Coupling Relationship between Soil Organic Carbon Storage and Soil Water Storage in Abandoned Economic Forests in the Loess Hilly Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
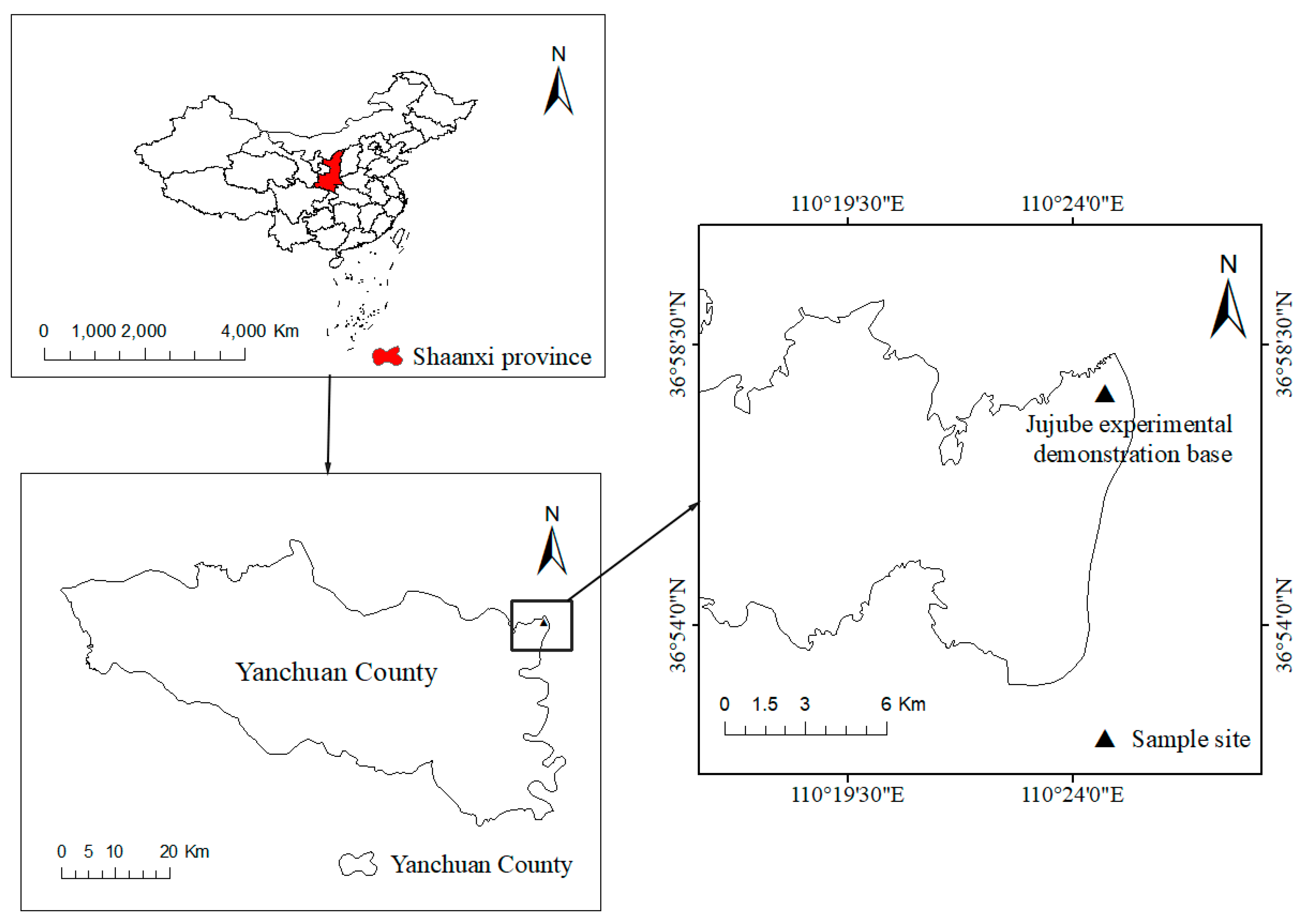
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Plot Design and Soil Sampling
2.3. Determination of Soil Samples
2.3.1. Soil Bulk Density
2.3.2. SOCS Was Calculated Using Equation (2) [30]
2.3.3. Calculation of Soil Water Storage by Formula (3)
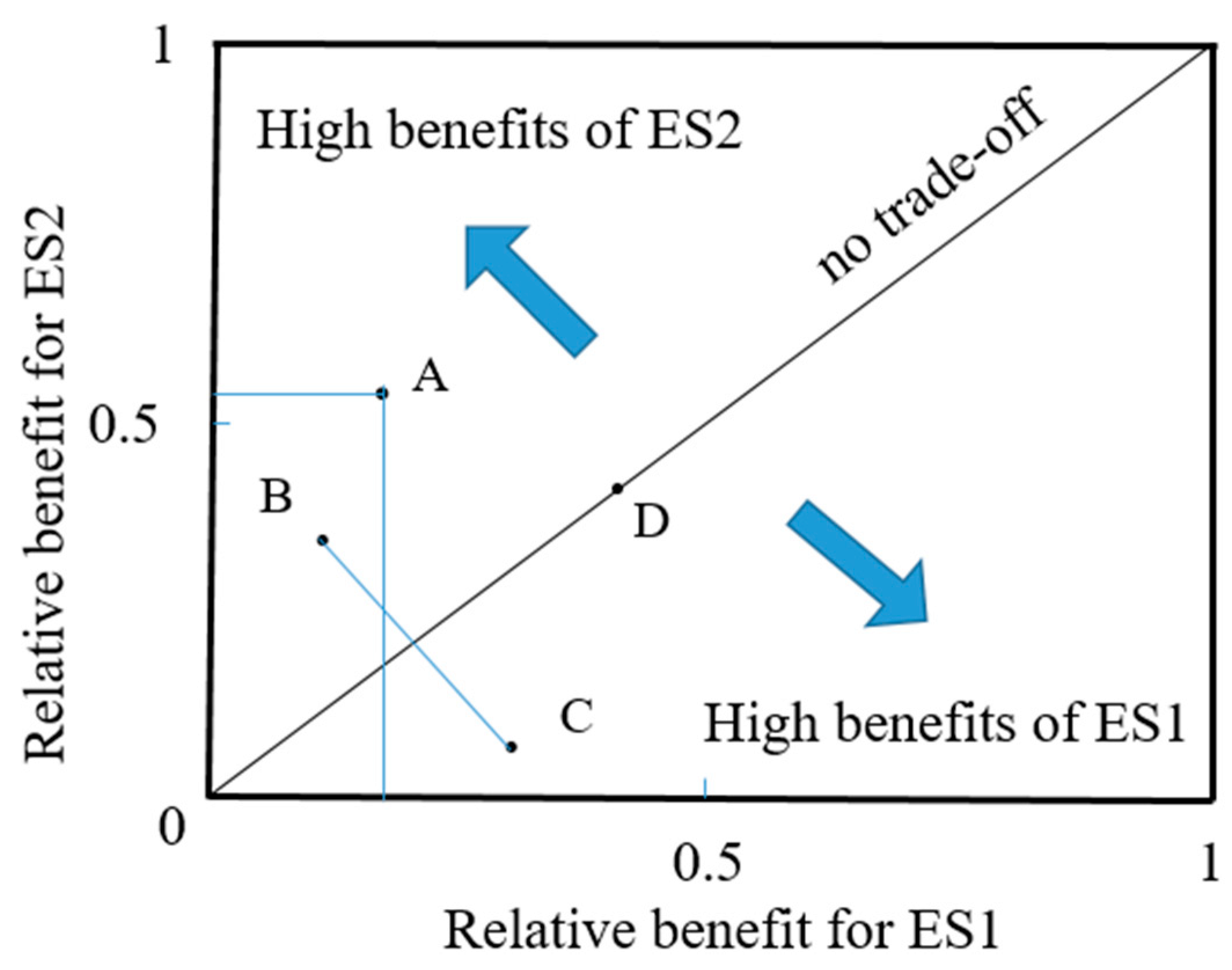
2.3.4. Trade-Off Analysis
2.3.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
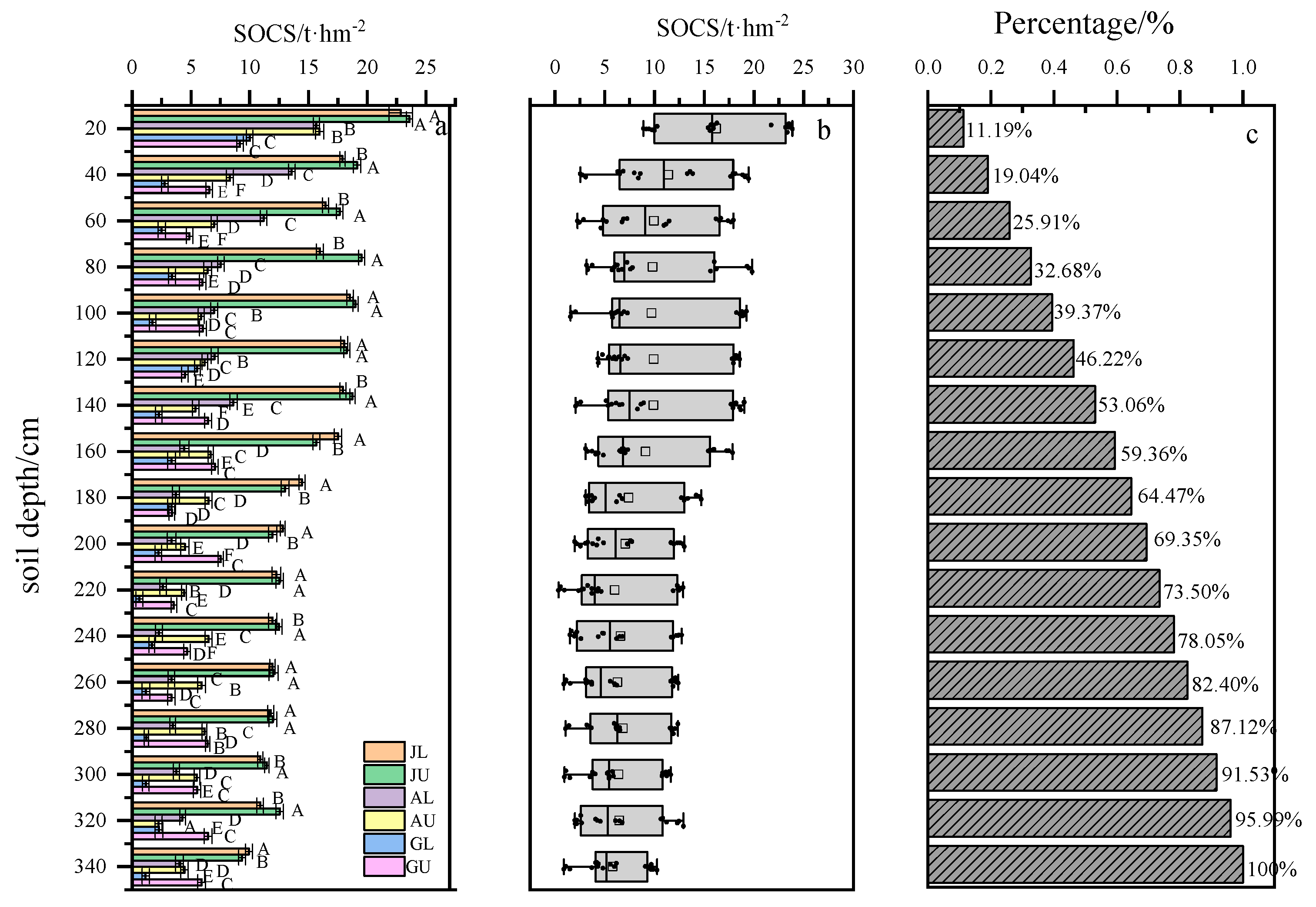
3.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of SOCS across Different Vegetation Types
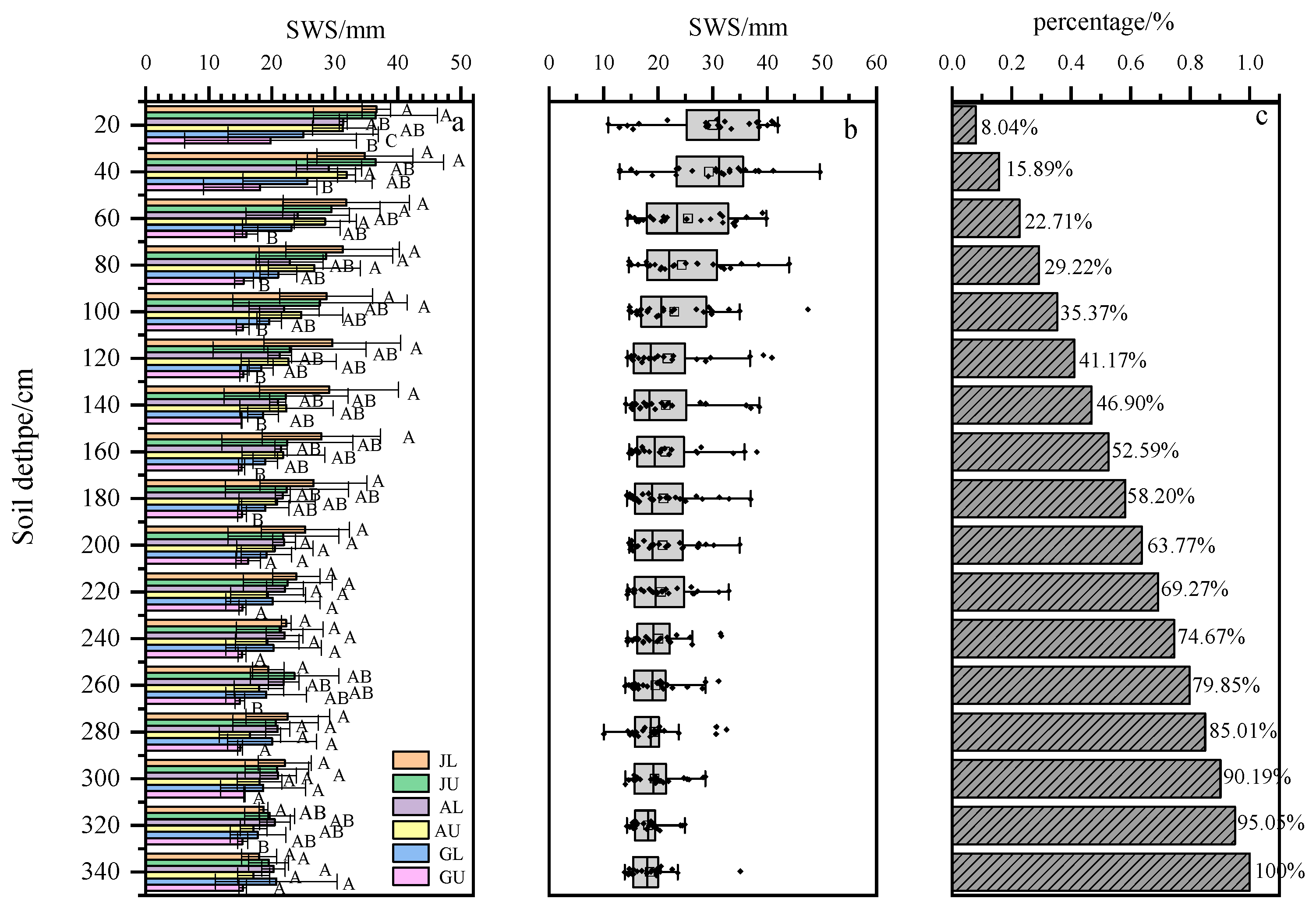
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of SWS across Different Vegetation Types
3.3. The Relative Benefit and Trade-Off between SOCS and SWS
3.3.1. Relative Benefits Analysis of SOCS and SWS
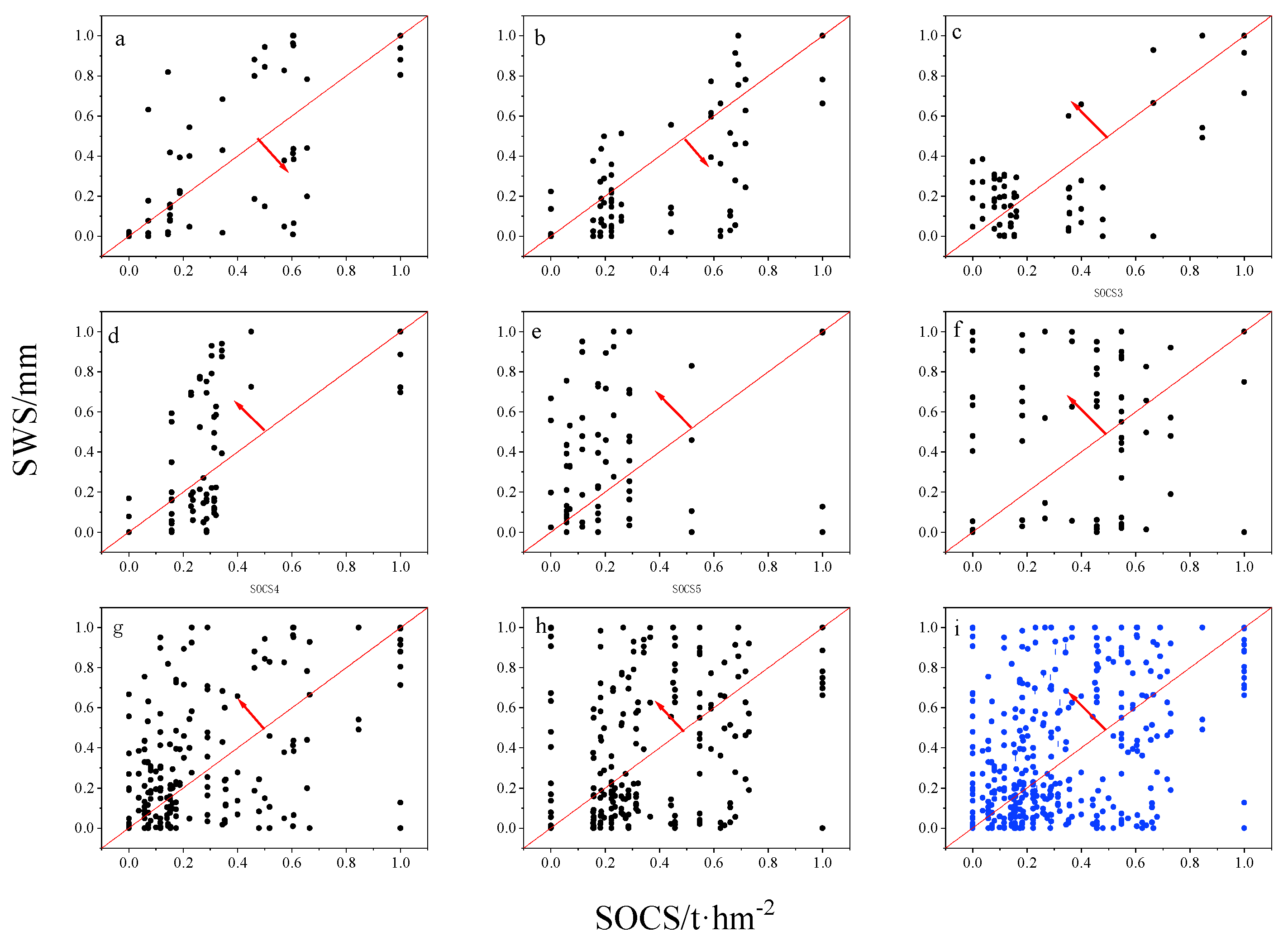
3.3.2. Trade-Off Analysis of SOCS and SWS
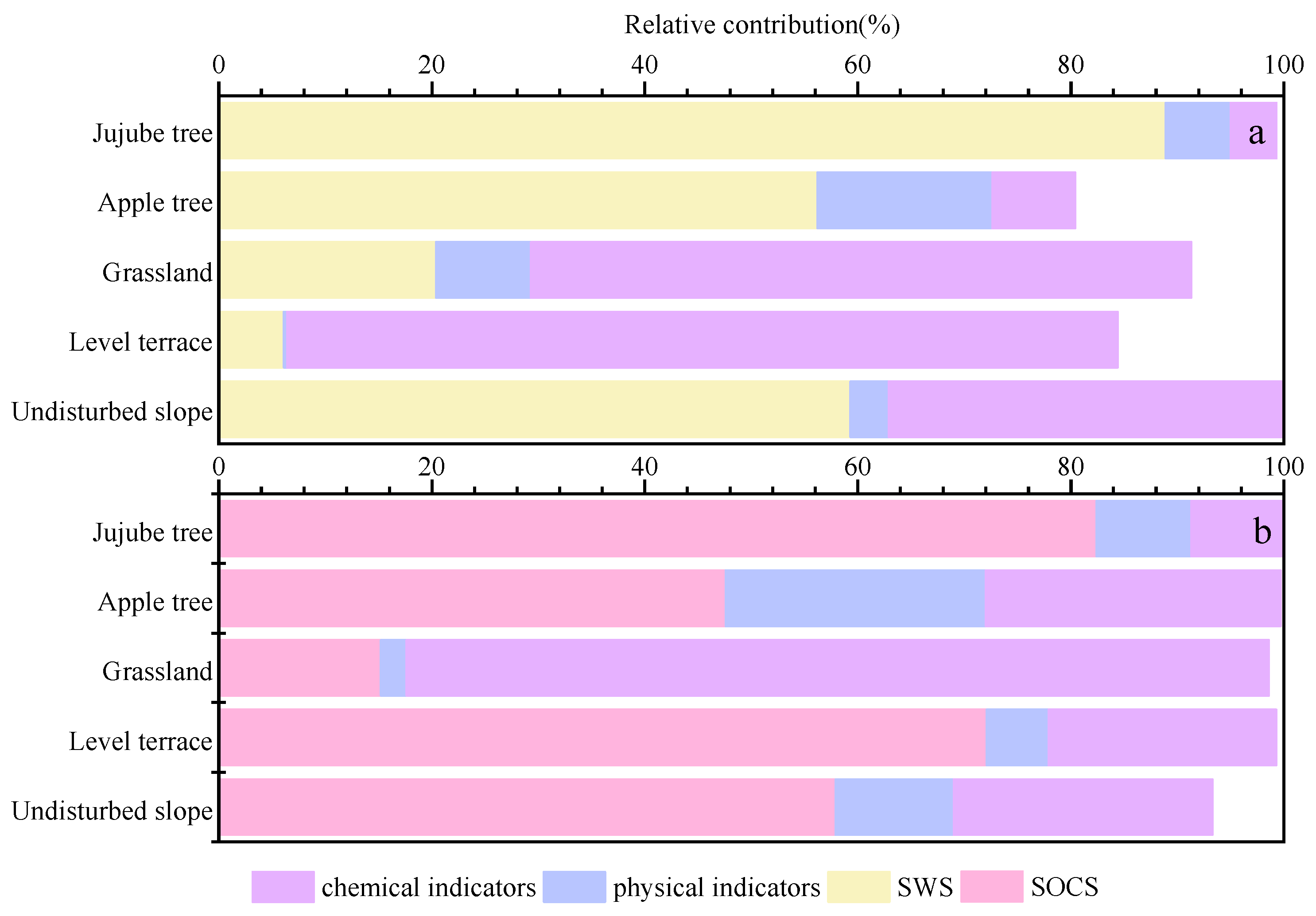
3.4. Analysis of Environmental Factors and Contribution of SOCS and SWS
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of SOCS to Vegetation
4.2. Response of SWS to Vegetation
4.3. Relative Trade-Offs between SOCS and SWS and Their Benefits
4.4. Environmental Influences on SOCS and SWS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.; Zha, T.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L. Vertical distribution and influencing factors of soil organic carbon in the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murty, D.; Kirschbaum, M.U.; Mcmurtrie, R.E.; Mcgilvray, H. Does conversion of forest to agricultural land change soil carbon and nitrogen? A review of the literature. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2002, 8, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Fu, B.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z. Hydrologic feasibility of artificial forestation in the semi-arid Loess Plateau of China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2519–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porporato, A.; D’odorico, P.; Laio, F.; Ridolfi, L.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. Ecohydrology of water-controlled ecosystems. Adv. Water Resour. 