To Achieve a Win–Win Situation: Reorganizing and Enhancing Agroforestry Ecosystem Assets and Productivity to Inform Karst Desertification Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Protocol Development
2.2. Literature Search Sources
2.3. Publication Selection Criteria
2.4. Synthesis Report
3. Results
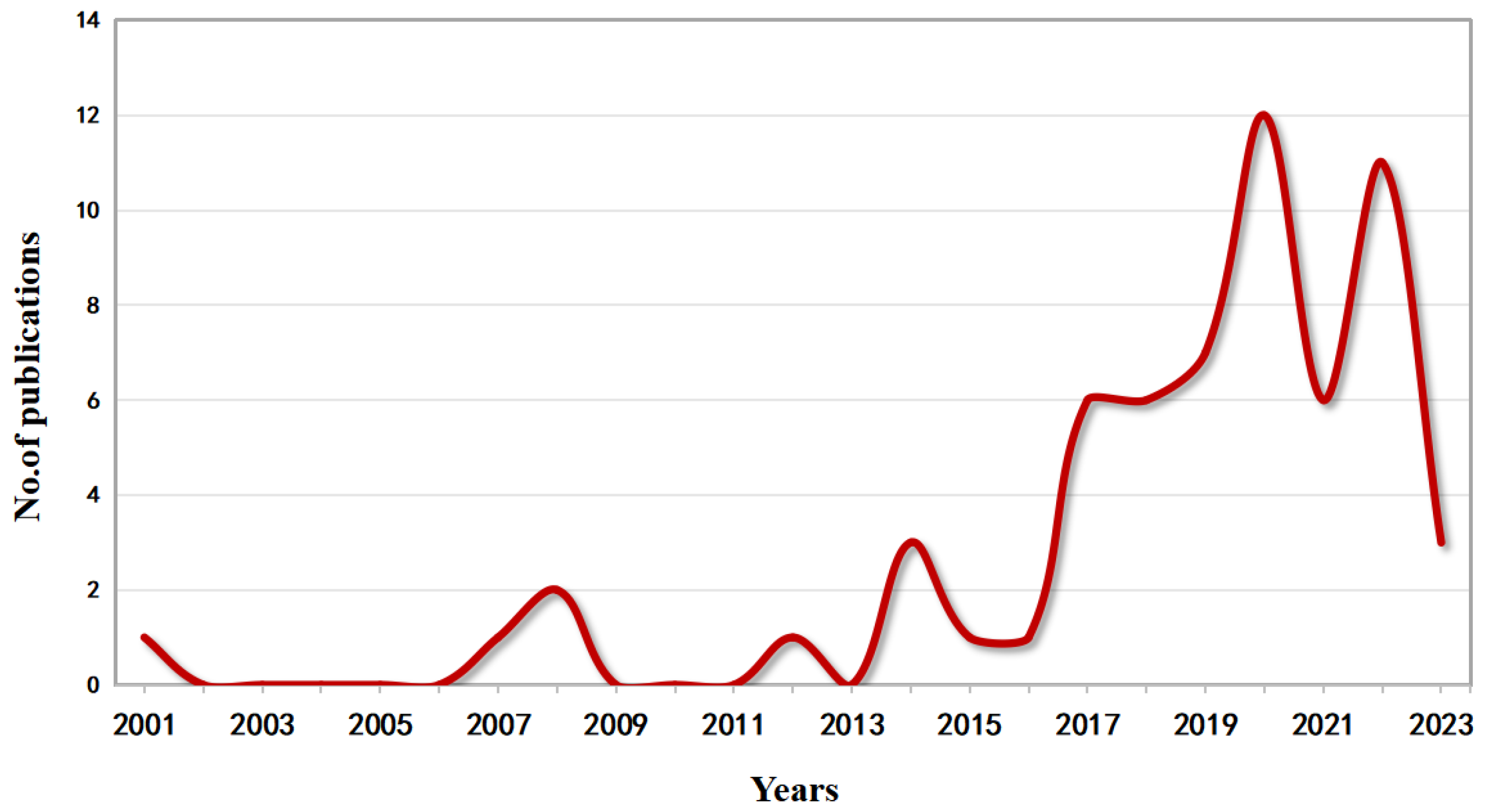
3.1. Annual Distribution and Research Contents of the Literature
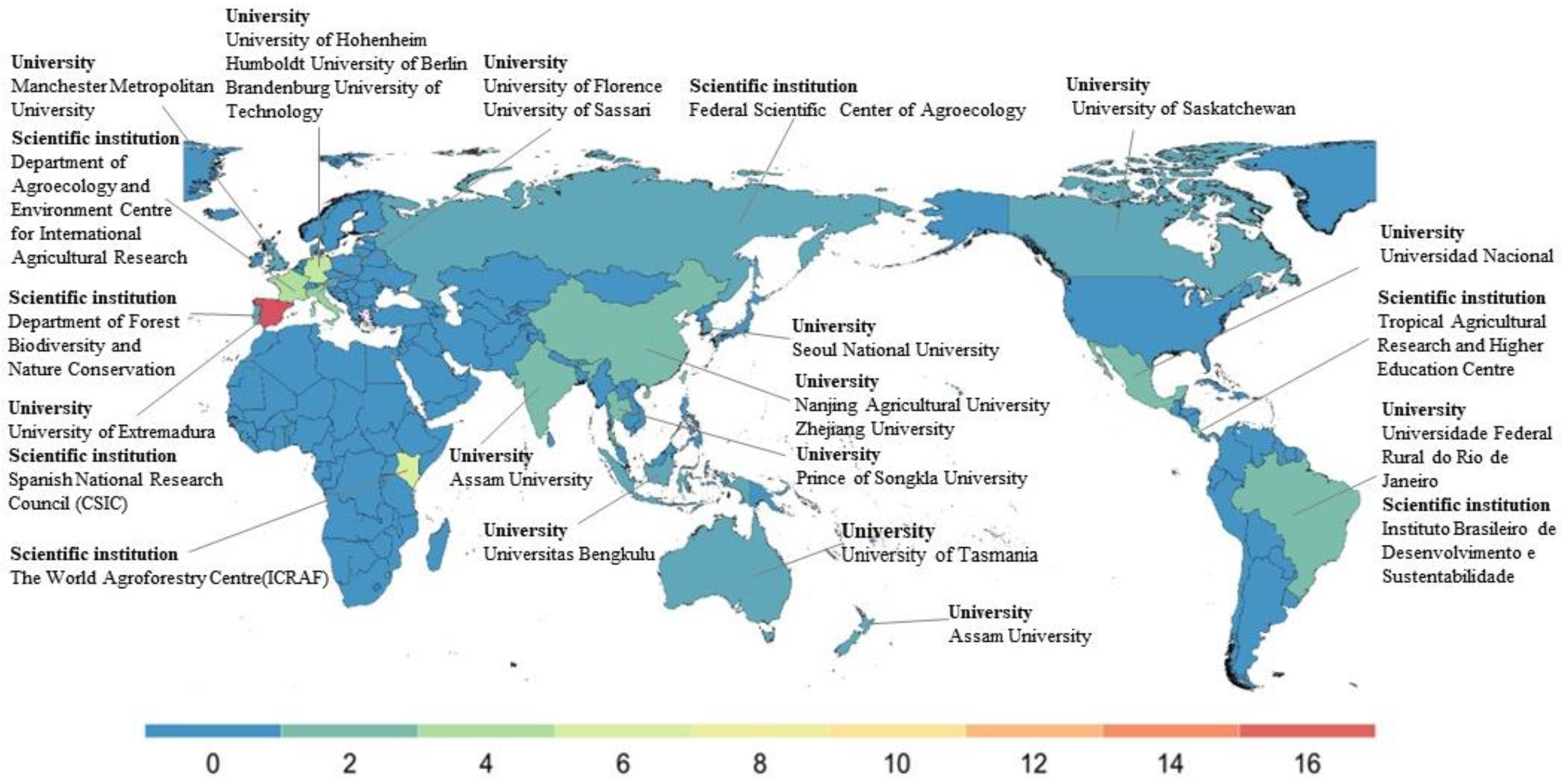
3.2. Distribution of Publications by Country and Organization
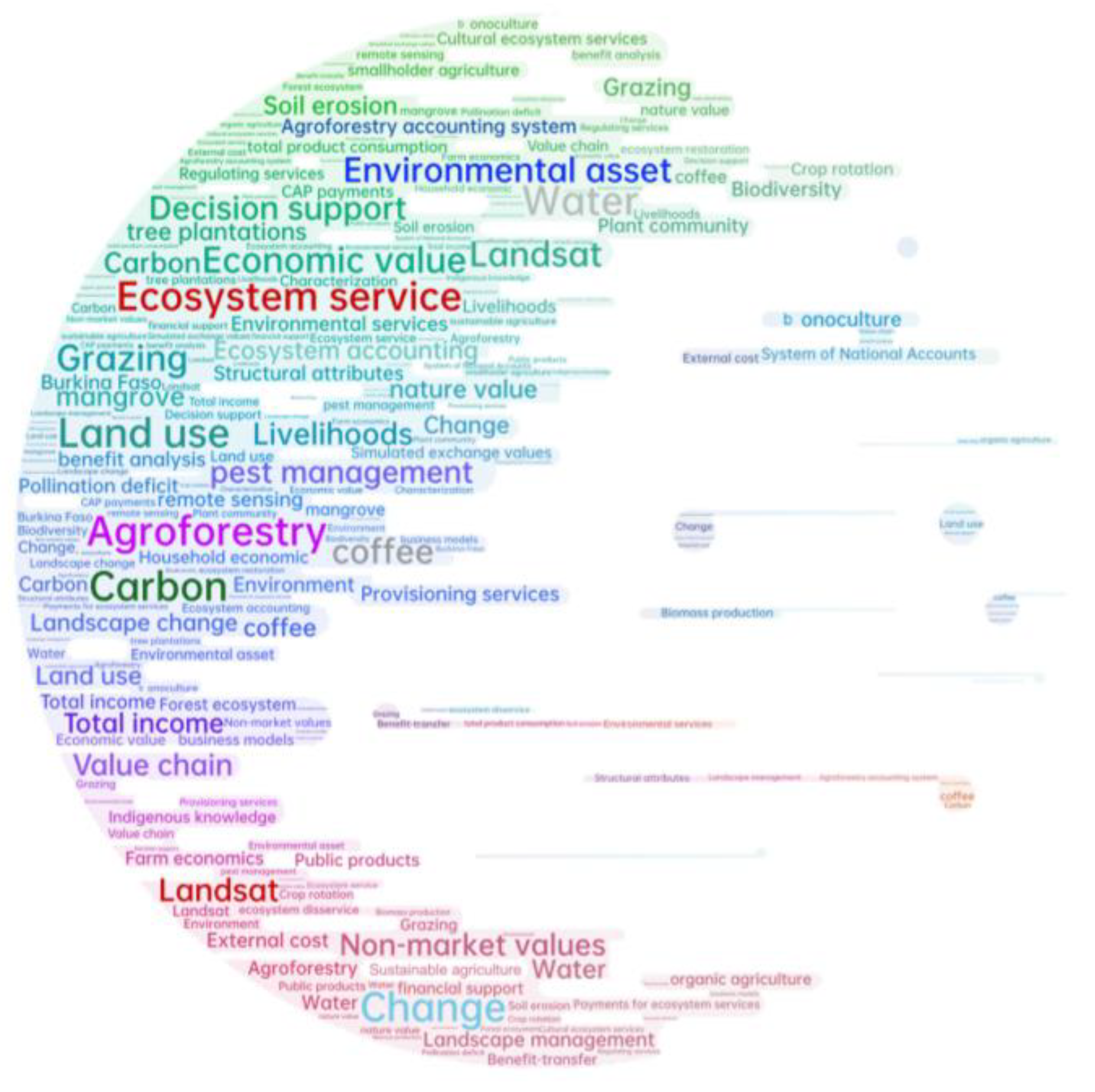
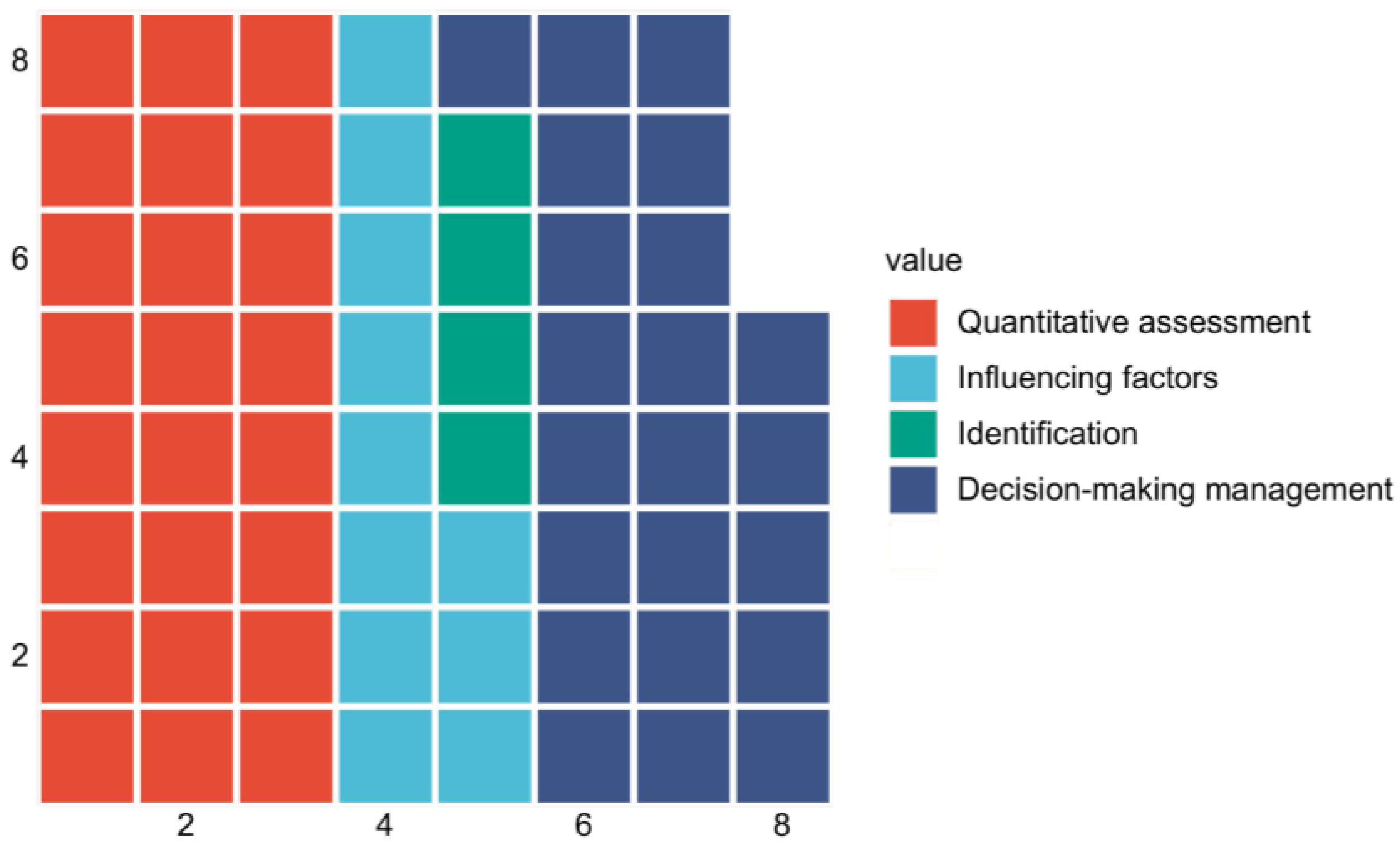
3.3. Distribution of Research Content of Publications
3.3.1. Identification
3.3.2. Quantitative Assessments
3.3.3. Decision-Making Management
3.3.4. Influencing Factors
3.4. Key Scientific Issues That Need to Be Addressed Urgently
3.5. Implications for Enhancing the Provision Capacity of Agroforestry ES in Rock Desertification Control
3.6. Comparison with Other Reviews and Limitations of the Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giddings, B.; Hopwood, B.; O’brien, G. Environment, economy and society: Fitting them together into sustainable development. Sustain. Dev. 2002, 10, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T.C.; Muhar, A.; Arnberger, A.; Aznar, O.; Boyd, J.W.; Chan, K.M.; Costanza, R.; Elmqvist, T.; Flint, C.G.; Gobster, P.H.; et al. Contributions of cultural services to the ecosystem services agenda. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8812–8819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Baggethun, E.; De Groot, R. Natural capital and ecosystem services: The ecological foundation of human society. Ecosyst. Serv. 2010, 30, 105–121. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Yang, W.; Ulgiati, S.; Yan, M.; Zhang, X. The impact of human activities on natural capital and ecosystem services of natural pastures in North Xinjiang, China. Ecol. Model. 2012, 225, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searchinger, T.; Waite, R.; Hanson, C.; Ranganathan, J.; Dumas, P.; Matthews, E.; Klirs, C. Creating a Sustainable Food Future: A Menu of Solutions to Feed nearly 10 Billion People by 2050; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wassie, S.B. Natural resource degradation tendencies in Ethiopia: A review. Environ. Syst. Res. 2020, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackernagel, M.; Rees, W.E. Perceptual and structural barriers to investing in natural capital: Economics from an ecological footprint perspective. Ecol. Econ. 1997, 20, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, W.E.; Westra, L. When Consumption Does Violence: Can There Be Sustainability and Environmental Justice in a Resource-Limited World? Just Sustainabilities; Routledge: London, UK, 2012; Volume 26, pp. 99–124. [Google Scholar]
- Goodland, R.; Ledec, G. Neoclassical economics and principles of sustainable development. Ecol. Model. 1987, 38, 19–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Bayo, F.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G. Worldwide decline of the entomofauna: A review of its drivers. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 232, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroth, G.; Harvey, C.A.; Vincent, G. Complex agroforests: Their structure, diversity, and potential role in landscape conservation. In Agroforestry and Biodiversity Conservation in Tropical Landscapes; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 227–260. [Google Scholar]
- McAdam, J.H.; Burgess, P.J.; Graves, A.R.; Rigueiro-Rodríguez, A.; Mosquera-Losada, M.R. Classifications and functions of agroforestry systems in Europe. Agrofor. Eur. Curr. Status Future Prospect. 2009, 6, 21–41. [Google Scholar]
- Lemenih, M. Effects of Land Use Changes on Soil Quality and Native Flora Degradation and Restoration in the Highlands of Ethiopia; Department of Forest Soils Uppsala: Uppsala, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Berta Aneseyee, A.; Noszczyk, T.; Soromessa, T.; Elias, E. The InVEST habitat quality model associated with land use/cover changes: A qualitative case study of the Winike Watershed in the Omo-Gibe Basin, Southwest Ethiopia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charter, M.; Tischner, U. Sustainable Solutions: Developing Products and Services for the Future; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, R.; Baste, I.; Larigauderie, A.; Leadley, P.; Pascual, U.; Baptiste, B.; Demissew, S.; Dziba, L.; Erpul, G.; Fazel, A.; et al. Summary for Policymakers of the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services; IPBES Secretariat: Bonn, Germany, 2019; pp. 22–47. [Google Scholar]
