Climate Effect on Ponderosa Pine Radial Growth Varies with Tree Density and Shrub Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
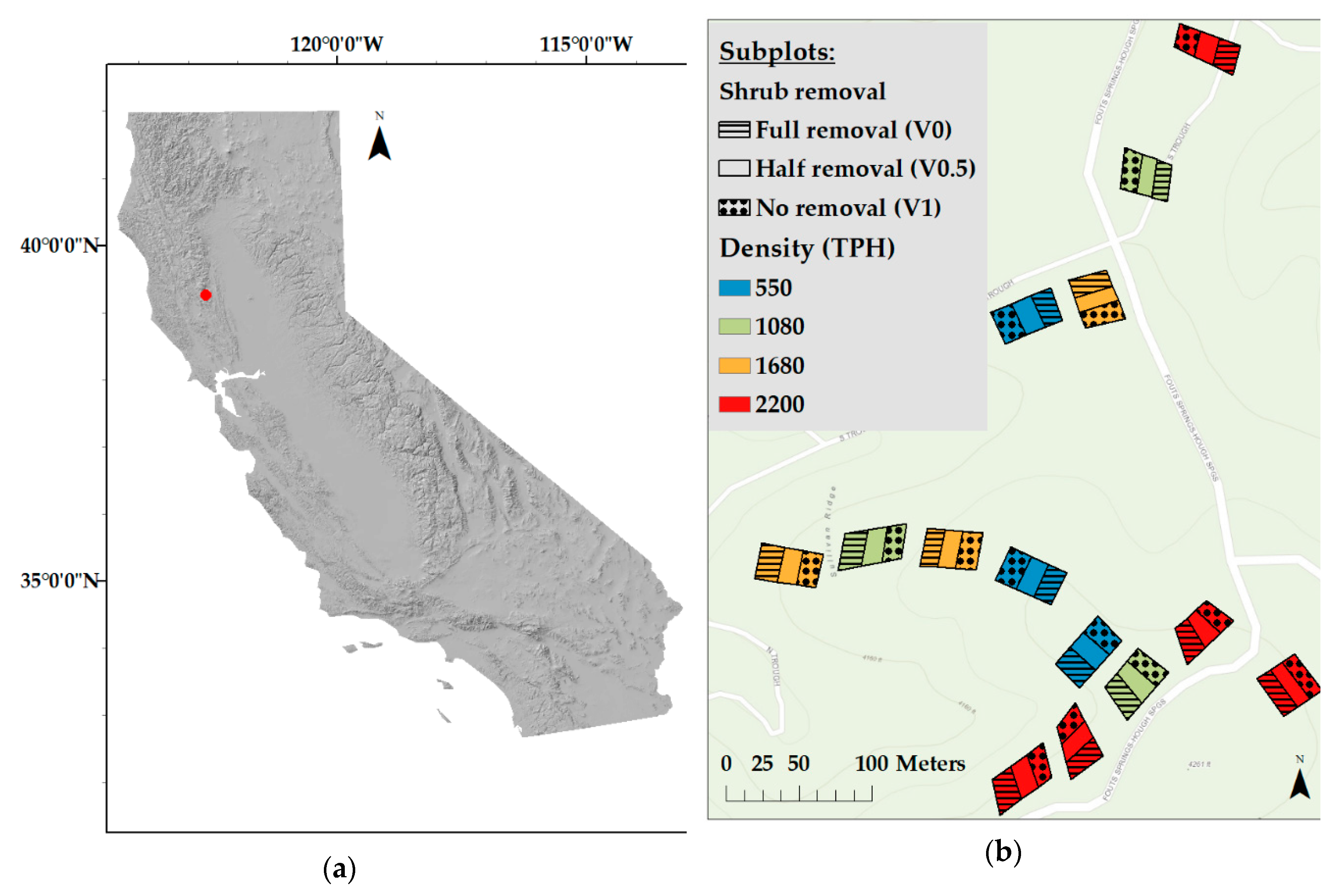
2.1. Study Site
- 2200 TPH (control)
- 1680 TPH (2.4 m spacing)
- 1080 TPH (3.0 m spacing)
- 550 TPH (4.3 m spacing).