2002, 25, 1335–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shao, M.; Li, Y. Soil desiccation in the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2008, 143, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L. Identification on threshold and efficiency of rainfall replenishment to soil water in semi-arid loess hilly areas. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Fu, B.; Jin, T.; Chang, R. Trade-off analyses of multiple ecosystem services by plantations along a precipitation gradient across Loess Plateau landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, L.; Sivakumar, B.; Zhang, F.; Sun, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, Q.; Voinov, A. Spatiotemporal features of the hydro-biogeochemical cycles in a typical loess gully watershed. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, R.; Khan, M.N.; Sial, T.A.; Si, B. Long-term vegetation restoration increases deep soil carbon storage in the Northern Loess Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Huang, M.; Li, C.; Wu, X.; Guo, T.; Zhu, M. Changes in soil moisture and organic carbon under deep-rooted trees of different stand ages on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 328, 107855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Han, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil organic carbon mineralization and microbial community structure. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-W.; Shangguan, Z.-P. The coupling interaction of soil water and organic carbon storage in the long vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Wang, J.; Xing, Z. Decline of virtual water inequality in China’s inter-provincial trade: An environmental economic trade-off analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, D.K.; Poe, M.R.; Francis, T.B.; Punt, A.E.; Levin, P.S.; Shelton, A.O.; Armitage, D.R.; Cleary, J.S.; Dressell, S.C.; Jones, R. Attending to spatial social–ecological sensitivities to improve trade-off analysis in natural resource management. Fish Fish. 2020, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Gao, P. Impact and trade off analysis of land use change on spatial pattern of ecosystem services in Chishui River Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 20234–20248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.M.; Santé, I.; Loureiro, X.; Miranda, D. Green infrastructure spatial planning considering ecosystem services assessment and trade-off analysis. Application at landscape scale in Galicia region (NW Spain). Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 43, 101115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yu, G. A review on the coupled carbon and water cycles in the terrestrial ecosystems. Prog. Geogr. 2008, 27, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Yu, G.; Li, S.; Ren, C.; Sun, X.; Mi, N.; Li, J.; Ouyang, Z. Canopy water use efficiency of winter wheat in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 93, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Su, Z.; Shangguan, Z. Trade-off analyses of plant biomass and soil moisture relations on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2021, 197, 104946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Song, N.P.; Yang, X.G. Trade-off between soil moisture and species diversity in semi-arid steppes in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, T.; Ren, K.; Sha, G.; Guo, X.; Fu, Y.; Yu, H. The coupling interaction of soil organic carbon stock and water storage after vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 306, 114481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Ren, F. Spatial Distribution and Characteristics of Economic Forest Resources in Shaanxi Province. For. Inventory Plan. 2019, 44, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Wang, G.; Liu, G.; Shangguan, Z. Effects of age and land-use changes on soil carbon and nitrogen sequestrations following cropland abandonment on the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Yuan, W.; Dong, W.; Xia, J.; Cao, Y.; Jia, Y. Loess Plateau check dams can potentially sequester eroded soil organic carbon. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2016, 121, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Jin, T.; Lü, Y.; Liu, G.; Fu, B. Soil carbon and nitrogen changes following afforestation of marginal cropland across a precipitation gradient in Loess Plateau of China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Dong, Y.; Chang, X.; Nie, X.; Liu, L.; Xiao, H.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, G. Response of soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks to soil erosion and land use types in the Loess hilly–gully region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 166, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Soil Science; Chinese Academy of Sciences. Soil Physical Properties Determination Method; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1978; Chapters 2, 4, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; Chapters 