Abstract
The objectives of this study were to assess land use changes and their hydrological impacts in the Nenjiang River Basin (NRB). The Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model was employed to evaluate the impacts of land use changes. The Cellular Automata-Markov model was used to predict a land use map in 2038. Streamflow under each land use state was simulated by the SWAT model. The results showed that there was a significant expansion of agriculture area at the expense of large areas of grassland, wetland, and forest during 1975–2000. The land use changes during the period of 1975 to 2000 had decreased the water yield (3.5%), surface runoff (1.7%), and baseflow (19%) while they increased the annual evapotranspiration (2.1%). For impacts of individual land use type, the forest proved to have reduced streamflow in the flood season (10%–28%) and increased surface runoff in the drought season (20%–38%). Conversely, grassland, dry land, and paddy land scenarios resulted in increase of streamflow during summer months by 7%–37% and a decrease of streamflow in the cold seasons by 11.7%–59.7%. When the entire basin was changed to wetland, streamflow reduced over the whole year, with the largest reduction during January to March. The 2038 land use condition is expected to increase the annual water yield, surface runoff and wet season flow, and reduce evapotranspiration and baseflow. These results could help to improve sustainable land use management and water utilization in the NRB.
1. Introduction
Converting land to other uses is one of the main forms of global change and may potentially have significant effects on the ecosystem and climate, including local hydrology and water resources. Therefore, investigating the processes and consequences of land use change is crucial for land managers, ecologists, and hydrologists [1,2]. Over the past decades, the land use change impacts on hydrology and water resources have attracted the attention of researchers across the globe [3,4,5]. Most have focused on the impacts of land use change on annual mean discharge and extreme hydrological events [6,7]. For instance, Siriwardena et al. [8] found that the clearing of forest vegetation from 83% to 38% increased the runoff by approximately 40% in Comet Catchment of Australia. Niehoff et al. [9] conducted research on flood prediction using both the Land Use Change modelling Kit (LUCK) and a physically based hydrological model (WaSiM-ETH), and the results indicated that land use has an impact on storm–runoff generation especially for convective storm events. Gwate et al. [10] found that the expansion of cultivated land (92%) and decrease of wooded land (35%) and grasslands (9.8%) between 2004 and 2013 increased the streamflow in Quaternary Catchment, South Africa. Profound land use changes and their effects on the hydrological cycle and water volume in China have also been reported in previous studies [11,12]. These changes represent a significant challenge to watershed water resource management. Although there has been abundant research on the impacts of land use changes on hydrology, the evidence from various studies may differ due to the variation in catchment characteristics coupled with land use changes [13,14,15]. For example, Beighley et al. [16] found that urbanization increased peak discharges and runoff volume but decreased streamflow variability and baseflow, whereas David et al. [17] and Kim et al. [18] indicated that an increase in the impervious area led to contrasting effects on baseflow and streamflow. Shi et al. [19] found that an increase in grassland had a positive relationship with surface runoff in the upstream region of the Luanhe River Basin, but a negative relationship in the downstream region.
The Nenjiang River Basin (NRB) lies in northeastern China. There are numbers of land use types in the area, but, in particular, the NRB is a major agricultural area and one of the most important wetland regions in China. Over the past few years, the NRB has experienced dramatic changes in land use patterns due to global warming and intensive human activities (e.g. agriculture, urban expansion, and water engineering construction) [20]. For example, Tang et al. [21] analyzed the land use maps and images of the basin and concluded that the most significant land use change in the basin appeared to be the spread of farmland, the destruction of forests, and the loss of grassland. Forests experienced the largest decrease among all landscape types, ascending from 45,003.07 km2 in 1954 to 36,972.56 km2 in 2010, and the gaining area of farmland as 11452.68 km2 mainly transformed from forest and grassland. Yuan et al. [22] showed that the natural wetland in the Songhua River Basin, where the NRB is located, had declined from 6.35 × 104 km2 to 5.94 × 104 km2 between 1995 and 2008, whereas the area of artificial wetland increased from 2.96 × 104 km2 to 3.77 × 104 km2 during the period. These studies addressed land use change characteristics based on certain land use types or in a small part of the basin. However, no study has investigated the transformations between different land use types in a holistic way to identify changes across the basin.
Streamflows are critical to agricultural and ecological water demands in the NRB, and notable variations have been revealed in streamflow across the basin [23,24]. Several studies have investigated the spatiotemporal variability of streamflow and its driving factors in the NRB. Most of them focused on the hydrological response to climate change rather than land use change. Therefore, this study addressed this knowledge gap by using land use data that covered different periods of time and used a hydrological model to predict how these changes may affect the hydrology of the NRB. The objectives of this study were to (1) identify the changing characteristics of land use in the NRB and (2) assess how hydrological components respond to land use changes in the basin.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
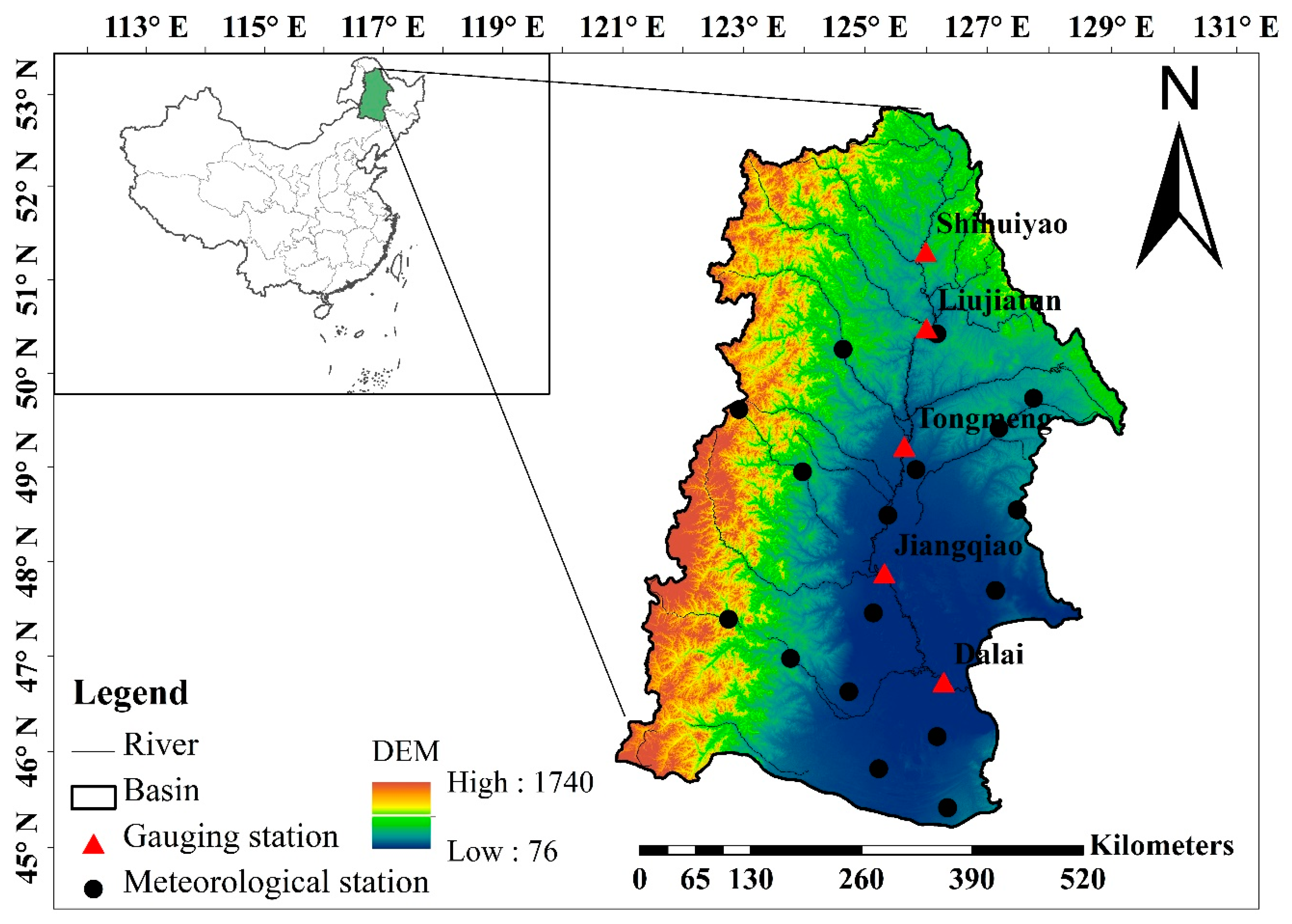
The source of the Nenjiang River is in the Great Khingan Mountains. It forms one of the largest tributaries of the Songhua River in northeast China (Figure 1) and has a drainage area of 297,000 km2. The annual precipitation and annual mean temperature during 1960–2009 of the NRB is 455 mm and 3.2 °C, respectively, and the annual streamflow in the basin is 2.28 billion cubic meters. The NRB topography in the upstream rivers is significantly different from that found in the lower basin areas. The upstream region is mostly covered by dense forest, but this transitions from mountains to plains in the midstream region. The area in the lower basin is mainly occupied by grassland, cropland, and wetland due to the flat terrain and fertile soil. The NRB contains numerous wetlands and is regarded as one of the most important wetland regions in China. There are many important wetland nature reserves (e.g., Zhalong, Xianghai, and Momoge), which sustain diverse ecosystems. In recent decades, the NRB has experienced extensive land use changes due to the growing population, deteriorating weather conditions, and government land use policies. All these factors may have significant impacts on hydrology.
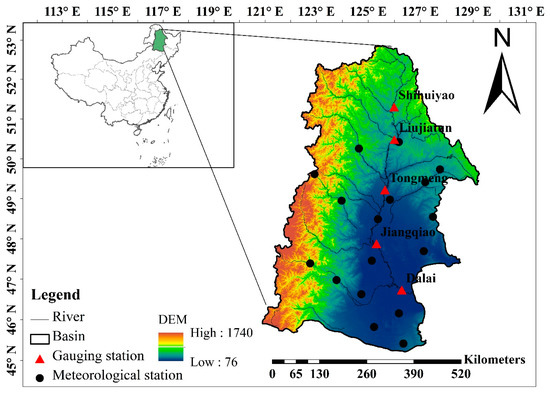
Figure 1.
