Forest Site and Stand Structure Affecting the Distribution of Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, 1888 (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), in Eastern Ukraine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Field Data
2.3. Modeling the Spread of the Emerald Ash Borer
- -
- Attributive data (variables for each subcompartment as an XLSS file) and subcompartment geometry (Esri shp format) were joined in one vector layer for the whole Luhansk region;
- -
- Subcompartments with a Fraxinus sp. presence were selected;
- -
- Vector layer projection was converted to EPSG:3856 (Pseudo-Mercator);
- -
- Values of each variable (columns or fields) in the attribute table (see Table 1) were converted to raster images in the GeoTIFF format;
- -
- All raster images obtained were converted to ASC files for further use in MaxEnt 3.4.4.
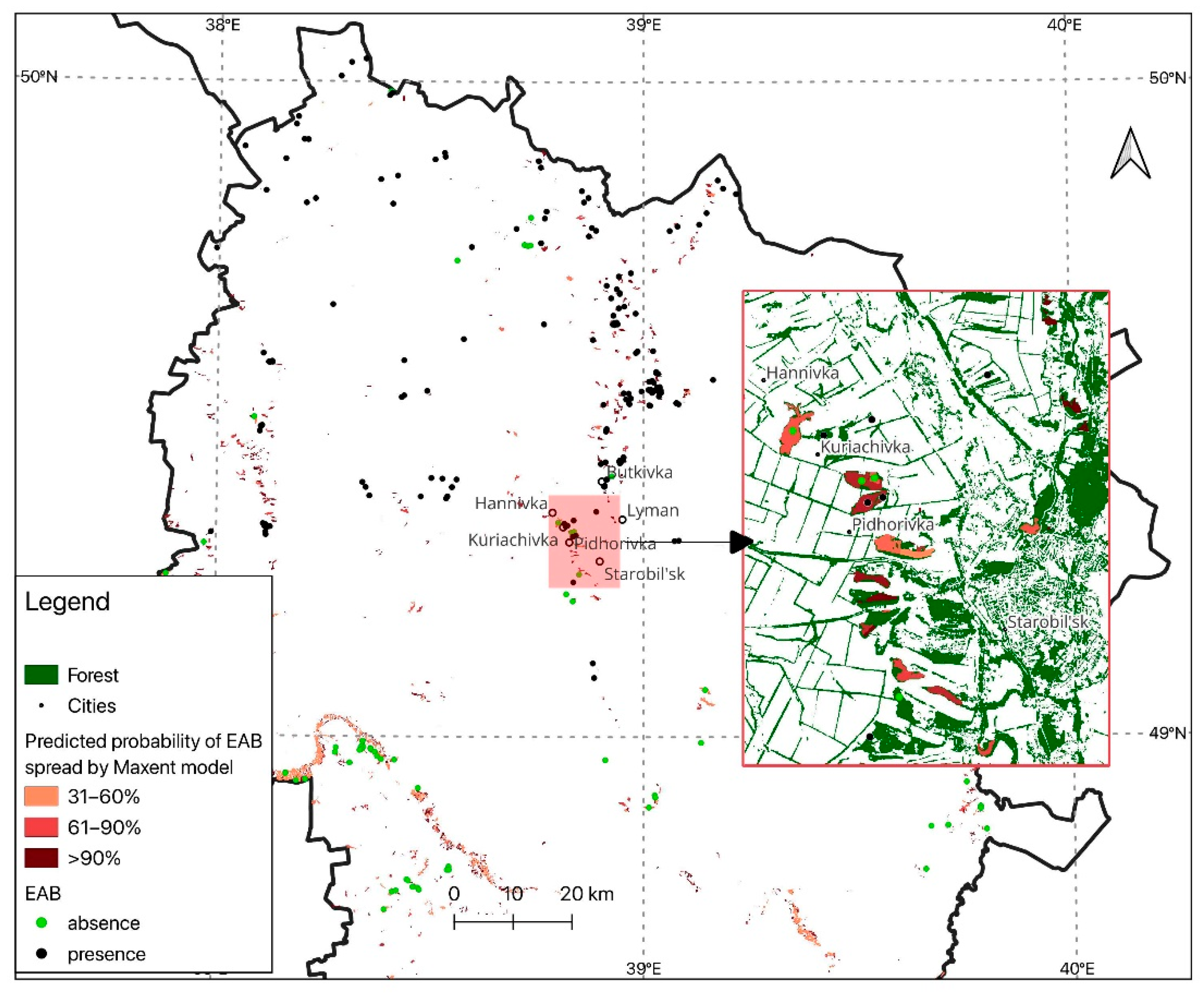
3. Results
3.1. Field Data
3.2. Modeling the Spread of the Emerald Ash Borer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.Y.; Yang, Z.Q.; Gould, J.R.; Zhang, Y.N.; Liu, G.J.; Liu, E.S. The biology and ecology of the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis, in China. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, R.A.; Baranchikov, Y.; Bauer, L.S.; Poland, T.M. Emerald ash borer biology and invasion history. In Biology and Control of Emerald Ash Borer; Van Driesche, R.G., Reardon, R.C., Eds.; FHTET-2014-09; Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2015; Chapter 1; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Herms, D.A.; McCullough, D.G. Emerald ash borer invasion of North America: History, biology, ecology, impacts, and management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipollini, D.; Rigsby, C.M.; Peterson, D.L. Feeding and development of emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) on cultivated olive, Olea europaea. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 1935–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M.J.; Bienkowski, A.O. Southern range expansion of the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis, in Russia threatens ash and olive trees in the Middle East and southern Europe. Forests 2022, 13, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Koski, T.M.; Wickham, J.D.; Baranchikov, Y.N.; Bushley, K.E. Emerald Ash Borer Management and Research: Decades of Damage and Still Expanding. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2024, 69, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drogvalenko, A.N.; Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M.J.; Bienkowski, A.O. Record of the Emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis) in Ukraine is confirmed. Insects 2019, 10, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M.J.; Drogvalenko, A.N.; Zabaluev, I.A.; Sazhnev, A.S.; Peregudova, E.Y.; Mazurov, S.G.; Komarov, E.V.; Struchaev, V.V.; Martynov, V.V.; Nikulina, T.V.; et al. Current range of Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, an alien pest of ash trees, in European Russia and Ukraine. Ann. For. Sci. 2020, 77, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshkova, V.; Borysenko, O.; Kucheryavenko, T.; Skrylnyk, Y.; Davydenko, K.; Holusa, J. Potential westward spread of emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, 1888 (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) from Eastern Ukraine. Forests 2023, 14, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strygun, O.O.; Fedorenko, V.P.; Chumak, P.Y.; Vygera, S.M.; Honcharenko, O.M.; Anyol, O.H. Emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) in Kyiv parks. In Plant Protection and Quarantine in the 21st Century: Problems and Prospects; Materials of the International Scientific-Practical Conference Dedicated to the Anniversaries of the Outstanding Phytopathologists Doctors of Biological Sciences, Professors V.K. Panteleev and M.M. Rodygin (Kharkiv, 20−21 October 2022); State Biotechnological Unoversity: Kharkiv, Ukraine, 2022; pp. 189–201. ISBN 978-614-581-554-6. Available online: https://biotechuniv.edu.ua/novini/vidbulasya-mizhnarodna-naukovo-praktychna-konferentsiya-zahyst-i-karantyn-roslyn-u-hhi-stolitti-problemy-i-perspektyvy/ (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Skrylnyk, Y.Y.; Kucheryavenko, T.V.; Zinchenko, O.V. Distribution of the Emerald ash Borer Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, 1888 (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in the Kharkiv Region. In Plant Protection and Quarantine in the 21st Century: Problems and Prospects; Materials of the International Scientific-Practical Conference Dedicated to the Anniversaries of the Outstanding Entomologists Doctors of Biological Sciences, Professors O.O. Migulin and O.V. Zakharenko (Kharkiv, 19−20 October 2023); Zhytomyr, Ruta, Ukraine; 2023; pp. 142–145. ISBN 978-617-581-597-7. Available online: https://dspace.pdau.edu.ua/server/api/core/bitstreams/0153a1df-a644-456d-b288-2fe66294969f/content (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Dang, Y.; Wei, K.; Wang, X.; Duan, J.J.; Jennings, D.E.; Poland, T.M. Introduced plants induce outbreaks of a native pest and facilitate invasion in the plants’ native range: Evidence from the emerald ash borer. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkach, V.; Rumiantsev, M.; Luk’yanets, V.; Kobets, O.; Pozniakova, S.; Obolonyk, I.; Sydorenko, S. Common ash (Fraxinus excelsior L.) in Ukrainian forests and its successful natural regeneration. For. Stud.|Metsanduslikud Uurim. 2020, 73, 26–42. Available online: http://mi.emu.ee/forestry.studies (accessed on 1 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Davydenko, K.; Skrylnyk, Y.; Borysenko, O.; Menkis, A.; Vysotska, N.; Meshkova, V.; Olson, A.; Elfstrand, M.; Vasaitis, R. Invasion of Emerald ash borer Agrilus planipennis and ash dieback pathogen Hymenoscyphus fraxineus in Ukraine—A concerted action. Forests 2022, 13, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, L.L.; Smith, S.M.; De Groot, P. Patterns in the within-tree distribution of the emerald ash borer Agrilus planipennis (Fairmaire) in young, green-ash plantations of south-western Ontario, Canada. Agric. For. Entomol. 2006, 8, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappaert, D.; McCullough, D.G.; Poland, T.M.; Siegert, N.W. Emerald ash borer in North America: A research and regulatory challenge. Am. Entomol. 2005, 51, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, J.J.; Fidgen, J.G.; Ryall, K.L.; Scarr, T.A. Estimates of emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) larval galleries in branch samples from asymptomatic urban ash trees (Oleaceae). Can. Entomol. 2016, 148, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tluczek, A.R.; McCullough, D.G.; Poland, T.M. Influence of host stress on emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) adult density, development, and distribution in Fraxinus pennsylvanica trees. Environ. Entomol. 2011, 40, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodka, S.; Konvicka, M.; Cizek, L. Habitat preferences of oak-feeding xylophagous beetles in a temperate woodland: Implications for forest history and management. J. Insect Conserv. 2009, 13, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, B.J.; Nealis, V.G.; Régnière, J. Insect defoliators as periodic disturbances in northern forest ecosystems. In Plant Disturbance Ecology; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2021; pp. 423–461. [Google Scholar]
- Lechowicz, M.J. Leaf quality and the host preferences of gypsy moth in the northern deciduous forest. In Forest Defoliation-Host Interactions: A Comparison between Gypsy Moth and Spruce Budworm; USDA FSNE-85, General Technical Report (5–7 April 1983); USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1983; pp. 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Meshkova, V. Rating of forest plot preferences for foliage-browsing insects. In Possible Limitation of Decline Phenomena in Broadleaved Stands; Oszako, T., Woodward, S., Eds.; IBL: Warsaw, Poland, 2006; pp. 