- (V1) no shrub removal
- (V0.5) half shrub removal
- (V0) complete shrub removal.
2.2. Sample Collection
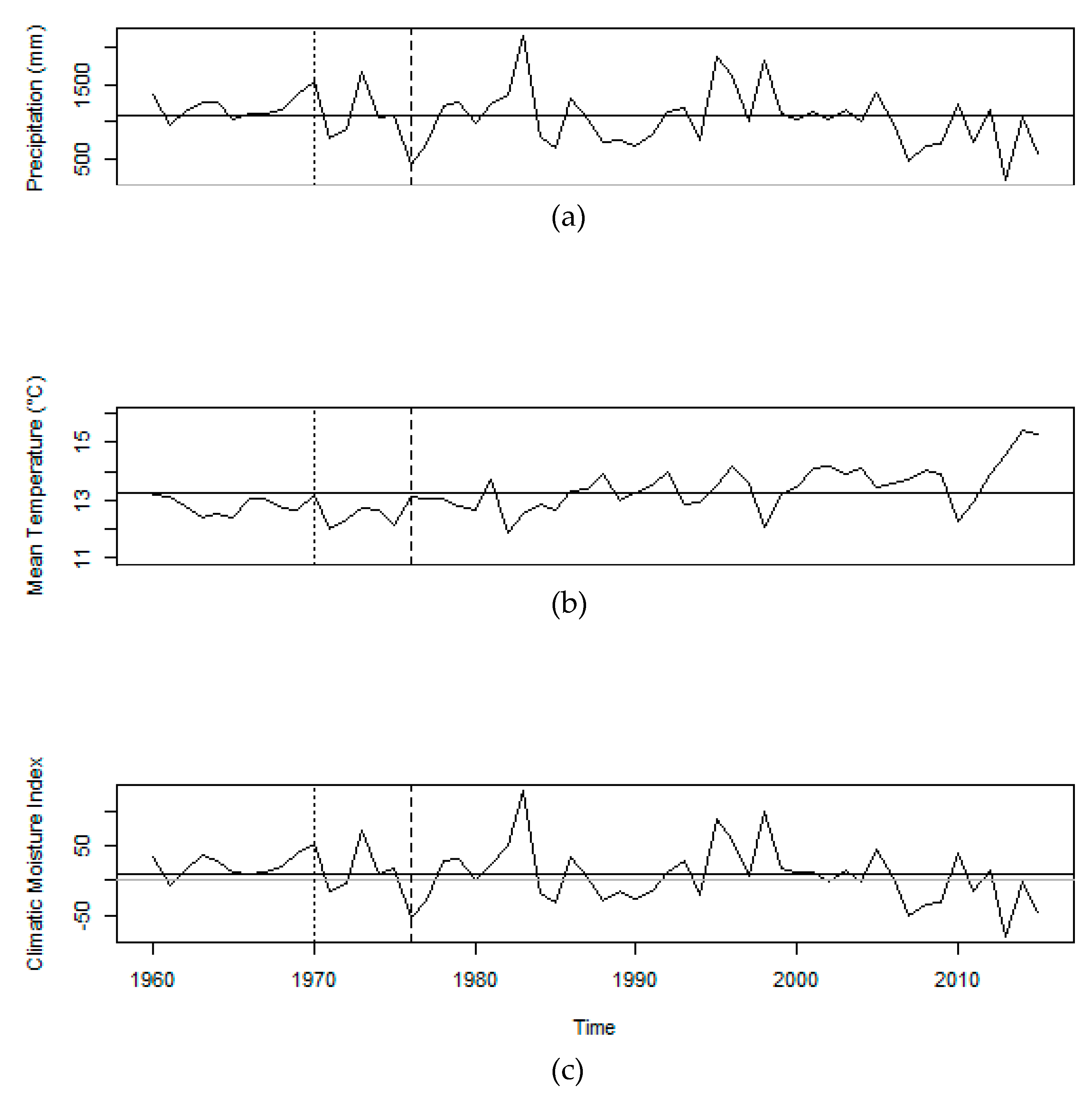
2.3. Climate Data
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
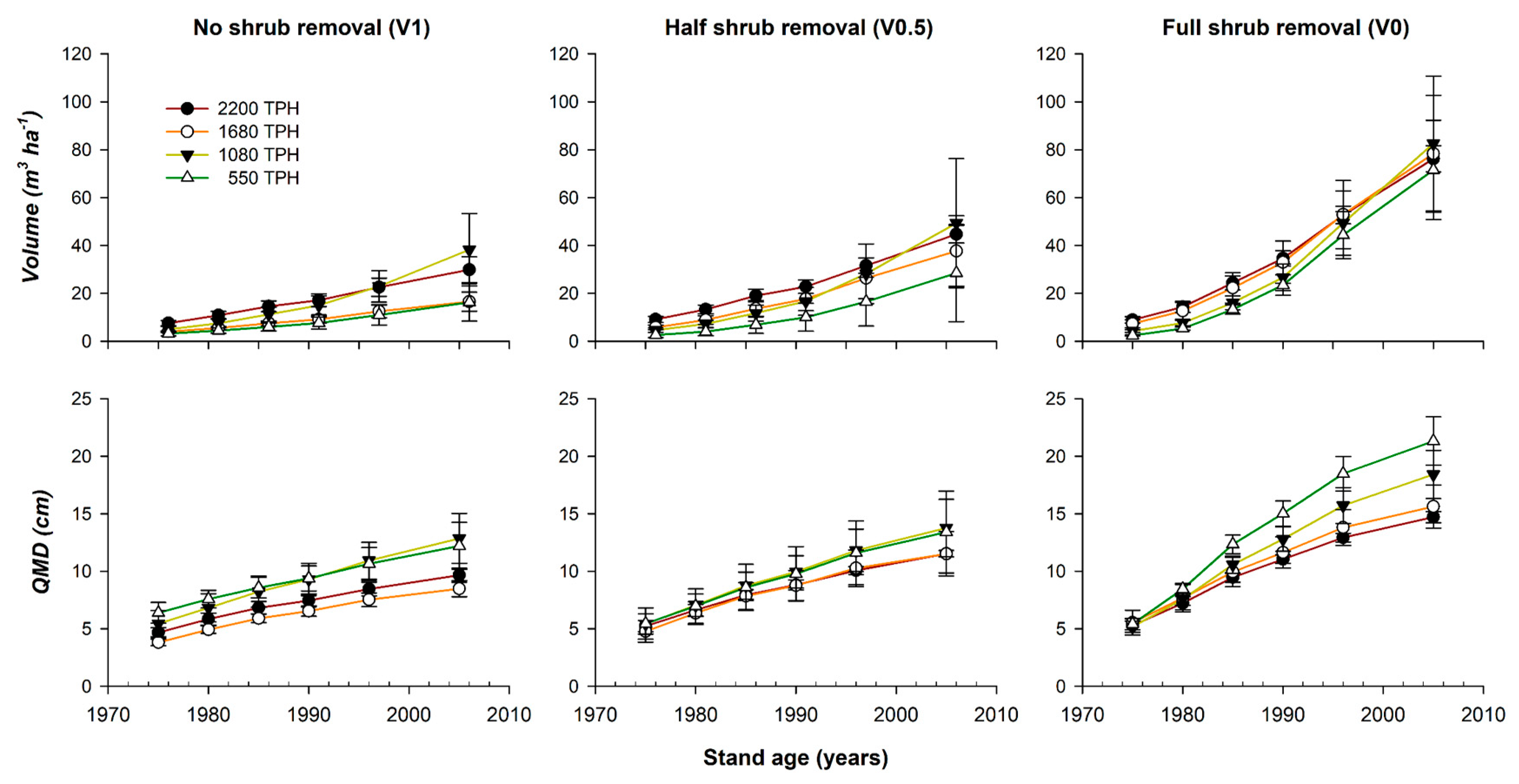
3.1. Treatment Effect on Growth and Chronology Statistics
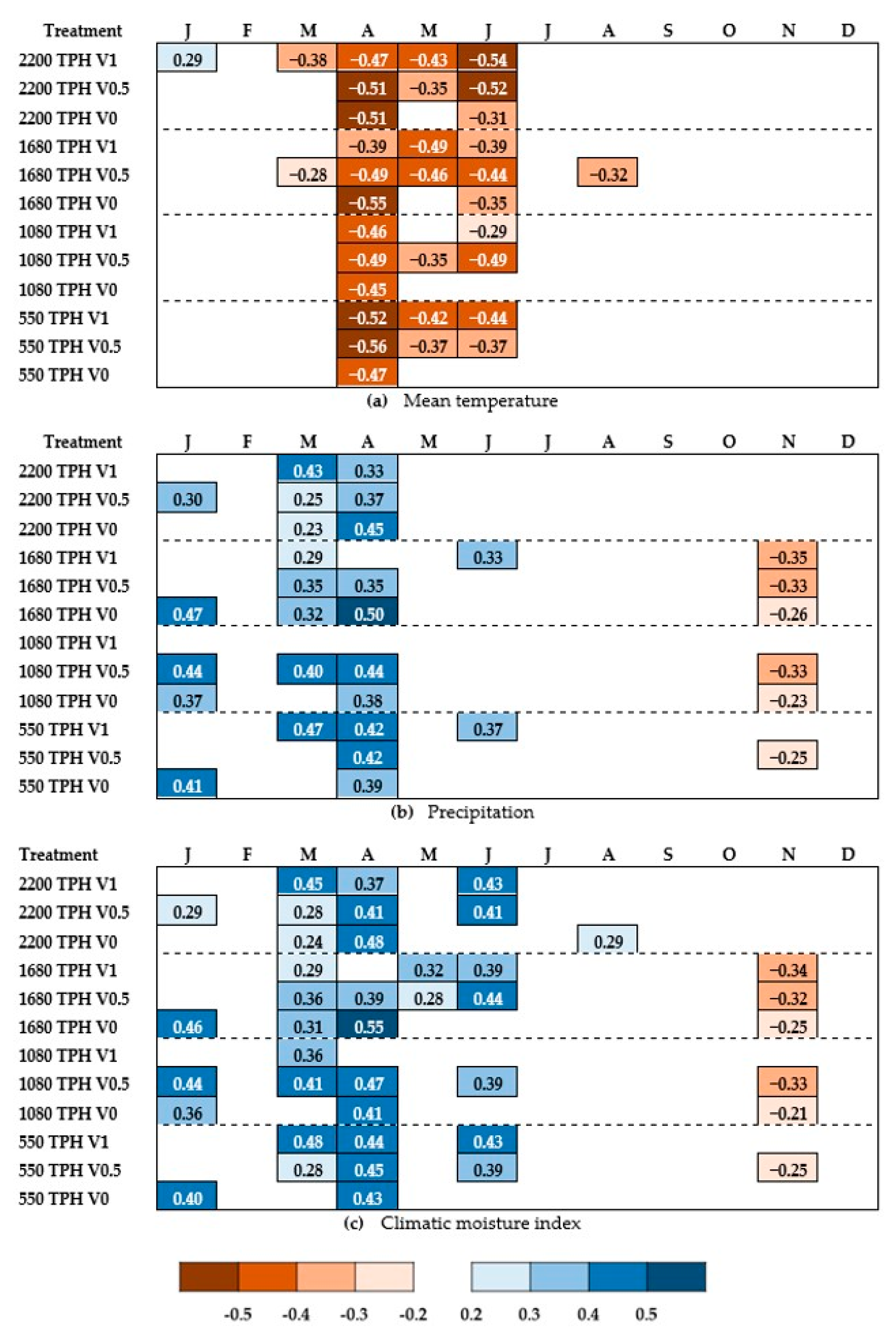
3.2. Climate-Growth Relationships
3.3. Treatment Effects on Resistance Correlation to Climate
4. Discussion
4.1. Treatment Effect on Long-Term Relationships between Growth and Climate
4.2. Treatment Effects on Tree Resistance Response to Climate
4.3. Study Limitations and Future Research Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleason, K.E.; Bradford, J.B.; Bottero, A.; D’Amato, A.W.; Fraver, S.; Palik, B.J.; Battaglia, M.A.; Iverson, L.; Kenefic, L.; Kern, C.C. Competition amplifies drought stress in forests across broad climatic and compositional gradients. Ecosphere 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.D.; Macalady, A.K.; Chenchouni, H.; Bachelet, D.; McDowell, N.; Vennetier, M.; Kitzberger, T.; Rigling, A.; Breshears, D.D.; Hogg, E.H.; et al. A global overview of drought and heat-induced tree mortality reveals emerging climate change risks for forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 660–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.G. Drought under global warming: A