- Munasinghe, M. The sustainomics trans-disciplinary meta-framework for making development more sustainable: Applications to energy issues. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. 2002, 5, 125–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, K.J. Classification of ecosystem services: Problems and solutions. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 139, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, L.; Obst, C.; Edens, B.; Remme, R.P. Progress and challenges in the development of ecosystem accounting as a tool to analyse ecosystem capital. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 14, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obst, C.; Hein, L.; Edens, B. National accounting and the valuation of ecosystem assets and their services. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2016, 64, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, L.; Bagstad, K.; Edens, B.; Obst, C.; de Jong, R.; Lesschen, J.P. Defining ecosystem assets for natural capital accounting. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Notte, A.; Rhodes, C. The theoretical frameworks behind integrated environmental, ecosystem, and economic accounting systems and their classifications. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 80, 106317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argüello, J.; Weber, J.L.; Negrutiu, I. Ecosystem natural capital accounting: The landscape approach at a territorial watershed scale. Quant. Plant Biol. 2022, 3, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edens, B.; Hein, L. Towards a consistent approach for ecosystem accounting. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 90, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallecillo, S.; La Notte, A.; Kakoulaki, G.; Roberts, N.; Kamberaj, J.; Dottori, F.; Feyen, L.; Rega, C.; Maes, J. Ecosystem Services Accounting. Part II-Pilot Accounts for Crop and Timber Provision, Global Climate Regulation and Flood Control; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- La Notte, A.; Vallecillo, S.; Maes, J. Capacity as “virtual stock” in ecosystem services accounting. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blignaut, J.; Mander, M.; Schulze, R.; Horan, M.; Dickens, C.; Pringle, C.; Mavundla, K.; Mahlangu, I.; Wilson, A.; McKenzie, M.; et al. Restoring and managing natural capital towards fostering economic development: Evidence from the Drakensberg, South Africa. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.P.; Hole, D.G.; Zavaleta, E.S. Harnessing nature to help people adapt to climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, G.M.; Hails, R.S.; Cryle, P.; Harlow, J.; Clarke, S.J. Towards a risk register for natural capital. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, T.H.; Heard, M.S.; Isaac, N.J.B.; Isaac, N.J.; Roy, D.B.; Procter, D.; Eigenbrod, F.; Freckleton, R.; Hector, A.; Orme, C.D.L.; et al. Biodiversity and resilience of ecosystem functions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, S.; Demissew, S.; Carabias, J.; Joly, C.; Lonsdale, M.; Ash, N.; Joly, C.; Lonsdale, M.; Ash, N.; Larigauderie, A.; et al. The IPBES Conceptual Framework—Connecting nature and people. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maseyk, F.J.F.; Mackay, A.D.; Possingham, H.P.; Dominati, E.J.; Buckley, Y.M. Managing natural capital stocks for the provision of ecosystem services. Conserv. Lett. 2017, 10, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spake, R.; Bellamy, C.; Graham, L.J.; Watts, K.; Wilson, T.; Norton, L.R.; Eigenbrod, F.; Wood, C.M.; Schmucki, R.; Bullock, J.M. An analytical framework for spatially targeted management of natural capital. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B. Capitalizing on Nature: Ecosystems as Natural Assets; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Potschin, M.; Haines-Young, R. Defining and measuring ecosystem services. Routledge Handb. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 1, 25–44. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, E.M.; Bruce, E.; Boruff, B.; Duncan, J.M.; Horsley, J.; Pauli, N.; McNeill, K.; Neef, A.; Ogtrop, F.V.; Curnow, J.; et al. Sustainable development and the water–energy–food nexus: A perspective on livelihoods. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potschin, M.B.; Haines-Young, R.H. Ecosystem services: Exploring a geographical perspective. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2011, 35, 575–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyers, B.; Biggs, R.; Cumming, G.S.; Elmqvist, T.; Hejnowicz, A.P.; Polasky, S. Getting the measure of ecosystem services: A social–ecological approach. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.N.; Li, P.; Zhou, Z.F.; An, Y.L.; Lv, T.; Lan, A.J. A Typical Study of Remote Sensing-GIS of Karst Desertification: Guizhou Province as an Example; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.J.; Liu, Q.M.; Zhang, D.F. Karst rocky desertification in southwestern China: Geomorphology, landuse, impact and rehabilitation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2004, 15, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Brandt, M.; Yue, Y.; Horion, S.; Wang, K.; Keersmaecker, W.D.; Tian, F.; Schurgers, G.; Xiao, X.; Luo, Y.; et al. Increased vegetation growth and carbon stock in China karst via ecological engineering. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Qi, X.; Wang, K.; Liao, C.; Tong, X.; Brandt, M.; Liu, B. Large scale rocky desertification reversal in South China karst. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2022, 46, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, D.; Williams, P.D. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S. Impact of China’s large-scale ecological restoration program on the environment and society in arid and semiarid areas of China: Achievements, problems, synthesis, and applications. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenleyside, K. Ecological Restoration for Protected Areas: Principles, Guidelines and Best Practices; IUCN: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.M.; Brandt, M.; Yue, Y.M.; Tong, X.W.; Wang, K.L.; Fensholt, R. The carbon sink potential of southern China after two decades of afforestation. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2022EF002674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Green, S.M.; Quine, T.A.; Liu, H.; Meersmans, J. Distinguishing the impacts of land use and climate change on ecosystem services in a karst landscape in China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 46, 101199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yue, Y.; Chen, H.; Zeng, F. Mechanisms and realization pathways for integration of scientific poverty alleviation and ecosystem services enhancement. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2020, 35, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Xiong, K.; Deng, X.; Kong, L.; Min, X. Impact of ecological restoration on ecosystem service trade-offs: Insight from karst desertification control. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2693–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.F.S. Agroforestry and the utilisation of fragile ecosystems. For. Ecol. Manag. 1979, 2, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.F.S. Concepts of Agroforestry; ICRAF: Nairobi, Kenya, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, P.K.R. Classification of agroforestry systems. Agrofor. Syst. 1985, 3, 97–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.K.R. State-of-the-art of agroforestry research and education. Agrofor. Syst. 1993, 23, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.N.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, D.Y. Research progress of agroforestry ecosystem services and its implications for industrial revitalization in karst regions. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 851–861. [Google Scholar]
- Torralba, M.; Fagerholm, N.; Burgess, P.J.; Moreno, G.; Plieninger, T. Do European agroforestry systems enhance biodiversity and ecosystem services? A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 230, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Pearce, B.D.; Wolfe, M.S. Reconciling productivity with protection of the environment: Is temperate agroforestry the answer? Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2013, 28, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, G.; Aviron, S.; Berg, S.; Crous-Duran, J.; Franca, A.; de Jalón, S.G.; Hartel, T.; Mirck, J.; Pantera, A.; Palma, J.H.N.; et al. Agroforestry systems of high nature and cultural value in Europe: Provision of commercial goods and other ecosystem services. Agrofor. Syst. 2018, 92, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S. Agroforestry for ecosystem services and environmental benefits: An overview. Agrofor. Syst. 2009, 76, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.A.; González Villalobos, J.A. Agroforestry systems conserve species-rich but modified assemblages of tropical birds and bats. Biodivers. Conserv. 2007, 16, 2257–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.A.; Medina, A.; Sánchez, D.M.; Vílchez, S.; Hernández, B.; Saenz, J.C.; Maes, J.M.; Casanoves, F.; Sinclair, F.L. Patterns of animal diversity in different forms of tree cover in agricultural landscapes. Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 1986–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Lai, S.D. Agroforestry Complex Management in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994; pp. 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.K.; Qi, D.H.; Lu, Q. Conservation and development of agroforestry in Northwest China. J. Nat. Resour. 2016, 31, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.Z.; Yang, H. A study on the models of eco-agricultural development in typical Karst Gorge Region: A case study from Dingtan District of Huajiang Gorge in Guizhou province. Chin. J. Ecol. Agric. 