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Andreieva, O.Y.; Goychuk, A.F. Forest site conditions and the threat for insect outbreaks in the scots pine stands of Polissya. Folia For. Pol. Ser. A—For. 2020, 6, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercader, R.J.; Siegert, N.W.; Liebhold, A.M.; McCullough, D.G. Dispersal of the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis, in newly-colonized sites. Agric. For. Entomol. 2009, 11, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.J.; Watt, T.; Taylor, P.; Larson, K.; Lelito, J.P. Effects of ambient temperature on egg and larval development of the invasive emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae): Implications for laboratory rearing. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caitano, B.; Chaves, T.P.; Dodonov, P.; Delabie, J.H.C. Edge effects on insects depend on life history traits: A global meta-analysis. J. Insect Conserv. 2020, 24, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girs, O.A.; Novak, B.I.; Kashpor, S.M. Forest Management; Phytosociocentre: Kyiv, Ukraine, 2013; 435p. [Google Scholar]
- Meshkova, V.L. Seasonal Development of Foliage Browsing Insects; Novoe Slovo: Kharkov, Ukraine, 2009; pp. 1–396. ISBN 978-966-2046-69-4. [Google Scholar]
- Borysenko, O.I.; Meshkova, V.L. Prediction of Fires and Insect Pests Foci Spread in the Pine Stands Using GIS; Planeta-Print: Kharkiv, Ukraine, 2021; pp. 1–150. ISBN 978-617-7897-67-4. [Google Scholar]
- Meshkova, V.L. (Ed.) Methodical Guidelines for a Survey, Assessment and Forecasting of the Spread of Forest Pests and Diseases for the Lowland Part of Ukraine; Planeta-Print: Kharkiv, Ukraine, 2020; 90p, ISBN 978-617-7897-00-1. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flø, D.; Krokene, P.; Økland, B. Invasion potential of Agrilus planipennis and other Agrilus beetles in Europe: Import pathways of deciduous wood chips and MaxEnt analyses of potential distribution areas. EPPO Bull. 2015, 45, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobek-Swant, S.; Crosthwaite, J.C.; Lyons, D.B.; Sinclair, B.J. Could phenotypic plasticity limit an invasive species? Incomplete reversibility of mid-winter deacclimation in emerald ash borer. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Graham, C.H. Do They? How Do They? WHY Do They Differ? On Finding Reasons for Differing Performances of Species Distribution Models. Ecography 2009, 32, 66–77. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/30244651 (accessed on 4 August 2022). [CrossRef]
- Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M.J.; Bieńkowski, A.O. Modeling long-distance dispersal of emerald ash borer in European Russia and prognosis of spread of this pest to neighboring countries within next 5 years. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 9295–9304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapenko, B.F.; Ulanovsky, M.S. Typological Diversity of Forests in Ukraine. Steppe; Kharkiv State Agrarian University: Kharkiv, Ukraine, 1999; 157p. [Google Scholar]
- DNVP Cartography. National Atlas of Ukraine; Maps; DNVP Cartography: Kyiv, Ukraine, 2007; 440p. [Google Scholar]
- Zubov, A.R.; Zubova, L.G. The Climate of Lugansk and Its Applied Aspects; Publishing House of V. Dahl LNU: Lugansk, Ukraine, 2016; 180p. [Google Scholar]
- Bondar, O.B.; Tkach, L.I.; Chuykova, O.O.; Zolotarova, A.S. Typological diversity of forests in the Siversky Donets river basin in the territory of Luhansk region. Ukr. J. Ecol. 2017, 7, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bila, Y.; Tupchiy, O.; Yuhnovskyi, V. Components of optimizing protective forest density in agro-landscapes of the northern (bayrak) steppe in Ukraine. In Modern Challenges and Current Issues in Forestry Education, Science, and Production, Proceedings of the II International Scientific and Practical Internet Conference, Bila Tserkva, Ukraine, 15 April 2022; BNAU: Bila Tserkva, Ukraine, 2022; pp. 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Bauer, L.S.; Gao, R.; Zhao, T.; Petrice, T.R.; Haack, R.A. Exploratory survey for the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), and its natural enemies in China. Great Lakes Entomol. 