review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, R.H.; Drew, D.M.; O’Grady, A.P.; Pinkard, E.A.; Paul, K.; Roxburgh, S.H.; Mitchell, P.J.; Bruce, J.; Battaglia, M.; Ramp, D. Safeguarding reforestation efforts against changes in climate and disturbance regimes. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 424, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.S.; Iverson, L.; Woodall, C.W.; Allen, C.D.; Bell, D.M.; Bragg, D.C.; D’Amato, A.W.; Davis, F.W.; Hersh, M.H.; Ibanez, I.; et al. The impacts of increasing drought on forest dynamics, structure, and biodiversity in the United States. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 2329–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaconu, D.; Kahle, H.P.; Spiecker, H. Thinning increases drought tolerance of European beech: A case study on two forested slopes on opposite sides of a valley. Eur. J. For. Res. 2017, 136, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, M.; Sohn, J.; Nagele, G.; Bauhus, J. Can drought tolerance of Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) be increased through thinning? Eur. J. For. Res. 2010, 129, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemot, J.; Klein, E.K.; Davi, H.; Courbet, F. The effects of thinning intensity and tree size on the growth response to annual climate in Cedrus atlantica: A linear mixed modeling approach. Ann. For. Sci. 2015, 72, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M.; Sanchez-Salguero, R.; Rodriguez, C.; Lazo, J.D.; Moreno-Rojas, J.M.; Palacios-Rodriguez, G.; Camarero, J.J. Is thinning an alternative when trees could die in response to drought? The case of planted Pinus nigra and P. Sylvestris stands in southern Spain. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 433, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottero, A.; D’Amato, A.W.; Palik, B.J.; Bradford, J.B.; Fraver, S.; Battaglia, M.A.; Asherin, L.A. Density-dependent vulnerability of forest ecosystems to drought. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyser, T.L.; Brown, P.M. Drought response of upland oak (Quercus L.) species in Appalachian hardwood forests of the southeastern USA. Ann. For. Sci. 2016, 73, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, L.T.; Law, B.E.; Meddens, A.J.H.; Hicke, J.A. Tree mortality from fires, bark beetles, and timber harvest during a hot and dry decade in the western United States (2003–2012). Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, M.P.; Stevens, J.T.; Greene, D.F.; Coppoletta, M.; Knapp, E.E.; Latimer, A.M.; Restaino, C.M.; Tompkins, R.E.; Welch, K.R.; York, R.A.; et al. Tamm Review: Reforestation for resilience in dry western US forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 432, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witty, J.H.; Graham, R.C.; Hubbert, K.R.; Doolittle, J.A.; Wald, J.A. Contributions