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.; Li, L.; Pan, G.; Zhang, Q. Topsoil organic carbon storage of China and its loss by cultivation. Biogeochemistry 2005, 74, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijuan, Y.; Guang, L.; Jiangqi, W.; Weiwei, M.; Haiyan, W. Effects of four typical vegetations on soil active organic carbon and soil carbon in Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 5546–5554. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Daryanto, S.; Cherubini, F. Trading-off ecosystem services for better ecological restoration: A case study in the Loess Plateau of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumiao, X.; Hengrui, W.; Wei, Z.; Baojiang, Z.; Gang, D.; Haidong, Z. Effects of Different Grazing Methods on the Production and Ecological Functions of Mountain Meadows and their Trade-off Relationships. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2022, 030. [Google Scholar]
- Bätz, N.; Verrecchia, E.P.; Lane, S.N. Organic matter processing and soil evolution in a braided river system. Catena 2015, 126, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, N.W.; Kuebbing, S.E.; Karlsen-Ayala, E.; Bradford, M.A. Evidence for the primacy of living root inputs, not root or shoot litter, in forming soil organic carbon. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, L.; Han, Q.S.; Zhang, C.; Tang, Z.S.; Shangguan, Z.P. Above-ground and below-ground ecosystem biomass accumulation and carbon sequestration with Caragana korshinskii Kom plantation development. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Schimel, J.P.; Jastrow, J.D. The importance of anabolism in microbial control over soil carbon storage. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xin, Z.; Hou, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Yuan, H.; Majid, A. Soil organic carbon stocks in an investigated watershed transect linked to ecological restoration practices on the Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1148–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Wang, Y.; Ai, N.; Liu, C.; Zong, Q.; Qiang, F. Characteristics and influencing factors of deep soil organic carbon in characteristic economic forest in Northern Shaanxi. J. For. Environ. 2021, 41, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Wang, K.