2003, 36, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atramentova, L.A.; Utevskaya, O.M. Statistical Methods in Biology; Likhtar: Gorlovka, Ukraine, 2008; 248p, ISBN 978-966-2129-26-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, O.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, S.J. A Brief Tutorial on Maxent [Internet]. 2014. Available online: http:// www.cs.princeton.edu/~schapire/maxent/ (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- Phillips, S.J.; Dudik, M.; Schapire, R.E. Maxent Software for Modeling Species Niches and Distributions. Available online: https://biodiversityinformatics.amnh.org/open_source/maxent/ (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- QGIS 3.28.1. Available online: https://qgis.org/en/site/ (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Van Erkel, A.R.; Peter, M. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis: Basic principles and applications in radiology. Eur. J. Radiol. 1998, 27, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanaga, D.; Van De Kerchove, R.; Daems, D.; De Keersmaecker, W.; Brockmann, C.; Kirches, G.; Wevers, J.; Cartus, O.; Santoro, M.; Fritz, S.; et al. ESA WorldCover 10 m 2021 v200. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M.J.; Bieńkowski, A.O. Low heat availability could limit the potential spread of the Emerald ash borer to Northern Europe (Prognosis Based on Growing Degree Days per Year). Insects 2022, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M.J.; Bieńkowski, A.O. Minimum winter temperature as a limiting factor of the potential spread of Agrilus planipennis, an alien pest of ash trees, in Europe. Insects 2020, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Xin, B.; Quinn, N.F.; Duan, J.J. Retrospective analysis of factors affecting the distribution of an invasive wood-boring insect using native range data: The importance of host plants. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebhold, A.M.; Brockerhoff, E.G.; Kalisz, S.; Nuñez, M.A.; Wardle, D.A.; Wingfield, M.J. Biological invasions in forest ecosystems. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 3437–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bauer, L.S.; Miller, D.L.; Zhao, T.; Gao, R.; Song, L.; Luan, Q.; Jin, R.; Gao, C. Seasonal abundance of Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) and its natural enemies Oobius agrili (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) and Tetrastichus planipennisi (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) in China. Biol. Control 2007, 42, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Fei, S. Divergence of the potential invasion range of emerald ash borer and its host distribution in North America under climate change. Clim. Chang. 2014, 122, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, C.R.; Mona, T.; Gilligan, C.A. Predicting the potential for spread of emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis) in Great Britain: What can we learn from other affected areas? Plants People Planet 2021, 3, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, V.; Moser, D.; Kuttner, M.; Peterseil, J.; Essl, F. A high-resolution map of emerald ash borer invasion risk for southern central Europe. Forests 2015, 6, 3075–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BenDor, T.K.; Metcalf, S.S.; Fontenot, L.E.; Sangunett, B.; Hannon, B. Modeling the spread of the emerald ash borer. Ecol. Model. 2006, 197, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-Y.; Wu, Y.; Reardon, R.; Sun, T.; Lu, M.; Sun, J. Biology and damage traits of emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire) in China. Insect Sci. 2007, 14, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, D.B.; de Groot, P.; Jones, G.C.; Scharbach, R. Host selection by Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae): Inferences from sticky-band trapping. Can. Entomol. 2009, 141, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, D.G.; Poland, T.M.; Cappaert, D. Attraction of the emerald ash borer to ash trees stressed by girdling, herbicide treatment, or wounding. Can. J. For. Res. 2009, 39, 1331–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, D.G.; Poland, T.M.; Anulewicz, A.C.; Cappaert, D. Emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) attraction to stressed or baited ash trees. Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 1668–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.M.; Storer, A.J.; Mastro, V.C. Efficacy of trap and lure types for detection of Agrilus planipennis (Col., Buprestidae) at low density. J. Appl. Entomol. 2010, 134, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.M.; Smith, E.L.; Mech, R.; Storer, A.J. Estimates of Agrilus planipennis infestation rates and potential survival of ash. Am. Midl. Nat. 2013, 169, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Poland, T.M. Biotic and abiotic factors affect green ash volatile production and emerald ash borer adult feeding preference. Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ulyshen, M.D. Differential utilization of ash phloem by emerald ash borer larvae: Ash species and larval stage effects. Agric. For. Entomol. 2012, 14, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercader, R.J.; Siegert, N.W.; Liebhold, A.M.; McCullough, D.G. Influence of foraging behavior and host spatial distribution on the localized spread of the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis. Popul. Ecol. 2011, 53, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, K.S.; Brown, J.P.; Long, R.P. Factors affecting the survival of ash (Fraxinus spp.) trees infested by emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis). Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selikhovkin, A.V.; Popovichev, B.G.; Merkuryev, S.A.; Volkovitsh, M.G.; Vasaitis, R.; Musolin, D.L. Invasive populations of Emerald ash borer Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, 1888 (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in Saint Petersburg, Russia: A “Hitchhiker”? Insects 2021, 13, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M.J.; Bienkowski, A.O. The life cycle of the emerald ash borer Agrilus planipennis in European Russia and comparisons with its life cycles in Asia and North America. Agric. For. Entomol. 2016, 18, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, T.M.; McCullough, D.G. Emerald ash borer: Invasion of the urban forest and the threat to North America’s ash resource. J. For. 2006, 104, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, J.D.; ·Paine, T.D.; ·Slippers, B.; Wingfield, M.J. (Eds.) Forest Entomology and Pathology. Volume 1: Entomology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; 810p, ISBN 978-3-031-11552-3/978-3-031-11553-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, F.; Wiegrefe, S. Susceptibility, preference, and suitability of Carpinus and Ostrya taxa for gypsy moth larvae (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae). Great Lakes Entomol. 2021, 54, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchin, P.; Theony, W.T. Quantifying dispersal of southern pine beetles with mark-recapture experiments and a diffusion model. Ecol. Appl. 1993, 3, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, E.; Castagneyrol, B.; Gibbs, M.; Jactel, H.; Barsoum, N.; Schönrogge, K.; Hector, A. Associational resistance to both insect and pathogen damage in mixed forests is modulated by tree neighbour identity and drought. J. Ecol. 2020, 108, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jactel, H.; Moreira, X.; Castagneyrol, B. Tree diversity and forest resistance to insect pests: Patterns, mechanisms, and prospects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.A.J.; Bauer, L.S.; Poland, T.M.; Windell, K.N. Flight performance of Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) on a flight mill and in free flight. J. Insect Behav. 2010, 23, 128–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muirhead, J.R.; Leung, B.; van Overdijk, C.; Kelly, D.W.; Nandakumar, K.; Marchant, K.R.; MacIsaac, H.J. Modelling local and long-distance dispersal of invasive emerald ash borer Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera) in North America. Divers. Distrib. 2006, 12, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Iverson, L.; Peters, M.; Bossenbroek, J.; Matthews, S.; Sydnor, T.D.; Schwartz, M. Modeling the invasive emerald ash borer risk of spread using a spatially explicit cellular model. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, L.R.; Prasad, A.; Bossenbroek, J.; Sydnor, D.; Schwartz, M.W. Modeling potential movements of the emerald ash borer: The model framework. In Advances in Threat Assessment and Their Application to Forest and Rangeland Management; Pye, J., Rauscher, H., Sands, Y., Lee, D., Beatty, J., Eds.; General Technical Reports PNW-802; Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest and Southern Research Stations: Portland, OR, USA, 2010; pp. 581–597. [Google Scholar]