of water supply from the weathered bedrock zone to forest soil quality. Geoderma 2003, 114, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbert, K.R.; Beyers, J.L.; Graham, R.C. Roles of weathered bedrock and soil in seasonal water relations of Pinus Jeffreyi and Arctostaphylos patula. Can. J. For. Res. 2001, 31, 1947–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayhoe, K.; Cayan, D.; Field, C.B.; Frumhoff, P.C.; Maurer, E.P.; Miller, N.L.; Moser, S.C.; Schneider, S.H.; Cahill, K.N.; Cleland, E.E.; et al. Emissions pathways, climate change, and impacts on California. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12422–12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayan, D.R.; Maurer, E.P.; Dettinger, M.D.; Tyree, M.; Hayhoe, K. Climate change scenarios for the California region. Clim. Chang. 2008, 87, S21–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shainsky, L.J.; Radosevich, S.R. Growth and water relations of Pinus ponderosa seedlings in competitive regimes with Arctostaphylos patula seedlings. J. Appl. Ecol. 1986, 23, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.W. Brush Reduces Growth of Thinned Ponderosa Pine in Northern California. 1984; Usda Forest Service Pacific Southwest Research Station Research Paper. Available online: https://www.fs.usda.gov/treesearch/pubs/28833 (accessed on 25 April 2019).