Location of the Nenjiang River Basin.
2.2. Data Collection
Daily precipitation, mean, maximum and minimum temperature, wind speed, sunshine hours, and relative humidity data were collected from 17 meteorological stations across the NRB (Figure 1). All meteorological data were obtained from the China Meteorological Administration (CMA). The dataset covered the period 1960–2009. Monthly discharge data during the same period were also gathered from five hydrological gauging stations (Figure 1), which were located in the mainstream part of the basin. The data were provided by the Hydrology Bureaus (HBs) of Inner Mongolia, and Heilongjiang and Jilin Provinces. The quality of the meteorological and hydrological data was highly controlled by the CMA and HBs before they were released.
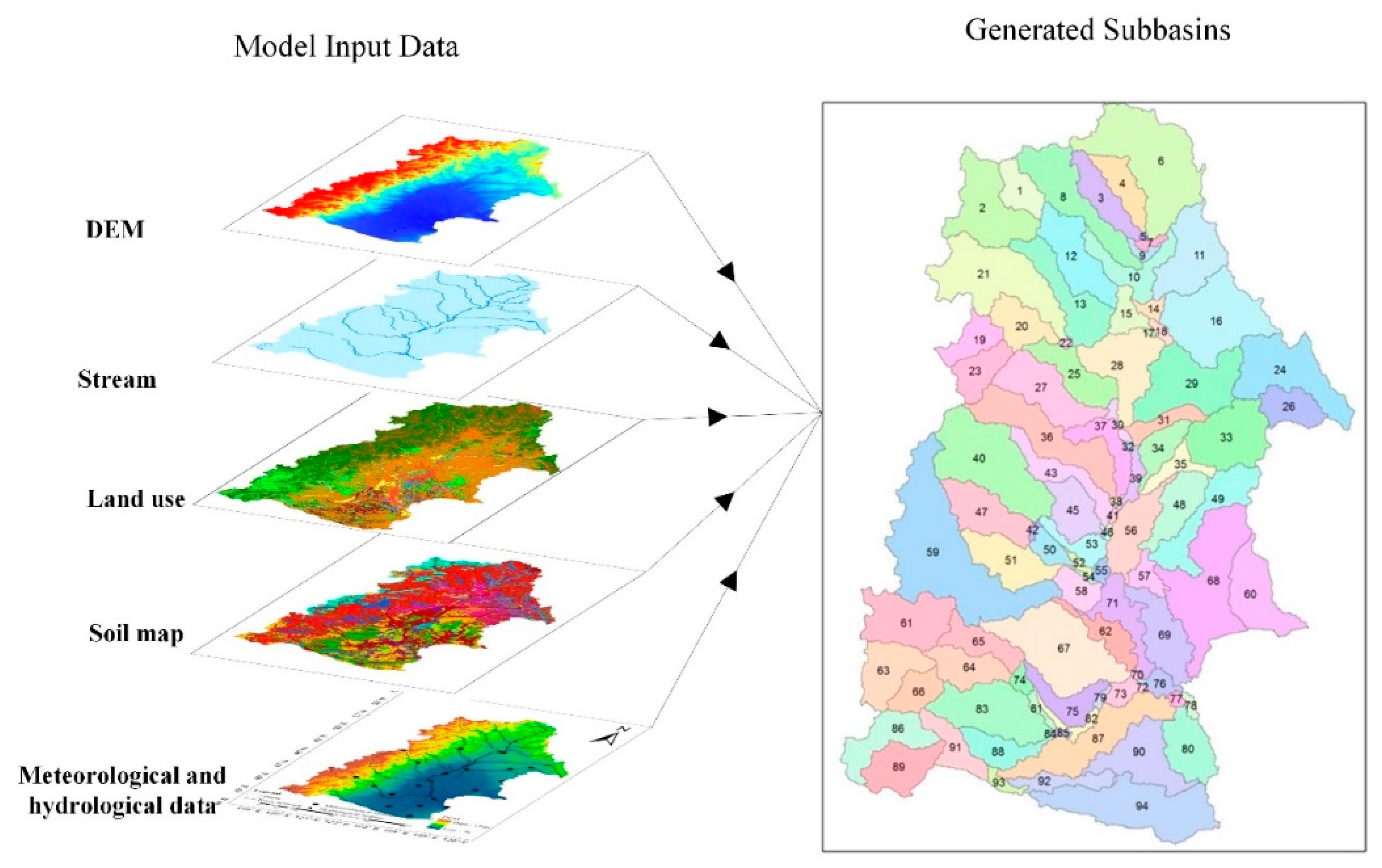
In addition, the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model requires geographical data. In this study, the 1:1,000,000 Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data and soil data for the NRB (Figure 2) were selected and converted into 1 km × 1 km raster datasets to develop the SWAT model. The soil data were obtained from the Soil Database, which is supported by the Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). The 1 km × 1 km soil map was created from digital soil maps that were based on different soil particulate sizes. Land use data for 1975, 2000, and 2010 were provided by the CAS with a spatial resolution of 1 km × 1 km.
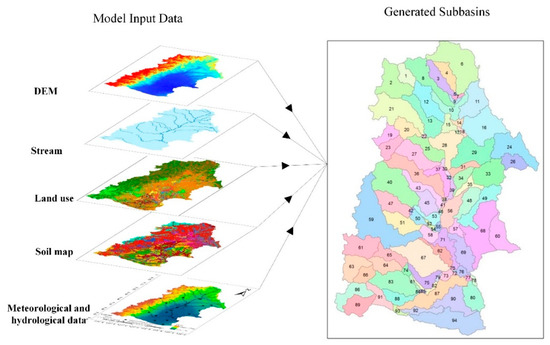
Figure 2.
Multiple Input data for SWAT (Soil and Water Assessment Tool) model development in this study.
2.3. Land Use/Land Cover Prediction
In this study, Cellular Automata-Markov (CA-Markov) model was used to predict the 2038 LULC (Land use/land cover) condition. CA-Markov is a robust model that combines the advantages of the Markov chain and Cellular automata.
The Markov model describes the land use change from one period to another, based upon which it predicts the future trends in the LULC change. The following formula can be used to predict the LULC:
where St and St+1 are the states of the land use structure at t and t + i, respectively, and Pij is the state transition matrix.
St+i = PijSt
Cellular automata represent a type of grid-dynamic model with strong space-computing power. The CA-Markov model can be expressed as follows:
where S is a finite, discrete states set of cells; N is the cellular neighborhood; t and t + i are different moments; and f is the cell transformation rule of the local space.
St+i = f(St,N)
Therefore, the model can simulate the spatiotemporal LULC evolution of complex systems and has been widely applied in many countries [25,26,27,28].
The detailed parameters and steps of the LULC prediction, using the CA-Markov model, are as follows: (1) Data format conversion and reclassification are performed to obtain fixed land use types. (2) The state transition probability matrix and the transfer area matrix are obtained through the Markov module. (3) A transition suitability image set is established. (4) The CA filter and the number of cycles is determined. (5) Assessment of the accuracies of the prediction images are according to the actual images.
We employed the 2010 classified map as a basis LULC image and the 2000 and 2010 maps for assembly transition probability matrix to predict the 2038 LUCC condition. The Kappa coefficients (higher than 0.75) indicated that the model performed pretty good in simulating the 2038 LUCC condition.
2.4. Model Description
SWAT was used to create a streamflow simulation for the NRB. It is a physically based hydrological model [28] that has been widely used and has been proven to be effective in investigating the impacts of climate and land use on water quantity and quality [29,30,31,32]. The SWAT was developed using various input data, such as topography, land use, soil properties, and weather data for the basin. The DEM was used to delineate the watershed, and then the area was divided into multiple sub-basins and hydrological response units (HRUs). The HRU was based on the unique combinations of land features, soil type, and slope classification within a sub-basin. Therefore, the SWAT is physically distributed and can effectively predict runoff changes under different land use conditions. Previous empirical analysis [7,11] was able to predict the comprehensive effects of land use change on runoff, but it was hard to clarify the specific impact of each individual land use type. Therefore, we have used the SWAT to address this challenge by setting up appropriate land use scenarios.
In this study, a 10% threshold for land use, soil type, and the slope was set, and the NRB was divided into 94 sub-basins and 884 HRUs. The Penman-Monteith method was used to estimate the evapotranspiration, and soil conservation service curve number (SCS-CN) and the Muskingum method were used to simulate the runoff generating and routing processes, respectively, in the SWAT model.
The runoff simulation in the NRB was divided into two periods. The calibration period was fixed as 1980–1994, and the validation period was 1995–2009. The Latin Hypercube One-Factor-at-a-Time (LH-OAT) technique was used to identify significantly sensitive parameters. The sensitivity analysis recognized 11 significant parameters that affected runoff. These were CN2 (Initial SCS runoff curve number for moisture condition II), ESCO (Soil evaporation compensation factor), CH_K2 (Effective hydraulic conductivity in main channel alluvium), SURLAG (Surface runoff lag coefficient), GW_DELAY (Delay time for aquifer recharge), ALPHA_BF (Baseflow alpha factor), GWQMN (Threshold depth of water in the shallow aquifer required for return flow to occur), GW_REVAP (Groundwater “revap” coefficient), REVAPMN (Threshold depth of water in the shallow aquifer for evaporation), SOL_AWC (Available water capacity of the soil layer), and SOL_K (Saturated hydraulic conductivity). Descriptions of these parameters can be found in our previous publication [33]. The sensitive parameters were then calibrated using the monthly discharge data for 1980–1994 from five hydrological gauging stations. We used monthly data because there was a lack of daily streamflow data. The calibration was carried out using the SUFI-2 optimization technique. Then the model was validated using the observed data for 1995–2009. The Nash-Suttcliffe coefficient of efficiency (Ens) [34], the relative error (Er) [35], and the coefficient of determination (R2), were used to evaluate whether the SWAT could simulate runoff in the NRB. For detailed information please refer to [33].
