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xianyong, Yaohui Liu, Qiang Wang, and Jiaan Liu. 2014. "Influence of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on the Corrosion Residual Strength of an AZ91D Magnesium Alloy" Materials 7, no. 10: 7118-7129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7107118
APA StyleZhu, X., Liu, Y., Wang, Q., & Liu, J. (2014). Influence of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on the Corrosion Residual Strength of an AZ91D Magnesium Alloy. Materials, 7(10), 7118-7129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7107118