- Powers, R.F.; Reynolds, P.E. Ten-year responses of ponderosa pine plantations to repeated vegetation and nutrient control along an environmental gradient. Can. J. For. Res. 1999, 29, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Powers, R.F.; Oliver, W.W.; Young, D.H. Response of ponderosa pine plantations to competing vegetation control in Northern California, USA: A meta-analysis. Forestry 2013, 86, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Busse, M.D.; Young, D.H.; Fiddler, G.O.; Sherlock, J.W.; TenPas, J.D. Aboveground biomass responses to organic matter removal, soil compaction, and competing vegetation control on 20-year mixed conifer plantations in California. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 401, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Ritchie, M.W.; Maguire, D.A.; Oliver, W.W. Thinning ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa) stands reduces mortality while maintaining stand productivity. Can. J. For. Res. 2013, 43, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girona, M.M.; Morin, H.; Lussier, J.-M.; Ruel, J.-C. Post-cutting mortality following experimental silvicultural treatments in unmanaged Boreal forest stsands. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2019, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.E.; Newton, M. Competitive interactions of whiteleaf manzanita, herbs, Douglas-fir, and ponderosa pine in southwest Oregon. Can. J. For. Res. 1989, 19, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.D.; Helms, J.A. Tissue water relations of Pinus ponderosa and Arctostaphylos patula exposed to various levels of soil-moisture depletion. Can. J. For. Res. 1994, 24, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, M.; Cole, E.C. Twenty-six-year response of ponderosa pine and Douglas-fir plantations to woody competitor density in treated stands of madrone and whiteleaf manzanita. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 256, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, N.; Pockman, W.T.; Allen, C.D.; Breshears, D.D.; Cobb, N.; Kolb, T.; Plaut, J.; Sperry, J.; West, A.; Williams, D.G.; et al. Mechanisms of plant survival and mortality during drought: Why do some plants survive while others succumb to drought? New Phytol. 2008, 178, 719–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.D.; Kolb, T.E. Tree growth response to drought and temperature in a mountain landscape in northern Arizona, USA. J. Biogeogr. 2005, 32, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry-Kientz, M.; Moran, E.V. Climate impacts on tree growth in the Sierra Nevada. Forests 2017, 8, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnwath, G.C.; Peterson, D.W.; Nelson, C.R. Effect of crown class and habitat type on climate-growth relationships of ponderosa pine and Douglas-fir. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 285, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannenberg, M.P.; Wise, E.K. Seasonal climate signals from multiple tree ring metrics: A case study of Pinus ponderosa in the upper Columbia River Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 1178–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Chhin, S.; Zhang, J. Effects of climate on competitive dynamics in mixed conifer forests of the Sierra Nevada. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 394, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusnierczyk, E.R.; Ettl, G.J. Growth response of ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa) to climate in the eastern Cascade Mountains, Washington, USA: Implications for climatic change. Ecoscience 2002, 9, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, I.M.; Davis, F.W.; Williams, A.P. A range of possibilities: Assessing geographic variation in climate sensitivity of ponderosa pine using tree rings. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 402, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, J.; Derose, R.; Long, J. Climatic drivers of ponderosa pine growth in central Idaho. Tree Ring Res. 2018, 74, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soule, P.T.; Knapp, P.A. Radial Growth and Increased Water-Use Efficiency for Ponderosa Pine Trees in Three Regions in the Western United States. Prof. Geogr. 2011, 63, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bigelow, S.W.; Papaik, M.J.; Caum, C.; North, M.P. Faster growth in warmer winters for large trees in a Mediterranean-climate ecosystem. Clim. Chang. 2014, 123, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, P.A.; Soule, P.T. Increasing water-use efficiency and age-specific growth responses of old-growth ponderosa pine trees in the Northern Rockies. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, K.C.; Pyke, D.A. Western juniper and ponderosa pine ecotonal climate-growth relationships across landscape gradients in southern Oregon. Can. J. For. Res. 2008, 38, 3021–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, J.H. Fundamentals of Tree-Ring Research; University of Arizona Press: Tucscon, AZ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, D.K. A simple method for cross-dating increment cores from living trees. Can. J. For. Res. 1991, 21, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, L. CooRecorder and Cdendro Programs of the CooRecorder/CdendroPackage, 8.1.1; Cybis: McLean, VA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Grissino-Mayer, H.D. Evaluating Crossdating Accuracy: A manual and tutorial for the computer program COFECHA. Tree Ring Res. 2001, 57, 205–221. [Google Scholar]
- PRISM Climate Group. Available online: http://prism.oregonstate.edu (accessed on 25 April 2019).