Annual change rates and the transition matrix for land use types were used to identify land use change over different periods in the NRB. In order to clarify the specific impacts of land use changes on hydrology, nine land use scenarios were assumed, and hydrological variables, such as evapotranspiration, surface runoff, baseflow, and total water yield, were simulated for each land use scenario. Furthermore, a flow duration curve (FDC) was also used to investigate the land use change impacts on streamflow regime.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Performance
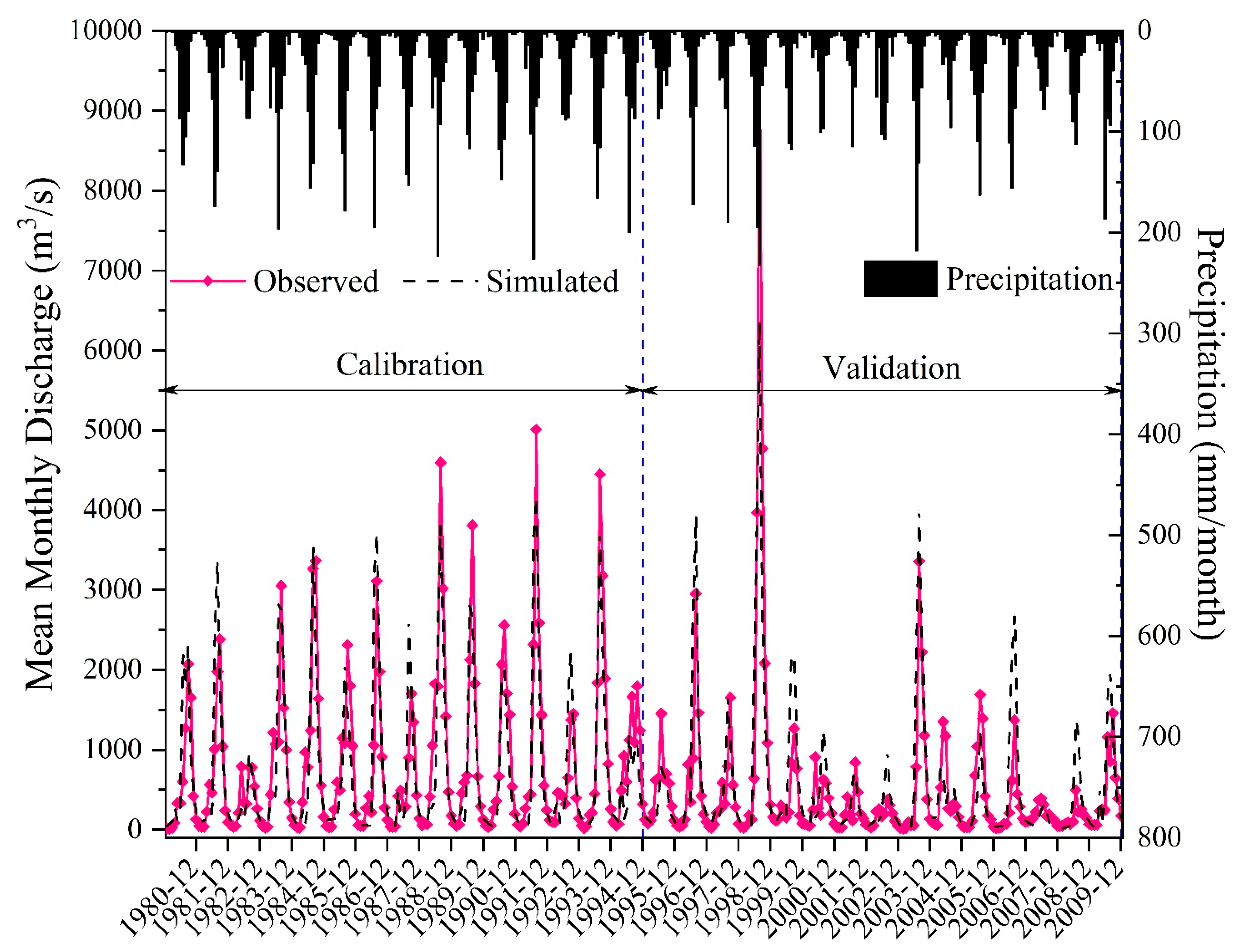
Simulation outputs for the calibration period (January 1980 to December 1994) and the validation period (January 1995 to December 2009) are shown in Figure 3. The simulated and observed discharge data matched well. All Ens and R2 values were above 0.5, and most Er values were in the ± 10% range (Table 1), which suggested satisfactory model performance [35]. However, there were certain differences between the simulated and observed streamflow. This could be attributed to the fact that many uncertainties may be involved in the calculation of recession by the model, such as the simplification of the complex channel network and the altered outlets, as indicated by the underestimation of outflows. The limited amount of observed hydrometeorological data and limited resolution (i.e., 1 km × 1 km) of regional physical geographic input (such as DEM, land use, and soil) also decreased the accuracy of the simulation. Generally, the good match between simulation and observation, the high Ens and R2 values, and the low absolute values for Er indicated that streamflow can be described by the calibrated model.
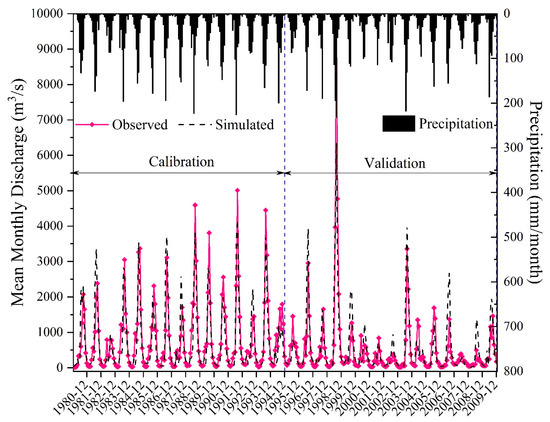
Figure 3.
Observed and simulated monthly streamflow hydrographs (Dalai station) for the calibration period (a) and the validation period (b).

Table 1.
Model evaluations for the calibration and validation periods.
3.2. Land Use Changes in the NRB
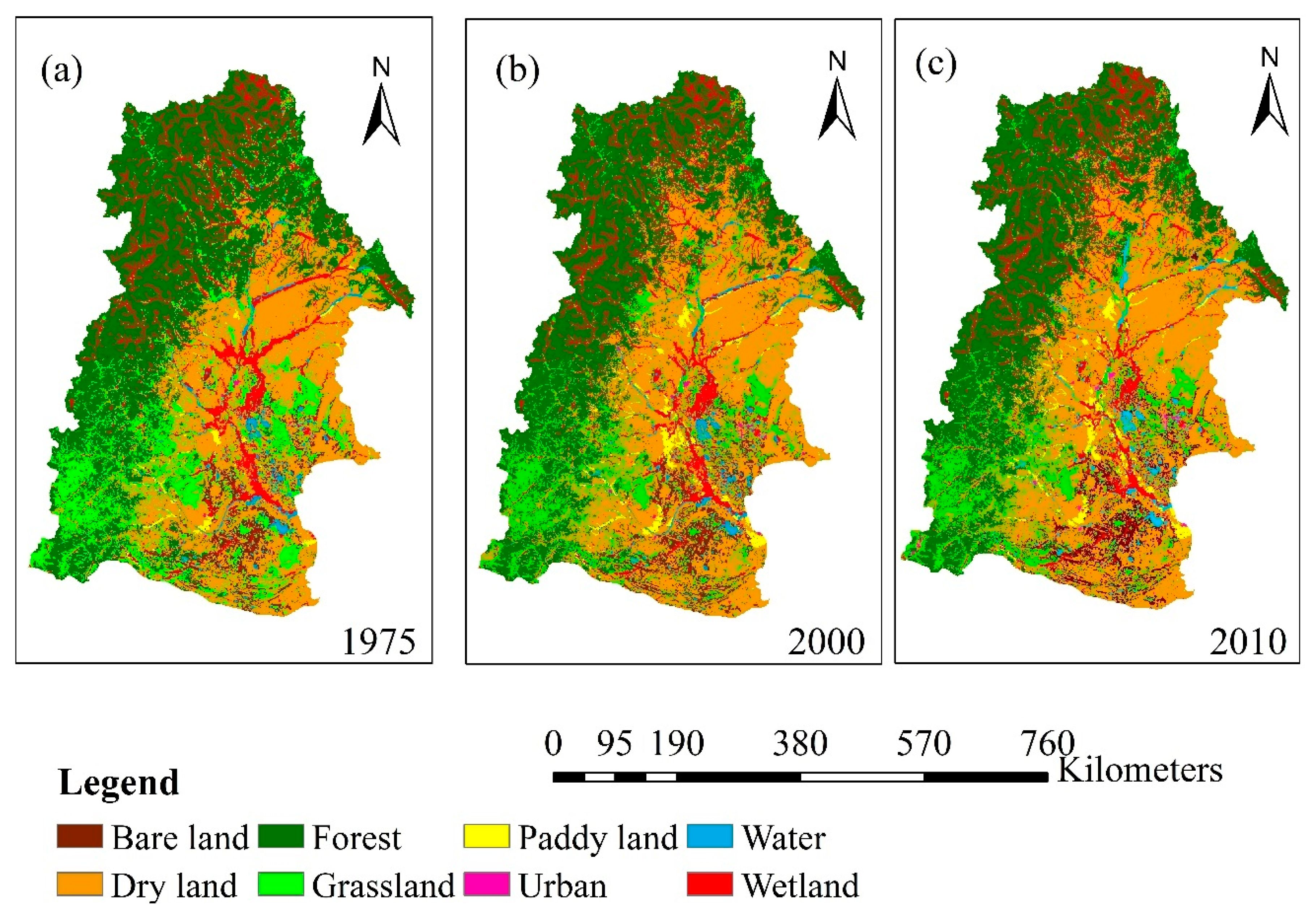
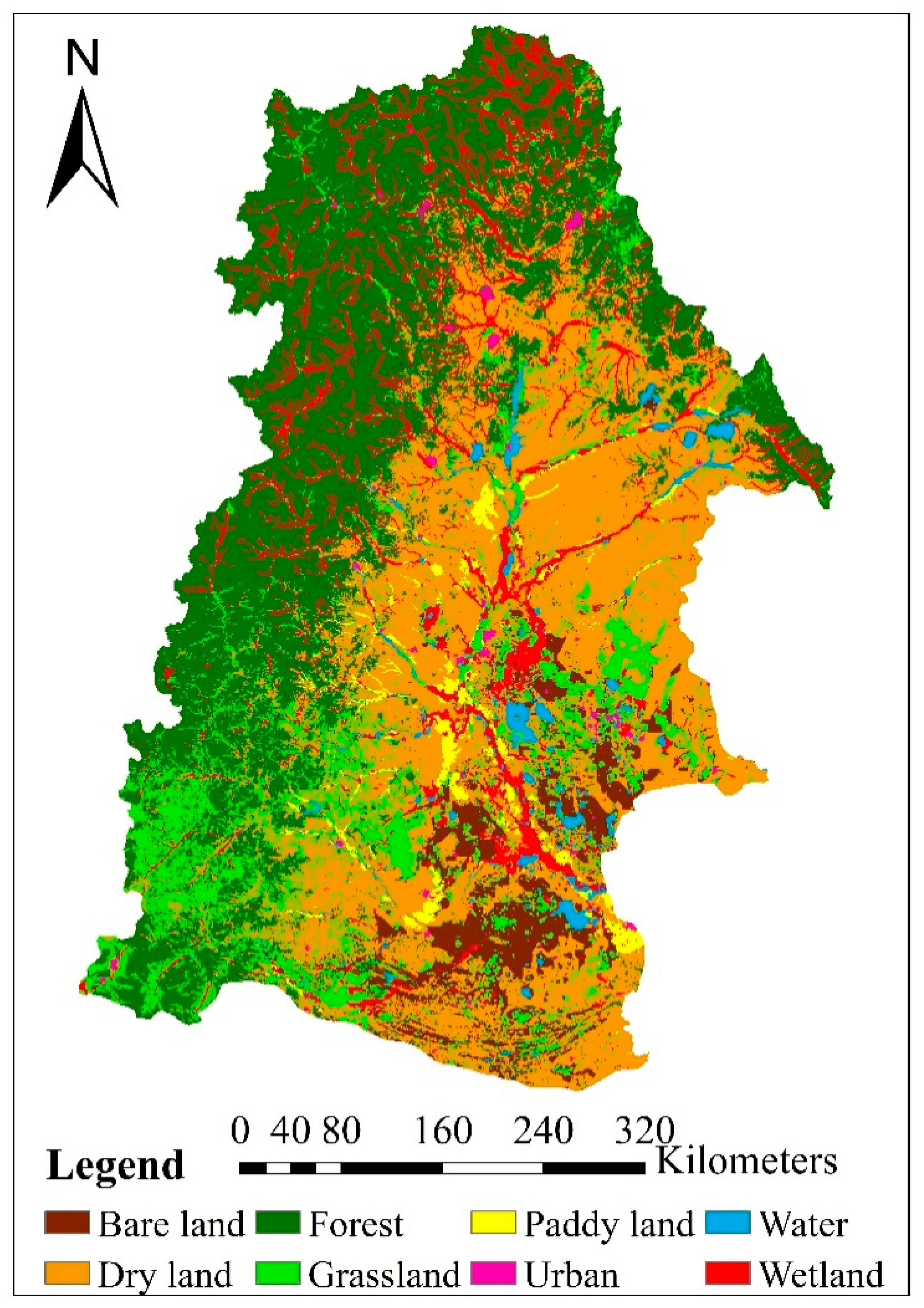
Land use in the NRB was categorized into eight types: forest, dry land, paddy land, urban, grassland, water, bare land, and wetland (Figure 4). Table 2 shows the total area occupied by each land use type across the NRB in 1975, 2000 and 2010. Forest, dry land, grassland, and wetland are the four dominant land use types, each of which accounts for more than 10% of the landscape in 1975. In general, it was found that there is an increasing human influence in the NRB through the development of cropland and urban area, but a decrease in forest, grassland and wetland area since the 1970s. The land use change was more obvious during 1975–2000. Both paddy land and dry land area showed a rapid expansion from 1975 to 2000 with an annual increasing rate of 137 km2/a and 656 km2/a, respectively. The total cropland area in the NRB increased by 23.5% during this period. According to the analysis of land use transition (Table 3), new paddy land predominantly gained from dry land (2078 km2) and wetland (1090 km2), but paddy land was rarely converted to other types. Similarly, 16 400 km2 of grassland, forest, and wetland in total was converted to dry land. However, less than 5% dry land was converted to other land uses. In contrast, although other types of land use were converted to grassland and forest, there were significant losses in forest and grassland areas (428 km2 and 384 km2 per year) due to their conversion to other land cover types (i.e., paddy land and dry land). For example, grassland gained nearly 5500 km2 from forest, wetland and dry land, but there was still a 20% reduction in total (Table 3 and Table 4). Wetland area lost about 14.5%, but received some new area from forest and grassland, which resulted in a final reduction of 9% in total (Table 4). Both urban and bare land accounted for small portions of the total area, but they increased by 20–30% because of their high preservation rates and conversions from dry land and grassland. The urban area in the NRB increased from 1130 km2 in 1975 to 1840 km2 in 2000 during this period. Figure 4 shows the spatial distribution of land use change in the NRB. From the figure we can find that large area of forest in the upstream and grassland and wetland in the downstream was transformed into dry land during the period of 1975–2000. It also indicated that development of the agricultural area in the catchment was at the expense of forest area, grassland area, and wetland area, resulting in a major loss in natural green area. Similar trends continued in the following years, but the annual rates of changes in all the land use types decreased a lot.
