Influence of Topography on UAV LiDAR-Based LAI Estimation in Subtropical Mountainous Secondary Broadleaf Forests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
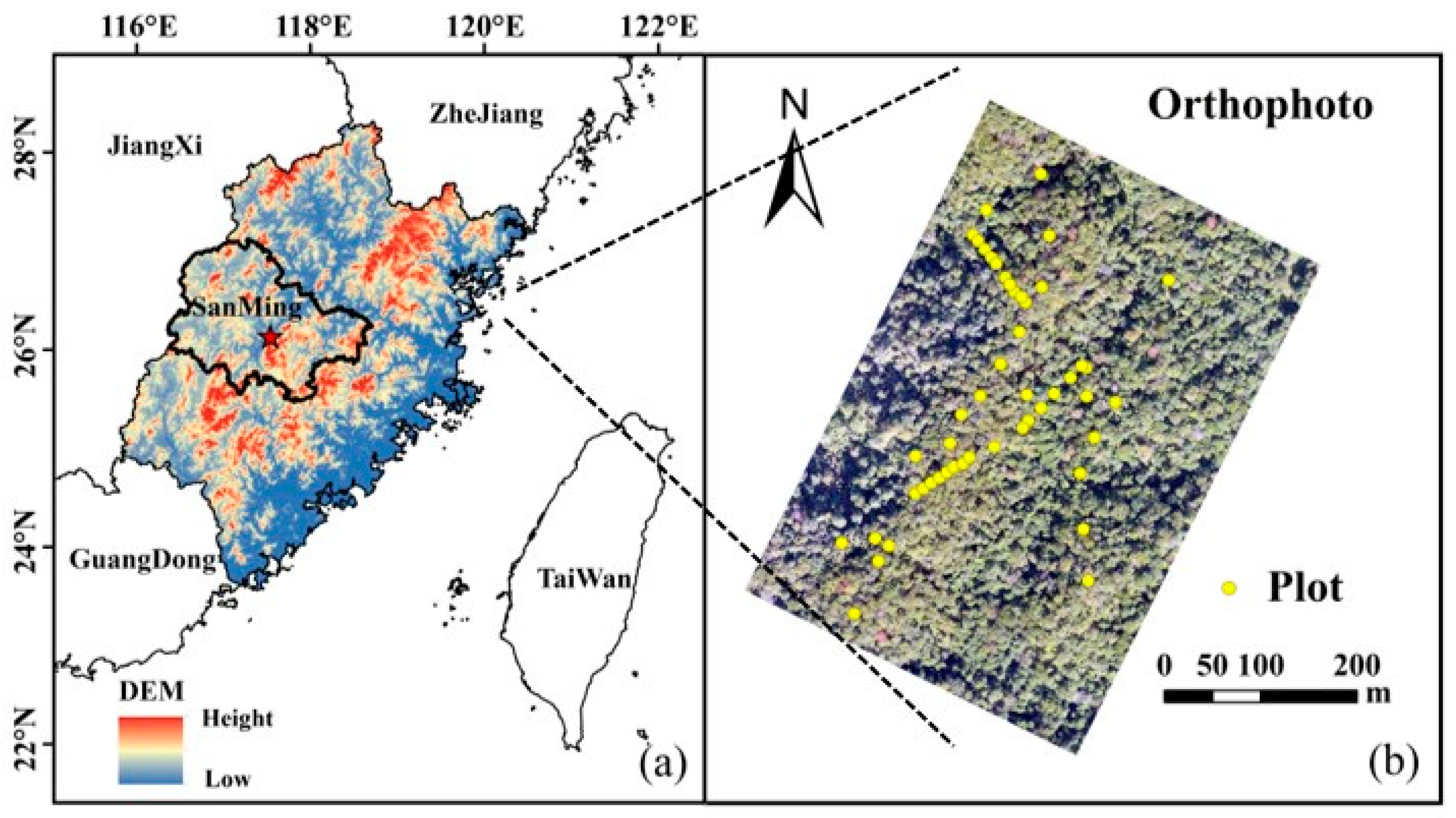
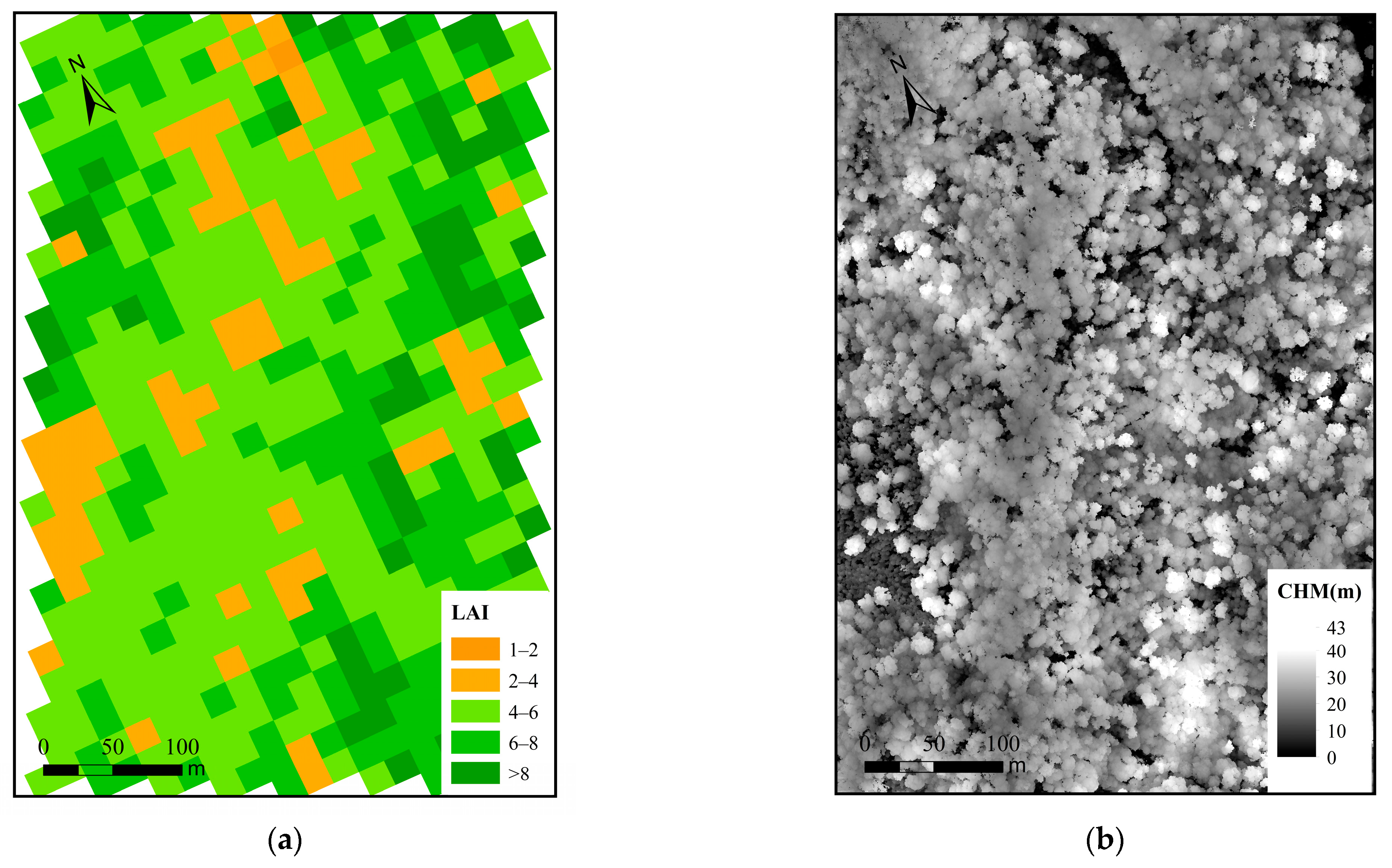
2.1. Study Area and Field Measurements
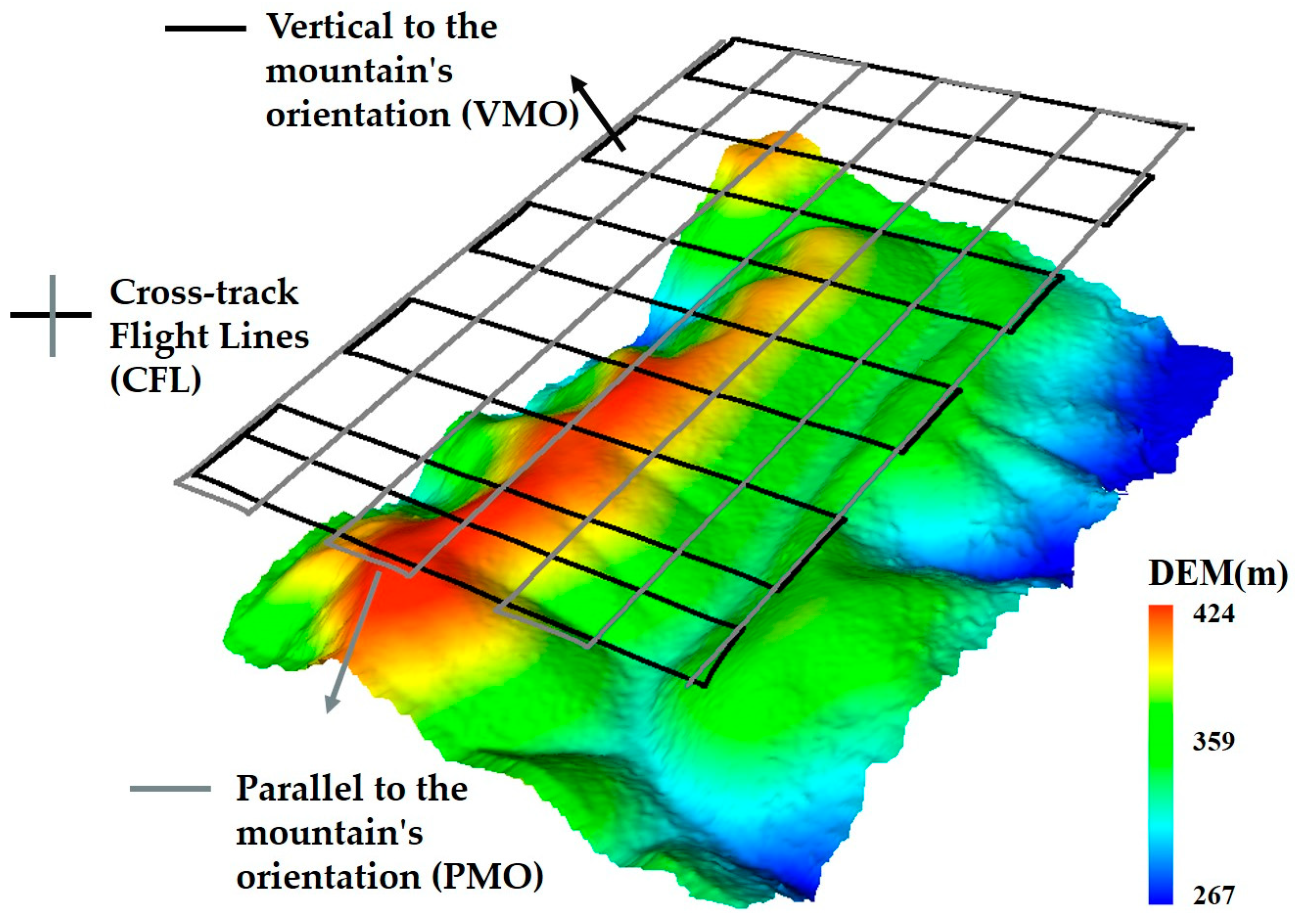
2.2. LiDAR Acquisition and Processing
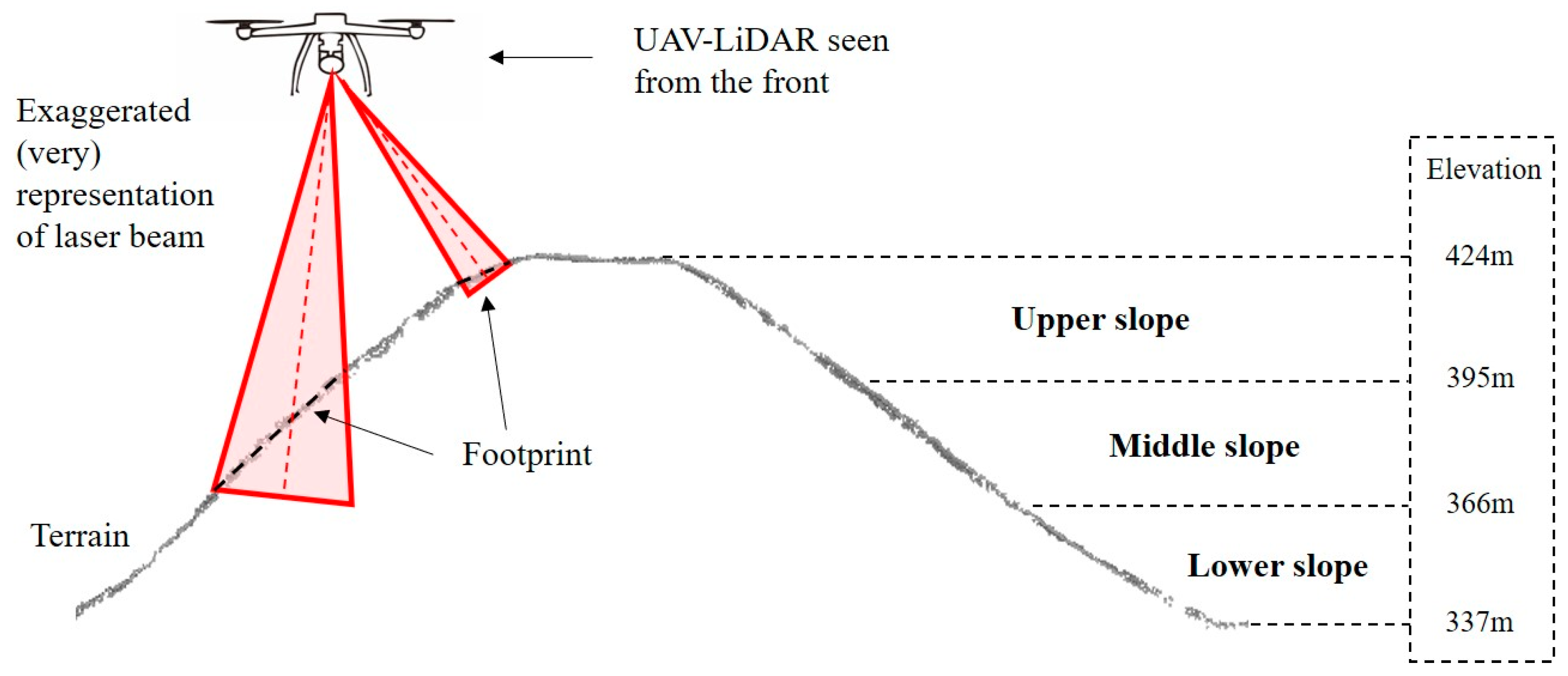
2.3. Beam Footprint and LAI Estimation
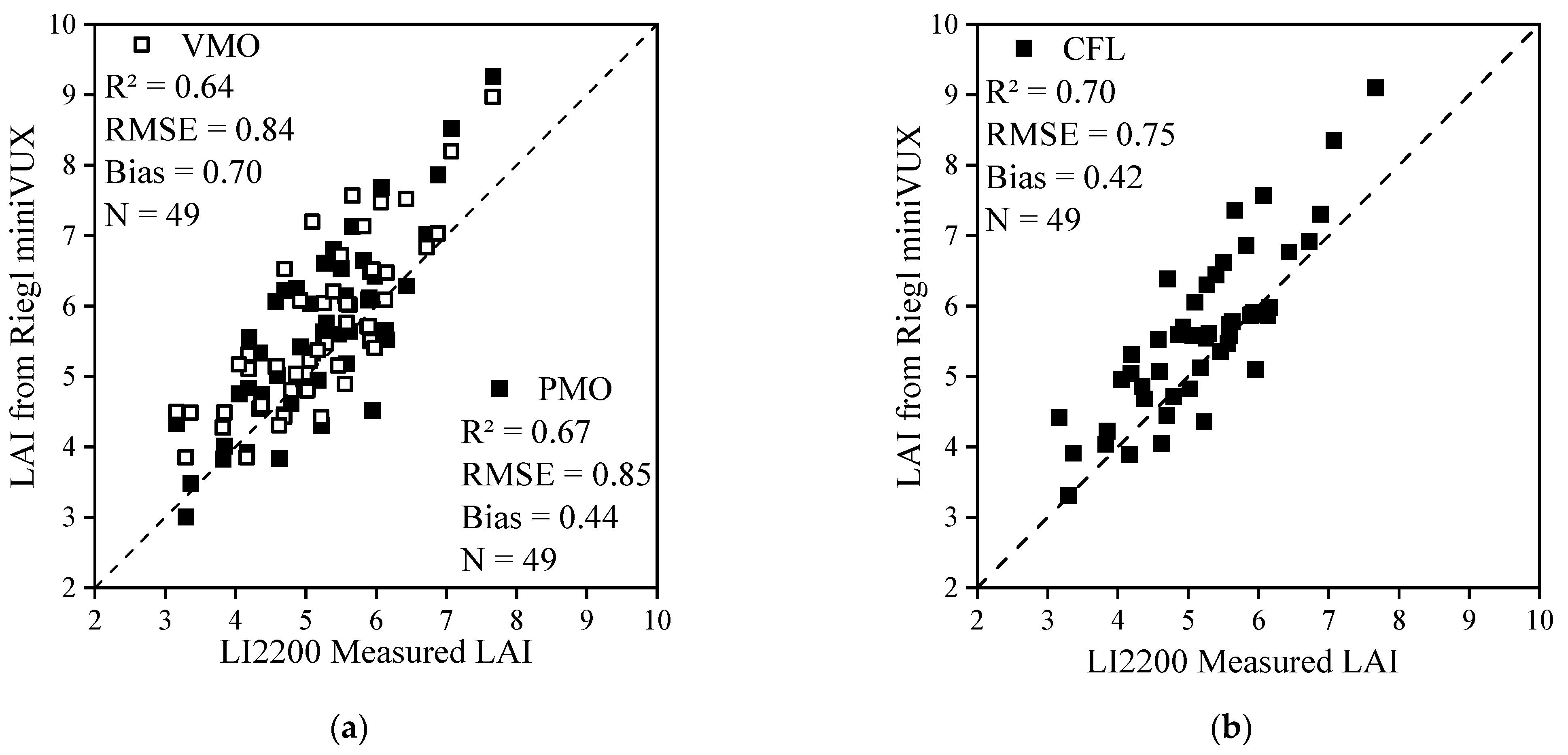
2.4. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
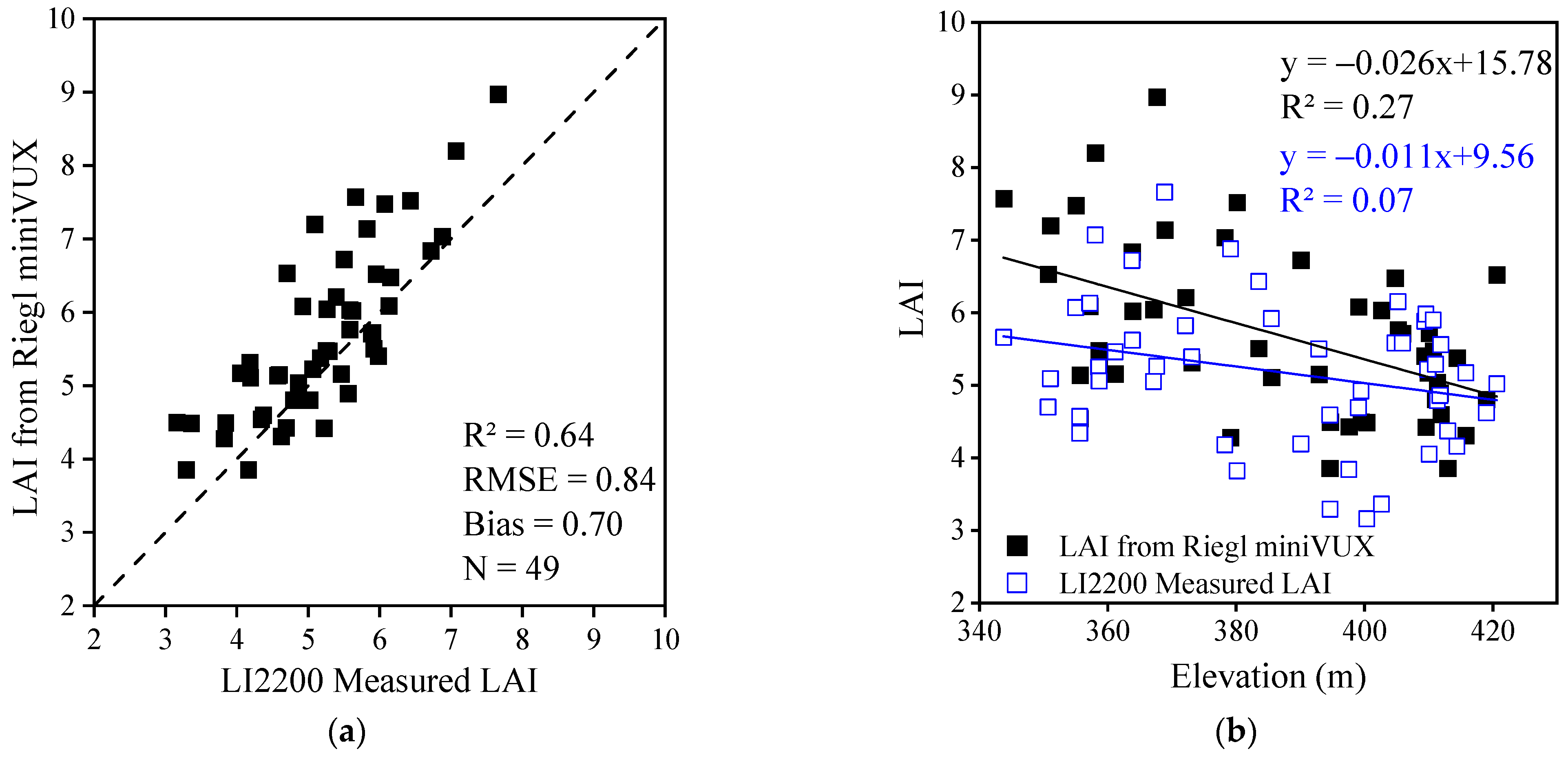
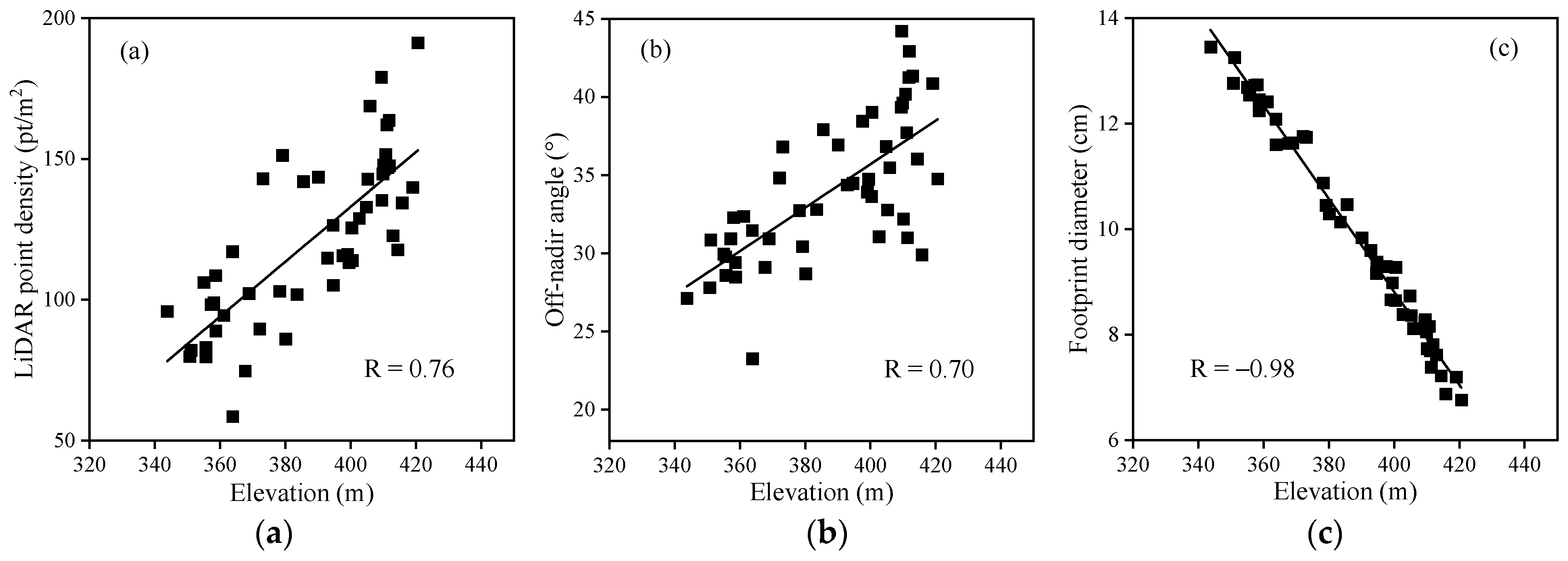
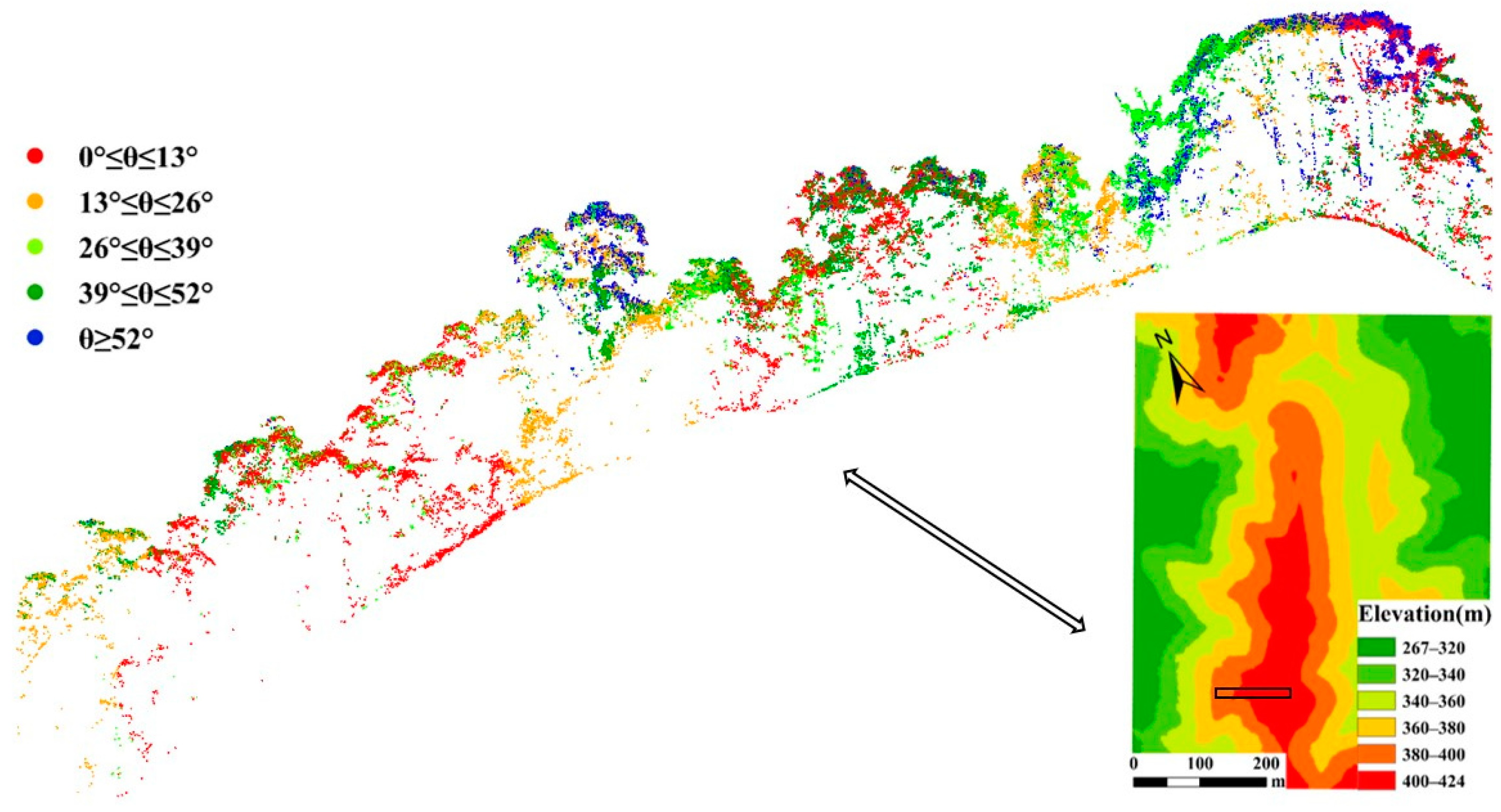
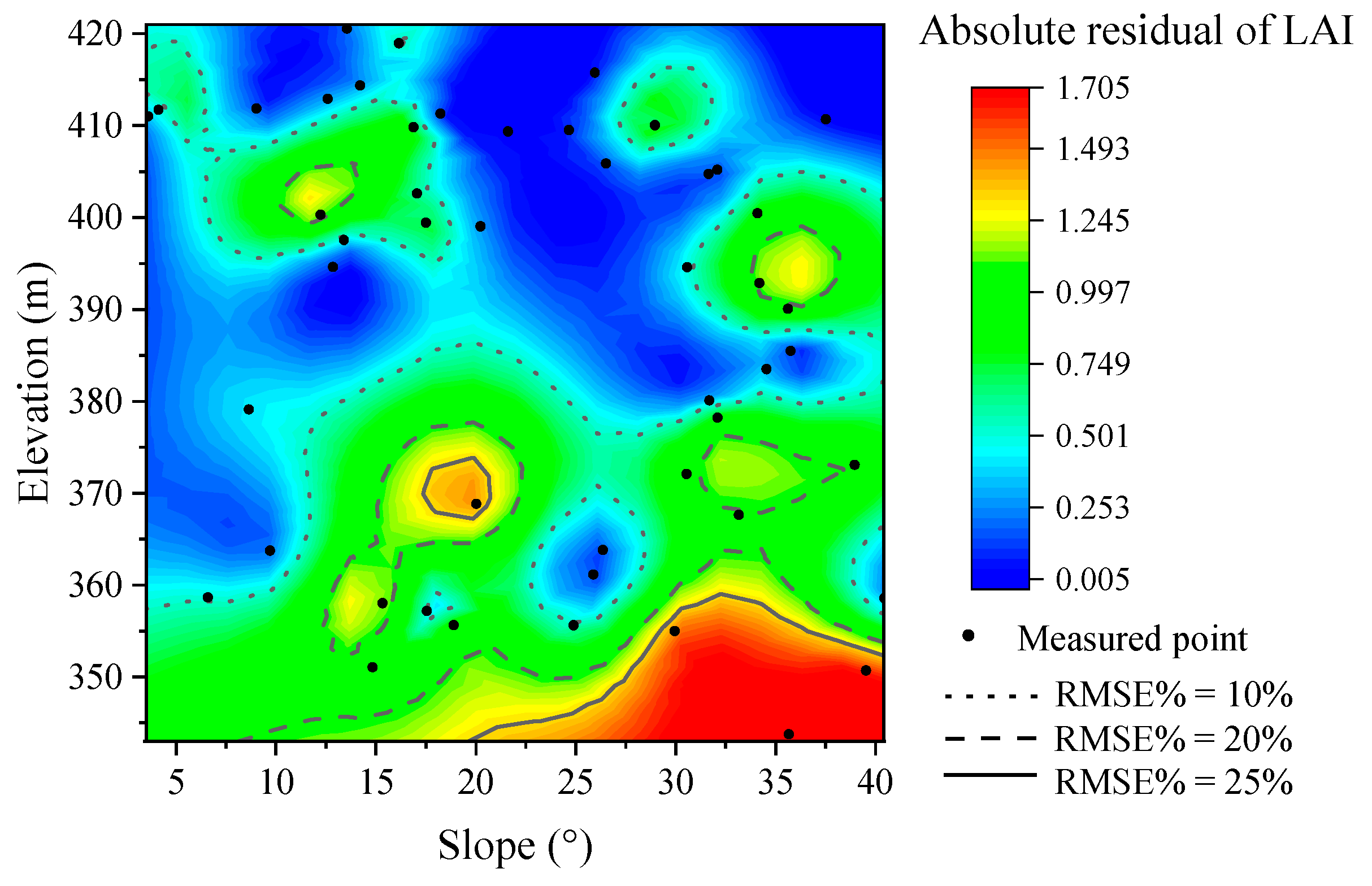
3.1. Influence of Elevation on Point Cloud Feature Information and LAI Estimation
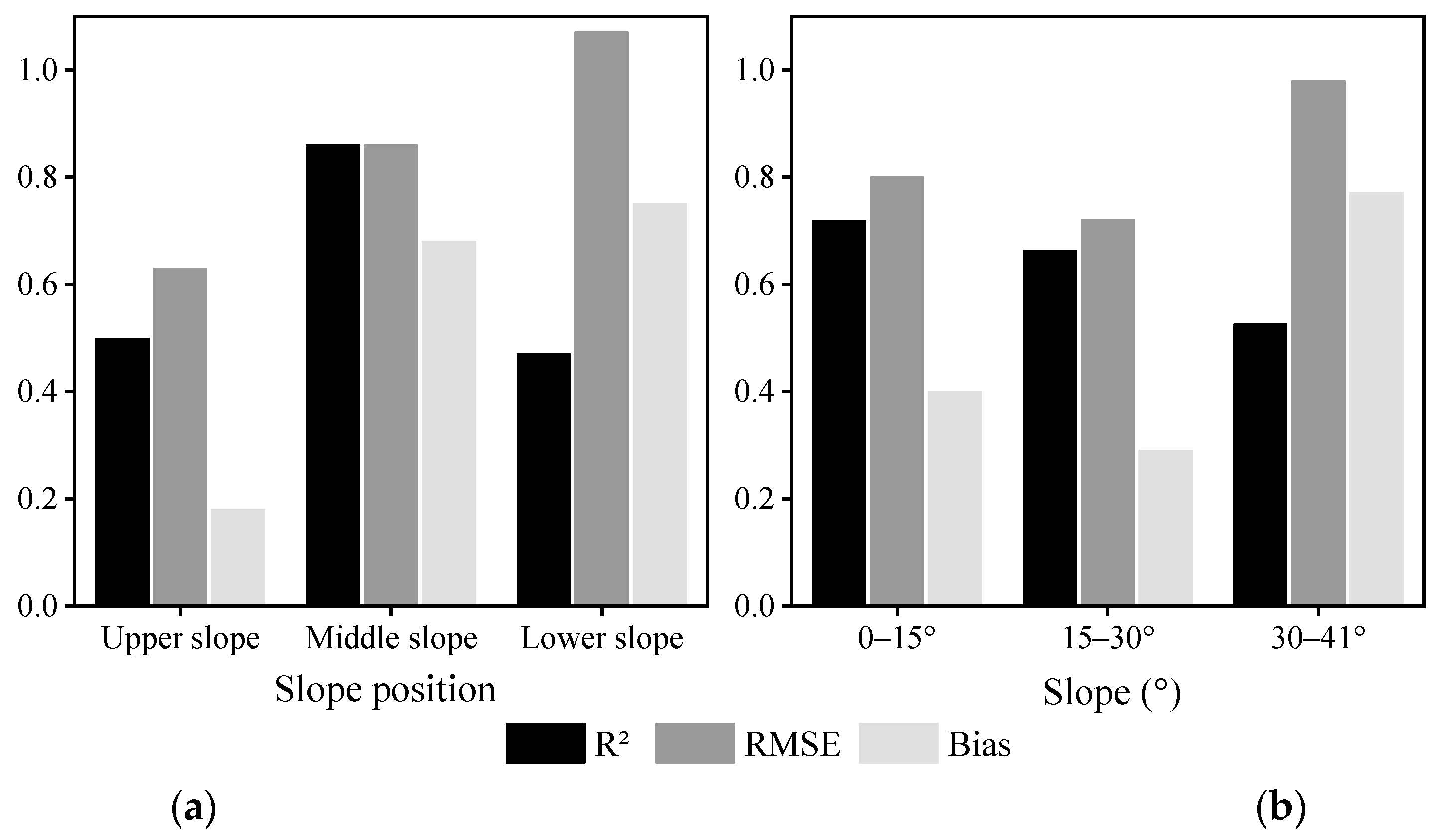
3.2. Comparison of LAI Estimation across Different Slope Positions and Slope Gradient Categories
3.3. Impact of Altering Flight Directions and Increasing Flight Lines on the Accuracy of LAI Estimation
4. Discussion
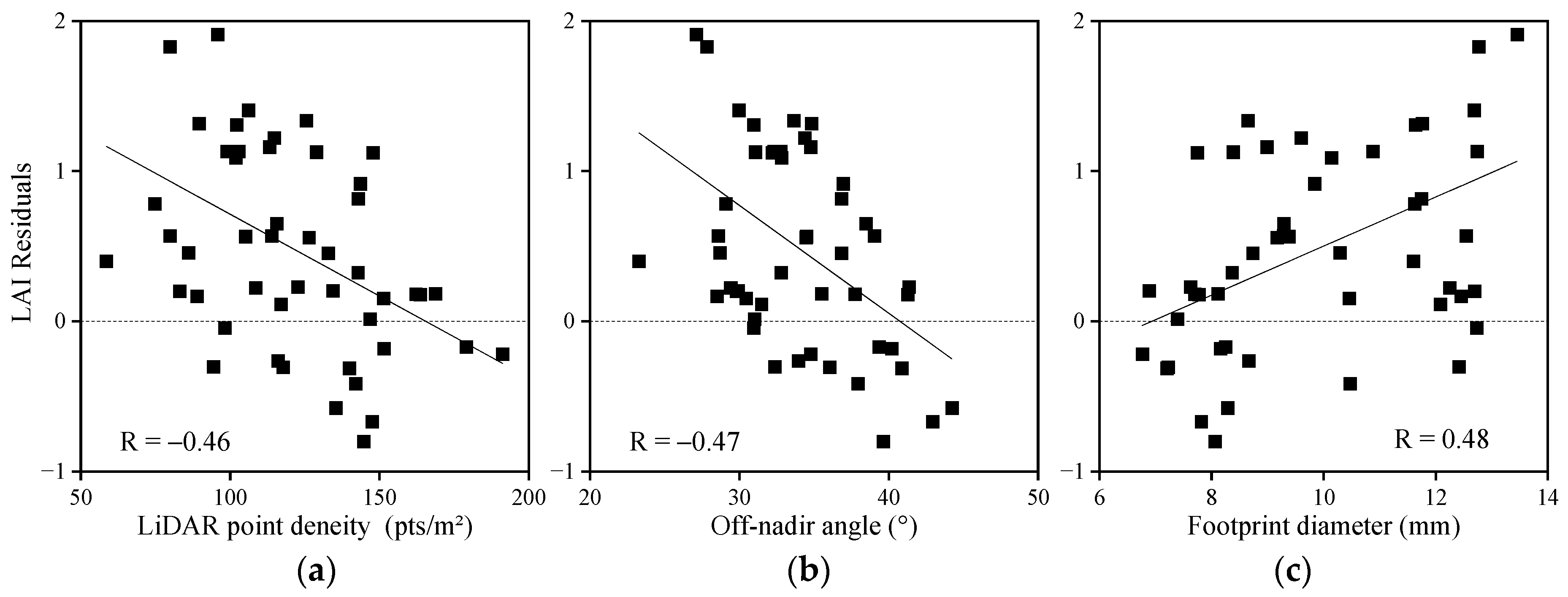
4.1. Terrain Relief’s Effect on LAI Estimation through Uneven Point Cloud Density
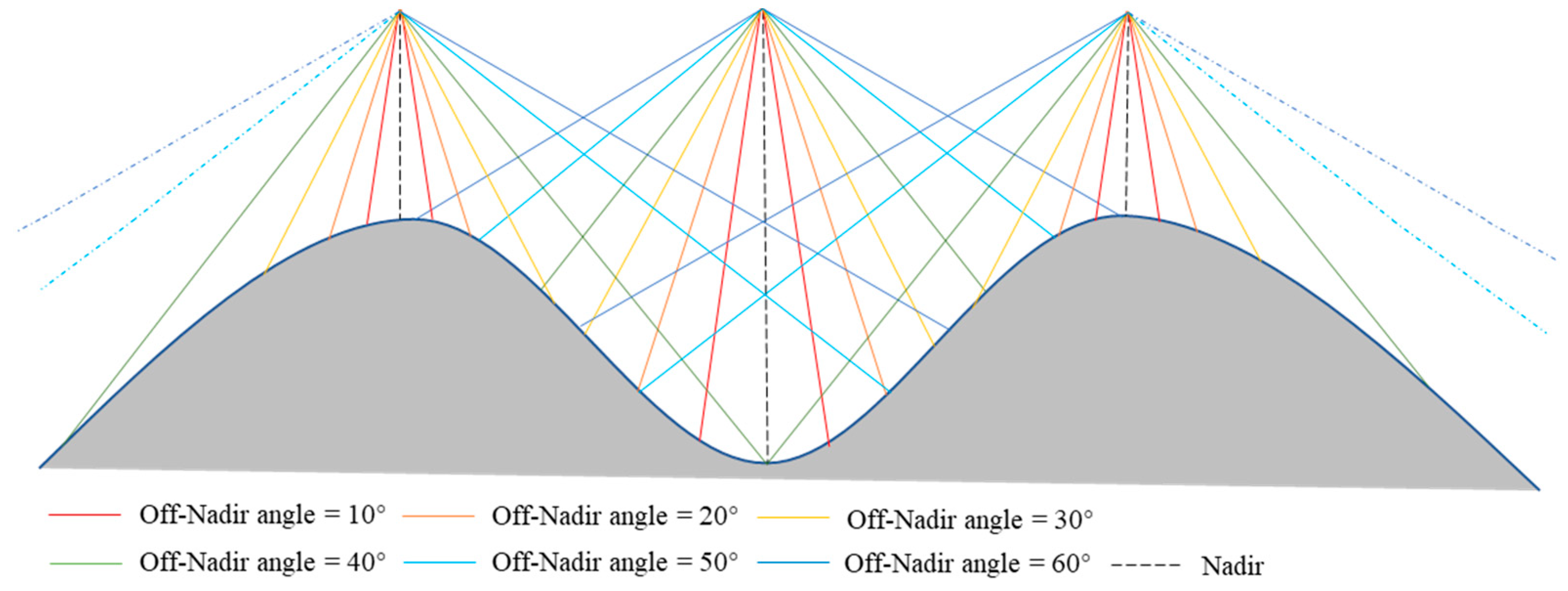
4.2. Impact of Terrain-Induced Beam Scan Angle and Footprint Spatial Heterogeneity on LAI Estimation
4.3. The Impact of Slope on LAI Estimation
4.4. Optimizing Flight Planning and Prospects for LAI Estimation in Mountainous Forests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.M.; Black, T.A. Defining leaf area index for non-flat leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, G.G. Tamm review: Leaf Area Index (LAI) is both a determinant and a consequence of important processes in vegetation canopies. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 477, 118496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Yu, S.; Yu, P.; Xu, L. Estimate canopy transpiration in larch plantations via the interactions among reference evapotranspiration, leaf area index, and soil moisture. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 481, 118749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.K.; Garkoti, S.C. Litter dynamics, leaf area index and forest floor respiration as indicators for understanding the role of Nepalese alder in white oak forests in central Himalaya, India. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Cheng, Y.; Ju, W.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Ruan, H. Afforestation promotes the enhancement of forest LAI and NPP in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 462, 117990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Cho, K.; Hong, J.; Hong, J.-W.; Jo, S.; Park, C.; Chun, J. A transiting temperate-subtropical mixed forest: Carbon cycle projection and uncertainty. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 094010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, W.; Jin, S.; Li, H.; Liu, B.; Gong, W.; Fan, R.; Li, H. Spatiotemporal variation of LAI in different vegetation types and its response to climate change in China from 2001 to 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Fan, W.; Shan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, C.; Nie, R.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.J.R.S. LAI-based phenological changes and climate sensitivity analysis in the Three-River headwaters region. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Liu, S. China Mountain Classification Research. J. Mt. Res. 2014, 32, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Yan, G. Optical methods for in situ measuring leaf area index of forest canopy: A review. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 21, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar]
- Haiying, J.; Kun, J.; Xiang, Z. Review on the theory, method, and research progress of leaf area index estimation in mountainous areas. J. Remote Sens. Chin. 2020, 24, 1433–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Mutanga, O.; Masenyama, A.; Sibanda, M. Spectral saturation in the remote sensing of high-density vegetation traits: A systematic review of progress, challenges, and prospects. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 198, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhong, R.; Yan, K.; Ma, X.; Chen, X.; Pu, J.; Gao, S.; Qi, J.; Yin, G.; Myneni, R.B. Evaluating the saturation effect of vegetation indices in forests using 3D radiative transfer simulations and satellite observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Hu, R.; Lou, J.; Mu, X.; Xie, D.; Zhang, W. Review of indirect methods for leaf area index measurement. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 20, 958–978. [Google Scholar]
