Characterization of Chinese Tallow Invasion in the Southern United States
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Analytical Approach
3. Results
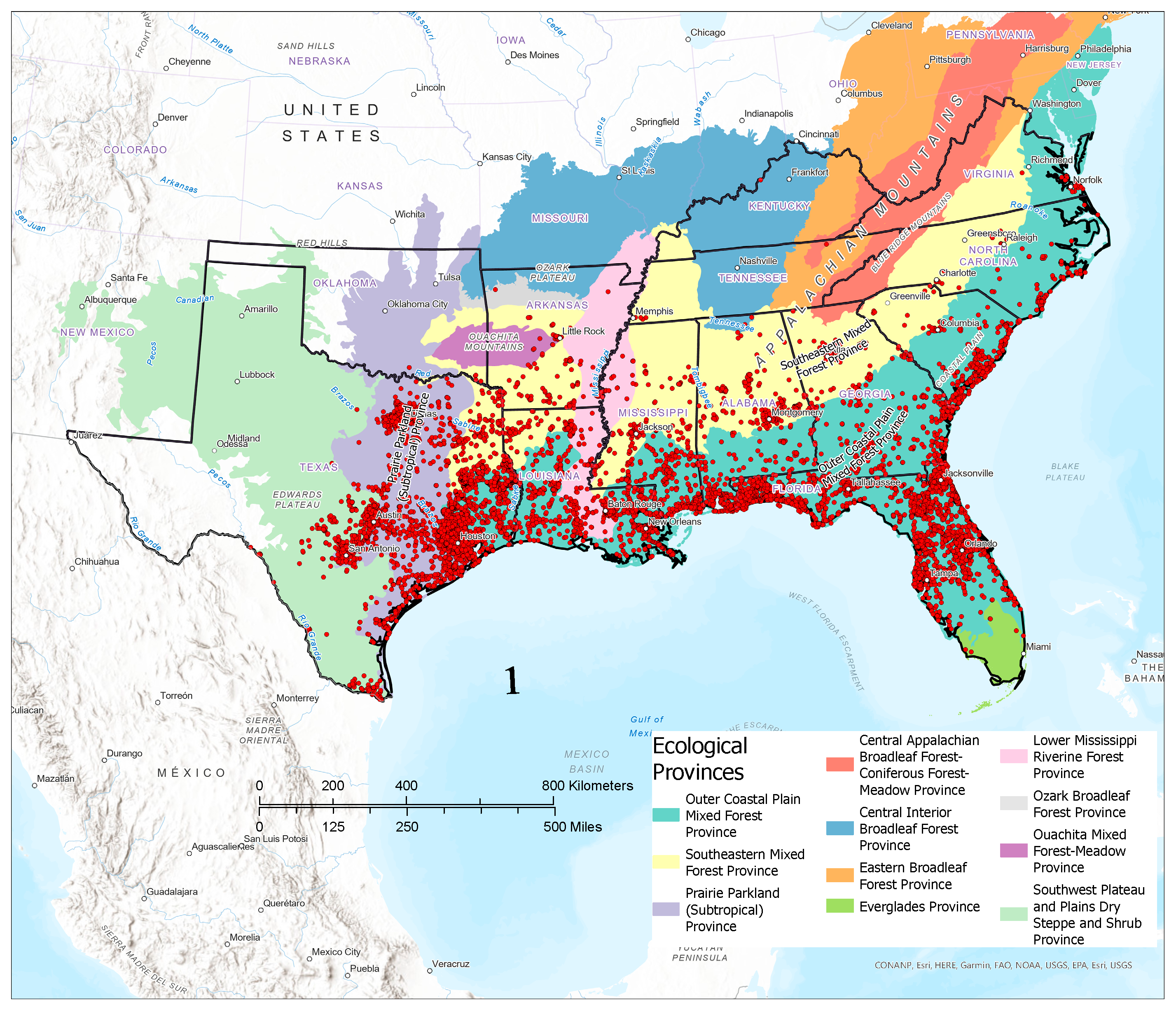
3.1. Contemporary Tallow Distribution by Political Boundary and Ecological Province
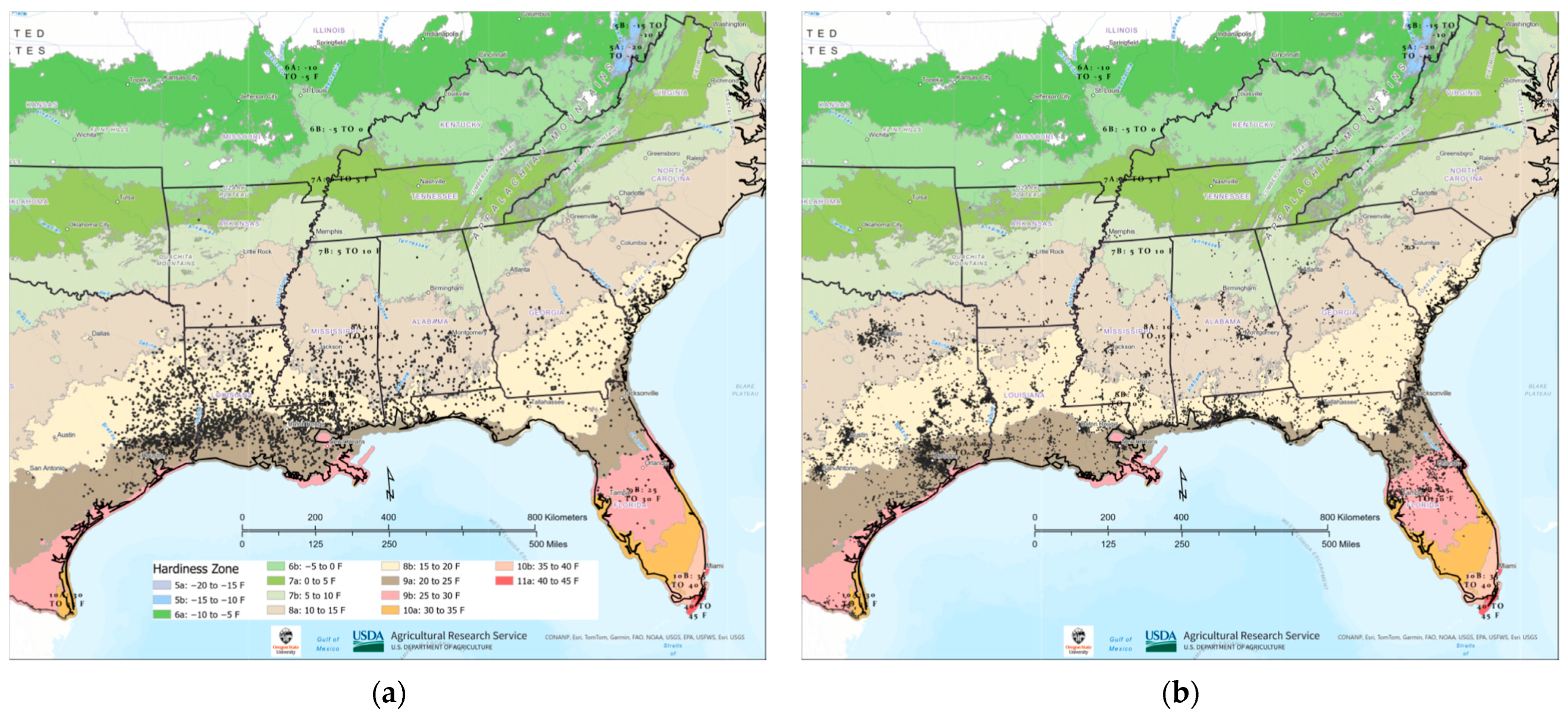
3.2. Tallow Distribution within Plant Hardiness Zones
3.3. Structural and Compositional Characteristics of Tallow-Invaded Forestlands
3.4. Temporal Shifts in Tallow Detection
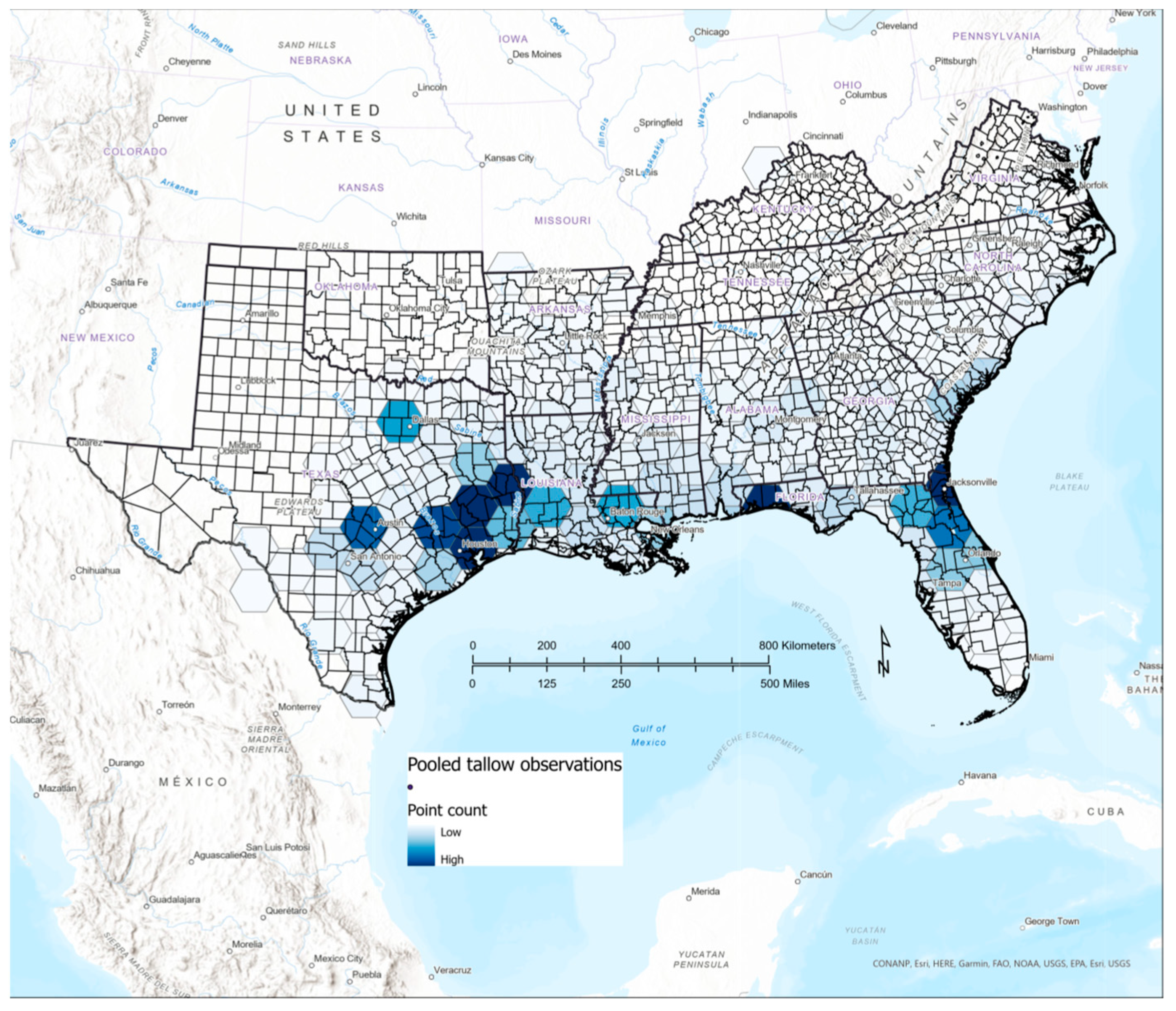
3.5. Comparison of Citizen Science and FIA Occurrence and Abundance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pile, L.S.; Wang, G.G.; Stovall, J.P.; Siemann, E.; Wheeler, G.S.; Gabler, C.A. Mechanisms of Chinese tallow (Triadica sebifera) invasion and their management implications—A review. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 404, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, K.A.; Cameron, G.N.; Harcombe, P.A.; Jubinsky, G. Introduction, Impact on Native Habitats, and Management of a Woody Invader, the Chinese Tallow Tree, Sapium sebiferum (L.) Roxb. Nat. Areas J. 1997, 17, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Pattison, R.R.; Mack, R.N. Potential distribution of the invasive tree Triadica sebifera (Euphorbiaceae) in the United States: Evaluating climex predictions with field trials. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWalt, S.J.; Siemann, E.; Rogers, W.E. Geographic distribution of genetic variation among native and introduced populations of Chinese tallow tree, Triadica sebifera (Euphorbiaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, J.T.; Olatinwo, R.; Ulyshen, M.D.; Lucardi, R.D.; Saenz, D.; McKenney, J.L. An overview of Triadica sebifera (Chinese Tallowtree) in the Southern United States, emphasizing pollinator impacts and classical biological control. Southeast Nat. 2021, 20, 536–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, G.; McKinney, R. Stillingia oil. Oil Soap 1938, 15, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, K.A.; Cameron, G.N.; Harcombe, P.A. Initiation of a new woodland type on the Texas Coastal Prairie by the Chinese tallow tree (Sapium sebiferum (L.) Roxb.). Torrey Bot. Soc. 1995, 122, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswalt, S.N. Chinese Tallow (Triadica sebifera (L.) Small) Population Expansion in Louisiana, East Texas, and Mississippi; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Southern Research Station: Asheville, NC, USA, 2010.