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Shangguan, Z. Changes of soil carbon in five land use stages following 10 years of vegetation succession on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2018, 171, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Ma, W.; Wu, P. Identifying a suitable revegetation technique for soil restoration on water-limited and degraded land: Considering both deep soil moisture deficit and soil organic carbon sequestration. Geoderma 2018, 319, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, R.D.; Newkirk, K.M.; Rullo, G.M. Carbon dioxide and methane fluxes by a forest soil under laboratory-controlled moisture and temperature conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sala, O.; Lauenroth, W.; Parton, W. Long-term soil water dynamics in the shortgrass steppe. Ecology 1992, 73, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Huang, Q.; Huang, S.; Leng, G.; Qu, Y.; Deng, M.; Han, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, D.; Bai, Q. Assessing the feedback relationship between vegetation and soil moisture over the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wei, T.; Xie, J.; Shi, X.; Gen-Batu, G.; Dong, Z.; Cheng, Z. Different types of vegetation cover and water conservation benefits. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 3, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, L.; Pei, Y.; Zheng, K.; Kong, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, M. Influence of Different Site Preparation on Soil Water Content in Dry-hot Valley of Yuanmou County. J. West China For. Sci. 2017, 46, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, F.; Xu, M. Comparison of Soil Hydrologic Properties Under Different Conversion Patterns in the Hilly-gully Region of the Loess Plateau. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Feng, Z.; Wang, H.; Dai, X.; Fu, X. Deep soil water extraction helps to drought avoidance but shallow soil water uptake during dry season controls the inter-annual variation in tree growth in four subtropical plantations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 234, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Han, D.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; Bray, M.; Islam, T. Selection of classification techniques for land use/land cover change investigation. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 50, 1250–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, B.; He, C.; Han, Z.; Bogena, H.R.; Huisman, J.A. Dynamic response patterns of profile soil moisture wetting events under different land covers in the Mountainous area of the Heihe River Watershed, Northwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 271, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Meena, R.S.; Lal, R.; Singh Yadav, G.; Mitran, T.; Meena, B.L.; Dotaniya, M.L.; El-Sabagh, A. Role of Legumes in Soil Carbon Sequestration. In Legumes for Soil Health and Sustainable Management; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Tan, Q.; Xu, M.; Liu, G. Mixed-species plantations can alleviate water stress on the Loess Plateau. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 458, 117767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jia, Q.; Xu, X.; Yao, S.; Chen, H.; Hou, X. Contribution of ecological policies to vegetation restoration: A case study from Wuqi County in Shaanxi Province, China. Land Use Policy 2018, 73, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Sun, K.; Zhang, X.; Winowiecki, L.; Vågen, T.-G.; Xu, J.; Qiu, L.; Sun, P.; et al. Predicting the climate change impacts on water-carbon coupling cycles for a loess hilly-gully watershed. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shao, M.A.; Wang, Y. Effect of environmental factors on regional soil organic carbon stocks across the Loess Plateau region, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 142, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callesen, I.; Liski, J.; Raulund-Rasmussen, K.; Olsson, M.; Tau-Strand, L.; Vesterdal, L.; Westman, C. Soil carbon stores in Nordic well-drained forest soils—Relationships with climate and texture class. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangid, K.; Williams, M.A.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Schmidt, T.M.; Coleman, D.C.; Whitman, W.B. Land-use history has a stronger impact on soil microbial community composition than aboveground vegetation and soil properties. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 2184–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P. Land use change and soil organic carbon dynamics. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2008, 81, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Qiang, F.F.; Liu, G.Q.; Liu, C.H.; Ai, N. Distribution characteristics of soil microbial communities and their responses to environmental factors in the sea buckthorn forest in the water-wind erosion crisscross region. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Feng, J.; Wu, H.; Lin, G. Distribution patterns and controlling factors for the soil organic carbon in four mangrove forests of China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 17, e00575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, D.