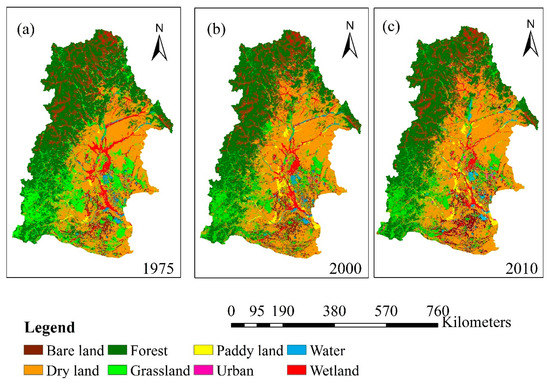
Figure 4.
Land use in 1975 (a), 2000 (b) and 2010 (c) in the Nenjiang River Basin.

Table 2.
Land use changes during the periods 1975–2000, and 2000–2010 across the Nenjiang River Basin, northeast China.

Table 3.
Matrix of land use change in the Nenjiang River Basin from 1975 to 2000.

Table 4.
Matrix of relative land use change in the Nenjiang River Basin from 1975 to 2000.
The result of this study was consistent with some previous studies, and the changes of land use in the NRB may be largely due to local socioeconomic development and population growth [36,37]. According to [38], population and gross domestic product (GDP) have dramatically increased over the past few years. To meet the higher requirements for food from both the local basin and other areas in China, the Chinese government is promoting northeastern China, where NRB is located, as the major crop production base for China in the near future. Therefore, the cropland, especially paddy land, has greatly increased with the implementation of this policy. In addition, the results for the transition matrix demonstrated that cropland had a high persistence at around 95–97% and gained area mainly from grassland, forest, and wetland, which resulted in a reduction of 7%, 21.6%, and 9.8%, respectively, in these areas between 1975 and 2000. This highly agrees with the results of Tang et al. [21], indicating that there had been a large transition from forest to farmland between 1976 and 2000.
Wetland is a unique ecosystem and plays important roles in both hydrology and ecology [39]. In this study, we found wetland area in the NRB has decreased between 1975 and 2000. This is in agreement with Wang et al. [38], who reported that there had been marsh shrinkage in the Songnen plain (lower part of the NRB), which possesses most of the wetlands in the basin. But we also found that lost wetland was mostly transformed into cropland (1090 km2 to paddy land and 1880 km2 to dry land). As investigated, hydropower projects were built in the basin from the 1970s to the 1990s. This might change the natural hydrological processes and water supplies to the wetlands and accelerate the degradation and fragmentation of the wetland [40]. In addition, the NRB experienced significant climate warming over the past 50 years [24,41]. The warmer climate resulted in less water supply to wetland and grassland areas, which will contribute to wetland and grassland loss, and land use conversion from wetland to grassland or bare land [41].
3.3. Hydrological Impacts of Land Use Change in the NRB
3.3.1. Combined Hydrological Impacts of Land Use Change under the Historical Landuse Scenarios
To identify the hydrological impacts of land use changes in the NRB, the classified (1975 and 2000) maps were used independently in the calibrated SWAT model while all other model inputs were kept similar. The evaluation included surface runoff, baseflow, evapotranspiration, and total water yields in the basin between 2000 and 2009.
The impacts of land use changes on the annual average surface runoff, lateral flow, groundwater flow, water yield, and ET are provided in Table 5. Correspondingly, the increase of croplands, urban and water areas, and the reduction of forest, grassland and wetland have resulted in the average evapotranspiration increase from 354.4 mm for land use in 1975 to 361.8 mm for land use 2000, increased by 2.1%. On the contrary, average annual value of water yield and surface runoff decreased by 3.5% and 1.7%, respectively. The annual basin baseflow had a larger decrease of 19.0% from 22.5 mm for land use in 1975 to 18.9 mm for land use in 2000.

Table 5.
Changes to the annual average values of hydrological variables under the historical land use scenarios in the Nenjiang River Basin.