- Gan, J.; Miller, J.H.; Wang, H.; Taylor, J.W. Invasion of tallow tree into southern US forests: Influencing factors and implications for mitigation. Can. J. For. Res. 2009, 39, 1346–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-H.; Buchhorn, J.L.; Grant, W.E. Effects of Management on Range Expansion by Chinese Tallow in the Forestlands of Eastern Texas. J. For. 2014, 112, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-H.; Grant, W.E.; Swannack, T.M.; Gan, J.; Rogers, W.E.; Koralewski, T.E.; Miller, J.H.; Taylor, J.W. Predicted range expansion of Chinese tallow tree (Triadica sebifera) in forestlands of the southern United States. Divers. Distrib. 2011, 17, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyamongkol, T.; McGrew, E.; Culpepper, L.; Beck, K.; Wang, H.-H.; Grant, W.E. Recent Range Expansions by Chinese Tallow (Triadica sebifera (L.) Small), the Most Prevalent Invasive Tree in the Forestlands of Eastern Texas. Southeast Nat. 2016, 15, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renne, I.J.; Gauthreaux, S.A., Jr.; Gresham, C.A. Seed dispersal of the Chinese tallow tree (Sapium sebiferum (L.) Roxb.) by birds in coastal South Carolina. Am. Midl. Nat. 2000, 144, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renne, I.J.; Spira, T.P.; Bridges, W.C. Effects of habitat, burial, age and passage through birds on germination and establishment of Chinese tallow tree in Coastal South Carolina. J. Torrey Bot. Soc. 2001, 128, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemann, E.; Rogers, W.E. Recruitment limitation, seedling performance and persistence of exotic tree monocultures. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pile, L.S.; Vickers, L.; Stambaugh, M.; Norman, C.; Wang, G.G. The tortoise and the hare: A race between native tree species and the invasive Chinese tallow. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 445, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.H.; McLeod, K.W. Shade tolerance in seedlings of Chinese tallow tree, American sycamore, and cherrybark oak. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 1989, 116, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Harcombe, P.A.; Fulton, M.R.; Hall, R.W. Sapling growth and survivorship as affected by light and flooding in a river floodplain forest of southeast Texas. Oecologia 2004, 139, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Tan, Y.; Crosby, M.K. Factors associated with the spread of Chinese Tallow in East Texas forestlands. Open J. Ecol. 2012, 2, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fan, Z.; Liu, X.; Ezell, A.W. Predicting the spread of Chinese tallow (Triadica sebifera) in the southeastern United States forestland: Mechanism and risk factors at the regional scale. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 482, 118892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, S.; Moser, W.K.; Fan, Z. Spatiotemporal Invasion Severity of Chinese Tallow (Triadica sebifera) and Invasibility of Forest Types in Southern US Forestlands. For. Sci. 2021, 67, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmair, H.H.; Scheffrahn, R.H.; Basille, M.; Boone, M. Evaluating the data quality of iNaturalist termite records. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, J.R.; Russell, M.B.; Senay, S.; Lazarus, W. Assessing the current and potential future distribution of four invasive forest plants in Minnesota, U.S.A., using mixed sources of data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, D.T.; Avers, P.E.; McNab, W.H.; Jensen, M.E.; Bailey, R.G.; King, T.; Russell, W.E. National Hierarchical Framework of Ecological Units; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- United States Census Bureau. 2020 Population Census Quick Facts. Available online: https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/geo/chart/US/POP010220 (accessed on 7 December 2023).
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Adminstration, SCIPP. Historical Climate Trends Tool. Available online: https://www.charts.climate.lsu.edu/trends (accessed on 7 December 2023).
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Adminstration, NCfEI. U.S. Climate Atlas. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/climateatlas (accessed on 7 December 2023).
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. Available online: https://www.planthardiness.ars.usda.gov (accessed on 7 December 2023).