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Deng, J.; Qiao, W.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Huang, J. Substrate quality and soil environmental conditions predict litter decomposition and drive soil nutrient dynamics following afforestation on the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2018, 325, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Jiao, F. Relationships between community characteristics and soil nutrients and moisture in abandoned hill country grassland. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2016, 25, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, T.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Yu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H. Effects of land preparations and vegetation types on soil chemical features in a loess hilly region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 3216–3225. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Duan, J.; Gao, W. Study on the benefits of slope runoff control afforestation in the gully area of Longdong Loess Plateau. Soil Water Conserv. China 2018, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PuYang, X.; Gou, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y. Soil Desiccation Effects of Micro-Topographic in Different Precipitation Locations in the Loess Region of Northern Shaanxi Province. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2020, 38, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Number | Plot Type | Altitude (m) | Slope Gradient (°) | Slope Aspect | Vegetation Coverage (%) | Land Preparation Method | Age of the Plantation (a) | Abandoned Years (a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | JL | 836 | 0 | Shady | 40 | Level terrace | 30 | 6 |
| 2 | JU | 860 | 25 | Shady | 43 | Undisturbed slope | 30 | 6 |
| 3 | AL | 900 | 0 | Shady | 50 | Level terrace | 30 | 6 |
| 4 | AU | 903 | 28 | Shady | 52 | Undisturbed slope | 30 | 6 |
| 5 | GL | 905 | 0 | Shady | 82 | Level terrace | 6 | |
| 6 | GU | 904 | 30 | Shady | 80 | Undisturbed slope | 6 |
| Soil Depth (cm) | JL | JU | AL | AU | GL | GU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 | 0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.56 |
| 20–40 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.55 | 0.77 | 0.60 |