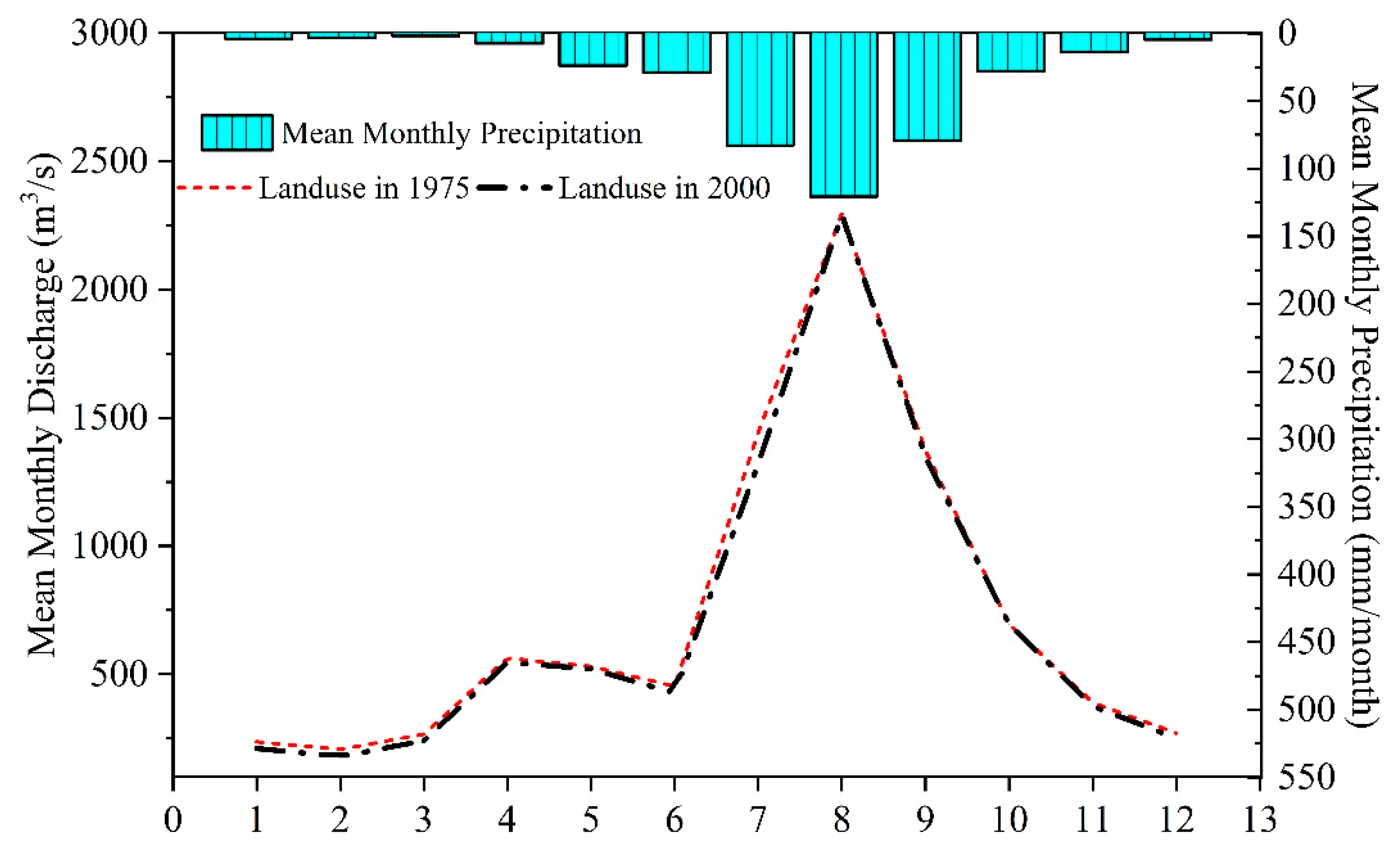
The intra-annual runoff distributions were similar to each other for land use conditions of 1975 and 2000. Although the effects of land use changes on streamflow can also been observed in the monthly average values (Figure 5). Generally, monthly streamflow decreased in almost every month for land use in 2000 compared to that under land use in 1975. However, the reduction is greater in dry season (i.e., November to March) streamflow (3.5–13.4%) than in wet season (i.e., July to October) streamflow (0.2–8.5%).
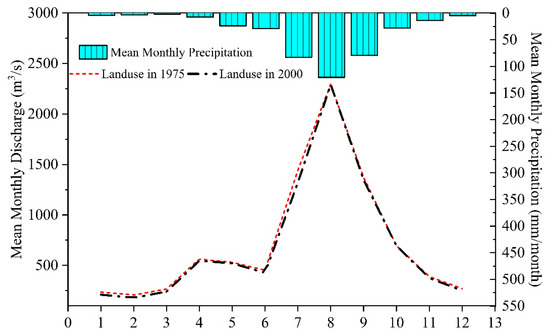
Figure 5.
Intra-annual changes in streamflow under historical land use scenarios across the Nenjiang River Basin.
Many studies have reported that land use change can significantly affect discharge by modifying the pattern, magnitude, frequency, and quality of water runoff [3,42,43]. In this study, land use in 1975 was found to produce more surface runoff and baseflow but less evapotranspiration than land use in 2000 due to the combined effects of the increase of croplands, urban and water areas, and reduction of forest, grassland and wetland. By comparison, increment of monthly streamflow was larger in the dry season than in wet season. This conforms to the conclusion by Bruijnzeel [44], noting that deforestation and cropland expansion leads to changes in soil hydro-physical conditions in tropical forests, which subsequently results in reduced low flows due to reduced infiltration and groundwater recharge. Other studies [45,46] also found similar results with increased dry season flows due to deforestation and they attributed this increase to a reduction in ET.
3.3.2. Individual Hydrological Impacts of Land Use Changes
Although the SWAT model results under historical land use conditions showed the changes in the hydrological components, the individual impacts of land use changes need to be further determined. Therefore, five extreme land use conditions were applied in this section (i.e., All Forest, All Grassland, All Dry land, All Paddy land, and All Wetland) to explore the hydrological impacts of dominant land use types in the NRB.
Simulation outputs by the SWAT model (Table 6) indicated annual evapotranspiration in the basin did not change to any great extent under different land use scenarios. Overall, the annual evapotranspiration values for the extreme condition scenarios were in the order: all wetland condition, all forest condition, all grassland condition, all dry land condition, and all paddy land condition. When all of the basin was converted to wetland, it resulted in the largest evapotranspiration probably due to its large water area. And the all forest land use condition got larger evapotranspiration (368.2 mm) than the rest of other scenarios; this is because vegetation in cultivated and grassland ecosystems generally have lower leaf area indices and shallow root depths in comparison to forest landscapes, which reduced evapotranspiration.

Table 6.
Changes of the hydrological variables under the extreme land use scenarios in the Nenjiang River Basin.
The surface runoff was small when the entire basin was converted to wetland (71.9 mm) or forest (59.2 mm). It was reduced by 29.6% and 14.4%, respectively, compared to the condition of land use in 2000. On the one hand, this may be due to the large evapotranspiration (372.5 mm and 368.2 mm, respectively), while on the other hand, the results showed strong water storage capacity of wetland and forest. In contrast, all the other scenarios produced surface runoff increases, especially when all of the basin is covered by dry land, which showed the largest surface runoff increase (27.3%) compared to the condition of land use in 2000.
The all forest land use condition produced the largest baseflow (28.8 mm) among different scenarios. This suggested that forests cannot only absorb water through leaves and roots, but also have greater infiltration of rainfall into the shallow and deep aquifer. The baseflow values were smallest for both all paddy land and wetland conditions (7.5 mm), which may be related to the large water storage capacity of long-term saturated paddy land and wetland soils. Annual average values of baseflow for all grassland condition and all dryland condition were respectively 11.3 mm and 10.5 mm. The results indicated that converting more forest and grassland area to dry land in the NRB may likely lead to an increase in surface runoff and a decrease in baseflow.