- USDA Forest Service. Forest Inventory and Analysis National Program. Forest Inventory EVALIDator Web-Application Version 2.1.0. Available online: https://apps.fs.usda.gov/fiadb-api/evalidator (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- USDA Forest Service. Forest Inventory and Analysis National Program. Forest Inventory DataMart Web-Application Version 2.0. Available online: https://apps.fs.usda.gov/fia/datamart/datamart.html (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- Stanke, H.; Finley, A.O.; Weed, A.S.; Walters, B.F.; Domke, G.M. rFIA: An R package for estimation of forest attributes with the US Forest Inventory and Analysis database. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 127, 104664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omernik, J.M.; Griffith, G.E. Ecoregions of the Conterminous United States: Evolution of a Hierarchical Spatial Framework. Environ. Manag. 2014, 54, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Widrlechner, M.P.; Halbleib, M.D.; Smith, J.I.; Gibson, W.P. Development of a new USDA plant hardiness zone map for the United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 242–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Henkel, T.K.; Chambers, J.Q.; Baker, D.A. Delayed tree mortality and Chinese tallow (Triadica sebifera) population explosion in a Louisiana bottomland hardwood forest following Hurricane Katrina. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 378, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, D.T.; Williams, B.; Williams, H.M.; Stroupe, M. Seedling survival and natural regeneration for a bottomland hardwood planting on sites differing in site preparation. In Proceedings of the 10th Biennial Southern Silvicultural Research Conference, USDA For. Serv., Gen. Tech. Rep. SRS-30, Southern Research Station, Asheville, NC, USA, 16–18 February 1999; pp. 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Pile, L.S.; Wang, G.G.; Knapp, B.O.; Walker, J.L.; Stambaugh, M.C. Chinese tallow (Triadica sebifera) invasion in maritime forests: The role of anthropogenic disturbance and its management implication. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 398, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Pile Knapp, L.S.; Yu, M.; Wang, G.G. Morphological and physiological response of Chinese tallow (Triadica sebifera) to an extreme cold spell in subtropical, coastal forests of China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 945886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.I. Some Notes and Refl Ections upon a Letter from Benjamin Franklin to Noble Wimberly Jones, 7 October 1772; Ashantilly Press: Darien, GA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, S. A Sketch of the Botany of South-Carolina and Georgia; JR Schenck: Charleston, SC, USA, 1821; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Howes, F. The Chinese tallow tree (Sapium sebiferum Roxb.): A source of drying oil. Kew Bull. 1949, 4, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Province | FIA 1 | Citizen Science |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Coastal Plain Mixed Forest | 74 | 62 |
| Southeastern Mixed Forest | 13 | 9 |
| Lower Mississippi Riverine Forest | 9 | 3 |
| Prairie Parkland (Subtropical) | 4 | 17 |
| Southwest Plateau and Plains Dry Steppe and Shrub | 0.02 | 5 |
| Variable | Non-Invaded | Invaded | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 12,018 | 1225 | |
| Basal area (m2 ha−1) | 20.88 (0.10) | 19.81 (0.31) | 0.0004 |
| Density (trees ha−1) | 1381.60 (10.61) | 1401.96 (34.13) | 0.5262 |
| Shannon’s diversity index | 1.15 (0.01) | 1.12 (0.01) | 0.0204 |
| Shannon’s equitability index | 0.19 (0.00) | 0.19 (0.00) | 0.9279 |
| Species richness | 5.98 (0.03) | 5.82 (0.08) | 0.4566 |
| Mean annual mortality (% BA) | 1.24 (0.02) | 1.61 (0.07) | 0.0037 |
| Mean annual removals (% BA) | 2.00 (0.04) | 2.37 (0.14) | 0.0018 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bataineh, M.M.; Fraser, J.S.; Pile Knapp, L.S. Characterization of Chinese Tallow Invasion in the Southern United States. Forests 2024, 15, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15010202
Bataineh MM, Fraser JS, Pile Knapp LS. Characterization of Chinese Tallow Invasion in the Southern United States. Forests. 2024; 15(1):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15010202
Chicago/Turabian StyleBataineh, Mohammad M., Jacob S. Fraser, and Lauren S. Pile Knapp. 2024. "Characterization of Chinese Tallow Invasion in the Southern United States" Forests 15, no. 1: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15010202
APA StyleBataineh, M. M., Fraser, J. S., & Pile Knapp, L. S. (2024). Characterization of Chinese Tallow Invasion in the Southern United States. Forests, 15(1), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15010202