- Hogg, E.H. Temporal scaling of moisture and the forest-grassland boundary in western Canada. Agric For. Meteorol. 1997, 84, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Oliver, W.W.; Busse, M.D. Growth and development of ponderosa pine on sites of contrasting productivities: Relative importance of stand density and shrub competition effects. Can. J. For. Res. 2006, 36, 2426–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, A.G. A dendrochronology program library in R (dplR). Dendrochronologia 2008, 26, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campelo, F.; Garcia-Gonzalez, I.; Nabais, C. detrendeR—A Graphical User Interface to process and visualize tree-ring data using R. Dendrochronologia 2012, 30, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigley, T.M.L.; Briffa, K.R.; Jones, P.D. On the average value of correlated time-series, with applications in dendroclimatology and hydrometeorology. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1984, 23, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhin, S.; Hogg, E.; Lieffers, V.; Huang, S. Potential effects of climate change on the growth of lodgepole pine across diameter size classes and ecological regions. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 256, 1692–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhin, S.; Hogg, E.; Lieffers, V.; Huang, S. Growth-climate relationships vary with height along the stem in lodgepole pine. Tree Physiol. 2010, 30, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhin, S.; O’Brien, J. Dendroclimatic analysis of red pine affected by Diplodia shoot blight in different latitudinal regions in Michigan. Can. J. For. Res. 2015, 45, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S., 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 4th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lloret, F.; Keeling, E.G.; Sala, A. Components of tree resilience: Effects of successive low-growth episodes in old ponderosa pine forests. Oikos 2011, 120, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Maaten-Theunissen, M.; van der Maaten, E.; Bouriaud, O. pointRes: An R package to analyze pointer years and components of resilience. Dendrochronologia 2015, 35, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, I.G.; Campelo, F.; Rivaes, R.; Albuquerque, A.; Ferreira, M.T.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, P.M. Tree rings reveal long-term changes in growth resilience in Southern European riparian forests. Dendrochronologia 2018, 52, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, C.; Biondi, F. Dendroclimatic calibration in R: The bootRes package for response and correlation function analysis. Dendrochronologia 2013, 31, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, F.; Waikul, K. DENDROCLIM2002: A C++ program for statistical calibration of climate signals in tree-ring chronologies. Comput. Geosci. 2004, 30, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buras, A. A comment on the expressed population signal. Dendrochronologia 2017, 44, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, R.F.; Ferrell, G.F. Moisture, nutrient, and insect constraints plantation growth: The “Garden of Eden” study. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 1996, 26, 126–144. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, T.E.; Holmberg, K.M.; Wagner, M.R.; Stone, J.E. Regulation of ponderosa pine foliar physiology and insect resistance mechanisms by basal area treatments. Tree Physiol. 1998, 18, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, A.; Peters, G.D.; McIntyre, L.R.; Harrington, M.G. Physiological responses of ponderosa pine in western Montana to thinning, prescribed fire and burning season. Tree Physiol. 2005, 25, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, M.; Antoine, N.; Joel, G. Effects of different thinning intensities on drought response in Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.). For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 183, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Guan, D.X.; Li, W.B.; Sun, D.; Jin, C.J.; Yuan, F.H.; Wang, A.Z.; Wu, J.B. The effects of forest thinning on soil carbon stocks and dynamics: A meta-analysis. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 429, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Benito, D.; Del Rio, M.; Heinrich, I.; Helle, G.; Canellas, I. Response of climate-growth relationships and water use efficiency to thinning in a Pinus nigra afforestation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagneri, D.; Nola, P.; Cherubini, P.; Motta, R. Temporal variability of size-growth relationships in a Norway spruce forest: The influences of stand structure, logging, and climate. Can. J. For. Res. 2012, 42, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Pederson, N.; Chen, Z.J.; Lawton, K.; Zhu, C.; Han, S.J. Recent rising temperatures drive younger and southern Korean pine growth decline. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helama, S.; Salminen, H.; Timonen, M.; Varmola, M. Dendroclimatological analysis of seeded and thinned Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) stands at the coniferous timberline. New For. 2008, 35, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.E.K.; Falk, D.A.; Arizpe, A.; Swetnam, T.L.; Babst, F.; Holsinger, K.E. Fusing tree-ring and forest inventory data to infer influences on tree growth. Ecosphere 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieniecki, M.A.; Newton, M. Seasonal pattern of water depletion from soil-rock profiles in a Mediterranean climate southwestern Oregon. Can. J. For. Res. 1996, 26, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magruder, M.; Chhin, S.; Palik, B.; Bradford, J. Thinning increases climatic resilience of red pine. Can. J. For. Res. 2013, 43, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.A.; Hartig, F.; Kohler, M.; Huss, J.; Bauhus, J. Heavy and frequent thinning promotes drought adaptation in Pinus sylvestris forests. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 2190–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girona, M.M.; Rossi, S.; Lussier, J.M.; Walsh, D.; Morin, H. Understanding tree growth responses after partial cuttings: A new approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.S.; Bell, D.M.; Kwit, M.C.; Zhu, K. Competition-interaction landscapes for the joint response of forests to climate change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1979–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Treatment | No. of Trees | Mean Ring Width (mm) | Mean Correlation | EPS | SSS | Interval (SSS > 0.85) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2200 (V1) | 24 | 0.71 | 0.36 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 1967–2011 |
| 2200 (V0.5) | 17 | 0.85 | 0.38 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 1966–2011 |
| 2200 (V0) | 19 | 1.25 | 0.27 | 0.88 | 0.99 | 1968–2011 |
| 1680 (V1) | 15 | 0.59 | 0.33 | 0.88 | 0.99 | 1969–2011 |
| 1680 (V0.5) | 16 | 0.99 | 0.39 | 0.91 | 0.98 | 1970–2011 |
| 1680 (V0) | 11 | 1.33 | 0.43 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 1969–2011 |
| 1080 (V1) | 11 | 0.73 | 0.33 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 1967–2011 |
| 1080 (V0.5) | 15 | 1.11 | 0.36 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 1968–2011 |
| 1080 (V0) | 15 | 1.61 | 0.25 | 0.84 | 0.97 | 1968–2011 |
| 550 (V1) | 16 | 0.68 | 0.39 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 1966–2011 |
| 550 (V0.5) | 16 | 1.03 | 0.41 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 1969–2011 |
| 550 (V0) | 15 | 1.91 | 0.45 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 1969–2011 |
| Source of Variation | Num df | Den df | Volume (m3ha−1) | QMD (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 3 | 6 | 0.17 | 0.11 |
| Shrub removal | 2 | 16 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Density × Shrub | 6 | 16 | 0.84 | 0.46 |
| Age | 5 | 174 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Age × Density | 15 | 174 | <0.69 | <0.01 |
| Age × Shrub | 10 | 174 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Age × Density × Shrub | 30 | 174 | 1.00 | 0.14 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Finley, K.; Zhang, J. Climate Effect on Ponderosa Pine Radial Growth Varies with Tree Density and Shrub Removal. Forests 2019, 10, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10060477
Finley K, Zhang J. Climate Effect on Ponderosa Pine Radial Growth Varies with Tree Density and Shrub Removal. Forests. 2019; 10(6):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10060477
Chicago/Turabian StyleFinley, Kaelyn, and Jianwei Zhang. 2019. "Climate Effect on Ponderosa Pine Radial Growth Varies with Tree Density and Shrub Removal" Forests 10, no. 6: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10060477
APA StyleFinley, K., & Zhang, J. (2019). Climate Effect on Ponderosa Pine Radial Growth Varies with Tree Density and Shrub Removal. Forests, 10(6), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10060477