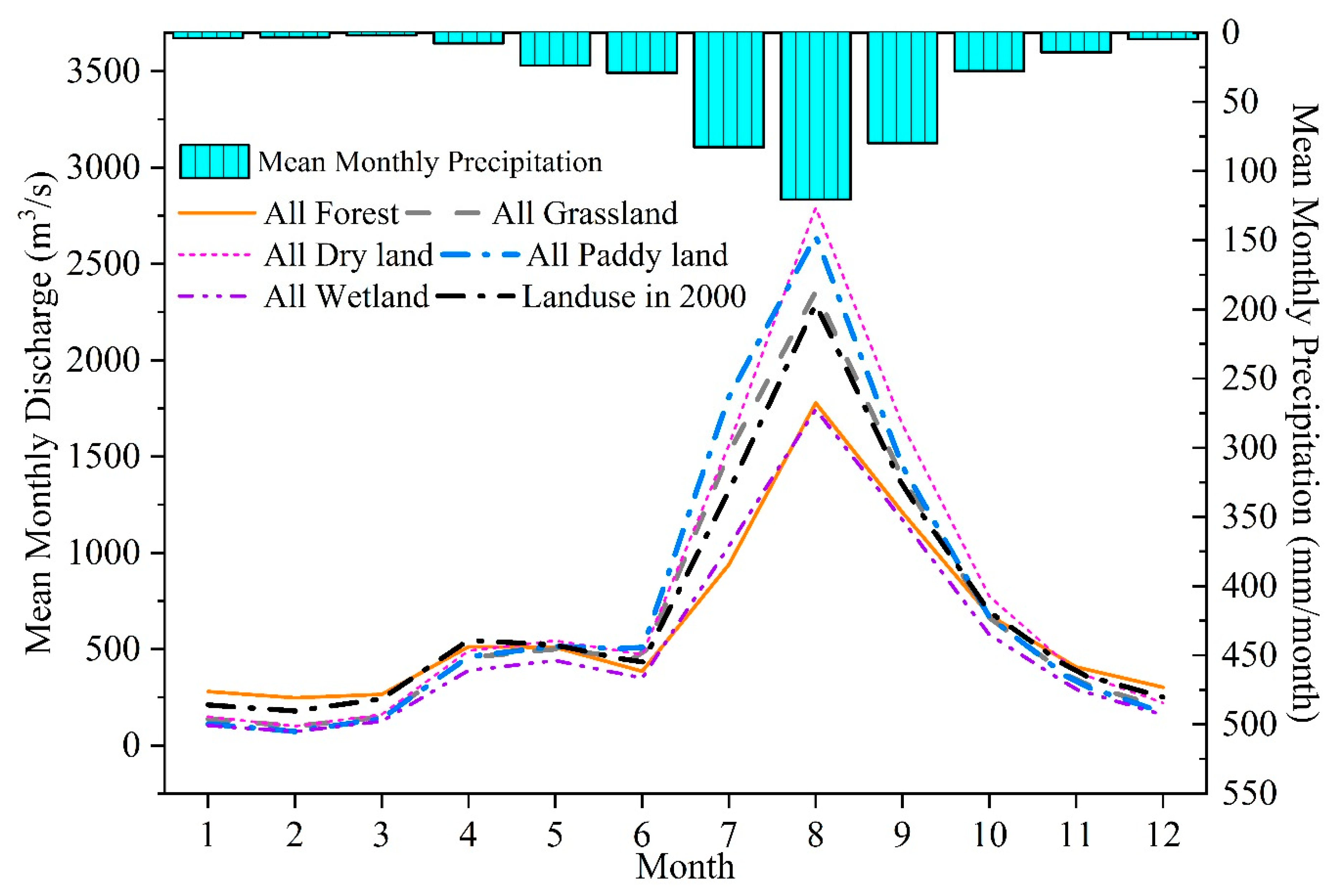
The intra-annual streamflow characteristics for the extreme scenarios were quite different from each other (Figure 6). Compared to the condition of land use in 2000, the streamflow increased by 7–37% during summer months (June to September) when the basin was covered by grassland, dry land, and paddy land, but streamflow in the cold seasons under these scenarios showed a dramatic reduction. On the contrary, when all the land use was changed into forest, the streamflow in the flood season decreased considerably, while it was increased to some extent in the dry season when comparing with the condition of land use in 2000. In particular, the streamflow from July to September decreased by 10–28%, whereas the streamflow from December to February increased by 20–38%. The results properly reflected that forests can redistribute the streamflow over a year, and that they can hold water and reduce streamflow in the flood season. In contrast, they recharge the streamflow in the dry season. The results also showed that when the land use type for the entire basin was changed to wetland, streamflow was reduced over the whole year, and the reduction was largest from January to March. This indicated that although wetlands can adjust the intra-annual distribution of streamflow, they may also sharply reduce the dry-season streamflow due to their considerable water capacity if the wetland area is large enough.
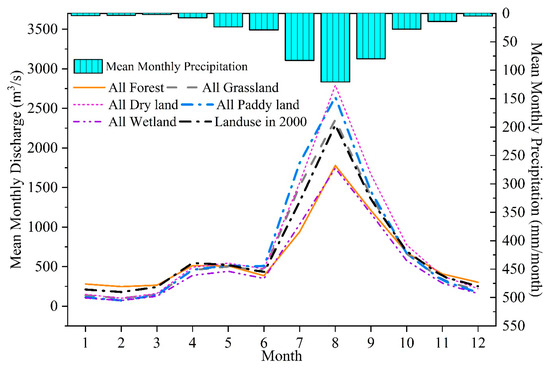
Figure 6.
Intra-annual changes in streamflow under extreme land use scenarios across the Nenjiang River Basin.
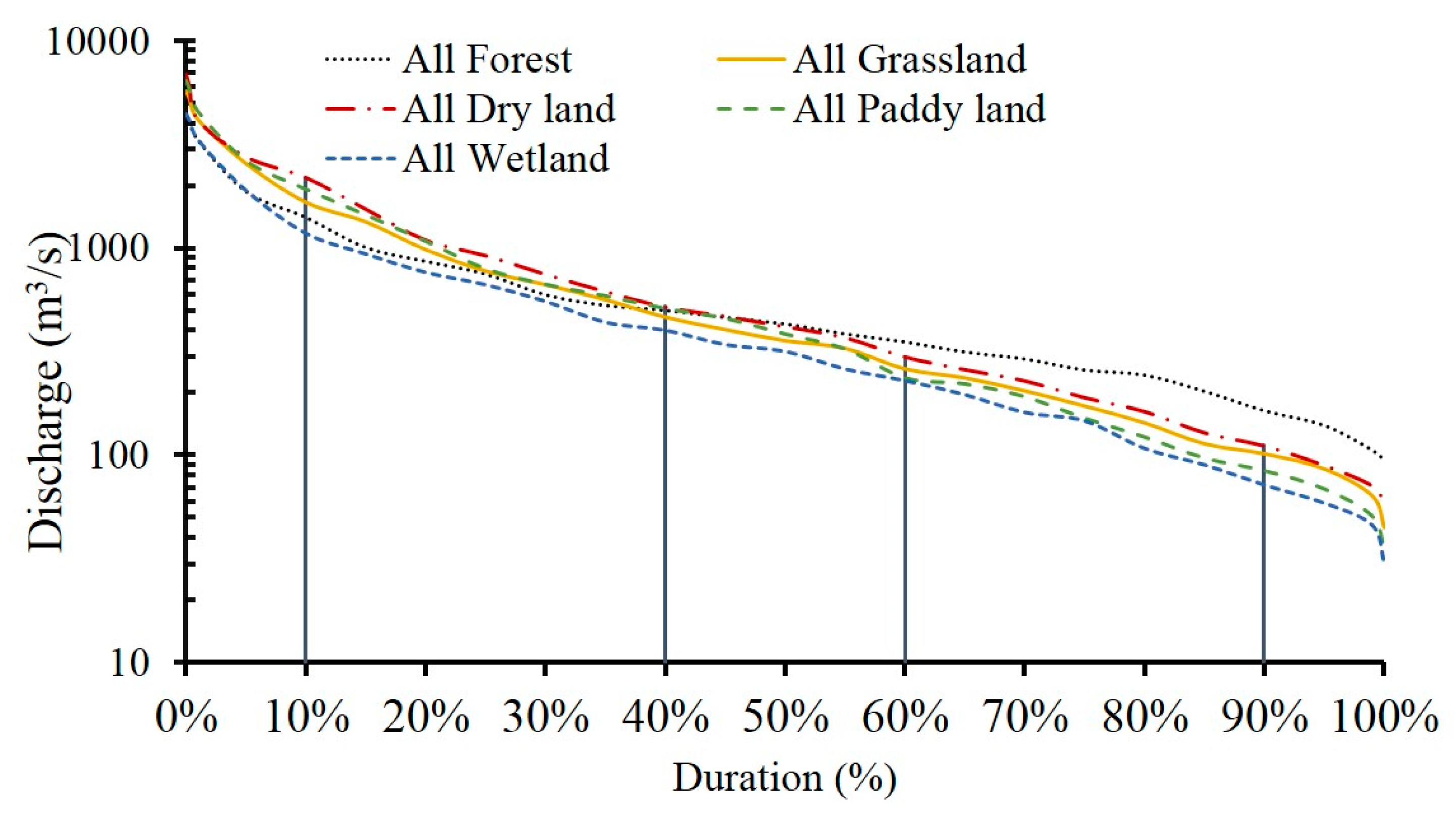
To further explore the impacts of land use changes on streamflow regime, the simulated monthly discharge under the different scenarios were ranked and the respective discharge values under different hydrological conditions were calculated (Table 7). A duration curve was generated based on these values (Figure 7). The results showed that the all wetland scenario produced the lowest discharge among all the extreme scenarios under the different hydrological conditions, which corresponded with the change characteristics for the intra-annual runoff distribution. During the flood period, wetlands can significantly retain the floods and reduce runoff because of their large water capacity. In the dry season, when there is little rain, some precipitation or runoff may still be held by wetlands and generate runoff. Therefore, all the discharge values under the different hydrological conditions were lowest for all wetland scenario compared to the other scenarios.

Table 7.
Discharge (m3/s) values under the different hydrological conditions in the Nenjiang River Basin.
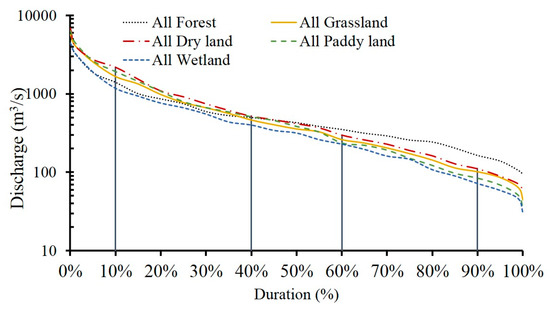
Figure 7.
Flow duration curves under the different land use scenarios in the Nenjiang River.
For the other four extreme scenarios, the cultivated land (dry land and paddy land) had the largest flow in the wet season, followed by grassland, whereas forest had the smallest flow, i.e.,, the capacity of forest to reduce flood peak and runoff was higher than that of grassland and dry land. The increase in canopy and litter interception, and evapotranspiration in all forest land use scenario meant that surface runoff was small. This suggested that these processes played an important role in flood reduction.
In this study, forest proved to considerably decrease flow in the flood season but led to a small flow increase in the dry season. This result is consistent with many previous studies. Forest canopies can intercept water and release it through evaporation, and they have a high rate of water loss through plant uptake. Furthermore, forests have a strong and healthy root system that can considerably improve soil conditions and consequently enhance soil infiltration, which makes forests conducive to storing water that can be used during the dry periods [47,48].
According to our simulation result, cropland produced the largest surface runoffs and the lowest baseflow among all the scenarios. And there was an increase in the steepness of the FDCs for the streamflow regime. The different effects of forest and crops on hydrologic regulation found in this study are similar with some previous studies [49,50,51,52], which indicated that forests generally have larger storage capacity than shallow-root systems plants such as crops.
The NRB is a typical wetland area in China and wetland is generally experiencing shrinkage and fragmentation [38]. Numerous studies have shown the hydrological functions of wetlands in regulating floods and baseflow conditions [53,54,55]. Our results highly conform to previous studies. Additionally, this study showed a runoff reduction in both the high and low flow periods for all wetland condition compared to 2000 land use condition. The reduction in runoff is largest from January to March. This may be due to the difference of soil characteristics of wetland and any of the other land use types. The soil in the wetland is saturated if the water supply is high enough. Consequently, a large amount of discharge was used to fulfill the water demand by the wetland and its soils, which resulted in reduced discharge, especially in the dry season (e.g. January to March, in this study) when the water supply is low.