2005, 13, 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.K.; Lv, S.H.; Jiang, Z.C.; He, C.X.; Lu, S.H.; Xiang, W.S.; Ou, Z.L. Optimization of composite agroforestry systems and vegetation restoration experiments in karst crest areas. J. Nat. Resour. 2005, 1, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Liang, H.; Xiong, K.; Li, R. Eco-benefits coupling of agroforestry and soil and water conservation under KRD environment: Frontier theories and outlook. Agrofor. Syst. 2019, 93, 1927–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Lu, H.; Ren, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Lu, X.; Huang, D.; Zhao, D. Integrated emergy and economic evaluation of three typical rocky desertification control modes in karst areas of Guizhou Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 1104–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temesgen, H.; Wu, W.; Shi, X.; Yirsaw, E.; Bekele, B.; Kindu, M. Variation in ecosystem service values in an agroforestry dominated landscape in Ethiopia: Implications for land use and conservation policy. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthika, A.; Parthiban, K.T. Quantification and economic valuation of carbon sequestration from smallholder multifunctional agroforestry: A study from the foothills of the Nilgiris, India. Curr. Sci. 2022, 122, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Yu, Y.; Peng, S. Ecosystem services and ecological valuation of the forest-fruit-grass-fish ecosystem in hilly region, Heshan, Guangdong, China. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 16, 584–591. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, P.; Álvarez, A.; Mesa, B.; Oviedo, J.L.; Caparrós, A. Linking standard Economic Account for Forestry and ecosystem accounting: Total Forest incomes and environmental assets in publicly-owned conifer farms in Andalusia-Spain. For. Policy Econ. 2021, 128, 102482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongrungrot, V.; Thungwa, S.; Snoeck, D. Tree-crop diversification in rubber plantations to diversity sources of income for small-scale rubber farmers in Southern Thailand. Bois For. Des. Trop. 2014, 321, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattalia, G.; Wezel, A.; Costet, P.; Jagoret, P.; Deheuvels, O.; Migliorini, P.; David, C. Contribution of cacao agroforestry versus mono-cropping systems for enhanced sustainability. A review with a focus on yield. Agrofor. Syst. 2022, 96, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.; Mesa, B.; Álvarez, A.; Oviedo, J.L.; Caparrós, A. Towards measuring environmental income through a refined United Nations SEEA EA: Application to publicly-owned, protected, pine-forest-farm case studies in Andalusia, Spain. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 201, 107570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.; Caparrós, A.; Oviedo, J.L.; Ovando, P.; Álvarez-Farizo, B.; Díaz-Balteiro, L.; Carranza, J.; Beguería, S.; Díaz, M.; Herruzo, A.C.; et al. Bridging the gap between national and ecosystem accounting application in Andalusian forests, Spain. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 157, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badi, S.; Murtagh, N. Green supply chain management in construction: A systematic literature review and future research agenda. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengist, W.; Soromessa, T.; Legese, G. Method for conducting systematic literature review and meta-analysis for environmental science research. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusenbauer, M.; Haddaway, N.R. Which academic search systems are suitable for systematic reviews or meta-analyses? Evaluating retrieval qualities of Google Scholar, PubMed, and 26 other resources. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 11, 181–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smiraglia, D.; Ceccarelli, T.; Bajocco, S.; Salvati, L.; Perini, L. Linking trajectories of land change, land degradation processes and ecosystem services. Environ. Res. 2016, 147, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA). Ecosystems and Human Well-Being; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Mooney, H.A.; Agard, J.; Capistrano, D.; DeFries, R.S.; Díaz, S.; Dietz, T.; Duraiappah, A.K.; Oteng-Yeboah, A.; Pereira, H.M.; et al. Science for managing ecosystem services: Beyond the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Zhen, L.; Miah, M.G.; Ahamed, T.; Sami, A. Impact of land use change on ecosystem services: A review. Environ. Dev. 2020, 34, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’neil, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; Raskin, R.G.