| Variable Short Name | Variable Description | Limits |
|---|---|---|
| Var_1 | Hygrotope index (humidity level) | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 |
| Var_2 | Trophotope index (A, B, C, D) | 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| Var_3 | The proportion of F. excelsior in the stand composition, % | 10–100 |
| Var_4 | The presence of any Fraxinus species in the stand composition | 1/0 |
| Var_5 | Age of trees, years | 30–110 |
| Var_6 | Mean height of trees, m | 6–25 |
| Var_7 | Mean diameter of trees, cm (DBH) | 4–36 |
| Var_8 | Relative density of stocking | 0.5–0.9 |
| Var_9 | Site index class | 1–5 |
| Var_10 | Area of forest subcompartment | 0.5–59.5 |
| Var_11 | Number of non-forested lands neighboring subcompartment | 0–8 |
| Variables | AUC | Contribution, % | Permutation, % | Aggregated Contribution, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age of trees, years (Var_5) | 0.7 | 38.9 | 31.4 | 38.9 |
| Area of forest subcompartment, ha (Var_10) | 0.6 | 13.9 | 11.2 | 52.8 |
| Mean height of trees, m (Var_6) | 0.7 | 11.2 | 17.1 | 64.0 |
| The proportion of F. excelsior in the stand composition, % (Var_3) | 0.6 | 10.6 | 4.3 | 74.6 |
| Hygrotope index (humidity level), points (Var_1) | 0.6 | 8.3 | 13.5 | 82.9 |
| Number of non-forested lands neighboring subcompartment, point (Var_11) | 0.6 | 5.3 | 3.6 | 88.2 |
| Site index class, point (Var_9) | 0.5 | 5.8 | 8.3 | 94.0 |
| Relative density of stocking, unit fraction (Var_8) | 0.6 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 96.1 |
| Mean diameter of trees, cm (DBH) (Var_7) | 0.6 | 1.7 | 5.5 | 97.8 |
| Trophotope index (soil richness level), points (Var_2) | 0.5 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 99.1 |
| The presence of any Fraxinus species in the stand composition, 1/0 (Var_4) | 0.6 | 0.9 | 1.4 | 100.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meshkova, V.; Borysenko, O.; Kucheryavenko, T.; Vysotska, N.; Skrylnyk, Y.; Davydenko, K.; Holusa, J. Forest Site and Stand Structure Affecting the Distribution of Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, 1888 (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), in Eastern Ukraine. Forests 2024, 15, 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030511
Meshkova V, Borysenko O, Kucheryavenko T, Vysotska N, Skrylnyk Y, Davydenko K, Holusa J. Forest Site and Stand Structure Affecting the Distribution of Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, 1888 (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), in Eastern Ukraine. Forests. 2024; 15(3):511. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030511
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeshkova, Valentyna, Oleksandr Borysenko, Tetiana Kucheryavenko, Natalia Vysotska, Yuriy Skrylnyk, Kateryna Davydenko, and Jaroslav Holusa. 2024. "Forest Site and Stand Structure Affecting the Distribution of Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, 1888 (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), in Eastern Ukraine" Forests 15, no. 3: 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030511
APA StyleMeshkova, V., Borysenko, O., Kucheryavenko, T., Vysotska, N., Skrylnyk, Y., Davydenko, K., & Holusa, J. (2024). Forest Site and Stand Structure Affecting the Distribution of Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, 1888 (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), in Eastern Ukraine. Forests, 15(3), 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030511