3.4. Prediction of Hydrological Process under Future Land Use Condition
Cellular Automata-Markov (CA-Markov) model was applied to predict the 2038 LULC condition based on 2000 and 2010 land use maps in the NRB (Figure 8). Compared to the land use condition in 2000, the land use in the NRB mainly remained stable, especially for forest and wetland. Grassland, dry land, and water showed a reduction of 3.7%, 3.0%, and 9.6% in area, respectively. While paddy land, urban, and bare land areas increased by 10.5%, 15.9%, and 35%.
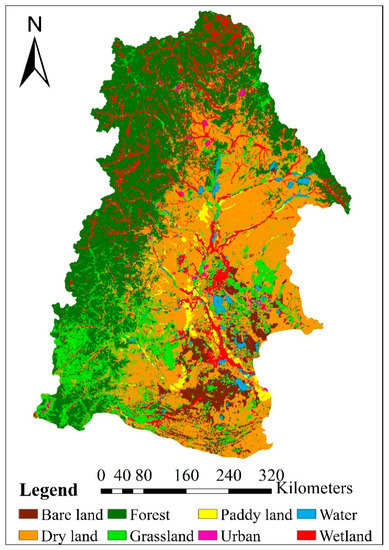
Figure 8.
Land use in 2038 in the Nenjiang River Basin.
According to the simulation of SWAT model, the average annual water yield in the NRB during 2000–2009 would increase from 100.5 mm under current land use condition (landuse in 2000) to 104.6 mm under the potential land use condition in 2038 (Table 8). The average value of annual surface runoff got a larger increase (4.8%) from 84.0 mm to 88.1 mm under the same meteorological conditions. On the contrary, baseflow in NRB showed a decrease of 3.2% from 18.9 mm to 18.3 mm. This may be potentially due to lower soil water interception of the paddy land, urban, and bare land compared to grassland and dry land. Specifically, urbanization restricts interactions between the stream and land while leading to increased runoff and subsequent higher peak flows, reductions in baseflows. In bare lands, where vegetation is absent, surface runoff is always higher and groundwater flow is lower. Meanwhile, the average annual evapotranspiration decreased from 361.8 mm to 356.1 mm due to the decrease of grassland, dry land, and water area in 2038 land use condition. The above hydrological process and reduction in evapotranspiration are probably the main reasons for the increase in surface runoff and decrease in baseflow in the future.

Table 8.
Comparison of hydrological components under current (2000) and potential (2038) land use scenarios in the Nenjiang River Basin.
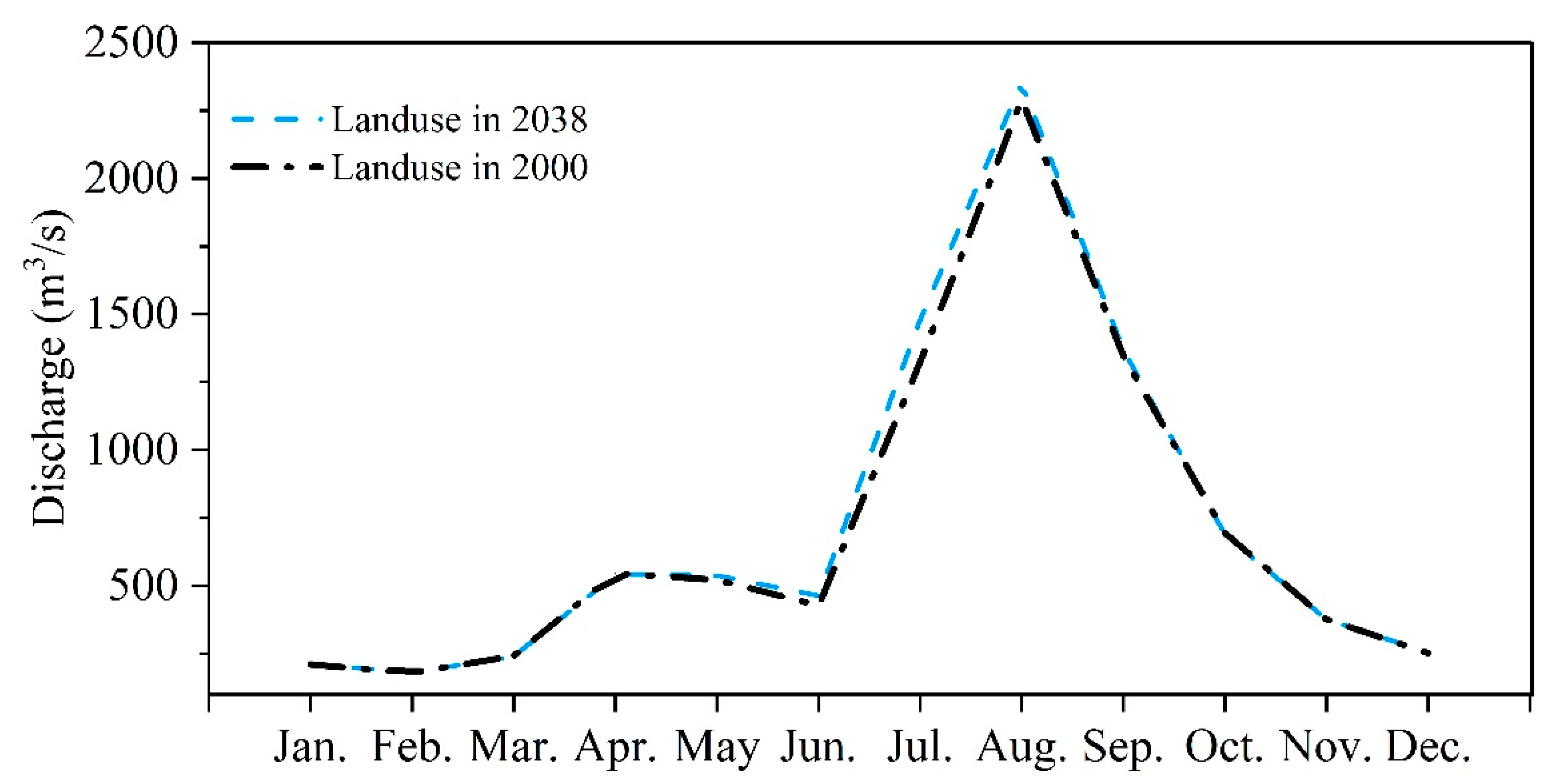
The intra-annual streamflow distribution pattern under 2038 land use condition was similar with that under 2000 land use condition (Figure 9). Compared to the streamflow under land use in 2000, streamflow in wet season showed an increase under land use condition of 2038. While, streamflow in dry season under these two land use conditions was close to each other, especially from November to March.
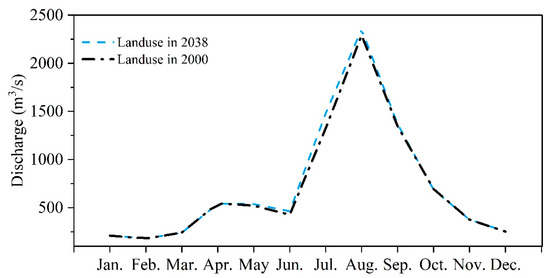
Figure 9.
Comparison of intra-annual changes in streamflow under current (2000) and potential (2038) land use scenarios in the Nenjiang River Basin.
3.5. Limitations of this Study
The findings of this study can be used to improve land use planning and water resources management in the basin. However, there are still some limitations and uncertainties in the current study. First, a SWAT model was employed to help assess the hydrological response to land use change scenarios. Although it was calibrated using the historical discharge data and is regarded to have a reasonable accuracy level, it does not easily show whether the parameters reflect the real hydrological conditions. Furthermore, the model output can be substantially affected by the model inputs and methods selected for simulation, such as stream routing, calibration, and sensitivity analysis. For example, geographical data is necessary for the model to generate watershed and distributed HRUs. In this study, the input geographical data was converted to 1 km × 1 km raster, which is somehow coarse, in order to reduce the calculating progress. This may probably affect the accuracy of the model. Another potential limitation is that this study implicitly assumed that the calibrated parameters remained valid for different land use scenarios, which might not be true. However, investigating these uncertainties in the hydrological simulation is beyond the scope of our present study. It needs to be explored in future studies.
Hydrological alteration is usually a result of the effects of various factors, including anthropogenic interventions such as land use changes as well as climate variability. However, this study only considered the impacts of land use change on hydrological components in the NRB. Therefore, further studies should incorporate both land use and climate changes into the scenarios in order to make reliable assessments of their hydrological impacts.