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TEEB. Mainstreaming the Economics of Nature; TEEB: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Garrity, D.P. Agroforestry and the achievement of the Millennium Development Goals. Agrofor. Syst. 2004, 61, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Koohafkan, P.; Altieri, M.A. Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems: A Legacy for the Future; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago-Freijanes, J.J.; Mosquera-Losada, M.R.; Rois-Díaz, M.; Ferreiro-Domínguez, N.; Pantera, A.; Aldrey, J.A.; Rigueiro-Rodríguez, A. Global and European policies to foster agricultural sustainability: Agroforestry. Agrofor. Syst. 2021, 95, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerlich, K.; Graeff-Hönninger, S.; Claupein, W. Erratum to: Agroforestry in Europe: A review of the disappearance of traditional systems and development of modern agroforestry practices, with emphasis on experiences in Germany. Agrofor. Syst. 2013, 87, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.Z.; He, X.G. Complex agroforestry initiatives in achieving sustainable agricultural development in China. Priv. Sci. Technol. 2010, 6, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Minang, P.A.; van Noordwijk, M.; Duguma, L.A. Policies for ecosystem services enhancement. In Sustainable Development through Trees on Farms: Agroforestry in Its Fifth Decade; Van Noordwijk, M., Ed.; World Agroforestry (ICRAF) Southeast Asia Regional Program: Bogor, Indonesia, 2019; pp. 361–376. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.C.; Ordoñez, P.J.; Brown, S.E.; Forrest, S.; Nava, N.J.; Hughes, K.; Baylis, K. The impacts of agroforestry on agricultural productivity, ecosystem services, and human well-being in low-and middle-income countries: An evidence and gap map. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2020, 16, e1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, D.C. Nature’s Services: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 151–176. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, H.; Czúcz, B.; Jackson, B.; Driver, A.; Nicholson, E.; Maes, J. A conceptual framework and practical structure for implementing ecosystem condition accounts. One Ecosyst. 2020, 5, e58216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czúcz, B.; Molnár, Z.; Horváth, F.; Nagy, G.G.; Botta-Duká, Z.; Török, K. Using the natural capital index framework as a scalable aggregation methodology for regional biodiversity indicators. J. Nat. Conserv. 2012, 20, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomer, R.J.; Trabucco, A.; Coe, R.; Place, F. Trees on farm: Analysis of global extent and geographical patterns of agroforestry. ICRAF Work. Pap.-World Agrofor. Cent. 2009, 89, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, T.; Sahoo, P.M.; Jally, S.K. Estimation of area under agroforestry using high resolution satellite data. Agrofor. Syst. 2016, 90, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikrant, K.K.; Chauhan, D.S.; Rizvi, R.H.; Maurya, A. Mapping the extent of agroforestry area in different altitudes of Tehri district, North Western Himalaya, India through GIS and remote sensing data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkemade, R.; Burkhard, B.; Crossman, N.D.; Nedkov, S.; Petz, K. Quantifying ecosystem services and indicators for science, policy and practice. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 37, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Harms, M.J.; Balvanera, P. Methods for mapping ecosystem service supply: A review. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2012, 8, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Egoh, B.; Drakou, E.G.; Dunbar, M.B.; Maes, J.; Willemen, L. Indicators for Mapping Ecosystem Services: A Review; European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC): Ispra, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, S. Assessment of Ecosystem Services Provided by Agroforestry Systems at the Landscape Scale; University of Zurich: Zurich, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Eigenbrod, F.; Armsworth, P.R.; Anderson, B.J.; Heinemeyer, A.; Gillings, S.; Roy, D.B.; Thomas, C.D.; Gaston, K.J. The impact of proxy-based methods on mapping the distribution of ecosystem services. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 47, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.; Tallis, H.T.; Ricketts, T.; Guerry, A.D.; Wood, S.A.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N.; et al. InVEST+ VERSION+ User’s Guide. The Natural Capital Project; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huth, N.I.; Carberry, P.S.; Poulton, P.L.; Brennan, L.E.; Keating, B.A. A framework for simulating agroforestry options for the low rainfall areas of Australia using APSIM. Eur. J. Agron. 2002, 18, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vicente, M.; Álvarez, S. Influence of DEM resolution on modelling hydrological connectivity in a complex agricultural catchment with woody crops. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N.A. A 100% Tree Inventory Using i-Tree Eco Protocol: A Case Study at Auburn University, Alabama; Auburn University: Auburn, AL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Giannitsopoulos, M.L.; Grave, A.R.; Burgess, P.J.; Crous-Duran, J.; Moreno, G.; Herzog, F.; Palma, J.H.N.; Kay, S.; de Jalón, S.J. Whole system valuation of arable, agroforestry and tree-only systems at three case study sites in Europe. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Alaejos, J.; Andivia, E.; Madejón, P.; Día, M.J.; Tapias, R. short rotation coppice of leguminous tree Leucaena spp. improves soil fertility while producing high biomass yields in Mediterranean environment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 157, 112911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations; European Commission; Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development; World Bank. System of Environmental-Economic Accounting Central Framework; United Nations Statistics Division: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Maes, J.; Driver, A.; Czúcz, B.; Keith, H.; Jackson, B.; Nicholson, E.; Dasoo, M. A review of ecosystem condition accounts: Lessons learned and options for further development. One Ecosyst. 2020, 5, e53485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvy, S. Developing the ecological balance sheet for agricultural sustainability. Sustain. Account. Manag. Policy J. 2015, 6, 110–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.; Oviedo, J.L.; Álvarez, A.; Mesa, B.; Caparrós, A. The role of non-commercial intermediate services in the valuations of ecosystem services: Application to cork oak farms in Andalusia, Spain. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 39, 100996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.; Oviedo, J.L.; Álvarez, A.; Ovando, P.; Mesa, B.; Caparrós, A. Measuring environmental incomes beyond standard national and ecosystem accounting frameworks: Testing and comparing the agroforestry Accounting System in a holm oak dehesa case study in Andalusia-Spain. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, C.J.A.; Sodhi, N.S.; Brook, B.W. Tropical turmoil: A biodiversity tragedy in progress. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Gole, T.W.; Baena, S.; Moat, J. The impact of climate change on indigenous arabica coffee (Coffea arabica): Predicting future trends and identifying priorities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şekercioğlu, Ç.H.; Primack, R.B.; Wormworth, J. The effects of climate change on tropical birds. Biol. Conserv. 2012, 148, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chain-Guadarrama, A.; Martínez-Salinas, A.; Aristizábal, N.; Ricketts, T.H. Ecosystem services by birds and bees to coffee in a changing climate: A review of coffee berry borer control and pollination. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 280, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, S.G.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Kremen, C.; Neumann, P.; Schweiger, O.; Kunin, W.E. Global pollinator declines: Trends, impacts and drivers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbach, P.; Fung, E.; Hannah, L.; Navarro-Racines, C.E.; Roubik, D.W.; Ricketts, T.H.; Harvey, C.A.; Donatti, C.I.; Läderach, P.; Locatelli, B.; et al. Coupling of pollination services and coffee suitability under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10438–10442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, T.C.; Tambosi, L.R.; Acosta, A.L.; Jaffe, R.; Saraiva, A.M.; Imperatriz-Fonseca, V.L.; Metzger, J.P. Safeguarding ecosystem services: A methodological framework to buffer the joint effect of habitat configuration and climate change. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, L.; Donatti, C.I.; Harvey, C.A.; Alfaro, E.; Rodriguez, D.A.; Bouroncle, C.; Castellanos, E.; Diaz, F.; Fung, E.; Hidalgo, H.G.; et al. regional modeling of climate change impacts on smallholder agriculture and ecosystems in Central America. Clim. Change 2017, 141, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jassogne, L.; van Asten, P.J.A.; Mukasa, D.; Wanyama, I.; Kagezi, G.; Giller, K.E. Evaluating coffee yield gaps and important biotic, abiotic, and management factors limiting coffee production in Uganda. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 63, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahn, E.; Liebig, T.; Ghazoul, J.; van Asten, P.; Läderach, P.; Vaast, P.; Sarmiento, A.; Garcia, C.; Jassogne, L. Opportunities for sustainable intensification of coffee agro-ecosystems along an altitudinal gradient on Mt. Elgon, Uganda. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 263, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokondoko, P.; Avila-Foucat, V.S.; Galeana-Pizaña, J.M. Biophysical drivers of yield gaps and ecosystem services across different coffee-based agroforestry management types: A global meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 337, 108024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, U.K.; Nath, A.J.; Lalnunpuii, K. Biomass estimation models, biomass storage and ecosystem carbon stock in sweet orange orchards: Implications for land use management. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroth, G.; da Fonseca, G.A.; Harvey, C.A.; Gascon, C.; Vasconcelos, H.L.; Izac, A.M.N. (Eds.) Agroforestry and Biodiversity Conservation in Tropical Landscapes; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Udawatta, R.P.; Rankoth, L.M.; Jose, S. Agroforestry and biodiversity. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lu, Z.; Li, Q.; Yan, D.; Chen, Y. Effects of Coffee Planting Patterns on Ant Diversity. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2019, 35, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Bisseleua, D.H.B.; Begoude, D.; Tonnang, H.; Vidal, S. Ant-mediated ecosystem services and disservices on marketable yield in cocoa agroforestry systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 247, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boreux, V.; Kushalappa, C.G.; Vaast, P.; Ghazoul, J. Interactive effects among ecosystem services and management practices on crop production: Pollination in coffee agroforestry systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8387–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meylan, L.; Gary, C.; Allinne, C.; Ortiz, J.; Jackson, L.; Rapidel, B. Evaluating the effect of shade trees on provision of ecosystem services in intensively managed coffee plantations. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 245, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesper, M.; Kueffer, C.; Krishnan, S.; Kushalappa, C.G.; Ghazoul, J. Shade tree diversity enhances coffee production and quality in agroforestry systems in the Western Ghats. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 247, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Rajab, Y.; Leuschner, C.; Barus, H.; Tjoa, A.; Hertel, D. Cacao cultivation under diverse shade tree cover allows high carbon storage and sequestration without yield losses. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, R.A.; Greenberg, R. Cacao cultivation and the conservation of biological diversity. AMBIO A J. Hum. Environ. 2000, 29, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento-Soler, A.; Rötter, R.P.; Hoffmann, M.P.; Jassogne, L.; van Asten, P.; Graefe, S.; Vaast, P. Disentangling effects of altitude and shade cover on coffee fruit dynamics and vegetative growth in smallholder coffee systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 326, 107786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Allen, S.C.; Nair, P.K.R. Tree-crop interactions: Lessons from temperate alley-cropping systems. Ecol. Basis Agrofor. 2008, 6000, 15–36. [Google Scholar]
- Marais, Z.E.; Baker, T.P.; Hunt, M.A.; Mendham, D. Shelterbelt species composition and age determine structure: Consequences for ecosystem services. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 329, 107884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiseve, S.M. Evaluation of Legume Cover Crops Intercropped with Coffee; University of Nairobi: Nairobi, Kenya, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.P.; Vaast, P.; Pagella, T.; Sinclair, F. Local knowledge about ecosystem services provided by trees in coffee agroforestry practices in northwest Vietnam. Land 2020, 9, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roughgarden, J.; Running, S.W.; Matson, P.A. What does remote sensing do for ecology? Ecology 1991, 72, 1918–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leijster, V.; Santos, M.J.; Wassen, M.W.; García, J.C.; Fernandez, I.L.; Verkuil, L.; Scheper, A.; Steenhuis, M.; Verweij, P.A. Ecosystem services trajectories in coffee agroforestry in Colombia over 40 years. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 48, 101246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F. Indicating ecosystem and landscape organisation. Ecol. Indic. 2005, 5, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandziora, M.; Burkhard, B.; Müller, F. Interactions of ecosystem properties, ecosystem integrity and ecosystem service indicators—A theoretical matrix exercise. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 28, 54–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.; Hoffmann-Kroll, R.; Wiggering, H. Indicating ecosystem integrity—Theoretical concepts and environmental requirements. Ecol. Model. 2000, 130, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, P.K.; Campagne, C.S. From ecosystem integrity to ecosystem condition: A continuity of concepts supporting different aspects of ecosystem sustainability. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2017, 29, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; Wainger, L.; Folke, C.; Mäler, K.G. Modeling complex ecological economic systems: Toward an evolutionary, dynamic understanding of people and nature. BioScience 1993, 43, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laniak, G.F.; Olchin, G.; Goodall, J.; Voinov, A.; Hill, M.; Glynn, P.; Whelan, G.; Geller, G.; Quinn, N.; Blind, M.; et al. Integrated environmental modeling: A vision and roadmap for the future. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 39, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.N.; Chi, Y.K. Problems and countermeasures facing karst ecosystems in southern China. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 31, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pen, W.X.; Wang, K.L.; Song, T.Q.; Zeng, F.P.; Wang, J.R. Controlling and restoration models of complex degradation of vulnerable Karst ecosystem. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 811–820. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Qi, X.; Fu, Z. Karst landscapes of China: Patterns, ecosystem processes and services. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 2743–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xiong, K.; Zhu, D.; Xiao, J. Revelation of coupled ecosystem quality and landscape patterns for agroforestry ecosystem services sustainability improvement in the karst desertification control. Agriculture 2022, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapp, G.; Walker, J.; Thackway, R. Linking vegetation type and condition to ecosystem goods and services. Ecol. Complex. 2010, 7, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Liu, C.C.; Dong, M. Ecological adaptation of plants and control of rocky-desertification on karst region of South-west China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2011, 35, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.Z.; Li, J.X.; Li, D.X.; Chen, T.; Wang, B.; Lu, S.H.; Li, X.K. Physiological and ecological adaptation of karst woody plants to drought. Guangxi Plants 2021, 41, 1644–1653. [Google Scholar]
- Van Beynen, P.; Townsend, K. A disturbance index for karst environments. Environ. Manag. 2005, 36, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Xiong, K. A review of agroforestry ecosystem services and its enlightenment on the ecosystem improvement of rocky desertification control. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, R. Human causes of soil loss in rural karst environments: A case study of Guizhou, China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Peng, J.; Zheng, H.; Xu, Z.; Meersmans, J. How can massive ecological restoration programs interplay with social-ecological systems? A review of research in the South China karst region. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovando, P.; Campos, P.; Oviedo, J.L.; Caparrós, A. Ecosystem accounting for measuring total income in private and public agroforestry farms. For. Policy Econ. 2016, 71, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y. Effectiveness and driving forces of ecological asset protection in national key ecological function regions. Chin. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 11, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, S.B.; O’Grady, A.P.; Mendham, D.S.; Smith, G.S.; Smethurst, P.J. Digital Tools for Quantifying the Natural Capital Benefits of Agroforestry: A Review. Land 2022, 11, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, Z.E.; Baker, T.P.; O’Grady, A.P.; England, J.R.; Tinch, D.; Hunt, M.A. A natural capital approach to agroforestry decision-making at the farm scale. Forests 2019, 10, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Xiong, K.; Xiao, J. To Achieve a Win–Win Situation: Reorganizing and Enhancing Agroforestry Ecosystem Assets and Productivity to Inform Karst Desertification Control. Forests 2024, 15, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030502
Huang Y, Xiong K, Xiao J. To Achieve a Win–Win Situation: Reorganizing and Enhancing Agroforestry Ecosystem Assets and Productivity to Inform Karst Desertification Control. Forests. 2024; 15(3):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030502
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yunting, Kangning Xiong, and Jie Xiao. 2024. "To Achieve a Win–Win Situation: Reorganizing and Enhancing Agroforestry Ecosystem Assets and Productivity to Inform Karst Desertification Control" Forests 15, no. 3: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030502
APA StyleHuang, Y., Xiong, K., & Xiao, J. (2024). To Achieve a Win–Win Situation: Reorganizing and Enhancing Agroforestry Ecosystem Assets and Productivity to Inform Karst Desertification Control. Forests, 15(3), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030502