| 40–60 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.5 | 0.64 | 0.19 |
| 60–80 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.46 | 0.53 | 0.16 |
| 80–100 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.42 | 0.46 | 0.14 |
| 100–120 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.22 | 0.38 | 0.46 | 0.21 |
| 120–140 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.42 | 0.19 |
| 140–160 | 0.15 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.39 | 0.18 |
| 160–180 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.23 | 0.3 | 0.37 | 0.26 |
| 180–200 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.35 | 0.26 |
| 200–220 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.31 |
| 220–240 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.32 |
| 240–260 | 0.13 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.35 |
| 260–280 | 0.13 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.33 |
| 280–300 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.33 |
| 300–320 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.32 |
| 320–340 | 0.12 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.24 | 0.30 | 0.31 |
| average | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.32 | 0.39 | 0.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, T.; Gao, R.; Qiang, F.; Yang, N.; Liu, G.; Liu, C.; Ai, N. Coupling Relationship between Soil Organic Carbon Storage and Soil Water Storage in Abandoned Economic Forests in the Loess Hilly Areas. Forests 2023, 14, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020221
Xiang T, Gao R, Qiang F, Yang N, Liu G, Liu C, Ai N. Coupling Relationship between Soil Organic Carbon Storage and Soil Water Storage in Abandoned Economic Forests in the Loess Hilly Areas. Forests. 2023; 14(2):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020221
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Ting, Rui Gao, Fangfang Qiang, Ni Yang, Guangquan Liu, Changhai Liu, and Ning Ai. 2023. "Coupling Relationship between Soil Organic Carbon Storage and Soil Water Storage in Abandoned Economic Forests in the Loess Hilly Areas" Forests 14, no. 2: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020221
APA StyleXiang, T., Gao, R., Qiang, F., Yang, N., Liu, G., Liu, C., & Ai, N. (2023). Coupling Relationship between Soil Organic Carbon Storage and Soil Water Storage in Abandoned Economic Forests in the Loess Hilly Areas. Forests, 14(2), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020221