4. Conclusions
This study analyzed the land use change and its hydrological effects in the NRB. The expansions of agriculture and urban area and the reduction of forest, grassland, and wetland during the period of 1975–2000 were observed. The land use changes had decreased the water yield, surface runoff, and baseflow while increasing the annual evapotranspiration. Individual impacts of each land use type on the streamflow varied considerably. Forest and wetland showed a stronger regulation of runoff, whereas runoff appeared to be higher when grassland, dry land, or urban areas expanded. The effects of land use changes on streamflow are very significant in both the annual and monthly average values. Forests can reduce the peak flow in the flood season and retain the surface runoff for further utilization during the drought season. Conversely, an increase in grassland and dry land areas may lead to a rise in flood season discharge, but a reduction in the drought season. There will be an increase in paddy land, urban, and bare land areas but a reduction in grassland, dry land, and water areas in 2038. The 2038 land use condition is expected to increase the annual water yield, surface runoff and wet season flow, and reduce evapotranspiration and baseflow. Understanding these effects can improve future land use planning and water resources management in the basin by regulating the proper land use to maintain the hydrological balance.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the design and development of this manuscript. F.L. carried out the modeling work and data analysis and prepared the first draft of the manuscript. G.Z. is the graduate advisor of F.L. and contributed many ideas to the study. H.L. and W.L. provided important advice on the concept of structuring of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2010CB428404); the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant number 41701020 and number 51379088; and the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province under Grant number 20170520086JH and number 20180101078JC.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Honglei Zhu for the technical support on land use prediction during the revision of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mallinis, G.; Koutsias, N.; Arianoutsou, M. Monitoring land use/land cover transformations from 1945 to 2007 in two peri-urban mountainous areas of Athens metropolitan area, Greece. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 490, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonestrom, D.A.; Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, L. Introduction to special section on impacts of land use change on water resources. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Yuan, Y.; Kepner, W.; Nash, M.S.; Jackson, M.; Erickson, C. Assessing impacts of Landuse and Landcover changes on hydrology for the upper San Pedro watershed. J. Hydrol. 2011, 407, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihdego, Y.; Webb, J. An Empirical Water Budget Model as a Tool to Identify the Impact of Land-use Change in Stream Flow in Southeastern Australia. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4941–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, G.M.; Lazo, P.X.; Célleri, R.; Wilcox, B.P.; Crespo, P. Runoff from tropical alpine grasslands increases with areal extent of wetlands. Catena 2015, 125, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremicael, T.G.; Mohamed, Y.A.; Betrie, G.D.; van der Zaag, P.; Teferi, E. Trend analysis of runoff and sediment fluxes in the Upper Blue Nile basin: A combined analysis of statistical tests, physically-based models and landuse maps. J. Hydrol. 2013, 482, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Chen, X.; Yao, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M.; Gao, L.; James, A. Analyses of landuse change impacts on catchment runoff using different time indicators based on SWAT model. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardena, L.; Finlayson, B.; McMahon, T. The impact of land use change on catchment hydrology in large catchments: The Comet River, Central Queensland, Australia. J. Hydrol. 2006, 326, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehoff, D.; Fritsch, U.; Bronstert, A. Land-use impacts on storm-runoff generation: scenarios of land-use change and simulation of hydrological response in a meso-scale catchment in SW-Germany. J. Hydrol. 2002, 267, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwate, O.; Woyessa, Y.; Wiberg, D. Dynamics of land cover and impact on streamflow in the Modder River Basin of South Africa: case study of a Quaternary catchment. Int. J. Environ. Prot. Policy 2015, 3, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Nan, Z.; Yu, W.; Ge, Y. Modeling Land-Use and Land-Cover Change and Hydrological Responses under Consistent Climate Change Scenarios in the Heihe River Basin, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 4701–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhou, P.; Jia, P.; Liu, Z.; Wei, L.; Tian, H. Spatial driving forces of dominant land use/land cover transformations in the Dongjiang River watershed, Southern China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmer, A.; Murdiyarso, D.; Bruijnzeel, L.A.; Ilstedt, U. Carbon sequestration in tropical forests and water: a critical look at the basis for commonly used generalizations. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, X.; Yan, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H. Spatial patterns of hydrological responses to land use/cover change in a catchment on the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 92, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Xu, Z.; Yao, W.; Jin, S.; Xiao, P.; Ran, D. Assessing the effects of changes in land use and climate on runoff and sediment yields from a watershed in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 544, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beighley, R.E.; Melack, J.M.; Dunne, T. IMPACTS OF CALIFORNIA’S CLIMATIC REGIMES AND COASTAL LAND USE CHANGE ON STREAMFLOW CHARACTERISTICS. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2003, 39, 1419–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, D.; Cavallo, G.J.; Nilson, M.L. BASE FLOW TRENDS IN URBANIZING WATERSHEDS OF THE DELAWARE RIVER BASIN. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2005, 41, 1377–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Engel, B.A.; Lim, K.J.; Larson, V.; Duncan, B. Runoff Impacts of Land-Use Change in Indian River Lagoon Watershed. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2002, 7, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yang, Z.; Yan, D.; Ying, L.I.; Zhe, Y. On hydrological response to land-use/cover change in Luanhe River basin. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 25, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, X.; Yu, L.; Xu, F. Land use and landscape pattern changes in Nenjiang River basin during 1988–2002. Front. Earth Sci. China 2010, 4, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Bu, K.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Chang, L. Multitemporal analysis of forest fragmentation in the upstream region of the Nenjiang River Basin, Northeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.H.; Jiang, W.G.; Luo, Z.L.; He, X.H.; Liu, Y.H. Analysis of wetland change in the Songhua River Basin from 1995 to 2008. In Proceedings of the 35th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment, IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Inst Remote Sensing & Digital Earth, Beijing, China, 22–26 April 2013; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, England, 2014; pp. 12125–12131. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, G.; Yin, X. Hydrological responses to climate change in Nenjiang River basin, Northeastern China. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J. Separating the Impacts of Climate Variation and Human Activities on Runoff in the Songhua River Basin, Northeast China. Water 2014, 6, 3320–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Mustak, S.; Srivastava, P.K.; Szabó, S.; Islam, T. Predicting Spatial and Decadal LULC Changes Through Cellular Automata Markov Chain Models Using Earth Observation Datasets and Geo-information. Environ. Process. 2015, 2, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, T.; Tulu, T.; Argaw, M.; Worqlul, A.W. Modeling the hydrological impacts of land use/land cover changes in the Andassa watershed, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1394–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanishakib, F.; Mirkarimi, S.H.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Poodat, F. Land use change modeling through scenario-based cellular automata Markov: improving spatial forecasting. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, P.; Ma, X.; Li, X. Detection and prediction of land use/land cover change using spatiotemporal data fusion and the Cellular Automata-Markov model. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment—Part 1: model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setegn, S.G.; Rayner, D.; Melesse, A.M.; Dargahi, B.; Srinivasan, R. Impact of climate change on the hydroclimatology of Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Water Resour. 2011, 47, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, R.; Bao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, W.; Shen, Z. Uncertainty of SWAT model at different DEM resolutions in a large mountainous watershed. Water Resour. 2014, 53, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, F.; Hao, Z.; Xu, C.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Tong, K. Impact of projected climate change on the hydrology in the headwaters of the Yellow River basin. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 4379–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J. Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Water Resources in the Songhua River Basin. Water 2016, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I-A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.A.; Nakagoshi, N. Changes in landscape spatial pattern in the highly developing state of Selangor. peninsular Malaysia. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Land use change analysis in the Zhujiang Delta of China using satellite remote sensing, GIS and stochastic modelling. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 64, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, N.; Luo, L.; Li, X.; Ren, C.; Song, K.; Chen, J.M. Shrinkage and fragmentation of marshes in the West Songnen Plain, China, from 1954 to 2008 and its possible causes. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinforma. 2011, 13, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, M. The resource and conservation suggestion of wetlands in China. Wetl. Sci. 2005, 3, 81–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. Impacts of reservoir project on hydrological and ecological environment of Xianghai wetlands. Resour. Sci. 2002, 24, 26–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Song, K.; Zhang, B.; Liu, D.; Guo, Z. Assessment for Salinized Wasteland Expansion and Land Use Change Using GIS and Remote Sensing in the West Part of Northeast China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 131, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Liu, S.; Wei, X. Impacts of forest changes on hydrology: a case study of large watersheds in the upper reach of Yangtze River Basin. Hydrol. Earth Sci. Discuss. 2012, 9, 6507–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, K.; Jackson, C.R.; Parker, A.J.; Reitan, T.; Dowd, J.; Cyterski, M. Effects of watershed land use and geomorphology on stream low flows during severe drought conditions in the southern Blue Ridge Mountains, Georgia and North Carolina, United States. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruijnzeel, L. Hydrological functions of tropical forests: not seeing the soil for the trees? Agric. Ecosyst. 2004, 104, 185–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbies, M.; Aust, W.; Burger, J.; Adams, M.B. Forest operations, extreme flooding events, and considerations for hydrologic modeling in the Appalachians—A review. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 242, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.; Jarrett, B.; Turner, L. Effects of plantation forest harvesting on water quality and quantity: Canobolas State Forest, NSW. In Proceedings of the 5th Australian Stream Management Conference, Australian Rivers: Making a Difference, Albury, New South Wales, Australia, 19–25 May 2007; Wilson, A., Deehan, R., Watts, R., Page, K., Bownan, K., Curtis, A., Eds.; Charles Sturt University: Thurgoona, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kheereemangkla, Y.; Shrestha, R.P.; Shrestha, S.; Jourdain, D. Modeling hydrologic responses to land management scenarios for the Chi River Sub-basin Part II, Northeast Thailand. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, F.; Xia, J.; Liu, W. Impact of LUCC on streamflow based on the SWAT model over the Wei River basin on the Loess Plateau in China. Hydrol. Earth Sci. 2017, 21, 1929–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, P.J.; Feyen, J.; Buytaert, W.; Bücker, A.; Breuer, L.; Frede, H.-G.; Ramirez, M.; Driemel, A. Identifying controls of the rainfall–runoff response of small catchments in the tropical Andes (Ecuador). J. Hydrol. 2011, 407, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dawes, W.R.; Walker, G.R. Response of mean annual evapotranspiration to vegetation changes at catchment scale. Water Resour. 2001, 37, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, R.P.; Kumar, S. Estimating the effects of potential climate and land use changes on hydrologic processes of a large agriculture dominated watershed. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, W.; Guo, Q.; Wu, S. Effects of landuse change on surface runoff and sediment yield at different watershed scales on the Loess Plateau. Int. J. Sediment 2010, 25, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Mcnulty, S.G.; Amatya, D.M.; Skaggs, R.W.; Liang, Y.; Kolka, R.K. A Comparison of the Watershed Hydrology of Coastal Forested Wetlands and Mountainous Uplands in the Southern U.S. J. Hydrol. 2002, 263, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, H.E.; Sander, H.A.; Lane, C.R.; Zhao, C.; Price, K.; D’Amico, E.; Christensen, J.R. Relative effects of geographically isolated wetlands on streamflow: a watershed-scale analysis. Ecohydrol. 2016, 9, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acreman, M.; Holden, J. How wetlands affect floods. Wetlands 2013, 33, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).