- María Luisa, E.; Frédéric, B.; Marie, W. Slope correction for LAI estimation from gap fraction measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.T.; Disney, M.I.; Lewis, P.; Armston, J.; Han, J.T.; Li, J.C. Sensitivity of direct canopy gap fraction retrieval from airborne waveform lidar to topography and survey characteristics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefsky, M.A.; Hudak, A.T.; Cohen, W.B.; Acker, S.A. Geographic variability in lidar predictions of forest stand structure in the Pacific Northwest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 532–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, L.; Korpela, I.; Heiskanen, J.; Maltamo, M. Airborne discrete-return LIDAR data in the estimation of vertical canopy cover, angular canopy closure and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1065–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, M.; Bookhagen, B.; McFadden, J.P.; Sun, A.; Roberts, D.A. Mapping urban forest leaf area index with airborne lidar using penetration metrics and allometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 162, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Ulrich, A.; Melzer, T.; Briese, C.; Kraus, K. From single-pulse to full-waveform airborne laser scanners: Potential and practical challenges. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2004, 35, 414–419. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Zhao, K.; Fan, W.; Xiru, X. Retrieving crop fractional cover and LAI based on airborne Lidar data. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 15, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Solberg, S. Mapping gap fraction, LAI and defoliation using various ALS penetration variables. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 1227–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lin, F.; Fang, S.; Wang, N.; Wang, N.; Hu, T.; Ren, H.; Mi, X.; Lin, L.; Yuan, Z.; et al. Effects of point cloud density on the accuracy of forest canopy structure parameters extracted from near-surface light detection and ranging data. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 681–692. [Google Scholar]
- Bakuła, K.; Pilarska-Mazurek, M.; Ostrowski, W.; Nowicki, A.; Kurczyński, Z. UAV Lidar data processing: Influence of flight height on geometric accuracy, radiometric information, and parameter setting in dtm production. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIII-B1-2020, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Sun, X.; Su, Y.; Guan, H.; Sun, Q.; Kelly, M.; Guo, Q. Development and Performance Evaluation of a Very Low-Cost UAV-Lidar System for Forestry Applications. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, J.-R.; Béland, M.; Caspersen, J.; Achim, A. A mathematical framework to describe the effect of beam incidence angle on metrics derived from airborne LiDAR: The case of forest canopies approaching turbid medium behaviour. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Skidmore, A.K.; Jones, S.; Wang, T.; Heurich, M.; Zhu, X.; Shi, Y. Large off-nadir scan angle of airborne LiDAR can severely affect the estimates of forest structure metrics. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 136, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Skidmore, A.K.; Heurich, M.; Wang, T. Significant effect of topographic normalization of airborne LiDAR data on the retrieval of plant area index profile in mountainous forests. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 132, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravipour, A.; Skidmore, A.K.; Wang, T.; Isenburg, M.; Khoshelham, K. Effect of slope on treetop detection using a LiDAR Canopy Height Model. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 104, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Qi, J.; Cook, B.D.; Morton, D.C.; Wei, S.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.-P. Modeling Small-Footprint Airborne Lidar-Derived Estimates of Gap Probability and Leaf Area Index. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.J.; Moskal, L.M.; Kim, S.-H. Modeling approaches to estimate effective leaf area index from aerial discrete-return LIDAR. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Yan, G.; Nerry, F.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Mu, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, D. Using Airborne Laser Scanner and Path Length Distribution Model to Quantify Clumping Effect and Estimate Leaf Area Index. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3196–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She-Zhou, L.; Cheng, W.; Gui-Bin, Z.; Xiao-Huan, X.; Gui-Cai, L. Forest Leaf Area Index (LAI) Estimation Using Airborne Discrete-Return Lidar Data. Chin. J. Geophys. 2013, 56, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torita, H.; Masaka, K. Influence of planting density and thinning on timber productivity and resistance to wind damage in Japanese larch (Larix kaempferi) forests. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268, 110298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamoske, A.G.; Dahlin, K.M.; Stark, S.C.; Serbin, S.P. Leaf area density from airborne LiDAR: Comparing sensors and resolutions in a temperate broadleaf forest ecosystem. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 433, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Ma, L.; Eitel, J.U.H.; He, W.; Magney, T.S.; Moskal, L.M.; Li, M. Retrieving Directional Gap Fraction, Extinction Coefficient, and Effective Leaf Area Index by Incorporating Scan Angle Information from Discrete Aerial Lidar Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brede, B.; Bartholomeus, H.M.; Barbier, N.; Pimont, F.; Vincent, G.; Herold, M. Peering through the thicket: Effects of UAV LiDAR scanner settings and flight planning on canopy volume discovery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brede, B.; Lau, A.; Bartholomeus, H.M.; Kooistra, L. Comparing RIEGL RiCOPTER UAV LiDAR Derived Canopy Height and DBH with Terrestrial LiDAR. Sensors 2017, 17, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkinson, C. The influence of flying altitude, beam divergence, and pulse repetition frequency on laser pulse return intensity and canopy frequency distribution. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 33, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Brolly, M.; Zhao, F.; Strahler, A.H.; Schaaf, C.L.; Ganguly, S.; Zhang, G.; Dubayah, R. Deriving and validating Leaf Area Index (LAI) at multiple spatial scales through lidar remote sensing: A case study in Sierra National Forest, CA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Yin, G.; Zeng, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhao, J. A Simulation-Based Analysis of Topographic Effects on LAI Inversion Over Sloped Terrain. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Li, A.; Xu, W.; Xiao, Z.; Jiang, J.; Xue, H. Evaluation of topographic effects on multiscale leaf area index estimation using remotely sensed observations from multiple sensors. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Wavelength (µm) | 1050 |
| Beam divergence (mrad) | 1.6 × 0.5 |
| 100m from the ground beam Foot (mm) | 160 × 50 |
| Pulse rate (kHz) | 100 |
| Max. Measuring Range (m) | 330 |
| Field of View (°) | 360 |
| Max. Number of Targets per Pulse | 5 |
| Accuracy (mm) | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zeng, H.; Xiong, J.; Miao, G. Influence of Topography on UAV LiDAR-Based LAI Estimation in Subtropical Mountainous Secondary Broadleaf Forests. Forests 2024, 15, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15010017
Li Y, Zeng H, Xiong J, Miao G. Influence of Topography on UAV LiDAR-Based LAI Estimation in Subtropical Mountainous Secondary Broadleaf Forests. Forests. 2024; 15(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yunfei, Hongda Zeng, Jingfeng Xiong, and Guofang Miao. 2024. "Influence of Topography on UAV LiDAR-Based LAI Estimation in Subtropical Mountainous Secondary Broadleaf Forests" Forests 15, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15010017
APA StyleLi, Y., Zeng, H., Xiong, J., & Miao, G. (2024). Influence of Topography on UAV LiDAR-Based LAI Estimation in Subtropical Mountainous Secondary Broadleaf Forests. Forests, 15(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15010017






